Effects of Deep Application of Fertilizer on Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Functions in Rice Paddies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Site and Design
2.2. Soil Sample Collection and Physicochemical Property Analysis
2.3. Metagenomic Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Organic Carbon (SOC) and Total Nitrogen (TN)
3.2. Microbial Diversity
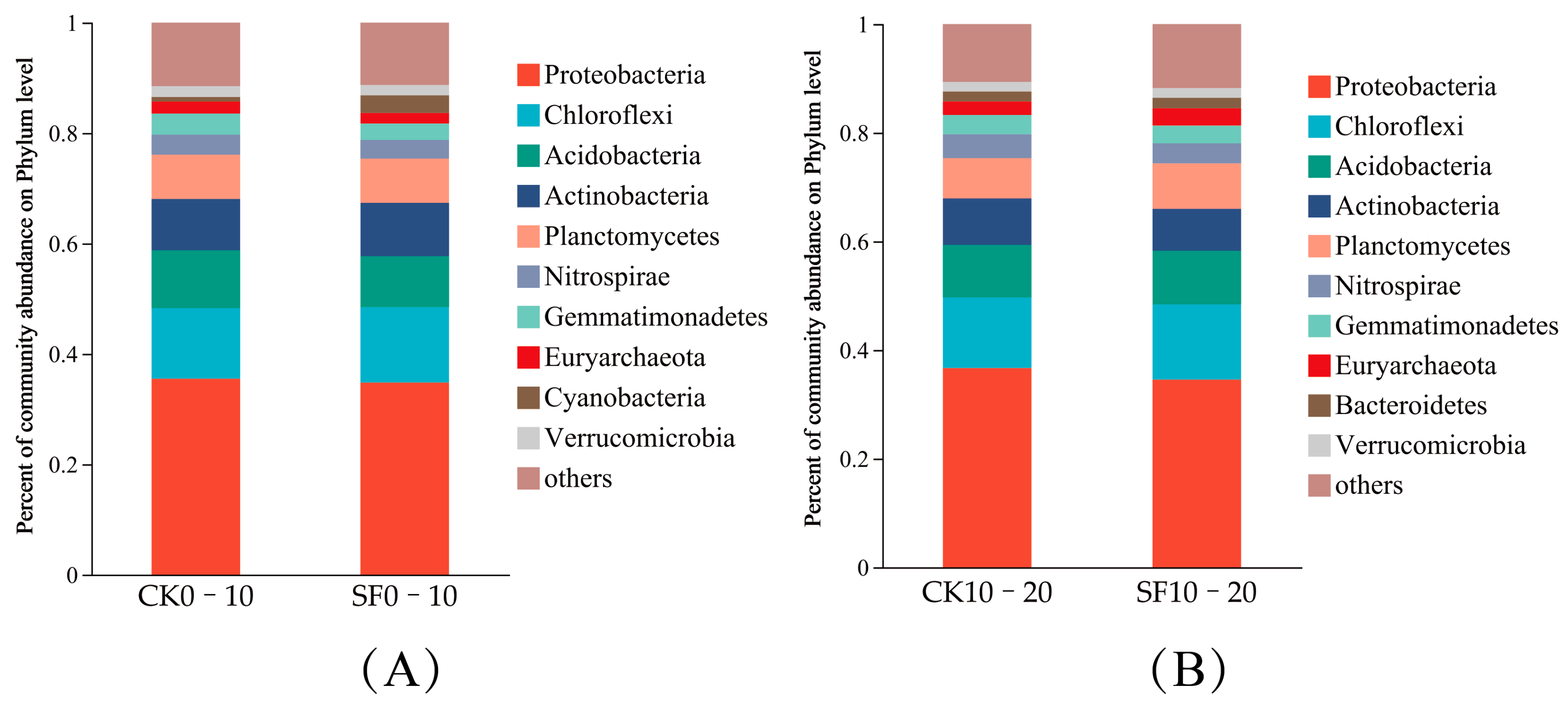
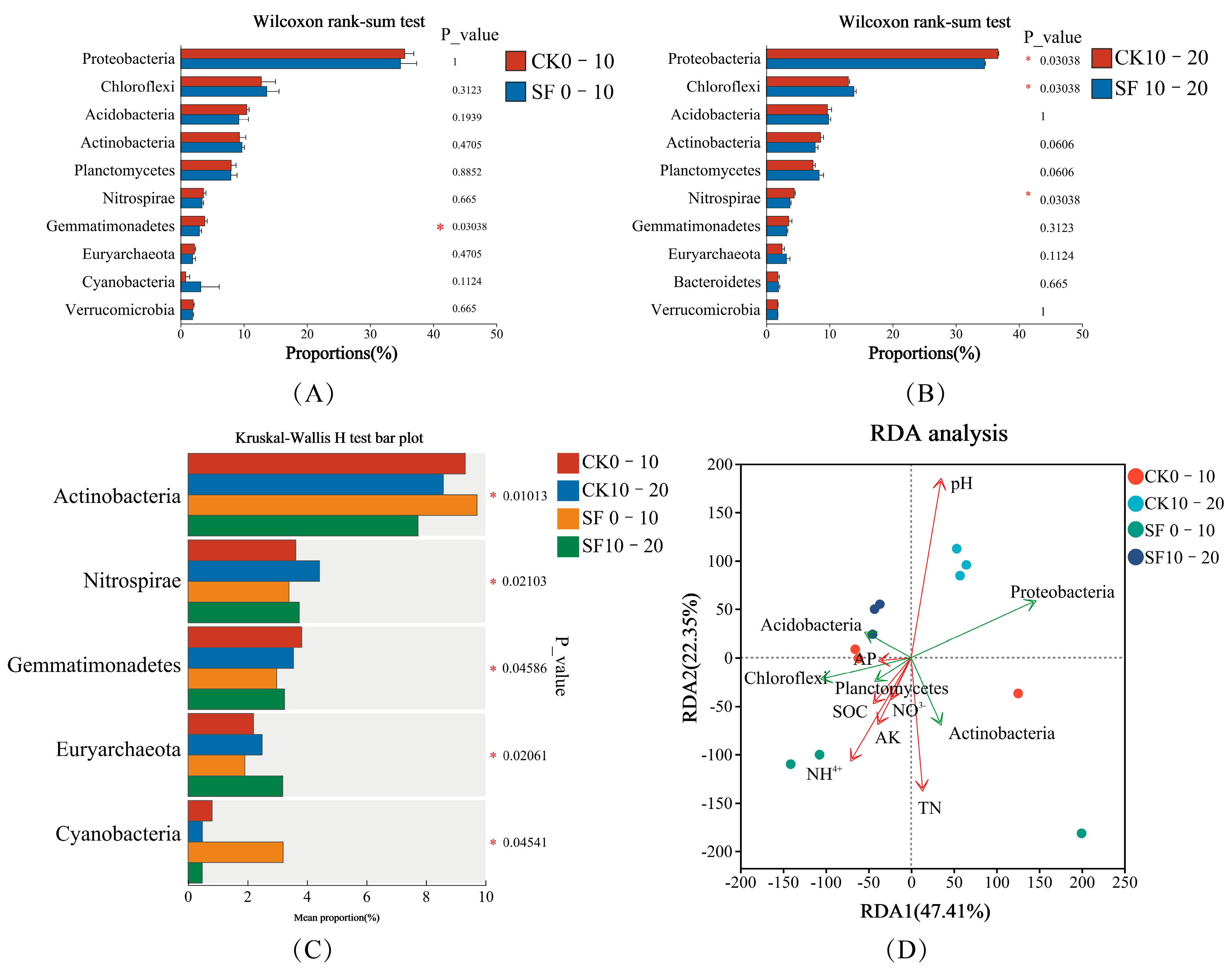
3.2.1. Analysis of Soil Microbial Composition
3.2.2. Analysis of Alpha and Beta Diversity Index
3.2.3. Association Between Soil Microbial Communities and Fundamental Physicochemical Properties
3.3. Microbial Function
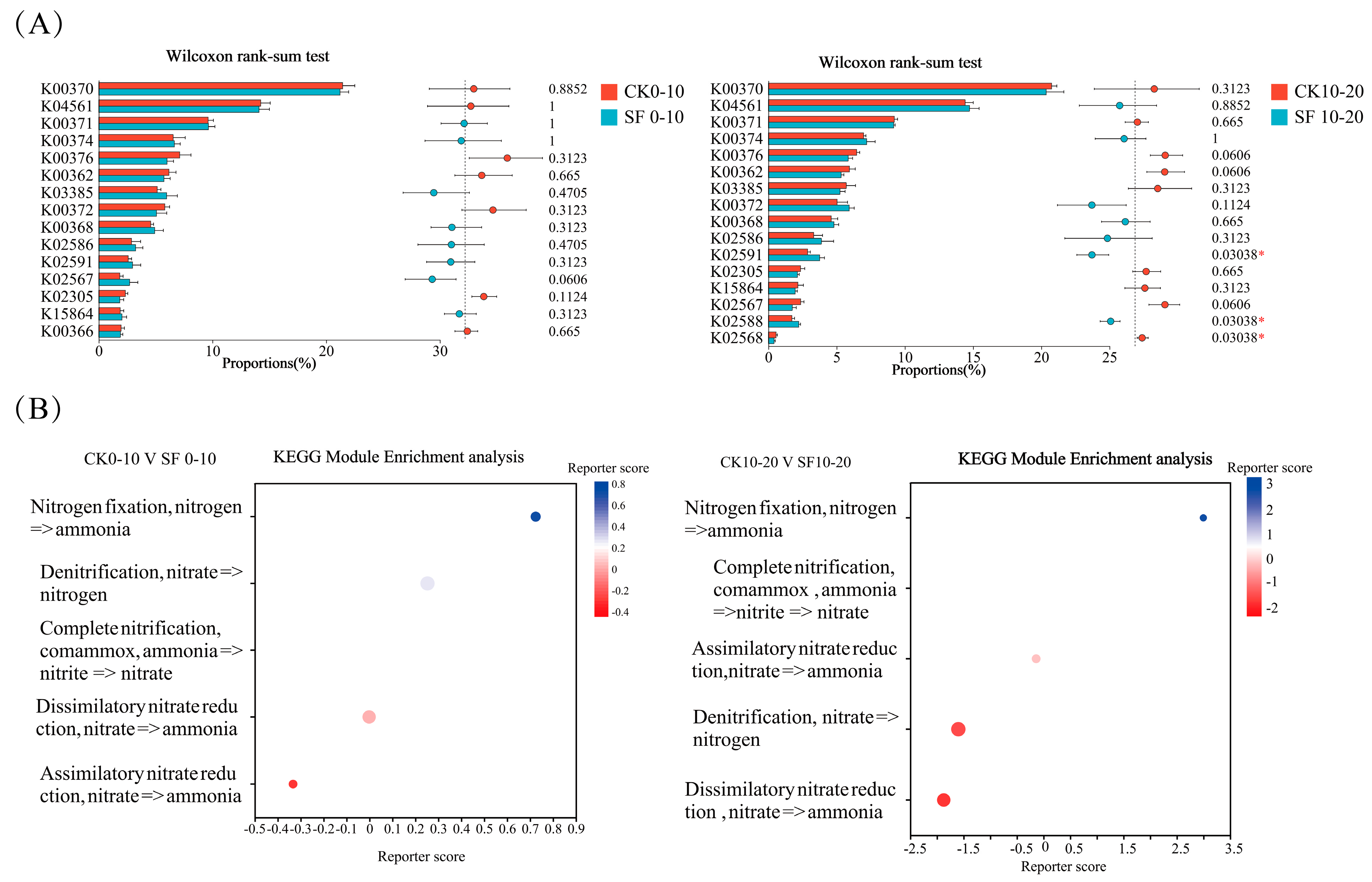
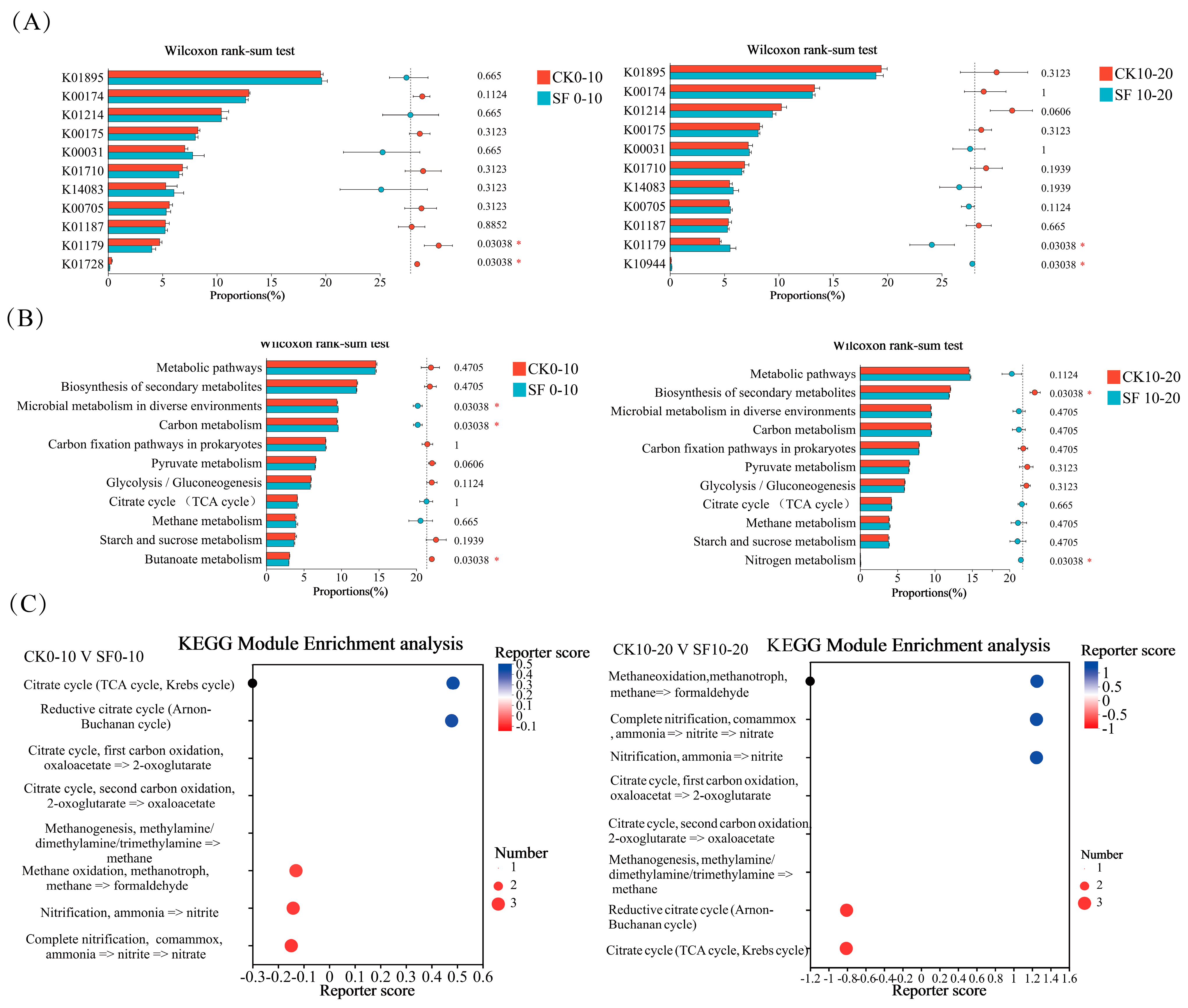
3.3.1. Effects of Deep Nitrogen Fertilization on Nitrogen Cycling Functional Genes in Paddy Soil
3.3.2. Effects of Deep Nitrogen Fertilization on Carbon Cycling Functional Genes in Paddy Soil
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Deep Nitrogen Fertilization on SOC and TN
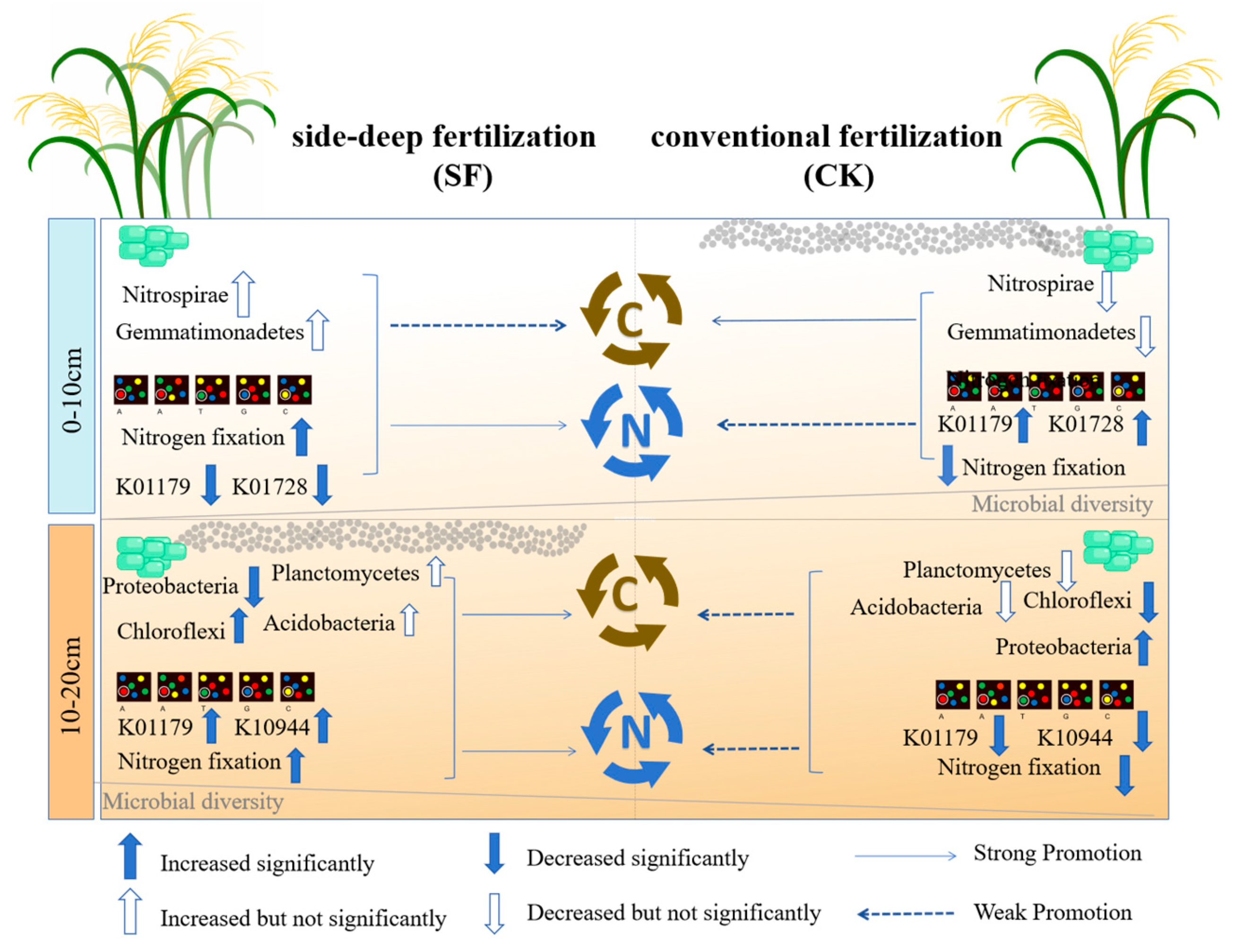
4.2. Variations in Microbial Diversity and Composition
4.3. Variations in Microbial Functions
4.3.1. Effects of Deep Nitrogen Fertilization on Nitrogen Cycling Functional Genes
4.3.2. Effects of Deep Nitrogen Fertilization on Carbon Cycling Functional Genes
4.4. Relationship Between Soil Microbial Communities and Basic Physicochemical Properties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bandumula, N. Rice Production in Asia: Key to Global Food Security. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 88, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmer, C.P. The Changing Role of Rice in Asia’s Food Security. Available online: https://www.google.ca/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/28552/adb-wp15-rice-food-security.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwj0-PyeoMeMAxXkavUHHUitLOIQFnoECBkQAQ&usg=AOvVaw0rqMIQ4WXoouJT1AUlngw3 (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Yin, X.; Huang, M.; Zou, Y. Changes in Rice Yield Stability in Southern China from 1949 to 2015. Agric. Environ. Lett. 2018, 3, 170038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Peng, J.; Kang, X.; Wu, Y.; Luo, G.; Hu, W.; Zhou, X. Optimizing Agronomic Traits and Increasing Economic Returns of Machine-Transplanted Rice with Side-Deep Fertilization of Double-Cropping Rice System in Southern China. Field Crops Res. 2021, 270, 108191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Q.; Fan, D.J.; Zhang, X.X.; Chen, J.; Li, C.F.; Cao, C.G. Deep Placement of Nitrogen Fertilizers Reduces Ammonia Volatilization and Increases Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency in No-Tillage Paddy Fields in Central China. Field Crops Res. 2015, 184, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Wen, X.; Wang, Z.; Ashraf, U.; Tian, H.; Duan, M.; Mo, Z.; Fan, P.; Tang, X. Benefits of Mechanized Deep Placement of Nitrogen Fertilizer in Direct-Seeded Rice in South China. Field Crops Res. 2017, 203, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.-F.; Pu, C.; Liu, S.-L.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, R.; Chen, F.; Xiao, X.-P.; Zhang, H.-L. Carbon and Nitrogen Footprint of Double Rice Production in Southern China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 64, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dou, Z.; He, P.; Ju, X.-T.; Powlson, D.; Chadwick, D.; Norse, D.; Lu, Y.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; et al. New Technologies Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Nitrogenous Fertilizer in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8375–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahrl, F.; Li, Y.; Su, Y.; Tennigkeit, T.; Wilkes, A.; Xu, J. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Nitrogen Fertilizer Use in China. Environ. Sci. Policy 2010, 13, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conant, R.T.; Berdanier, A.B.; Grace, P.R. Patterns and Trends in Nitrogen Use and Nitrogen Recovery Efficiency in World Agriculture. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2013, 27, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing Nitrogen for Sustainable Development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Zhao, X.; Pittelkow, C.M.; Fan, M.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X. Optimal Nitrogen Rate Strategy for Sustainable Rice Production in China. Nature 2023, 615, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, H.; Pan, J.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Gu, B.; Liu, S.; Zhai, L.; Lindsey, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Nitrogen Application Rates Need to Be Reduced for Half of the Rice Paddy Fields in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Zhong, X.; Huang, N.; Lampayan, R.M.; Liu, Y.; Pan, J.; Peng, B.; Hu, X.; Fu, Y. Nitrogen Losses and Greenhouse Gas Emissions under Different N and Water Management in a Subtropical Double-Season Rice Cropping System. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Zhou, X.; Luo, G.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cao, R.; Tian, C.; Peng, J. Soil Mineral Nitrogen, Soil Urease Activity, Nitrogen Losses and Nitrogen Footprint under Machine-Planted Rice with Side-Deep Fertilization. Plant Soil 2024, 494, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.-X.; Du, B.; Jiang, S.-C.; Zhang, H.-W.; Zhu, J.-Q. Side Deep Fertilizing of Machine-Transplanted Rice to Guarantee Rice Yield in Conservation Tillage. Agriculture 2022, 12, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Zhang, L.; Liu, P.; He, S.; Rong, X.; Peng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, C.; Han, Y. Side-Deep Fertilization Stabilizes Double-Cropping Rice Yield, Increases N and P Utilization, and Reduces N and P Losses. Land 2023, 12, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Hu, J.; Wei, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J. Relationship between Plant Roots, Rhizosphere Microorganisms, and Nitrogen and Its Special Focus on Rice. Agriculture 2021, 11, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Huang, H.; Qian, Z.; Jiang, H.; Liu, G.; Xu, K.; Hu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Huo, Z. Effect of Side Deep Placement of Nitrogen on Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Single Season Late Japonica Rice. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1487–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafdar, J.C.; Meena, S.C.; Kathju, S. Influence of Straw Size on Activity and Biomass of Soil Microorganisms during Decomposition. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2001, 37, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Cotrufo, M.F.; Rumpel, C.; Paustian, K.; Kuikman, P.J.; Elliott, J.A.; McDowell, R.; Griffiths, R.I.; Asakawa, S.; Bustamante, M.; et al. Biogeochemical Cycles and Biodiversity as Key Drivers of Ecosystem Services Provided by Soils. Soil 2015, 1, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Veen, J.A.; Kuikman, P.J. Soil Structural Aspects of Decomposition of Organic Matter by Micro-Organisms. Biogeochemistry 1990, 11, 213–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, T.; Qadir, M.F.; Khan, K.S.; Eash, N.S.; Yousuf, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Manzoor, R.; ur Rehman, S.; Oetting, J.N. Unraveling the Potential of Microbes in Decomposition of Organic Matter and Release of Carbon in the Ecosystem. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.V.S.R.; Germida, J.J. Soil Aggregation: Influence on Microbial Biomass and Implications for Biological Processes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 80, A3–A9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, C.; Zheng, M.; Li, W.; Cai, Z.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Shen, R.F. Fertilization Practices Affect Biological Nitrogen Fixation by Modulating Diazotrophic Communities in an Acidic Soil in Southern China. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, D.; Chen, X.; Hou, J.; Zhao, F.; Li, P. Soil Properties and Microbial Functional Attributes Drive the Response of Soil Multifunctionality to Long-Term Fertilization Management. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 192, 105095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ke, X.; Wu, L.; Lu, Y. Community Composition of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria and Archaea in Rice Field Soil as Affected by Nitrogen Fertilization. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 32, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Chen, Y.; Zang, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Lu, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhuang, H.; Huang, L. The Effects of Cultivation Patterns and Nitrogen Levels on Fertility and Bacterial Community Characteristics of Surface and Subsurface Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1072228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tecon, R.; Or, D. Biophysical Processes Supporting the Diversity of Microbial Life in Soil. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 599–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, D.; McClure, R.; Jansson, J. Trends in Microbial Community Composition and Function by Soil Depth. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, N.W.; Slessarev, E.; Marschmann, G.L.; Nicolas, A.; Blazewicz, S.J.; Brodie, E.L.; Firestone, M.K.; Foley, M.M.; Hestrin, R.; Hungate, B.A.; et al. Life and Death in the Soil Microbiome: How Ecological Processes Influence Biogeochemistry. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Lai, J.; Chen, Y.; Sun, F.; Ye, X.; Wu, Y. Responses of Soil Microbial Metabolism, Function and Soil Quality to Long-Term Addition of Organic Materials with Different Carbon Sources. Biochar 2024, 6, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhong, H.; Guo, X.; Li, H.; Xia, J.; Chen, Q. Nitrogen Fertilization and Soil Nitrogen Cycling: Unraveling the Links among Multiple Environmental Factors, Functional Genes, and Transformation Rates. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garlapati, D.; Charankumar, B.; Ramu, K.; Madeswaran, P.; Ramana Murthy, M.V. A Review on the Applications and Recent Advances in Environmental DNA (eDNA) Metagenomics. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 389–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.; Silvério, S.C.; Costa, A.M.A.; Rodrigues, L.R. Metagenomic Approaches as a Tool to Unravel Promising Biocatalysts from Natural Resources: Soil and Water. Catalysts 2022, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staley, C.; Sadowsky, M.J. Application of Metagenomics to Assess Microbial Communities in Water and Other Environmental Matrices. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2016, 96, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossart, H.-P.; Massana, R.; McMahon, K.D.; Walsh, D.A. Linking Metagenomics to Aquatic Microbial Ecology and Biogeochemical Cycles. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, S2–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.M.; Hughes, D.J.; Fu, Q.; Abadie, M.; Hirsch, P.R. Metagenomic Approaches Reveal Differences in Genetic Diversity and Relative Abundance of Nitrifying Bacteria and Archaea in Contrasting Soils. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temperton, B.; Giovannoni, S.J. Metagenomics: Microbial Diversity through a Scratched Lens. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavicchioli, R.; DeMaere, M.Z.; Thomas, T. Metagenomic Studies Reveal the Critical and Wide-Ranging Ecological Importance of Uncultivated Archaea: The Role of Ammonia Oxidizers. BioEssays 2007, 29, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Gu, H.; Liu, J.; Wei, D.; Zhu, P.; Cui, X.; Zhou, B.; Chen, X.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; et al. Metagenomics Reveals Divergent Functional Profiles of Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Cycling under Long-Term Addition of Chemical and Organic Fertilizers in the Black Soil Region. Geoderma 2022, 418, 115846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, H.; Han, M.; Yang, L. Soil Metagenomics Reveals the Effect of Nitrogen on Soil Microbial Communities and Nitrogen-Cycle Functional Genes in the Rhizosphere of Panax Ginseng. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1411073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harindintwali, J.D.; Zhou, J.; Muhoza, B.; Wang, F.; Herzberger, A.; Yu, X. Integrated Eco-Strategies towards Sustainable Carbon and Nitrogen Cycling in Agriculture. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thamdrup, B. New Pathways and Processes in the Global Nitrogen Cycle. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 407–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Cui, H.; Fu, C.; Li, R.; Qi, F.; Liu, Z.; Yang, G.; Xiao, K.; Qiao, M. Unveiling the Crucial Role of Soil Microorganisms in Carbon Cycling: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soussana, J.-F.; Lemaire, G. Coupling Carbon and Nitrogen Cycles for Environmentally Sustainable Intensification of Grasslands and Crop-Livestock Systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 190, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; Olsen, S.R., Ed.; Circular/United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Analysis: An Interpretation Manual; Peverill, K., Sparrow, L., Reuter, D., Eds.; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 1999; ISBN 978-0-643-10135-7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.-M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.-W. MEGAHIT: An Ultra-Fast Single-Node Solution for Large and Complex Metagenomics Assembly via Succinct de Bruijn Graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.-L.; LoCascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic Gene Recognition and Translation Initiation Site Identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Lam, T.-W.; Yiu, S.-M.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, J. SOAP2: An Improved Ultrafast Tool for Short Read Alignment. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1966–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A New Generation of Protein Database Search Programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, C.; Condron, L.M.; Stewart, A.; Di, H.J.; O’Callaghan, M. Influence of Organic and Mineral Amendments on Microbial Soil Properties and Processes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2007, 35, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, S.; Raupp, J.; Joergensen, R.G. Effects of Fertilizer and Spatial Heterogeneity in Soil pH on Microbial Biomass Indices in a Long-Term Field Trial of Organic Agriculture. Plant Soil 2010, 328, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xiong, X.; Wu, C. Effects of Deep Placement of Fertilizer on Periphytic Biofilm Development and Nitrogen Cycling in Paddy Systems. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; He, R.; Hou, P.; Ding, C.; Ding, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Tang, S.; Ding, C.; Chen, L.; et al. Combined Controlled-Released Nitrogen Fertilizers and Deep Placement Effects of N Leaching, Rice Yield and N Recovery in Machine-Transplanted Rice. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Liu, F.; Li, H.; Cai, T.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z. Suitable Fertilizer Application Depth Can Increase Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Maize Yield by Reducing Gaseous Nitrogen Losses. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, G.; Li, Z.; Fan, F.; Chu, G.; Hou, Z.; Liang, Y. Soil Biological Activity and Their Seasonal Variations in Response to Long-Term Application of Organic and Inorganic Fertilizers. Plant Soil 2010, 326, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tu, P.; Yang, Y.; Xue, X.; Feng, Z.; Dan, C.; Cheng, F.; Yang, Y.; Deng, L. Diversity of Rice Rhizosphere Microorganisms under Different Fertilization Modes of Slow-Release Fertilizer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, H.; Lücker, S.; Albertsen, M.; Kitzinger, K.; Herbold, C.; Spieck, E.; Nielsen, P.H.; Wagner, M.; Daims, H. Expanded Metabolic Versatility of Ubiquitous Nitrite-Oxidizing Bacteria from the Genus Nitrospira. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11371–11376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Deng, S.; Wu, Y.; Yi, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, X.; Xing, P.; Gu, Q.; Qi, J.; Tang, X. A Rapid Increase of Soil Organic Carbon in Paddy Fields after Applying Organic Fertilizer with Reduced Inorganic Fertilizer and Water-Saving Irrigation Is Linked with Alterations in the Structure and Function of Soil Bacteria. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 379, 109353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, B.; Zeng, K.; Zhao, M.; Yin, B. Urea Deep Placement in Combination with Azolla for Reducing Nitrogen Loss and Improving Fertilizer Nitrogen Recovery in Rice Field. Field Crops Res. 2018, 218, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarula; Yang, H.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Meng, F.; Ma, J. Impact of Drip Irrigation and Nitrogen Fertilization on Soil Microbial Diversity of Spring Maize. Plants 2022, 11, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wu, P.; Dai, Z.; Wang, G.; He, S.; Gong, X.; Li, X. Effect of Side-Deep Fertilization on Yield, Nutrient Uptake and Economic Benefits of Rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2024, 38, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, B. Microbial Community Structure and Functional Metabolic Diversity Are Associated with Organic Carbon Availability in an Agricultural Soil. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 2500–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Nie, S.; Liang, J.; Zeng, G.; Wu, H.; Hua, S.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Xiao, H.; Deng, L.; et al. Effects of Heavy Metals and Soil Physicochemical Properties on Wetland Soil Microbial Biomass and Bacterial Community Structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, A.A.; Haq, S.; Bhat, R.A. Actinomycetes Benefaction Role in Soil and Plant Health. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, S.; Jogler, M.; Jogler, C. On the Maverick Planctomycetes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 739–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
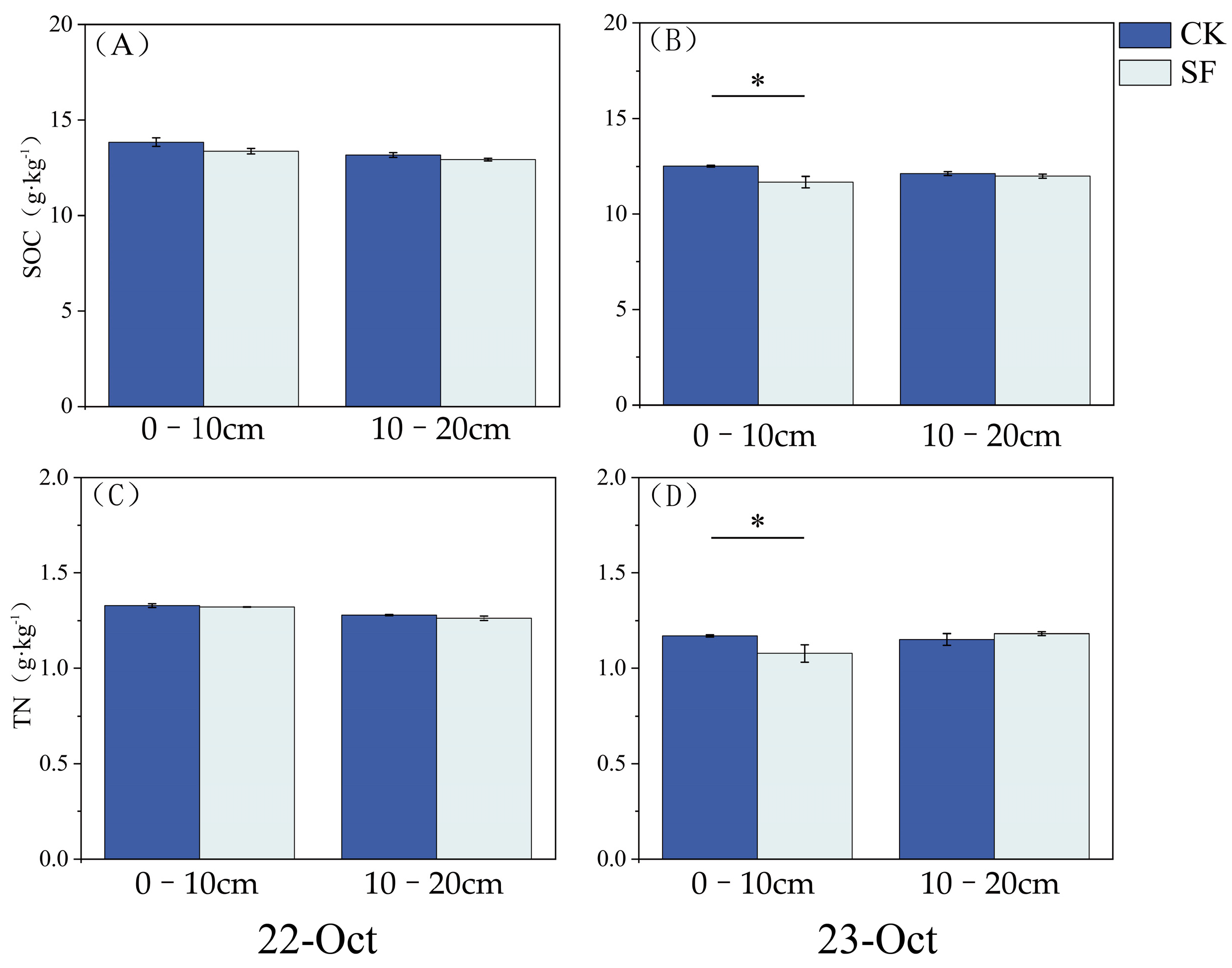

| Sampling Season | Soil Layer (cm) | Treatment | pH | TN (g kg−1) | SOC (g kg−1) | Available P (mg kg−1) | Available K (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022.10 | 0–10 | CK | 5.24 ± 0.02 a | 1.33 ± 0.01 a | 13.85 ± 0.22 a | 33.00 ± 0.47 a | 24.67 ± 0.88 a |
| SF | 5.04 ± 0.02 b | 1.32 ± 0.00 a | 13.38 ± 0.14 a | 36.96 ± 0.41 b | 20.33 ± 0.67 b | ||
| 10–20 | CK | 5.37 ± 0.01 a | 1.28 ± 0.00 a | 13.18 ± 0.12 a | 35.04 ± 0.18 a | 15.67 ± 0.67 a | |
| SF | 5.18 ± 0.00 b | 1.26 ± 0.01 a | 12.94 ± 0.07 a | 40.75 ± 0.44 b | 23.33 ± 0.33 b | ||
| 2023.10 | 0–10 | CK | 1.17 ± 0.01 a | 12.52 ± 0.05 a | 23.22 ± 0.23 a | 22.67 ± 2.19 a | |
| SF | 1.08 ± 0.05 b | 11.67 ± 0.30 b | 25.70 ± 0.74 b | 22.00 ± 0.58 a | |||
| 10–20 | CK | 1.15 ± 0.03 a | 12.10 ± 0.10 a | 27.30 ± 0.53 a | 19.33 ± 0.88 a | ||
| SF | 1.18 ± 0.01 a | 11.97 ± 0.10 a | 27.42 ± 0.50 a | 20.67 ± 1.45 a |
| KO | KEGG Name | KO Description | Pathway ID | Pathway Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K04561 | norB | nitric oxide reductase subunit B [EC:1.7.2.5] | ko01100; ko01120; ko00910 | Metabolic pathways; Microbial metabolism in diverse environments; Nitrogen metabolism |
| K00371 | narH, narY, nxrB | nitrate reductase/nitrite oxidoreductase, beta subunit [EC:1.7.5.1 1.7.99.-] | ko01120; ko01100; ko00910 | Microbial metabolism in diverse environments; Metabolic pathways; Nitrogen metabolism |
| K02591 | nifK | nitrogenase molybdenum-iron protein beta chain [EC:1.18.6.1] | ko00910; ko00625; ko01100; ko01120 | Nitrogen metabolism; Chloroalkane and chloroalkene degradation; Metabolic pathways; Microbial metabolism in diverse environments |
| K02567 | napA | nitrate reductase (cytochrome) [EC:1.9.6.1] | ko01120; ko01100; ko00910 | Microbial metabolism in diverse environments; Metabolic pathways; Nitrogen metabolism |
| K02588 | nifH | nitrogenase iron protein NifH | ko01100; ko01120; ko00625; ko00910 | Metabolic pathways; Microbial metabolism in diverse environments; Chloroalkane and chloroalkene degradation; Nitrogen metabolism |
| K02568 | napB | nitrate reductase (cytochrome), electron transfer subunit | ko01120; ko01100; ko00910 | Microbial metabolism in diverse environments; Metabolic pathways; Nitrogen metabolism |
| K00370 | narG, narZ, nxrA | nitrate reductase/nitrite oxidoreductase, alpha subunit [EC:1.7.5.1 1.7.99.-] | ko01100; ko01120; ko00910 | Metabolic pathways; Microbial metabolism in diverse environments; Nitrogen metabolism |
| K00376 | nosZ | nitrous-oxide reductase [EC:1.7.2.4] | ko01120; ko01100; ko00910 | Microbial metabolism in diverse environments; Metabolic pathways; Nitrogen metabolism |
| K00374 | narI, narV | nitrate reductase gamma subunit [EC:1.7.5.1 1.7.99.-] | ko00910; ko01120; ko01100 | Nitrogen metabolism; Microbial metabolism in diverse environments; Metabolic pathways |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Q.-H.; Yao, X.-B.; Yang, Y.; Li, D.-J.; Qi, J.-Y. Effects of Deep Application of Fertilizer on Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Functions in Rice Paddies. Agronomy 2025, 15, 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040938
Xie Q-H, Yao X-B, Yang Y, Li D-J, Qi J-Y. Effects of Deep Application of Fertilizer on Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Functions in Rice Paddies. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):938. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040938
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Qi-Huan, Xiang-Bin Yao, Ya Yang, De-Jin Li, and Jian-Ying Qi. 2025. "Effects of Deep Application of Fertilizer on Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Functions in Rice Paddies" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040938
APA StyleXie, Q.-H., Yao, X.-B., Yang, Y., Li, D.-J., & Qi, J.-Y. (2025). Effects of Deep Application of Fertilizer on Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Functions in Rice Paddies. Agronomy, 15(4), 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040938







