Impacts of Chemical and Microbial Additives on the Quality of Forage Sorghum Silage During the Fermentation Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design, Harvesting, and Ensiling
2.3. Fermentation Profile and Dry Matter Losses
2.4. Chemical Composition
2.5. Microbial Populations and Organic Acids
2.6. Aerobic Stability
2.7. Bacterial 16S rRNA Gene Diversity
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Composition
3.2. Fermentation Characteristics
3.3. Microbial Populations
3.4. Organic Acids
3.5. Aerobic Stability
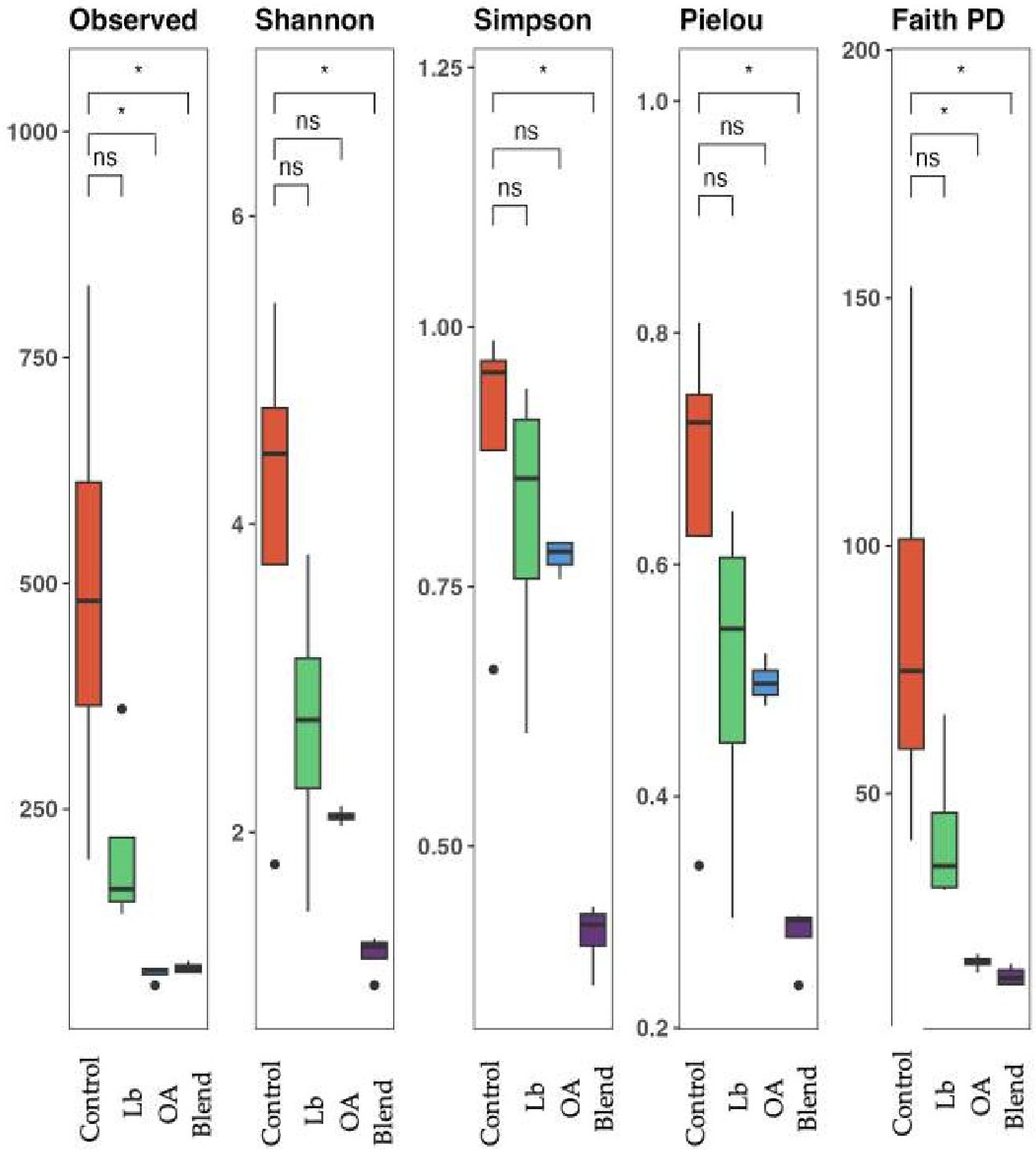
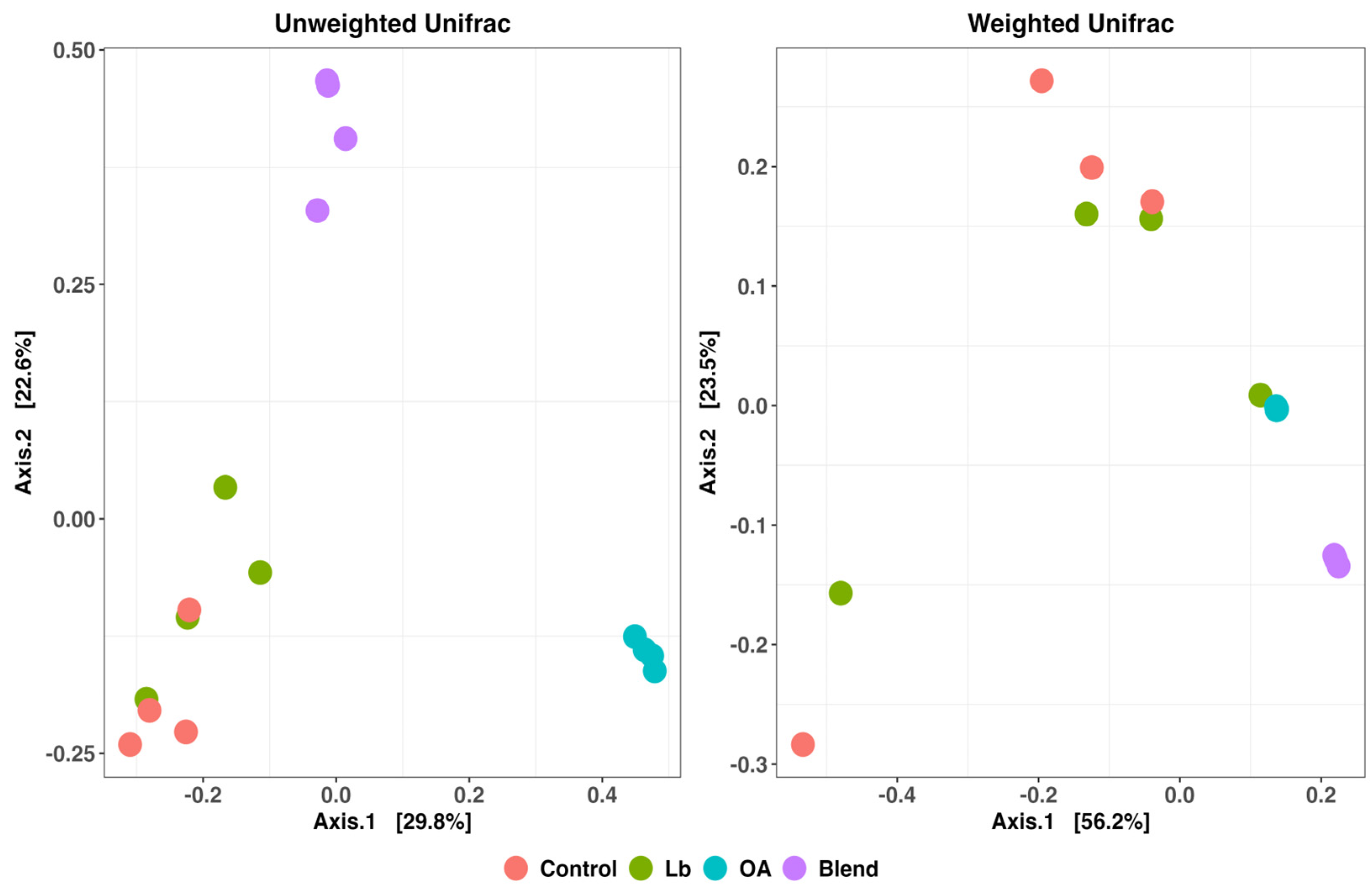
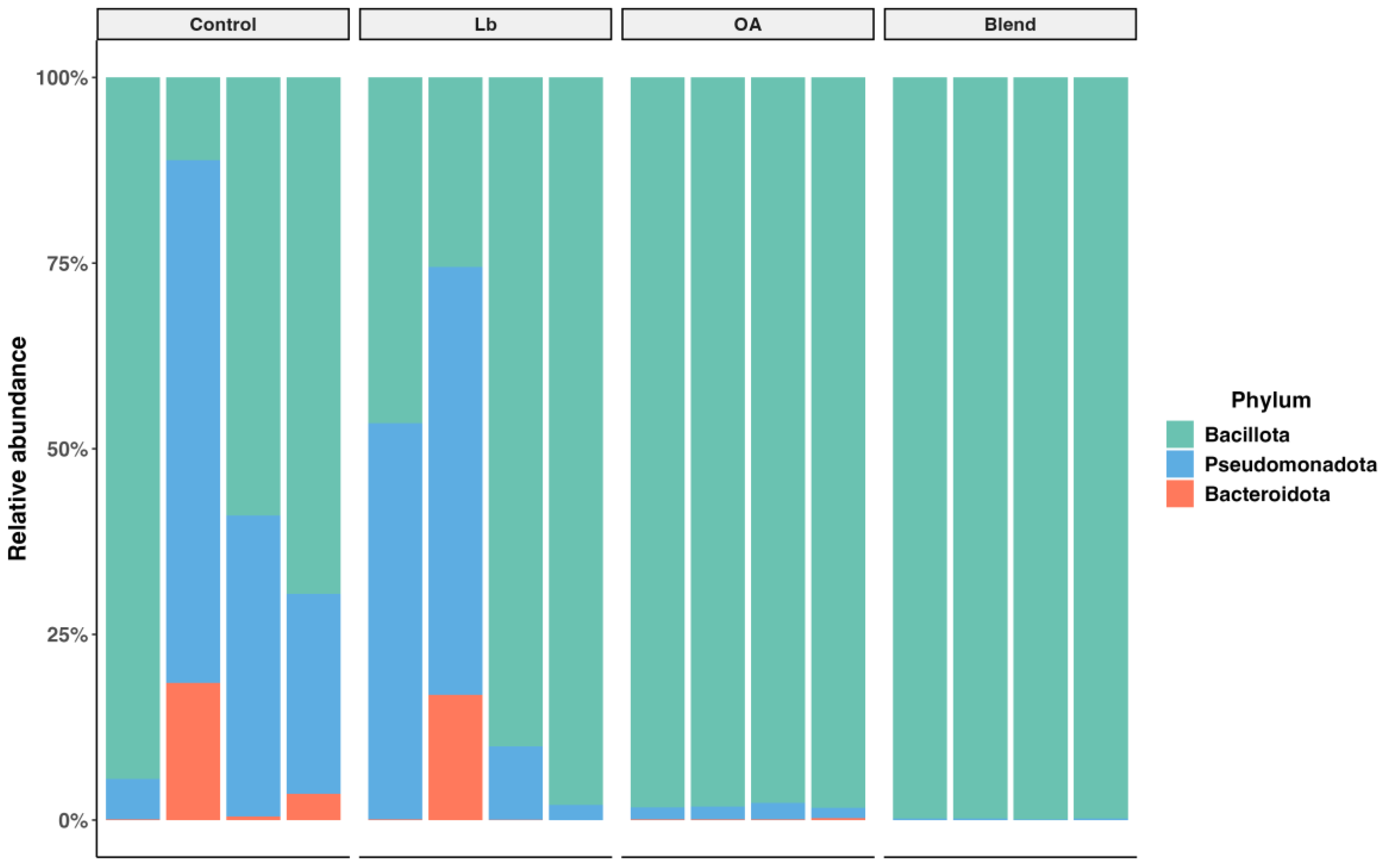
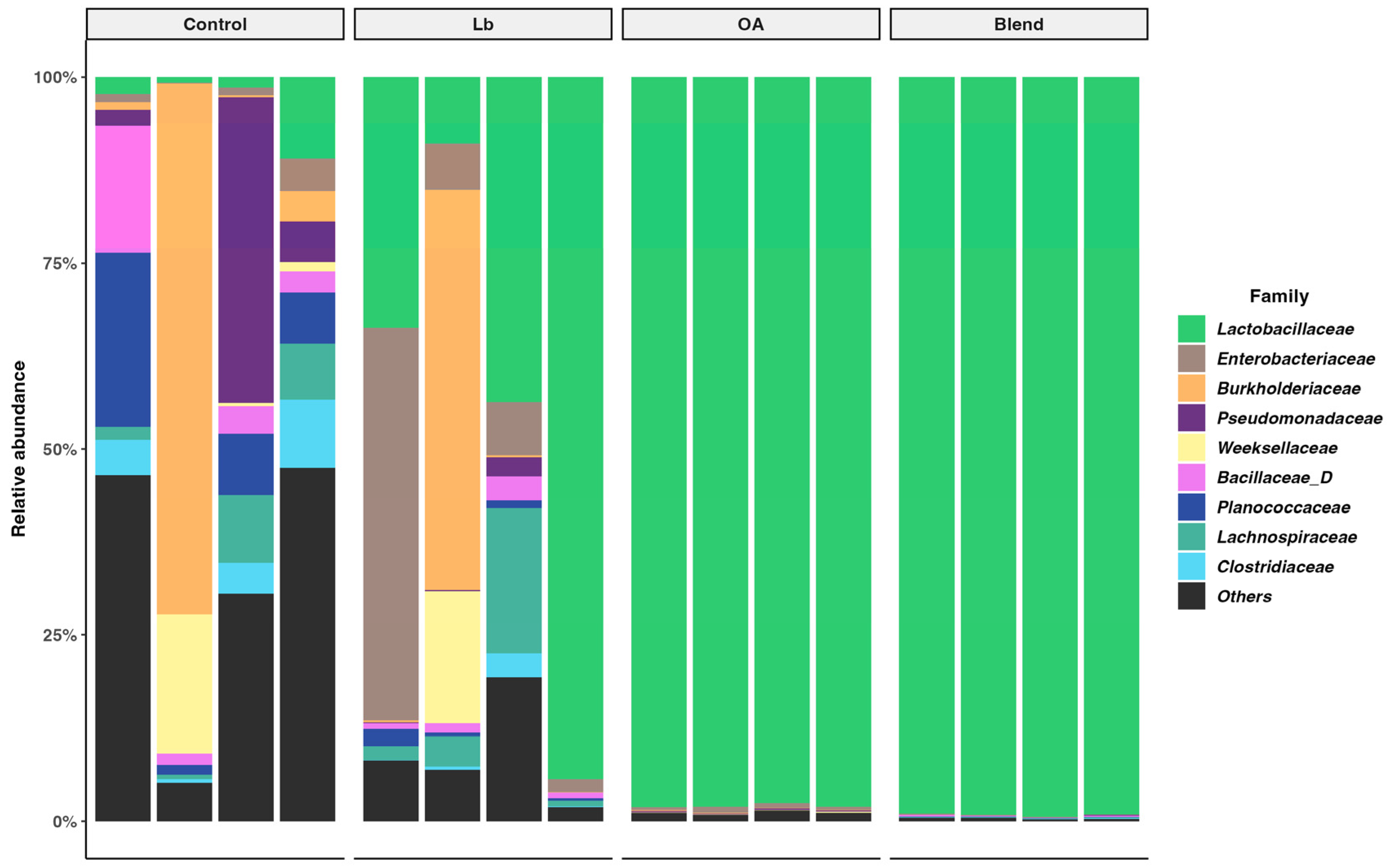
3.6. Bacterial Diversity in the Silage
4. Discussion
4.1. Chemical Composition
4.2. Fermentation Characteristics
4.3. Microbial Populations
4.4. Organic Acids
4.5. Aerobic Stability
4.6. Bacterial Community Diversity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Queiroz, O.C.M.; Arriola, K.G.; Daniel, J.L.P.; Adesogan, A.T. Effects of 8 Chemical and Bacterial Additives on the Quality of Corn Silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 5836–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero, F.; Piano, S.; Tabacco, E.; Borreani, G. Effects of Conservation Period and Lactobacillus hilgardii Inoculum on the Fermentation Profile and Aerobic Stability of Whole Corn and Sorghum Silages. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2530–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabacco, E.; Piano, S.; Cavallarin, L.; Bernardes, T.F.; Borreani, G. Clostridia Spore Formation during Aerobic Deterioration of Maize and Sorghum Silages as Influenced by Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus plantarum Inoculants. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 1632–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, R.; Lourenço, M.; Díaz, R.F.; Castro, A.; Fievez, V. Effect of Combined Ensiling of Sorghum and Soybean with or without Molasses and Lactobacilli on Silage Quality and In Vitro Rumen Fermentation. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2010, 155, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.E.; Foster, J.L.; McCuistion, K.C.; Redmon, L.A.; Jessup, R.W. Nutritive Value, Fermentation Characteristics, and in Situ Disappearance Kinetics of Sorghum Silage Treated with Inoculants. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 7120–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyś, J.B.; Karpowicz, A.; Szałata, A. The Effect of Harvest Date and Additives on Chemical Composition and Aerobic Stability of Sorghum Silage. Slovak J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 43, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Khota, W.; Pholsen, S.; Higgs, D.; Cai, Y. Fermentation Quality and In Vitro Methane Production of Sorghum Silage Prepared with Cellulase and Lactic Acid Bacteria. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.P.M.; Santos, E.M.; Oliveira, J.S.; Ribeiro, O.L.; Perazzo, A.F.; Pinho, R.M.A.; Macêdo, A.J.S.; Pereira, G.A. Effects of Urea Addition on the Fermentation of Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) Silage. Afr. J. Range Forage Sci. 2018, 35, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.H.M.; Pinedo, L.A.; Meyer, P.M.; Silva, T.H.; Guimarães, I.C.S.B. Sorghum Silage Quality as Determined by Chemical-Nutritional Factors. Grass Forage Sci. 2020, 75, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmit, D.H.; Schmidt, R.J.; Kung, L. The Effects of Various Antifungal Additives on the Fermentation and Aerobic Stability of Corn Silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunade, I.M.; Jiang, Y.; Kim, D.H.; Pech Cervantes, A.A.; Arriola, K.G.; Vyas, D.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Jeong, K.C.; Adesogan, A.T. Fate of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Bacterial Diversity in Corn Silage Contaminated with the Pathogen and Treated with Chemical or Microbial Additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 1780–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovanda, L.; Zhang, W.; Wei, X.; Luo, J.; Wu, X.; Atwill, E.R.; Vaessen, S.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activities of Organic Acids and Their Derivatives on Several Species of Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria. Molecules 2019, 24, 3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, L., Jr.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage Review: Interpretation of Chemical, Microbial, and Organoleptic Components of Silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huisden, C.M.; Adesogan, A.T.; Kim, S.C.; Ososanya, T. Effect of Applying Molasses or Inoculants Containing Homofermentative or Heterofermentative Bacteria at Two Rates on the Fermentation and Aerobic Stability of Corn Silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filya, I.; Sucu, E. The Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria on the Fermentation, Aerobic Stability and Nutritive Value of Maize Silage. Grass Forage Sci. 2010, 65, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjit, N.K.; Kung, L., Jr. The Effect of Lactobacillus buchneri, Lactobacillus plantarum, or a Chemical Preservative on the Fermentation and Aerobic Stability of Corn Silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvares, C.A.; Stape, J.L.; Sentelhas, P.C.; Gonçalves, J.L.M.; Sparovek, G. Köppen’s Climate Classification Map for Brazil. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embrapa. Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos, 3rd ed.; Centro Nacional de Pesquisa de Solos, Ed.; Embrapa: Brasilia, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bolsen, K.K.; Lin, C.; Brent, B.E.; Feyerherm, A.M.; Urban, J.E.; Aimutis, W.R. Effect of Silage Additives on the Microbial Succession and Fermentation Process of Alfalfa and Corn Silages. J. Dairy Sci. 1992, 75, 3066–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.T.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, F.A.; Valadares Filho, S.C.; Menezes, G.C.C.; Machado, M.G.; Zanetti, D.; Pina, D.S.; Pereira, O.G.; Paulino, M.F. Chemical Composition and Fermentative Losses of Sugar Cane Ensilage with Different Brix Degrees, with or without Calcium Oxide. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2012, 41, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 15th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for Dietary Fiber, Neutral Detergent Fiber, and Nonstarch Polysaccharides in Relation to Animal Nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, L., Jr.; Taylor, C.C.; Lynch, M.P.; Neylon, J.M. The Effect of Treating Alfalfa with Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 on Silage Fermentation, Aerobic Stability, and Nutritive Value for Lactating Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salfinger, Y.; Tortorello, M.L. (Eds.) Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination of Foods; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, R.; Ruckemann, H.; Stumpf, G. Method for the Determination of Organic Acids in Silage by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Landwirtsch. Forsch. 1984, 37, 298–304. [Google Scholar]
- Kung, L., Jr.; Savage, R.M.; da Silva, E.B.; Polukis, S.A.; Smith, M.L.; Johnson, A.C.B.; Miller, M.A. The Effects of Air Stress during Storage and Low Packing Density on the Fermentation and Aerobic Stability of Corn Silage Inoculated with Lactobacillus buchneri 40788. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 4206–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thukral, A.K. A Review on Measurement of Alpha Diversity in Biology. Agric. Res. J. 2017, 54, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R. The Unifrac Significance Test Is Sensitive to Tree Topology. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.F. Sisvar: A Computer Analysis System to Fixed Effects Split Plot Type Designs. Braz. J. Biom. 2019, 37, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic Biomarker Discovery and Explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkosi, B.D.; Meeske, R.; Langa, T.; Motiang, M.D.; Modiba, S.; Mkhize, N.R.; Groenewald, I.B. Effects of Ensiling Forage Soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) with or without Bacterial Inoculants on the Fermentation Characteristics, Aerobic Stability and Nutrient Digestion of the Silage by Damara Rams. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 134, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandra, J.R.; Takiya, C.S.; Del Valle, T.A.; Pedrini, C.A.; Gandra, E.R.S.; Antônio, G.; de Oliveira, E.R.; Severo, I.K.; Rennó, F.P. Effect of Chemical and Microbial Additives on Fermentation Profile, Chemical Composition, and Microbial Populations of Whole-Plant Soybean Silage. Fermentation 2024, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, K.S.; Salvati, G.G.S.; Morais, G.; Carvalho-Estrada, P.A.; Santos, W.P.; Salvatte, J.M.S.; Gritti, V.C.; Salvo, P.A.R.; Arthur, B.A.V.; Nazato, L.M.; et al. Effect of Length of Storage and Chemical Additives on the Nutritive Value and Starch Degradability of Reconstituted Corn Grain Silage. Agronomy 2023, 13, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.E.L.; Edvan, R.L.; Santos, E.M.; de Oliveira, J.S.; Miranda, R.S.; Nascimento, R.R.; Barros, L.S.; de Oliveira, C.J.B.; Santos, F.N.S.; Pereira, D.M.; et al. Effect of Lactobacillus buchneri and Sodium Benzoate on the Fermentative Profile, Bacterial Taxonomic Diversity, and Aerobic Stability of Sorghum Silages at Different Fermentation Times. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2023, 83, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.C.P.; Santos, E.M.; Carvalho, G.G.P.; Perazzo, A.F.; Araújo, M.L.G.M.L.; de Oliveira, J.S.; Pereira, G.A.; Macêdo, A.J.S.; Sá, W.C.C.S.; Pereira, D.M. Fermentation Profile, Microbial Populations and Aerobic Stability of Sorghum Silages Enriched with Urea and Lactobacillus buchneri. New Zealand J. Agric. Res. 2023, 66, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salawu, M.B.; Warren, E.H.; Adesogan, A.T. Fermentation Characteristics, Aerobic Stability and Ruminal Degradation of Ensiled Pea/Wheat Bi-Crop Forages Treated with Two Microbial Inoculants, Formic Acid or Quebracho Tannins. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesogan, A.T.; Salawu, M.B. Effect of Applying Formic Acid or Lactobacillus buchneri Inoculants with or without Homofermentative Lactic Acid Bacteria on the Fermentation Characteristics and Aerobic Stability of Intercropped Pea-Wheat Silages and Whole Crop Wheat or Pea Silages. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2002, 84, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ni, K.; Pang, H.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Jin, Q. Identification and Antimicrobial Activity Detection of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Corn Stover Silage. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 28, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrolová, Y.; Bartoň, L.; Loučka, R. Effects of Biological and Chemical Additives on Fermentation Progress in Maize Silage. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 62, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, R.J.; Stratford, M. Weak-Acid Preservatives: Modelling Microbial Inhibition and Response. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 86, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junges, D.; Morais, G.; Spoto, M.H.F.; Santos, P.S.; Adesogan, A.T.; Nussio, L.G.; Daniel, J.L.P. Short Communication: Influence of Various Proteolytic Sources during Fermentation of Reconstituted Corn Grain Silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 9048–9051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oude Elferink, S.J.W.H.; Krooneman, J.; Gottschal, J.C.; Spoelstra, S.F.; Faber, F.; Driehuis, F. Anaerobic conversion of lactic acid to acetic acid and 1,2-propanediol by Lactobacillus buchneri. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, K.; Kroschewski, B.; Auerbach, H. Effects of Air Exposure, Temperature and Additives on Fermentation Characteristics, Yeast Count, Aerobic Stability and Volatile Organic Compounds in Corn Silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 8053–8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.N.S.; Ghedini, C.P.; Coelho, L.M.; Ezequiel, J.M.B.; Júnior, G.A.A.; Almeida, M.T.C. Meta-analysis of the effects of silage additives on high-moisture grain silage quality and performance of dairy cows. Livest. Sci. 2021, 251, 104618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Shao, T. Influences of organic acid salts and bacterial additives on fermentation profile, aerobic stability, and in vitro digestibility of total mixed ration silage prepared with wet hulless barley distillers’ grains. Agronomy 2023, 13, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheller, L.S.; Ghizzi, L.G.; Takiya, C.S.; Grigoletto, N.T.S.; Silva, T.B.P.; Marques, J.A.; Dias, M.S.S.; Freu, G.; Rennó, F.P. Different organic acid preparations on fermentation and microbiological profile, chemical composition, and aerobic stability of whole-plant corn silage. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2021, 281, 115083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marte-Pereira, D.; Oliveira, J.S.; Sousa-Santos, F.N.; Silva-Macêdo, A.J.; Batista-Gomes, P.G.; Pereira-Santana, L.; Silva, E.S.; Lima-Cruz, G.F.; Fernandes-Perazzo, A.; Mauro-Santos, E. Forage cactus as a modulator of forage sorghum silage fermentation: An alternative for animal feed in drylands. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2025, 85, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Neto, A.B.; Ribeiro, A.P.; Volpato, A.; Machado, J.; Nazato, L.M.; Santos, D.P.; Francisco, L.F.; Arthur, B.A.V.; Morais, G.; Reis, R.H.P.; et al. Propionic acid-based additive with surfactant action on the feeding value of rehydrated corn grain silage for dairy cows performance. Livest. Sci. 2023, 275, 105292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, F.; Hu, J.; Ma, R.; Liu, H.; Shao, T. Improving total mixed ration silage: Effects of lactic acid bacteria inoculants and antimicrobial additives on fermentation quality and aerobic stability. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharechahi, J.; Kharazian, Z.A.; Sarikhan, S.; Jouzani, G.S.; Aghdasi, M.; Hosseini Salekdeh, G. The dynamics of the bacterial communities developed in maize silage. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1663–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, S.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Nishino, N. Effects of inoculation with lactic acid bacteria on the bacterial communities of Italian ryegrass, whole crop maize, guinea grass and rhodes grass silages. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2010, 160, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nishino, N. Bacterial and fungal communities of wilted Italian ryegrass silage inoculated with and without Lactobacillus rhamnosus or Lactobacillus buchneri. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 52, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Nishino, N. Monitoring the bacterial community of maize silage stored in a bunker silo inoculated with Enterococcus faecium, Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus buchneri. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, K.; Wang, F.; Zhu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhou, G.; Pan, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhong, J. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and molasses additives on the microbial community and fermentation quality of soybean silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Benno, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Kumai, S. Effect of applying lactic acid bacteria isolated from forage crops on fermentation characteristics and aerobic deterioration of silage. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ji, S.; Hou, C.; Tang, H.; Wang, Q.; Shen, Y. Effects of chemical additives on the fermentation quality and N distribution of alfalfa silage in south of China. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 87, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
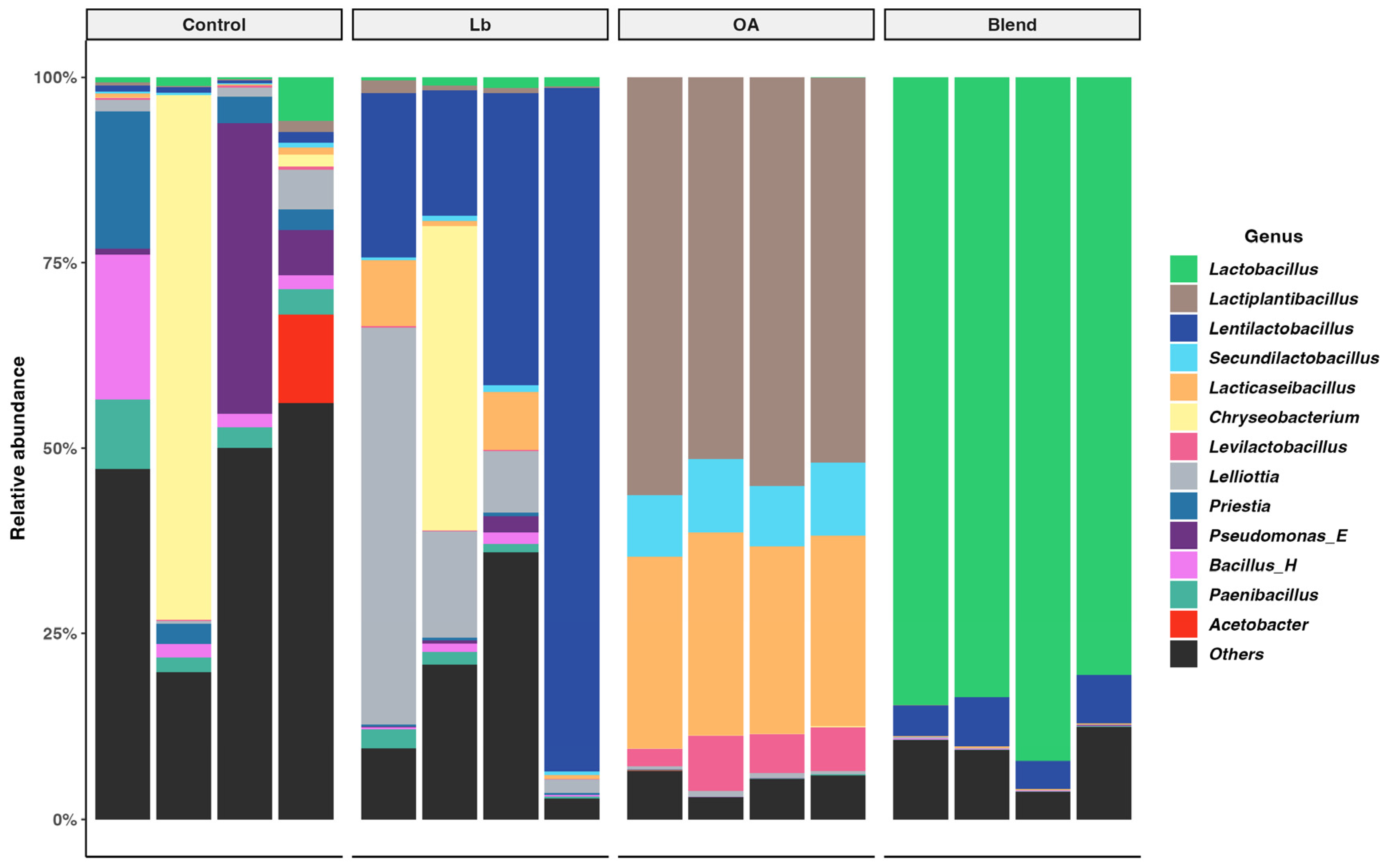
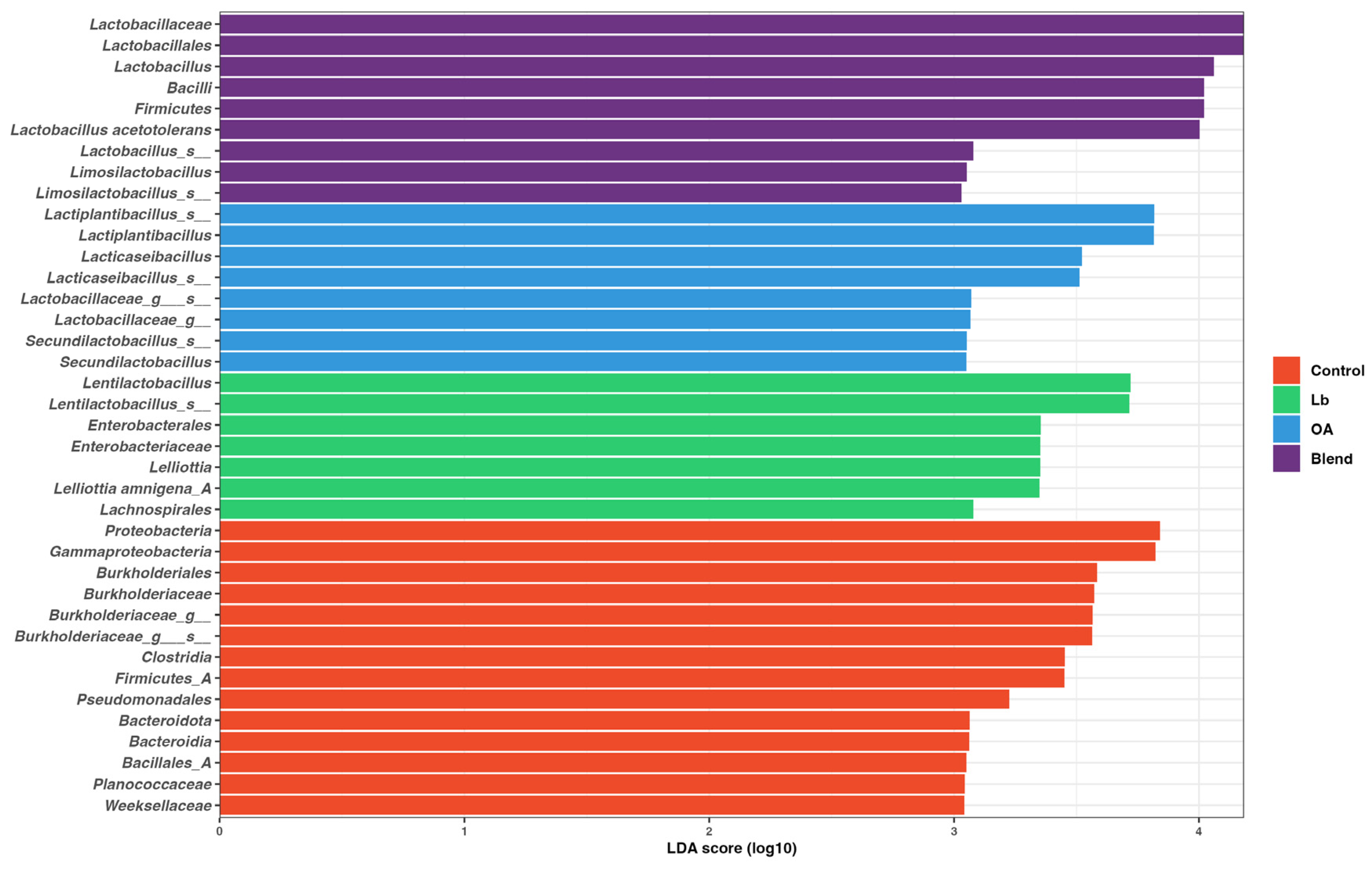
| Item | Additive a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Lb | OA | Blend | |
| Dry matter (g/kg natural matter) | 273.80 | 252.55 | 253.20 | 253.30 |
| Organic matter (g/kg DM b) | 953.30 | 958.82 | 949.62 | 948.50 |
| Mineral matter (g/kg DM) | 46.69 | 41.18 | 50.37 | 51.50 |
| Crude protein (g/kg DM) | 70.93 | 52.85 | 55.62 | 61.61 |
| Neutral detergent fiber (g/kg DM) | 569.27 | 586.84 | 578.56 | 529.03 |
| pH | 5.87 | 5.90 | 5.75 | 5.69 |
| Water-soluble carbohydrates (g/kg DM) | 122.88 | 139.37 | 142.41 | 132.85 |
| Buffering capacity (Emg NaOH/100 g DM) c | 0.135 | 0.161 | 0.167 | 0.162 |
| Lactic acid bacteria (CFU/g) d | 5.38 | 5.36 | 6.14 | 5.98 |
| Yeasts (CFU/g) | 5.57 | 5.59 | 5.50 | 5.64 |
| Filamentous fungi (CFU/g) | 5.25 | 5.19 | 5.09 | 5.03 |
| Item a | p-Value b | SEM c | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | Additive d | Period × Additive | ||
| Dry matter (g/kg natural matter) | <0.001 | 0.0012 | <0.001 | 1.745 |
| Organic matter (g/kg DM) | 0.122 | <0.001 | 0.041 | 0.460 |
| Mineral matter | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.017 | 0.013 |
| Crude protein | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.622 |
| Neutral detergent fiber | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.163 |
| pH | <0.001 | 0.046 | <0.001 | 0.045 |
| Lactic acid bacteria | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.042 |
| Yeasts | <0.001 | 0.085 | 0.010 | 0.496 |
| Filamentous fungi | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.843 | 0.276 |
| Ammonia nitrogen | 0.594 | 0.754 | 0.822 | 1.470 |
| Lactic acid (g/kg DM) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.771 |
| Acetic acid (g/kg DM) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.659 |
| Lactic acid/acetic acid ratio | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.024 |
| Propionic acid (g/kg DM) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.917 |
| Butyric acid (g/kg DM) | 0.007 | <0.001 | 0.023 | 0.001 |
| Fermentation losses | 0.122 | <0.001 | 0.041 | 3.707 |
| Water-soluble carbohydrates | <0.001 | 0.3224 | 0.0205 | 1.117 |
| Aerobic stability | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 5.454 |
| Maximum temperature | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.163 |
| Minimum temperature | <0.001 | 0.046 | <0.001 | 0.045 |
| Average temperature | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.042 |
| Time (h) to reach maximum temperature | <0.001 | 0.085 | 0.010 | 3.383 |
| Fermentation Period | Additive a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Lb | OA | Blend | |
| Dry matter (g/kg natural matter) | ||||
| 15 d | 225.67 Cb | 254.24 Ab | 237.27 BCa | 242.67 ABa |
| 30 d | 243.44 Ca | 254.24 Aa | 247.24 BCa | 248.15 BCa |
| 90 d | 238.56 ABCab | 224.15 Cc | 241.45 ABa | 244.95 Aa |
| Organic matter (g/kg DM) b | ||||
| 15 d | 949.22 Aa | 949.78 Aab | 949.57 Aa | 944.56 Ba |
| 30 d | 945.03 Cb | 952.17 Aa | 949.59 ABa | 946.08 BCa |
| 90 d | 948.78 Aa | 947.97 Ab | 939.39 Bb | 947.97 Aa |
| Mineral matter (g/kg DM) | ||||
| 15 d | 50.78 Bb | 50.22 Bab | 50.42 Bb | 55.44 Aa |
| 30 d | 54.97 Aa | 47.83 Cb | 50.41 BCb | 53.92 ABa |
| 90 d | 51.22 Bb | 52.03 Ba | 60.61 Aa | 52.03 Ba |
| Crude protein (g/kg DM) | ||||
| 15 d | 57.06 Da | 71.22 Aa | 57.35 CDa | 62,76 BCb |
| 30 d | 56.32 Ba | 72.15 Aa | 58.14 Ba | 69.48 Aa |
| 90 d | 58.69 BCa | 59.17 BCb | 55.45 Ca | 65.12 Aab |
| Neutral detergent fiber (g/kg DM) | ||||
| 15 d | 629.40 Ab | 606.60 Ab | 636.59 Aa | 621.02 Aa |
| 30 d | 713.45 Aa | 628.42 Bab | 630.35 Ba | 614.69 Ba |
| 90 d | 640.24 Ab | 674.95 Aa | 633.53 Aa | 622.34 Aa |
| Fermentation Period | Additive a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Lb | OA | Blend | |
| pH | ||||
| 15 d | 3.59 Ca | 3.70 Aa | 3.67 BCa | 3.64 Ca |
| 30 d | 3.63 Ba | 3.76 Aa | 3.64 Ba | 3.60 Bab |
| 90 d | 3.46 Bb | 3.51 ABb | 3.58 ABa | 3.50 ABb |
| Lactic acid bacteria (CFU/g) b | ||||
| 15 d | 6.96 Aa | 6.97 ABba | 6.81 ABa | 7.03 Aa |
| 30 d | 6.87 Ba | 7.53 Aa | 6.50 Cb | 6.65 BCb |
| 90 d | 6.07 Bb | 6.41Ac | 6.18 ABc | 6.10 Bc |
| Yeasts (CFU/g) | ||||
| 15 d | 3.40 Aa | 2.78 Aa | 2.76 Aa | 2.50 Aa |
| 30 d | 2.07 Ab | 1.53 Bb | 1.63 Bb | 2.32 Aab |
| 90 d | 1.50 Ab | 1.03 Bb | 1.10 Ab | 1.38 Ab |
| Dry matter losses (g/kg DM) c | ||||
| 15 d | 168.74 Aa | 91.86 Ca | 125.93 Ba | 92.68 BCa |
| 30 d | 134.45 Ab | 94.20 ABa | 96.96 Bb | 93.52 Ba |
| 90 d | 132.54 Ab | 91.86 Ba | 97.03 Bb | 94.89 Ba |
| Water-soluble carbohydrates (g/kg DM) | ||||
| 15 d | 36.23 Ab | 30.28 Ab | 29.32 Ab | 34.11 Aa |
| 30 d | 28.80 Bab | 36.61 ABab | 39.42 Aa | 39.32 Aa |
| 90 d | 38.26 Aa | 39.36 Aa | 37.05 Aab | 42.11 Aa |
| Filamentous fungi (CFU/g) b | ||||
| 15 d | 4.05 | 2.20 a | 1.70 | 0.92 |
| 30 d | 2.63 | 1.77 a | 1.96 | 1.37 |
| 90 d | 2.21 | 0.55 b | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Ammonia nitrogen (g NH3-N/kg total N) | ||||
| 15 d | 15.84 | 17.48 | 18.15 | 21.46 |
| 30 d | 18.58 | 15.89 | 17.86 | 13.30 |
| 90 d | 16.29 | 19.70 | 16.26 | 28.91 |
| Fermentation Period | Additive a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Lb | OA | Blend | |
| Lactic acid (g/kg DM) b | ||||
| 15 d | 65.45 Ab | 62.07 Aa | 65.17 Aa | 65.26 Aa |
| 30 d | 49.15 Bc | 54.34 ABb | 57.13 Ab | 58.41 Ab |
| 90 d | 72.80 Aa | 57.27 BCab | 56.27 BCb | 60.16 Aab |
| Acetic acid (g/kg DM) | ||||
| 15 d | 32.29 ABa | 32.76 ABc | 35.31 Aa | 31.38 ABa |
| 30 d | 26.74 Bb | 38.96 Ab | 28.29 Bb | 26.18 Bb |
| 90 d | 35.68 Ba | 49.69 Aa | 27.94 Cb | 27.13 Cab |
| Lactic acid: acetic acid ratio | ||||
| 15 d | 2.02 ABa | 1.91 ABa | 1.85 Ba | 2.08 Aa |
| 30 d | 1.83 Bb | 1.41 Cb | 2.04 ABa | 2.24 Aa |
| 90 d | 2.04 Aa | 1.22 Bb | 2.03 Aa | 2.22 Aa |
| Propionic acid (g/kg DM) | ||||
| 15 d | 14.99 BCa | 7.09 Cb | 25.76 Aa | 16.13 Bb |
| 30 d | 11.81 Aa | 8.42 Ab | 15.17 Ab | 9.72 Ab |
| 90 d | 14.10 Ca | 26.42 Ba | 25.39 Ba | 30.59 ABa |
| Butyric acid (g/kg DM) | ||||
| 15 d | 0.020 Aa | 0.010 Ba | 0.020 Aa | 0.020 Aa |
| 30 d | 0.017 Aa | 0.010 Ba | 0.017 Aa | 0.017 Aab |
| 90 d | 0.017 Aa | 0.010 Ba | 0.010 Bb | 0.012 ABb |
| Fermentation Period | Additive a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Lb | OA | Blend | |
| Aerobic stability (h) b | ||||
| 15 d | 97.15 Ab | 144.00 Aa | 120.73 Aa | 97.13 Ab |
| 30 d | 144.00 Aa | 144.00 Aa | 144.00 Aa | 144.00 Aa |
| 90 d | 33.90 Bc | 144.00 Aa | 39.97 Bb | 37.63 Bc |
| Maximum temperature (°C) | ||||
| 15 d | 25.12 Ab | 25.06 Aa | 24.90 Ac | 24.80 Ac |
| 30 d | 25.14 Ab | 25.38 Aa | 26.32 Ab | 26.36 Ab |
| 90 d | 36.46 Aa | 25.58 Ca | 34.26 Ba | 35.60 ABa |
| Minimum temperature (°C) | ||||
| 15 d | 22.70 Cc | 22.70 Cc | 23.18 ABc | 22.86 BCc |
| 30 d | 23.84 Ab | 23.72 ABb | 23.88 Ab | 23.60 ABb |
| 90 d | 24.50 Aa | 24.28 Aa | 24.42 Aa | 24.56 Aa |
| Average temperature (°C) | ||||
| 15 d | 24.32 Ab | 24.36 Ab | 24.40 Ab | 24.20 Ac |
| 30 d | 24.63 Ab | 24.54 Aab | 24.71 Ab | 24.53 Ab |
| 90 d | 28.30 Aa | 24.83 Ba | 28.53 Aa | 28.23 Aa |
| Time to reach maximum temperature (h) | ||||
| 15 d | 53.82 Aa | 36.52 Ab | 36.35 Ab | 30.17 Ac |
| 30 d | 55.65 Aa | 93.66 Aa | 84.25 Aa | 94.28 Aa |
| 90 d | 68.12 Ba | 96.62 Aa | 70.77 ABa | 62.60 Bb |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Júnior, P.d.C.T.; Rodrigues, L.M.P.; Macêdo, A.J.d.S.; Oliveira, J.S.d.; Lemos, M.L.P.; Santos, F.N.d.S.; Moura, B.R.d.; Pereira, A.L.; Silva, E.d.S.d.; Correia, T.B.D.; et al. Impacts of Chemical and Microbial Additives on the Quality of Forage Sorghum Silage During the Fermentation Process. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051176
Júnior PdCT, Rodrigues LMP, Macêdo AJdS, Oliveira JSd, Lemos MLP, Santos FNdS, Moura BRd, Pereira AL, Silva EdSd, Correia TBD, et al. Impacts of Chemical and Microbial Additives on the Quality of Forage Sorghum Silage During the Fermentation Process. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051176
Chicago/Turabian StyleJúnior, Paulo da Cunha Tôrres, Luana Milena Pinheiro Rodrigues, Alberto Jefferson da Silva Macêdo, Juliana Silva de Oliveira, Mateus Lacerda Pereira Lemos, Francisco Naysson de Sousa Santos, Bruno Rocha de Moura, Anderson Lopes Pereira, Evandro de Sousa da Silva, Thácyla Beatriz Duarte Correia, and et al. 2025. "Impacts of Chemical and Microbial Additives on the Quality of Forage Sorghum Silage During the Fermentation Process" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051176
APA StyleJúnior, P. d. C. T., Rodrigues, L. M. P., Macêdo, A. J. d. S., Oliveira, J. S. d., Lemos, M. L. P., Santos, F. N. d. S., Moura, B. R. d., Pereira, A. L., Silva, E. d. S. d., Correia, T. B. D., Costa, G. A. d., Mantovani, H. C., & Santos, E. M. (2025). Impacts of Chemical and Microbial Additives on the Quality of Forage Sorghum Silage During the Fermentation Process. Agronomy, 15(5), 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051176







