Identification of Vitis riparia as Donor of Black Rot Resistance in the Mapping Population V3125 x ‘Börner’ and Additive Effect of Rgb1 and Rgb2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phenotyping of Leaf Resistance to Black Rot
2.2. Genetic Map
2.3. QTL Analysis
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Improvement of the Genetic Map
3.2. QTL Analysis
3.3. Vitis riparia Is the Donor of Black Rot Resistance
3.4. Additive Effect of Rgb1 and Rgb2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CIM | Composite interval mapping |
| cM | centiMorgan |
| LOD | Logarithm of the odds |
| IM | Interval mapping |
| MAS | Marker-assisted selection |
| QTL | Quantitative trait loic |
| Rgb | Resistance Guignardia bidwellii |
References
- Viala, M.P.; Ravaz, L. Sur De Nouvelles Espèces Du Genre Phoma Se Développant Sur Les Fruits De La Vigne. Bull. De La Société Bot. De Fr. 1886, 33, LXI–LXX. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Aa, H.A.; Vanev, S. A Revision of the Species Described in Phyllosticta; Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures (CBS): Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pezet, R.; Jermini, M. Black rot of grapevine: Symptoms, epidemiology and control. Rev. Suisse De Vitic. D’arboricult. D’horticult. 1989, 21, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsdell, D.C.; Milholland, R.D. Black Rot. Compend. Grape Dis. 1988, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Reddick, D. The black-rot disease of grapes. Riv. Di Patol. Veg. 1911, 5, 116–119. [Google Scholar]
- Lüstner, B. Auftreten der Schwarzfäule (Black Rot) der Rebe in Deutschland. Nachrbl. Dtsch. Pflanzenschutzd. 1935, 15, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Jermini, M.; Gessler, C. Epidemiology and control of grape black rot in southern Switzerland. Plant Dis. 1996, 80, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, M.; Holz, B.; Hoffmann, C.; Lipps, H.-P.; Silvanus, W. Occurrence of Guignardia bidwellii, the causal fungus of black rot on grapevine, in the vine-growing areas of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. In Proceedings of the Plant Protection and Plant Health in Europe: Introduction and Spread of Invasive Species, Humboldt University, Berlin, Germany, 9–11 June 2005; pp. 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi, P.A.; Broggini, G.A.L.; Gessler, C.; Molitor, D.; Sofia, J.; Mugnai, L. Guignardia bidwellii, the agent of black rot of grapevine, is spreading in European vineyards. In Proceedings of the 10th Congress of Plant Pathology (ICPP), Beijing, China, 25–30 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pirrello, C.; Mizzotti, C.; Tomazetti, T.C.; Colombo, M.; Bettinelli, P.; Prodorutti, D.; Peressotti, E.; Zulini, L.; Stefanini, M.; Angeli, G.; et al. Emergent Ascomycetes in Viticulture: An Interdisciplinary Overview. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, M.; Csikász-Krizsics, A.; Dula, T.; Farkas, E.; Roznik, D.; Kozma, P.; Deák, T. Black Rot of Grapes (Guignardia bidwellii)—A Comprehensive Overview. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, W.; Hoffman, L.E. Black Rot. In Compendium of Grape Diseases, Disorders and Pests, 2nd ed.; Wilcox, W., Gubler, W.D., Uyemoto, J.K., Eds.; American Phytopathological Society: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2015; pp. 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Lipps, H.; Harms, M. Schwarzfäule—Ein neues Problem. Das Dtsch. Weinmagazin 2004, 11, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenmann, B.; Wingerter, C.; Dressler, M.; Freund, C.; Kortekamp, A.; Bogs, J. Fungicide-Saving Potential and Economic Advantages of Fungus-Resistant Grapevine Cultivars. Plants 2023, 12, 3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitis International Variety Catalogue. Available online: www.vivc.de (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Pertot, I.; Caffi, T.; Rossi, V.; Mugnai, L.; Hoffmann, C.; Grando, M.S.; Gary, C.; Lafond, D.; Duso, C.; Thiery, D.; et al. A critical review of plant protection tools for reducing pesticide use on grapevine and new perspectives for the implementation of IPM in viticulture. Crop. Prot. 2017, 97, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rex, F.; Fechter, I.; Hausmann, L.; Töpfer, R. QTL mapping of black rot (Guignardia bidwellii) resistance in the grapevine rootstock ‘Börner’ (V. riparia Gm183 × V. cinerea Arnold). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalbò, M.A.; Weeden, N.F.; Reisch, B.I. QTL analysis of disease resistance in interspecific hybrid grapes. Acta Hortic. 2000, 528, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausmann, L.; Rex, F.; Töpfer, R. Evaluation and genetic analysis of grapevine black rot resistances. Acta Hortic. 2017, 1188, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettinelli, P.; Nicolini, D.; Constantini, L.; Stefanini, M.; Hausmann, L.; Vezzulli, S. Towards marker-assisted breeding for black rot bunch resistance: Identification of a major QTL in the grapevine cultivar ‘Merzling’. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fechter, I.; Hausmann, L.; Zyprian, E.; Daum, M.; Holtgrawe, D.; Weisshaar, B.; Topfer, R. QTL analysis of flowering time and ripening traits suggests an impact of a genomic region on linkage group 1 in Vitis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 1857–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepho, H.P.; Möhring, J.; Melchinger, A.E.; Büchse, A. BLUP for phenotypic selection in plant breeding and variety testing. Euphytica 2007, 161, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P. Phenotype: A Tool for Phenotypic Data Processing. Version 0.1.0. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=Phenotype (accessed on 9 November 2024).
- Margarido, G.R.; Souza, A.P.; Garcia, A.A. OneMap: Software for genetic mapping in outcrossing species. Hereditas 2007, 144, 78–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenzke, L.; Röckel, F.; Wenke, T.; Schwander, F.; Grutzmann, K.; Naumann, J.; Zakrzewski, F.; Heinekamp, T.; Maglione, M.; Wenke, A.; et al. Genotyping-by-sequencing-based high-resolution mapping reveals a single candidate gene for the grapevine veraison locus Ver1. Plant Physiol. 2024, 196, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canaguier, A.; Grimplet, J.; Di Gaspero, G.; Scalabrin, S.; Duchene, E.; Choisne, N.; Mohellibi, N.; Guichard, C.; Rombauts, S.; Le Clainche, I.; et al. A new version of the grapevine reference genome assembly (12X.v2) and of its annotation (VCost.v3). Genom. Data 2017, 14, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dag, O.; Ilk, O. An algorithm for estimating Box–Cox transformation parameter in ANOVA. Commun. Stat.-Simul. Comput. 2017, 46, 6424–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broman, K.W.; Wu, H.; Sen, S.; Churchill, G.A. R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 889–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazaffi, R.; Amadeu, R.R.; Mollinari, M.; Rosa, J.R.B.F.; Taniguti, C.H.; Margarido, G.R.A.; Garcia, A.A.F. fullsibQTL: An R package for QTL mapping in biparental populations of outcrossing species. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, E.S.; Botstein, D. Mapping Mendelian Factors Underlying Quantitative Traits Using RFLP Linkage Maps. Gentics Soc. Am. 1989, 121, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, O.; Curnow, R.N. Estimating the locations and the sizes of the effects of quantitative trait loci using flanking markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1992, 85, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akond, Z.; Alam, J.; Hasan, M.N.; Uddin, S.; Alam, M.; Mollah, N.H. A comparison on some interval mapping approaches for QTL detection. Bioinformation 2019, 15, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettinelli, P.; Nicolini, D.; Giovannini, O.; Stefanini, M.; Hausmann, L.; Vezzulli, S. Breeding for black rot resistance in grapevine: Advanced approaches for germplasm screening. Euphytica 2023, 219, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
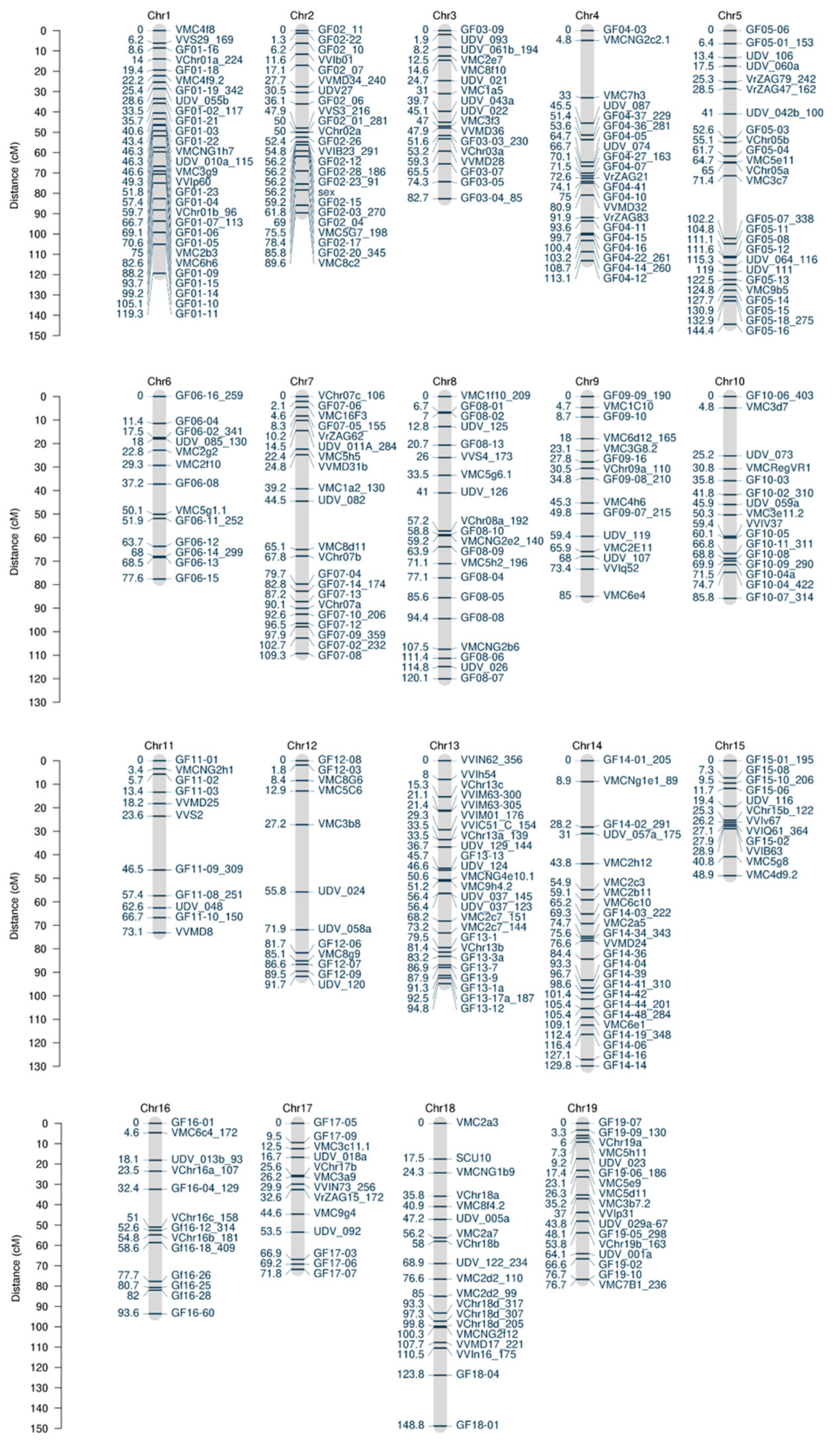

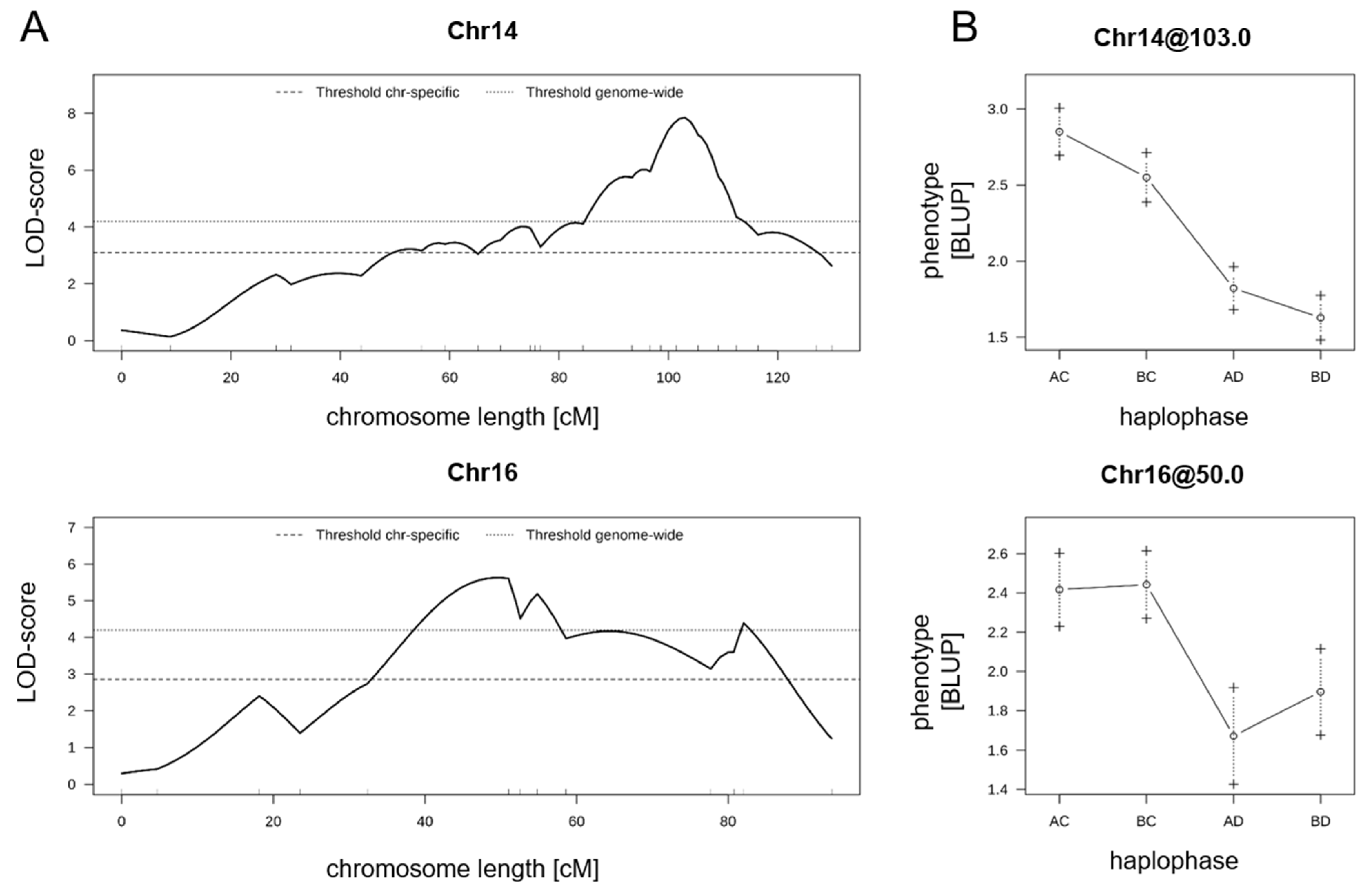
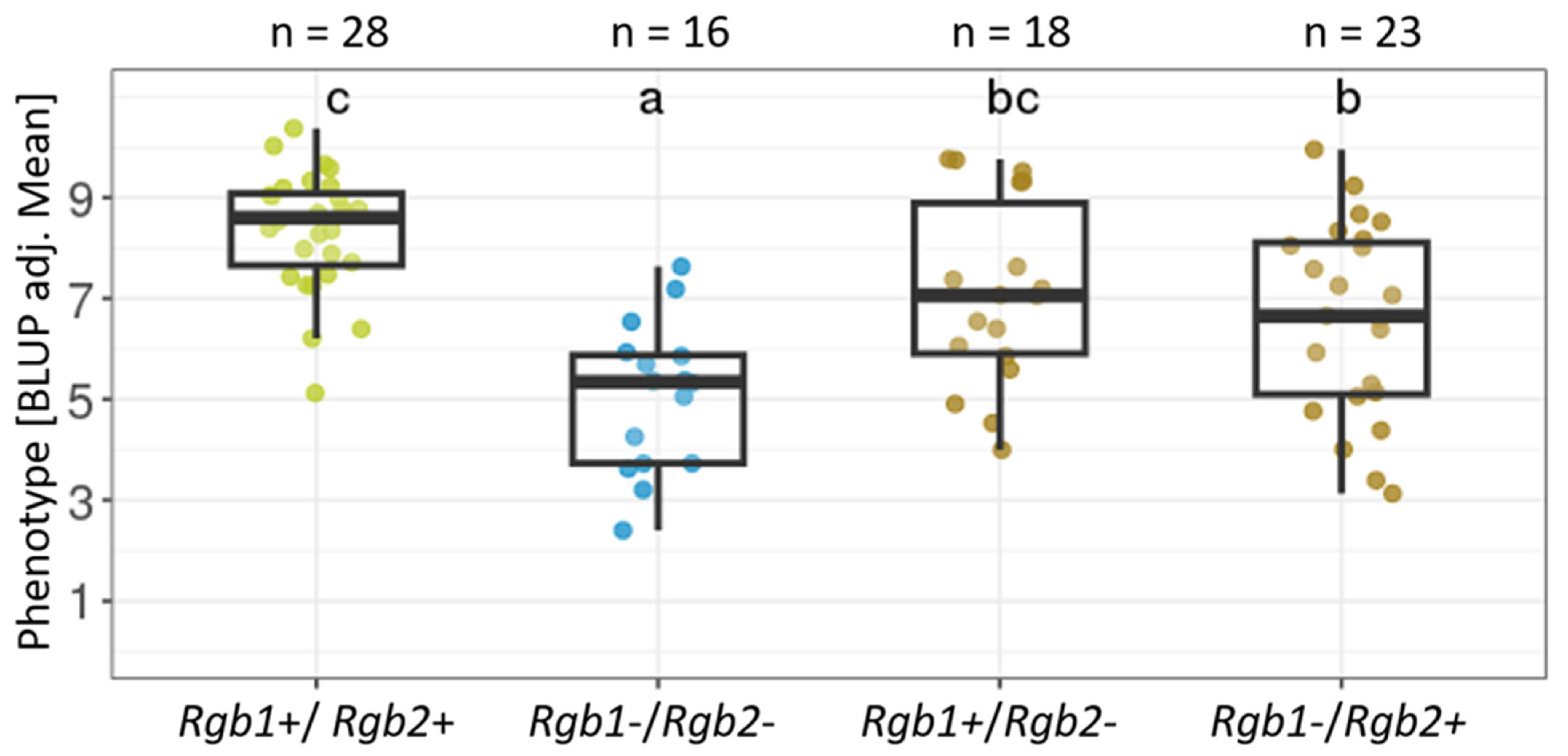
| Chr | LODmax | LODmax Marker | LODmax-2 Lower Boundary | LODmax-2 Upper Boundary | % Phenotypic Variance Explained | LOD Threshold Genome | LOD Threshold Chromosome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IM | 14 | 7.8 | GF14-42 | GF14-04 | VMC6e1 | 18.2 | 4.2 | 3.1 |
| 16 | 5.6 | VChr16c_158 | GF16-04_129 | GF16-60 | 13.4 | 4.2 | 2.9 | |
| CIM | 14 | 8.5 | loc103 | GF14-39 | VMC6e1 | 20.3 | 4.6 | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weber, P.; Werner, A.; Rex, F.; Röckel, F.; Trapp, O.; Töpfer, R.; Hausmann, L. Identification of Vitis riparia as Donor of Black Rot Resistance in the Mapping Population V3125 x ‘Börner’ and Additive Effect of Rgb1 and Rgb2. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061484
Weber P, Werner A, Rex F, Röckel F, Trapp O, Töpfer R, Hausmann L. Identification of Vitis riparia as Donor of Black Rot Resistance in the Mapping Population V3125 x ‘Börner’ and Additive Effect of Rgb1 and Rgb2. Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061484
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeber, Patricia, Anna Werner, Friederike Rex, Franco Röckel, Oliver Trapp, Reinhard Töpfer, and Ludger Hausmann. 2025. "Identification of Vitis riparia as Donor of Black Rot Resistance in the Mapping Population V3125 x ‘Börner’ and Additive Effect of Rgb1 and Rgb2" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061484
APA StyleWeber, P., Werner, A., Rex, F., Röckel, F., Trapp, O., Töpfer, R., & Hausmann, L. (2025). Identification of Vitis riparia as Donor of Black Rot Resistance in the Mapping Population V3125 x ‘Börner’ and Additive Effect of Rgb1 and Rgb2. Agronomy, 15(6), 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061484







