Abstract
The increasing demand for high-quality forage alternatives necessitates the exploration of novel feed resources such as giant juncao (GJ). This study evaluated the feasibility of giant juncao (GJ) as silage by analyzing its fermentation products, bacterial community, and metabolic profiles during ensiling. After the natural fermentation of giant juncao (NGJ) for 1, 3, 7, 15, 30, and 60 days, a random sampling of NGJ was conducted to analyze its chemical composition, fermentation parameters, and microbial number. Fresh, 3-day, and 60-day ensiled GJ were further analyzed via high-throughput sequencing and KEGG functional prediction. Following 60 days of ensiling, NGJ displayed acetate-type fermentation with high acetic acid and ammonia nitrogen concentrations, and low lactic acid concentration and the ratio of lactic-to-acetic acid. A microbial community analysis indicated Weissella as the predominant genus during the initial fermentation phase (3-day NGJ), whereas Lactobacillus emerged as the dominant taxonomic group in the late-stage fermentation (60-day NGJ). A comparative functional analysis revealed statistically significant divergences (p < 0.05) in KEGG pathway distributions between fresh and ensiled GJ. The ensiling process notably inhibited pathways associated with lipid synthesis, cofactor and vitamin metabolism, energy production, and amino acid utilization while concurrently enhancing carbohydrate and nucleotide metabolic activities. A nutritional evaluation confirmed GJ’s suitability as a sustainable silage maize alternative, with favorable water-soluble carbohydrate (8.57% DM) and crude protein (14.6% DM) levels. To ensure optimal preservation efficacy, the experimental findings emphasize the necessity of a minimum 30-day fermentation period for stabilizing GJ silage quality. These findings offer valuable insight into the microbial and metabolic mechanisms of high-moisture silage fermentation.
1. Introduction
As global animal husbandry continues to expand, the supply–demand imbalance for conventional forage resources like silage maize and alfalfa has intensified. Currently, China annually imports approximately 2 million metric tons (MMT) of high-quality forage, yet the country faces an annual deficit exceeding 50 MMT [1]. The widening gap between surging demand for premium forage and inadequate domestic production threatens the sustainability of livestock industries. Consequently, advancing novel forage development and utilization represents a vital pathway to diversify feed resources and address the substantial forage deficit for animal husbandry. Giant juncao (Pennisetum giganteum Z. X. Lin), a perennial grass species in the Poaceae family, originates from eastern and northeastern Africa [2]. Through selective breeding initiatives, this crop has been successfully established in over 80 nations and across 30 Chinese provinces [3]. Similar to other C4 grasses, giant juncao exhibits high tolerance to drought, elevated temperatures, and nutrient-deficient environments due to its high use efficiency of water, light, and nitrogen. Agricultural data suggest that giant juncao exhibits high productivity, permitting 6–8 annual harvest cycles with fresh biomass yields reaching approximately 254 metric tonnes per hectare [4]. In recent years, GJ has been expanded as an emerging and popular feed source due to its good palatability and high nutrition content [5]. However, as with other tropical grasses, fresh giant juncao is harvested with low dry matter (DM) content. In view of the rainy climate and seasonal surplus in the planting area, ensilage is the optimal processing and preservation method for giant juncao. Most importantly, as it is a potential forage, the exploration of fermentation quality in giant juncao silage lags far behind alfalfa and maize.
Ensiling represents a microbially mediated anaerobic process predominantly governed by lactic acid bacteria (LAB), marked by complex biochemical pathways and interspecies microbial dynamics. Given these complexities, expanded investigations into the ecological succession of microbial populations during ensiling are imperative [6]. Traditional culturing methods, while foundational, now fall short in resolving the full spectrum of bacterial community transitions from fresh forage to preserved silage. Contemporary advancements in molecular biology, particularly high-throughput genomic sequencing, have enabled comprehensive profiling of bacterial diversity and structural adaptations across varied silage microenvironments [7]. In addition to the microbial community insights, functional annotation of microbial communities is increasingly found to be extremely important for microbial ecology research. Asshauer et al. [8] argued that the analysis of microbial communities should take into account both phylogenetic and functional diversity, which are critical factors in the characterization of such communities. Functional annotation of microbial communities complements high-throughput sequencing (HTS)-based taxonomic profiling [9], elucidating metabolic mechanisms critical for optimizing silage fermentation.
Hence, the objective of this research was to analyze the ensiling process of GJ by evaluating its fermentation quality, examining the bacterial community dynamics, and elucidating the metabolic shifts involved, thereby (1) diversifying roughage sources by developing and ensiling new grass species; (2) providing valuable data and theoretical references for the fermentation regulation of high-moisture silage based on the integration of microbial sequencing with functional prediction of metabolic pathways. These findings thus offer critical insights into the metabolic pathways governing fermentation dynamics under high moisture content, essential for optimizing silage production protocols.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Silage Production
The GJ was cultivated in an experimental plot of Nanjing Agricultural University (32′04° N, 118′85° E, a.s.l. 25.1 m, Nanjing, China) and harvested at the maturity stage (after 2.8 months of growth). Fresh GJ was mechanically chopped into uniform 20-mm segments and homogenized. Portions (450 g) were packed into polyethylene silage containers (300 × 400 mm), vacuum-sealed, and stored under controlled ambient conditions (28 ± 3 °C). Triplicate containers per treatment group were randomly sampled at sequential chronological intervals (1, 3, 7, 15, 30, and 60 days). Fresh GJ and naturally fermented GJ (NGJ) were homogenized prior to subsequent analytical procedures.
2.2. Chemical Composition and Fermentation Quality Analyses
The chemical composition and microbial counts were determined using the analytical techniques described in our previous study [10]. In brief, DM content was measured after oven-dry at 65 °C for 48 h. The analysis of chemical components involved measuring water-soluble carbohydrate (WSC) content using the sulfuric acid anthrone method, determining neutral and acid detergent fiber (NDF and ADF) content using an Ankom 200 fiber analyzer (Ankom Technology, New York, NY, USA), and analyzing total nitrogen (TN) and crude protein (CP) content with a Kjeltec® 8400 Kjeldahl N analyzer (Foss Analytics, Höganäs, Sweden). Buffering capacity (BC) was determined based on acid-base titration method [5]. After homogenization with sterile saline solution at a ratio of 1:9 and shaking at 37 °C, 120 rpm for 2 min, 1 mL of the above solution was subjected to serial dilution for microbial enumeration. Under 37 °C anaerobic incubation, LAB was counted on MRS agar medium after 3 days. Under 30 °C aerobic incubation, aerobic bacteria and fungi (yeast and molds) were respectively counted on NA and PDA medium after 2 days and enterobacteria on VRBGA medium after 1 day. Microbial counts were logarithmically transformed and expressed as Log10 colony-forming units (CFU) per gram of fresh matter (FM). For fermentation profiling, fresh GJ and NGJ underwent aqueous extraction (3:1 w/v deionized water) for 30 min at 4 °C. Post-extraction, sequential filtration through four gauze layers and filter paper preceded pH determination using a calibrated pH meter. The ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) concentration of NGJ was obtained in microplates (H803-96, BDBIO, Hangzhou, China) using a colorimetric method after reacting with phenol and hypochloric acid [11]. The concentration of fermentation products including lactic (LA), acetic (AA), propionic (PA), butyric acid (BA), ethanol, and 1,2-propanediol of NGJ was determined by a 1260 Infinity HPLC (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) equipped with a Carbomix® H-NP5 column (5 μm, 7.8 × 300 mm, Sepax Technologies, Inc., Newark, DE, USA) and refractive index detector using an eluent of 2.5 mM H2SO4 at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min, with a run temperature of a column of 55 °C. Organic acid standards were purchased from Solabio (Beijing, China) and Sigma-Aldrich reagent platforms (Shanghai, China) and dissolved in ultrapure water (A102, Witcel biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). The V-score method was adopted to evaluate the quality of NGJ [12].
2.3. HTS and Functional Prediction Analyses
Given the importance of microbial succession patterns across fermentation phases (pre-ensiling, initial, and terminal stages) for quality determination, fresh GJ and its naturally fermented derivatives at critical timepoints (3-day NGJ and 60-day NGJ) were selected for HTS. Bacterial total deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was extracted by SPARKeasy Kit (AA0202-B, Shandong Sparkjade Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Jinan, Shandong, China). Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification prior to sequencing was conducted in accordance with the protocols described by Zhao et al. [5]. Bacterial genomic DNA isolation initiated with centrifugation (10,000× g, 15 min, 4 °C) to pelletize microbial biomass. Subsequent DNA purification employed the FastDNA® Spin Kit (MP Biomedicals, Santa Ana, CA, USA) following manufacturer protocols. The DNA concentration and integrity were detected using NanoDrop® 2000 ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer (260/280 nm, Thermo Scientific, Wilmington, DE, USA) and 1% sodium borate agarose gel electrophoresis. Targeting the V3–V4 hypervariable region of bacterial 16S rRNA, custom barcoded primers were designed and synthesized. Amplification was conducted using the ABI GeneAmp® 9700 system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) with primer pair 338F/806R. Post-amplification, products underwent purification via the AxyPrep® DNA Gel Recovery Kit (Axygen Biotech, Union City, CA, USA), followed by Tris-HCl elution and subsequent purification through 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. Based on the preliminary quantitative outcome of electrophoresis, the purified PCR products were quantitatively assessed using the QuantiFluorTM-ST blue fluorescence quantitative system (Promega Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Madison, WI, USA), and mixed in proportion in accordance with the sequencing specifications for each sample. Amplicon libraries were normalized to equimolar ratios and processed for bidirectional sequencing using the Illumina MiSeq PE300 system (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA).
Bioinformatic processing followed established protocols [13]. Specifically, paired-end reads underwent initial merging via FLASH v1.2.11, followed by QIIME (v1.9.1) quality control (Q-score > 20). Sequence clustering at 97% similarity using UPARSE v7.0.0 generated operational taxonomic units (OTUs), with UCHIME (v4.1) eliminating chimeric sequences. The taxonomic assignment of OTUs was performed by comparing sequences against the SILVA database (v132) using the RDP classifier (v2.11). Bacterial alpha (α)-diversities (Shannon, Chao, Ace, Sobs, Simpson, and coverage indices) and Bray-Curtis metric beta (β)-diversities were calculated using QIIME (v1.9.1). Bacterial β-diversity was analyzed via Bray-Curtis dissimilarity matrices, visualized through principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) plots generated with the vegan package (R v4.1.2). Intervariable associations between fermentation metabolites and microbial taxa were assessed using Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients, plotted as heatmaps via the pheatmap package (R 4.1.2). Additionally, the Tax4Fun tool developed by Asshauer et al. [8] was utilized to predict KEGG functional profiles of the bacterial communities in GJ, NGJ-3, and NGJ-60.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
A statistical analysis of silage characteristics (chemical composition, fermentation metrics, and microbial counts) across fermentation durations was conducted using a general linear model (GLM) framework within SAS (v9.2; Statistical Analysis System Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Simultaneously, Student’s t-test, ANOSIM with 999 permutations, and the Wilcoxon rank-sum test were employed to assess differences in α-diversity and β-diversity indices, as well as KEGG functional profiles of bacterial communities, respectively. p < 0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. Composition of Fresh GJ
Table 1 summarizes the biochemical characteristics and microbial ecology of fresh GJ. Biochemical profiling identified a dry matter (DM) content of 16.6% fresh matter (FM), with WSC at 8.57% DM, crude protein (CP) at 14.6% DM, and buffering capacity measuring 39.6 mEq/kg DM. A microbiological analysis revealed lactic acid bacteria (LAB) counts below the 5.0 log10 CFU/g FM threshold (4.60 log10 CFU/g FM). Aerobic bacteria dominated the microbial community (5.85 log10 CFU/g FM), followed by yeast (4.76 log10 CFU/g FM), enterobacteria (5.70 log10 CFU/g FM), and molds (4.60 log10 CFU/g FM).

Table 1.
The chemical and microbial parameters of fresh GJ (means ± SD).
3.2. Fermentation Characteristics of NGJ
Ensiling days had significant (p< 0.05) effects on pH, DM and WSC content, LA, AA, PA, VFA, and NH3-N concentration, as well as the LA/AA value (Table 2). NGJ maintained stable pH levels throughout the initial 7 days of ensiling, followed by a significant decline (p < 0.05) to 4.03 by day 30. Conversely, the LA concentration increased to a maximum of 4.23% DM on day 30, showing an inverse trend to the pH value. Throughout the ensiling process, the AA and VFA concentrations of NGJ continuously increased, while the LA/AA value showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing with the highest value on day 30 of ensiling. Except for NGJ-60, the BA was not detected in all NGJ. With the progress of ensiling, the DM and WSC content was reduced, but the NH3-N concentration was enhanced (p < 0.05).

Table 2.
The chemical and fermentative parameters of NGJ.
A statistical analysis (Table 3) revealed significant temporal variations (p < 0.05) in microbial populations during ensiling, particularly affecting lactic acid bacteria (LAB), aerobic bacteria, yeast, molds, and enterobacteria. LAB concentrations showed gradual growth during the initial week of fermentation, followed by a substantial surge (p < 0.05) culminating in peak abundance (7.94 log10 CFU/g FM) by day 30. Conversely, populations of aerobic bacteria, yeast, and molds progressively diminished to trace or non-detectable levels throughout the storage period.

Table 3.
The microbial count of NGJ.
3.3. The Bacterial Community of Fresh GJ and NGJ
Alpha diversity profiling of bacterial communities in fresh GJ and NGJ is summarized in Figure 1. Fresh GJ demonstrated the highest values for Shannon, Chao, Ace, and Sobs indices, with progressive declines observed in NGJ-3 and further reductions in NGJ-60. Sequencing coverage exceeded 99.5% for all analyzed samples. Beta diversity patterns, as visualized through PCoA in Figure 2, revealed marked compositional divergence across treatments. Spatial distribution of GJ, NGJ-3, and NGJ-60 datapoints within the PCoA plot confirmed distinct clustering in separate quadrants.
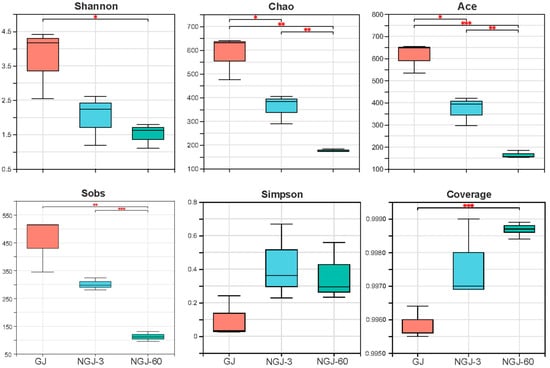
Figure 1.
Bacterial α-diversities (Shannon, Chao, Ace, Sobs, Simpson, and coverage indices) of fresh GJ and NGJ. GJ, giant juncao; NGJ, naturally ensiled GJ. *, p < 0.05; **, 0.001 < p ≤ 0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001.
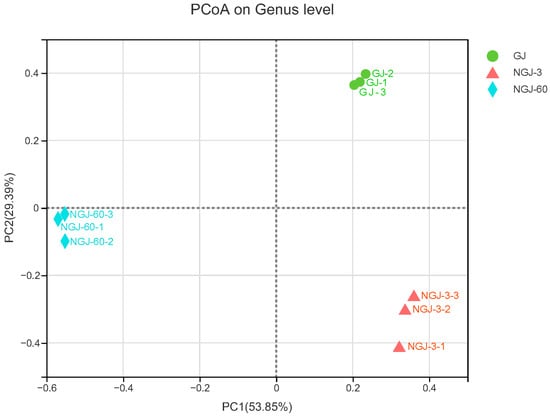
Figure 2.
Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) of bacterial β-diversity between fresh GJ and NGJ samples. GJ, giant juncao; NGJ, naturally ensiled GJ.
At the phylum level (top left of Figure 3), the bacterial community in fresh GJ was mainly dominated by Proteobacteria, which accounted for 73.9% of the total relative abundance (RA). After 3 days of ensiling, the RA of Proteobacteria, Actinobacteriota, and Bacteroidota decreased, whereas the RA of Firmicutes increased. After 60 days of ensiling, Firmicutes became the overwhelmingly dominant phylum (>85%) in NGJ.
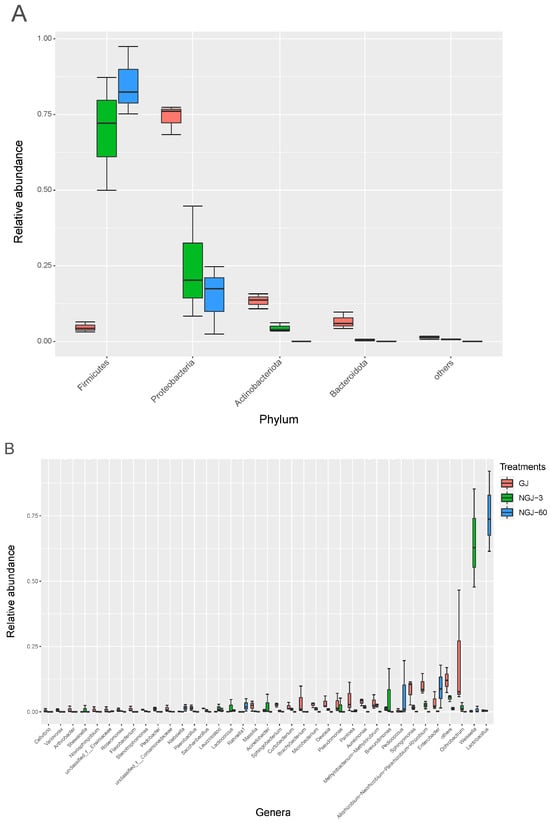
Figure 3.
The RA of bacterial community at the phylum (A) and genus level (B). GJ, giant juncao; NGJ, naturally ensiled GJ.
At the genus level (Figure 3), Sphingomonas (8.18%), Rhizobium (10.1%), and Ochrobactrum (20.0%) were the main genera in fresh GJ. After 3 days of ensiling, Weissella became the dominant genus, and its RA increased from 0.21% to 65.3%. Following 60 days of ensiling, the bacterial community of NGJ was dominated by Lactobacillus, which accounted for 75.7% of the RA. With the progress of ensiling, the RA of Ochrobactrum, Allorhizobium-Neorhizobium-Pararhizobium-Rhizobium, Sphingomonas, Aureimonas, Pantoea, etc. sharply decreased to less than 1%. However, non-negligible RAs of Enterobacter (9.36%) were still observed in NGJ-60.
3.4. Interrelationships Between Fermentation Metabolites and Microbial Consortia
Spearman’s rank correlation analysis (Figure 4) demonstrated significant microbial–metabolic linkages. Lactobacillus RA exhibited strong positive associations with lactic acid (LA) concentrations (R = 0.886, p < 0.05) and the lactic-to-acetic acid ratio (LA/AA: R = 0.943, p < 0.01). Concurrent negative interactions were identified between Lactobacillus populations and yeast (R = −0.829, p < 0.05), enterobacteria (R = −0.928, p < 0.01), and water-soluble carbohydrate (WSC) levels (R = −0.886, p < 0.05). Weissella and Leuconostoc showed negative correlations with AA (R = −0.714, p > 0.05; R = −0.543, p > 0.05) concentration, while Rahnella1, Lactobacillus, and Enterobacter displayed positive correlations with AA (R = 0.841, p < 0.05; R = 0.771, p > 0.05; R = 0.657, p > 0.05) concentration. A positive correlation was observed between pH value and Weissella (R = 0.829, p < 0.05), as well as NH3-N concentration and Enterobacter (R = 0.543, p > 0.05).
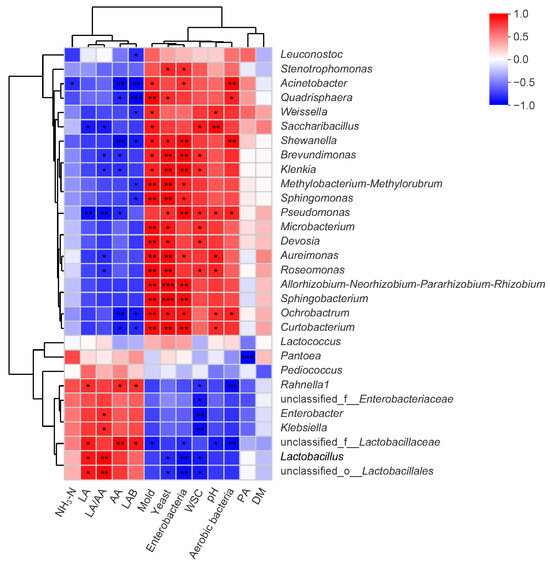
Figure 4.
Correlation heatmap illustrating the relationships between fermentation parameters and the top 30 genera in NGJ. Red squares refer to positive correlation (0 < R < 1), whereas blue squares refer to negative correlation (−1 < R < 0). *, p < 0.05; **, 0.001 < p ≤ 0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001. NH3-N, ammonia nitrogen; LA, lactic acid; LA/AA, the ratio of lactic to acetic acid; AA, acetic acid; LAB, lactic acid bacteria; WSC, water-soluble carbohydrates; PA, propionic acid; DM, dry matter.
3.5. Functional Profiling of the Bacterial Community
Figure 5 illustrates the predicted KEGG functional profiles of the bacterial community. Under pathway level 1, the activity of ‘Metabolism’ was prominently higher than that of other functional categories. Under pathway level 2, carbohydrate metabolism and amino acid metabolism were the major functional categories of ‘Metabolism’. Functional metabolic profiling revealed statistically distinct variations (p < 0.05) in carbohydrate and amino acid metabolic activities across GJ, NGJ-3, and NGJ-60. Notably, carbohydrate-related pathway enrichment peaked in NGJ-60, exhibiting a sequential decline through NGJ-3 to GJ. Conversely, amino acid metabolic functions displayed an inverse trend, with GJ demonstrating maximal activity and NGJ-60 showing minimal engagement.
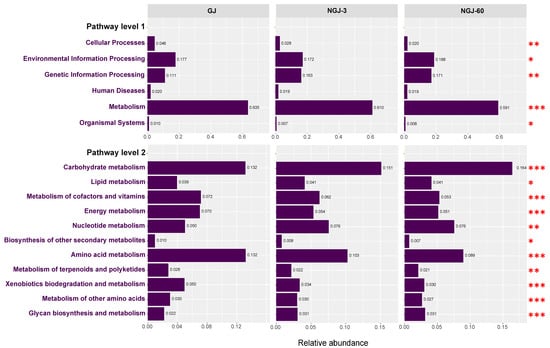
Figure 5.
KEGG functional annotation of bacterial communities at pathway levels 1 and 2 (p < 0.05). Letters denote significant differences; *: p < 0.05, **: 0.001 < p ≤ 0.01, ***: p ≤ 0.001.
Carbohydrate and amino acid metabolic pathways underwent granular subcategorization at level 3 (Figure 6). Compared to GJ, NGJ exhibited significantly higher activities (p < 0.05) in glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, interconversions of pentose and glucuronate, and metabolism of fructose, mannose, galactose, starch, sucrose, amino sugars, and nucleotide sugars. Conversely, NGJ showed significantly lower activities (p < 0.05) in the TCA cycle, ascorbate and aldarate metabolism, pyruvate metabolism, glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism, propanoate and butanoate metabolism, and C5-branched dibasic acid metabolism. And for amino acid metabolism, the activity of alanine, aspartate, glutamate, cysteine, and methionine metabolism, as well as lysine biosynthesis, was significantly (p < 0.05) increased in NGJ compared with GJ, whilst the activity of glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism, valine, leucine, and isoleucine degradation, valine, leucine, and isoleucine biosynthesis, lysine degradation, arginine, proline, histidine, tyrosine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan metabolism was significantly (p < 0.05) decreased in NGJ in comparison with GJ.
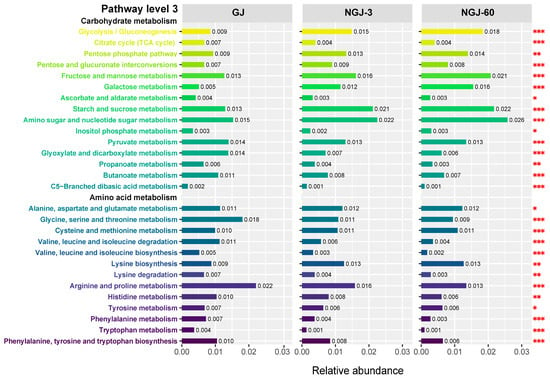
Figure 6.
KEGG functional annotation of bacterial communities at pathway level 3. Letters denote significant differences; *: p < 0.05, **: 0.001 < p ≤ 0.01, ***: p ≤ 0.001.
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Fresh GJ
Although fresh GJ met the criteria for well-preserved silage with a WSC content exceeding 5% DM and a BC of 30.8 mEq/kg DM [14,15], the low DM content (<20% FM) and LAB count (<5.0 log10 CFU/g FM) presented challenges for producing high-quality silage in this study.
4.2. Effects of Ensiling Days on Fermentation Quality of NGJ
The pH dynamics during ensiling serve as a critical marker for evaluating silage preservation efficacy [16]. A sluggish acidification rate inherently heightens the risk of fermentation failure. In this investigation, NGJ exhibited limited pH reduction during the initial fermentation phase, directly attributable to suboptimal epiphytic lactic acid bacteria (LAB) populations (<5.0 log10 CFU/g FM) in raw GJ. Acetic acid (AA) accumulation mirrored trends observed in prior studies, likely driven by acetogenic microbial activity during early ensiling and metabolic shifts from homolactic to heterolactic fermentation pathways in later stages. And the marked increase in AA after 30 days of ensiling could be related to secondary fermentation, which can be supported by the increasing relative abundance of Enterobacter and hetero-type Lactobacillus. Enterobacter and hetero-type Lactobacillus (e.g., Lactobacillus buchneri) are known to produce AA as fermentative products. Notably, AA emerged as the exclusive organic acid detected in NGJ within the first 24 h of fermentation. This observation corroborates earlier findings [16] identifying AA as the primary acidification agent during silage initiation, effectively establishing a subacidic environment (pH ≈ 5.0) through early-stage production. While clostridial butyric acid (BA) synthesis typically characterizes low DM silage (<30% DM) [17], its negligible detection in mature NGJ (60-day) confirmed the absence of substantial clostridial metabolic activity.
Ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) generation, indicative of proteolytic degradation and amino acid deamination, exceeded the recommended threshold for premium silage quality (10% TN) [14], reaching 16.7% TN in NGJ. This pronounced proteolysis likely stemmed from synergistic interactions between plant-derived proteases, enterobacteria activity, and inadequate pH-mediated suppression during the critical early fermentation window [17]. The delayed LAB-driven acidification permitted sustained enzymatic and microbial protein breakdown, compounded by GJ’s inherent high moisture content—a known factor for protease activation as demonstrated by He et al. [18].
The retarded LAB proliferation during primary fermentation stages correlated strongly with insufficient indigenous LAB colonization in raw feedstock. Obligate aerobes (aerobic bacteria, molds) experienced rapid population collapse under anaerobic silo conditions. Residual yeast and enterobacteria populations ultimately diminished in response to terminal pH suppression.
4.3. Effects of Ensiling Days on the Bacterial Community of NGJ
The coverage index >99% indicated that the majority of the bacterial community in each sample was successfully captured. Consistent with previous findings [17], a decline in pH was associated with reduced microbial diversity, likely due to the inactivation of acid-sensitive aerobic bacteria [18,19]. In this study, lower pH levels corresponded with decreased bacterial α-diversity, as evidenced by reduced Chao, Shannon, Ace, and Sobs indices in NGJ-60 samples. The distinct clustering of GJ, NGJ-3, and NGJ-60 in the PCoA plot reflected significant differences in bacterial community composition, attributed to the suppression of epiphytic aerobic and acid-sensitive bacteria during ensiling.
The ensiling process favored Firmicutes over Proteobacteria, as Firmicutes are predominant under anaerobic and acidic conditions [20]. This shift from Proteobacteria to Firmicutes was linked to the suppression of aerobic bacteria like Ochrobactrum, Sphingomonas, and Aureimonas, and the proliferation of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) such as Weissella and Lactobacillus. Similar to Pang et al. [21] and Zhao et al. [19], Weissella and Lactobacillus were the most dominant genera during ensiling in this study. Notably, Weissella, an early colonizer in the ensiling microenvironment [22,23], creates a mildly acidic environment conducive to Lactobacillus growth [24]. Consequently, the bacterial community in NGJ transitioned from being dominated by Weissella on day 3 to Lactobacillus on day 60. Interestingly, Enterobacter reappeared at the end of ensiling, likely due to a rise in pH. There are some acid-resistant species of Enterobacter [25], which can hibernate at low pH and become active again when silage pH increases.
4.4. Relationships Between Fermentation Parameters and Bacterial Communities of NGJ
Microbial correlation analysis revealed Lactobacillus RA exhibited a positive association with acetic acid (AA) levels in NGJ, while Weissella, Leuconostoc, and Enterobacter demonstrated inverse relationships. This pattern implies heterofermentative Lactobacillus strains likely drove AA production. Unexpectedly, lactic acid (LA) concentrations showed significant negative associations with Enterococcus and Pediococcus—contrary to the established understanding of coccoid LAB typically enhancing LA biosynthesis. This may be attributed to the supersedure of Enterococcus or Pediococcus by Lactobacillus as LA accumulated and pH declined, causing the observed decrease in RAs of Enterococcus or Pediococcus in silages with high LA concentration. The generation of NH3-N during the ensiling process is primarily attributed to plant-derived proteases, enterobacteria, and clostridial species, as indicated in prior research [14]. Yet, no clostridia were found in NGJ, and there was only a slight negative correlation between Enterobacter and NH3-N. These findings suggest that enterobacteria and clostridia were not primary contributors to NH3-N formation in NGJ. The NH3-N formation in NGJ could be mainly related to plant proteases, but further research is necessary.
4.5. Effects of Ensiling Days on the Potential Functions of the Bacterial Community in NGJ
HTS is an effective tool for assessing the composition and diversity of bacterial communities but exhibits limitations in resolving metabolic functional profiles, even though functional diversity serves as a critical determinant in microbial ecology assessments [8]. Functional profiling of bacterial communities in fresh and ensiled GJ employed Tax4Fun, selected for implementation due to its demonstrated enhanced accuracy over PICRUSt in silage microbiome studies. The ensiling microenvironment, characterized by anaerobic conditions and progressive acidification, selectively constrained the metabolic activities of spoilage-associated microbiota. Consequently, native microbial–metabolic activity in fresh GJ underwent significant attenuation during fermentation, consistent with established preservation mechanisms. In this study, the predominant bacterial engagement in carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism during the ensiling process is in agreement with the outcomes of Bai et al. [26]. Amino acids serve as critical substrates for microbial biosynthesis and metabolic processes, directly influencing bacterial protein production and core biochemical pathways. The phylogenetically diverse epiphytic microbiota in fresh GJ likely drives its elevated amino acid metabolic activity. In contrast, ensiled GJ (NGJ) exhibited reduced amino acid pathway engagement, a phenomenon resulting from its acidic environment (pH < 4.20). This aligns with findings that low pH selectively inhibits amino acid metabolism in spoilage-associated microbiota [27]. Concurrently, Liu et al. [28] observed significant vitamin depletion during ensiling, corroborating nutrient loss under anaerobic fermentation conditions. That is why the activity of cofactors and vitamin metabolism in fresh GJ decreased after ensiling. Bai et al. [26] stated that the increasing activity of cofactors and vitamin metabolism helps compensate for vitamin loss during ensiling. Therefore, vitamin-synthesizing LAB strains represent a viable strategy to enhance the nutritional quality of GJ-based silage in practical applications. The energy metabolism of GJ was not enhanced by ensiling, which might be related to the unsatisfactory quality (high NH3-N and low LA/AA) of the resulting silage, as Xu et al. [29] reported that energy metabolism can be stimulated in high-quality silages. Pessione et al. [30] found that the energy metabolism of LAB is essential to promote LA production in silage. Nucleotides are known for their ability to synthesize nucleic acid and provide energy for cellular processes [31]. Notably, energy and nucleotide metabolism exhibited inverse activity patterns during ensiling. This counteractive relationship underscores the need for multi-omics investigations (e.g., proteomics, metagenomics, metabolomics) to resolve bacterial metabolic dynamics across fermentation phases.
To identify core bacterial functions, carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism underwent targeted analysis in fresh and ensiled GJ. Enhanced metabolism activity of most saccharide components during ensiling validated LAB’s capacity to metabolize diverse carbon substrates under anaerobic conditions. Concretely, the higher metabolism activity of saccharide components (amino sugar, nucleotide sugar, fructose, mannose, galactose, and sucrose) in NGJ could be mainly associated with Weissella and Lactobacillus. Glycolysis/gluconeogenesis and pentose phosphate pathway are essential for lactic acid bacteria to carry out homolactic and heterolactic fermentation. Thus, the high activity of PPP pathway might be attributed to the high RA of Weissella (day 3) and heterofermentative Lactobacillus (day 60), as these genera are known to possess PPP pathway [32]. Amino acid metabolism in silage fermentation is of significance in explaining NH3-N formation. The unacceptable NH3-N concentration in NGJ may be attributed to the increased metabolism activity of alanine, aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, and methionine. To sum up, microbial communities and their functions regulate the type, quantity and concentration of metabolites by driving metabolic pathways, and ultimately affect the nutritional value of silage.
5. Conclusions
The results support the great potential of giant fungus grass as a source of roughage with adequate WSC and CP content. But it should be noted that its low DM and LAB levels negatively altered NGJ’s chemical and microbial composition, as well as metabolic signatures. Management strategies such as postponing harvest or inoculating with LAB are needed to lower NH3-N production, improve its fermentation quality, and reduce economic losses of livestock farming. While 16S rRNA-based functional predictions necessitate additional verification through targeted analyses, a more detailed understanding of anaerobic microbial interactions from the metabolic pathway perspective enables novel perspectives for evaluating high-moisture silage preservation efficacy and advancing understanding of anaerobic metabolic regulation networks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and investigation, J.Z. and T.S.; methodology and software, J.Z. and J.-F.L.; validation, formal analysis, J.Z. and Z.-H.D.; resources and data curation, J.Z. and T.S.; writing—original draft preparation, X.-Y.L.; writing—review and editing, J.Z., supervision, J.Z.; funding acquisition, J.Z. and T.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, 2024T170419, the General Program of NSFC, 32171690, the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, 2022M721653, the Youth Project of NSFC, 32201464, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, KYQN2023001.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from J.Z. upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors report no conflict of interest in this work.
References
- Yang, F.; Wu, M.; Wang, X. Research Progress in Woody Forage. Feed Industry. 2025, 46, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, B.; Liu, J.; Lv, Z.; Luo, M.; Lin, Z. Preparation and properties of immobilized particles containing highly efficient nitrogen-fixing Klebsiella variicola GN02 cells isolated from the Pennisetum giganteum z. x. lin roots. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2020, 56, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xiang, C.; Xu, L.; Cui, J.; Fu, S.; Chen, B.; Yang, S.; Wang, P.; Xie, Y.; Wei, M.; et al. SMRT sequencing of a full-length transcriptome reveals transcript variants involved in C18 unsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis and metabolism pathways at chilling temperature in Pennisetum giganteum. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang JinGuo, Z.J.; Lei HeXian, L.H.; Li JiFeng, L.J.; Zhao JianGang, Z.J.; Yang GuiFen, Y.G.; Ren MingJin, R.M.; Yang XueSong, Y.X. Growth performance of Pennisetum sp. at different elevation. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences. Sci. 2013, 41, 112–115. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Yin, X.; Dong, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Dong, D.; Shao, T. Using gamma-ray irradiation and epiphytic microbiota inoculation to separate the effects of chemical and microbial factors on fermentation quality and bacterial community of ensiled Pennisetum giganteum. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshri, J.; Chen, Y.; Pinto, R.; Kroupitski, Y.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Sela Saldinger, S. Bacterial dynamics of wheat silage. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, C.O.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Jiang, J. The performance of lactic acid bacteria in silage production: A review of modern biotechnology for silage improvement. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 266, 127212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asshauer, K.P.; Wemheuer, B.; Daniel, R.; Meinicke, P. Tax4Fun: Predicting functional profiles from metagenomic 16S rRNA data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2882–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Bai, Y.; Jia, Y.; Shao, T. Ensiling as pretreatment of rice straw: The effect of hemicellulase and Lactobacillus plantarum on hemicellulose degradation and cellulose conversion. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J.H. Automated simultaneous determination of ammonia and total amino acids in ruminal fluid and in vitro media. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Horiguchi, K.; Goto, M. Effect of crushing unhulled rice and the addition of fermented juice of epiphytic lactic acid bacteria on the fermentation quality of whole crop rice silage, and its digestibility and rumen fermentation status in sheep. Anim. Sci. J. 2005, 76, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Mu, C.; Wang, H.; Shen, J.; Zoetendal, E.G.; Zhu, W. Amino acid utilization allows intestinal dominance of Lactobacillus amylovorus. ISME J. 2022, 16, 2491–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.; Henderson, A.R.; Heron, S.J.E. The Biochemistry of Silage, 2nd ed.; Chalcombe Publications: Marlow, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Benno, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Kumai, S. Effect of applying lactic acid bacteria isolated from forage crops on fermentation characteristics and aerobic deterioration of silage. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.; Shaver, R. Interpretation and use of silage fermentation analysis reports. Focus Forage 2001, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- van Niekerk, W.A.; Hassen, A.; Bechaz, F.M. Influence of growth stage at harvest on fermentative characteristics of Panicum maximum silage. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 40, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, C.; Xing, Y.; Zhou, W.; Pian, R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Ensiling characteristics, proteolysis and bacterial community of high-moisture corn stalk and stylo silage prepared with Bauhinia variegate flower. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 296, 122336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yin, X.J.; Wang, S.R.; Li, J.F.; Shao, T. Separating the effects of chemical and microbial factors on fermentation quality and bacterial community of Napier grass silage by using gamma-ray irradiation and epiphytic microbiota transplantation. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 280, 115082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, F.; Zhu, W.; Yuan, X.; Hu, Y.; Cui, Z.; Wang, X. Effect of ensiling and silage additives on biogas production and microbial community dynamics during anaerobic digestion of switchgrass. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Zhang, M.; Qin, G.; Tan, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y. Identification of lactic acid bacteria isolated from corn stovers. Anim. Sci. J. 2011, 82, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.E. Recent advances in silage microbiology. Agric. Food Sci. 2013, 22, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, K.; Ulrich, A.; Idler, C.; Klocke, M. Bacterial community dynamics during ensiling of perennial ryegrass at two compaction levels monitored by terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 1479–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Benno, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Ohmomo, S.; Kumai, S.; Nakase, T. Influence of Lactobacillus spp. from an inoculant and of Weissella and Leuconostoc spp. from forage crops on silage fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2982–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarvey, J.A.; Franco, R.B.; Palumbo, J.D.; Hnasko, R.; Stanker, L.; Mitloehner, F.M. Bacterial population dynamics during the ensiling of Medicago sativa (alfalfa) and subsequent exposure to air. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ding, Z.; Ke, W.; Xu, D.; Wang, M.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Guo, X. Different lactic acid bacteria and their combinations regulated the fermentation process of ensiled alfalfa: Ensiling characteristics, dynamics of bacterial community and their functional shifts. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flythe, M.D.; Russell, J.B. The effect of pH and a bacteriocin (bovicin HC5) on Clostridium sporogenes MD1, a bacterium that has the ability to degrade amino acids in ensiled plant materials. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 47, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.H.; Wu, J.X.; Shao, T. Roles of microbes and lipolytic enzymes in changing the fatty acid profile, α-tocopherol and β-carotene of whole-crop oat silages during ensiling and after exposure to air. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2019, 253, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, N.; Rinne, M.; Ke, W.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Da, M.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Guo, X. The bacterial community and metabolome dynamics and their interactions modulate fermentation process of whole crop corn silage prepared with or without inoculants. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Nielsen, J.; Dai, Z. Integrated microbiology and metabolomic analysis reveal the improvement of rice straw silage quality by inoculation of Lactobacillus brevis. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2023, 16, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilstrup, M.; Hammer, K.; Ruhdal Jensen, P.; Martinussen, J. Nucleotide metabolism and its control in lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 555–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Tashiro, Y.; Sonomoto, K. Lactic acid production from lignocellulose-derived sugars using lactic acid bacteria: Overview and limits. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 156, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).