Reducing Cation Leaching and Improving Greenhouse Cucumber’s Nutritional Yield Through Optimized Organic–Inorganic Fertilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Location and Experimental Design
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Key Parameter Calculations
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
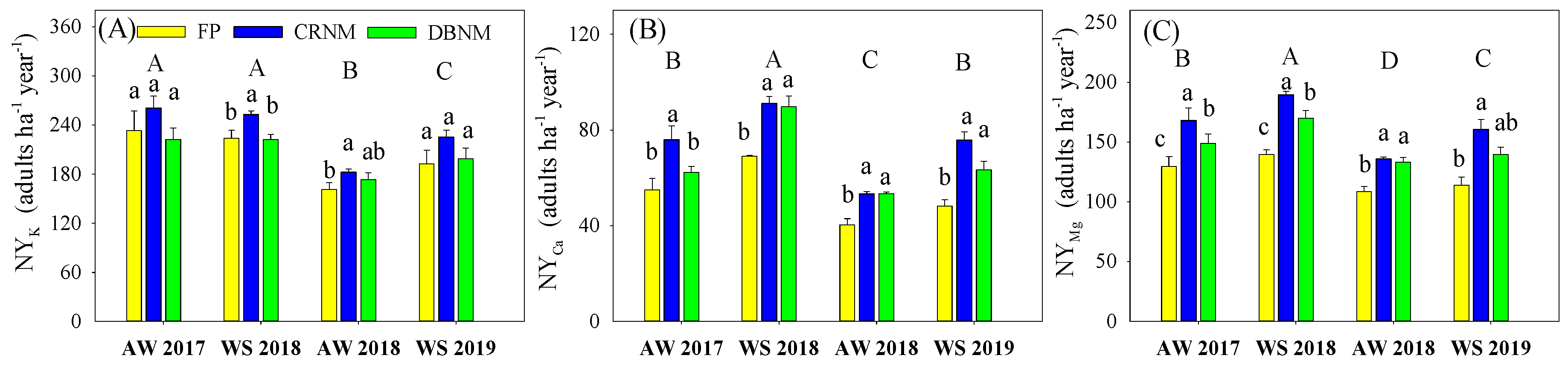
3.1. Nutritional Yield and Fruit Quality
3.2. Surpluses and Leaching Losses of Potassium, Calcium, and Magnesium
3.3. Soil Nutrient Content, pH, and the Relationship Between pH and Leaching Losses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stanaway, J.D.; Afshin, A.; Ashbaugh, C.; Bisignano, C.; Brauer, M.; Ferrara, G.; Garcia, V.; Haile, D.; Hay, S.I.; He, J.; et al. Health effects associated with vegetable consumption: A burden of proof study. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2066–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Lin, S.; Wang, Y.; Lian, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Du, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Drip fertigation significantly reduces nitrogen leaching in solar greenhouse vegetable production system. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Gao, S.; Qi, Z.; Hu, K.; Xu, J. Leaching loss of dissolved organic nitrogen from cropland ecosystems. Environ. Rev. 2020, 29, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, J. Strategies to mitigate nitrate leaching in vegetable production in China: A meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18382–18391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hina, N.S. Global meta-analysis of nitrate leaching vulnerability in synthetic and organic fertilizers over the past four decades. Water 2024, 16, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, Q.; Chen, S.; Chen, F.; Lv, H.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, J.; Liang, B. Nitrate leaching is the main driving factor of soil calcium and magnesium leaching loss in intensive plastic-shed vegetable production systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 293, 108708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrenti, G.; Toselli, M. Soil leaching as affected by the amendment with biochar and compost. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 226, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cen, B.; Yu, Z.; Qiu, R.; Gao, T.; Long, X. The key role of biochar in amending acidic soil: Reducing soil acidity and improving soil acid buffering capacity. Biochar 2025, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, M.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z. Optimal use of irrigation water and fertilizer for strawberry based on weighing production benefits and soil environment. Irrig. Sci. 2025, 43, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, W.; Ma, L. Dynamics of potassium concentrations in soil solution and characteristics of potassium leaching from soil in greenhouses with cucumber. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2016, 31, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Han, W.; Zhang, W.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tao, T.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Small, G.E.; Johnson, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, S.; et al. Forms of nitrogen inputs regulate the intensity of soil acidifcation. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 4044–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Lin, W.; Lv, W.; Liao, P.; Yu, J.; Mu, C.; Wu, L.; Muneer, M.A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhan, R.; et al. Effects of different nitrogen fertilizer rates on soil magnesium leaching in tea garden. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2024, 24, 6630–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zou, C.; Gao, X.; Guan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.; Chen, X. Nitrate leaching from open-field and greenhouse vegetable systems in China: A meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31007–31016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, B.; Xia, L.; Fan, C.; Xiong, Z. Organic-substitute strategies reduced carbon and reactive nitrogen footprints and gained net ecosystem economic benefit for intensive vegetable production. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Chadwick, D.; Chen, X. Combined applications of organic and synthetic nitrogen fertilizers for improving crop yield and reducing reactive nitrogen losses from China’s vegetable systems: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farneselli, M.; Tosti, G.; Onofri, A.; Benincasa, P.; Guiducci, M.; Pannacci, E.; Tei, F. Effects of N sources and management strategies on crop growth, yield and potential N leaching in processing tomato. Eur. J. Agron. 2018, 98, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K. Conversion of biobased substances into biochar to enhances nutrient adsorption and retention capacity. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, H.J.; Cameron, K.C. Effects of the nitrification inhibitor dicyandiamide on potassium, magnesium and calcium leaching in grazed grassland. Soil Use Manag. 2004, 20, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Hu, Y.; Yang, M.; Lei, N.; Chen, H.; Ma, J.; Chen, X.; Xie, H.; He, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. Straw retention and inhibitor application reduce the leaching risk of mineral N in no-tillage systems of Northeast China. Plant Soil. 2024, 500, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornes, F.; Lidón, A.; Belda, R.M.; Macan, G.P.F.; Cayuela, M.L.; Sánchez-García, M.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A. Soil fertility and plant nutrition in an organic olive orchard after 5 years of amendment with compost, biochar or their blend. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Ma, W.; Velthof, G.; Hou, Y.; Oenema, O.; Zhang, F. Benefits and trade-offs of replacing synthetic fertilizers by animal manures in crop production in China: A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvenranta, K.; Virkajärvi, P.; Heinonen-Tanski, H. The flows and balances of P, K, Ca and Mg on intensively managed Boreal high input grass and low input grass-clover pastures. Agric. Food Sci. 2014, 23, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Raza, S.; Miao, N.; Wang, P.; Ju, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Dramatic loss of inorganic carbon by nitrogen-induced soil acidification in Chinese croplands. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 3738–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFries, R.; Fanzo, J.; Remans, R.; Palm, C.; Wood, S.; Anderman, T. Metrics for land-scarce agriculture: Nutrient content must be better integrated into planning. Science 2015, 349, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Tian, T.; Gao, L.; Tian, Y. Nutrients, heavy metals and phthalate acid esters in solar greenhouse soils in Round-Bohai Bay-Region, China: Impacts of cultivation year and biogeography. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 13076–13087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Guan, X.; Zou, C.; Chen, X. Effects of different organic materials on the growth of greenhouse cucumber and soil properties. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Feyereisen, G.W.; Hristov, A.N.; Dell, C.J.; Kaye, J.; Beegle, D. Effects of dietary protein concentration on ammonia volatilization, nitrate leaching, and plant nitrogen uptake from dairy manure applied to lysimeters. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, Q.; Cao, J.; Zhang, C.; Song, Z.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X. Reducing nitrogen leaching in a subtropical vegetable system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 241, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Rees, R.M.; Rahman, G.K.M.M.; Miah, M.G.; Drewer, J.; Bhatia, A.; Sutton, M.A. Leaching and volatilization of nitrogen in paddy rice under diferent nitrogen management. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys. 2024, 129, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Khan, S.; Alam, M.; Khan, M.A.; Aamir, M.; Qamar, Z.; Rehman, Z.U.; Perveen, S. Toxic metal interactions affect the bioaccumulation and dietary intake of macro- and micro-nutrients. Chemosphere 2016, 146, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habtamu, M.; Elias, E.; Argaw, M.; Soromessa, T. Nutrient Balances in Fertilized Wheat-Faba Bean Intercropping System of Humid Highlands of Ethiopia. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2025, 25, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langyan, S.; Yavada, P.; Khan, F.Z.; Bhardwaj, R.; Tripathi, K.; Bhardwaj, V.; Bhardwaj, R.; Gautam, R.K.; Kumar, A. Nutritional and Food Composition Survey of Major Pulses Toward Healthy, Sustainable, and Biofortified Diets. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 876269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Busse, M.; Naumann, M.; Jákli, B.; Smit, I.; Cakmak, I.; Hermans, C.; Pawelzik, E. Differential effects of varied potassium and magnesium nutrition on production and partitioning of photoassimilates in potato plants. Physiol. Plant. 2019, 166, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Liu, D.; Liu, B.; Wu, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Zou, C.; Chen, X. Critical leaf magnesium concentrations for adequate photosynthate production of soilless cultured cherry tomato-interaction with potassium. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, P.; Dong, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B.; Ren, B. Nitrogen placement at sowing affects root growth, grain yield formation, N use efficiency in maize. Plant Soil 2020, 457, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J. Nutrient Accumulations and Changes of Exchangeable Cation Ions in Soils under Sunlight Greenhouse Vegetable Cultivation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2007, 21, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Zhao, J.; Li, D.; Guo, L.; Dou, L.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Yi, Y. Accumulation of NPK nutrients tend to decrease the effectiveness of calcium in greenhouse soil in the long term. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2018, 24, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Gao, J.; Wang, S.; Cai, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, J. Excessive nutrient balance surpluses in newly built solar greenhouses over five years leads to high nutrient accumulations in soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 288, 106717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etesami, H.; Jeong, B.R. Silicon (Si): Review and future prospects on the action mechanisms in alleviating biotic and abiotic stresses in plants. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 881–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, X.; Gong, H.; Yin, J.; Liu, Y. Silicon confers cucumber resistance to salinity stress through regulation of proline and cytokinins. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 156, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, T.; Yang, L.; Hu, W.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, J.; Gong, H. Silicon improves the growth of cucumber under excess nitrate stress by enhancing nitrogen assimilation and chlorophyll synthesis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 152, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Rong, X.; Jiang, P.; Xia, Y.; Xie, G.; Luo, G.; Yan, X. Bio-organic fertilizer application improves cucumber growth, disease resistance, and soil fertility by regulating rhizosphere microbiomes. Plant Soil. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, W.; Liu, H.; Long, X.; Zhou, J.; Xu, M.; Cao, H.; Wang, F. Organic fertilizer substitution for chemical fertilizer has a stronger efect on soil bacterial specialists than on generalists. Plant Soil. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, K.; Feng, P.; Qin, W.; Leghari, S.J. Determining the effects of organic manure substitution on soil pH in Chinese vegetable fields: A meta-analysis. J. Soil. Sediment 2023, 23, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Tian, D.; Zeng, H.; Li, Z.; Yi, C.; Niu, S. Global soil acidification impacts on belowground processes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 074003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, S. Factors contributing to soil acidifcation in the past two decades in China. Environ. Earth. Sci. 2023, 82, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhonza, N.P.; Buthelezi-Dube, N.N.; Muchaonyerwa, P. Efects of lime application on nitrogen and phosphorus availability in humic soils. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenyika, P.; Enesi, R.O.; Gorim, L.Y.; Dyck, M. Efects of liming on soil biota and related processes in agroecosystems: A review. Discov. Soil 2025, 2, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Xing, J.; Wei, L.; Liu, C.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, E.; Ren, X.; Jia, Z.; et al. The potential of biochar to mitigate soil acidifcation: A global meta-analysis. Biochar 2025, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.C.; Datta, M.; Sharma, V. Managing Soil Acidity. In Soil Acidity; Progress in Soil Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.R.; Sepaskhah, A.R. Nitrogen leaching and groundwater N contamination risk in saffron/wheat intercropping under different irrigation and soil fertilizers regimes. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Zhou, W.; Dong, J.; He, S.; Chen, F.; Bi, M.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Liang, B. Irrigation amount dominates soil mineral nitrogen leaching in plastic shed vegetable production systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 317, 107474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Chang, J.; Chen, X.; Song, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B. Study on Soil Magnesium Leaching Loss in Main Producing Areas of Wax Gourd in South China. Soils 2024, 56, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qiu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Tu, C.; Bowman, D.C.; Burkey, K.O.; Bian, X.; Zhang, W.; et al. Atmospheric CO2 enrichment and reactive nitrogen inputs interactively stimulate soil cation losses and acidification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6895–6902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, T.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Q.; Zeng, M.; Chen, X.; Yang, L.; Shen, J.; Shi, X.; Zhang, F.; de Vries, W. Quantifying drivers of soil acidification in three Chinese cropping systems. Soil Res. 2022, 215, 105230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment | FP | CRNM | DBNM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrients from organic materials | |||
| Organic materials | Chicken manure | bio-organic fertilizer | Plant-source materials |
| Rate (t ha−1) | 33.3 | 6.0 | 10.2 |
| N (kg N ha−1) | 570 | 87 | 87 |
| P (kg P2O5 ha−1) | 615 | 115 | 25 |
| K (kg K2O ha−1) | 540 | 56 | 56 |
| Ca (kg Ca ha−1) | 881 | 220 | 202 |
| Mg (kg Mg ha−1) | 182 | 46 | 38 |
| Nutrients from chemical fertilizer | |||
| N (kg N ha−1) | 500 | 313 | 196 |
| P (kg P2O5 ha−1) | 400 | 130 | 75 |
| K (kg K2O ha−1) | 635 | 419 | 314 |
| Ca (kg Ca ha−1) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mg (kg Mg ha−1) | 0 | 35 | 26 |
| Total nutrient inputs | |||
| N (kg N ha−1) | 1070 | 400 | 283 |
| P (kg P2O5 ha−1) | 1015 | 245 | 100 |
| K (kg K2O ha−1) | 1175 | 475 | 370 |
| Ca (kg Ca ha−1) | 881 | 220 | 202 |
| Mg (kg Mg ha−1) | 182 | 81 | 64 |
| Season | Treatment | Fruit DW (t ha−1) | Plant DW (t ha−1) | Fruit Nutrient Concentration (g kg−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (S) | (T) | K | Ca | Mg | ||
| 2017 A–W | FP | 1.37a | 4.18a | 74.1a | 9.5b | 3.8b |
| CRNM | 1.58a | 4.58a | 72.6a | 11.4a | 4.3a | |
| DBNM | 1.34a | 4.46a | 72.4a | 11.0a | 4.4a | |
| 2018 S–S | FP | 2.00b | 5.65a | 48.8a | 8.2b | 2.8b |
| CRNM | 2.21a | 5.99a | 50.0a | 9.8a | 3.4a | |
| DBNM | 2.02b | 5.72a | 48.3a | 10.5a | 3.4a | |
| 2018 A–W | FP | 1.52b | 5.25a | 46.4a | 6.3b | 2.9b |
| CRNM | 1.74a | 5.58a | 45.7a | 7.3a | 3.1a | |
| DBNM | 1.70a | 5.39a | 45.0a | 7.3a | 3.2a | |
| 2019 S–S | FP | 1.68b | 5.09a | 49.8a | 6.8b | 2.7b |
| CRNM | 2.02a | 5.61a | 48.9a | 8.9a | 3.2a | |
| DBNM | 1.79ab | 5.16a | 49.2a | 8.6a | 3.1a | |
| T | *** | ** | ns | *** | *** | |
| S | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| S × T | ns | ns | ns | ns | * | |
| Season (S) | Treatment (T) | Water Percolation (mm) | Cations Leaching Loss (kg ha−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | Ca | Mg | |||
| AW 2017 | FP | 99a | 1.9a | 279a | 24a |
| CRNM | 98a | 1.5a | 244b | 22a | |
| DBNM | 101a | 1.5a | 226b | 22a | |
| WS 2018 | FP | 97a | 0.7a | 188a | 17a |
| CRNM | 95a | 0.6a | 164ab | 16a | |
| DBNM | 98a | 0.5a | 134b | 14a | |
| AW 2018 | FP | 99a | 1.4a | 298a | 27a |
| CRNM | 99a | 0.9b | 236b | 19a | |
| DBNM | 97a | 1.0ab | 238b | 23a | |
| WS 2019 | FP | 116a | 2.8a | 356a | 40a |
| CRNM | 111a | 1.0b | 266b | 31a | |
| DBNM | 119a | 0.7b | 239b | 29a | |
| AVA | FP | 103a | 1.7a | 280a | 27a |
| CRNM | 101a | 1.0b | 227b | 22b | |
| DBNM | 104a | 0.9b | 209c | 22b | |
| T | ns | *** | *** | * | |
| S | ** | *** | *** | *** | |
| S × T | ns | *** | ns | ns | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, X.; Cao, W.; Liu, D.; Zhao, H.; Lu, M.; Gao, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Tian, S. Reducing Cation Leaching and Improving Greenhouse Cucumber’s Nutritional Yield Through Optimized Organic–Inorganic Fertilization. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071523
Guan X, Cao W, Liu D, Zhao H, Lu M, Gao X, Chen X, Liu Y, Tian S. Reducing Cation Leaching and Improving Greenhouse Cucumber’s Nutritional Yield Through Optimized Organic–Inorganic Fertilization. Agronomy. 2025; 15(7):1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071523
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Xilin, Wenqing Cao, Dunyi Liu, Huanyu Zhao, Ming Lu, Xinhao Gao, Xinping Chen, Yumin Liu, and Shenzhong Tian. 2025. "Reducing Cation Leaching and Improving Greenhouse Cucumber’s Nutritional Yield Through Optimized Organic–Inorganic Fertilization" Agronomy 15, no. 7: 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071523
APA StyleGuan, X., Cao, W., Liu, D., Zhao, H., Lu, M., Gao, X., Chen, X., Liu, Y., & Tian, S. (2025). Reducing Cation Leaching and Improving Greenhouse Cucumber’s Nutritional Yield Through Optimized Organic–Inorganic Fertilization. Agronomy, 15(7), 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071523








