A Method for Identifying Picking Points in Safflower Point Clouds Based on an Improved PointNet++ Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
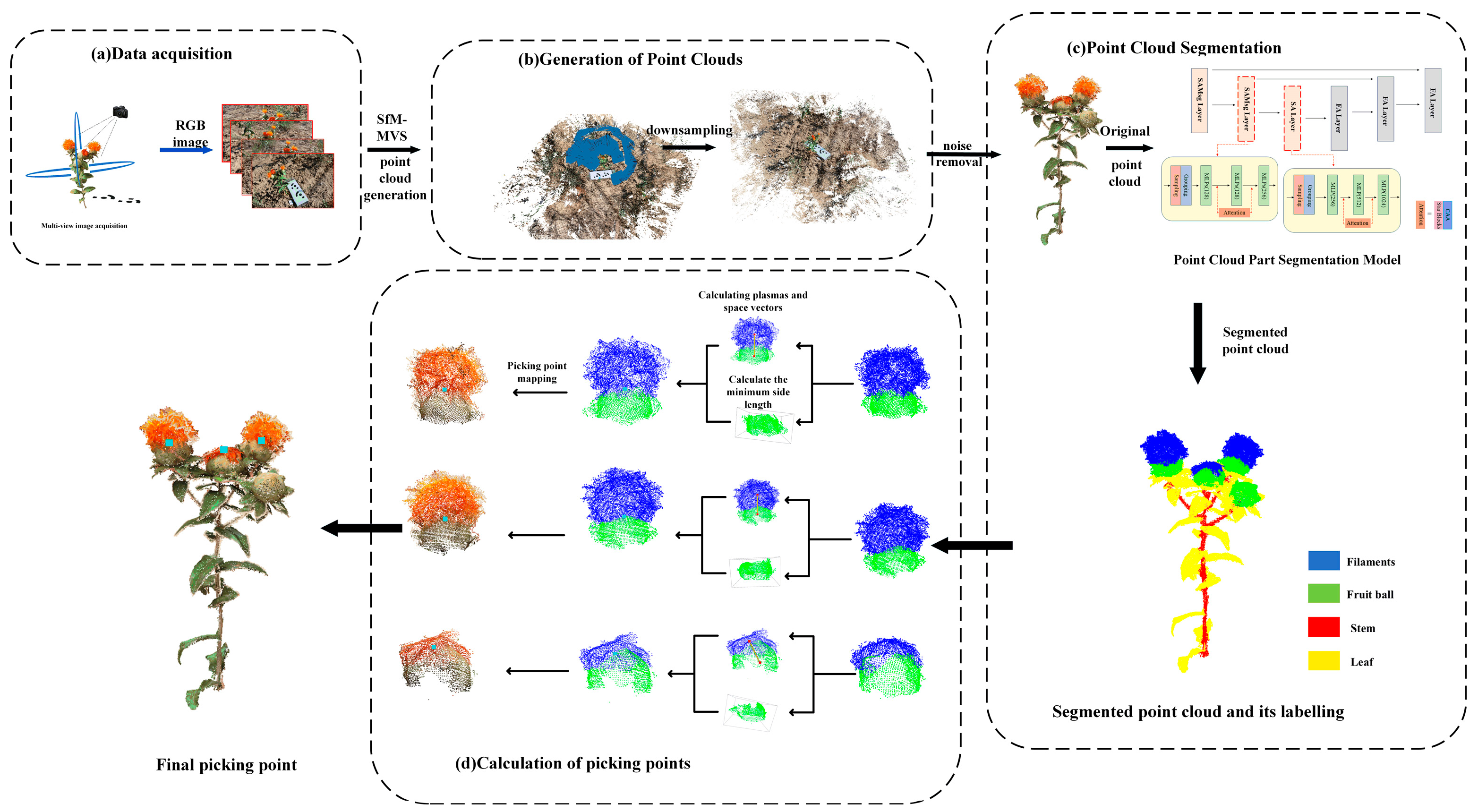
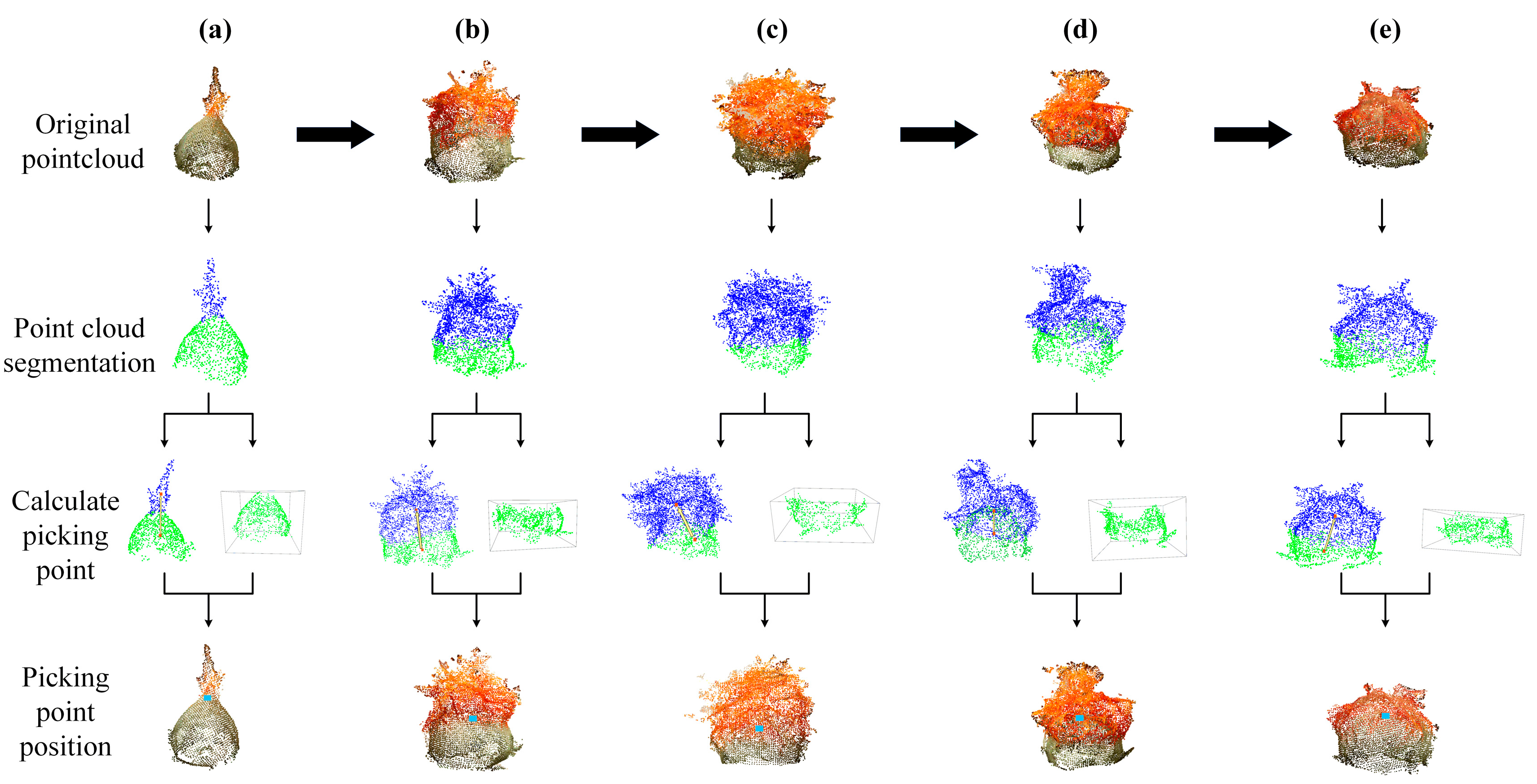
2.1. The Overall Process of Identifying Safflower Picking Points
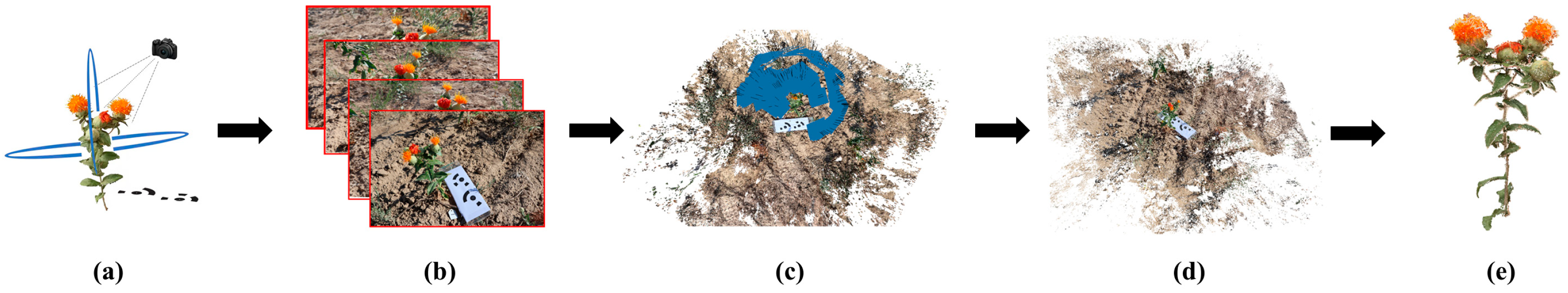
2.2. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction and Preprocessing of Safflower Plants
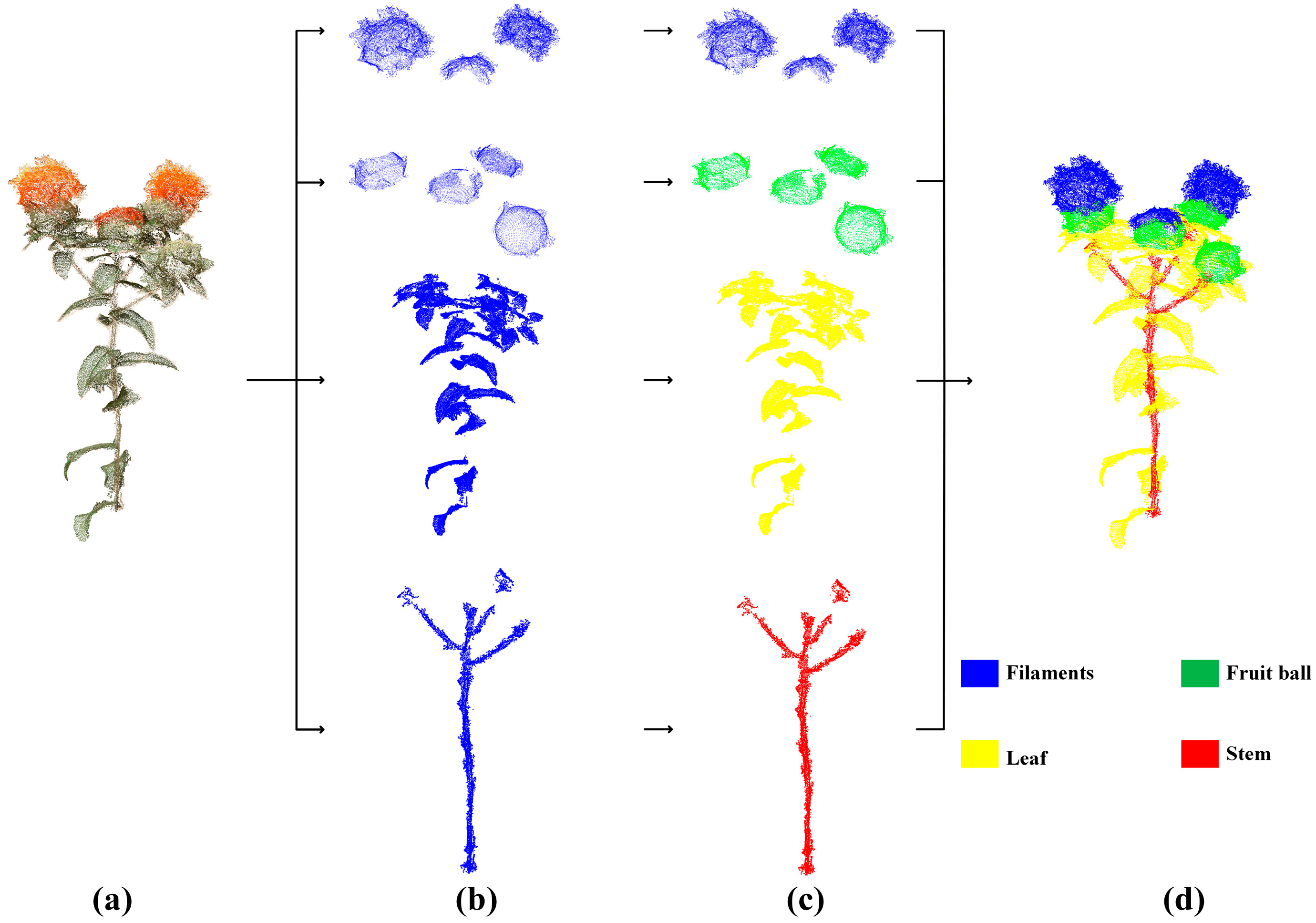
2.3. Annotation of the Point Cloud of Safflower Plants and Model Training
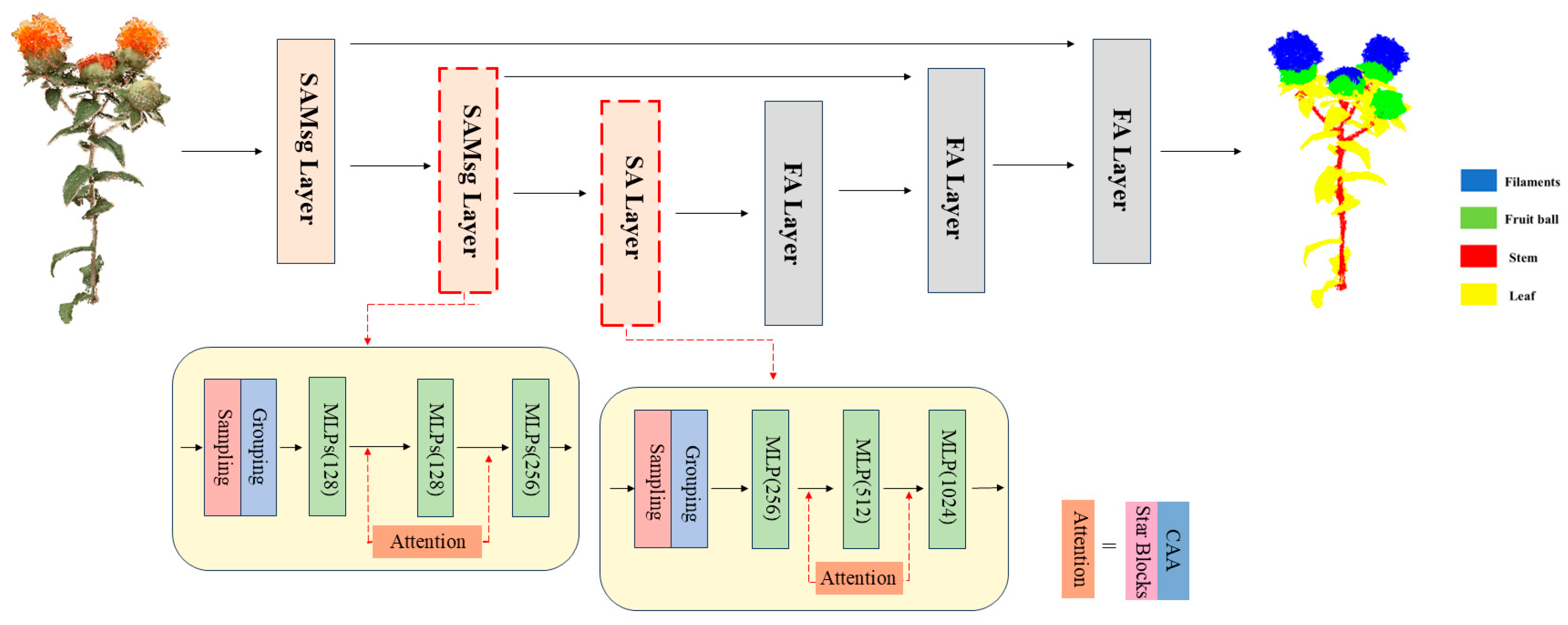
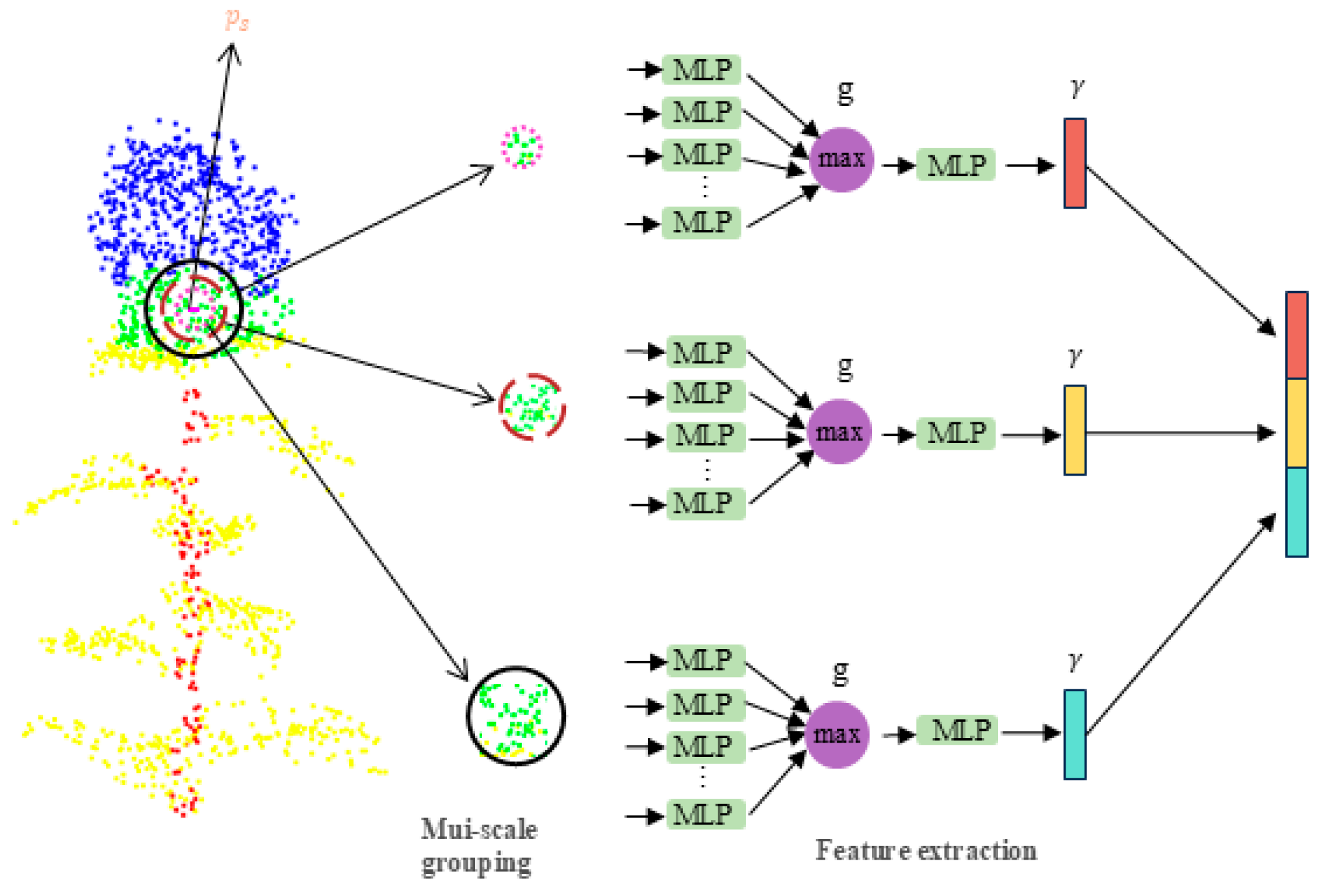
2.4. PointSafNet Model
2.4.1. Star Blocks Model
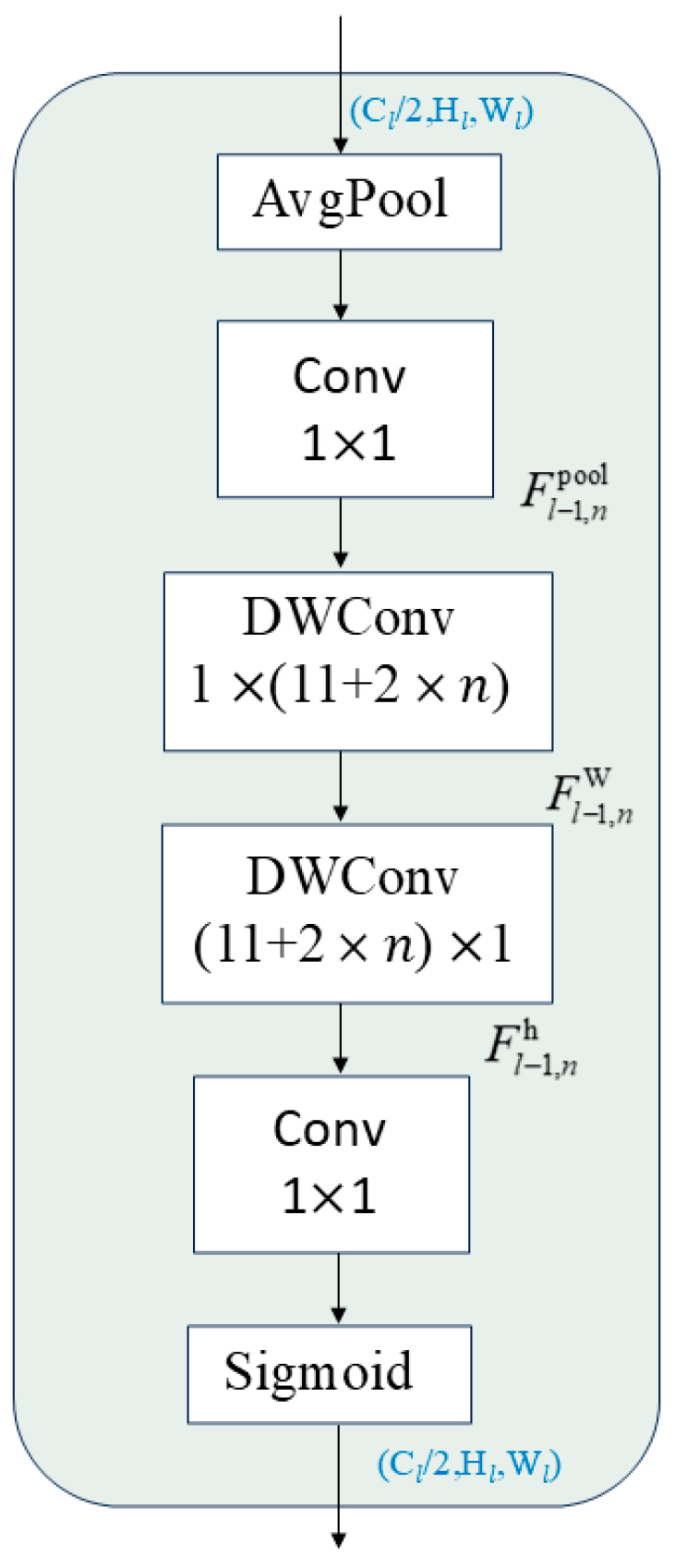
2.4.2. Contextual Anchor Attention (CAA) Model
2.5. Harvesting Point Recognition Method
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Evaluation
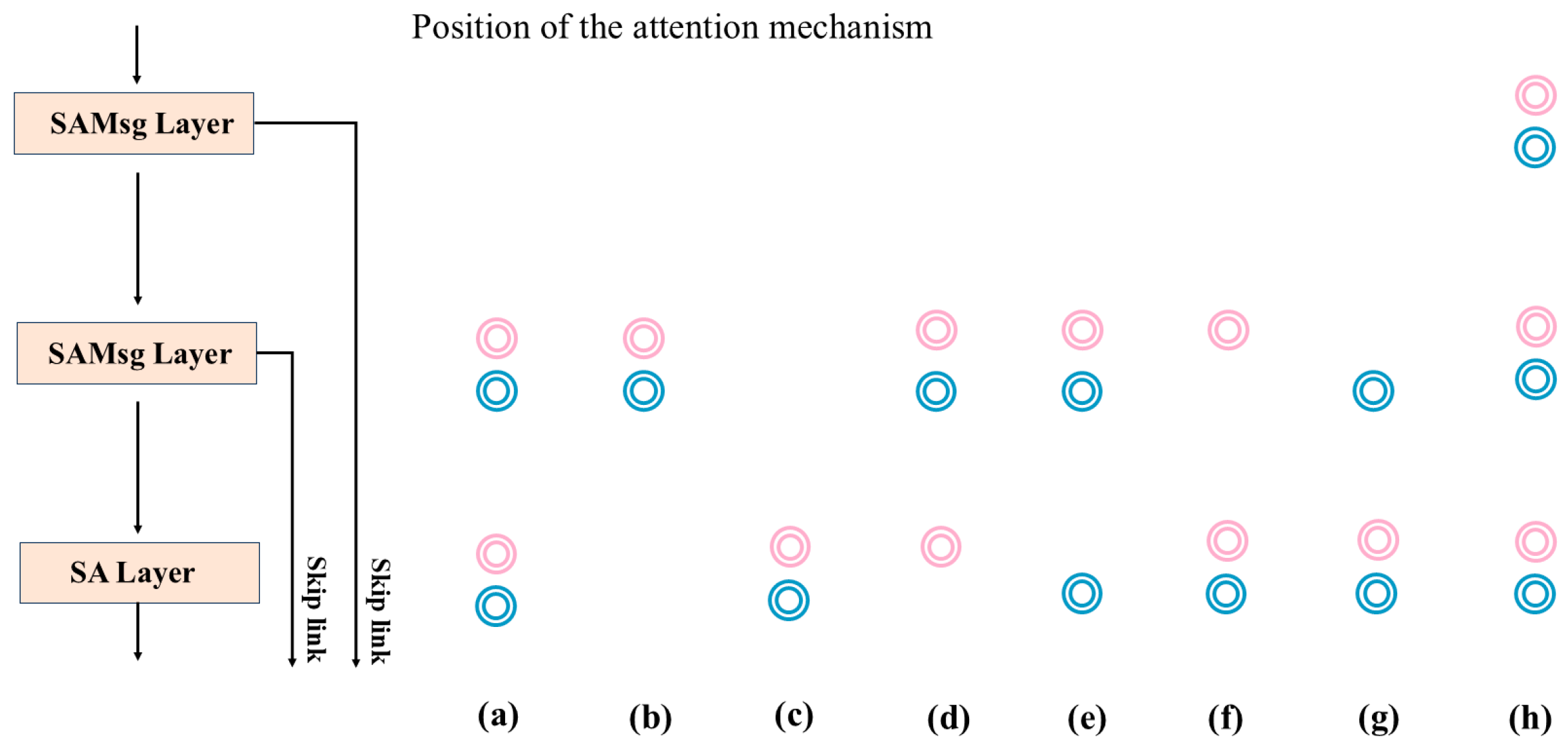
3.2. Ablation Experiments
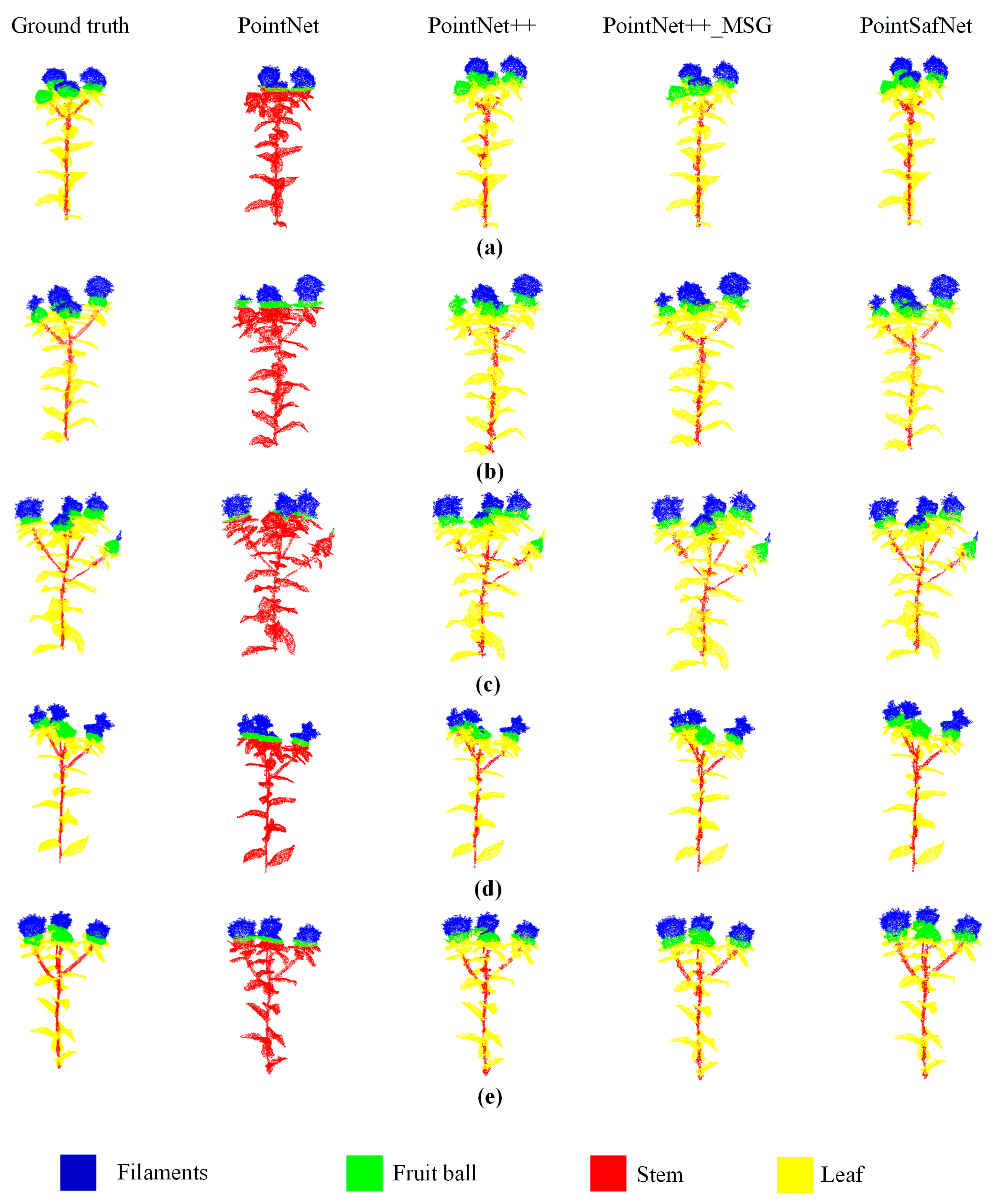
3.3. Performance Comparison of Different Models
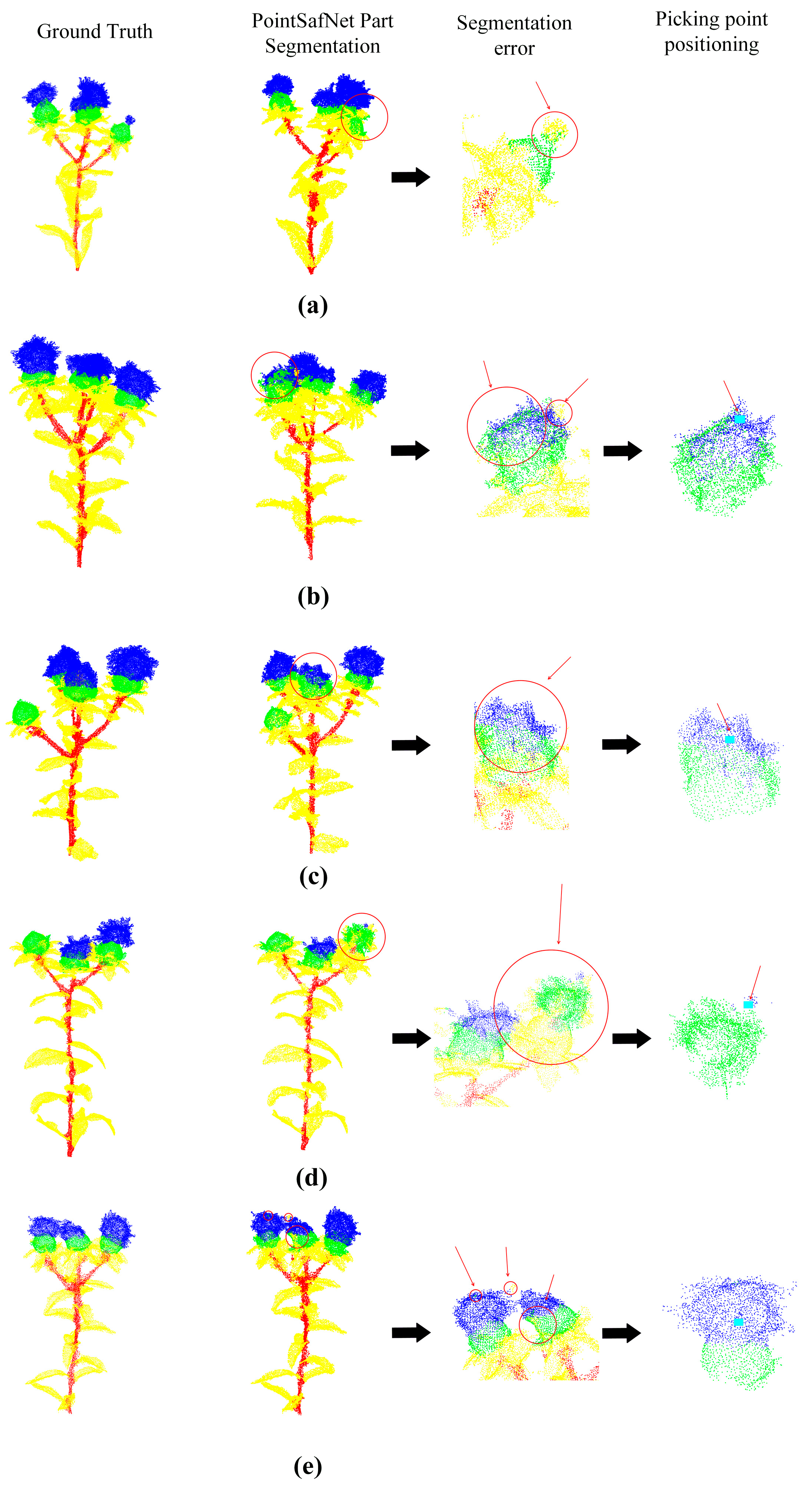
3.4. Picking Point Identification and Error Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, B.; Ding, F.; Ma, B.; Wang, L.; Ning, S. A Method for Real-Time Recognition of Safflower Filaments in Unstructured Environments Using the YOLO-SaFi Model. Sensors 2024, 24, 4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Luo, D.; Gao, G.; Wu, T.; Diao, H. Design and experiment of a safflower picking robot based on a parallel manipulator. Eng. Agric. 2022, 42, e20210129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, R.; Xing, Z.; Guo, Q.; Zeng, C. Improved Faster Region-Based Convolutional Neural Networks (R-CNN) Model Based on Split Attention for the Detection of Safflower Filaments in Natural Environments. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xing, Z.; Yang, S.; Feng, N.; Liang, R.; Zhao, M. Design and experiments of the circular arc progressive type harvester for the safflower filaments. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Xing, Z.; Liu, X. Design and test of double-acting opposite direction cutting end effector for safflower harvester. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, L. Design and experiment of the vertical brush-roller picking device for dry-safflower harvesters. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2024, 40, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xing, Z.; Zhao, M.; Yang, S.; Guo, Q.; Shi, R.; Zeng, C. Detecting safflower filaments using an improved YOLOv3 under complex environments. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J. Safflower picking recognition in complex environments based on an improved YOLOv7. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wu, D.; Zheng, X. Detection of Chrysanthemums Inflorescence Based on Improved CR-YOLOv5s Algorithm. Sensors 2023, 23, 4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-M.; Park, J.-H. YOLO Network with a Circular Bounding Box to Classify the Flowering Degree of Chrysanthemum. AgriEngineering 2023, 5, 1530–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Luo, J.; Ye, Q.; Leng, W.; Qin, J.; Lin, J.; Xie, X.; Sun, Y.; Huang, S.; Pang, J. Advancing jasmine tea production: YOLOv7-based real-time jasmine flower detection. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 9297–9311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinoda, R.; Motoki, K.; Hara, K.; Kataoka, H.; Nakano, R.; Nakazaki, T.; Noguchi, R. RoseTracker: A system for automated rose growth monitoring. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 5, 100271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatehi, F.; Bagherpour, H.; Amiri Parian, J. Enhancing the Performance of YOLOv9t Through a Knowledge Distillation Approach for Real-Time Detection of Bloomed Damask Roses in the Field. Smart Agric. Technol. 2025, 10, 100794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Tripathi, A.K. Flora-NET: Integrating dual coordinate attention with adaptive kernel based convolution network for medicinal flower identification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 230, 109834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Chang, C.; Bao, G.; Fan, J.; Xun, Y. Recognition and localization system of the robot for harvesting Hangzhou White Chrysanthemums. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Luo, S.; Chang, C.; Xun, Y.; Bao, G. Segmentation algorithm for Hangzhou white chrysanthemums based on least squares support vector machine. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2019, 12, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, R.; Guo, Q.; Zeng, C. Filament-necking localization method via combining improved PSO with rotated rectangle algorithm for safflower-picking robots. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 215, 108464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Q.; Hu, C.; Hu, X.; Xu, M. Picking point recognition for ripe tomatoes using semantic segmentation and morphological processing. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 210, 107923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Y.; Cui, C.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J. Location of safflower filaments picking points in complex environment based on improved Yolov5 algorithm. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 227, 109463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ge, Y.; Xia, H.; Sun, C. Safflower picking points localization method during the full harvest period based on SBP-YOLOv8s-seg network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 227, 109646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lu, J.; Zhou, M.; Yi, J.; Liao, M.; Gao, Z. A YOLOv3-based computer vision system for identification of tea buds and the picking point. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 107116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Tenorio, G.L.; From, P.J. Fruit Localization and Environment Perception for Strawberry Harvesting Robots. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 147642–147652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, L.; Jia, J.; Lv, J.; Chen, J.; Qiao, X.; Wu, C. In-field tea shoot detection and 3D localization using an RGB-D camera. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 185, 106149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, S.; He, L.; Tong, J.; Zhao, R.; Jia, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, C. Development and field evaluation of a robotic harvesting system for plucking high-quality tea. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 206, 107659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, G.; Chen, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, S. Detection and Localization of Tea Bud Based on Improved YOLOv5s and 3D Point Cloud Processing. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Fukao, T.; Hasegawa, T. A Tomato Recognition Method for Harvesting with Robots using Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Paris, France, 14–16 January 2019; pp. 456–461. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, C.A.; Pérez, D.S.; Miatello, H.; Bromberg, F. Grapevine buds detection and localization in 3D space based on Structure from Motion and 2D image classification. Comput. Ind. 2018, 99, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, M.; Han, B.; Peng, C.; Huang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhou, G.; Xu, S. Point clouds segmentation of rapeseed siliques based on sparse-dense point clouds mapping. Front Plant Sci 2023, 14, 1188286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, D.; Luo, L.; Yi, T. PointResNet: A grape bunches point cloud semantic segmentation model based on feature enhancement and improved PointNet++. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 224, 109132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, A.; Li, B.; Schnable, J.C.; Lyons, E.; Pauli, D.; Barnard, K.; Benes, B. PlantSegNet: 3D point cloud instance segmentation of nearby plant organs with identical semantics. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 221, 108922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, F.; Sun, S.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, J.; Snider, J.; Liu, T.; Li, C. Cotton plant part 3D segmentation and architectural trait extraction using point voxel convolutional neural networks. Plant Methods 2023, 19, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wu, T.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Gao, P.; Zhang, L. Organ Segmentation and Phenotypic Trait Extraction of Cotton Seedling Point Clouds Based on a 3D Lightweight Network. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Tan, F.; Li, C.; Jin, S.; Zhang, C.; Gao, P.; Xu, W. Stem–Leaf segmentation and phenotypic trait extraction of individual plant using a precise and efficient point cloud segmentation network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 220, 108839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayati, H.; Najafi, A.; Vahidi, J.; Gholamali Jalali, S. 3D reconstruction of uneven-aged forest in single tree scale using digital camera and SfM-MVS technique. Scand. J. For. Res. 2021, 36, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Corfu, Greece, 20–27 September 1999; Volume 1152, pp. 1150–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Seitz, S.M.; Curless, B.; Diebel, J.; Scharstein, D.; Szeliski, R. A Comparison and Evaluation of Multi-View Stereo Reconstruction Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’06), New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; pp. 519–528. [Google Scholar]
- Jarahizadeh, S.; Salehi, B. A Comparative Analysis of UAV Photogrammetric Software Performance for Forest 3D Modeling: A Case Study Using AgiSoft Photoscan, PIX4DMapper, and DJI Terra. Sensors 2024, 24, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-P.; Wu, M.-H.; Tsang, P.W.M. 3D display by binary computer-generated holograms with localized random down-sampling and adaptive intensity accumulation. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 24526–24537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirikolias, K. Low level image processing and analysis using radius filters. Digit. Signal Process. 2016, 50, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.X.; Funkhouser, T.; Guibas, L.; Hanrahan, P.; Huang, Q.; Li, Z.; Savarese, S.; Savva, M.; Song, S.; Su, H.; et al. ShapeNet: An Information-Rich 3D Model Repository. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.00593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space. In Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Dai, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y. Rewrite the Stars. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.19967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Lai, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, Z.; Yao, Y. Poly Kernel Inception Network for Remote Sensing Detection. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 27706–27716. [Google Scholar]



| Model | Accuracy (%) | mIoUsafflower filaments (%) | mIoUfruit ball (%) | mIoUleaf (%) | mIoUstem (%) | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| base | 79.46 | 61.74 | 28.44 | 75.81 | 35.46 | 55.11 |
| (a) | 73.98 | 39.32 | 10.08 | 60.49 | 15.65 | 43.46 |
| (b) | 66.13 | 18.60 | 2.30 | 46.75 | 0.23 | 29.48 |
| (c) | 81.66 | 56.94 | 30.45 | 77.20 | 46.19 | 59.71 |
| (d) | 77.30 | 55.32 | 25.19 | 73.45 | 34.79 | 51.87 |
| (e) | 85.72 | 72.48 | 41.29 | 81.52 | 52.71 | 66.26 |
| Model | Accuracy (%) | mIoUsafflower filaments (%) | mIoUfruit ball (%) | mIoUleaf (%) | mIoUstem (%) | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| base | 79.46 | 61.74 | 28.44 | 75.81 | 35.46 | 55.11 |
| (a) | 86.83 | 75.52 | 44.14 | 82.50 | 54.65 | 68.82 |
| (b) | 85.67 | 72.36 | 41.27 | 81.95 | 52.93 | 66.33 |
| (c) | 85.50 | 72.81 | 41.64 | 81.58 | 52.29 | 66.40 |
| (d) | 85.63 | 73.19 | 41.42 | 81.34 | 51.79 | 66.32 |
| (e) | 86.29 | 75.13 | 42.19 | 81.68 | 51.72 | 67.78 |
| (f) | 86.20 | 75.67 | 41.96 | 81.42 | 51.33 | 67.79 |
| (g) | 86.24 | 74.21 | 42.32 | 81.85 | 52.24 | 67.41 |
| (h) | 71.74 | 50.80 | 22.54 | 65.10 | 32.06 | 48.37 |
| Model | Accuracy (%) | mIoUsafflower filaments (%) | mIoUfruit ball (%) | mIoUleaf (%) | mIoUstem (%) | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PointNet | 71.69 | 50.77 | 10.75 | 70.65 | 0.12 | 35.37 |
| PointNet++ | 79.46 | 61.74 | 28.44 | 75.81 | 35.46 | 55.11 |
| PointNet++_MSG | 82.28 | 67.87 | 35.64 | 79.61 | 48.40 | 61.48 |
| PointSafNet | 86.83 | 75.52 | 44.14 | 82.50 | 54.65 | 68.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, B.; Xia, H.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, D. A Method for Identifying Picking Points in Safflower Point Clouds Based on an Improved PointNet++ Network. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051125
Ma B, Xia H, Ge Y, Zhang H, Wu Z, Li M, Wang D. A Method for Identifying Picking Points in Safflower Point Clouds Based on an Improved PointNet++ Network. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051125
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Baojian, Hao Xia, Yun Ge, He Zhang, Zhenghao Wu, Min Li, and Dongyun Wang. 2025. "A Method for Identifying Picking Points in Safflower Point Clouds Based on an Improved PointNet++ Network" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051125
APA StyleMa, B., Xia, H., Ge, Y., Zhang, H., Wu, Z., Li, M., & Wang, D. (2025). A Method for Identifying Picking Points in Safflower Point Clouds Based on an Improved PointNet++ Network. Agronomy, 15(5), 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051125







