Stem Rust Resistance in 62 Cultivars and Elite Lines from Northern Huanghuai Region of China
Abstract
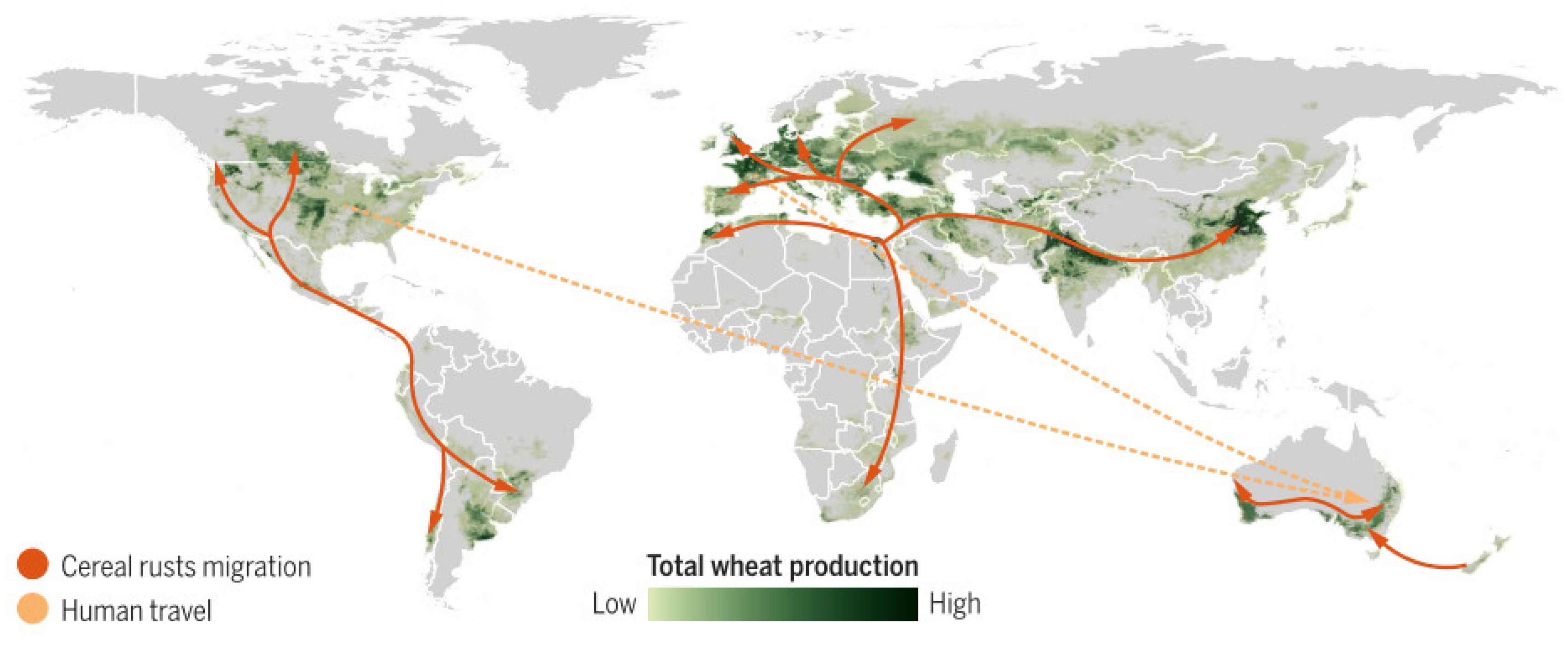
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wheat Lines and P. graminis f. sp. tritici Races
2.2. Identification of Adult Plant Resistance in the Field
2.3. Molecular Markers of Resistance Genes
3. Results
3.1. Resistance Evaluation in Adult Stage
3.2. Molecular Detection of Stem Rust Resistance Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pardey, P.G.; Beddow, J.M.; Kriticos, D.J.; Hurley, T.; Park, R.F.; Duveiller, E.; Sutherst, R.W.; Burdon, J.J.; Hodson, D. Right-sizing stem-rust research. Science 2013, 340, 147–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.X.; Lin, Q.J.; Ni, X.Y.; Sun, Q.; Chen, R.Z.; Xu, X.F.; Qiu, Y.C.; Li, T.Y. Characterization of wheat monogenic lines with known Sr genes and wheat lines with resistance to the Ug99 race group for resistance to prevalent races of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici in China. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 1939–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.S.; Huang, Z.T. Twenty year’s racial identification and fluctuation analysis of Puccinia graminis var. tritici in China. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 1987, 18, 105–108. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Fetch, T.G.; Knox, R.E.; Singh, A.K.; Clarke, J.M.; DePauw, R.; Cuthbert, R.D.; Campbell, H.L.; Singh, D.P.; Bhavani, S. Mapping of Ug99 stem rust resistance in Canadian durum wheat. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 43, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.Y.; Chen, W.Q.; Zhao, Z.H.; Zeng, J. Threat of new Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici race Ug99 to wheat production in China and counter measure. China Plant Prot. 2007, 27, 14–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, R.; Chen, S.; Ni, X.; Gao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, T. Identification of wheat stem rust resistance genes in wheat cultivars from Hebei province, China. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1156936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretorius, Z.A.; Singh, R.P.; Wagoire, W.W.; Payne, T.S. Detection of virulence to wheat stem rust resistance gene Sr31 in Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici in Uganda. Plant Dis. 2000, 84, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Hodson, D.P.; Huerta-Espino, J.; Jin, Y.; Bhavani, S.; Njau, P.; Herrera-Foessel, S.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, S.; Govindan, V. The emergence of Ug99 races of the stem rust fungus is a threat to world wheat production. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Pretoriou, Z.A.; Singh, R.P. New virulence with in race TTKS (Ug99) of the stem rust pathogen and effective resistant genes. Phytopathology 2007, 97, S137. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.P.; Hodson, D.P.; Huerta-Espino, J.; Jin, Y.; Njau, P.; Wanyera, R.; Herrera-Foessel, S.A.; Ward, R.W. Will stem rust destroy the world’s wheat crop? Adv. Agron. 2008, 98, 271–309. [Google Scholar]
- Patpour, M.; Baidya, S.; Basnet, R.; Justesen, A.F.; Hodson, D.; Thapa, D.; Hovmøller, M.S. First report of Ug99 wheat stem rust caused by Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici in South Asia. Plant Dis. 2024, 108, 2570. [Google Scholar]
- Moscou, M.J.; van Esse, H.P. The quest for durable resistance. Science 2017, 358, 1541–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.Y.; Si, B.B.; Zhu, G.Q.; Xu, X.F.; Li, W.H.; Chen, S.; Zhao, J.; Li, T.Y. Race and virulence of asexual and sexual populations of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici in China from 2009 to 2015. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 153, 545–555. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, R.F.; Campbell, A.B.; Hannah, A.E. A diagrammatic scale for estimating rust intensity of leaves and stem of cereals. Can. J. Res. 1948, 26, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelfs, A.P.; Singh, R.P.; Saari, E.E. Rust Diseases of Wheat: Concepts and Methods of Disease Management; CIMMYT: Tulantongo, Mexico, 1992. Available online: https://books.google.co.uk/books?hl=ko&lr=&id=GHOD3FOZRfAC&oi=fnd&pg=PR6&dq=Rust+diseases+of+wheat:+Concepts+and+methods+of+disease+management&ots=i0tjiZ60JB&sig=lVJ0q3K2MLTcIWEm7-SU12I51PU#v=onepage&q=Rust%20diseases%20of%20wheat%3A%20Concepts%20and%20methods%20of%20disease%20management&f=false (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Dong, J.Z.; Yang, J.S.; Wu, W.; Wu, Y.S. The application of three mathematical models in the research of the wheat slow-rusting resistance. J. Heilongjiang Bayi Agric. Univ. 1986, 2, 1–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Wu, X.X.; Sun, H.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Chen, S.; Zou, L.M.; Yang, J.J.; Wei, Y.F.; Ni, X.Y.; Sun, Q.; et al. Identification of wheat rust resistance genes in Triticum wheat cultivars and evaluation of their resistance to Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici. Agriculture 2024, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.X.; Yu, L.X.; Singh, P.P.; JIN, Y.; Sorrells, M.E.; Anderson, J.A. Diagnostic and co-dominant PCR markers for wheat stem rust resistance genes Sr25 and Sr26. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 120, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.K.; Saini, A.; Bhagwat, S.G.; Jawali, N. Development of SCAR markers for identification of stem rust resistance gene Sr31 in the homozygous or heterozygous condition in bread wheat. Plant Breed. 2006, 125, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mago, R.; Spielmeyer, W.; Lawrence, G.; Lagudah, E.; Ellis, J.; Pryor, A. Identification and mapping of molecular markers linked to rust resistance genes located on chromosome 1RS of rye using wheat-rye translocation lines. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 104, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mago, R.; Bariana, H.S.; Dundas, I.S.; Spielmeyer, W.; Lawrence, G.J.; Pryor, A.J.; Ellis, J.G. Development of PCR markers for the selection of wheat stem rust resistance genes Sr24 and Sr26 in diverse wheat germplasm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutam, U.; Kukreja, S.; Yadav, R.; Salaria, N.; Thakur, K.; Goyal, A.K. Recent trends and perspectives of molecular markers against fungal diseases in wheat. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, S.; Anderson, J.A.; Singh, R.P.; Jin, Y.; Dubcovsky, J.; Brown-Guidera, G.; Bhavani, S.; Morgounov, A.I.; He, Z.; et al. Haplotype diversity of stem rust resistance loci in uncharacterized wheat lines. Mol. Breed. 2010, 26, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.R.; Bariana, H.S.; Dholakia, B.B.; Naik, S.V.; Lagu, M.D.; Rathjen, A.J.; Bhavani, S.; Gupta, V.S. Molecular mapping of stem and leaf rust resistance in wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.G.; Qiu, J.; Zhou, Y.L.; Xu, S.C.; Chen, H.G.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, B.; Zheng, C.L.; Chen, W.Q. Multi-disease resistance evaluation of Chinese advanced winter wheat lines for the national regional test. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2015, 48, 2967. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, D.; Sun, H.; Song, W.; Li, T. Stem rust resistance and resistance-associated genes in 64 wheat cultivars from Southern Huanghuai, China. Plants 2024, 13, 2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bariana, H.S.; McIntosh, R.A. Cytogenetic studies in wheat. XV. Location of rust resistance genes in VPM1 and their genetic linkage with other disease resistance genes in chromosome 2A. Genome 1993, 36, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helguera, M.; Khan, I.A.; Kolmer, J.; Lijavetzky, D.; Zhong-qi, L.; Dubcovsky, J. PCR assays for the Lr37-Yr17-Sr38 cluster of rust resistance genes and their use to develop isogenic hard red spring wheat lines. Crop Sci. 2003, 43, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, P.; Newcomb, M.; Szabo, L.J.; Rouse, M.; Johnson, J.; Gale, S.; Luster, D.G.; Hodson, D.; Cox, J.A.; Burgin, L.; et al. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of race TKTTF of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici that caused a wheat stem rust epidemic in southern Ethiopia in 2013-14. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Race | Ineffective Sr Genes | Effective Sr Genes |
|---|---|---|
| 21C3CTHQM | 6, 7b, 8a, 9a, 9b, 9d, 9f, 9g, 10, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16, 17, 18, 20, 24, 27, 32, 34, 39, Tmp, McN | 5, 9e, 14, 19, 21, 22, 23, 25, 26, 28, 29, 30, 31, 33, 35, 36, 37, 38, 47, Tt3 |
| 34MKGQM | 5, 6, 7b, 8a, 9a, 9b, 9d, 9f, 9g, 12, 15, 16, 22, 24, 27, 28, 29, 39, GT, McN | 9e, 10, 11, 13, 14, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 23, 25, 26, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 47, Tmp |
| Infection Types | Classification Criteria | Resistance Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Asymptomatic | Immunity, IM |
| ; | Produce dead spots or chlorosis, no uredinia. | Near immunity, NIM |
| 1 | Uredinia are very small, few in number, often not broken, and there is a dead reaction around them. | Resistance, R |
| 2 | Uredinia are small to medium, with dieback and chlorosis around them. | Moderately Resistant, MR |
| 3 | The urediospore pile is medium in size, rarely heals, and the surrounding tissues have no dieback reaction, but there is slight chlorosis. | Moderately susceptible, MS |
| 4 | The uredinia are large and numerous, often fused together, and the surrounding tissues do not die. The early chlorosis phenomenon is not obvious. | Susceptible, S |
| Gene | Primer | Size (bp) | Sequence of Primer (5′→3′) | PCR Amplification Conditions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C)/Time | Number of Cycles | ||||
| Sr24 | Sr24#50 | 500 | CACCCGTGACATGCTCGTA AACAGGAAATGAGCAACGATGT | 94/3 min | 1 |
| 94/30 s; 57/30 s; 72/40 s | 30 | ||||
| 72/5 min | 1 | ||||
| Sr25 | Gb | 191 | CATCCTTGGGGACCTC CCAGCTCGCATACATCCA | 94/3 min | 1 |
| 94/30 s; 60/30 s; 72/40 s | 30 | ||||
| 72/5 min | 1 | ||||
| Sr26 | Sr26#43 | 207 | AATCGTCCACATTGGCTTCT CGCAACAAAATCATGCACTA | 94/3 min | 1 |
| 94/30 s; 56/30 s; 72/40 s | 30 | ||||
| 72/5 min | 1 | ||||
| Sr31 | SCSS30.2576 | 576 | GTCCGACAATACGAACGATT CCGACAATACGAACGCCTTG | 95/5 min | 1 |
| 95/15S; 60/15S; 72/30 s | 35 | ||||
| 72/5 min | 1 | ||||
| Sr31 | Iag95 | 1100 | CTCTGTGGATAGTTACTTGATCGA CCTAGAACATGCATGGCTGTTACA | 94/3 min | 1 |
| 94/30 s; 55/60 s; 72/70 s | 30 | ||||
| 72/5 min | 1 | ||||
| Sr38 | VENTRIUP-LN2 | 259 | GGGGCTACTGACCAAGGCT TGCAGCTACAGCAGTATGTACACAAAA | 94/3 min | 1 |
| 94/30 s; 65/30 s; 72/30 s | 30 | ||||
| 72/5 min | 1 | ||||
| Cultivar (Lines) | 21C3CTHQM | 34MKGQM | Sr Gene | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023IR a | AUDPC | 2024IR | AUDPC | 2023IR | AUDPC | 2024IR | AUDPC | ||
| Qingmai H068 | 100S100 | 250.0 | 100S100 | 250.0 | 70S40 | 212.5 | 100S100 | 400.0 | - |
| RZ1901 | 70S70 | 175 | 100S100 | 120.5 | 100S100 | 262.5 | 70S50 | 200.0 | - |
| Taikemai 46 | 100S100 | 250.0 | 100S100 | 130.0 | 40MS50 | 100.0 | 30MR30 | 75.0 | - |
| Shannong 711006 | 30MS50 | 75.0 | 70S70 | 575.0 | 30MS50 | 75.0 | 30MS50 | 75.0 | - |
| LS1471 | 100S100 | 250.0 | 100S100 | 475.0 | 80S60 | 212.5 | 100S100 | 300.0 | - |
| Kexing 3302 | 5R5 | 12.5 | 5R5 | 37.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 38 |
| Hanke 4898 | 100S100 | 675.0 | 100S100 | 250.0 | 100S100 | 262.5 | 100S100 | 350.0 | - |
| YF6092 | 50S60 | 125.0 | 50S50 | 125.0 | 100S100 | 275.0 | 100S100 | 350.0 | - |
| Cunmai 116 | 60S70 | 150.0 | 70S50 | 175.0 | 100S100 | 262.5 | 100S100 | 512.5 | - |
| Zhongyuanguoke10 | 100S100 | 250.0 | 100S100 | 550.0 | 70S70 | 212.5 | 70S60 | 175.0 | - |
| Shannong K43057 | 100S100 | 250.0 | 100S100 | 425.0 | 30MR30 | 75.0 | 50MR50 | 150 | - |
| U1912 | 100S100 | 250.0 | 50S50 | 125.0 | 70MS60 | 175.0 | 50MS50 | 225.0 | - |
| Luqingmai 6 | 70S80 | 175.0 | 100S100 | 425.0 | 100S100 | 275.0 | 100S100 | 250.0 | - |
| Linmai 1900 | 60MS50 | 150.0 | 50MS50 | 125.0 | 100S100 | 275.0 | 100S100 | 250.0 | - |
| Jinghua 301 | 100S100 | 300.0 | 100S100 | 550.0 | 100S100 | 425.0 | 100S100 | 250 | - |
| Keda 166 | 100S100 | 750.0 | 100S100 | 510.0 | 100S100 | 150.0 | 100S100 | 100.0 | - |
| Jiushenghe 169 | 50MR50 | 650.0 | 50MR40 | 125.0 | 30MR40 | 75.0 | 30MR20 | 75.0 | 31 |
| Shangmai 207 | 10R5 | 37.5 | 10R10 | 50.0 | 10R10 | 25.0 | 10R10 | 25.0 | 31, 38 |
| Taikemai 51 | 70S60 | 175.0 | 50S50 | 125.0 | 50MS50 | 125.0 | 30MS30 | 75.0 | - |
| Xingmai 40 | 40S50 | 150.0 | 100S100 | 500.0 | 70MS80 | 175.0 | 40MS60 | 100.0 | - |
| Kemai 316 | 40S50 | 112.5 | 50S50 | 125.0 | 50MS60 | 125.0 | 30MR10 | 75.0 | - |
| Shannong K31565 | 100S100 | 350.0 | 100S100 | 575.0 | 100S100 | 262.5 | 100S100 | 250.0 | - |
| Kemai 301 | 20MR20 | 62.5 | 20MR40 | 50.0 | 50MS80 | 125.0 | 50MS50 | 150.0 | - |
| Jimai 5086 | 100S100 | 250.0 | 100S100 | 300.0 | 100S100 | 275.0 | 100S100 | 300.0 | - |
| Linmai 12 | 30MR30 | 75.0 | 40MR50 | 100.0 | 5R5 | 12.5 | 10R10 | 25.0 | - |
| 19CA29 | 20R10 | 50.0 | 50MR50 | 150.0 | 40MR40 | 100.0 | 10R20 | 25.0 | - |
| Nongda 8136 | 5R5 | 12.5 | 10MR20 | 25.0 | 80MS70 | 200.0 | 60MS50 | 150.0 | - |
| Xinong 862 | 50MR60 | 125.0 | 40MR60 | 150.0 | 10MR30 | 100.0 | 20R10 | 50.0 | 31 |
| Xinong 303 | 50MR70 | 150.0 | 50MR50 | 175.0 | 50MR70 | 125.0 | 50MR50 | 175.0 | 31 |
| Xinong 5195 | 20MR70 | 75.0 | 30MR60 | 250.0 | 40MR40 | 100.0 | 30R10 | 75.0 | 31 |
| Fumai 1508 | 100S100 | 475.0 | 70S70 | 625.0 | 100S100 | 275.0 | 100S100 | 275.0 | - |
| Jimai 220014 | 50MS50 | 25.0 | 100S100 | 250.0 | 20MR10 | 100.0 | 30MR30 | 75.0 | - |
| Xinshiji 9 | 70MS60 | 175.0 | 50MS50 | 150.0 | 20MR10 | 50.0 | 40R30 | 100.0 | - |
| Xinliang 16 | 10R10 | 25.0 | 20R20 | 50.0 | 20R70 | 50.0 | 20R20 | 50.0 | 31 |
| SN1463 | 100S100 | 300.0 | 100S100 | 300.0 | 100S100 | 250.0 | 100S100 | 250.0 | - |
| Anke 2105 | 100S100 | 450.0 | 100S100 | 625.0 | 100S100 | 275.0 | 100S100 | 300.0 | - |
| Shi 6158 | 10R5 | 125.0 | 40R10 | 100.0 | 50MR50 | 150.0 | 40MR20 | 100.0 | - |
| Han 174291 | 10R5 | 125.0 | 10R10 | 25.0 | 30R60 | 75.0 | 5R5 | 12.5 | 31 |
| Womai 19 | 0 | 0 | 10R30 | 25.0 | 40MR30 | 125.0 | 20R10 | 150.0 | 31, 38 |
| Liumai 1186 | 100S100 | 300.0 | 100S100 | 550.0 | 100S100 | 52.5 | 100S100 | 350.0 | - |
| Jimai CHC4 | 100S100 | 300.0 | 100S100 | 600.0 | 100S100 | 52.5 | 100S100 | 350.0 | - |
| Jimai 5858 | 100S100 | 400.0 | 100S100 | 475.0 | 100S100 | 55.0 | 100S100 | 350.0 | - |
| Guanmai 99 | 80S80 | 250.0 | 100S100 | 525.0 | 80S70 | 90.0 | 100S100 | 250.0 | - |
| Zhongke 19021 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5R5 | 5.0 | 10R10 | 25.0 | 31 |
| JK64109 | 50S40 | 150.0 | 100S100 | 250.0 | 100S100 | 50.0 | 100S100 | 250.0 | - |
| Shengmai 186 | 100S100 | 850.0 | 100S100 | 925.0 | 70S70 | 160.0 | 100S100 | 400.0 | - |
| Shi 17T5248 | 0 | 0 | 5R5 | 12.5 | 0 | 0 | 5R5 | 12.5 | 31 |
| Jimai 6266 | 30MR60 | 75.0 | 20MR70 | 75.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 |
| Heng H175087 | 100S100 | 350.0 | 100S100 | 900.0 | 100S100 | 62.5 | 100S100 | 250.0 | - |
| Jimai U87 | 60S50 | 150.0 | 100S100 | 500.0 | 70S60 | 35.0 | 100S100 | 250.0 | - |
| Shi 1750903 | 10R30 | 25.0 | 20R60 | 50.0 | 20R60 | 10.0 | 20R20 | 50.0 | 38 |
| Huacheng 138 | 100S100 | 300.0 | 100S100 | 250.0 | 80S80 | 40.0 | 70S40 | 175.0 | - |
| Huaifeng 36 | 10R10 | 200.0 | 10R10 | 25.0 | 5R5 | 5.0 | 5R5 | 12.5 | 31 |
| Shijingmai 138 | 70S70 | 175.0 | 70S70 | 175.0 | 60MS70 | 30.0 | 50MR70 | 125.0 | - |
| Jinong 17287 | 100S100 | 300.0 | 100S100 | 650.0 | 80S80 | 40.0 | 100S100 | 300.0 | - |
| Yannong 199 | 100S100 | 275.0 | 100S100 | 450.0 | 80S80 | 42.5 | 100S100 | 275.0 | - |
| Shannong 534421 | 20MR60 | 50.0 | 30MR50 | 75.0 | 10R10 | 10.0 | 5R5 | 12.5 | - |
| Jimai 5189 | 100S100 | 300.0 | 100S100 | 450.0 | 100S100 | 52.5 | 100S100 | 250.0 | - |
| Jimai 5209 | 30MS40 | 75.0 | 100S100 | 250.0 | 70S80 | 35.0 | 50S50 | 125.0 | - |
| Zhongyuanguoke 9 | 70MR70 | 175.0 | 30MR30 | 75.0 | 10R30 | 7.5 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Liangxing 87 | 5R5 | 12.5 | 10R10 | 25.0 | 5R5 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 | 31 |
| Yannong 31 | 100S100 | 275.0 | 100S100 | 525.0 | 100S100 | 52.5 | 70MS60 | 175.0 | - |
| Races | Immune | Resistant–Moderately Resistant | Moderately Susceptible–Susceptible | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| 21C3CTHQM | 3 (4.8) a | 1 (1.6) | 20 (32.3) | 22 (35.5) | 39 (62.9) | 39 (62.9) |
| 34MKGQM | 3 (4.8) | 4 (6.5) | 23 (37.1) | 23 (37.1) | 36 (58.1) | 35 (56.5) |
| All races | 1 (1.6) | 0 (0) | 20 (32.3) | 21 (33.9) | 41 (66.1) | 41 (66.1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Y.; Zhao, D.; Cao, T.; Sun, H.; Zou, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, T.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Q.; et al. Stem Rust Resistance in 62 Cultivars and Elite Lines from Northern Huanghuai Region of China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051174
Wei Y, Zhao D, Cao T, Sun H, Zou L, Yang J, Zhang G, Li T, Zhang C, Chen Q, et al. Stem Rust Resistance in 62 Cultivars and Elite Lines from Northern Huanghuai Region of China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051174
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Yifan, Di Zhao, Tingjie Cao, Huiyan Sun, Longmei Zou, Jinjing Yang, Gongjun Zhang, Tong Li, Conghao Zhang, Qiutong Chen, and et al. 2025. "Stem Rust Resistance in 62 Cultivars and Elite Lines from Northern Huanghuai Region of China" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051174
APA StyleWei, Y., Zhao, D., Cao, T., Sun, H., Zou, L., Yang, J., Zhang, G., Li, T., Zhang, C., Chen, Q., & Li, T. (2025). Stem Rust Resistance in 62 Cultivars and Elite Lines from Northern Huanghuai Region of China. Agronomy, 15(5), 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051174






