Abstract
Climate-change-driven elevation of atmospheric CO2 (e[CO2]) disrupts rice physiology by impairing nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) and leaf carbon balance. This study investigated how sodium chloride (NaCl) amendment modulates these processes in upland rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. CMG 2085) under current (400 μmol mol−1) and elevated (700 μmol mol−1) CO2 concentrations. Using a randomized block design with factorial treatments (CO2 × NaCl), we analyzed leaf nutrients, gas exchange, chlorophyll fluorescence, and yield parameters. Our findings revealed that 3 mmol L−1 NaCl under ambient CO2 (1) reduced photorespiration by half, (2) increased grain yield, and (3) enhanced leaf area despite lower leaf N content, indicating improved NUE. Conversely, under e[CO2], NaCl supplementation decreased rice yield by 15%, demonstrating CO2-dependent reversal of sodium benefits. Photosynthetic modeling showed higher Vcmax and J values at ambient CO2, while e[CO2] increased J/Vcmax, suggesting altered nitrogen allocation to photosynthetic reactions. These results demonstrate that applying low-dose NaCl (3 mmol L−1) can optimize carbon and nitrogen economy under current CO2 concentrations, although its efficacy diminishes under e[CO2]. These findings support climate-resilient cultivation strategies for upland rice in tropical and subtropical regions where mild salinity can be used to enhance nitrogen use efficiency and yield under present-day atmospheric conditions.
1. Introduction
Global socio-economic and environmental projections for 2050 emphasize the urgent need to increase food production under worsening climatic conditions. These challenges pose a threat to crop productivity by increasing carbon losses through respiratory and photorespiratory processes, while also impairing carbon uptake [1,2]. Grasses such as maize, rice, wheat, sorghum, and sugarcane are fundamental to global food security, serving as staple crops for both human and animal nutrition [1,2,3]. Safeguarding their morphophysiological processes and enhancing resource use efficiency under abiotic stresses is essential to meet future food demands and to develop technologies aligned with climate-smart agriculture [1,2,3,4].
In C3 grasses like rice, abiotic stresses such as drought and nutrient deficiency reduce quantum yield, water use efficiency, and nitrogen use efficiency (NUE), thereby increasing carbon losses through photorespiration and limiting the crop’s genetic yield potential [5,6,7]. While elevated atmospheric CO2 (e[CO2]) is theorized to mitigate photorespiration by reducing the oxygenase activity of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO), this does not always translate into higher yields. Under e[CO2], mineral uptake declines due to reduced transpiration, phenological development accelerates, and leaf senescence is hastened, offsetting gains in net photosynthesis and ultimately reducing carbon use efficiency, biomass accumulation, and grain yield [2,3,4,5,6,7,8].
Photorespiration remains a critical but inefficient process in C3 plants, consuming energy and releasing previously fixed CO2. It can account for 20–50% of carbon loss during photosynthesis under ambient conditions [2,7,9,10]. These losses are further exacerbated by abiotic stress and contribute to lower NUE, given the close metabolic link between photorespiration and nitrogen assimilation. Photorespiration consumes glycine and serine—key precursors in nitrogen metabolism—and generates ammonia, which must be reassimilated via the GS-GOGAT cycle, imposing additional energy costs. Recent studies suggest that modulating photorespiration—through either genetic engineering or nutritional strategies—can enhance NUE by redirecting resources toward productive nitrogen assimilation [2,8,11]. In this context, sodium may enhance nitrate reductase activity, potentially mitigating photorespiratory losses by improving nitrogen recycling efficiency [12,13], although this mechanism remains untested under e[CO2].
When evaluating the effects of elevated CO2 and a 2 °C temperature increase on rice crops, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium levels were found to decrease under the combined conditions [10]. This suggests that the anticipated yield gains from CO2 enrichment were limited by reduced nutrient use efficiency at higher temperatures. These findings underscore the importance of the present study in assessing the effects of low doses of NaCl as a biostimulant under elevated CO2 conditions, since previous results under current CO2 levels have shown positive effects on rice growth, development, and yield [5]. However, higher NaCl concentrations are detrimental under elevated CO2 due to the adverse effects of salinity [14].
Emerging evidence suggests that low concentrations of sodium may counteract these limitations by promoting nitrate reductase activity and supporting carbon fixation. Sodium has been proposed as a beneficial nutrient for glycophytes under mild salinity or nutrient-deficient conditions [13,14]. Notably, the beneficial effects of e[CO2] on C3 crops are strongly influenced by nitrogen availability, which governs key metabolic pathways. For example, nitrogen limitation under e[CO2] suppresses nitrogen assimilation and protein synthesis, thereby reducing biomass and yield [8,11,15,16]. Sodium can partially substitute for potassium in osmotic regulation and may also enhance carbon metabolism [11,12,13,14], but its role in NUE under e[CO2] remains poorly understood.
To explore this potential, we selected a sodium chloride concentration of 3 mmol L−1, based on previous studies demonstrating physiological benefits of low-dose NaCl without inducing salt stress. For instance, [13] reported that NaCl concentrations between 2 and 5 mmol L−1 enhanced growth and nitrate reductase activity in lettuce. Similarly, ref. [15] showed that even a low dose of 5 mmol L−1 NaCl improved growth, development, and nutrient use efficiency—including potassium, chloride, zinc, and copper—in Arabidopsis thaliana. In upland rice, ref. [17] demonstrated that a 3 mmol L−1 NaCl application increased grain yield across multiple genotypes, including the CMG 2085 line used in the present study. These findings support the use of 3 mmol L−1 NaCl as an effective and non-toxic dose to investigate sodium’s physiological roles in C3 crop performance.
The potential of high CO2 enrichment in C3 plants is limited by different factors such as temperature and nutritional limitation to meet these conditions, as demonstrated in [11,12,15], which evaluated the influence on the nutritional and productive contents of the factors of high CO2 and a temperature increase of 2 °C in the rice crop. The changes in the nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium contents decreased when there was a combination of these factors, demonstrating that the productive potential expected by CO2 enrichment in rice was limited by the reduction in the efficiency of nutrient use with the increase in temperature, highlighting the need for the present work to evaluate the effects of the use of low doses of NaCl as a biostimulant in high CO2 conditions, because higher doses of NaCl are detrimental to the development of rice in high CO2 conditions due to the harmful effects of salinity [11,17].
This study tests the hypothesis that low-dose sodium chloride (NaCl) supplementation reduces photorespiratory losses, enhances NUE, and increases yield in upland rice. We use e[CO2] as an experimental tool to suppress photorespiration, enabling us to isolate sodium’s role in regulating nitrogen assimilation and carbon allocation. We assess the physiological and biochemical impacts of NaCl and CO2 treatments on leaf nutrient content, photosynthetic performance, and grain yield, aiming to elucidate the mechanisms by which sodium can improve the productivity of C3 crops under current and future climate conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Growth Conditions
The study was conducted from November 2019 to March 2020 in a greenhouse located in Lavras, Brazil (21°13′40″ S, 44°57′50″ W). We used the upland rice line CMG 2085, developed by EMBRAPA-EPAMIG-UFLA, which was selected for its 120-day growth cycle, upright architecture, and ~1.0 m plant height based on previous research [17,18]. Seeds were sown in 4 L pots (Citropote®—Citrogessal Inc., Araras, SP, Brazil ) filled with a 1:2 mixture of clay and sand (clay: dystrophic red latosol; sand: washed). Fertilization followed recommendations for upland rice [14], with each plant receiving 10 g of (NH4)2SO4, 4 g of NH4H2PO4, and 3.63 g of KNO3 (equivalent to 120 kg ha−1 P2O5, 100 kg ha−1 N, and 80 kg ha−1 K2O), applied biweekly until the inflorescence emergence stage (R4) [14,18,19]. Irrigation was provided daily at 17:00 using a lysimeter system to meet 100% evapotranspiration demand. Ten days after sowing, plants were thinned to one plant per pot to serve as the experimental unit.
2.2. Treatments and Experimental Design
The experiment followed a 2 × 2 factorial design combining two atmospheric CO2 concentrations (p[CO2]), ±400 µmol mol−1 (ambient; C1) and ±700 µmol mol−1 (elevated; C2), with two NaCl concentrations ([NaCl]), 0 mmol L−1 (control; S1) and 3 mmol L−1 (S2). The p[CO2] levels were maintained using open-top chambers (1.3 m base diameter, 0.5 m top diameter, 1.8 m height). The CO2 amount was read by an infrared CO2 sensor (MH-Z14—Winsen Electronics Technology Co., Ltd., Zhengzhou, China), connected to a microcontroller (arduino-uno—Arduino AG, Turin, Italy), which was calibrated based on another sensor (SBA-5 CO2 Gas Analyzer—PP systems, Amesbury, MA, USA). The CO2 levels of the treatments were maintained during operating hours between 06:00 am and 06:00 pm, and more detailed information can be found in Figure S1 (Supplementary Materials).
The 3 mmol L−1 NaCl dose was selected based on previous studies [17,18] and was applied at the time of substrate preparation using reagent-grade NaCl (PA-ACS, Synth—Diadema, SP, Brazil). Leachate was collected and reapplied during irrigation to stabilize NaCl concentration in the soil. Mean environmental conditions during the experimental period were 26.7 °C and 77.3% RH for ambient CO2, and 26.3 °C and 79.2% RH for elevated CO2, ensuring that observed plant responses were driven by CO2, NaCl, or their interaction.
2.3. Evaluated Traits and Measurements
Leaf nutrient content (N, K, and Na), gas exchange parameters, and leaf area were measured at the V13 stage (flag leaf formation) [19,20,21]. To determine leaf nutrient content, leaves were oven-dried at 65 °C prior to analysis. Leaf area was quantified using Easy Leaf Area [22]. Gas exchange measurements were conducted on flag leaves using an infrared gas analyzer (IRGA) (LI-6800-XT—LI-COR Biosciences, Lincoln, NE, USA) under controlled conditions (30 °C leaf temperature, 2 kPa vapor pressure deficit).
A/Ci response curves were generated under both 2% and 21% O2 conditions at a photosynthetic photon flux density of 1500 µmol photons m−2 s−1. CO2 concentrations ranged from 50 to 1800 µmol mol−1. From these curves, we derived the following parameters:
- Vcmax: Maximum carboxylation rate of RuBisCO, reflecting enzyme activity capacity;
- J: Rate of photosynthetic electron transport, indicating the efficiency of light-dependent reactions;
- J/Vcmax: Ratio reflecting the balance between electron transport capacity and RuBisCO activity [23,24,25].
Photorespiration was estimated as the percentage difference between maximum net photosynthesis at 21% and 2% O2, divided by the maximum net photosynthesis under 2% O2, using the following equation [24]:
Photorespiration = [(Amax21%O2 − Amax2%O2)/Amax2%O2]
Light–response curves (A/PAR) were measured under 21% O2 at photosynthetic flux densities ranging from 2000 to 0 µmol photons m−2 s−1, enabling calculation of:
- LCP (light compensation point): The light intensity at which photosynthesis equals respiration;
- Amax: Maximum photosynthetic rate under light saturation, indicating photosynthetic potential;
- q: Curvature factor, representing the efficiency of the transition from light-limited to light-saturated photosynthesis, with higher values indicating smoother transition [23,24,25].
Chlorophyll fluorescence (Fv/Fm) was measured after 30 min of dark adaptation.
The instantaneous NUE was assessed using the Amax/N ratio, while integrative NUE was evaluated through grain yield per plant (GWP), adjusted to 13% moisture content [19], and the GWP/N ratio.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using RStudio (v2023.06.0) using the packages agricolae [26], ggplot2 [27], Rmisc [28], and ggpubr [29]. Data normality was assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test. Treatment effects (p[CO2], NaCl, and interaction) were analyzed via two-way ANOVA (α = 0.05). When significant differences were detected, means were compared using Tukey’s HSD test. For variables that did not meet normality assumptions, non-parametric tests were applied: the Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc test with Bonferroni correction.
3. Results
3.1. Leaf Nutrient Content and Leaf Area
The experimental treatments significantly influenced leaf ion accumulation (Figure 1). Sodium (Na) content showed a strong response to both NaCl supplementation and its interaction with CO2 (p < 0.05), with the 3 mmol L−1 NaCl treatment (S2) increasing leaf Na content 2.8-fold compared to the control across both CO2 concentrations. This result confirms effective Na uptake regardless of atmospheric conditions.
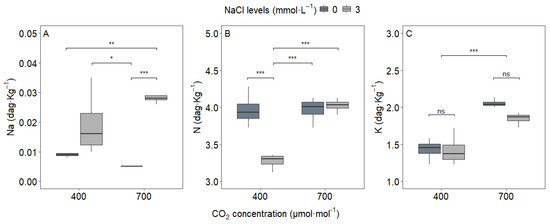
Figure 1.
Leaf content of (A) sodium, (B) nitrogen, and (C) potassium in upland rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. CMG 2085) grown under two NaCl concentrations (0 and 3 mmol L−1) and two atmospheric CO2 levels (400 and 700 μmol mol−1). Measurements were taken at the V13 phenological stage (flag leaf formation). Significance levels according to Tukey’s HSD test (p < 0.05, n = 20): *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05, ns = not significant (p > 0.05). Note: 1 dag kg−1 = 10 g kg−1.
Nitrogen (N) content showed a more complex pattern, with significant responses to NaCl, CO2, and their interaction (p < 0.05). While CO2 alone did not alter leaf N content in the control treatment (C1S1 vs. C2S1), the combination of e[CO2] and NaCl supplementation (C2S2) boosted N content by about 30% compared to NaCl-treated plants under ambient CO2 (C1S2), suggesting a CO2-dependent enhancement of nitrogen assimilation under NaCl addition.
Potassium (K) content was predominantly affected by CO2, with e[CO2] (C2) increasing leaf K content by 25%, independent of NaCl treatment. This consistent response highlights potassium’s role in osmotic adjustment under high CO2 conditions.
Leaf area responses followed a treatment-specific pattern (Figure 2). Under ambient CO2 (400 μmol mol−1), NaCl supplementation increased leaf area by over 22%, indicating improved vegetative growth. However, this beneficial effect was not observed under elevated CO2 (700 μmol mol−1), where leaf area remained statistically unchanged regardless of NaCl treatment. This interaction suggests that the growth-promoting effects of low-dose NaCl may be diminished or negated under future atmospheric CO2 conditions.
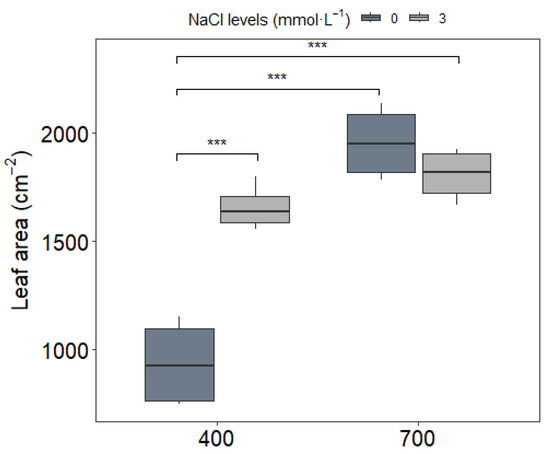
Figure 2.
Leaf area of upland rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. CMG 2085) grown under two NaCl concentrations (0 and 3 mmol L−1) and two atmospheric CO2 levels (400 and 700 μmol mol−1). Measurements were taken at the V13 phenological stage (flag leaf formation). Significance levels according to Tukey’s HSD test (p < 0.05, n = 20): *** p < 0.001.
3.2. Gas Exchange Parameters
The A/Ci curve analysis under 21% O2 revealed distinct patterns in photosynthetic parameters across treatments (Figure 3). Neither NaCl supplementation nor its interaction with CO2 significantly influenced the maximum carboxylation rate (Vcmax), electron transport rate (J), or their ratio (J/Vcmax) (p > 0.05 for all NaCl and NaCl × CO2 effects). However, e[CO2] (C2) alone induced notable changes: Vcmax decreased by 50% (Figure 3B) and J by 15% (Figure 3C) compared to ambient CO2, while the J/Vcmax ratio increased by 80% (Figure 3D). These coordinated adjustments suggest photosynthetic acclimation to e[CO2], with rice plants reallocating resources from RuBisCO-driven carboxylation toward light-dependent reactions.
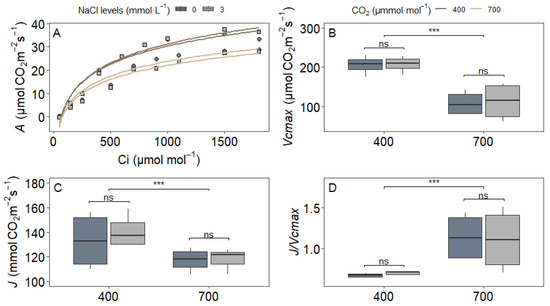
Figure 3.
Photosynthetic parameters derived from A/Ci curves under 21% O2 in upland rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. CMG 2085) grown under two NaCl levels (0 and 3 mmol L−1) and two CO2 concentrations (400 and 700 μmol mol−1). (A) Representative A/Ci curves; (B) maximum RuBisCO carboxylation rate (Vcmax); (C) electron transport rate (J); (D) J/Vcmax ratio. Significance levels according to Tukey’s HSD test (p < 0.05, n = 4): *** p < 0.001, ns = not significant (p > 0.05).
In contrast, under low oxygen (2% O2) where photorespiration is minimized, Vcmax, J, or J/Vcmax remained unaffected by NaCl, CO2, or their interaction (Figure 4). This lack of variation under 2% O2 confirms that the photosynthetic apparatus retains its intrinsic functionality and that treatment effects observed at 21% O2 are mediated specifically through photorespiratory processes.
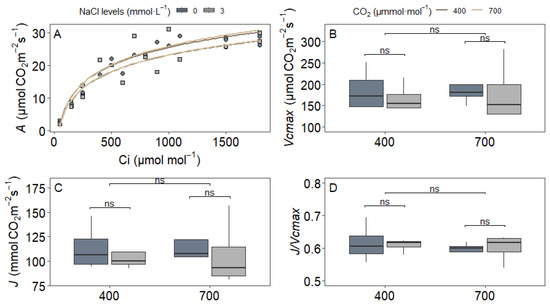
Figure 4.
Photosynthetic parameters derived from A/Ci curves under 2% O2 in upland rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. CMG 2085) grown under two NaCl levels (0 and 3 mmol L−1) and two CO2 concentrations (400 and 700 μmol mol−1). (A) Representative A/Ci curves; (B) maximum RuBisCO carboxylation rate (Vcmax); (C) electron transport rate (J); (D) J/Vcmax ratio. Significance levels according to Tukey’s HSD test (p < 0.05, n = 4): ns = not significant (p > 0.05).
Photorespiration rates exhibited a significant interaction between NaCl and CO2 treatments (p < 0.05; Figure 5). Under ambient CO2 (C1), NaCl supplementation (S2) reduced photorespiration by 48% compared to the control (C1S1). Remarkably, C1S2 plants exhibited photorespiration levels 48% lower than the ambient control (C1S1), and comparable to or slightly lower than those under e[CO2] without NaCl (C2S1), highlighting the efficacy of NaCl in suppressing photorespiration under ambient conditions. These results imply that NaCl and CO2 may act through different physiological mechanisms and that NaCl’s benefits are strongly dependent on ambient CO2 conditions.
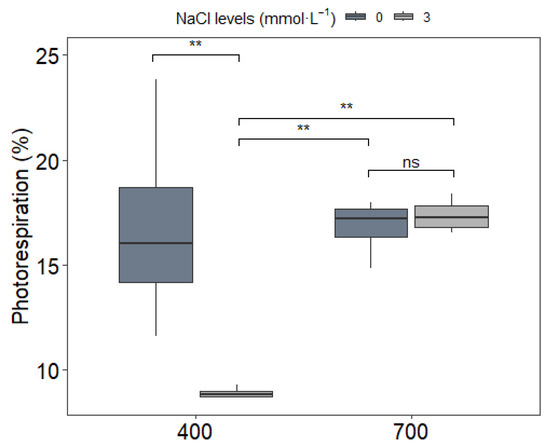
Figure 5.
Photorespiration (%) in upland rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. CMG 2085) grown under two NaCl levels (0 and 3 mmol L−1) and two CO2 concentrations (400 and 700 μmol mol−1). Significance levels according to Tukey’s HSD test (p < 0.05, n = 4): ** p < 0.01, ns = not significant (p > 0.05).
These results of A/Ci curves collectively suggest that (1) elevated CO2 induces photosynthetic acclimation primarily through photorespiration-dependent pathways, (2) NaCl’s effects on photosynthesis are mediated through modulation of photorespiratory processes rather than direct impacts on the light or dark reactions, and (3) the low NaCl dose used in this study (3 mmol L−1) does not impair fundamental photosynthetic function even when combined with elevated CO2. The differential responses between oxygen levels provide strong evidence that photorespiration serves as a key regulatory node integrating the effects of both NaCl and CO2 on photosynthetic performance in this upland rice line.
The analysis of light–response curves (A/PAR) under 21% O2 revealed important insights into the photosynthetic performance of upland rice under different treatment conditions (Figure 6). Neither NaCl supplementation nor its interaction with CO2 significantly influenced the light compensation point (LCP), maximum net assimilation rate (Amax), or curvature parameter (q) (p = 0.47 for NaCl and 0.32 for the interaction effect). However, e[CO2] alone led to a 37% reduction in LCP compared to ambient CO2, indicating improved light use efficiency under e[CO2]. This increase in efficiency occurred without changes in Amax, which remained stable across all treatments (Figure 6C), suggesting that the enhanced carbon economy under elevated CO2 did not stem from higher maximum photosynthetic capacity.
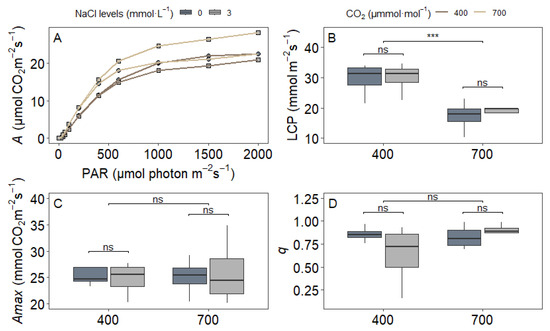
Figure 6.
Photosynthetic parameters derived from A/PAR under 21% O2 in upland rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. CMG 2085) grown under two NaCl levels (0 and 3 mmol L−1) and two CO2 concentrations (400 and 700 μmol mol−1). (A) Representative A/Ci curves; (B) light compensation point (LCP), (C) maximum net assimilation rate (Amax), and (D) curvature (q). Significance levels according to Tukey’s HSD test (p < 0.05, n = 4): *** p < 0.001, ns = not significant (p > 0.05).
The curvature parameter (q), which reflects the efficiency of transitioning from light-limited to light-saturated photosynthesis, also remained consistent across CO2 treatments (p = 0.85). This stability indicates that the basic relationship between light intensity and photosynthetic response was maintained regardless of NaCl or CO2 exposure. Together, these results suggest that while elevated CO2 improves light use efficiency at low irradiance, the light-dependent reactions in this upland rice genotype are resilient to mild NaCl stress. The consistent Amax and q values across treatments imply that the photosynthetic machinery maintains its core functional integrity under both ambient and elevated CO2, regardless of sodium supplementation.
3.3. Rice Yield and Photosystem Efficiency
The analysis of photosystem II efficiency (Fv/Fm) revealed consistent values across all treatment combinations (Figure 7A), with measurements remaining within the optimal range of 0.78–0.82, indicating maintained photochemical efficiency regardless of NaCl or CO2. The stability of Fv/Fm values across treatments suggests that there were no changes in basic photochemical efficiency, but rather any photosynthetic response was caused by downstream metabolic or allocation processes affected by the interaction between NaCl and CO2.
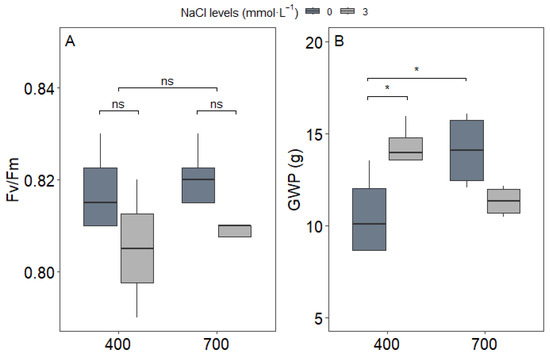
Figure 7.
(A) Chlorophyll fluorescence (Fv/Fm), (B) grain yield per plant (GWP, g) in upland rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. CMG 2085) grown under two NaCl levels (0 and 3 mmol L−1) and two CO2 concentrations (400 and 700 μmol mol−1). Significance levels according to Tukey’s HSD test (p < 0.05, n = 4 for Fv/Fm and n = 8 for GWP): * p < 0.05, ns = not significant (p > 0.05).
The grain yield per plant (GWP) showed a significant interaction between NaCl and CO2 treatments (p < 0.05; Figure 7B). Under ambient CO2 (C1), NaCl supplementation increased grain yield by 26% compared to non-supplemented plants (C1S2 vs. C1S1). However, this positive effect was reversed under e[CO2], where NaCl application resulted in a 15% reduction in yield (C2S1 vs. C2S2).
This contrasting response highlights that the beneficial effects of NaCl on upland rice productivity are strongly dependent on CO2. While NaCl promotes yield under current CO2 levels, its effectiveness is diminished—and even counterproductive—under elevated CO2 conditions.
3.4. Nitrogen Use Efficiency—NUE
The interaction between NaCl and CO2 significantly influenced all measured NUE indices (p < 0.05). For leaf area per unit nitrogen content (Figure 8A), plants grown under ambient CO2 (C1) with NaCl supplementation (S2) showed a 24% increase compared to the non-supplemented control (C1S1). Although this ratio was numerically higher under elevated CO2 (C2S2), the difference was not statistically significant compared to C1S2.
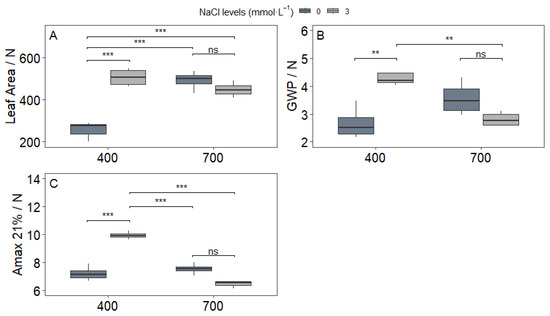
Figure 8.
Nitrogen use efficiency indices: (A) Leaf area/N content (n = 8); (B) GWP/N content (n = 8); (C) Amax/N content (n = 4) in upland rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. CMG 2085) grown under two NaCl levels (0 and 3 mmol L−1) and two CO2 concentrations (400 and 700 μmol mol−1). Significance levels according to Tukey’s HSD test (p < 0.05): *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, ns = not significant (p > 0.05).
In contrast, the grain yield per plant to nitrogen content ratio (GWP/N; Figure 8B) displayed divergent trends depending on CO2 levels. NaCl improved this yield-based NUE metric by 19% under C1 conditions (C1S2 > C1S1), but under elevated CO2, it resulted in a 15% decrease (C2S2 < C2S1). The most pronounced effect was observed in instantaneous NUE (Amax/N; Figure 8C), which peaked in the C1S2 treatment, surpassing all other combinations by 27–34%. This finding underscores that NaCl’s enhancement of photosynthetic nitrogen utilization is most effective under current atmospheric CO2 levels. Collectively, these results demonstrate that NaCl-mediated improvements in nitrogen economy are highly dependent on atmospheric CO2 concentration. While NaCl can enhance NUE under ambient conditions, its benefits are diminished—and in some cases reversed—under future e[CO2] scenarios.
4. Discussion
Our results demonstrate that low-dose NaCl (3 mmol L−1) elicits CO2-dependent physiological responses in upland rice, with significant implications for photosynthetic efficiency and grain production. Under ambient CO2 (400 μmol mol−1), NaCl supplementation reduced photorespiration by 48%—a reduction greater than that achieved by elevated CO2 (700 μmol mol−1) alone—while simultaneously increasing grain yield by 26%. These patterns are consistent with more recent findings showing cultivar-specific responses of nitrogen metabolism and carbon partitioning under e[CO2] and moderate salt stress [11,12,17,30].
Total plant nitrogen content was not measured in this study. However, previous reports have shown that under controlled conditions, flag leaf nitrogen is strongly correlated with total shoot nitrogen in rice, allowing its use as a reliable physiological proxy for NUE [3,5,21]. The reduction in N content with the presence of NaCl under ambient CO2 (400 μmol mol−1) compared to the control is due to a greater use of N to meet plant demands and thus enabling a higher GWP as our results demonstrate. This remarkable performance appears to arise from three interconnected mechanisms: (1) improved NUE, as evidenced by higher leaf area per unit of nitrogen and GWP/N ratios despite a reduction in leaf N concentration [10,11,12,13,14,15]; (2) sodium–potassium synergy with a 2.8-fold increase in Na+ accumulation complementing K+ availability [5,11,12,31,32,33], thereby enhancing enzymatic activity; and (3) carbon conservation through photorespiration suppression, allowing greater resource allocation toward structural growth, including increased leaf area and grain filling [3,4,11,12,15,16]. Although only leaf N content was quantified, it has been shown to represent plant nitrogen status under well-managed conditions and thus supports interpretation of NUE in this context [3]. While total biomass was not quantified, the observed increase in leaf area likely contributed to enhanced source capacity, suggesting that NaCl under ambient CO2 may stimulate vegetative vigor as well as reproductive output. Further experimentation must include biometric measurements to better clarify this hypothesis.
Low sodium concentrations were beneficial to rice and did not affect K+ content; in fact, K+ levels increased only under elevated CO2 conditions. This indicates that low doses of NaCl do not impair K+ uptake and, according to the literature, sodium and potassium can act synergistically. Na+ may partially substitute for K+ as a vacuolar osmotic agent, thereby allowing more K+ to remain in the cytosol, where it fulfills essential roles such as the electrical neutralization of anions and macromolecules, pH homeostasis, regulation of membrane potential, and control of cellular osmotic pressure. Additionally, Na+ and K+ share common ion channels (Shaker, TPK/KCO, and TPC) and are transported by three major families of carriers (HAK, HKT, and CPA), which mediate ion movement across the plasma membrane and internal membranes with varying degrees of selectivity [16,31].
The leaf mineral dynamics further support this interpretation as part of a sophisticated adaptation strategy. Although elevated CO2 increased both Na+ and K+ content (Figure 1A,C), the effects of NaCl supplementation under ambient CO2 were particularly pronounced. The maintenance of optimal Fv/Fm values (0.78–0.82) across all treatments confirms that ionic adjustments in the leaf occurred without compromising the integrity of photosystem II [7,9,31,32,33]. These results support the emerging view that sodium can function as a beneficial nutrient in glycophytes at low concentrations, particularly through its role in nitrate uptake and chloroplast metabolism [7,12,13,14,15,30].
Under elevated CO2, leaf area expansion did not significantly differ from ambient conditions, even with NaCl supplementation (Figure 2), suggesting a limitation in structural growth that likely constrained biomass accumulation. This outcome may reflect a physiological ceiling imposed by nutrient availability and nitrogen allocation patterns. Our photosynthetic modeling showed a decrease in Vcmax and an increase in the J/Vcmax ratio under e[CO2] (Figure 3), indicating a reallocation of nitrogen toward light-dependent reactions. While this adjustment improves photochemical efficiency, it may restrict carbon assimilation capacity over time due to a decline in RuBisCO content. In this scenario, the reduced expansion of leaf area could limit light capture and source strength, thereby constraining total biomass accumulation despite enhanced instantaneous photosynthetic efficiency. Consequently, although grain yield was maintained or slightly reduced, the absence of increased leaf area under e[CO2] likely suppressed biomass gains, highlighting the need to interpret yield data in conjunction with structural and physiological traits.
Photosynthetic modeling revealed two key insights into the interaction between CO2 and NaCl. First, the stability of Vcmax and J under 2% O2 proves that NaCl’s effects are dependent on active photorespiration. Second, the increase in the J/Vcmax ratio under NaCl at ambient CO2 suggests a strategic reallocation of nitrogen from RuBisCO (typically comprising up to 50% of leaf protein) [6,7,8] to components of the electron transport chain. This shift likely contributes to enhanced light use efficiency [33], explaining why the 37% reduction in LCP under elevated CO2 did not result in higher Amax: the photosynthetic apparatus had already optimized internal resource allocation.
This divergence illustrates how altered nitrogen allocation functions as an adaptive strategy under different environmental stimuli. Under elevated CO2, rice plants reallocate nitrogen toward components of the electron transport chain (as evidenced by increased J/Vcmax), enhancing photochemical capacity while reducing investment in carboxylation enzymes like RuBisCO. This shift aligns with known acclimation responses to e[CO2]. In contrast, NaCl supplementation under ambient CO2 promotes nitrogen use in leaf expansion and grain filling, indicating a distinct optimization strategy geared toward maximizing structural growth and yield. These findings underscore the context-specific nature of nitrogen partitioning: while CO2 enrichment drives functional acclimation of the photosynthetic machinery, sodium biostimulation supports enhanced growth by favoring productive nitrogen utilization [11,12,13,14,15,16,17].
The CO2-dependent reversal of NaCl benefits presents both a caution and an opportunity. While NaCl reduced grain yield by 15% under elevated CO2, this is likely due to functional redundancy rather than toxicity, as all major photosynthetic parameters remained unaffected. This suggests that future breeding could focus on CO2-responsive sodium utilization traits, preserving NaCl’s current benefits while minimizing its diminished returns under future atmospheric scenarios. The outstanding performance of the CMG 2085 line—which did not show photosynthetic downregulation under elevated CO2—highlights genotype-specific responses within upland rice, suggesting that this line may have distinct physiological traits that enhance its resilience.
Overall, our study challenges and expands the current understanding of sodium’s role in C3 crop physiology under climate change. By demonstrating that NaCl can suppress photorespiration to a degree comparable to elevated CO2—yet through distinct physiological pathways—this study positions low-dose NaCl as a viable biostimulant for enhancing photosynthetic efficiency and grain yield. These insights offer immediate applications for improving rice productivity under current atmospheric conditions, while also highlighting the need for dynamic nutrient management strategies as atmospheric CO2 levels continue to rise.
5. Conclusions
Our study demonstrates that low-dose NaCl supplementation (3 mmol L−1) positively influences photosynthetic processes in upland rice, primarily through photorespiration reduction and improved nitrogen use efficiency. Under current atmospheric CO2 (400 μmol mol−1), NaCl treatment enabled the CMG 2085 line to achieve physiological performance and grain yield comparable to plants grown under elevated CO2 (700 μmol mol−1), confirming sodium’s role in enhancing photosynthetic efficiency. These benefits were mediated through three interconnected mechanisms: (1) an important reduction in photorespiration, conserving both carbon and nitrogen resources; (2) improved allocation of photoassimilates to grain production, evidenced by higher yield under ambient CO2 with NaCl; and (3) increased nitrogen use efficiency, allowing optimal growth despite lower leaf N concentration. These outcomes are aligned with recent physiological findings that support sodium-based biostimulation as a potential tool for enhancing nitrogen economy in C3 crops. However, the reversal of these benefits under elevated CO2 (−15% yield with NaCl) reveals that sodium’s positive effects are context-dependent, becoming redundant when photorespiration is already suppressed by high CO2. While NaCl supplementation shows immediate promise for improving rice productivity under controlled conditions, its application in the field must be approached with caution due to the potential mobility and accumulation of sodium in soil. These findings underscore the need for adaptive strategies as atmospheric CO2 continues to rise, but field-based studies are essential to validate the agronomic viability and long-term sustainability of NaCl use in upland rice systems.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy15051212/s1, Figure S1: Open top chambers (A); demonstration of the automated system with a pressure gauge and solenoid valve for CO2 (B); CO2 reading display inside the chamber, Arduino UNO microcontroller and relay (C); Fan (D); Figure S2: Net photosynthesis vs intercellular CO2 concentration (A/Ci), based on averages values, under conditions of 2% O2 in the air, for the combination of treatments: 400 µmol mol−1 CO2 and 0 mmol L−1 NaCl (C1S1); 400 µmol mol−1 CO2 and 3 mmol L−1 NaCl (C1S2); 700 µmol mol−1 CO2 and 0 mmol L−1 NaCl (C2S1); and 700 µmol mol−1 CO2 and 3 mmol L−1 NaCl (C2S2); Figure S3: Net photosynthesis vs intercellular CO2 concentration (A/Ci), based on averages values, under conditions of 21% O2 in the air, for the combination of treatments: 400 µmol mol−1 CO2 and 0 mmol L−1 NaCl (C1S1); 400 µmol mol−1 CO2 and 3 mmol L−1 NaCl (C1S2); 700 µmol mol−1 CO2 and 0 mmol L−1 NaCl (C2S1); and 700 µmol mol−1 CO2 and 3 mmol L−1 NaCl (C2S2); Figure S4: Net photosynthesis vs photosynthetic active radiation (A/PAR), based on averages values, for the combination of treatments: 400 µmol mol−1 CO2 and 0 mmol L−1 NaCl (C1S1); 400 µmol mol−1 CO2 and 3 mmol L−1 NaCl (C1S2); 700 µmol mol−1 CO2 and 0 mmol L−1 NaCl (C2S1); and 700 µmol mol−1 CO2 and 3 mmol L−1 NaCl (C2S2); Table S1: Physicochemical analysis of the substrate used in the experiment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.A.V. and J.P.R.A.D.B.; methodology, D.A.V., J.P.R.A.D.B., P.E.R.M., M.A.T.-H. and J.P.P.; validation, D.A.V., J.P.R.A.D.B., P.E.R.M., M.A.T.-H., J.P.P., F.B.S.B. and M.M.P.C.; formal analysis, D.A.V., J.P.R.A.D.B., M.A.T.-H., J.P.P. and M.M.P.C.; investigation, D.A.V. and J.P.R.A.D.B.; resources, D.A.V. and J.P.R.A.D.B.; data curation, D.A.V., J.P.R.A.D.B., M.A.T.-H. and J.P.P.; writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, D.A.V., J.P.R.A.D.B., P.E.R.M., M.A.T.-H. and J.P.P.; validation, D.A.V., J.P.R.A.D.B., P.E.R.M., M.A.T.-H., J.P.P., F.B.S.B. and M.M.P.C.; visualization, D.A.V. and J.P.R.A.D.B.; validation, D.A.V., J.P.R.A.D.B., P.E.R.M., M.A.T.-H., J.P.P., F.B.S.B. and M.M.P.C.; supervision, J.P.R.A.D.B.; project administration, D.A.V. and J.P.R.A.D.B.; funding acquisition, J.P.R.A.D.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the following Brazilian funding agencies: Minas Gerais State Research Foundation (FAPEMIG) [Processo RED-00144-23]; RedeBIORREG Minas—Rede de Desenvolvimento e Pesquisa em Biorreguladores e Bioestimulantes Agrícolas; National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) [Grant 406455/2022-8 (INCT-Plant Stress Physiology)]; Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) [Finance Code 001 to MATH and PNPD scholarship to JPP]; The authors also acknowledge individual research fellowships from CNPq: JPRADB [PQ 312488/2022-0], and PERM [PQ 312663/2021-8].
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), the Minas Gerais State Research Foundation (FAPEMIG), and the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES). We extend our sincere appreciation to Carla Maria Alexandre Pinheiro and Vitor de Laia Nascimento for their expert guidance, and to Layane Silva for essential technical contributions to this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- FAO. FAO Strategy on Climate Change 2022–2031; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhut, M.; Weber, A.P.M. Improving Crop Yield. Science 2019, 363, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, J.P.R.A.D.; Cruz, A.B.; dos Santos Botelho, A.; Pennacchi, J.P.; Santana, G.F. Crop Physiology, the Technology and the Production Gap. Theor. Exp. Plant Physiol. 2024, 36, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahad, S.; Bajwa, A.A.; Nazir, U.; Anjum, S.A.; Farooq, A.; Zohaib, A. Crop Production under Drought and Heat Stress: Plant Responses and Management Options. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Xia, J.Q.; Alfatih, A.; Song, Y.; Huang, Y.J.; Sun, L.Q.; Wan, G.Y.; Wang, S.M.; Wang, Y.P.; Hu, B.H.; et al. Rice NIN-LIKE PROTEIN 3 modulates nitrogen use efficiency and grain yield under nitrate-sufficient conditions. Plant Cell Environ. 2022, 45, 1520–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauwe, H. Humboldt Review: Photorespiration—Rubisco’s repair crew. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 280, 153899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, M.E.; Yeo, A.R.; Flowers, T.J. Photosynthesis and Photorespiration in the Genus Oryza. J. Exp. Bot. 1994, 45, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, K.; Knowles, V.L.; Plaxton, W.C.; Hüner, N.P.A. Enhancement of Photosynthetic Performance, Water Use Efficiency and Grain Yield During Long-Term Growth Under Elevated CO2 in Wheat and Rye Is Growth Temperature and Cultivar Dependent. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 106, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-On, Y.M.; Milo, R. The Global Mass and Average Rate of Rubisco. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4738–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, S. Measurements of Photosynthesis and Respiration in Plants. Physiol. Plant. 2003, 117, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cai, C.; He, J.; Gu, J.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, W.; Liu, G. Yield, Dry Matter Distribution and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Rice Under Elevated CO2 and Increased Temperature Conditions. Field Crops Res. 2020, 248, 107605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, S.; Eshghizadeh, H.R.; Zahedi, M. Responses of Four Rice Varieties to Elevated CO2 and Different Salinity Levels. Rice Sci. 2018, 25, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbarao, G.V.; Wheeler, R.M.; Levine, L.H.; Stutte, G.W. Low Concentrations of Sodium Stimulate Specific Physiological Responses in Leaf Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Plant Cell Environ. 2003, 26, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, P. (Ed.) Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongqiao, L.; Suyama, A.; Mitani-Ueno, N.; Hell, R.; Maruyama-Nakashita, A. A Low Level of NaCl Stimulates Plant Growth by Improving Carbon and Sulfur Assimilation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants 2021, 10, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccolo, E.L.; Ceccanti, C.; Guidi, L.; Landi, M. Role of beneficial elements in plants: Implications for the photosynthetic process. Photosynthetica 2021, 59, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, D.A.; Toro-Herrera, M.A.; Pennacchi, J.P.; Mendonça, A.M.C.; Marchiori, P.E.R.; Botelho, F.B.S.; Barbosa, J.P.R.A.D. Mapping Phenotypic Parameters Linked to Salt Stress Tolerance Strategies in Rice Lines. Bragantia 2022, 81, e20210172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, D.A. Agronomic and Physiological Responses of Rice to Sodium Treatments and High CO2. Ph.D. Thesis, Federal University of Lavras (UFLA), Lavras, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, R.C.F.; Crusciol, C.A.C.; Nascente, A.S. Análise de crescimento e produtividade de cultivares de arroz de terras altas dos tipos tradicional, intermediário e moderno. Pesq. Agropec. Trop. 2012, 42, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, P.K.; Sahu, B.B. Botany of Rice Plant. In Panicle Architecture of Rice and Its Relationship with Grain Filling; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Counce, P.A.; Keisling, T.C.; Mitchell, A.J. A Uniform, Adaptative System for Expressing Rice Development. Crop Sci. 2000, 40, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easlon, H.M.; Bloom, A.J. Easy Leaf Area: Automated Digital Image Analysis for Rapid and Accurate Measurement of Leaf Area. Appl. Plant Sci. 2014, 2, 1400033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arantes, M.K.; da Silva Filho, M.P.; Pennacchi, J.P.; das Chagas Mendonca, A.M.; Barbosa, J.P. Phenotypic Plasticity of Leaf Anatomical Traits Helps to Explain Gas-Exchange Response to Water Shortage in Grasses of Different Photosynthetic Types. Theor. Exp. Plant Physiol. 2020, 32, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, B.; Biscoe, P.V. A Model for C3 Leaves Describing the Dependence of Net Photosynthesis on Irradiance: II. Application to the Analysis of Flag Leaf Photosynthesis. J. Exp. Bot. 1980, 31, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornley, J.H.M.; Johnson, I.R. Plant and Crop Modelling: A Mathematical Approach to Plant and Crop Physiology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- De Mendiburu, F. Agricolae: Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research, R package version 1.3-6; 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=agricolae (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Hope, R.M. Rmisc: R Miscellaneous Functions, R package version 1.5; 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=Rmisc (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Kassambara, A. Ggpubr: ‘ggplot2’ Based Publication Ready Plots, R package version 0.6.0; 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggpubr (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Reddy, I.N.B.L.; Kim, B.K.; Yoon, I.S.; Kim, K.H.; Kwon, T.R. Salt Tolerance in Rice: Focus on Mechanisms and Approaches. Rice Sci. 2017, 24, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieves-Cordones, M.; Al Shiblawi, F.R.; Sentenac, H. Roles and Transport of Sodium and Potassium in Plants. In The Alkali Metal Ions: Their Role for Life; Sigel, A., Sigel, H., Sigel, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, Q.; Ou, Y.; Wang, L.; Gao, Y.; Lucas, G.R.; Resco de Dios, V.; Yao, Y. Transcriptome and low-affinity sodium transport analysis reveals salt tolerance variations between two poplars. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, T.; Liu, M.; Kreslavski, V.D.; Zharmukhamedov, S.K.; Nie, C.; Yu, M.; Shabala, S. Non-stomatal limitation of photosynthesis by soil salinity. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 51, 791–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).