The Effect of Combined Application of Rhodochrosite Slag and Biochar on Cadmium Uptake in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Materials
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Sampling and Analysis
2.4.1. Sample Collection
2.4.2. Measurements
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Combined Application of Rhodochrosite Slag and Biochar on Cd Content in Different Parts of Rice
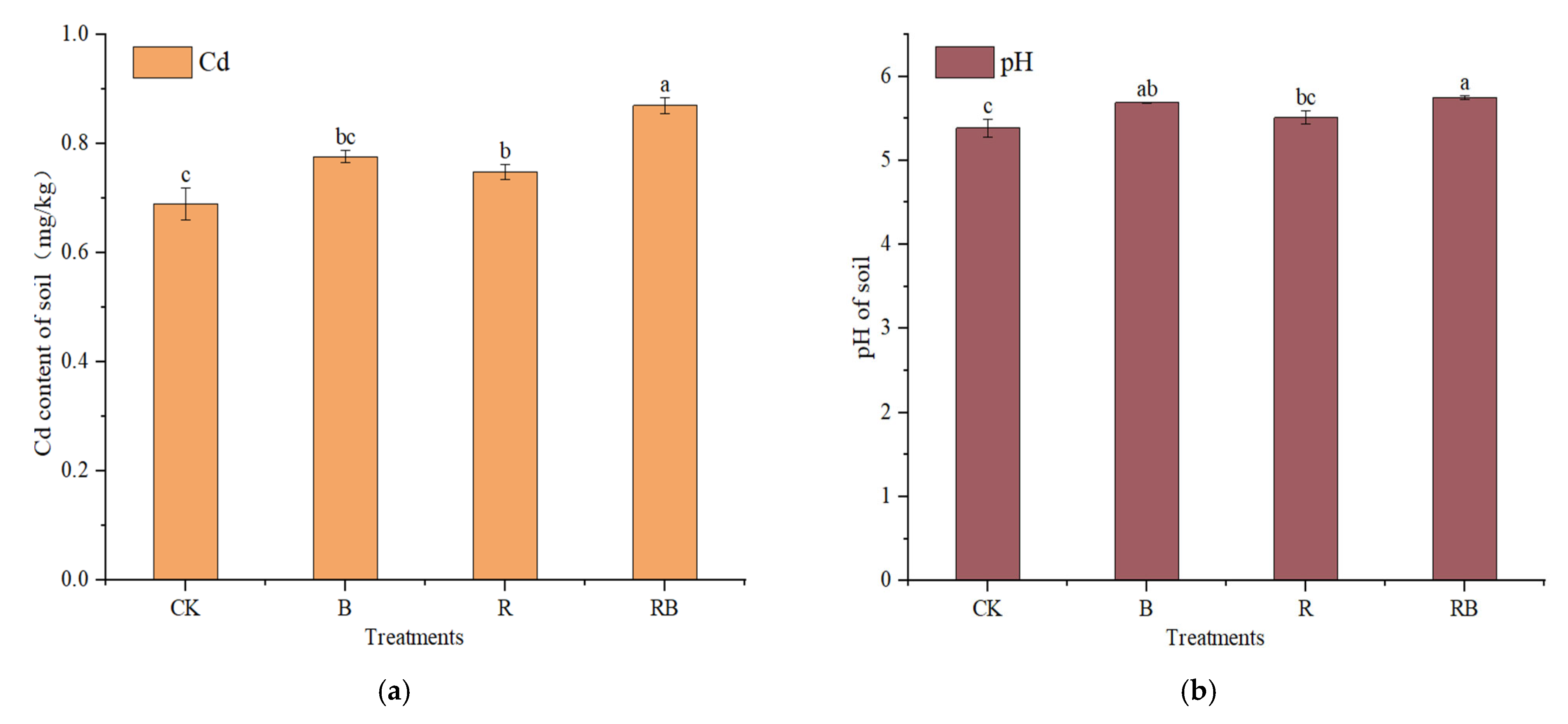
3.2. Effects of Combined Application of Rhodochrosite Slag and Biochar on Soil Total Cd Content and pH
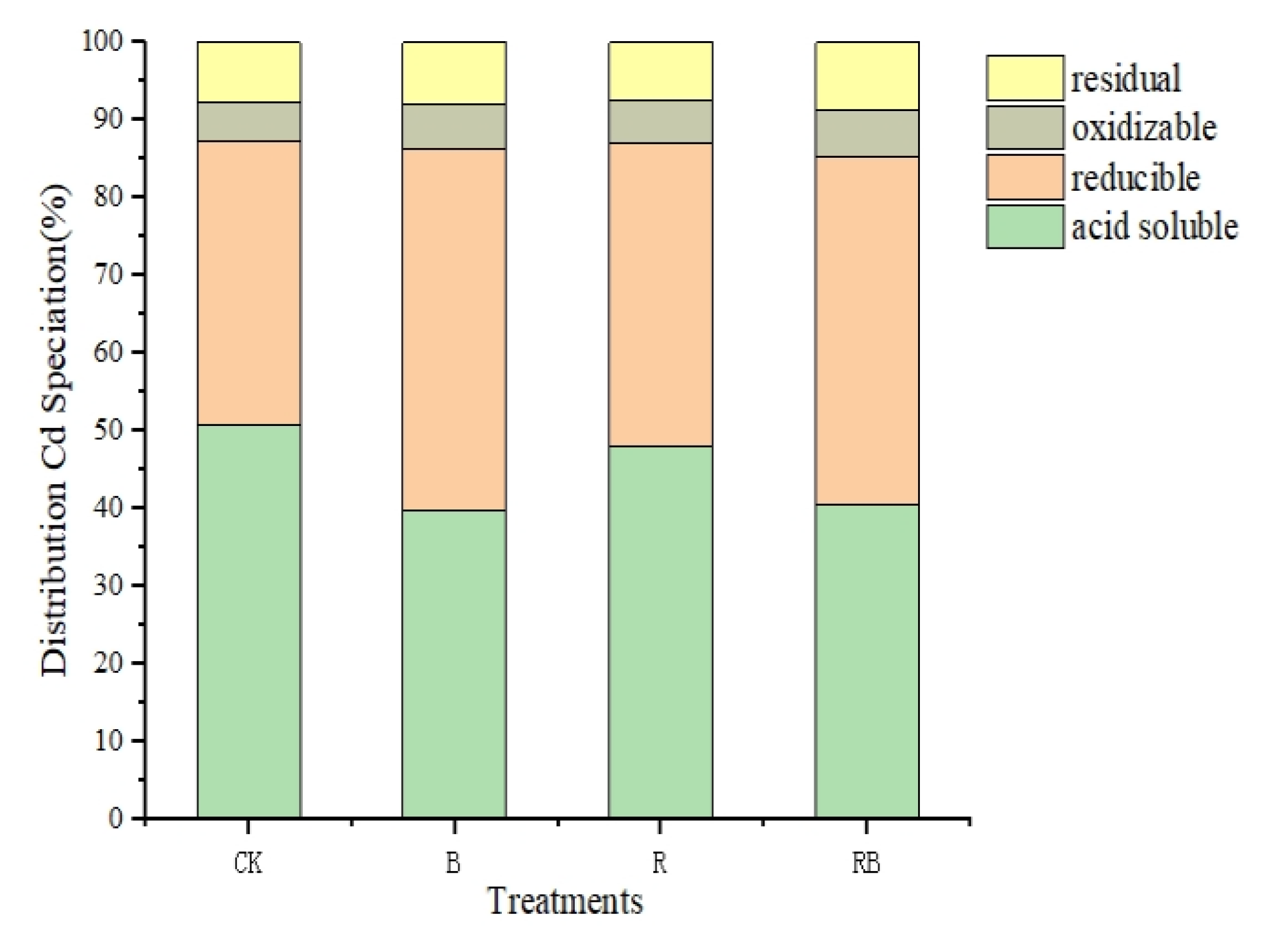
3.3. Effects of Combined Application of Rhodochrosite Slag and Biochar on Soil Cd Fractions
3.4. Effects of Combined Application of Rhodochrosite Slag and Biochar on Cadmium Translocation and Bioaccumulation Factors in Rice
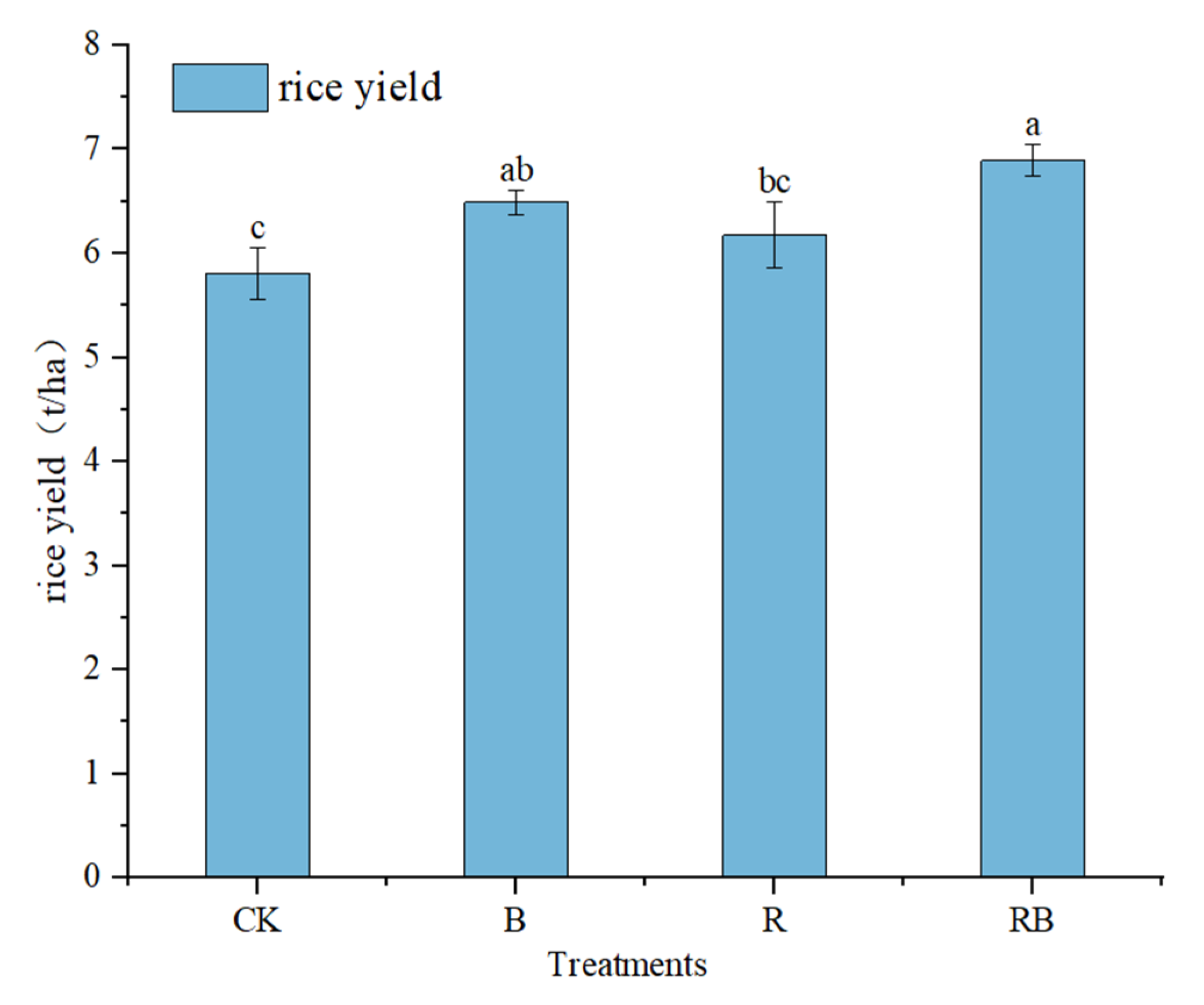
3.5. Effects of Combined Application of Rhodochrosite Slag and Biochar on Rice Yield
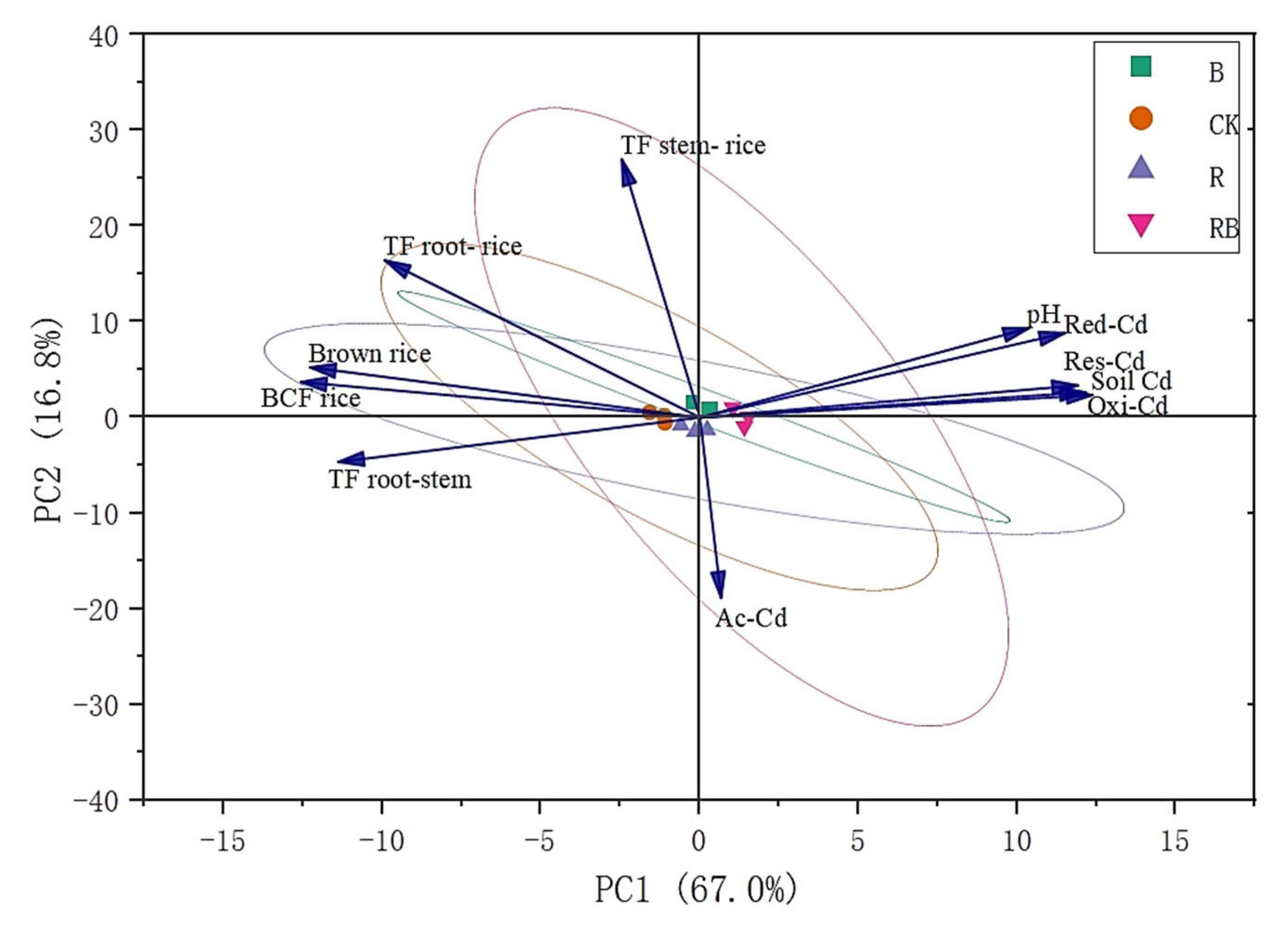
3.6. Relationships Between Brown Rice Cadmium Content and Soil Cadmium Fixation
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Rhodochrosite Slag and Biochar on Soil pH and Cadmium Availability
4.2. Effects of Rhodochrosite Slag and Biochar on Cd Uptake and Yield in Rice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RS | Rhodochrosite slag |
| TF | Translocation factor |
| BCF | Bioaccumulation factor |
| BC | Biochar |
References
- Bastami, K.D.; Afkhami, M.; Mohammadizadeh, M.; Ehsanpour, M.; Chambari, S.; Aghaei, S.; Esmaeilzadeh, M.; Neyestani, M.R.; Lagzaee, F.; Baniamam, M. Bioaccumulation and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments and mullet Liza klunzingeri in the northern part of the Persian Gulf. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 94, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; Li, F. Complexities surrounding china’s soil action plan. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 2315–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Chen, A.; Wang, Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, M. Effects of blast furnace slag on the immobilization, plant uptake and translocation of Cd in a contaminated paddy soil. Environ. Int. 2023, 179, 108162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.N.; Wu, P.; Jeyakumar, P.; Bolan, N.; Wang, H.L.; Gao, B.; Wang, S.S.; Wang, B. Biochar as a potential strategy for remediation of contaminated mining soils: Mechanisms, applications, and future perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 313, 114973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wei, W.; Xu, C.; Meng, Y.; Bai, W.; Yang, W.; Lin, A. Manganese-modified biochar for highly efficient sorption of cadmium. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 9126–9134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlangeni, A.T.; Chinthenga, E.; Kapito, N.J.; Namaumbo, S.; Feldmann, J.; Raab, A. Safety of African grown rice: Comparative review of As, Cd, and Pb contamination in African rice and paddy fields. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Mehmood, S.; Mahmood, M.; Ali, S.; Nunez-Delgado, A.; Li, W. Simultaneous immobilization of lead and arsenic and improved phosphorus availability in contaminated soil using biochar composite modified with hydroxyapatite and oxidation: Findings from a pot experiment. Environ. Res. 2023, 235, 116640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danso, O.P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Niu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Wang, X.; Zheng, L.; Dai, J.; Yin, X.; et al. Effects of foliar selenium, biochar, and pig manure on cadmium accumulation in rice grains and assessment of health risk. Environ. Res. 2024, 256, 119160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, L.; Alvarenga, P.; Pena, D.; Fernandez, D.; Albarran, A.; Rato-Nunes, J.M.; Lopez-Pineiro, A. Controlling As, Cd, and Pb bioaccumulation in rice under different levels of alternate wetting and drying irrigation with biochar amendment: A 3-year field study. Chemosphere 2025, 372, 144114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.; Guo, Z.; Shi, L.; Feng, W.; Xiao, X.; Peng, C.; Xue, Q. Effects of mixed amendments on the phytoavailability of Cd in contaminated paddy soil under a rice-rape rotation system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 14128–14136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Su, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, J.-Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Yin, J.; Jin, L. In-situ biochar amendment mitigates dietary risks of heavy metals and PAHs in aquaculture products. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palansooriya, K.N.; Shaheen, S.M.; Chen, S.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Hashimoto, Y.; Hou, D.; Bolan, N.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S. Soil amendments for immobilization of potentially toxic elements in contaminated soils: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vithanage, M.; Herath, I.; Joseph, S.; Bundschuh, J.; Bolan, N.; Ok, Y.S.; Kirkham, M.B.; Rinklebe, J. Interaction of arsenic with biochar in soil and water: A critical review. Carbon 2017, 113, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Sharma, P.; Li, B.; Liu, K.; Liu, J.; Flury, M.; Shang, J. Effect of naphthalene on transport and retention of biochar colloids through saturated porous media. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 530, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, H.-X. Modified-biochar adsorbents (MBAs) for heavy-metal ions adsorption: A critical review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Lu, K.; Dong, H.; Wang, D.; Zhao, F.-J.; Huang, C.-F.; et al. OsNRAMP5 contributes to manganese translocation and distribution in rice shoots. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 4849–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Christl, I.; Wang, P.; Kretzschmar, R.; Zhao, F.-J. Two-year and multi-site field trials to evaluate soil amendments for controlling cadmium accumulation in rice grain. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Lin, L.; Qiu, W.; Song, Z.; Liao, B. Supplementation with ferromanganese oxide-impregnated biochar composite reduces cadmium uptake by indica rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Chen, W. Manganese, Zinc, and pH Affect Cadmium Accumulation in Rice Grain under Field Conditions in Southern China. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.-b.; Huang, D.-y.; Zhu, Q.-H.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.-L.; He, H.-B.; Zhu, H.-H.; Xu, C. A three-season field study on theinsitu remediation of Cd-contaminated paddy soil using lime, two industrial by-products, and a low-Cd-accumulation rice cultivar. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 136, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangviroon, P.; Endo, Y.; Fujinaka, R.; Kobayashi, M.; Igarashi, T.; Yamamoto, T. Change in Arsenic Leaching from Silty Soil by Adding Slag Cement. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Meng, J.; Huang, Y.; Dai, Z.; Tang, C.; Xu, J. Effects of carbide slag, lodestone and biochar on the immobilization, plant uptake and translocation of As and Cd in a contaminated paddy soil. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bert, V.; Lors, C.; Ponge, J.-F.; Caron, L.; Biaz, A.; Dazy, M.; Masfaraud, J.-F. Metal immobilization and soil amendment efficiency at a contaminated sediment landfill site: A field study focusing on plants, springtails, and bacteria. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 169, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Xie, Y.; Chen, K.; Yi, L.K.X.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhang, Y.K. Bioleaching assisted conversion of refractory low-grade ferruginous rhodochrosite to Mn-Fe based catalysts for sulfathiazole degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 130804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, K.; Xiong, R.; Long, P.; Xu, Y.; Ma, X.; Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Fu, Z. Ferrate-Modified Biochar for Greenhouse Gas Mitigation: First-Principles Calculation and Paddy Field Trails. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, S.; Ahmed, W.; Rizwan, M.; Ditta, A.; Irshad, S.; Chen, D.-Y.; Bashir, S.; Mahmood, M.; Li, W.; Imtiaz, M. Biochar, slag and ferrous manganese ore affect lead, cadmium and antioxidant enzymes in water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica) grown in multi-metal contaminated soil. Crop Pasture Sci. 2023, 74, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, F.; Xiao, C.; Hu, W.; Ye, M.; Xie, Q.; Wei, H.; He, J.; Yang, J.; et al. Cadmium Uptake and Translocation in Wheat Differing in Grain Cadmium Accumulation. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil Agricultural Chemical Analysis, 3rd ed.; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J. Measurement of cadmium content in soils and vegetables by FAAS. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 1999, 19, 613–615. [Google Scholar]
- Rauret, G.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.F.; Sahuquillo, A.; Rubio, R.; Davidson, C.; Ure, A.; Quevauviller, P. Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J. Environ. Monit. 1999, 1, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Liu, Y.L.; Yang, Y.H.; Li, L.; Fu, X.; Peng, L.; Zeng, Q.R. Straw removal or non-removal affects cadmium (Cd) accumulation in soil-rice (Oryza sativa L.) system at different ambient air Cd levels. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.-y.; Xue, S.-g.; Cui, M.-q.; Wu, C.; Li, W.-c. Arsenic availability and transportation in soil-rice system affected by iron-modified biochar. J. Cent. South Univ. 2021, 28, 1901–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xie, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, X.; Ren, J.; Shi, Y.; Liu, D.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J. Biochar co-pyrolyzed from peanut shells and maize straw improved soil biochemical properties, rice yield, and reduced cadmium mobilization and accumulation by rice: Biogeochemical investigations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.; Noman, A.; Shang, J.; Mahmood, A.; Mubashir, M.; Irshad, M.K.; Khoo, K.S.; Ng, H.S.; Show, P.L. Elucidating the impact of goethite-modified biochar on arsenic mobility, bioaccumulation in paddy rice(Oryza sativa L.) along with soil enzyme activities. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 160, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahori, A.H.; Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Demiraj, E.; Idir, R.; Bui, T.T.X.; Vu, D.D.; Channa, A.; Samoon, N.A.; Zhang, Z. Clays, Limestone and Biochar Affect the Bioavailability and Geochemical Fractions of Cadmium and Zinc from Zn-Smelter Polluted Soils. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lin, H.; Jin, X.; Dong, Y.; Luo, M. Simultaneous reduction of arsenic and cadmium bioavailability in agriculture soil and their accumulation in Brassica chinensis L. by using minerals. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xie, Z.; Hu, T.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, R.; Jin, P. Biochar application increases biological nitrogen fixation in soybean with improved soil properties in an Ultisol. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 3095–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ding, A. Effects of Passivating Agents on the Availability of Cd and Pb and Microbial Community Function in a Contaminated Acidic Soil. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, S.; Alghanem, S.M.S.; Alsudays, I.M.; Malik, Z.; Abbasi, G.H.; Ali, A.; Noreen, S.; Ali, M.; Irfan, M.; Rizwan, M. Effect of biochar, zeolite and bentonite on physiological and biochemical parameters and lead and zinc uptake by maize (Zea mays L.) plants grown in contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ding, A.; Li, T.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Naidu, R. Immobilization of Cd and Pb in a contaminated acidic soil amended with hydroxyapatite, bentonite, and biochar. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 2262–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Yao, A.; Qiu, R.; Li, W.C.; Ye, Z. Growth and Cd uptake by rice (Oryza sativa) in acidic and Cd-contaminated paddy soils amended with steel slag. Chemosphere 2017, 189, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Xu, H.; Song, F.; Ge, H.; Chen, L.; Yue, S.; Yang, W. Effect of biochar on immobilization remediation of Cd-contaminated soil and environmental quality. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Tao, S.; Li, M.; Li, Q.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Enhanced Cd removal from aqueous solution by biologically modified biochar derived from digestion residue of corn straw silage. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassaei, F.; Hoodaji, M.; Abtahi, S.A. Cadmium speciation as influenced by soil water content and zinc and the studies of kinetic modeling in two soils textural classes. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, D.; Nie, M.; Wang, H.; Li, L. Adsorption of Cr6+on Polyethyleneimine-functionalized Straw Biochar from Aqueous Solution. Chem. J. Chin. Univ.-Chin. 2020, 41, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.-W.; Yao, Q.-X.; Su, D.-C. Influencing Factors of Cadmium Bioaccumulation Factor in Crops. Huanjing Ke Xue 2021, 42, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crusciol, C.A.C.; Artigiani, A.C.C.A.; Arf, O.; Carmeis Filho, A.C.A.; Soratto, R.P.; Nascente, A.S.; Alvarez, R.C.F. Soil fertility, plant nutrition, and grain yield of upland rice affected by surface application of lime, silicate, and phosphogypsum in a tropical no-till system. Catena 2016, 137, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xue, G.; Fan, F.; Liang, Y. Silicon-enhanced resistance to cadmium toxicity in Brassica chinensis L. is attributed to Si-suppressed cadmium uptake and transport and Si-enhanced antioxidant defense capacity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Cai, Y.; Pan, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Cai, K.; Wang, W. Significant Synergy Effects of Biochar Combined with Topdressing Silicon on Cd Reduction and Yield Increase of Rice in Cd-Contaminated Paddy Soil. Agronomy 2024, 14, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.; da Silveira Silveira, S.F.; Daloso, D.d.M.; Mendes, G.C.; Merchant, A.; Kuki, K.N.; Oliva, M.A.; Loureiro, M.E.; Miyasaka Almeida, A. Ecophysiological responses to excess iron in lowland and upland rice cultivars. Chemosphere 2017, 189, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Xiao, Q.; Yuan, M.; Huang, R.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H. Effects of steel slag amendments on accumulation of cadmium and arsenic by rice (Oryza sativa) in a historically contaminated paddy field. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 40001–40008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Zhou, H.; Li, A.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, S.; Zhang, N.; Bao, L. The Effects of the Combined Application of Biochar and Phosphogypsum on the Physicochemical Properties of Cd-Contaminated Soil and the Yield Quality of Chinese Cabbage. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Total Nitrogen (%) | Total Phosphorus (mg/kg) | Total Potassium (mg/kg) | Available Nitrogen (mg/kg) | Rapidly Available Phosphorus (mg/kg) | Rapidly Available Potassium (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.26 | 5.77 × 103 | 4.72 × 104 | 176.00 | 242.00 | 2.2 × 104 |
| Molecular Formula | SiO2 | MnO | Al2O3 | CaO | Fe2O3 | SO3 | K2O | MgO | Na2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | BaO | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (%) | 39.72 | 18.12 | 13.88 | 10.92 | 5.26 | 4.42 | 3.12 | 2.23 | 0.98 | 0.56 | 0.46 | 0.13 | 0.20 |
| Treatment | Root (mg/kg) | Stem (mg/kg) | Leaf (mg/kg) | Brown Rice (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 3.641 ± 0.046 a | 2.497 ± 0.076 a | 0.293 ± 0.003 a | 0.274 ± 0.007 a |
| B | 2.899 ± 0.030 b | 1.722 ± 0.062 c | 0.215 ± 0.005 b | 0.198 ± 0.012 b |
| R | 3.608 ± 0.291 a | 2.197 ± 0.052 b | 0.221 ± 0.009 b | 0.191 ± 0.006 b |
| RB | 2.678 ± 0.056 b | 1.315 ± 0.055 d | 0.196 ± 0.011 b | 0.135 ± 0.014 c |
| Treatment | Ac-Cd (mg/kg) | Red-Cd (mg/kg) | Oxi-Cd (mg/kg) | Res-Cd (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.350 ± 0.015 ab | 0.253 ± 0.021 b | 0.037 ± 0.002 c | 0.053 ± 0.003 c |
| B | 0.308 ± 0.012 b | 0.362 ± 0.018 a | 0.046 ± 0.001 b | 0.062 ± 0.003 b |
| R | 0.360 ± 0.017 a | 0.293 ± 0.005 b | 0.041 ± 0.001 c | 0.056 ± 0.001 bc |
| RB | 0.353 ± 0.015 ab | 0.391 ± 0.007 a | 0.052 ± 0.002 a | 0.077 ± 0.002 a |
| Treatment | TF | BCF | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFroot-stem | TFroot-rice | TFstem-rice | BCFroot | BCFstem | BCFleaf | BCFrice | |
| CK | 0.686 ± 0.022 a | 0.075 ± 0.003 a | 0.110 ± 0.004 ab | 5.300 ± 0.247 a | 3.626 ± 0.050 a | 0.427 ± 0.021 a | 0.399 ± 0.019 a |
| B | 0.594 ± 0.016 b | 0.068 ± 0.004 a | 0.115 ± 0.003 a | 3.736 ± 0.087 b | 2.220 ± 0.106 c | 0.277 ± 0.005 b | 0.255 ± 0.019 b |
| R | 0.614 ± 0.033 ab | 0.054 ± 0.006 b | 0.087 ± 0.005 b | 4.814 ± 0.320 a | 2.936 ± 0.029 b | 0.295 ± 0.014 b | 0.255 ± 0.013 b |
| RB | 0.492 ± 0.028 c | 0.050 ± 0.004 b | 0.103 ± 0.013 ab | 3.079 ± 0.053 b | 1.515 ± 0.089 d | 0.226 ± 0.016 c | 0.154 ± 0.015 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Ye, Z.; Chen, F.; Zhou, W.; Ma, X.; Fu, Z. The Effect of Combined Application of Rhodochrosite Slag and Biochar on Cadmium Uptake in Rice. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061321
He J, Ye Z, Chen F, Zhou W, Ma X, Fu Z. The Effect of Combined Application of Rhodochrosite Slag and Biochar on Cadmium Uptake in Rice. Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061321
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jing, Zhixi Ye, Fugui Chen, Wentao Zhou, Xin Ma, and Zhiqiang Fu. 2025. "The Effect of Combined Application of Rhodochrosite Slag and Biochar on Cadmium Uptake in Rice" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061321
APA StyleHe, J., Ye, Z., Chen, F., Zhou, W., Ma, X., & Fu, Z. (2025). The Effect of Combined Application of Rhodochrosite Slag and Biochar on Cadmium Uptake in Rice. Agronomy, 15(6), 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061321







