Abstract
Soil nitrogen (N) is critical for crop yield. Although previous studies have shown that straw return enhances soil mineral N availability, the response of soil aggregate microbes to straw return and its impact on soil mineral N availability remains unclear. We conducted a 13-year experiment to explore how soil N mineralization potential, fungi, and bacteria within soil aggregates responded to straw return. Our findings indicated that straw return significantly increased mineral N concentrations in soil macroaggregates, with no statistically significant effect observed on microaggregate composition. We observed increased microbial community α-diversity, enhanced co-occurrence network stability, and an increase in functional groups associated with N (nitrate respiration, denitrification, nitrite denitrification) and carbon (saprotrophs, saprotroph–symbiotrophs, patho-saprotrophs) cycling within the aggregates. Additionally, microorganisms in macroaggregates were influenced by total N, while those in microaggregates were affected by soil total organic carbon and C–N ratio. A sensitivity network analysis identified specific microorganisms responding to straw return. Within macroaggregates, microbial community shifts explained 42.88% of mineral N variation, with bacterial and fungal β-diversity contributing 27.82% and 12.58%, respectively. Moreover, straw return upregulated N-cycling genes (N ammonification: sub, ureC, and chiA; nitrification: amoA-AOB; denitrification: nirK, nirS, nosZ, norB, and narG; and N fixation: nifH) in macroaggregates. Partial least squares path modeling revealed that N availability in macroaggregates was mainly driven by ammonification, with bacterial β-diversity explaining 23.22% and fungal β-diversity 15.16% of the variation. Our study reveals that macroaggregates, which play a crucial role in soil N supply, are highly sensitive to tillage practices. This finding provides a practical approach to reducing reliance on synthetic N fertilizers by promoting microbial-mediated N cycling, while sustaining high crop yields in intensive agricultural systems.
1. Introduction
Nitrogen (N) is a critical element for soil productivity in terrestrial agro-ecosystems, with microbe-mediated N cycling processes fulfilling over half of crops’ N requirements biochemical transformations [1,2,3]. However, the reliance of conventional agriculture on inorganic fertilizers has led to soil degradation and threatens microbial diversity and function [4,5,6]. To address these issues, straw incorporation has been widely adopted to improve soil structure and maintain ecosystem balance [7,8,9]. However, soil structure is complex, and agricultural practices induce various changes in N cycling, microbial community structure, and metabolic activity across different aggregates [10,11,12,13,14]. Understanding how straw returned to the soil affects N supply within soil aggregates is crucial for assessing agroecosystem functionality.
Soil N availability is determined by ammonification, nitrification, denitrification, and N fixation, driven by microbial enzymes [3,15]. Key functional genes encoding these enzymes include amoA (for nitrification), narG, nirK/nirS, and nosZ (for denitrification), nifH (for N fixation), and ureC (for urea hydrolysis, a subset of ammonification), which serve as markers for microbial communities involved in the soil N cycle [3,16,17]. Several studies have shown that straw return increases the N supply capacity of paddy soils, depending on the amount of straw used, application duration, and other factors [18]. However, studies on the effects of straw return on soil N cycling genes have yielded inconsistent results; this may be due to variations in soil characteristics and straw or fertilizer application rates [19,20,21,22,23].
Bacteria and fungi that share aggregated microhabitats are major drivers of soil ecological functioning and are influenced by tillage practices and soil structure [8]. Their diversity is closely related to the soil N cycle [24,25]. Study has demonstrated that microbial diversity, encompassing both richness and evenness, is a significant predictor of organic matter mineralization, with bacterial richness accounting for 32.2% and fungal richness contributing 17% diversity [26]. Due to their smaller cell size, bacteria can rapidly access and absorb small organic molecules, leading to faster growth compared to fungi. In contrast, fungi are primary decomposers of complex organic compounds through their production of extracellular enzymes (e.g., cellulases, ligninases) [27,28]. Straw return has been demonstrated to shape soil microbial communities [29,30], specifically by enhancing soil microbial diversity (Shannon and Chao1 indices), enriching copiotrophic microbial populations, and increasing the modularity of microbial co-occurrence networks [30,31]. The changes in soil microbial communities induced by straw returning can further influence the functional traits of microorganisms [32,33], including their roles in maintaining soil carbon (C) and N cycles [23,34], as well as their involvement in functional processes related to straw decomposition [33,35]. High-C–N-ratio (approximately 60:1) straw favors fungal growth and stimulates fungi’s role in organic matter decomposition [9,36,37], whereas N fertilizer application reduces the relative importance of fungal decomposition [38]. However, there is a lack of attention to the core differential microbial community diversity in soil nutrient cycling in response to long-term straw reduction.
Straw return changes the physicochemical properties of microhabitats by impacting soil aggregation [8,39]. Soil aggregates, which are important structural units, create spatial heterogeneity for soil biomes and mediate various biogeochemical processes due to their different physicochemical properties [11,40,41,42,43]. Macroaggregates (>0.25 mm) have higher resource efficiency, promoting fast-growing copiotrophic microorganisms, while microaggregates (<0.25 mm) may favor slow-growing oligotrophic bacteria [42]. Functional microbial genes that encode elemental transformation are jointly influenced by the structural effects and resource availability within soil aggregates [44]. However, the response of microbial communities and ecological functions in soil aggregates to long-term straw return remains unclear.
We conducted a 13-year study within an irrigated rice and rainfed wheat rotation system to explore the effects of straw return on N availability, microbial community structure, and ecological function in soil aggregates. We hypothesized that (i) mineral N availability in soil aggregates of various sizes would respond differently to long-term straw incorporation, (ii) long-term straw incorporation would shape microbial communities by influencing soil substrates and would be regulated by the aggregate structure, and (iii) differences would exist in the composition and diversity of specific bacteria and fungi in response to straw return, contributing to the N supply.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Soil Sampling
The long-term straw return experiment was established at the Experimental Station of Nanjing Agricultural University (31°54′ N, 119°28′ E) in Danyang, Jiangsu Province, China. Various nutrient management regimes, including straw return, have been established since 2009 to assess their long-term effects on soil fertility and crop yield. The experimental soil type was Ferric Lixisols [45], with a particle size distribution of 4.6% sand, 58.4% silt, and 37.0% clay. The soil’s primary chemical composition consisted of SiO2, Al2O3, and Fe2O3.
The experiment, as described in our previous study [46], involved two treatments: chemical fertilizer (CF) and chemical fertilizer combined with straw (CS). These treatments were randomly assigned to plots measuring 7.3 m × 4.6 m, with three replicates per treatment. Fertilizers used were urea (N), phosphorus pentoxide (P), and potassium oxide (K). Application rates for both CF and CS were 300, 150, and 240 kg ha−1 for N, P, and K, respectively, during the rice seasons, and 225, 105, and 105 kg ha−1, respectively, during the wheat seasons. In the CS treatment, rice and wheat straw were uniformly incorporated into the topsoil (0–20 cm) using a rotary tiller immediately after each harvest, while the CF treatment received chemical fertilizers only, without straw addition.
In late October 2022, undisturbed soil samples were sampled from all replicates of both CF and CS treatments using a five-point sampling method, one week before the rice harvest. Surface impurities were removed before sampling. Soil cores (5 cm diameter, 20 cm height) were placed in rigid plastic boxes to maintain their structure during transport and stored at 4 °C upon arrival at the laboratory.
2.2. Soil Aggregate Separation and Chemical Property Analysis
Moist soil was gently broken along natural breaks and sieved through a 5 mm mesh. Water-stable aggregates were separated by particle size through wet sieving, following Stemmer et al. (1998) [47]. Approximately 100 g of soil was separated into four aggregates sizes: large macroaggregates (LM, >2 mm), small macroaggregates (SM, 0.25–2 mm), microaggregates (MA, 0.25–0.053 mm), and fine microaggregates (FMA, <53 μm). Ten replicates were taken per treatment, for the analysis of the particle size distribution, and the remaining soil was freeze-dried and stored at −80 °C.
Soil total N (TN) and total organic C (TOC) contents were measured using an elemental analyzer (Vario PYRO cube, Elementar, Hanau, Germany). The largest dynamic ranges for measurements were 0–20 mg abs for C and 0–15 mg abs for N, with an external precision of <0.1% for both elements. Concentrations of NH4+-N and NO3−-N (2 mol L−1 KCl, 1:5 soil–solution) were determined by colorimetry with a segmented flow autoanalyzer (Skalar San++, Breda, The Netherlands). Mineral N content was subsequently calculated as the sum of the measured NH4+-N and NO3−-N concentrations. Dissolved organic C (DOC) and dissolved organic N (DON) were measured using a TOC/TN analyzer (Multi N/C 3100, Analytik Jena TOC Analyzer, Jena, Germany) [48].
2.3. Sequencing and Bioinformatics
Microbial DNA was extracted from soil aggregate samples using the E.Z.N.A.® DNA Kit (Omega Bio-tek, Norcross, GA, USA). Microbial communities were analyzed using paired-end amplicon sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene and the ITS region, on an Illumina MiSeq PE 300 platform. The V4–V5 region of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene was amplified by PCR using primers 515F 5′-barcode-GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGG-3′ and 907R 5′-CCGTCAATTCMTTTRAGTTT-3′. Bacterial sequencing yielded an average depth of 25,000 reads per sample with 98% coverage. The fungal ITS gene were amplified by PCR using primers ITS1F 5′-barcode-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3′ and ITS2R 5′-GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3′. Fungal sequencing achieved an average depth of 36,828 reads per sample with 100% coverage. Sequences were processed using Trimmomatic [49] and in-house scripts. Dereplicated 16S rRNA gene sequences were analyzed with the DADA2 algorithm and taxonomically classified with the Silva database (SSU138.1). Fungal OTUs were clustered with 97% similarity using UPARSE and assigned taxonomy using the Unite database.
2.4. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
We quantified the abundance of genes representing N ammonification (ureC, sub, and chiA), nitrification (amoA-AOA and amoB-AOB), denitrification (nirK, nirS, narG, norB, and nosZ), and N fixation (nifH) in the DNA extracted from soil aggregate samples, using appropriate primers (Table S1). All functional genes were amplified by PCR using a QuantStudio 6 Flex Real-Time PCR System (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) in 96-well plates, with a detection threshold of 10 copies per reaction (equivalent to 2 copies ng−1 DNA). All samples and standards were analyzed in six replicates. Each 20 µL qPCR reaction mixture contained 10.0 µL of 2× ChamQ SYBR qPCR Master Mix, 0.4 µL each of forward and reverse primers (10 µM), 0.4 µL of 50× ROX Reference Dye 1, 1.5 µL of template DNA/cDNA, and 7.3 µL of ddH2O to adjust the final volume. Reactions were performed under the following cycling conditions: the thermocycler program was 95 °C for 2 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s, 56 °C for 15 s, and 72 °C for 20 s. Standards for each gene were generated from amplicons of mixed soil samples, quantified, and serially diluted. All samples and standards were analyzed in six replicates. Fluorescence data were translated into gene copies ng−1 of DNA using calibration curves created for each gene from a series of diluted standards with known concentrations.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
We conducted a two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction to analyze the effects of straw return, aggregate fraction, and their interactions on response variables. Mean was compared using Student’s t-test with significance set at p < 0.05. A principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) and permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) were used to assess changes in microbial community composition based on the Bray–Curtis distance. FAPROTAX and FUNGuild were used to predict functional information of bacterial and fungal communities, respectively [50,51]. A co-occurrence network analysis was conducted using the “psych (v2.2.9)” and “igraph (v1.3.5)” packages in R (v4.2.2) and visualized with Gephi (v0.9.2, Gephi Consortium, Paris, France) software. A redundancy analysis (RDA) was conducted using CANOCO 5.0 (Microcomputer Power, Ithaca, NY, USA) to assess relationships between soil properties and microbial communities. Spearman’s correlation analysis was conducted using the “psych (v2.2.9) packages in R (v4.2.2). Sensitive networks were constructed to identify microbial communities (significant OTUs) affected by straw return, using a likelihood ratio test and indicator species analysis. Pairwise Spearman rank correlations were computed, retaining only correlations (ρ > 0.7, p < 0.001). Network modules were identified using a greedy optimization algorithm in the “igraph” package. A variance partitioning analysis (VPA) was conducted using the “rdacca.hp” package to determine the extent to which bacterial and fungal diversity and composition explained mineral N availability. Partial least squares path modeling (PLS-PM) was conducted using “SmartPLS 3.0” (SmartPLS GmbH, Bönningstedt, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany) to identify paths mediating the response of mineral N contribution in soil aggregates, with R2 coefficients indicating variance in dependent variables.
3. Results
3.1. Impact of Straw Return on N Supply and Physicochemical Properties of Soil Aggregates
Straw return significantly increased NH4+-N and mineral N concentrations in LM and SM, as well as that of NO3−-N in LM (Figure 1a,c). Soil chemical properties were notably influenced by straw return and aggregate fractions (Table S2). Specifically, TOC, TN, C–N ratio, and DOC were significantly higher in straw-amended plots, with elevated values in LM and SM compared to those in MA and FMA (Table S2). Under the CF treatment, the mass fractions of LM, SM, MA, and FMA were 11.39%, 26.13%, 21.37%, and 41.11%, respectively, whereas the CS treatment exhibited values of 12.44%, 29.53%, 20.36%, and 37.66% for these fractions. Compared to the CF treatment, the CS treatment significantly increased the mass fractions of LM and SM by 9.22% and 13.01%, respectively, while significantly reducing the FMA mass fraction by 8.39% (Table S2).
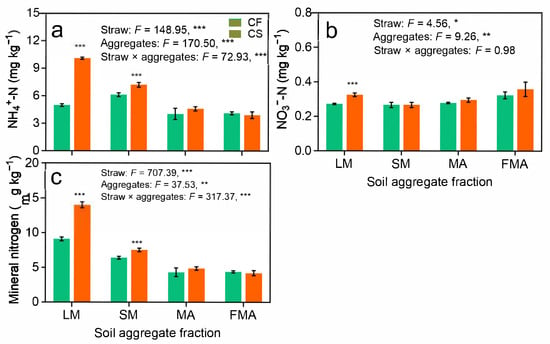
Figure 1.
Long-term straw return promotes mineral N availability in soil aggregates. NH4+-N (a), NO3−-N (b), and mineral nitrogen (c). CF, chemical fertilizer; CS, chemical fertilizer plus straw. LM, large macroaggregates (>2 mm); SM, small macroaggregates (0.25–2 mm); MA, microaggregates (0.053–0.25 mm); and FMA, fine microaggregates (<0.053 mm). Mineral nitrogen is the sum of NH4+-N and NO3−-N. F values indicate F-statistics from a two-way ANOVA testing the effects of straw return, aggregate size fractions, and their interactions. *, **, and *** indicate p < 0.05, p < 0.01, and p < 0.001, respectively.
3.2. Microbial Communities Within Soil Aggregates
The α-diversity indices of bacterial communities (Shannon, Chao1, ACE, Simpson) exhibited no significant variations under straw return but showed significant differences across aggregate size fractions (Table S3). In contrast, fungal α-diversity indices were significantly regulated by straw return but remained unresponsive to aggregate size. PCoA and PERMANOVA analyses further demonstrated that both straw return and aggregate size fractions significantly shaped the β-diversity of bacterial and fungal communities (Figure 2b,d; Table S4). For bacterial communities, management practice explained 68% of β-diversity variation (R2 = 0.68, p < 0.01), followed by aggregate size (R2 = 0.30, p < 0.01). Fungal communities displayed an inverse pattern: aggregate size accounted for 66% of β-diversity variation (R2 = 0.66, p < 0.05), while management practice contributed 51% of the explanatory power (R2 = 0.51, p < 0.05).
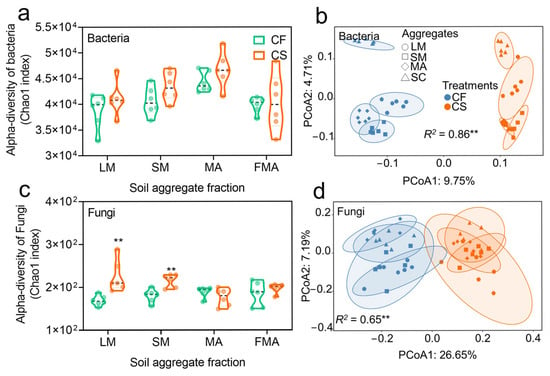
Figure 2.
Microbial community diversity and composition in soil aggregates. Bacterial (a) and fungal (c) community alpha-diversity. The structure of bacterial (b) and fungal (d) communities was assessed by principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) based on the Bray–Curtis distance. CF, chemical fertilizer; CS, chemical fertilizer plus straw. LM, large macroaggregates (>2 mm); SM, small macroaggregates (0.25–2 mm); MA, microaggregates (0.053–0.25 mm); and FMA, fine microaggregates (<0.053 mm). ** indicates differences between the CF and CS treatments at p < 0.01 based on Student’s t-test. Similarity values (R2) of samples among the four size aggregates and between two treatments were examined.
The two-way ANOVA results revealed that the relative abundance of dominant bacterial phyla was primarily influenced by straw return, whereas that of dominant fungal phyla was mainly affected by aggregate size fractions rather than straw return (Table S5). Among them, Proteobacteria (42.68–47.11%), as the dominant bacterial phylum, showed a significant inhibition in abundance under straw return treatment. In contrast, Bacteroidetes in LM, SM, MA, and FMA fractions was significantly upregulated by straw return, with increases of 5.49%, 26.49%, 29.33%, and 34.80%, respectively. Additionally, compared to the CF treatment, Verrucomicrobia under CS treatment exhibited an increase ranging from 9.33% to 20.82%.
FAPROTAX predictions indicated that CS increased the abundance of microbial functional groups related to chemoheterotrophs, aerobic chemoheterotrophs, and N cycling processes, such as nitrate respiration, denitrification and nitrite denitrification in the LM and SM (Figure S1a). FUNGuild prediction showed that CS decreased the abundance of functional guilds associated with patho-symbiotrophs, symbiotrophs, and patho-sapro-symbiotrophs, while increasing functional guilds linked to saprotrophs, saprotroph–symbiotrophs, and patho-saprotrophs (Figure S1b). Bacterial and fungal networks in straw-amended soil aggregates were more densely connected, with more edges, nodes, and robustness compared to conventionally managed soil aggregates (Figure S2, Table S6).
RDA indicated that TN was the primary environmental factor influencing both bacterial (adjusted R2 = 0.64, p < 0.01) and fungal (adjusted R2 = 0.67, p < 0.01) communities in the >0.25 mm aggregates (Figure 3a,b; Table S7). In the <0.25 mm aggregates, bacterial communities were significantly affected mainly by TOC (adjusted R2 = 0.53, p < 0.01) and the C–N ratio (adjusted R2 = 0.17, p < 0.01) (Figure 3c; Table S7), while fungal communities were primarily affected by the C–N ratio (adjusted R2 = 0.55, p < 0.01) (Figure 3d; Table S7).
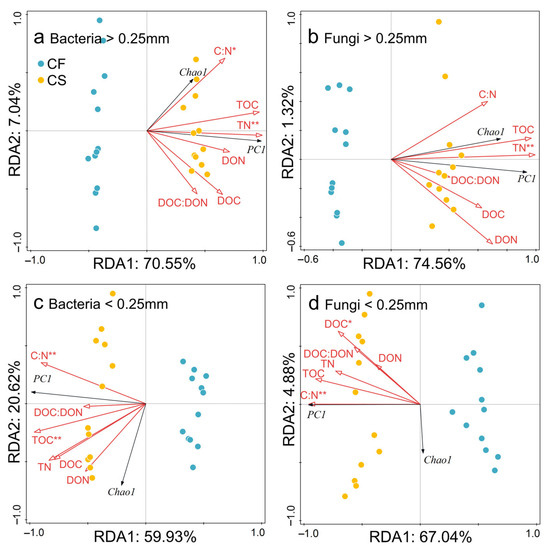
Figure 3.
RDA showing the relationship between microbial communities and soil properties in aggregates. Panels (a,c) show bacterial communities, while (b,d) show fungal communities in >0.25 mm aggregates (a,b) and <0.25 mm aggregates (c,d). The RDA model in panel (a) had an R2 = 0.78 and adjusted R2 = 0.71, p = 0.02. The RDA model in panel (b) had an R2 = 0.76 and adjusted R2 = 0.69, p = 0.02 (Table S7). The RDA model in panel (c) had an R2 = 0.81 and adjusted R2 = 0.75, p = 0.02. The RDA model in panel (d) had an R2 = 0.72 and adjusted R2 = 0.64, p = 0.02. In the panels, black and red arrows represent microbial diversity and soil properties, respectively. CF, chemical fertilizer; CS, chemical fertilizer plus straw. TOC, soil total organic carbon; TN, soil total nitrogen; C–N, TOC–TN; DOC, dissolved organic carbon; DON, dissolved organic nitrogen. * and ** indicate p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, respectively.
3.3. Enrichment of Specific Microbial Communities by Straw Return
We analyzed the co-occurrence patterns of key differential species responding to straw return and their modules using a sensitivity network analysis in soil aggregates (Figure 4a–d). In the >0.25 mm aggregates, the co-occurrence networks of bacteria (Modules 1 and 3) and fungi (Modules 1 and 2) contained two modules each with more than 10 OTUs (Figure 4a,b). The relative abundance of species in bacterial Module 1 (r = 0.42, p < 0.05) and fungal Modules 1 (r = 71, p < 0.001) and 2 (r = 0.37, p < 0.05) was significantly positively correlated with mineral N concentration (Figure 4e,f). Dominant species in bacterial Module 1 included Pseudolabrys, Chthoniobacter, and Syntrophobacter, while those in Module 3 were Flavisolibacter, Ramlibacter, Acidibacter, Sphingomonas, and Dongia. Amongst fungi, Module 1 was dominated by Phoma, Schizothecium, and Septoriella, and Module 2 by Zopfiella, Podospora, Echria, and Mortierella. The relative abundance of these specific species was higher in CS compared to CF (Figure S3). Moreover, in the network analysis, five bacterial genera—Pseudolabrys, Dongia, Chthoniobacter, Sphingomonas, and Ramlibacter—were identified as keystone species, demonstrating notably high betweenness centrality (Table S8).
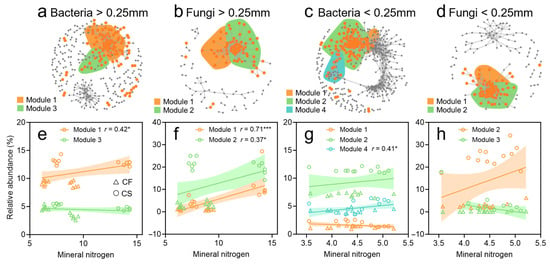
Figure 4.
Long-term straw return enriched specific microbiota to increase N availability in soil aggregates. Sensitive networks reflect significant correlations between specific OTUs of bacteria (a) and fungi (b) in the >0.25 mm aggregates and bacteria (c) and fungi (d) in the <0.25 mm aggregates responding to straw return (Spearman’s correlation >0.7, p < 0.001, indicated by gray lines). Shaded areas represent network modules containing significantly different OTUs (only modules with more than 10 OTUs are shown). Regressions between specific OTUs diversity of bacteria (e) and fungi (f) in >0.25 mm aggregates and bacteria (g) and fungi (h) in <0.25 mm aggregates and mineral N concentration. Shading associated with lines in the panel indicates 95% confidence interval. Gray dots represent non-module-forming differential OTUs (unassigned to network modules). * and *** indicate p < 0.05 and p < 0.001, respectively.
The VPA indicated that microbial community shifts explained 42.88% of mineral N variation, with bacterial and fungal β-diversity contributing 27.82% and 12.58%, respectively, in the >0.25 mm aggregate fraction (Figure 5a,c).
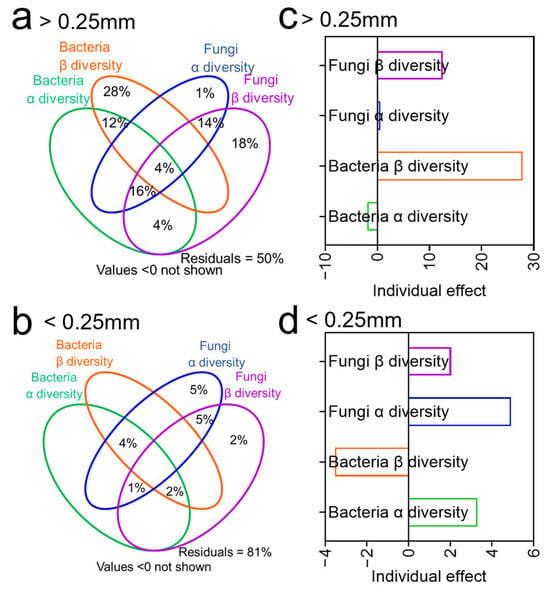
Figure 5.
Variation partitioning analysis (VPA) revealed the contribution of different variables to mineral nitrogen in >0.25 mm (a) and <0.25 mm (b) aggregates. The hierarchical partitioning identifies the individual contributions of each explanatory variable in >0.25 mm (c) and >0.25 mm (d) aggregates.
3.4. Abundance of N Cycling Genes in Soil Aggregates
Genes related to N ammonification (sub, chiA, and ureC), nitrification (amoA-AOA and amoB-AOB), denitrification (nirS, nirK, narG, norB, and nosZ), and N fixation (nifH) were significantly influenced by straw return’s aggregate fractions. CS significantly enhanced the abundance of N cycling genes in LM and SM but had no effect on those in MA and FMA. Gene expression tended to decrease with decreasing aggregate size (Figure 6). Spearman’s correlation analysis revealed that NH4+-N concentration showed significant positive correlations with the abundance of all N-cycling functional genes except amoA. In contrast, NO3−-N concentration demonstrated significant negative correlations with the abundance of sub and nosZ (Figure S4). Normalization indices of N ammonium, nitrification, denitrification, and N fixation genes were all significantly and positively correlated with bacterial and fungal β-diversity (Figure S5).
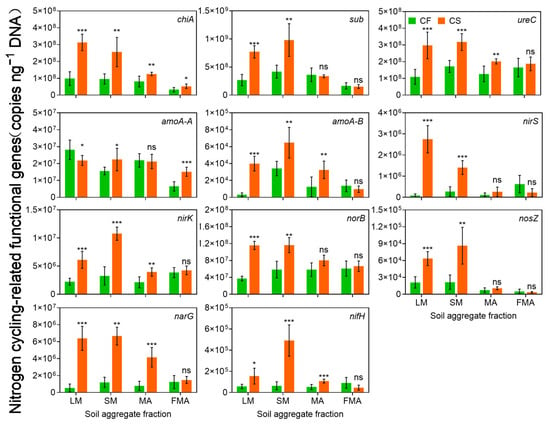
Figure 6.
Nitrogen cycling-related functional genes in soil aggregates. Ammonification genes include chiA, sub, and ureC; nitrification genes include amoA-AOA and amoA-AOB; denitrification genes include norB, nosZ, nirS, nirK, and narG; nitrogen fixation genes include nifH. CF, chemical fertilizer; CS, chemical fertilizer plus straw. LM, large macroaggregates (>2 mm); SM, small macroaggregates (0.25–2 mm); MA, microaggregates (0.053–0.25 mm); and FMA, fine microaggregates (<0.053 mm). *, **, and *** indicate p < 0.05, p < 0.01, and p < 0.001, respectively, ns-not significant.
3.5. Linking Specific Microbiomes and Soil Properties to Mineral N in Soil Aggregates
PLS-PM was used to elucidate the pathways influencing soil mineral N content with straw return. Results showed that straw return significantly regulated mineral N content in LM and SM, with selected variables explaining 60% of the variation in mineral N (GOF = 0.65, Figure 7a,b). Mineral N content was directly and positively correlated with the abundance of genes representing N ammonification and fixation, which were mainly influenced by the specific bacterial and fungal β-diversity. TN was the main factor regulating bacterial communities. Conversely, mineral N content in MA and FMA was not regulated by straw return (GOF = 0.37, Figure 7c).
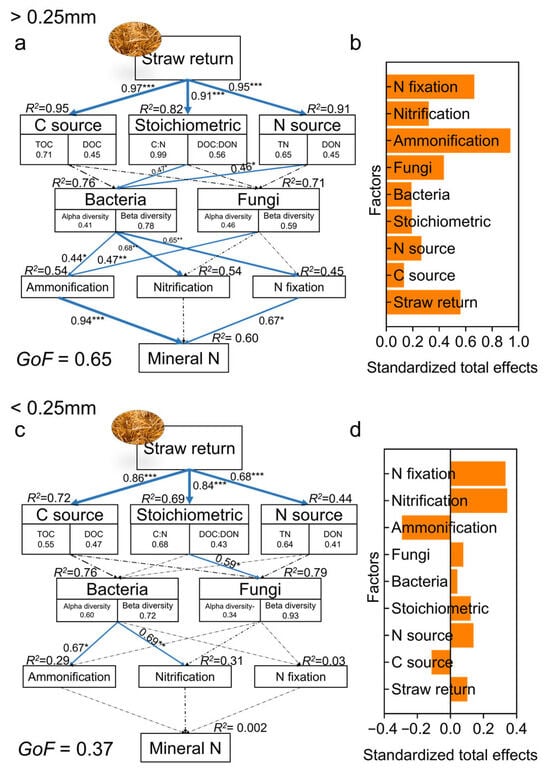
Figure 7.
PLS-PM illustrating the direct and indirect effects of straw return, soil chemistry, specific microbial diversity, and nitrogen cycling genes on mineral nitrogen in aggregates. Panels (a,c) show effects in >0.25 mm and <0.25 mm aggregates, respectively. Panels (b,d) show normalized total effects in >0.25 mm and <0.25 mm aggregates, respectively. C source is a latent variable, denoted by TOC and DOC; stoichiometry is a latent variable, denoted by C–N ratio and DOC–DON; N source is a latent variable, denoted by TN and DON; bacterial diversity and fungal diversity are latent variables, denoted by Chao1 and PC1. Black and blue arrows indicate negative and positive causality, respectively. Numbers on arrows and arrow thickness indicate normalized path coefficients. The number under the variable represents the loading coefficient. Dashed arrows indicate non-significant path relationships. R2 next to the latent variable is the coefficient of determination. GoF index represents goodness of fit. Asterisks represent significant effects: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
4. Discussion
4.1. Long-Term Straw Return Improves the Microbial Community Structure of Aggregates
Long-term straw return and soil aggregate size influenced the microbial community. TN primarily shaped the microbial community in macroaggregates, while TOC played a more significant role in microaggregates (Figure 3a,b), suggesting that microenvironmental conditions dictate the impact of straw return on soil microorganisms [8]. C-rich straw addition significantly enhanced TOC, DOC, and the C:N ratios in macroaggregates. According to the theory of ecological stoichiometry [52], microbial communities are N-limited when the C–N ratios exceed their critical requirement. Conversely, microbial growth and metabolism are primarily driven by TOC due to the lesser impact of straw [52].
Long-term straw return increased microbial species richness and diversity in soil aggregates (Figure 2a–d; Table S3), indicating that combining mineral fertilizers with straw can improve soil nutrients and microbial community structure [53]. The increased microbial diversity is likely due to the additional C source from straw, which promotes microbial proliferation and diversity [54]. However, some studies have reported no significant effect of organic management practices like straw return on microbial diversity, possibly due to differences in experimental systems and methodologies [55].
Long-term straw return also improved the complexity and stability of bacterial and fungal networks in soil aggregates (Figure S2; Table S6). Microbial communities were more stable in macroaggregates than in microaggregates. Complex networks with stronger connectivity are more resilient to environmental disturbances [56,57]. Stabilized soil microbial communities support various ecological processes, including nutrient cycling [58], TOC pools and degradation [59], and primary productivity maintenance [60]. However, increased network connectivity may not always indicate beneficial adaptation. Some studies suggest that microbial networks can become more interconnected under stress conditions (e.g., fertilization or straw decomposition byproducts), potentially reflecting compensatory community reorganization rather than functional optimization [55,61]. For instance, excessive N input has been shown to increase network complexity while reducing functional diversity, indicating a stress response rather than true ecological resilience [62]. While intensive agriculture can weaken soil microbial complexity and stability, organic management practices like straw return can mitigate the negative effects of fertilizers on microbial covariance networks [29,63,64] and enhance soil microbial stability [65].
4.2. Relationship Between Microbial Community Diversity and N Supply in Response to Straw Incorporation
The β-diversity of specific bacterial communities showed a stronger association with N supply than that of fungal communities (Figure 4 and Figure 5). This may be attributed to the improvement in soil nutrient and resource conditions, though β-diversity per se likely reflects a structural reorganization of communities rather than direct functional causality. Bacteria typically have higher nutrient requirements than fungi due to smaller stoichiometric ratios [66]. Our study, along with others, shows that long-term straw incorporation increases soil TN and other nutrients [46,67]. Soil TN is the primary driver for both bacterial and fungal communities (Figure 3a,b). Thus, straw incorporation promotes bacterial dominance over fungi [68,69]. A positive correlation also exists between fungal dominance and the soil C–N ratio [70]. The difference in our results may be due to our focus on microbial groups specifically responding to straw incorporation.
Continuous cultivation in tested soils may also explain why bacterial communities respond more to straw incorporation. Bacteria, being single-celled, adapt better to agricultural disturbances than fungi, which exhibit hyphal growth and transfer nutrients over long distances [69,71]. Traditional tillage practices and other agricultural disturbances may disrupt more fungal growth compared to that of bacterial [72]. Combining straw return with mineral N fertilizer has been shown to reduce fungal diversity while increasing bacterial abundance [73,74]. Thus, intensive management practices may reduce fungal involvement in ecosystem processes [75,76]. The β-diversity of specific microbial communities responding to long-term straw incorporation exhibited a stronger correlation with N supply than their α-diversity (Figure 5). This aligns with findings that differences in microbial community composition are often associated with ecosystem functions [77], though structural variability (β-diversity) may serve as a proxy for functional redundancy or niche partitioning rather than a direct driver. Differences in community composition play a crucial role in soil nutrient cycling [78]. Studies have shown that β-diversity of bacterial communities is closely related to soil nutrient cycling [79,80]. Our results support the hypothesis that differences in species composition response to agricultural practices are closely linked to nutrient cycling. While our results support the hypothesis that compositional shifts correlate with nutrient cycling, further mechanistic studies are needed to disentangle whether these changes directly drive N supply or arise from parallel environmental filtering.
4.3. Effects and Mechanisms of Long-Term Straw Return on N Supply in Soil Aggregates
Incorporating straw into the soil increases mineral N concentration in macroaggregates by enhancing microbial diversity (a biotic property) and improving substrate availability, such as TN and TOC concentration (abiotic properties) (Figure 7a,b). Our results support previous finding that soil resource availability and microbial diversity jointly determine ecosystem multifunctionality [11,81]. Straw return significantly affected genes involved in the N cycle (Figure 6). These genes encode enzymes involved in N cycling processes, linking microbial composition to potential ecological functions [82,83]. Specifically, straw incorporation significantly increased the abundance of genes for ammonification, nitrification, denitrification, and N fixation in macroaggregates. Ammonification and N assimilation significantly regulated N supply in macroaggregates (Figure 7a,b), validating the view that soil N mineralization is the primary driver of terrestrial N supply, with N assimilation as a supplement [84,85].
The shifts in microbial community composition induced by straw incorporation predominantly enhanced the relative abundance of genes associated with N cycling. Key species responding to straw incorporation included Pseudolabrys, Ramlibacter, Sphingomonas, and Podospora (Figure S3). Pseudolabrys is considered an important species for maintaining the stability of the rice rhizosphere ecological network and is closely related to soil C and N cycling processes [86,87,88]. Ramlibacter has been found to participate in various N cycling processes [89]. Sphingomonas and Podospora, as oligotrophs specialized in degrading recalcitrant organic compounds [90,91], facilitate the mineralization of organic N (e.g., proteins and microbial biomass) into NH4+-N. This aligned with the observed strong positive correlations between NH4+-N concentration and ammonification functional gene (Figure S4). Resource availability, such as TOC and TN, was crucial for mineral N supply in soil aggregates (Figure 7a,b). Soil organic N (comprising proteins, amino acids, and microbial biomass), which accounts for over 90% of TN, serves as the primary source of soil mineral N [15]. Increased soil TN concentration from straw incorporation provides ample substrate for mineralization, enhancing N availability [92]. Enhanced soil substrates promote the proliferation of copiotrophic microbes, further improving soil nutrient availability [93,94].
It is noteworthy that the alternating flooded (rice) and upland (wheat) regimes in rice–wheat rotation systems may fundamentally alter straw-induced N cycling dynamics [95]. Anaerobic conditions in paddy soils suppress nitrification (reduced AOA/AOB abundance) but enhance denitrification (enriched nosZ genes) and proliferation of diazotrophs, favoring NH4+-N dominance [96,97]. In contrast, aerobic wheat soils promote nitrification (AOB-dominated) and ammonium oxidation, leading to NO3− accumulation. Furthermore, flooding shifts microbial community assembly toward deterministic processes, while stochastic processes prevail in upland soils [98]. These systemic differences underscore the necessity to disentangle phase-specific mechanisms when optimizing straw management in rotation systems.
5. Conclusions
Soil structure and microorganisms significantly impact agroecosystem function. Our study demonstrated that the chemical properties and microbial communities of soil aggregates of different grain sizes responded differently to straw return. Notably, macroaggregates, which are key to soil N supply, showed heightened sensitivity to straw return. Among the microorganisms, the bacterial composition had the greatest effect on mineral N concentration. Observed differences in soil structure and microbial responses to tillage practices highlight the importance of analyzing a variety of soil structures simultaneously. This provides valuable insights into how agricultural practices, such as fertilization, tillage, and crop rotations, affect the ecological functioning of farmland. Understanding the influences of management practices on soil properties and microbial communities on the ecological functions they mediate provides new opportunities for developing more sustainable and productive agroecosystems.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy15051208/s1, Figure S1. The main ecological functions’ profiles of microbial communities in soil aggregates under long-term straw return; Figure S2. Soil microbial co-occurrence networks in different treatments and size aggregates; Figure S3. Relative abundance of genera in different modules of sensitive network; Figure S4. Relationships between functional gene abundances and soil mineral N concentrations assessed by Spearman correlation; Figure S5. Linear relationships between microbial community diversity and N cycle genes; Table S1. Genes quantified using qPCR; Table S2. Effects of long-term straw return on soil chemistry across different aggregate fractions; Table S3. Alpha-diversity of microbial communities; Table S4. PMANOVA results revealing the effect of straw return, aggregate size, and their interactions with microbial community structures; Table S5. Effects of long-term straw return on dominant bacterial and fungal phyla; Table S6. Microbial community co-occurrence network characteristics; Table S7. The goodness-of-fit (R2), adjusted goodness-of-fit (R2), explained fitted variation (contribution), F-value, and p-value of soil variables for microbial communities based on Monte Carlo permutation test for RDA (conditional effect). Table S8. Betweenness centrality of key species.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.X.; methodology, L.X.; formal analysis, L.X.; investigation, L.X.; data curation, L.X.; writing—original draft preparation, L.X.; writing—review and editing, L.X.; project administration, G.L.; funding acquisition, G.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (31871573), the Key Research and Development Program of Jiangsu Province (BE2021361, BE2019343-5, BE2019377, and BE2020319), and National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFE0110100). Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX24_0958).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
CF: chemical fertilizer; CS: chemical fertilizer combined with straw; LM: large macroaggregates; SM: small macroaggregates; MA: microaggregates; FMA: fine microaggregates; TN: soil total nitrogen; TOC: total organic carbon; DOC: dissolved organic carbon; and DON: dissolved organic nitrogen.
References
- Yan, M.; Pan, G.; Lavallee, J.M.; Conant, R.T. Rethinking Sources of Nitrogen to Cereal Crops. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBauer, D.S.; Treseder, K.K. Nitrogen Limitation of Net Primary Productivity in Terrestrial Ecosystems Is Globally Distributed. Ecology 2008, 89, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuypers, M.M.M.; Marchant, H.K.; Kartal, B. The Microbial Nitrogen-Cycling Network. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the Nitrogen Cycle: Recent Trends, Questions, and Potential Solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant Acidification in Major Chinese Croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, K.; Furey, G.N.; Hobbie, S.E.; Isbell, F.; Tilman, D.; Reich, P.B. Diversity-Dependent Soil Acidification under Nitrogen Enrichment Constrains Biomass Productivity. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 6594–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lu, M.; Cui, J.; Li, B.; Fang, C. Effects of Straw Carbon Input on Carbon Dynamics in Agricultural Soils: A Meta-Analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 1366–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Six, J. Soil Structure and Microbiome Functions in Agroecosystems. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qiu, T.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Tan, W.; Wei, X.; Cui, Y.; Cui, Q.; Wu, C.; Liu, L.; et al. Crop Residue Return Sustains Global Soil Ecological Stoichiometry Balance. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 2203–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Chakraborty, D.; Singh, V.K.; Aggarwal, P.; Singh, R.; Dwivedi, B.S.; Mishra, R.P. Effect of Integrated Nutrient Management Practice on Soil Aggregate Properties, Its Stability and Aggregate-Associated Carbon Content in an Intensive Rice–Wheat System. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 136, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Luo, X.; Liu, Y.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Chen, W.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Q. Soil Aggregate Size-Dependent Relationships between Microbial Functional Diversity and Multifunctionality. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 154, 108143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Li, R.; Guan, E.; Chen, H.; Zhao, X.; Wei, G.; Shu, D. Fertilization Regimes Affect Crop Yields through Changes of Diazotrophic Community and Gene Abundance in Soil Aggregation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, S.; Xue, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X. Long-Term Tillage and Cropping Systems Affect Soil Organic Carbon Components and Mineralization in Aggregates in Semiarid Regions. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 231, 105742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Ni, S.; Wang, J.; Cai, C. Aggregate Pore Structure, Stability Characteristics, and Biochemical Properties Induced by Different Cultivation Durations in the Mollisol Region of Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 233, 105797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrold, D.D. Transformations of Nitrogen. In Principles and Applications of Soil Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 385–421. ISBN 978-0-12-820202-9. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, L.A.; Schefe, C.R.; Fridman, M.; O’Halloran, N.; Armstrong, R.D.; Mele, P.M. Organic Nitrogen Cycling Microbial Communities Are Abundant in a Dry Australian Agricultural Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 86, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Reeve, J.R.; Norton, J.M. Soil Enzyme Activities and Abundance of Microbial Functional Genes Involved in Nitrogen Transformations in an Organic Farming System. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 54, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Yin, M.; Chu, G.; Xu, C.; Zhang, X.; Abliz, B.; Tang, C.; Wang, D.; Chen, S. Fifteen Years of Crop Rotation Combined with Straw Management Alters the Nitrogen Supply Capacity of Upland-Paddy Soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 215, 105219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Pan, G.; Qaiser, H.; Liu, Y. Impact of Long-Term Fertilization on Community Structure of Ammonia Oxidizing and Denitrifying Bacteria Based on amoA and nirK Genes in a Rice Paddy from Tai Lake Region, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 2286–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, A.; Zhang, W.; Wei, W.; Sheng, R. Impact of Fertilization Regimes on Diazotroph Community Compositions and N2-Fixation Activity in Paddy Soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 247, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Liu, T.; Jiang, S.; Cao, C.; Li, C.; Chen, B.; Liu, J. Combined Effects of Straw Returning and Chemical N Fertilization on Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Yield from Paddy Fields in Northwest Hubei Province, China. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Jia, S.; Yu, M.; Chen, X.; Shen, A.; Su, Y. Long-Term Straw Return Increases Biological Nitrogen Fixation by Increasing Soil Organic Carbon and Decreasing Available Nitrogen in Rice–Rape Rotation. Plant Soil 2022, 479, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, F.; Peng, P.; Yang, K.; Shu, Y.; Wang, J. Straw Return of Maize and Soybean Enhances Soil Biological Nitrogen Fixation by Altering the N-Cycling Microbial Community. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 192, 105094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Spor, A.; Hénault, C.; Bru, D.; Bizouard, F.; Jones, C.M.; Sarr, A.; Maron, P.-A. Loss in Microbial Diversity Affects Nitrogen Cycling in Soil. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, K.; Ise, Y.; Kato, H.; Oda, T.; Vincenot, C.E.; Koba, K.; Tateno, R.; Senoo, K.; Ohte, N. Consequences of Microbial Diversity in Forest Nitrogen Cycling: Diverse Ammonifiers and Specialized Ammonia Oxidizers. ISME J. 2020, 14, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardy, V.; Spor, A.; Mathieu, O.; Lévèque, J.; Terrat, S.; Plassart, P.; Regnier, T.; Bardgett, R.D.; van der Putten, W.H.; Roggero, P.P.; et al. Shifts in Microbial Diversity through Land Use Intensity as Drivers of Carbon Mineralization in Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 90, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, J.J.; Zuberer, D.A. 13—Carbon Transformations and Soil Organic Matter Formation. In Principles and Applications of Soil Microbiology, 3rd ed.; Gentry, T.J., Fuhrmann, J.J., Zuberer, D.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 327–361. ISBN 978-0-12-820202-9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Kuzyakov, Y. Mechanisms and Implications of Bacterial–Fungal Competition for Soil Resources. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrae073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Liao, X.; Yi, Q.; Zhang, W.; Lin, H.; Liu, K.; Peng, P.; Wang, K. Long-Term Returning Agricultural Residues Increases Soil Microbe-Nematode Network Complexity and Ecosystem Multifunctionality. Geoderma 2023, 430, 116340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Dang, P.; Haegeman, B.; Han, X.; Wang, X.; Pu, X.; Qin, X.; Siddique, K.H.M. The Effects of Straw Return on Soil Bacterial Diversity and Functional Profiles: A Meta-Analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 195, 109484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Sun, R.; He, T.; Sun, Y.; Wu, M.; Xue, Y.; Meng, F.; Wang, J. Disentangling the Impact of Straw Incorporation on Soil Microbial Communities: Enhanced Network Complexity and Ecological Stochasticity. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Wu, M.; Che, S.; Yuan, S.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Tian, P.; Wu, L.; Yang, M.; Wu, Z. Effects of Continuous Straw Returning on Soil Functional Microorganisms and Microbial Communities. J. Microbiol. 2023, 61, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahdan, S.F.M.; Ji, L.; Schädler, M.; Wu, Y.-T.; Sansupa, C.; Tanunchai, B.; Buscot, F.; Purahong, W. Future Climate Conditions Accelerate Wheat Straw Decomposition alongside Altered Microbial Community Composition, Assembly Patterns, and Interaction Networks. ISME J. 2023, 17, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Miao, C.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Jiang, Y.; Li, G. The Coupling Effects of Long-Term Straw Return and Plant Selection Facilitate Rhizosphere Nitrogen Supply by Promoting Recruitment of Core Genera. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 207, 105936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cheng, M.; Yang, L.; Gu, X.; Jin, J.; Fu, M. Regulation of Straw Decomposition and Its Effect on Soil Function by the Amount of Returned Straw in a Cool Zone Rice Crop System. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksen, T.M.; Breland, T.A. Nitrogen Availability Effects on Carbon Mineralization, Fungal and Bacterial Growth, and Enzyme Activities during Decomposition of Wheat Straw in Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiet, R.K.; Frey, S.D.; Six, J. Do Growth Yield Efficiencies Differ between Soil Microbial Communities Differing in Fungal:Bacterial Ratios? Reality Check and Methodological Issues. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Groenigen, K.-J.; Six, J.; Harris, D.; Van Kessel, C. Elevated CO2 Does Not Favor a Fungal Decomposition Pathway. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2168–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, Z.; Lu, X.; Li, Z.; Lin, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhang, D.; Shen, S.; Liu, X.; Zheng, J.; Drosos, M.; et al. Macroaggregates Serve as Micro-Hotspots Enriched with Functional and Networked Microbial Communities and Enhanced under Organic/Inorganic Fertilization in a Paddy Topsoil from Southeastern China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 831746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Rochester, I.J.; Trivedi, C.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Zhou, J.; Karunaratne, S.; Anderson, I.C.; Singh, B.K. Soil Aggregate Size Mediates the Impacts of Cropping Regimes on Soil Carbon and Microbial Communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 91, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillig, M.C.; Muller, L.A.H.; Lehmann, A. Soil Aggregates as Massively Concurrent Evolutionary Incubators. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, E.M.; Williams, R.J.; Hargreaves, S.K.; Yang, F.; Hofmockel, K.S. Greatest Soil Microbial Diversity Found in Micro-Habitats. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 118, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Hao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, F.; Xu, M.; Cai, P.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q. Soil Aggregate Modulates Microbial Ecological Adaptations and Community Assemblies in Agricultural Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 172, 108769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, A.L.; Rossmann, M.; Brearley, C.; Akkari, E.; Guyomar, C.; Clark, I.M.; Allen, E.; Hirsch, P.R. Land-Use Influences Phosphatase Gene Microdiversity in Soils. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 2740–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Guidelines for Soil Description; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Nadeem, M.Y.; Miao, C.; You, J.; Li, W.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. Long-Term Straw Returning Improved Soil Nitrogen Sequestration by Accelerating the Accumulation of Amino Acid Nitrogen. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 362, 108846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemmer, M.; Gerzabek, M.H.; Kandeler, E. Organic Matter and Enzyme Activity in Particle-Size Fractions of Soils Obtained after Low-Energy Sonication. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, A.; Dexter, M.; Perrott, K.W. Hot-Water Extractable Carbon in Soils: A Sensitive Measurement for Determining Impacts of Fertilisation, Grazing and Cultivation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Doebeli, M. Decoupling Function and Taxonomy in the Global Ocean Microbiome. Science 2016, 353, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Song, Z.; Bates, S.T.; Branco, S.; Tedersoo, L.; Menke, J.; Schilling, J.S.; Kennedy, P.G. FUNGuild: An Open Annotation Tool for Parsing Fungal Community Datasets by Ecological Guild. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 20, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooshammer, M.; Wanek, W.; Hämmerle, I.; Fuchslueger, L.; Hofhansl, F.; Knoltsch, A.; Schnecker, J.; Takriti, M.; Watzka, M.; Wild, B.; et al. Adjustment of Microbial Nitrogen Use Efficiency to Carbon:Nitrogen Imbalances Regulates Soil Nitrogen Cycling. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Ge, T.; Luo, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.; Tong, C.; Shibistova, O.; Guggenberger, G.; Wu, J. Microbial Stoichiometric Flexibility Regulates Rice Straw Mineralization and Its Priming Effect in Paddy Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 121, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; He, X.; Wang, G.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Su, Y.; Wang, K.; Soromotin, A.V.; et al. Network Analysis Reveals Bacterial and Fungal Keystone Taxa Involved in Straw and Soil Organic Matter Mineralization. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 173, 104395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Kirkby, C.A.; Schmutter, D.; Bissett, A.; Kirkegaard, J.A.; Richardson, A.E. Network Analysis Reveals Functional Redundancy and Keystone Taxa amongst Bacterial and Fungal Communities during Organic Matter Decomposition in an Arable Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santolini, M.; Barabási, A.-L. Predicting Perturbation Patterns from the Topology of Biological Networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E6375–E6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.M.; Guo, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, N.; Ning, D.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; et al. Climate Warming Enhances Microbial Network Complexity and Stability. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressler, Y.; Zhou, J.; He, Z.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Smith, A.P. Post-Agricultural Tropical Forest Regeneration Shifts Soil Microbial Functional Potential for Carbon and Nutrient Cycling. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 145, 107784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-H.; Chen, S.-Y.; Chen, J.-W.; Xue, K.; Chen, S.-L.; Wang, X.-M.; Chen, T.; Kang, S.-C.; Rui, J.-P.; Thies, J.E.; et al. Reduced Microbial Stability in the Active Layer Is Associated with Carbon Loss under Alpine Permafrost Degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2025321118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, R.; Wang, C.; Zhao, L.; Sun, B.; Wang, B. Agricultural Intensification Weakens the Soil Health Index and Stability of Microbial Networks. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 339, 108118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, D.J.; David, A.S.; Menges, E.S.; Searcy, C.A.; Afkhami, M.E. Environmental Stress Destabilizes Microbial Networks. ISME J. 2021, 15, 1722–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Meng, Z.; Xu, R.; Duoji, D.; Zhang, J.; He, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; et al. Soil Microbial Network Complexity Predicts Ecosystem Function along Elevation Gradients on the Tibetan Plateau. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 172, 108766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Du, X.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Liang, W. Organic Substitutions Improve Soil Quality and Maize Yield through Increasing Soil Microbial Diversity. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 347, 131323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; He, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xia, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Chu, H.; Liu, W.; et al. Organic Amendments Enhance Soil Microbial Diversity, Microbial Functionality and Crop Yields: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, N.; Zhu, C.; Xue, C.; Chen, H.; Duan, Y.; Peng, C.; Guo, S.; Shen, Q. Insight into How Organic Amendments Can Shape the Soil Microbiome in Long-Term Field Experiments as Revealed by Network Analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 99, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güsewell, S.; Gessner, M.O. N: P Ratios Influence Litter Decomposition and Colonization by Fungi and Bacteria in Microcosms. Funct. Ecol. 2009, 23, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhao, W.; Li, T.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Q. Balancing Straw Returning and Chemical Fertilizers in China: Role of Straw Nutrient Resources. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2695–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Chapin, F.S.; Firestone, M.K.; Field, C.B.; Chiariello, N.R. Nitrogen Limitation of Microbial Decomposition in a Grassland under Elevated CO2. Nature 2001, 409, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, M.S.; Rousk, J. Considering Fungal:Bacterial Dominance in Soils—Methods, Controls, and Ecosystem Implications. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Strickland, M.S.; Liptzin, D.; Bradford, M.A.; Cleveland, C.C. Global Patterns in Belowground Communities. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 1238–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, S.D.; Six, J.; Elliott, E.T. Reciprocal Transfer of Carbon and Nitrogen by Decomposer Fungi at the Soil–Litter Interface. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butenschoen, O.; Poll, C.; Langel, R.; Kandeler, E.; Marhan, S.; Scheu, S. Endogeic Earthworms Alter Carbon Translocation by Fungi at the Soil–Litter Interface. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2854–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Qin, H.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J.; Wei, W. Effect of Long-Term Fertilization on Bacterial Composition in Rice Paddy Soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Lv, J.L.; Yu, M.; Ma, Z.H.; Xi, H.; Kou, C.L.; He, Z.C.; Shen, A.L. Long-Term Decomposed Straw Return Positively Affects the Soil Microbial Community. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Wal, A.; Van Veen, J.A.; Smant, W.; Boschker, H.T.S.; Bloem, J.; Kardol, P.; Van Der Putten, W.H.; De Boer, W. Fungal Biomass Development in a Chronosequence of Land Abandonment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voříšková, J.; Baldrian, P. Fungal Community on Decomposing Leaf Litter Undergoes Rapid Successional Changes. ISME J. 2013, 7, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Peng, Z.; Qi, J.; Gao, J.; Wei, G. Linking Bacterial-Fungal Relationships to Microbial Diversity and Soil Nutrient Cycling. mSystems 2021, 6, e01052-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.S.; Isbell, F.; Seidl, R. β-Diversity, Community Assembly, and Ecosystem Functioning. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Du, N.; Li, Q.; Wei, G. Soil Microbiomes with Distinct Assemblies through Vertical Soil Profiles Drive the Cycling of Multiple Nutrients in Reforested Ecosystems. Microbiome 2018, 6, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hao, X.; Lu, Y. Core Microbiota in Agricultural Soils and Their Potential Associations with Nutrient Cycling. mSystems 2019, 4, e00313-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Maestre, F.T.; Reich, P.B.; Jeffries, T.C.; Gaitan, J.J.; Encinar, D.; Berdugo, M.; Campbell, C.D.; Singh, B.K. Microbial Diversity Drives Multifunctionality in Terrestrial Ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Trivedi, C.; Hu, H.; Anderson, I.C.; Jeffries, T.C.; Zhou, J.; Singh, B.K. Microbial Regulation of the Soil Carbon Cycle: Evidence from Gene–Enzyme Relationships. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2593–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L. Linking Microbial Functional Gene Abundance and Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activity: Implications for Soil Carbon Dynamics. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 1322–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, P.; Mo, J. Global Pattern and Controls of Biological Nitrogen Fixation under Nutrient Enrichment: A Meta-Analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 3018–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmett, B.D.; Buckley, D.H.; Drinkwater, L.E. Plant Growth Rate and Nitrogen Uptake Shape Rhizosphere Bacterial Community Composition and Activity in an Agricultural Field. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 960–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Wang, S.; Liao, T.; Luo, H. Evolutionary Origin and Ecological Implication of a Unique Nif Island in Free-Living Bradyrhizobium Lineages. ISME J. 2021, 15, 3195–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, G.A.A.; Abdelhameed, A.; Banat, I.M.M.; Berrar, D.; Doerr, S.H.H.; Dudley, E.; Francis, L.W.W.; Gazze, S.A.A.; Hallin, I.; Matthews, G.P.T.; et al. Complementary Protein Extraction Methods Increase the Identification of the Park Grass Experiment Metaproteome. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 173, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yan, Q.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, Z.; Peng, Q. Root Endophyte Shift and Key Genera Discovery in Rice under Barnyardgrass Stress. Rice Sci. 2023, 30, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Gu, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, J.; Wang, G. Distinct Influence of Conventional and Biodegradable Microplastics on Microbe-Driving Nitrogen Cycling Processes in Soils and Plastispheres as Evaluated by Metagenomic Analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 451, 131097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, D.L.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Romine, M.F. Sphingomonas and Related Genera. In The Prokaryotes: Volume 7: Proteobacteria: Delta, Epsilon Subclass; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K.-H., Stackebrandt, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 605–629. ISBN 978-0-387-30747-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Li, S.; Bol, R.; Zhu, P.; Peng, C.; An, T.; Cheng, N.; Liu, X.; Li, T.; Xu, Z.; et al. Differential Long-Term Fertilization Alters Residue-Derived Labile Organic Carbon Fractions and Microbial Community during Straw Residue Decomposition. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, D.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; He, N.; Niu, S. Microbes Drive Global Soil Nitrogen Mineralization and Availability. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.P.; Bennett, J. Nitrogen Mineralization: Challenges of a Changing Paradigm. Ecology 2004, 85, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, M.; Li, P.; Ti, C.; Zhu, S.; Yan, X.; Chang, S.X. Soil Gross Nitrogen Transformations Are Related to Land-Uses in Two Agroforestry Systems. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 127, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhu, D.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Yan, B.; Mao, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Converting Upland to Paddy Fields Alters Soil Nitrogen Microbial Functions at Different Depths in Black Soil Region. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 372, 109089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; Jin, X.; Ni, H. The Salt-Tolerant Phenazine-1-Carboxamide-Producing Bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa NF011 Isolated from Wheat Rhizosphere Soil in Dry Farmland with Antagonism against Fusarium graminearum. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 245, 126673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zheng, S.; Ma, C.; Rui, Y.; He, H.; Huang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Ge, T.; et al. Contrasting Pathways of Carbon Sequestration in Paddy and Upland Soils. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2478–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Guo, Z.; Pan, K.; Wang, C.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J.; Pan, X. Increasing Land-Use Durations Enhance Soil Microbial Deterministic Processes and Network Complexity and Stability in an Ecotone. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 181, 104630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).