The Effect of Biochar Addition in Potato Fields on Microbial Communities in the Arid Region of Northern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Biochar
2.2.2. Experimental Arrangement
2.3. Measurements and Calculations
2.3.1. Soil Chemical Properties
2.3.2. Soil PLFA Extraction and Measurement
2.3.3. Soil Enzyme Activity Soil Enzyme Dynamics
2.3.4. Soil Microbial Activity
2.3.5. Potato Yield and Nutrient Use Efficiency
2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
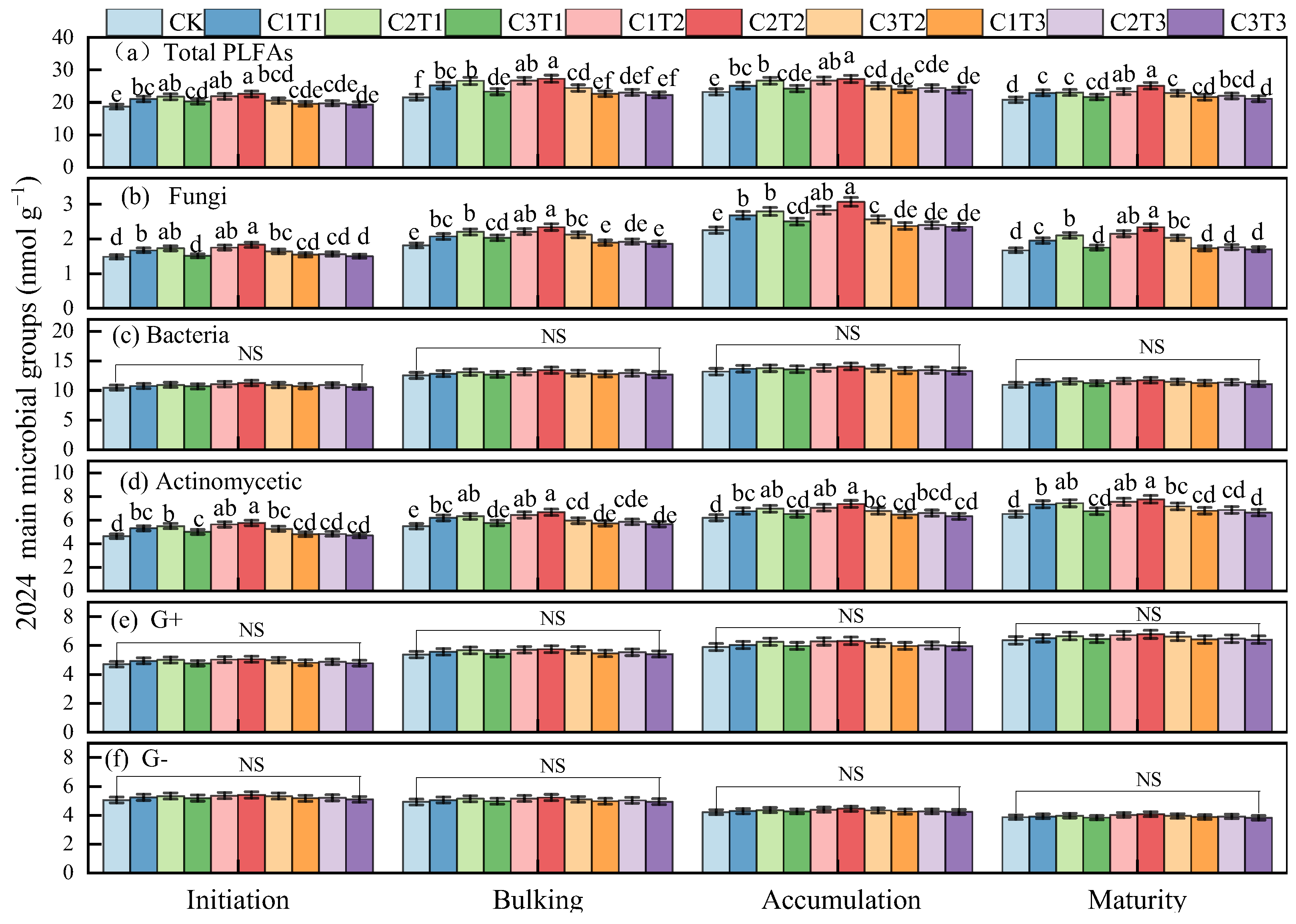
3.1. Soil Microbial Community Structure
3.2. Microbial Death Rate and Regeneration Cycle
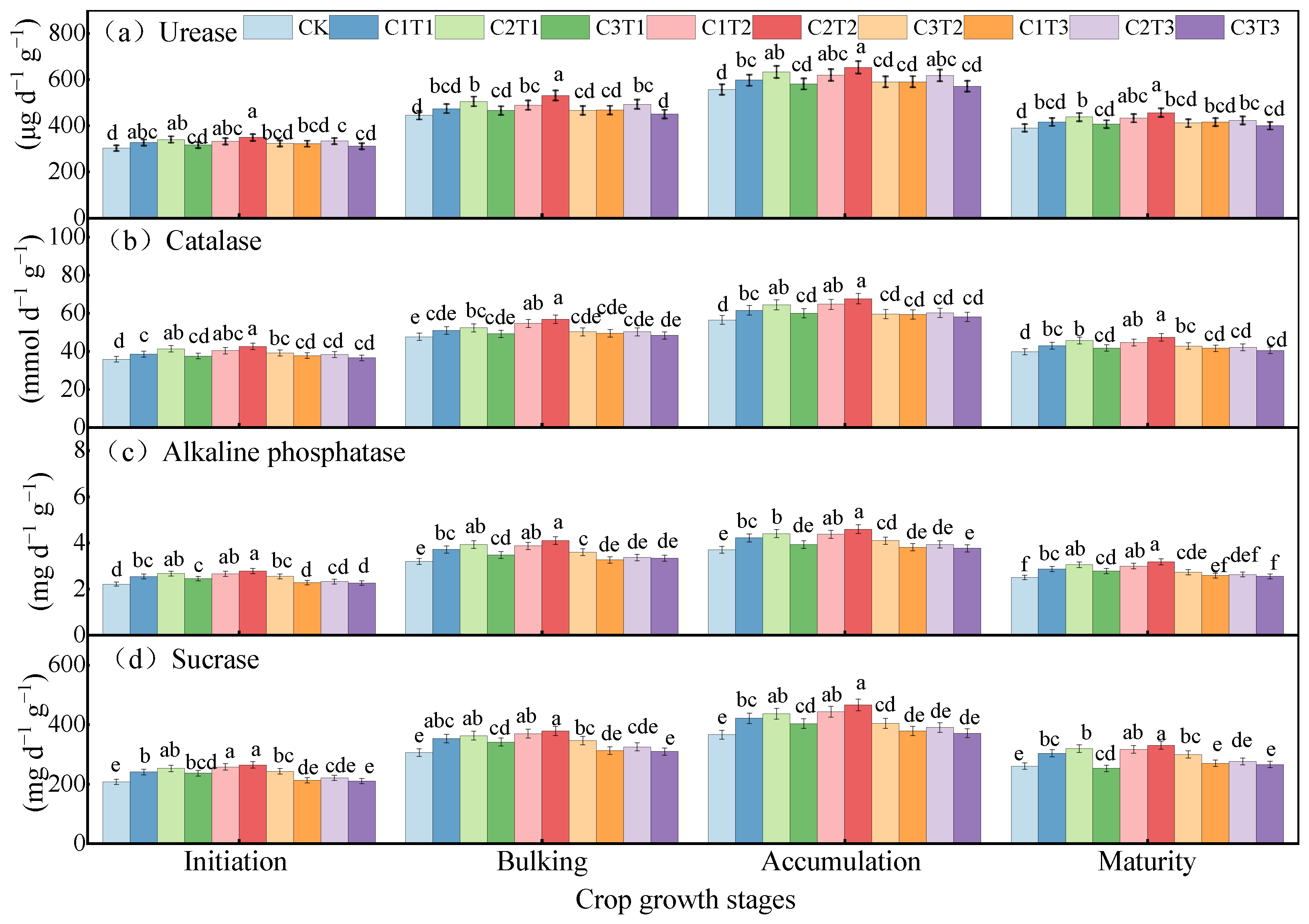
3.3. Soil Enzyme Activity
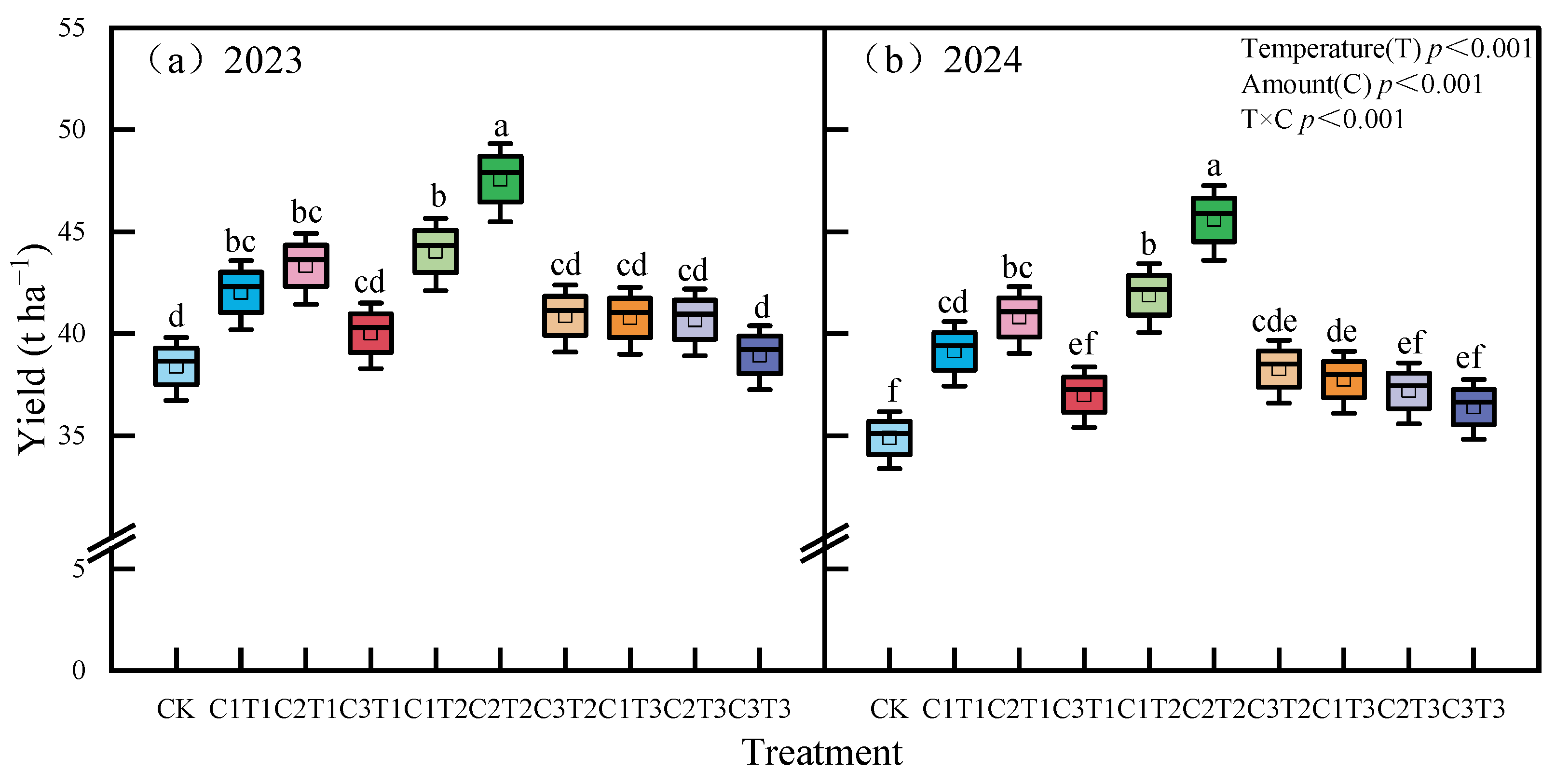
3.4. Nutrient Use Efficiency of Potatoes and Its Relationship with Soil Chemical Properties, Microbial Community Structure, and Enzyme Activity
4. Discussion
4.1. The Effect of Biochar on Soil Microbial Abundance and Community Composition
4.2. Effect of Biochar on Soil Enzyme Activity
4.3. Impact and Mechanisms of Biochar on Potato Nutrient Use Efficiency
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.J.; Liu, H.; Zeng, F.K.; Yang, Y.C.; Xu, D.; Zhao, Y.C.; Singh, J. Potato processing industry in China: Current scenario, future trends and global impact. Potato Res. 2023, 66, 543–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; He, P.; Xu, X.-P.; Qu, X.-J.; Zhou, W. Current situation and potential of potato fertilizer reduction in China. J. Plant Nutr. Fertilizer. 2023, 29, 2059–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.W.; Toth, Z. Effect of drought stress on potato production: A review. Agronomy 2022, 12, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Xing, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; Duan, Y.; Zhao, H. Increase in potato yield by the combined application of biochar and organic fertilizer: Key role of rhizosphere microbial diversity. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1389864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Northup, B.K.; Rice, C.W.; Prasad, P.V.V. Biochar applications influence soil physical and chemical properties, microbial diversity, and crop productivity: A meta-analysis. Biochar 2022, 4, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Belal, E.E.; Rady, M.O.A.; Abd El-Mageed, S.A.; Mansour, E.; Awad, M.F.; Semida, W.M. Acidified biochar as a soil amendment to drought-stressed (Vicia faba L.) plants: Influences on growth and productivity, nutrient status, and water use efficiency. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammeorg, P.; Simojoki, A.; Mäkelä, P.; Stoddard, F.L.; Alakukku, L.; Helenius, J. Short-term effects of biochar on soil properties and wheat yield formation with meat bone meal and inorganic fertiliser on a boreal loamy sand. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zwieten, L.; Kimber, S.; Morris, S.; Chan, K.Y.; Downie, A.; Rust, J.; Joseph, S.; Cowie, A. Effects of biochar from slow pyrolysis of papermill waste on agronomic performance and soil fertility. Plant Soil 2009, 327, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, S.; Yan, P.; Aurangzeib, M. Effect of biochar application method and amount on the soil quality and maize yield in Mollisols of Northeast China. Biochar 2022, 4, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, X.; Li, Y.; Han, L. Effect of pyrolysis temperature and correlation analysis on the yield and physicochemical properties of crop residue biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 296, 122318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Jones, D.L.; Hill, P.; Bastami, M.S.; Tu, C.L. Influence of biochar produced from different pyrolysis temperatures on nutrient retention and leaching. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 64, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.A.; Khalid, M.; Aon, M.; Abbas, G.; Tahir, M.; Amjad, M.; Murtaza, B.; Yang, A.; Akhtar, S.S. Effect of wheat and rice straw biochar produced at different temperatures on maize growth and nutrient dynamics of a calcareous soil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 63, 2048–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shi, Y.; Kong, L.; Tong, L.; Cao, H.; Zhou, H.; Lv, Y. Long-term application of bio-compost increased soil microbial community diversity and altered its composition and network. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Xiong, X.; Zhu, H.; Xu, H.; Leng, P.; Li, J.; Tang, C.; Xu, J. Association of biochar properties with changes in soil bacterial, fungal and fauna communities and nutrient cycling processes. Biochar 2021, 3, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhan, L.; Xu, X.; Bi, R.; Xiong, Z. Biochar addition stabilized soil carbon sequestration by reducing temperature sensitivity of mineralization and altering the microbial community in a greenhouse vegetable field. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 313, 114972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jing, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lu, H. Responses of soil microbial community structure changes and activities to biochar addition: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.D.; Denef, K.; Stewart, C.E.; Zheng, J.; Cotrufo, M.F. Biochar addition rate influences soil microbial abundance and activity in temperate soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 65, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Whalen, J.K.; Thomas, B.W.; Sachdeva, V.; Deng, H. Physico-chemical properties and microbial responses in biochar-amended soils: Mechanisms and future directions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 206, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, D.; Liang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Ai, C.; Zhou, W. Maize biochar addition rate influences soil enzyme activity and microbial community composition in a fluvo-aquic soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 96, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, A.T.; Ncube, B.; Mulidzi, R.; Lewu, F.B. Potential use of soil enzymes as soil quality indicators in agriculture. In Frontiers in Soil and Environmental Microbiology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Muneer, M.A.; Fatima, S.; Hussain, N.; Mashifana, T.; Sayed, A.; Boczkaj, G.; Rajoka, M.S.R. Enzyme Conjugation—A Promising Tool for Bio-catalytic and Biotransformation Applications—A Review. Top. Catal. 2024, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoakwah, E.; Arthur, E.; Frimpong, K.A.; Lorenz, N.; Rahman, M.A.; Nziguheba, G.; Islam, K.R. Biochar amendment impacts on microbial community structures and biological and enzyme activities in a weathered tropical sandy loam. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 172, 104364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Kang, H.; Haidar, G.; Wang, W.; Malghani, S. The impact of biochar on the activities of soil nutrients acquisition enzymes is potentially controlled by the pyrolysis temperature: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2022, 411, 115692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.; Sokołowska, Z.; Boguta, P. Biochar physicochemical properties: Pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio./Technol. 2020, 19, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datt, N.; Singh, D. Enzymes in relation to soil biological properties and sustainability. Sustain. Manag. Soil Environ. 2019, 3, 383–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, O.L.; Tang, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhang, R. Effects of amendment of different biochars on soil enzyme activities related to carbon mineralisation. Soil Res. 2014, 52, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dong, X.; da Silva, E.B.; de Oliveira, L.M.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.Q. Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: Biochar characteristics and modifications. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, W.; Liang, G.; Song, D.; Zhang, X. Characteristics of maize biochar with different pyrolysis temperatures and its effects on organic carbon, nitrogen and enzymatic activities after addition to fluvo-aquic soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameloot, N.; De Neve, S.; Jegajeevagan, K.; Yildiz, G.; Buchan, D.; Funkuin, Y.N.; Prins, W.; Bouckaert, L.; Sleutel, S. Short-term CO₂ and N₂O emissions and microbial properties of biochar amended sandy loam soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansu, M. Handbook of Soil Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 551–579. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, K.R. Organic carbon content assessment methods. In Encyclopedia of Soil Science, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1164–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.K. Methods of Soil and Agro-Chemical Analysis; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 127–332. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Luo, X.; Xing, B. Enhanced growth of halophyte plants in biochar-amended coastal soil: Roles of nutrient availability and rhizosphere microbial modulation. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 41, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Chapman, S.J.; Thornton, B.; Paterson, E. 13C PLFAs: A key to open the soil microbial black box? Plant Soil 2014, 392, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, P.A. Signature fatty acids provide tools for determination of the distribution and interactions of mycorrhizal fungi in soil. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1999, 29, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Li, Y.; Chapman, S.J.; Khan, S.; Yao, H. Microbial utilization of rice straw and its derived biochar in a paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, E.M.; Baer, S.G.; Meyer, C.K.; Six, J. Soil texture affects soil microbial and structural recovery during grassland restoration. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 2182–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, D.; Xu, Q.; Fuhrmann, J.J.; Li, L.; Pan, G.; Li, Y.; Qin, H.; Liang, C.; Sun, X. Organic carbon quality, composition of main microbial groups, enzyme activities, and temperature sensitivity of soil respiration of an acid paddy soil treated with biochar. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 55, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeler, E.G. Short-term assay of soil urease activity using colorimetric determination of ammonium. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1988, 6, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L. Effect and Mechanism of Biochar on Improving Water and Fertilizer Utilization of Tomato in Greenhouse; Northwest AF University: Xianyang, China, 2021; pp. 44–54, (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Camina, F.; Leiros, M.C.; Gil-Sotres, F. An improved method to measure catalase activity in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joergensen, R.G.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. Survival of the soil microbial biomass at elevated temperatures. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnolli, R.N.; Lopes, P.R.M.; Bidoia, E.D. Fluorinated waste and firefighting activities: Biodegradation of hydrocarbons from petrochemical refinery soil co-contaminated with halogenated foams. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 36002–36013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, D.S. Determination of microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in soil. In Advances in Nitrogen Cycling in Agricultural Ecosystems; Wilson, J.R., Ed.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1988; pp. 368–386. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, S.; Fan, J.; Feng, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Xiang, Y. Optimization of irrigation amount and fertilization rate of drip-fertigated potato based on Analytic Hierarchy Process and Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation methods. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 256, 107130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, W.; Li, P.; Shi, P.; Xu, G.; Cheng, S.; Cheng, Y.; Fan, Z.; Wang, X. Effects of irrigation and fertilization on different potato varieties’ growth, yield and resource use efficiency in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 261, 107351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Peng, J.; Feng, X.; Li, Y.; Zhan, X.; Han, X. Effects of biochar and carbon-based fertilizer on soil microbial community structure. Chin. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 51, 1920–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Sindhu, R.; Vinayak, V.; Thanh, N.C.; Brindhadevi, K.; Yuan, D. An assessment of biochar as a potential amendment to enhance plant nutrient uptake. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, S.A.; Ostle, N.; Bardgett, R.D.; Hopkins, D.W.; Vanbergen, A.J. Biochar in bioenergy cropping systems: Impacts on soil faunal communities and linked ecosystem processes. GCB Bioenergy 2013, 5, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.; Hussain, M.; Ullah, W.; Khan, T.A.; Ali, S.; Akbar, A.; Aziz, R.; Rafiq, M.K.; Bachmann, R.T.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; et al. Biochar for sustainable soil and environment: A comprehensive review. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokharel, P.; Ma, Z.; Chang, S.X. Biochar increases soil microbial biomass with changes in extra- and intracellular enzyme activities: A global meta-analysis. Biochar 2020, 2, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Gautam, S.; Ram, L.C. Feedstock and pyrolysis conditions affect the suitability of biochar for various sustainable energy and environmental applications. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 2023, 170, 105881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, A.; Raiesi, F. Influence of biochar on potential enzyme activities in two calcareous soils of contrasting texture. Geoderma 2017, 308, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, F.U.; Coulter, J.A.; Cai, L.; Hussain, S.; Cheema, S.A.; Wu, J.; Zhang, R. An overview on biochar production, its implications, and mechanisms of biochar-induced amelioration of soil and plant characteristics. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 107–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Reddy, N.G.; Huang, X.; Chen, P.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Garg, A. Effects of pyrolysis temperature, feedstock type and compaction on water retention of biochar amended soil. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzobair, K.A.; Stromberger, M.E.; Ippolito, J.A.; Lentz, R.D. Contrasting effects of biochar versus manure on soil microbial communities and enzyme activities in an Aridisol. Chemosphere 2016, 142, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, J.; Pan, G.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Bian, R.; Cheng, K.; Jinwei, J. Biochar decreased microbial metabolic quotient and shifted community composition four years after a single incorporation in a slightly acid rice paddy from southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palansooriya, K.N.; Wong, J.T.F.; Hashimoto, Y.; Huang, L.; Rinklebe, J.; Chang, S.X.; Bolan, N.; Wang, H.; Ok, Y.S. Response of microbial communities to biochar-amended soils: A critical review. Biochar 2019, 1, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

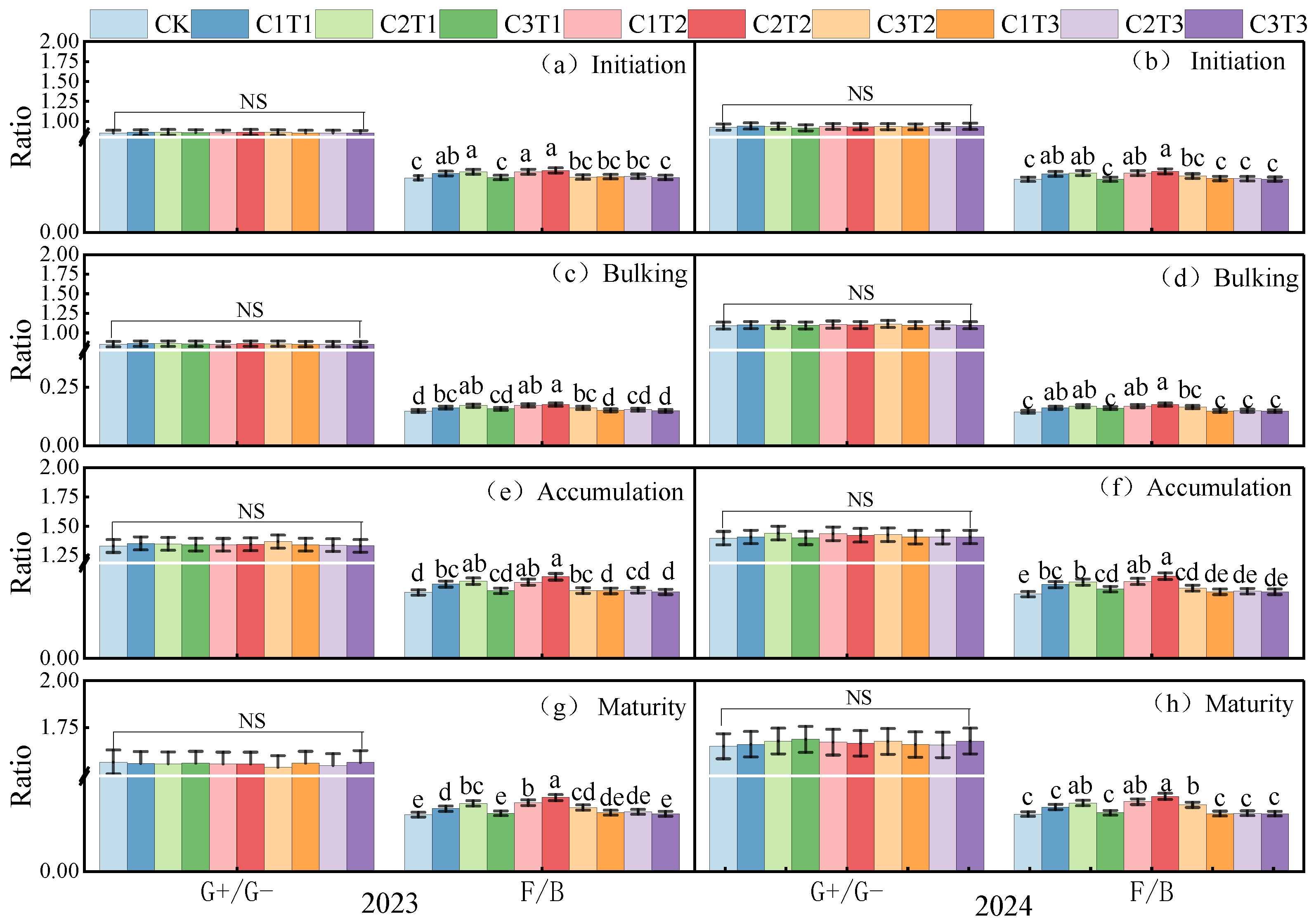
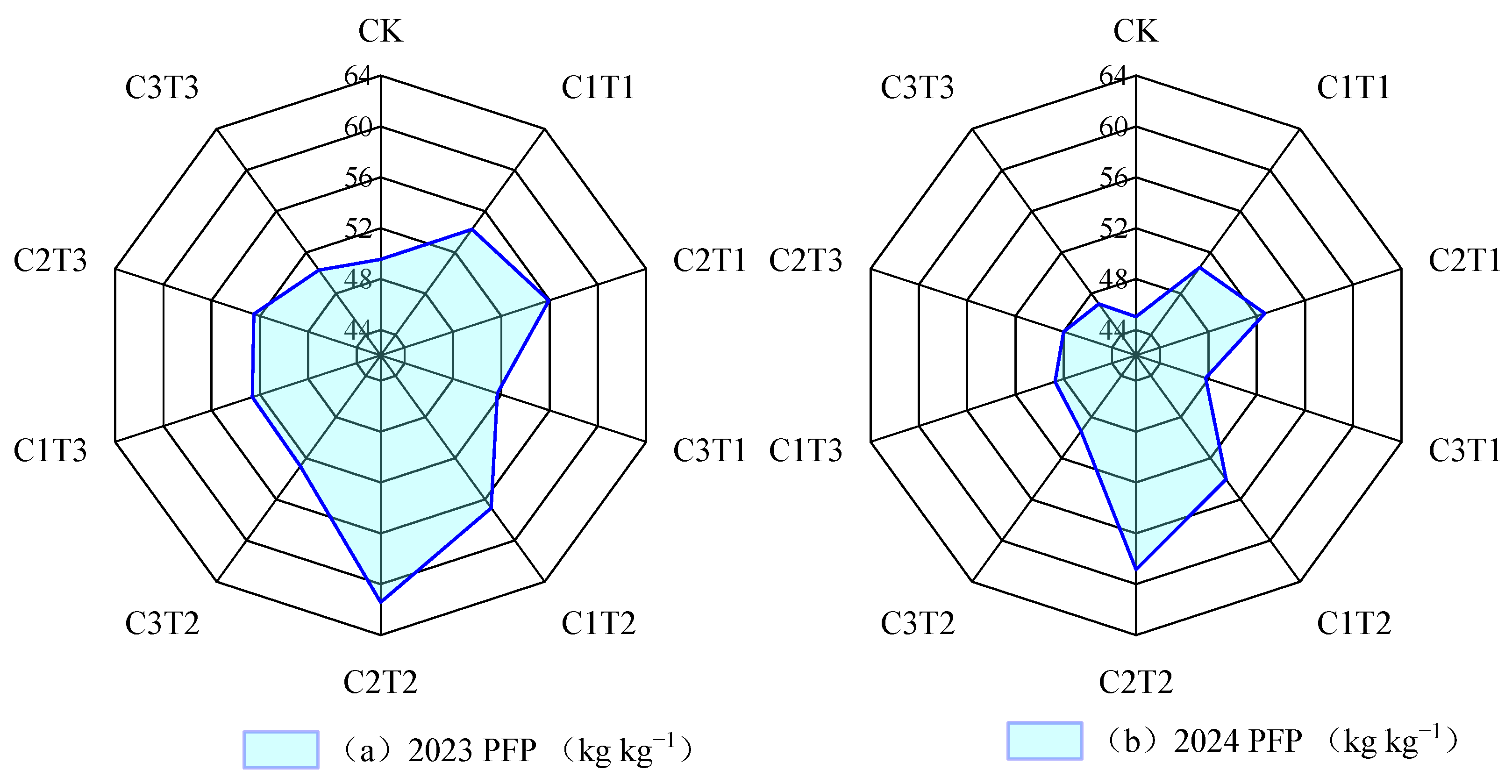
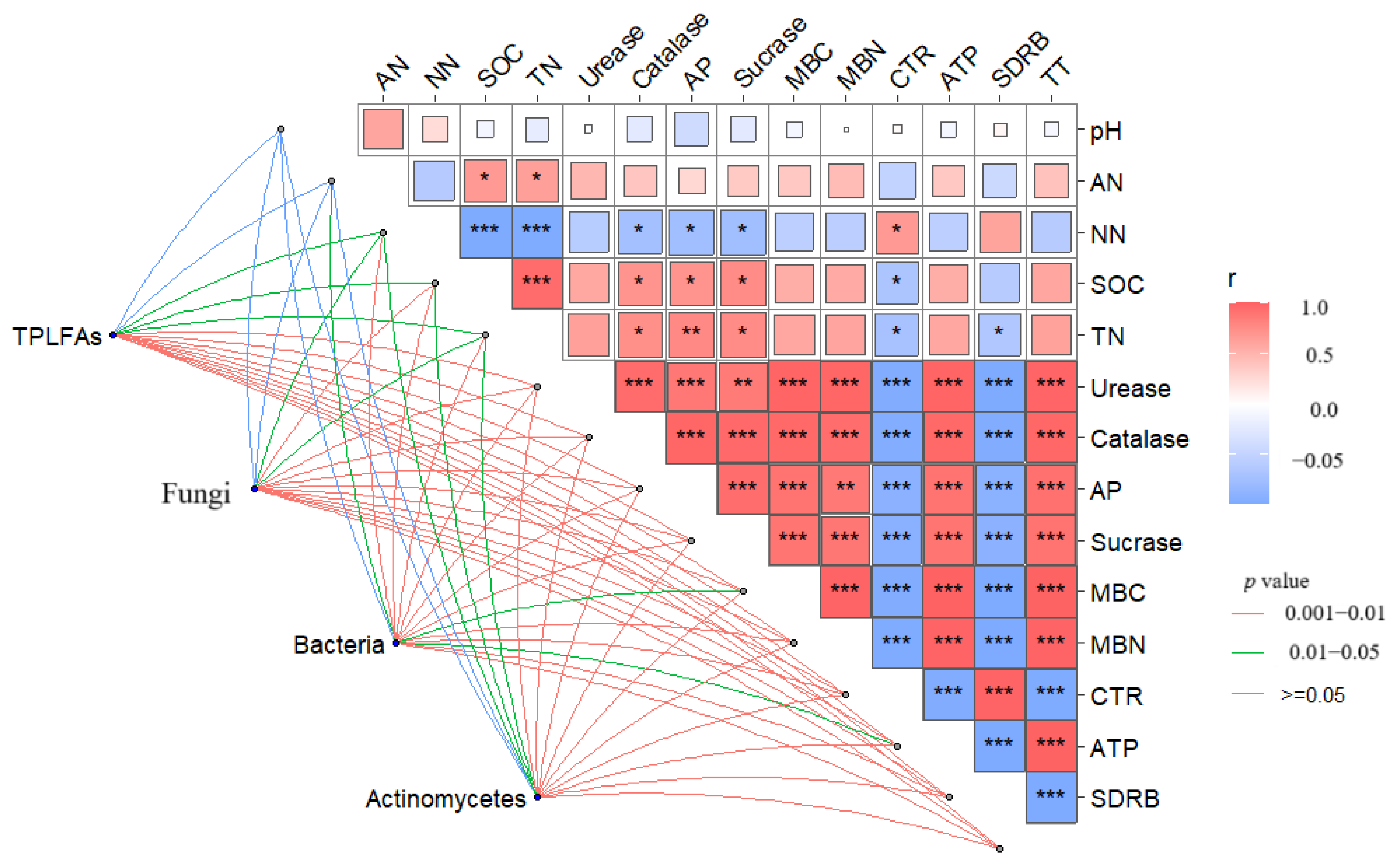
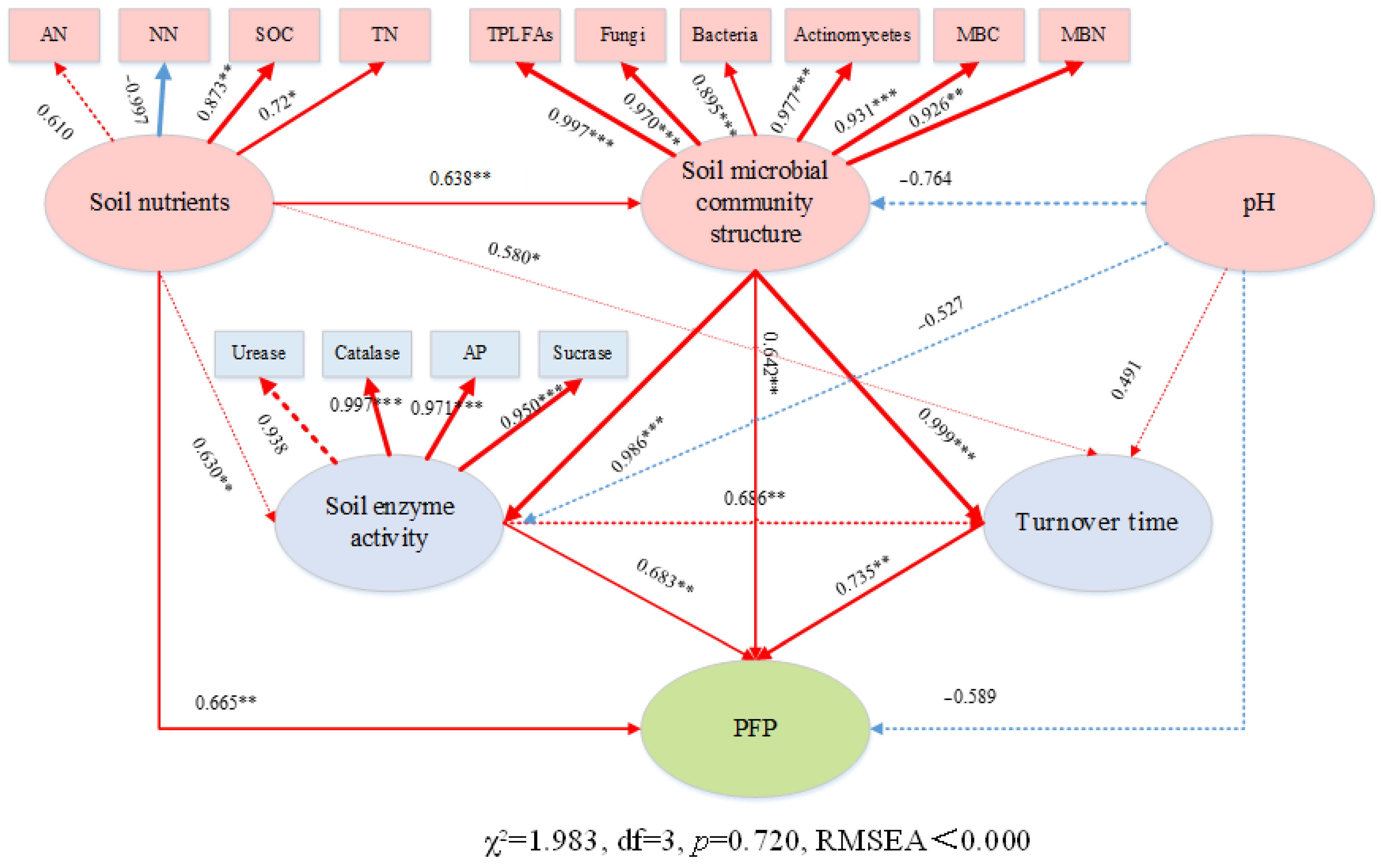
| Years | Treatments | MBC (mg kg−1) | MBN (mg kg−1) | CER (mg kg−1 d−1) | ATP (mmol kg−1) | SDRB (mg kg−1 d−1) | TT (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | CK | 168.55f | 17.23f | 13.62d | 2.01f | 0.060a | 16.72f |
| C1T1 | 187.75cd | 19.52bcd | 12.49bc | 2.24cd | 0.049d | 20.31c | |
| C2T1 | 203.51b | 19.98bc | 12.28ab | 2.43b | 0.045e | 22.40b | |
| C3T1 | 177.81def | 18.50de | 13.05bcd | 2.12def | 0.054c | 18.41de | |
| C1T2 | 198.80bc | 20.53b | 12.20ab | 2.38bc | 0.045e | 22.02b | |
| C2T2 | 217.20a | 22.18a | 11.57a | 2.59a | 0.039f | 25.37a | |
| C3T2 | 182.35de | 19.04cde | 12.70bc | 2.18de | 0.052cd | 19.40cd | |
| C1T3 | 183.07de | 18.50de | 12.90bcd | 2.19de | 0.052bcd | 19.18cde | |
| C2T3 | 189.30cd | 20.26bc | 12.68bc | 2.26cd | 0.050d | 20.17c | |
| C3T3 | 174.83ef | 17.82ef | 13.17cd | 2.09ef | 0.056b | 17.94e | |
| 2024 | CK | 165.82f | 16.67f | 11.71d | 1.98f | 0.052a | 19.14h |
| C1T1 | 193.92cd | 19.21cd | 10.62bc | 2.32cd | 0.041e | 24.68d | |
| C2T1 | 210.82b | 20.63ab | 10.48abc | 2.52b | 0.037f | 27.18c | |
| C3T1 | 175.14e | 17.76ef | 11.13cd | 2.09ef | 0.047bc | 21.26gf | |
| C1T2 | 203.32bc | 20.35bc | 10.23ab | 2.43bc | 0.037f | 26.86c | |
| C2T2 | 223.92a | 22.06a | 9.89a | 2.68a | 0.033g | 30.60b | |
| C3T2 | 179.15e | 18.46e | 10.94bc | 2.14e | 0.045bc | 22.13gf | |
| C1T3 | 182.50de | 18.23de | 10.97bcd | 2.18de | 0.044cd | 22.48ef | |
| C2T3 | 192.46cd | 19.92d | 10.83bc | 2.30cd | 0.042de | 24.01e | |
| C3T3 | 172.69ef | 17.53ef | 11.20cd | 2.06ef | 0.048b | 20.84g |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.; Zhou, H.; Jia, L.; Wang, Y.; Fan, M.; Shi, X. The Effect of Biochar Addition in Potato Fields on Microbial Communities in the Arid Region of Northern China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040945
Guo J, Zhou H, Jia L, Wang Y, Fan M, Shi X. The Effect of Biochar Addition in Potato Fields on Microbial Communities in the Arid Region of Northern China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040945
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jiawei, Hui Zhou, Liguo Jia, Yongqiang Wang, Mingshou Fan, and Xiaohua Shi. 2025. "The Effect of Biochar Addition in Potato Fields on Microbial Communities in the Arid Region of Northern China" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040945
APA StyleGuo, J., Zhou, H., Jia, L., Wang, Y., Fan, M., & Shi, X. (2025). The Effect of Biochar Addition in Potato Fields on Microbial Communities in the Arid Region of Northern China. Agronomy, 15(4), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040945





