Optimization of Subsurface Drainage Parameters in Saline–Alkali Soils to Improve Salt Leaching Efficiency in Farmland in Southern Xinjiang
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
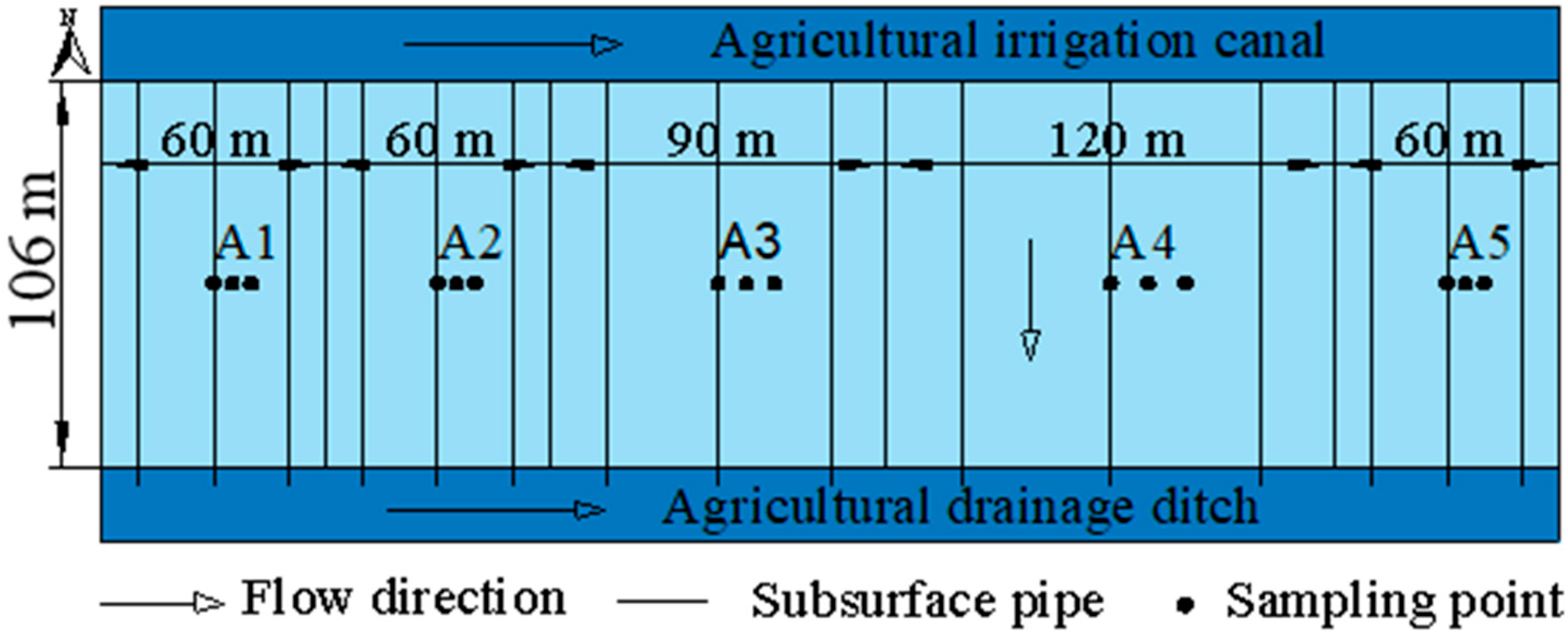
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Data Collection and Analysis
2.3.1. Water Sample Processing
2.3.2. Soil Measurements
2.3.3. Theoretical Analysis
3. Results
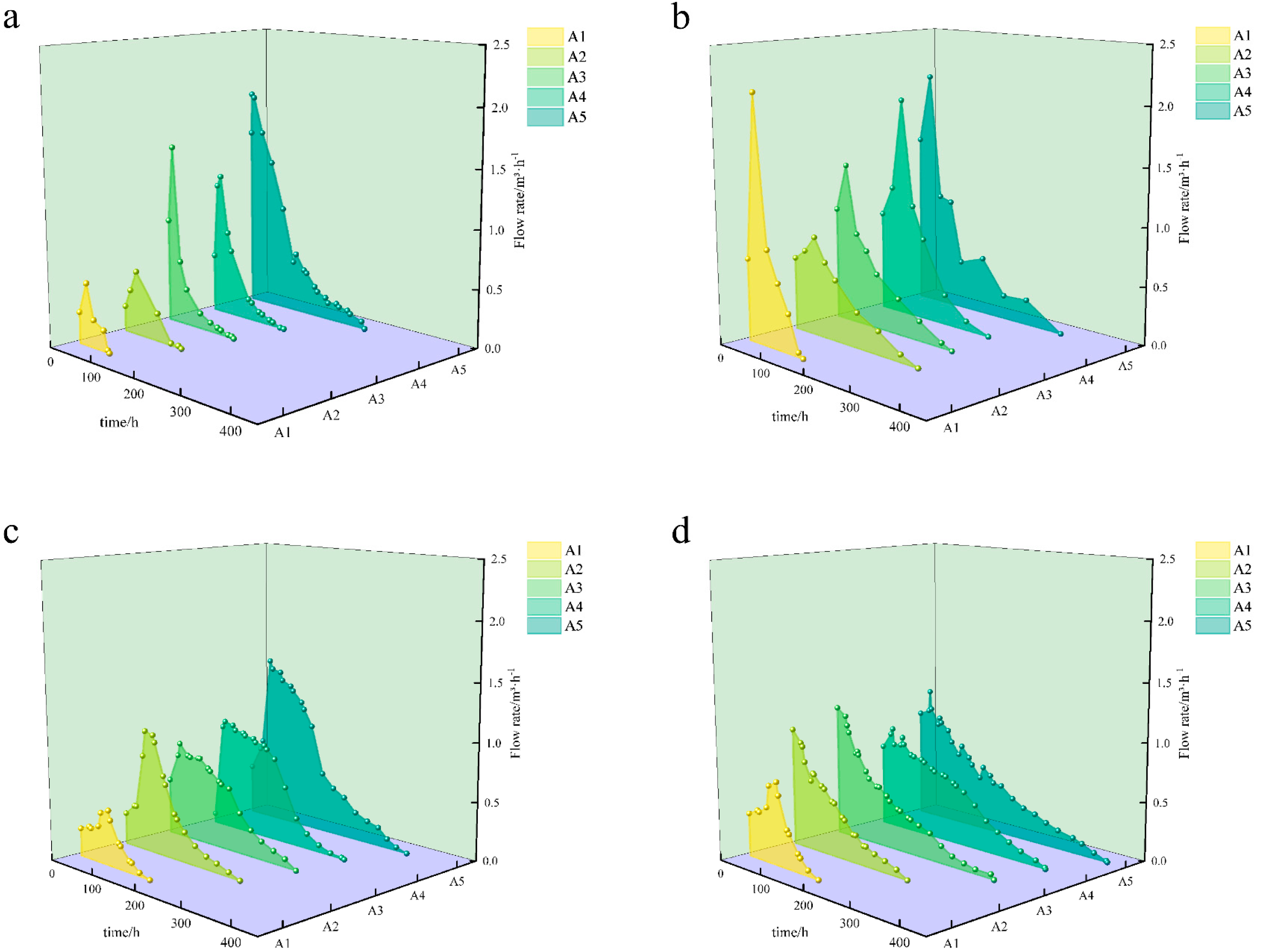
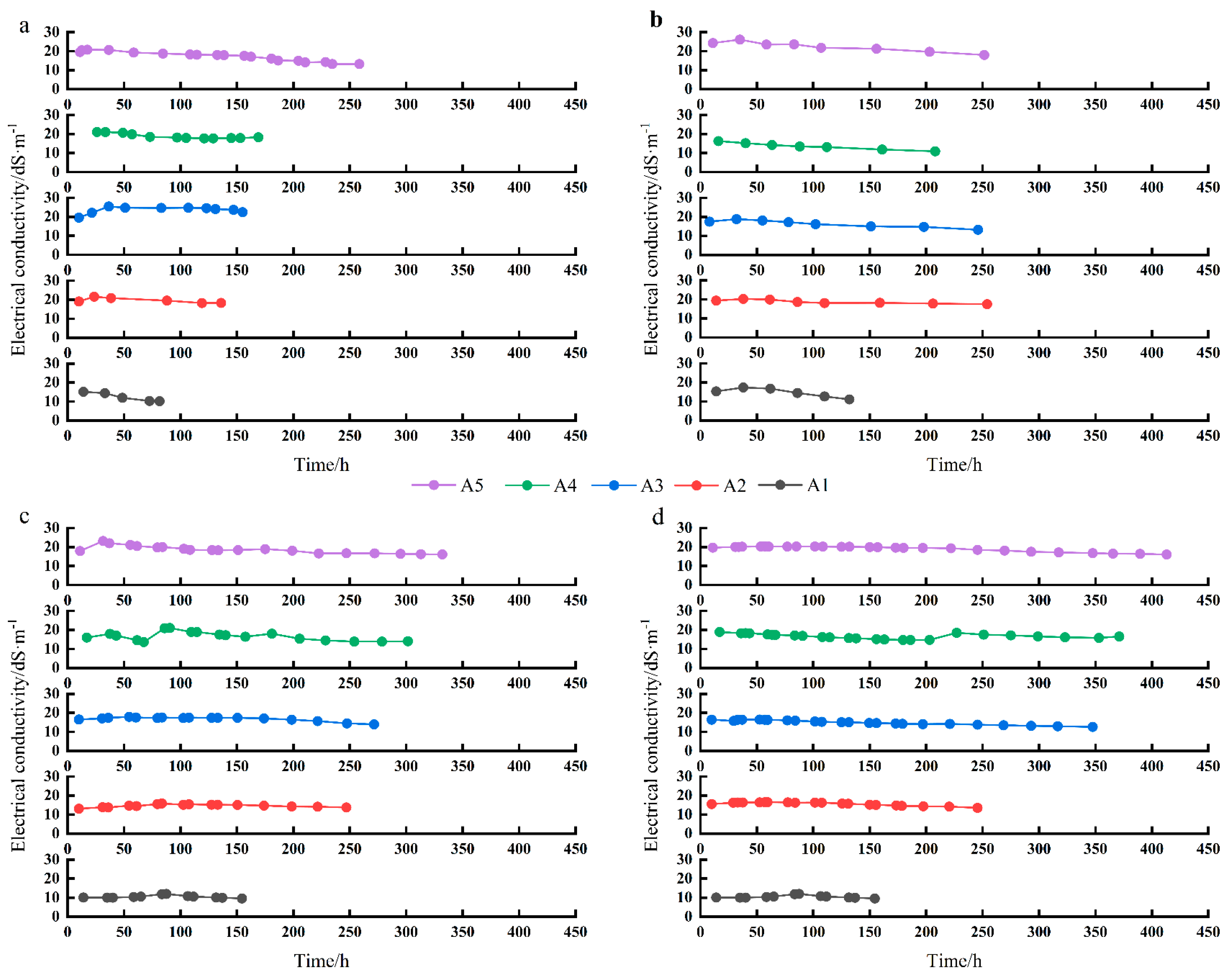
3.1. Variations in Drainage Flow and Electrical Conductivity
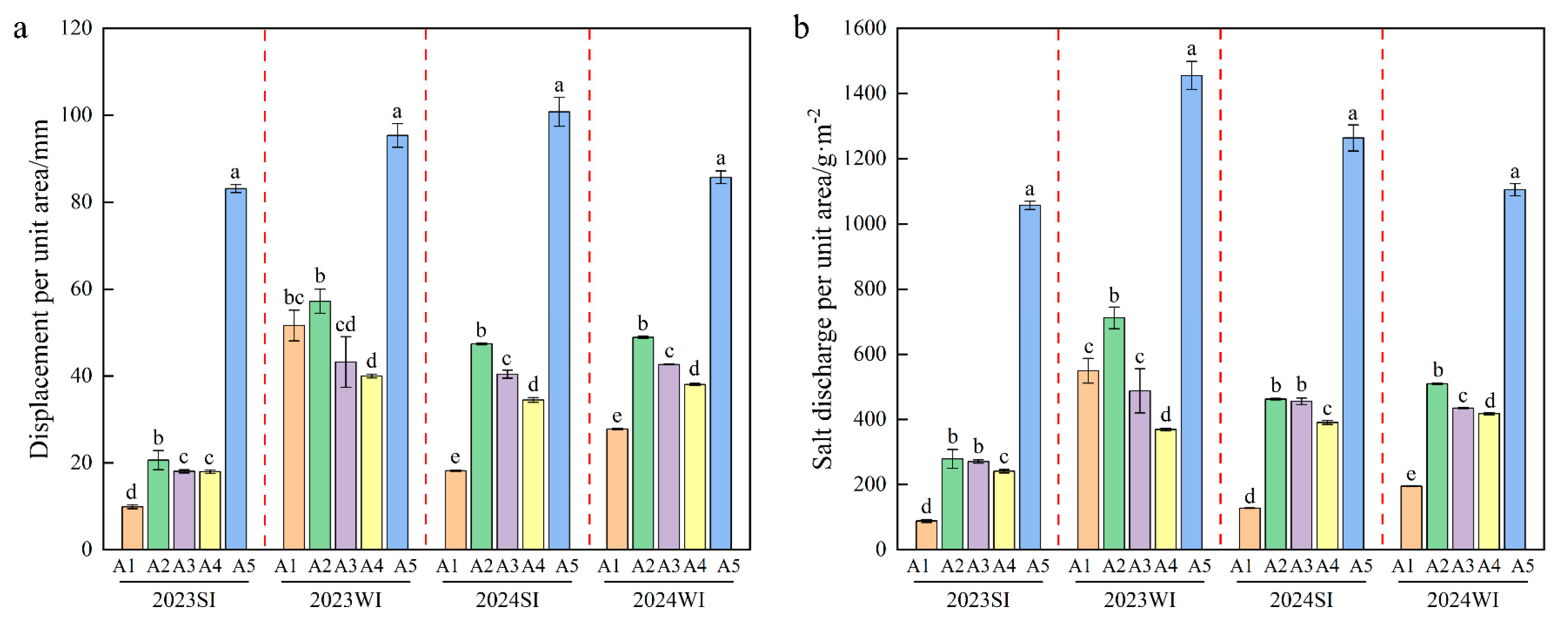
3.2. Variations in Drainage Volume and Salt Discharge
3.3. Variations in Drainage-to-Irrigation Ratio and Salt Discharge Efficiency Coefficient
3.4. Changes in Water Allocation During the Leaching Process
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Subsurface Drainage Layout on Unit-Area Drainage and Salt Removal
4.2. Effects of Subsurface Drainage Layout on the Drainage-to-Irrigation Ratio and Salt Removal Efficiency Coefficient
4.3. Effects of Leaching Season on Soil Water Allocation and Optimization Strategies
4.4. Research Horizons
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EC | Electric conductivity |
| Rd/i | The ratio of drainage to irrigation |
| DSEC | Drainage salt efficiency coefficient |
References
- Zou, M.Z.; Kang, S.Z.; Niu, J. Water-suitable reclamation can mitigate the amplified agricultural water stress driven by climate change in arid inland basin. J. Hydrol. 2024, 640, 131736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.P.; Shan, L.; Zhang, H. Improving agricultural water use efficiency in arid and semiarid areas of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 80, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.P.; Hou, Z.N.; Wu, L.S. Evaluating salinity distribution in soil irrigated with saline water in arid regions of northwest China. (Special Issue: Salinity management in China). Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 2001–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, Q.Q.; Pan, Y.Z. Effect of subsurface drainpipe parameters on soil water and salt distribution in a localized arid zone: A field-scale study. Agronomy 2025, 15, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.R.; Zhou, B.B.; Shi, J.C. Soil water/salt balance and water productivity of typical irrigation schedules for cotton under film mulched drip irrigation in northern Xinjiang. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.W.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhao, Y.L. Optimizing cotton yield and soil salinity management: Integrating brackish water leaching and freshwater drip irrigation with subsurface drainage. Field Crops Res. 2024, 314, 109454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.N.; Chen, C.; Wang, F. Effects of subsurface pipe drainage spacing on soil salinity movement in Jiangsu coastal reclamation area. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addab, H.; Bailey, R.T. Simulating the effect of subsurface tile drainage on watershed salinity using SWAT. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 262, 107431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauren, E.B. Evaluation of macroscopic porosity-permeability relationships in heterogeneous mineral dissolution and precipitation scenarios. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 10217–10230. [Google Scholar]
- Zied, H.A.; Salem, B. Subsurface drainage system performance, soil salinization risk, and shallow groundwater dynamic under irrigation practice in an arid land. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 467–477. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, T.; LI, N.; Wang, S.L. Simulation study on performance of nitrogen loss of an improved subsurface drainage system for one-time drainage using HYDRUS-2D. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 246, 106698. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.Z.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, J.S. Key parameters for the optimal layout of subsurface drainage pipe in arid areas. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 117–126. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.Y.; Guo, C.Y.; Wu, J.W. Effective radius of corrugated drainage pipes wrapped with a thin geotextile envelope. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2024, 150, 04024023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Liu, S.T.; Li, Q. Study on the annual dynamic pattern of soil salinity and the depth of groundwater suitable for salt control in open irrigation and dark drainage areas. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2025, 1–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Fan, L.Q. Salt drainage efficiency and anti-clogging effects of subsurface pipes wrapped with geotextiles. Water 2024, 16, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Miao, Q.F.; Shi, H.B. Simulating water and salt migration through soils with a clay layer and subsurface pipe drainage system at different depths using the DRAINMOD-S model. Agronomy 2023, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Y. Research on Water-Salt Migrating Characteristics Under the Subsurface Pipe Drainage of Shallow-Tight Type in Yinbei. Master’s Thesis, Ningxia University, Ningxia, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Qin, W.B.; Li, M.S.; Li, Y.F. Proposed gravel filters for pipe-drain to improve the efficacy ofthe drainage system under drip irrigation. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2017, 36, 80–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Heng, T.; He, X.L.; Yang, L.L. Mechanism of Saline–Alkali land improvement using subsurface pipe and vertical well drainage measures and its response to agricultural soil ecosystem. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askri, B.; Khodmi, S.; Bouhlila, R. Impact of subsurface drainage system on waterlogged and saline soils in a Saharan palm grove. Catena 2022, 212, 106070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, P.S.; Ramos, T.B.; Bengal, A. Coping with salinity in irrigated agriculture: Crop evapotranspiration and water management issues. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 227, 105832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ma, Y.J.; Wang, G.N. The impact of different configurations of subsurface drainage pipes on soil water and salt dynamics and the efficacy of salt leaching through drainage during the spring-to-autumn irrigation season in southern Xinjiang. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2024, 41, 1422–1432. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.H.; Li, S.E.; Cui, Y.K. Effect of drip irrigation on soil water balance and water use efficiency of maize in northwest China. Water 2021, 13, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.W.; Zuo, Q.; Shi, J.C. Evaluation of salt discharge by subsurface pipes in the cotton field with film mulched drip irrigation in Xinjiang, China I. Calibration to models and parameters. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 47, 537–544. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.Z.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, M. Experiment and numerical simulation for designing layout parameters of subsurface drainage pipes in arid agricultural areas. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingre, S.K.; Gorantiwar, S.D. Determination of the water requirement and crop coefficient values of sugarcane by field water balance method in semiarid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 23, 106042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolars, K.; Jia, X.H.; Steele, D.D. A soil water balance model for subsurface water management. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2019, 35, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Wang, Z.M.; Guo, W.Z. Influences of different treatments on soil evaporation after irrigation. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 34, 74–78. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Chen, S.; Nachshon, U. Modeling evaporation dynamics from soils with major chlorides and high salinity. J. Hydrol. 2025, 655, 132943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Huang, W.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Dong, X.; Wang, X. Effects of Subsurface Drainage on Soil Salinity and Groundwater Table in Drip Irrigated Cotton Fields in Oasis Regions of Tarim Basin. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.Y.; Yao, C.Z.; Wu, J.W. Field and numerical experiments of subsurface drainage systems in saline and low-permeability interlayered fields in arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 300, 108898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiao, P.J.; Dong, Q.G. Effects of spacing and depth of subsurface drain on water and salt transport in the field. J. Irrig. Drain. 2023, 42, 92–101. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.G.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wan, C.Y. Effects of saline water irrigation on soil salinity and yield of summer maize (Zea mays L.) in subsurface drainage system. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 19, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.J.; Zhao, C.Y.; Zhu, H. Hydrosalinity balance and critical ratio of drainage to irrigation (RDI) for salt balance in Weigan River irrigation district of the Tarim basin (China). Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.D.; Zhao, C.Y.; Zheng, J.Q. Evolution of soil salinity and the critical ratio of drainage to irrigation (CRDI) in the Weigan Oasis in the Tarim Basin. CATENA 2021, 201, 105210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, H.; He, X.; Lin, E.; Yang, G. Winter Irrigation Effects on Soil Moisture, Temperature and Salinity, and on Cotton Growth in Salinized Fields in Northern Xinjiang, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.W.; Chen, F.H.; Zhang, J.W. Humidity variability in the arid northwest China during LIA derived from different proxy records. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2008, 63, 23–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.F.; Zhao, A.Z.; Li, Y.Z. Impact of irrigation on climate. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 4816–4828. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Wallach, R.; Mao, X.M. Understanding evaporation from salinized soils in Xinjiang: Impact of sodium adsorption ratio, salt type, and concentrations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2025, 89, e20796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Xiang, Y.; Fan, J. Spatial distribution and variability of soil salinity in film-mulched cotton fields under various drip irrigation regimes in southern Xinjiang of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 223, 105470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, I.; Salman, S.A.; Elnazer, A.A. Salinization of groundwater during 20 years of agricultural irrigation, Luxor, Egypt. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 3821–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banin, A.; Fish, A. Secondary desertification due to salinization of intensively irrigated lands: The Israeli experience. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1995, 37, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, S.; Pulido-Bosch, A.; Vallejos, Á.; Molina, L.; Llop, A.; MacDonald, A.M. Impact of irrigated agriculture on groundwater-recharge salinity: A major sustainability concern in semi-arid regions. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 2781–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavi, I.; Thevs, N.; Priori, S. Soil salinity and sodicity in drylands: A review of causes, effects, monitoring, and restoration measures. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 712831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachshon, U. Cropland soil salinization and associated hydrology: Trends, processes and examples. Water 2018, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, N.; Hassani, A.; Sahimi, M. Multi-Scale Soil Salinization Dynamics from Global to Pore Scale: A Review. Rev. Geophys. 2024, 62, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Soil Depth/cm | Particle Composition Volume Fraction/% | Bulk Density/(g·cm−3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | Silt | Clay | ||
| 0~10 | 12.35 | 65.21 | 22.44 | 1.52 |
| 10~20 | 9.04 | 72.41 | 18.55 | 1.65 |
| 20~40 | 16.22 | 66.03 | 17.75 | 1.60 |
| 40~60 | 14.27 | 67.20 | 18.53 | 1.42 |
| 60~80 | 23.25 | 61.71 | 15.04 | 1.50 |
| 80~100 | 26.82 | 59.41 | 13.77 | 1.60 |
| 100~120 | 28.64 | 56.09 | 15.27 | 1.58 |
| 120~140 | 40.97 | 47.38 | 11.65 | 1.53 |
| 140~160 | 40.26 | 48.49 | 11.26 | 1.57 |
| Parameter | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interval/m | 20 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 20 |
| Burial depth/m | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.5 |
| Pipe diameter/mm | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| Area/m2 | 6360 | 6360 | 9540 | 12,720 | 6360 |
| Spring Irrigation (2023)/% | Winter Irrigation (2023)/% | Spring Irrigation (2024)/% | Winter Irrigation (2024)/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 3.34 | 11.78 | 6.45 | 7.17 |
| A2 | 7.25 | 13.12 | 18.16 | 13.75 |
| A3 | 6.48 | 10.02 | 16.19 | 12.07 |
| A4 | 6.66 | 9.26 | 14.82 | 10.77 |
| A5 | 34.16 | 22.48 | 48.42 | 24.35 |
| Item | df | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth | 2 | 17.219 | 0.001 ** | |
| Spacing | 2 | 0.190 | 0.829 | |
| DSEC | Depth | 2 | 72.768 | 0.001 ** |
| Spacing | 2 | 1.015 | 0.386 | |
| Item | Mean Value | Standard Error | t | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth | 100–120 | −5.885 | 4.487 | −1.312 | 0.209 | |
| 100–150 | −25.167 | 4.487 | −5.609 | 0.000 ** | ||
| 120–150 | −19.282 | 4.487 | −4.298 | 0.001 ** | ||
| DSEC | 100–120 | −0.700 | 0.232 | −3.016 | 0.009 ** | |
| 100–150 | −2.697 | 0.232 | −11.624 | 0.000 ** | ||
| 120–150 | −1.997 | 0.232 | −8.608 | 0.000 ** | ||
| Spacing | 2000–3000 | 1.880 | 4.487 | 0.419 | 0.681 | |
| 2000–4000 | 2.692 | 4.487 | 0.600 | 0.557 | ||
| 3000–4000 | 0.813 | 4.487 | 0.181 | 0.859 | ||
| DSEC | 2000–3000 | 0.182 | 0.232 | 0.786 | 0.444 | |
| 2000–4000 | 0.330 | 0.232 | 1.422 | 0.175 | ||
| 3000–4000 | 0.148 | 0.232 | 0.636 | 0.535 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, H.; Wang, G.; Song, Z.; Xu, P.; Li, X.; Ma, L. Optimization of Subsurface Drainage Parameters in Saline–Alkali Soils to Improve Salt Leaching Efficiency in Farmland in Southern Xinjiang. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051222
Guo H, Wang G, Song Z, Xu P, Li X, Ma L. Optimization of Subsurface Drainage Parameters in Saline–Alkali Soils to Improve Salt Leaching Efficiency in Farmland in Southern Xinjiang. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051222
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Han, Guangning Wang, Zhenliang Song, Pengfei Xu, Xia Li, and Liang Ma. 2025. "Optimization of Subsurface Drainage Parameters in Saline–Alkali Soils to Improve Salt Leaching Efficiency in Farmland in Southern Xinjiang" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051222
APA StyleGuo, H., Wang, G., Song, Z., Xu, P., Li, X., & Ma, L. (2025). Optimization of Subsurface Drainage Parameters in Saline–Alkali Soils to Improve Salt Leaching Efficiency in Farmland in Southern Xinjiang. Agronomy, 15(5), 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051222






