Physiological and Transcriptomic Analysis of a Sepal Mutant in Phalaenopsis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3. Metabolite Extraction
2.4. HPLC-MS/MS Analysis
2.5. RNA-Seq and DEG Analysis
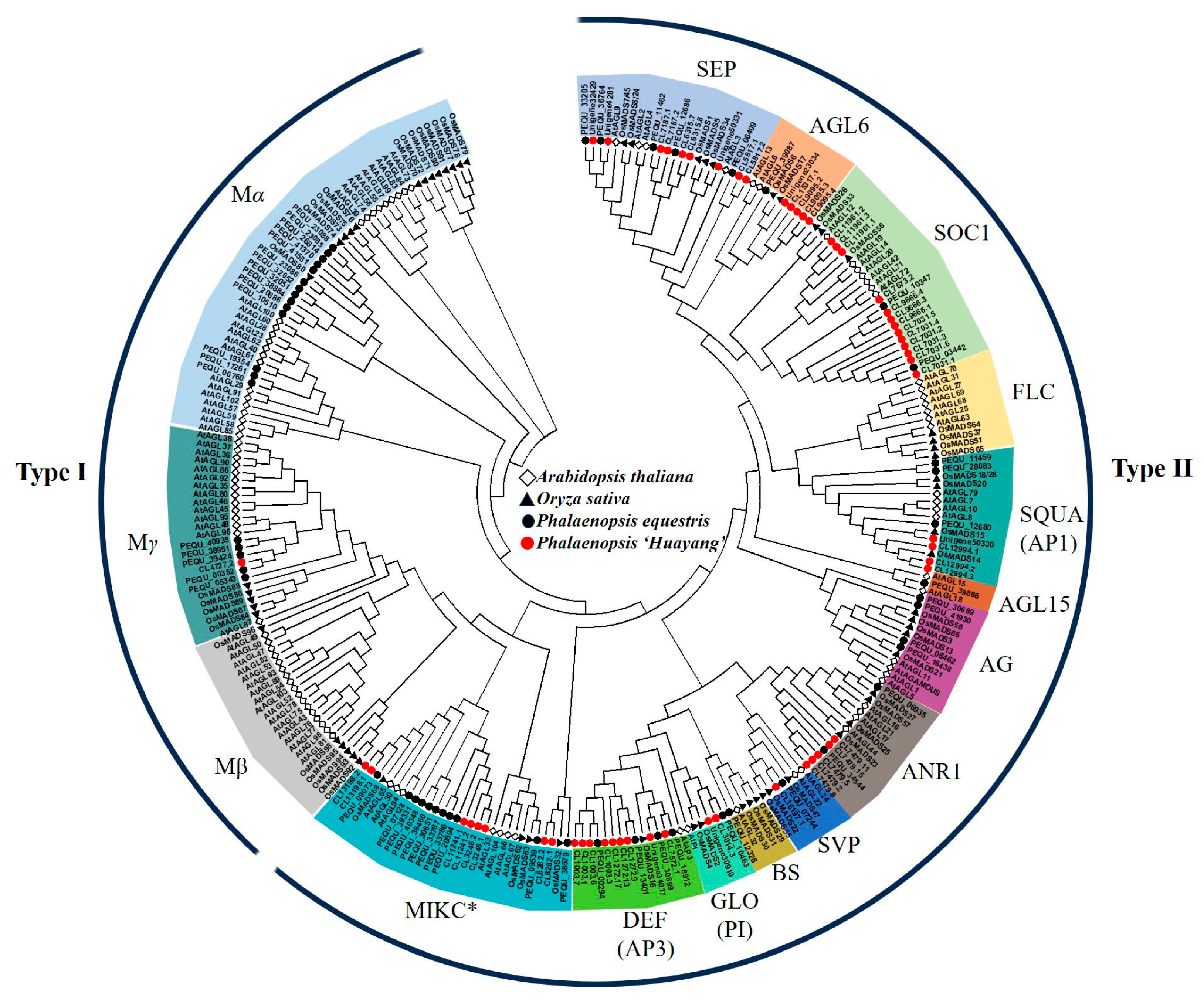
2.6. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.7. Protein Interaction Network Prediction
2.8. Heatmap Construction
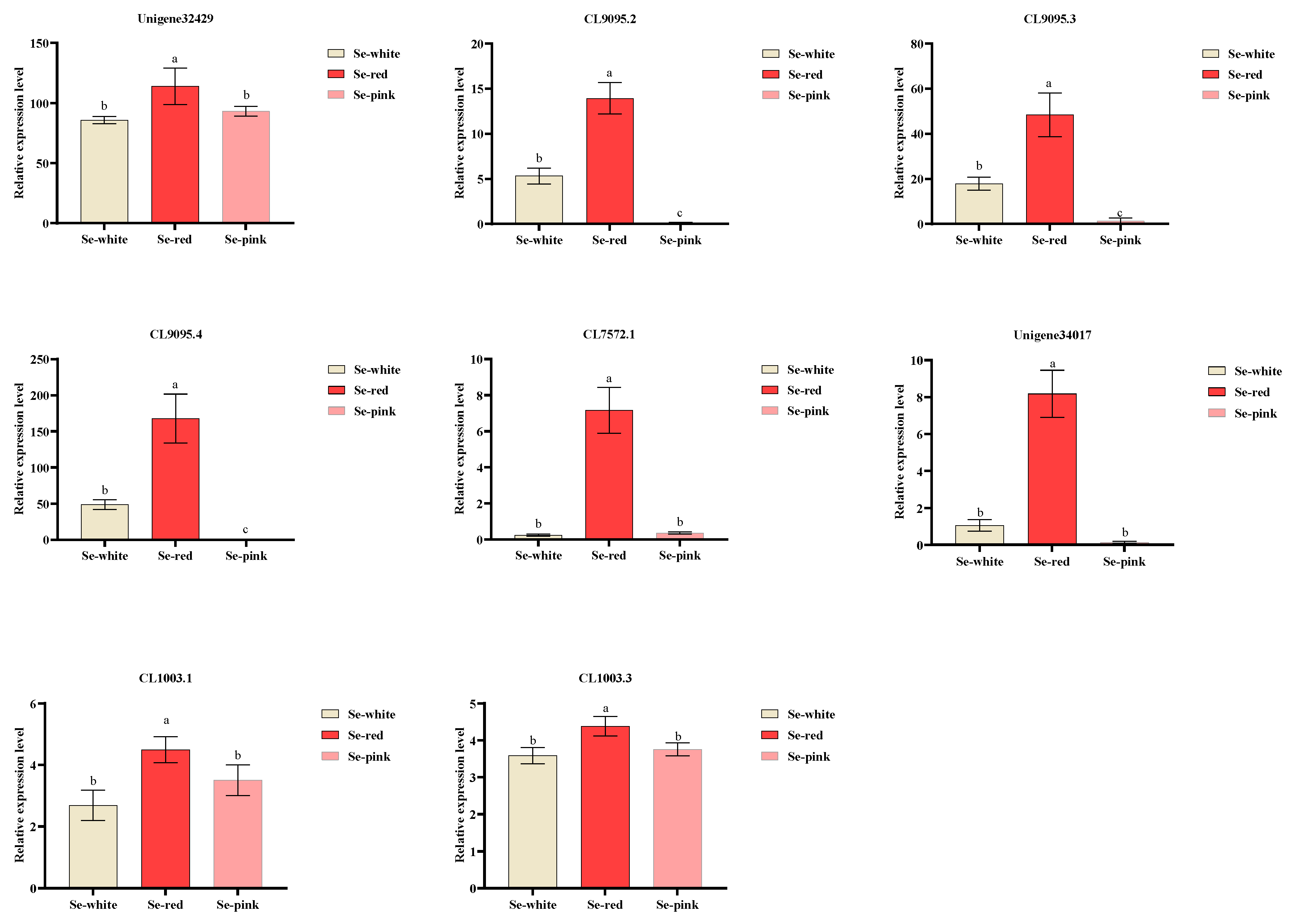
2.9. Expression Profile Analysis
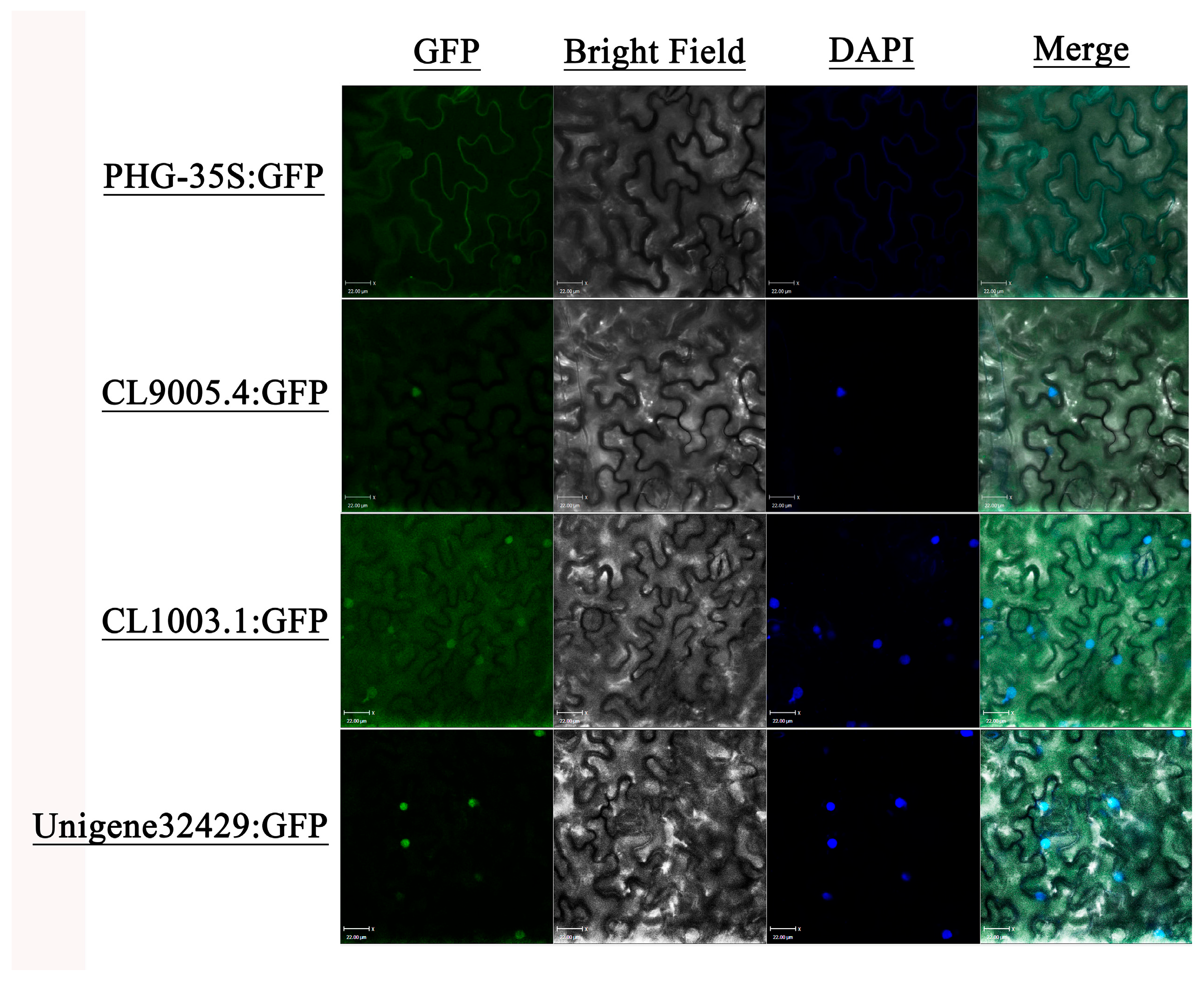
2.10. Subcellular Localization Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
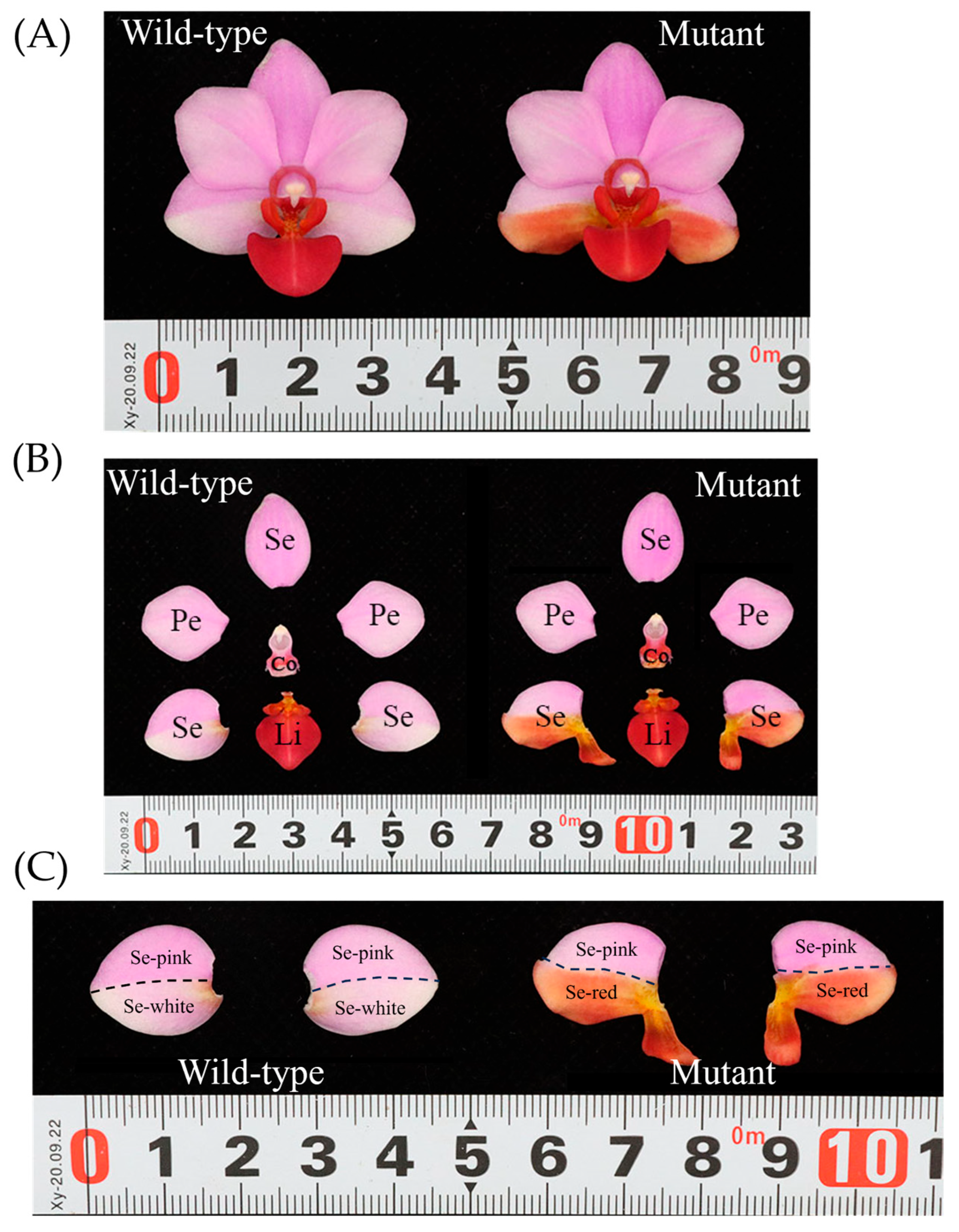
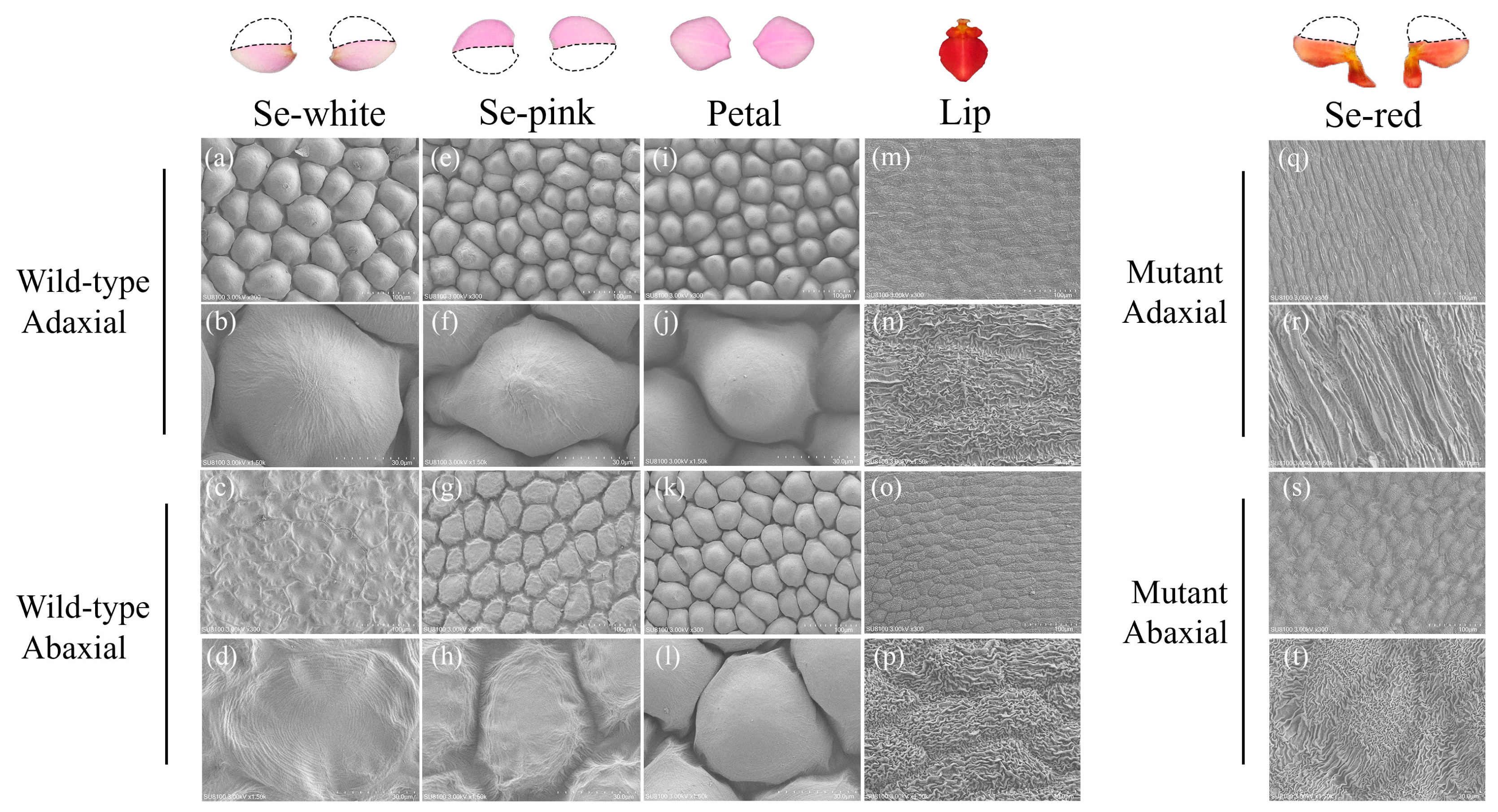
3.1. Morphological Study of Sepal Mutants in Phalaenopsis ‘Huayang’
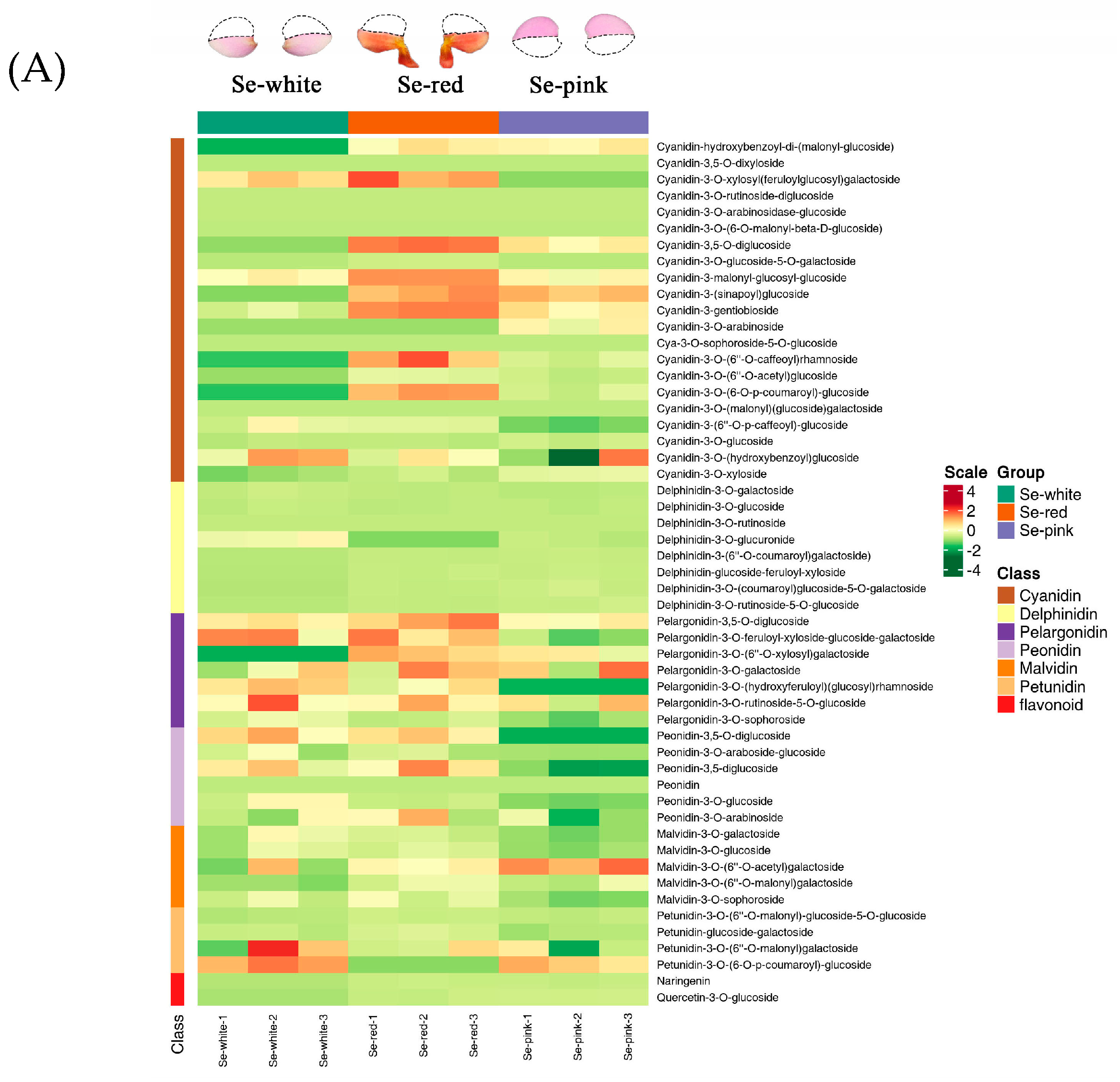
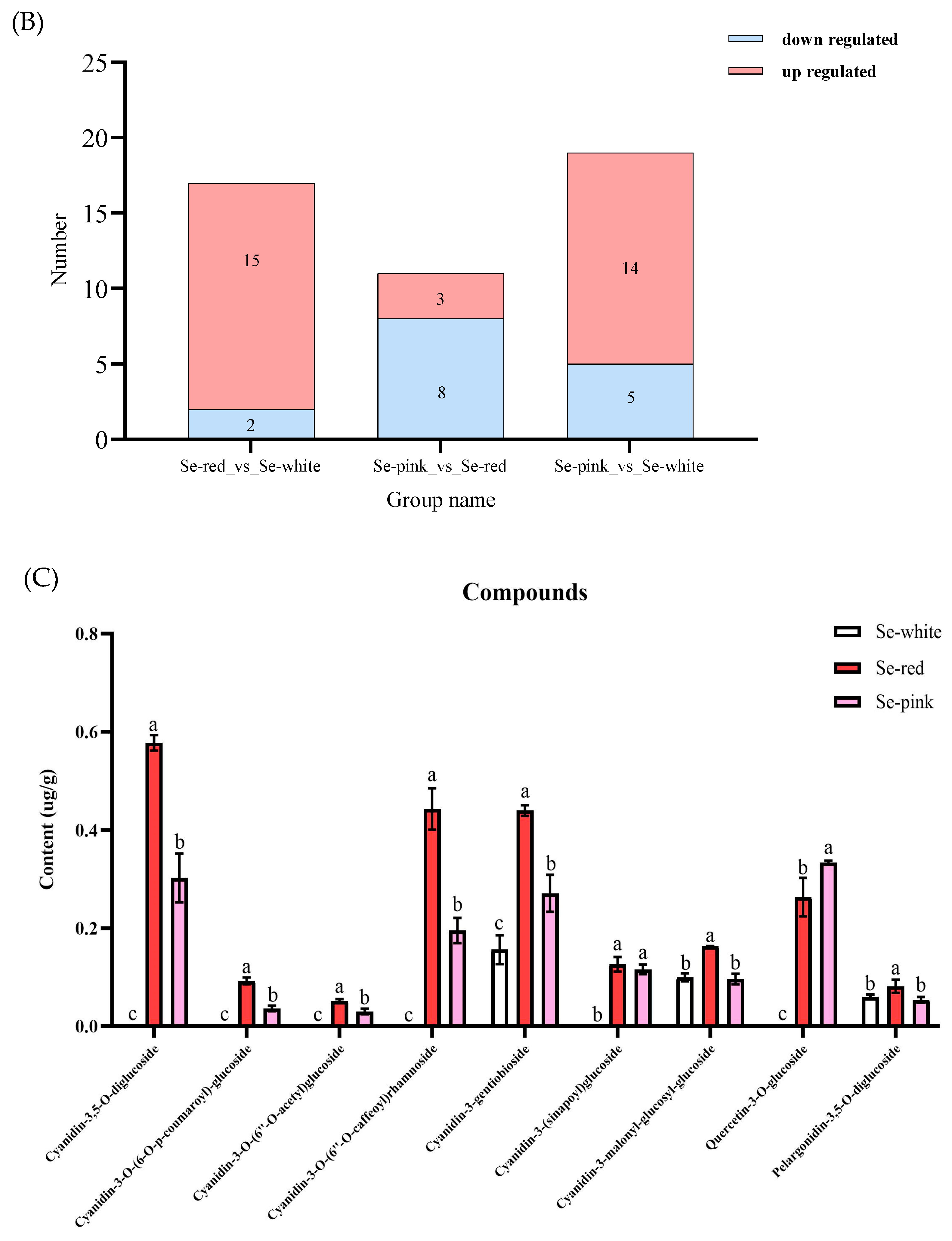
3.2. Identification and Quantification of Anthocyanin Components in Phalaenopsis ‘Huayang’
3.3. Transcriptome Sequencing and Differentially Expressed Genes
3.4. Identification of MADS Genes in Phalaenopsis ‘Huayang’
3.5. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) Associated with Morphological Mutations in Sepals
3.6. Analysis of Protein Interactions and Putative Functions of PaMADSs
3.7. Subcellular Localization of Three Key MADS Genes
4. Discussion
4.1. Morphological and Anthocyanin Analysis of Lip-like Sepal of Peloric Mutant in Phalaenopsis ‘Huayang’
4.2. Transcriptome Analysis and Identification of MADS-Box Genes Reveal Sepal Variation in Phalaenopsis ‘Huayang’
4.3. Regulatory Network and Interaction Patterns of MADS-Box Transcription Factors Reveal Sepal Variation in Phalaenopsis ‘Huayang’
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dreni, L.; Zhang, D. Flower Development: The Evolutionary History and Functions of the AGL6 Subfamily MADS-Box Genes. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopy, M.; Binaghi, M.; Cannarozzi, G.; Halitschke, R.; Boachon, B.; Heutink, R.; Bomzan, D.P.; Jäggi, L.; van Geest, G.; Verdonk, J.C.; et al. A Single MYB Transcription Factor with Multiple Functions during Flower Development. New Phytol. 2023, 239, 2007–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Klasfeld, S.; Zhu, Y.; Fernandez Garcia, M.; Xiao, J.; Han, S.K.; Konkol, A.; Wagner, D. LEAFY Is a Pioneer Transcription Factor and Licenses Cell Reprogramming to Floral Fate. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.; He, H.; Chang, Y.; Miao, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Dong, F.; Xiong, L. Multiple Roles of NAC Transcription Factors in Plant Development and Stress Responses. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2025, 67, 510–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, D.R. How Flower Development Genes Were Identified Using Forward Genetic Screens in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 2023, 224, iyad102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea-Cortines, M.; Saedler, H.; Sommer, H. Ternary Complex Formation between the MADS-Box Proteins SQUAMOSA, DEFICIENS and GLOBOSA Is Involved in the Control of Floral Architecture in Antirrhinum majus. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 5370–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, S.H.; Yasui, Y.; Ohmori, S.; Tanaka, W.; Hirano, H.Y. Rice Flower Development Revisited: Regulation of Carpel Specification and Flower Meristem Determinacy. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 1284–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Fan, W.; Liu, M.; Huang, J.; Li, B.; Sang, Q.; Song, B. Cross-Species Single-Nucleus Analysis Reveals the Potential Role of Whole-Genome Duplication in the Evolution of Maize Flower Development. BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudall, P.J.; Bateman, R.M.; Bateman, R.M. Roles of Synorganisation, Zygomorphy and Heterotopy in Floral Evolution: The Gynostemium and Labellum of Orchids and Other Lilioid Monocots. Biol. Rev. 2002, 77, 403–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, S.; Widmer, A. Orchid Diversity: An Evolutionary Consequence of Deception? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.C.; Pan, Z.J.; Hsiao, Y.Y.; Chen, L.J.; Liu, Z.J. Evolution and Function of MADS-Box Genes Involved in Orchid Floral Development. J. Syst. Evol. 2014, 52, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Buylla, E.R.; Pelaz, S.; Liljegren, S.J.; Gold, S.E.; Burgeff, C.; Ditta, G.S.; Ribas de Pouplana, L.; Martínez-Castilla, L.; Yanofsky, M.F. An Ancestral MADS-Box Gene Duplication Occurred before the Divergence of Plants and Animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5328–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, D.; Zhao, X.; Ni, C.; Li, M.; Han, L.; Cheng, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Yao, D.; Liu, S.; et al. The SEPALLATA-like Gene HrSEP1 in Hippophae rhamnoides Regulates Flower Development by Interacting with Other MADS-Box Subfamily Genes. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1503346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, K.; Melzer, R. MIKC-Type MADS-Domain Proteins: Structural Modularity, Protein Interactions and Network Evolution in Land Plants. Gene 2005, 347, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaczniak, C.; Immink, R.G.H.; Angenent, G.C.; Kaufmann, K. Developmental and Evolutionary Diversity of Plant MADS-Domain Factors: Insights from Recent Studies. Development 2012, 139, 3081–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verelst, W.; Saedler, H.; Münster, T. MIKC* MADS-Protein Complexes Bind Motifs Enriched in the Proximal Region of Late Pollen-Specific Arabidopsis Promoters. Plant Physiol. 2007, 143, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollmann, H.; Mica, E.; Todesco, M.; Long, J.A.; Weigel, D. On Reconciling the Interactions between APETALA2, MiR172 and AGAMOUS with the ABC Model of Flower Development. Development 2010, 137, 3633–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondragón-Palomino, M.; Theißen, G. MADS about the Evolution of Orchid Flowers. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.J.; Cheng, C.C.; Tsai, W.C.; Chung, M.C.; Chen, W.H.; Hu, J.M.; Chen, H.H. The Duplicated B-Class MADS-Box Genes Display Dualistic Characters in Orchid Floral Organ Identity and Growth. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 1515–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hsu, H.-F.; Hsu, W.-H.; Lee, Y.-I.; Mao, W.-T.; Yang, J.-Y.; Li, J.-Y.; Yang, C.-H. Model for Perianth Formation in Orchids. Nat. Plants 2015, 1, 15046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Shao, X.; Zhu, C.; Xu, J.; Lu, H.; Tang, Y.; Jiao, K.; Guo, W.; Xiao, W.; Liu, Z.; et al. Transcriptome-Wide Analysis Reveals the Origin of Peloria in Chinese Cymbidium (Cymbidium sinense). Plant Cell Physiol. 2018, 59, 2064–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Lee, P.F.; Hsiao, Y.Y.; Wu, W.L.; Pan, Z.J.; Lee, Y.I.; Liu, K.W.; Chen, L.J.; Liu, Z.J.; Tsai, W.C. C-and D-Class MADS-Box Genes from Phalaenopsis equestris (Orchidaceae) Display Functions in Gynostemium and Ovule Development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W.C.; Kuoh, C.S.; Chuang, M.H.; Chen, W.H.; Chen, H.H. Four DEF-like MADS Box Genes Displayed Distinct Floral Morphogenetic Roles in Phalaenopsis Orchid. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.Z.; Lin, C.P.; Cheng, T.C.; Chang, B.C.H.; Cheng, S.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Lee, C.Y.; Chin, S.W.; Chen, F.C. A de Novo Floral Transcriptome Reveals Clues into Phalaenopsis Orchid Flower Development. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola-Naranjo, R.D.; Sánchez-Sánchez, J.; González-Paramás, A.M.; Rivas-Gonzalo, J.C. Liquid Chromatographic-Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Anthocyanin Composition of Dark Blue Bee Pollen from Echium plantagineum. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1054, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ferrars, R.M.; Czank, C.; Saha, S.; Needs, P.W.; Zhang, Q.; Raheem, K.S.; Botting, N.P.; Kroon, P.A.; Kay, C.D. Methods for Isolating, Identifying, and Quantifying Anthocyanin Metabolites in Clinical Samples. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 10052–10058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo De la Cruz, A.; Hilbert, G.; Rivière, C.; Mengin, V.; Ollat, N.; Bordenave, L.; Decroocq, S.; Delaunay, J.C.; Delrot, S.; Mérillon, J.M.; et al. Anthocyanin Identification and Composition of Wild Vitis Spp. Accessions by Using LC-MS and LC-NMR. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 732, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Feng, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. DEGseq: An R Package for Identifying Differentially Expressed Genes from RNA-Seq Data. Bioinformatics 2009, 26, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callens, C.; Tucker, M.R.; Zhang, D.; Wilson, Z.A. Dissecting the Role of MADS-Box Genes in Monocot Floral Development and Diversity. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 2435–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.L.; Chen, W.C.; Lee, A.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, Y.C.A.; Chao, Y.T.; Shih, M.C. A Modified ABCDE Model of Flowering in Orchids Based on Gene Expression Profiling Studies of the Moth Orchid Phalaenopsis aphrodite. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, T.; Li, Y.; Hou, J.; He, J.; Ma, N.; Zhou, X. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of MIKCC Genes in Rose Provide Insight into Their Effects on Flower Development. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1059925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Zou, H.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y. Transcriptome-Based Identification and Expression Analysis of the Glutathione S-Transferase (GST) Family in Tree Peony Reveals a Likely Role in Anthocyanin Transport. Hortic. Plant J. 2022, 8, 787–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, X. BcAP3, a MADS Box Gene, Controls Stamen Development and Male Sterility in Pak-Choi (Brassica rapa ssp. Chinensis). Gene 2020, 747, 144698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yan, W.; Fu, L.Y.; Kaufmann, K. Architecture of Gene Regulatory Networks Controlling Flower Development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondragõn-Palomino, M.; Theißen, G. Conserved Differential Expression of Paralogous DEFICIENS- and GLOBOSA-like MADS-Box Genes in the Flowers of Orchidaceae: Refining the “Orchid Code”. Plant J. 2011, 66, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitoma, M.; Kajino, Y.; Hayashi, R.; Endo, M.; Kubota, S.; Kanno, A. Molecular Mechanism Underlying Pseudopeloria in Habenaria radiata (Orchidaceae). Plant J. 2019, 99, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucibelli, F.; Valoroso, M.C.; Theißen, G.; Nolden, S.; Mondragon-palomino, M.; Aceto, S. Extending the Toolkit for Beauty: Differential Co-expression of Drooping Leaf-like and Class B MADS-box Genes during Phalaenopsis Flower Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Du, J.S.; Chen, Y.Y.; Chung, M.C.; Tsai, W.C.; Wang, C.N.; Chen, H.H. Flower Development of Phalaenopsis Orchid Involves Functionally Divergent SEPALLATA-like Genes. New Phytol. 2014, 202, 1024–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.Y.; Rengasamy, K.P.; Huang, L.M.; Hsu, C.C.; Jeng, M.F.; Chen, W.H.; Chen, H.H. Assessment of Violet-Blue Color Formation in Phalaenopsis Orchids. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pařenicová, L.; De Folter, S.; Kieffer, M.; Horner, D.S.; Favalli, C.; Busscher, J.; Cook, H.E.; Ingram, R.M.; Kater, M.M.; Davies, B.; et al. Molecular and Phylogenetic Analyses of the Complete MADS-Box Transcription Factor Family in Arabidopsis: New Openings to the MADS World. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1538–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, R.; Agarwal, P.; Ray, S.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, V.P.; Tyagi, A.K.; Kapoor, S. MADS-Box Gene Family in Rice: Genome-Wide Identification, Organization and Expression Profiling during Reproductive Development and Stress. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Li, K.; Wang, F.; Sun, K. Genome-Wide Analysis of the MADS-Box Gene Family of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides ssp. Sinensis) and Their Potential Role in Floral Organ Development. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1387613. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, F. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Mads-Box Transcription Factor Family in Solanum melongena. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sri, T.; Gupta, B.; Tyagi, S.; Singh, A. Homeologs of Brassica SOC1, a Central Regulator of Flowering Time, Are Differentially Regulated Due to Partitioning of Evolutionarily Conserved Transcription Factor Binding Sites in Promoters. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020, 147, 106777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, R.; Francioso, A.; Trovato, M. Proline Affects Flowering Time in Arabidopsis by Modulating FLC Expression: A Clue of Epigenetic Regulation? Plants 2022, 11, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Severing, E.I.; Koornneef, M.; Aarts, M.G.M. FLC and SVP Are Key Regulators of Flowering Time in the Biennial/Perennial Species Noccaea Caerulescens. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 582577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Z.; Lin, C.P.; Cheng, T.C.; Huang, Y.W.; Tsai, Y.J.; Cheng, S.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Lee, C.P.; Chung, W.C.; Chang, B.C.H.; et al. The Genome and Transcriptome of Phalaenopsis Yield Insights into Floral Organ Development and Flowering Regulation. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yang, J.; Wan, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, L.; Rong, J.; Chen, L.; He, T.; Zheng, Y. Genome-Wide Identification of MIKCc-Type MADS-Box Family Gene and Floral Organ Transcriptome Characterization in Ma Bamboo (Dendrocalamus latiflorus Munro). Genes 2023, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.C.; Lee, P.F.; Chen, H.I.; Hsiao, Y.Y.; Wei, W.J.; Pan, Z.J.; Chuang, M.H.; Kuoh, C.S.; Chen, W.H.; Chen, H.H. PeMADS6, a GLOBOSA/PISTILLATA-like Gene in Phalaenopsis equestris Involved in Petaloid Formation, and Correlated with Flower Longevity and Ovary Development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005, 46, 1125–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Iqbal, A.; Yang, M.; Yang, Y. Research Progress on Gene Regulation of Plant Floral Organogenesis. Genes 2025, 16, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, Q.; Lyu, P.; Lin, R.; Sun, C. Identification and Expression Profiling of Selected MADS-Box Family Genes in Dendrobium officinale. Genetica 2019, 147, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Gai, R.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Q.; He, G.; Wu, J.H.; et al. PeNAC67-PeKAN2-PeSCL23 and B-Class MADS-Box Transcription Factors Synergistically Regulate the Specialization Process from Petal to Lip in Phalaenopsis equestris. Mol. Hortic. 2024, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dong, F.; Zhu, J.; Lv, X. Physiological and Transcriptomic Analysis of a Sepal Mutant in Phalaenopsis. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061361
Qi Y, Wang Y, Dong F, Zhu J, Lv X. Physiological and Transcriptomic Analysis of a Sepal Mutant in Phalaenopsis. Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061361
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Yu, Yenan Wang, Fei Dong, Jiao Zhu, and Xiaohui Lv. 2025. "Physiological and Transcriptomic Analysis of a Sepal Mutant in Phalaenopsis" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061361
APA StyleQi, Y., Wang, Y., Dong, F., Zhu, J., & Lv, X. (2025). Physiological and Transcriptomic Analysis of a Sepal Mutant in Phalaenopsis. Agronomy, 15(6), 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061361





