Candidate Gene Variants Linked to Brown Rot Susceptibility in the European Plum Genome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Brown Rot Susceptibility Evaluation in European Plum Cultivars
2.2. Plant Material for Molecular Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction and Whole-Genome Sequencing of the European Plum
2.4. SNP Identification and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Brown Rot Susceptibility Evaluation
3.2. Whole-Genome Sequencing of European Plum
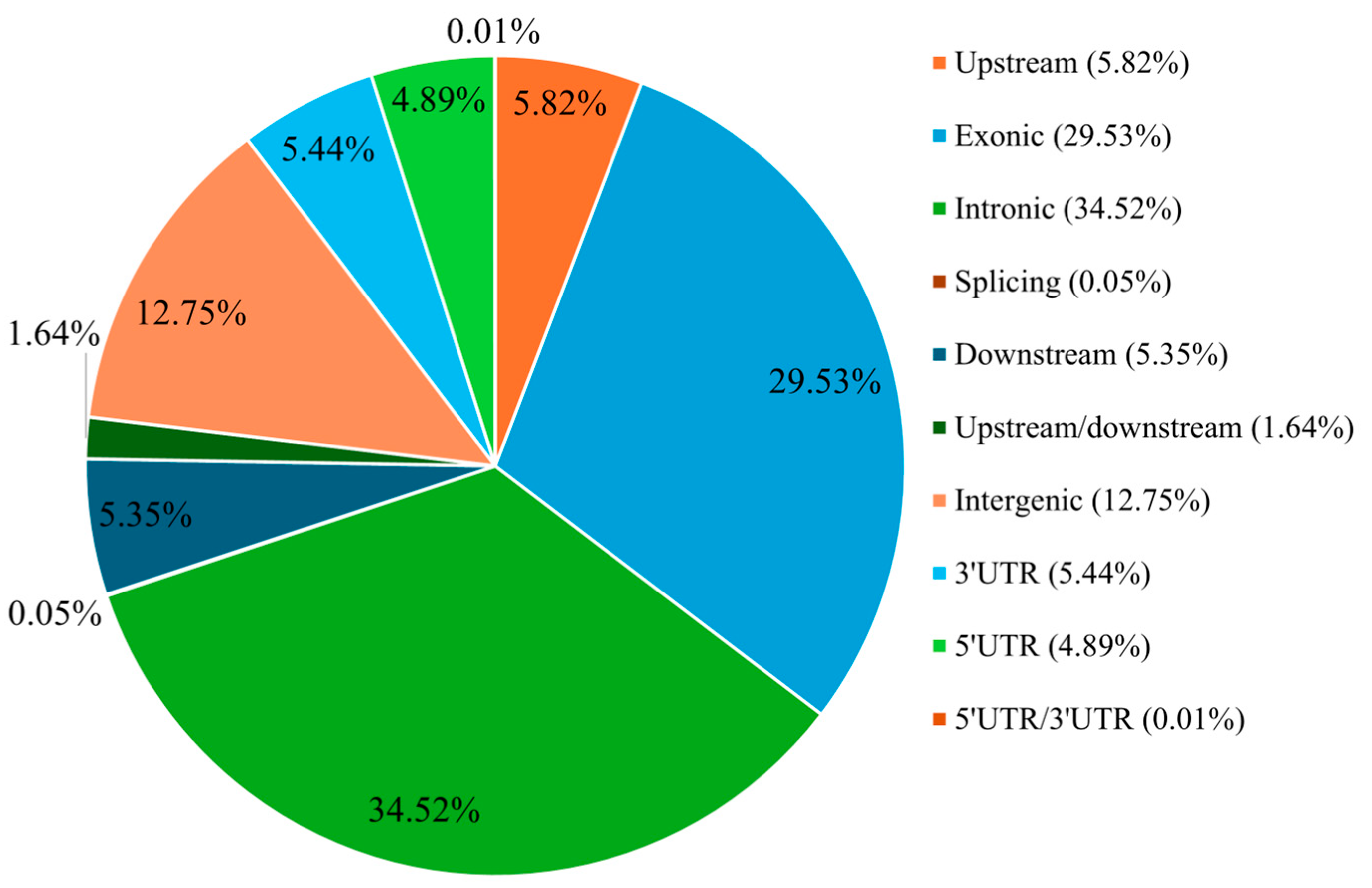
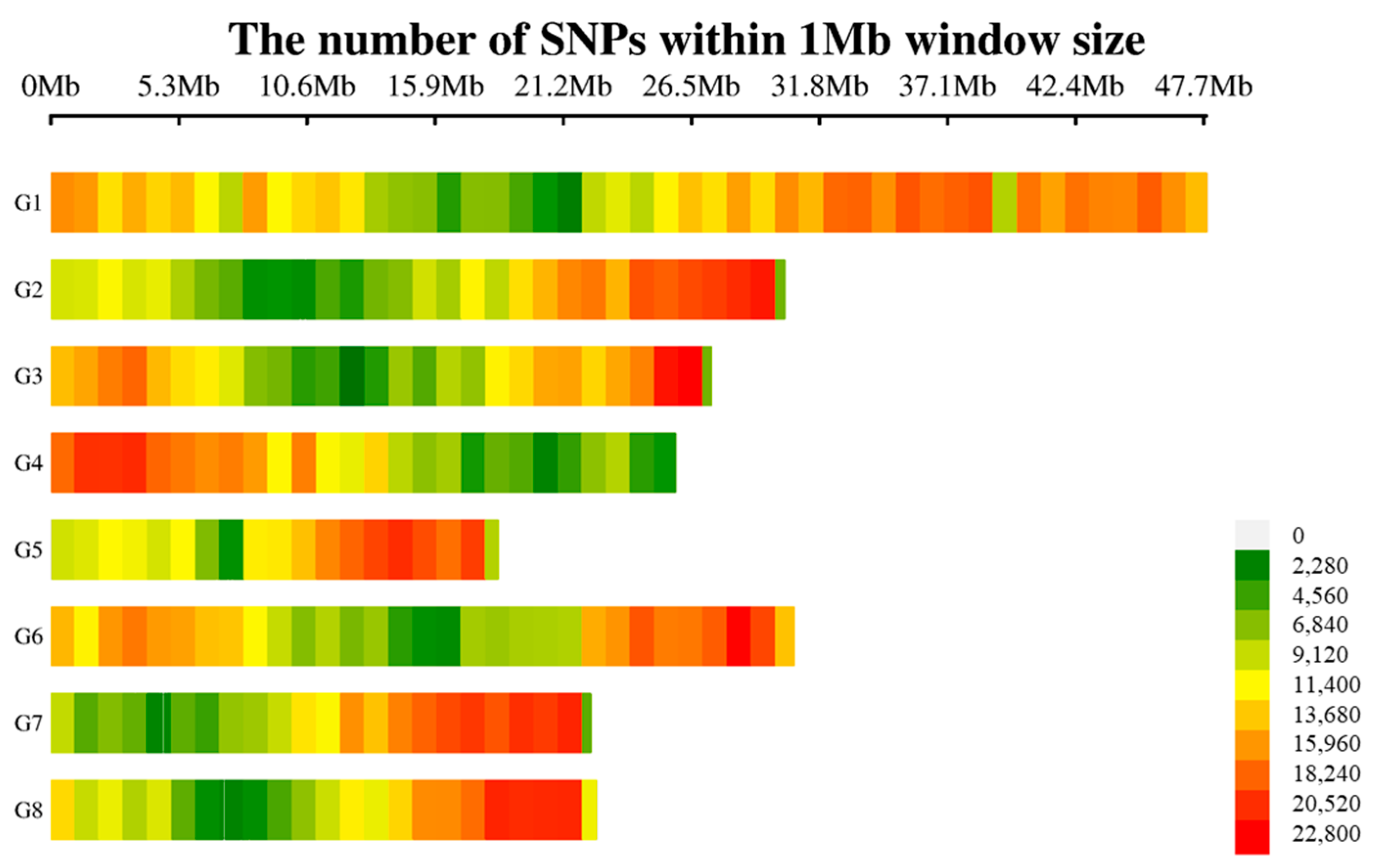
3.3. SNPs Detection Across European Plum Genome
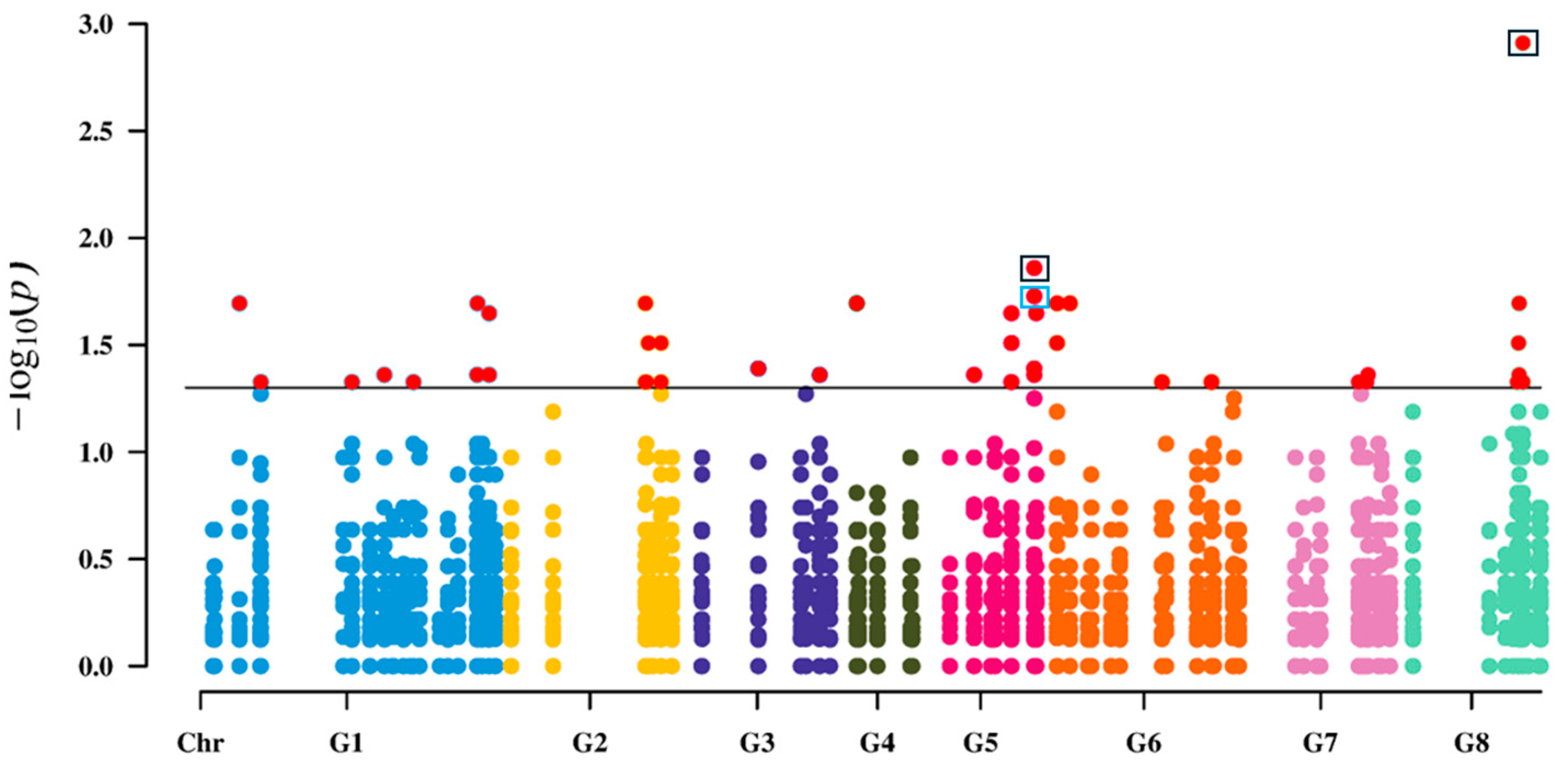
3.4. SNPs Associated with Brown Rot Identification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RAPD | random amplified polymorphic DNA |
| RFLP | restriction fragment length polymorphism |
| SSR | simple sequence repeat |
| SNP | single nucleotide polymorphism |
| GBS | genotyping by sequencing |
| WGS | whole-genome sequencing |
| NGS | next-generation sequencing |
| CTAB | cetyltrimethylammonium bromide |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| UTR | untranslated region |
| DEG | differentially expressed gene |
| MLO | mildew resistance locus O |
| PR | pathogenesis-related |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
References
- FAOSTAT. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. FAOSTAT Statistical Database. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#home (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Butac, M. Plum Breeding. In Prunus, 2nd ed.; Küden, A., Küden, A., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Butac, M.; Militaru, M.; Chitu, E.; Plopa, C.; Sumedrea, M.; Sumedrea, D. Differences and Similarities between Some European and Japanese Plum Cultivars. Acta Hortic. 2019, 1260, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, M.B.; Lawrence, W.J.C. The Genetic of Garden Plants; Macmillan and Co.: London, UK, 1934; Volume xvi+236. [Google Scholar]
- Endlich, J.; Murawski, H. Beiträge Zur Züchtungsforschung an Pflaumen. Der Züchter 1962, 32, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eryomine, G.V. New data on origin of Prunus domestica L. Acta Hortic. 1990, 283, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybin, W.A. Spontane Und Experimentell Erzeugte Bastarde Zwischen Schwarzdorn Und Kirschpflaume Und Das Abstammungsproblem Der Kulturpflaume. Planta 1936, 1, 22–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Ahmed, N.; Singh, P. Prunus Diversity- Early and Present Development: A Review. Int. J. Biodivers. Conserv. 2011, 3, 721–734. [Google Scholar]
- Van Leeuwen, G.C.M.; Baayen, R.P.; Holb, I.J.; Jeger, M.J. Distinction of the Asiatic Brown Rot Fungus Monilia polystroma sp. nov. from M. fructigena. Mycol. Res. 2002, 106, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrustic, J.; Mihajlovic, M.; Grahovac, M.; Delibasic, G.; Bulajic, A.; Krstic, B.; Tanovic, B. Genus Monilinia on Pome and Stone Fruit Species. Pestic. I Fitomedicina 2012, 27, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.J.; Cox, K.D.; Schnabel, G.; Luo, C.X. Monilinia Species Causing Brown Rot of Peach in China. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, C.; Mari, M. Monilinia Fructicola, Monilinia laxa (Monilinia Rot, Brown Rot). In Postharvest Decay; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pagán, I.; García-Arenal, F. Tolerance to Plant Pathogens: Theory and Experimental Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, L.A. Harnessing Genetic Diversity for Improving Southern Anthracnose Resistance and Quality Traits in Red Clover. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, University of Hohenheim, Stuttgart, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Callahan, A.M.; Zhebentyayeva, T.N.; Humann, J.L.; Saski, C.A.; Galimba, K.D.; Georgi, L.L.; Scorza, R.; Main, D.; Dardick, C.D. Defining the ‘HoneySweet’ insertion event utilizing NextGen sequencing and a de novo genome assembly of plum (Prunus domestica). Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhebentyayeva, T.; Shankar, V.; Scorza, R.; Callahan, A.; Ravelonandro, M.; Castro, S.; DeJong, T.; Saski, C.A.; Dardick, C. Genetic Characterization of Worldwide Prunus domestica (Plum) Germplasm Using Sequence-Based Genotyping. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, D.; Hartmann, W.; Stösser, R. Cultivar identification in Prunus domestica using random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Acta Hortic. 1994, 359, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, A.M.; Igartua, E.; Balaguer, G.; Moreno, M.A. Genetic Diversity of Prunus Rootstocks Analyzed by RAPD Markers. Euphytica 1999, 110, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, H.; Uematsu, C. Structural Analysis of Chloroplast DNA in Prunus (Rosaceae): Evolution, Genetic Diversity and Unequal Mutations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrestarazu, J.; Errea, P.; Miranda, C.; Santesteban, L.G.; Pina, A. Genetic Diversity of Spanish Prunus domestica L. Germplasm Reveals a Complex Genetic Structure Underlying. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antanynienė, R.; Šikšnianienė, J.B.; Stanys, V.; Frercks, B. Fingerprinting of Plum (Prunus domestica) Genotypes in Lithuania Using SSR Markers. Plants 2023, 12, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decroocq, V.; Hagen, L.S.; Favé, M.G.; Eyquard, J.P.; Pierronnet, A. Microsatellite Markers in the Hexaploid Prunus domestica Species and Parentage Lineage of Three European Plum Cultivars Using Nuclear and Chloroplast Simple-Sequence Repeats. Mol. Breed. 2004, 13, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antanynienė, R.; Kurgonaitė, M.; Mažeikienė, I.; Frercks, B. Time-Series Transcriptome Analysis of the European Plum Response to Pathogen Monilinia fructigena. Agriculture 2025, 15, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, J.A.; Pacheco, I.; Shinya, P.; Zapata, P.; Silva, C.; Aradhya, M.; Velasco, D.; Ruiz, D.; Martínez-Gómez, P.; Infante, R. Genotyping by Sequencing for Snp-Based Linkage Analysis and Identification of QTLs Linked to Fruit Quality Traits in Japanese Plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevenger, J.; Chavarro, C.; Pearl, S.A.; Ozias-Akins, P.; Jackson, S.A. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Identification in Polyploids: A Review, Example, and Recommendations. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, S.; Llaca, V.; May, G.D. Genotyping-by-Sequencing in Plants. Biology 2012, 1, 460–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; da Silva Linge, C.; Gasic, K. Genome-Wide Association Study of Brown Rot (Monilinia spp.) Tolerance in Peach. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 635914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-García, P.J.; Mas-Gómez, J.; Prudencio, Á.S.; Barriuso, J.J.; Cantín, C.M. Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Monilinia fructicola Lesion in a Collection of Spanish Peach Landraces. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1165847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uffelmann, E.; Huang, Q.Q.; Munung, N.S.; De Vries, J.; Okada, Y.; Martin, A.R.; Martin, H.C.; Lappalainen, T.; Posthuma, D. Genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2021, 1, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Y.G. Does One Subgenome Become Dominant in the Formation and Evolution of a Polyploid? Ann. Bot. 2023, 131, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitre, I., Jr.; Tripon, A.; Mitre, I.; Mitre, V. The Response of Several Plum Cultivars to Natural Infection with Monilinia laxa, Polystigma rubrum and Stigmina carpophila. Not. Sci. Biol. 2015, 7, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postman, J.; Volk, G.; Aldwinckle, H. Standardized Plant Disease Evaluations Will Enhance Resistance Gene Discovery. HortScience 2010, 45, 1317–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frercks, B. Kaulavaisinių Moniliozės Sukėlėjų Ir Trešnės Bei Paprastorios Vyšnios Genetinė Variacija. Ph.D. Thesis, Philosophy in agronomy, Akademija, Lithuania, Lithuanian Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry, Akademija, Lithuania, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Stanys, V.; Baniulis, D.; Morkunaite-Haimi, S.; Siksnianiene, J.B.; Frercks, B.; Gelvonauskiene, D.; Stepulaitiene, I.; Staniene, G.; Siksnianas, T. Characterising the Genetic Diversity of Lithuanian Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) Cultivars Using SSR Markers. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 142, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 1990, 12, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Vasimuddin, M.; Misra, S.; Li, H.; Aluru, S. Efficient Architecture-Aware Acceleration of BWA-MEM for Multicore Systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium (IPDPS), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 20–24 May 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 314–324. [Google Scholar]
- Garrison, E.; Marth, G. Haplotype-Based Variant Detection from Short-Read Sequencing. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1207.3907. [Google Scholar]
- Dyer, S.C.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barba, M.; Barnes, I.; Barrera-Enriquez, V.P.; Becker, A.; Bennett, R.; Beracochea, M.; Berry, A.; et al. Ensembl 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D948–D957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littell, R.C.; Henry, P.R.; Ammerman, C.B. Statistical Analysis of Repeated Measures Data Using SAS Procedures. J. Anim. Sci. 1998, 76, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Chen, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y. SRplot: A Free Online Platform for Data Visualization and Graphing. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Studio Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Studio Team: Boston, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 3, Available online: http://www.r-project.org (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- de los Cobos, F.P.; García-Gómez, B.E.; Orduña-Rubio, L.; Batlle, I.; Arús, P.; Matus, J.T.; Eduardo, I. Exploring Large-Scale Gene Coexpression Networks in Peach (Prunus persica L.): A New Tool for Predicting Gene Function. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhad294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poland, J.A.; Rife, T.W. Genotyping-by-Sequencing for Plant Breeding and Genetics. Plant Genome 2012, 5, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, C.; Roşu- Mareş, S.D.; Georgeta Maria, G.; Zagrai, L.A.; Zagrai, I.; Chiorean, A.M.; Maxim, A. The Behaviour of Some Plum Cultivars to Brown Rot Fruit Infection in Northern Transylvania. Rom. J. Hortic. 2023, 4, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmane, E.; Ikase, L.; Seglina, D. Pomological characteristics of dessert plum cultivars in Latvia. Acta Hortic. 2010, 874, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, J.; Cai, Z.X.; Ma, R.; Yu, M.; Shen, Z. Comparative Transcriptomics of Monilinia fructicola—Resistant and—Susceptible Peach Fruit Reveals Gene Networks Associated with Peach Resistance to Brown Rot Disease. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 219, 113254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antanynienė, R.; Frercks, B. Naminės Slyvos (Prunus domestica) Genetinė Įvairovė Pagal Atsparumą Kaulavaisinių Moniliozei. In 11-Oji Jaunųjų Mokslininkų Konferencija Jaunieji Mokslininkai—Žemės Ūkio Pažangai; Lietuvos Mokslų Akademijos Žemės Ūkio Ir Miškų Mokslų Skyrius: Vilnius, Lithuania, 2022; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Liu, W.; Yao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Chan, Z. Alcohol Dehydrogenase 1 (ADH1) Confers Both Abiotic and Biotic Stress Resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2017, 262, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Anduro, G.; Ceniceros-Ojeda, E.A.; Casados-Vázquez, L.E.; Bencivenni, C.; Sierra-Beltrán, A.; Murillo-Amador, B.; Tiessen, A. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Beta-Glucosidase Gene Family in Maize (Zea mays L. Var B73). Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 77, 159–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morant, A.V.; Jørgensen, K.; Jørgensen, C.; Paquette, S.M.; Sánchez-Pérez, R.; Møller, B.L.; Bak, S. β-Glucosidases as Detonators of Plant Chemical Defense. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1795–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongdin, M. Characterization of Rice Phytohormone Beta-Glucosidase. Ph.D. Thesis, Philosophy in biochemistry, Suranaree University of Technology, Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand, 2018. [Google Scholar]
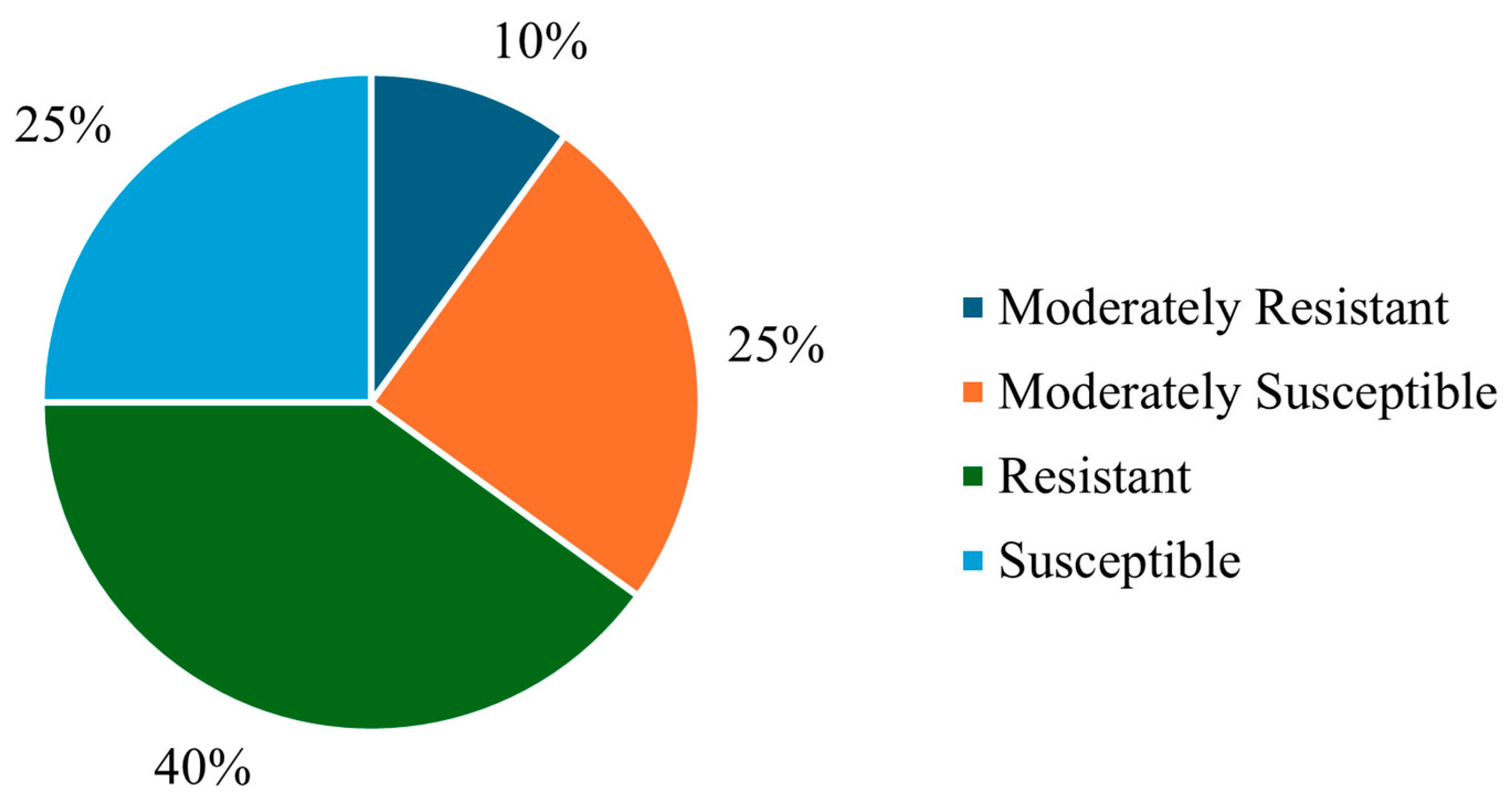

| Resistance/Susceptibility | European Plum Cultivar/Hybrid |
|---|---|
| Susceptible | Kometa |
| 212 (Amitar × Jure) | |
| 250 (Harmonija × Jure) | |
| 251(Aleksona × Jure) | |
| 252 (6002a × Jure) | |
| Moderately susceptible | Ive |
| Jubileum | |
| Valor | |
| Victoria | |
| 249 (2134 × Harmonija) | |
| Moderately resistant | Opal |
| 241 (Vilniaus Vengrine × Harmonija) | |
| Resistant | Hanita |
| Staro Vengrine | |
| Stenley | |
| Top | |
| 216 (Vilniaus Vengrine × Jure) | |
| 244 (Tarantovskaja krasavica × Jure) | |
| 245 (Dabrowicka × Jure) | |
| 293 (Free pollination of Cacanska najbolja) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antanynienė, R.; Kurgonaitė, M.; Bendokas, V.; Frercks, B. Candidate Gene Variants Linked to Brown Rot Susceptibility in the European Plum Genome. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071562
Antanynienė R, Kurgonaitė M, Bendokas V, Frercks B. Candidate Gene Variants Linked to Brown Rot Susceptibility in the European Plum Genome. Agronomy. 2025; 15(7):1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071562
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntanynienė, Raminta, Monika Kurgonaitė, Vidmantas Bendokas, and Birutė Frercks. 2025. "Candidate Gene Variants Linked to Brown Rot Susceptibility in the European Plum Genome" Agronomy 15, no. 7: 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071562
APA StyleAntanynienė, R., Kurgonaitė, M., Bendokas, V., & Frercks, B. (2025). Candidate Gene Variants Linked to Brown Rot Susceptibility in the European Plum Genome. Agronomy, 15(7), 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071562






