Remediation of Coastal Wetland Soils Co-Contaminated with Microplastics and Cadmium Using Spartina alterniflora Biochar: Soil Quality, Microbial Communities, and Plant Growth Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biochar Preparation
2.2. Selection and Preparation of MPs
2.3. Soil Collection and Incubation Experiment
2.4. Soil Properties Analyses
2.5. Pot Experiment of Suaeda salsa (S. salsa)
2.6. Analysis of Microbial Communities
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results Analysis and Discussion
3.1. Soil Properties
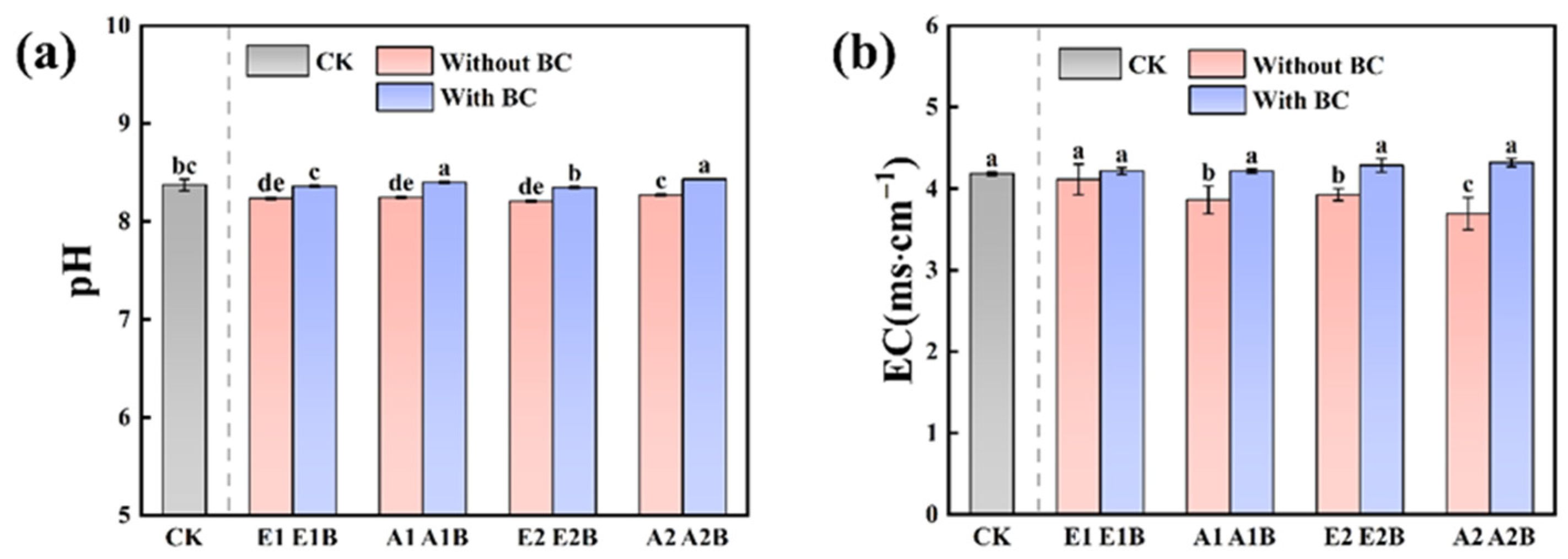
3.1.1. Soil pH and EC
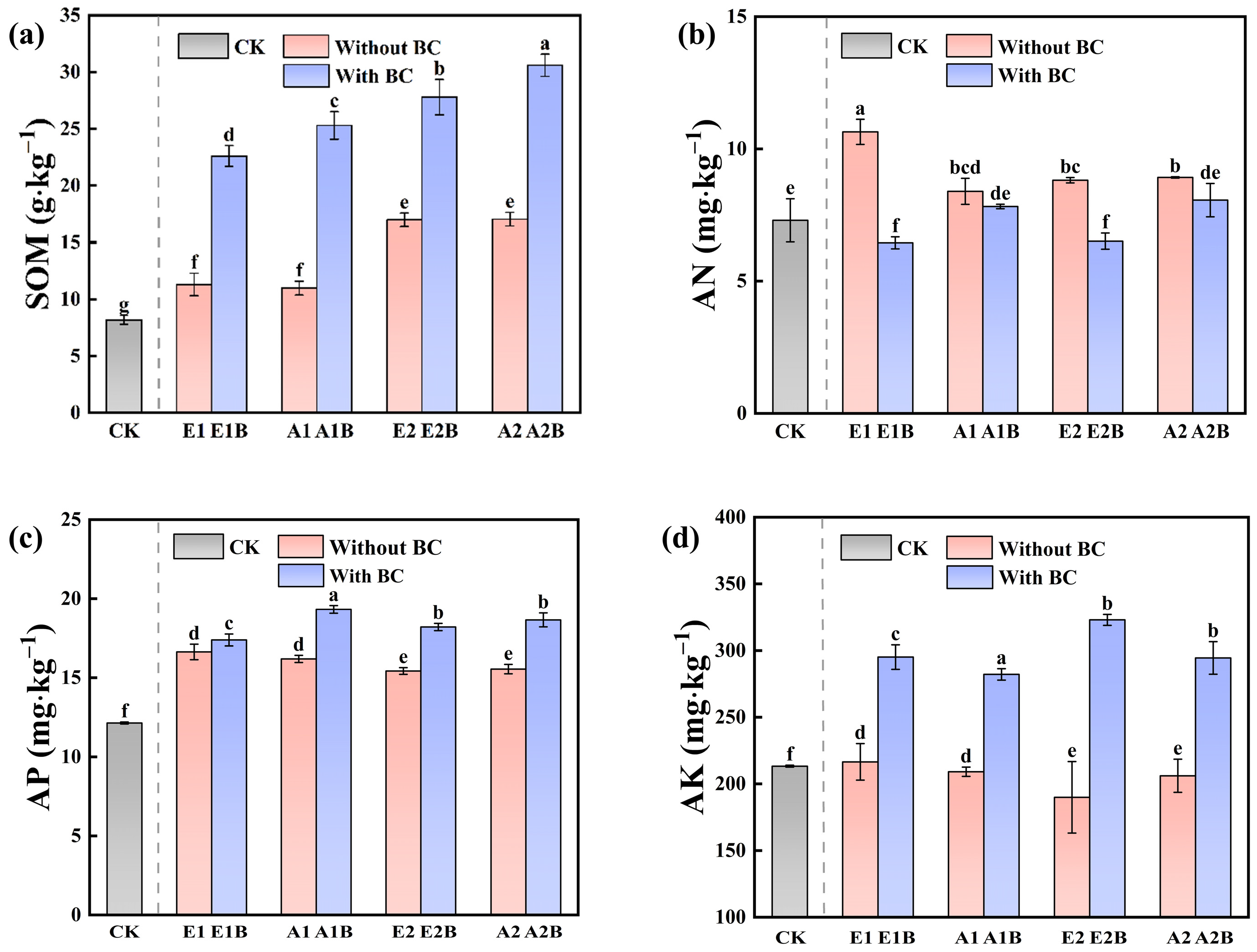
3.1.2. Soil Basic Nutrients
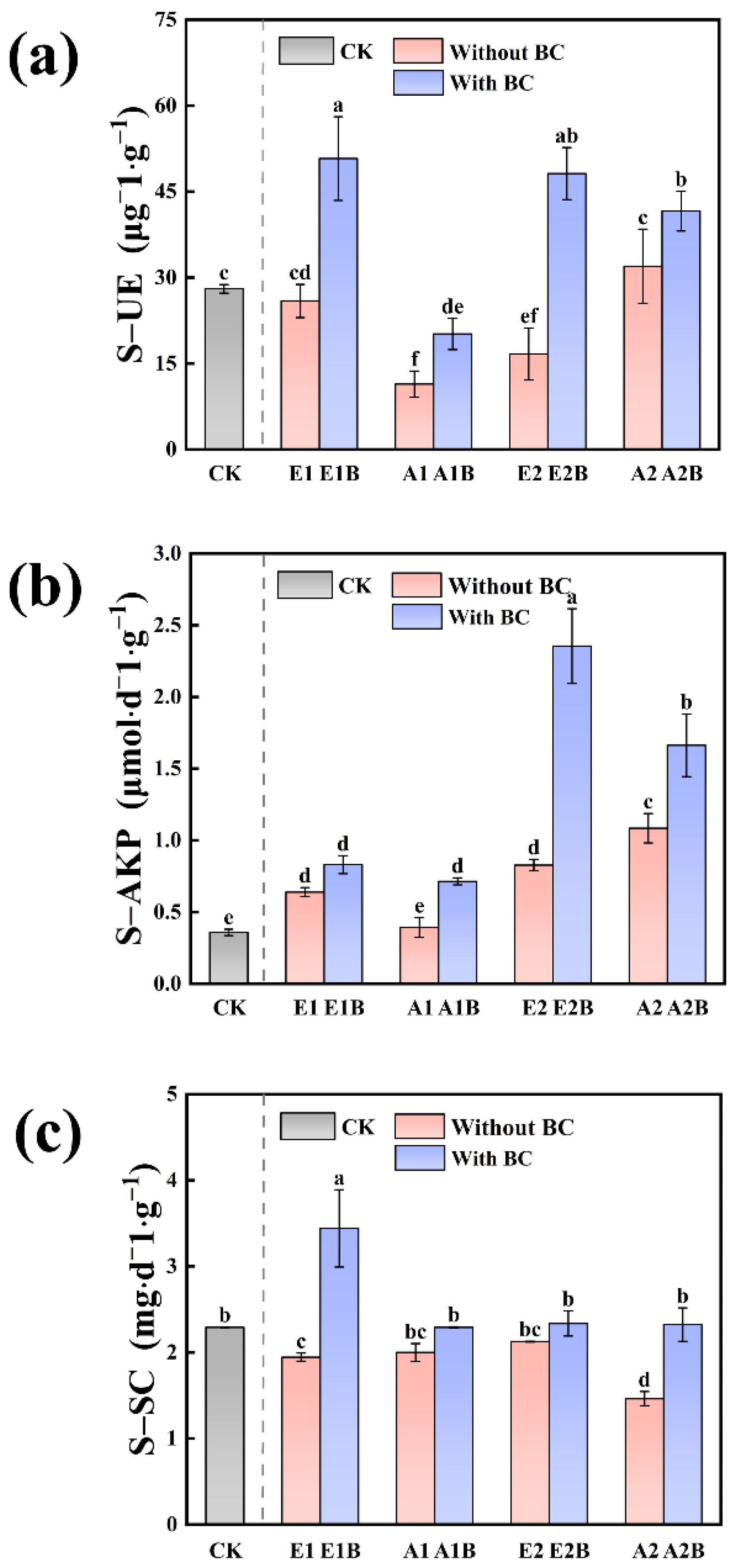
3.1.3. Enzyme Activities
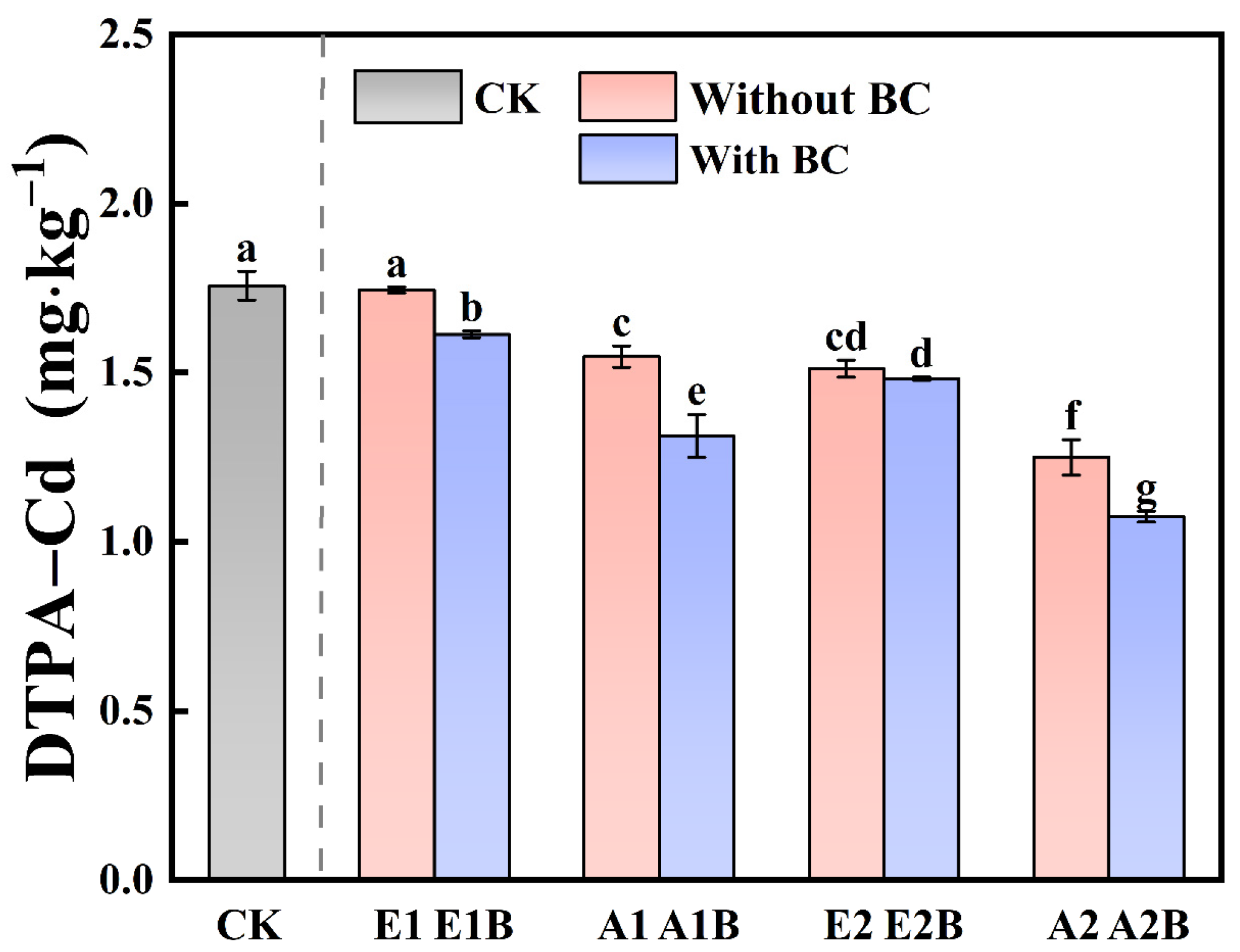
3.2. Soil Available Cd
3.3. Bacterial Community Diversity and Structure
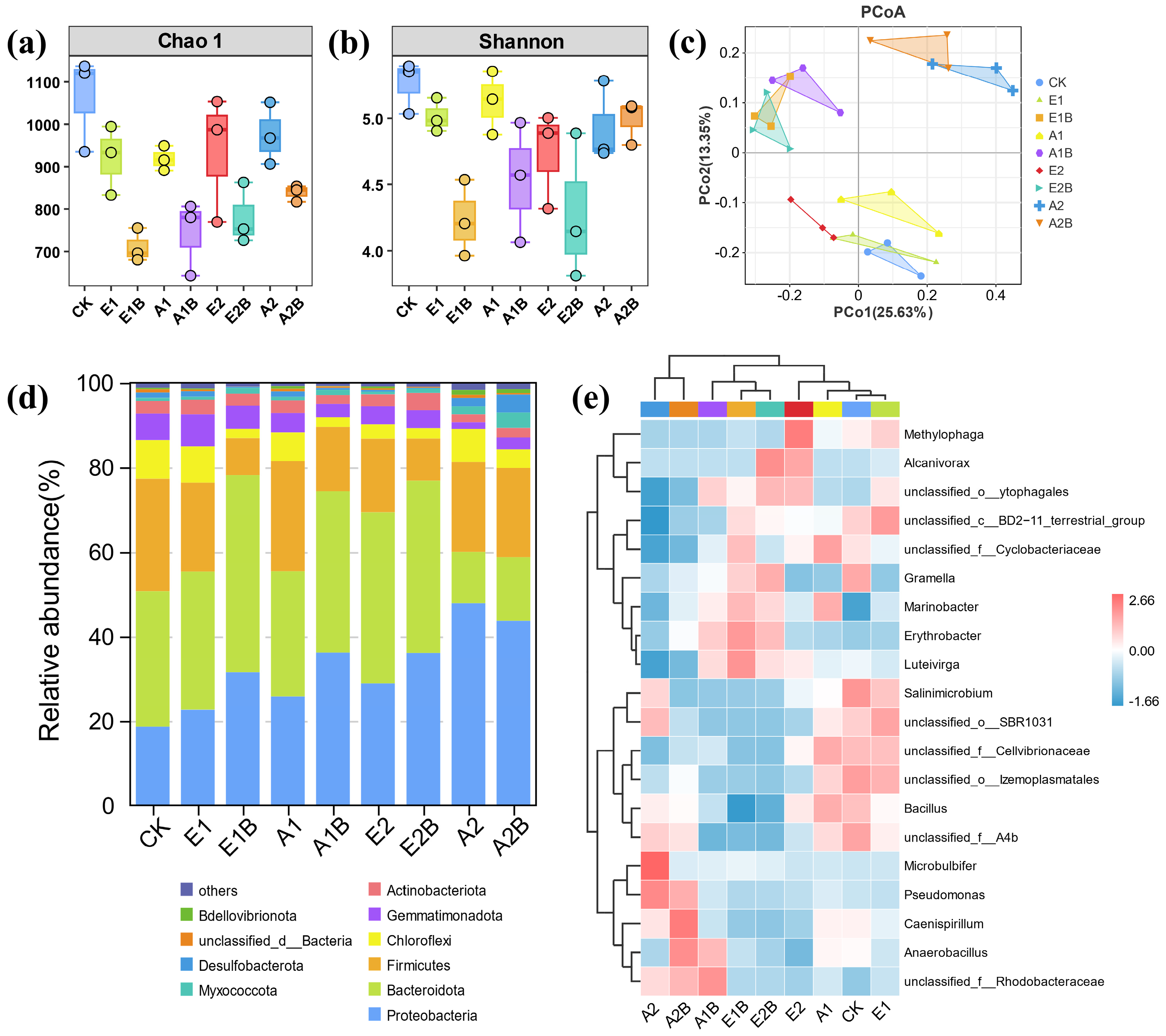
3.3.1. Microbial Diversity
3.3.2. Characteristics of Bacterial Community Structure
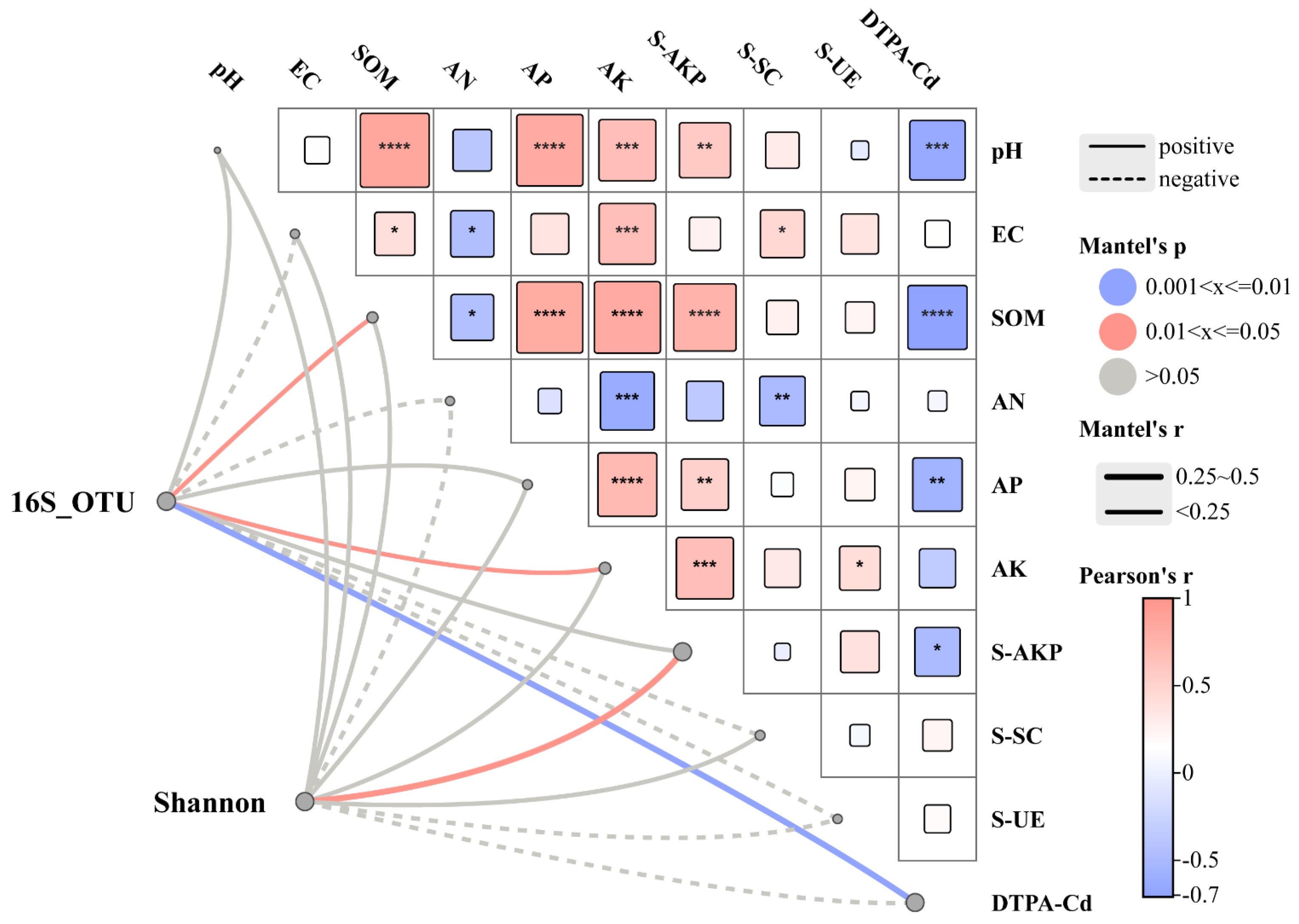
3.3.3. Environmental Factor Analysis of Microorganisms
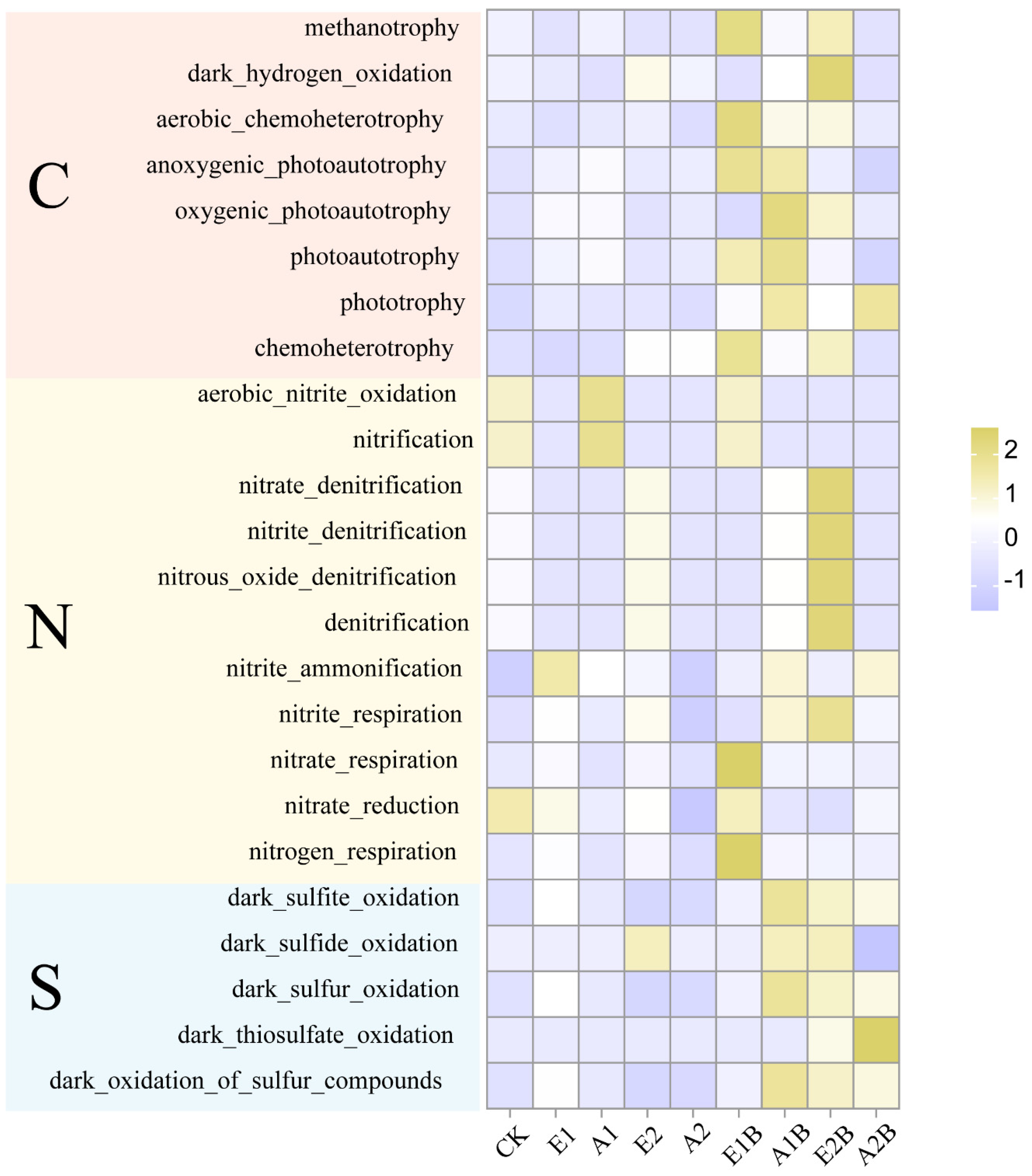
3.4. Response of Microbial Community Functions to Restoration
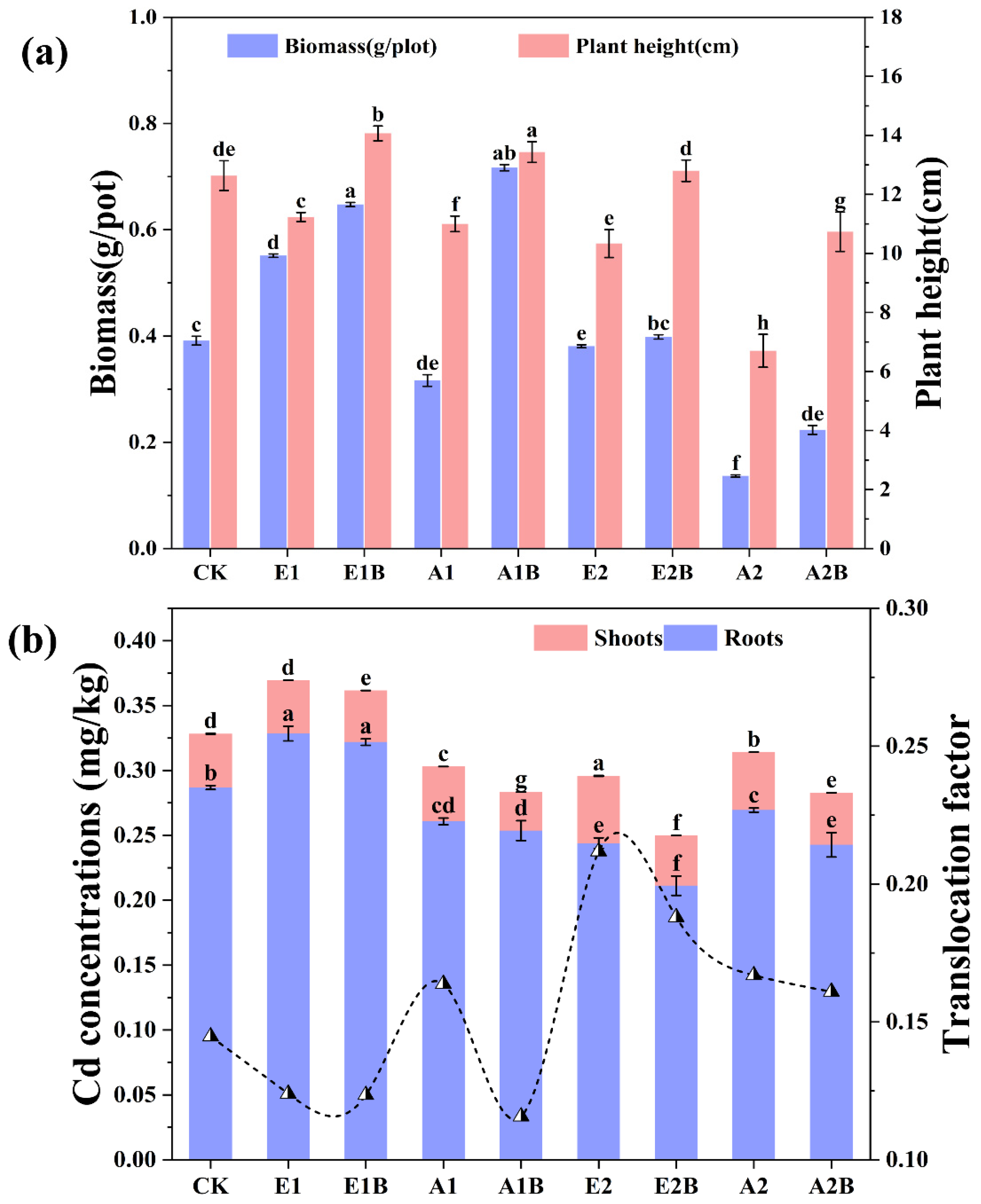
3.5. Enhancement of BC on S. salsa Growth
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drewniok, M.P.; Gao, Y.; Cullen, J.M.; Cabrera Serrenho, A. What to Do about Plastics? Lessons from a Study of United Kingdom Plastics Flows. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 4513–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Paul Chen, J. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection. Water Res. 2018, 137, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Hamidian, A.H.; Tubic, A.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, J.K.H.; Wu, C.; Lam, P.K.S. Understanding plastic degradation and microplastic formation in the environment: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 116554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Luo, Y.; Li, R.; Zhou, Q.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Yin, N.; Yang, J.; Tu, C.; Zhang, Y. Effective uptake of submicrometre plastics by crop plants via a crack-entry mode. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Lee, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Hu, H. Distribution of Heavy Metal Pollution in Surface Soil Samples in China: A Graphical Review. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 97, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Song, N. Polyethylene microplastics increase cadmium uptake in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) by altering the soil microenvironment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, D.; Wu, D.; Guo, H.; Han, S. Influence of polyethylene-microplastic on environmental behaviors of metals in soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 28329–28336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medyńska-Juraszek, A.; Jadhav, B. Influence of Different Microplastic Forms on pH and Mobility of Cu2+ and Pb2+ in Soil. Molecules 2022, 27, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Xu, J.; Allen, S.D.; Khan, S.; Nadir, S.; Arif, M.S.; Yasmeen, T. Unraveling consequences of soil micro- and nano-plastic pollution on soil-plant system: Implications for nitrogen (N) cycling and soil microbial activity. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, G.; Zhai, J.; Xu, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. Ecotoxicological effects of co-exposure biodegradable microplastics polylactic acid with cadmium are higher than conventional microplastics polystyrene with cadmium on the earthworm. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Kong, F.; Xi, M. The amelioration and improvement effects of modified biochar derived from Spartina alterniflora on coastal wetland soil and Suaeda salsa growth. Environ. Res. 2024, 240, 117426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.-F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.-X.; Li, H.-L.; Xia, H.-J.; Kong, W.-J.; Yu, F.-H. Remediation of cadmium-contaminated coastal saline-alkaline soil by Spartina alterniflora derived biochar. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Bing, X.; Jiao, L.; Xiao, H.; Li, B.; Sun, H. Amelioration effects of coastal saline-alkali soil by ball-milled red phosphorus-loaded biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Xu, Z.; Hou, D.; Gao, B.; Cao, X.; Ok, Y.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Bolan, N.S.; Tsang, D.C.W. Waste-derived biochar for water pollution control and sustainable development. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 444–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.M.; Mosa, A.; Natasha; Arockiam Jeyasundar, P.G.S.; Hassan, N.E.E.; Yang, X.; Antoniadis, V.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; et al. Pros and Cons of Biochar to Soil Potentially Toxic Element Mobilization and Phytoavailability: Environmental Implications. Earth Syst. Environ. 2023, 7, 321–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Tang, Z.; Luo, X.; Zheng, Z. Spartina alterniflora-derived porous carbon using as anode material for sodium-ion battery. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Tang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q. Remediation of cadmium-contaminated soil with biochar simultaneously improves biochar’s recalcitrance. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Mo, X.; Meng, W.; Hu, B.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Lu, X.; Sparks, J.P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Biochar may alter plant communities when remediating the cadmium-contaminated soil in the saline-alkaline wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 165677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, Q.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qian, G. Cu(II) removal from aqueous solution by Spartina alterniflora derived biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 141, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, F. Microplastics change soil properties, heavy metal availability and bacterial community in a Pb-Zn-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 18668-2002; Marine Sediment Quality. Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Yuan, Y.; Tang, X.; Jia, Z.; Li, C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J. The Effects of Ecological Factors on the Main Medicinal Components of Dendrobium officinale Under Different Cultivation Modes. Forests 2020, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; Dong, H.; Sarkar, B.; Song, H.; Li, J.; Bolan, N.; Quin, B.F.; Yang, X.; Li, F.; et al. Chitin and crawfish shell biochar composite decreased heavy metal bioavailability and shifted rhizosphere bacterial community in an arsenic/lead co-contaminated soil. Environ. Int. 2023, 176, 107989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Long, C.; Wang, D.; Yang, J. Phytoremediation of cadmium (Cd) and uranium (U) contaminated soils by Brassica juncea L. enhanced with exogenous application of plant growth regulators. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Guo, H.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Z. Cr(VI) immobilization in soil using lignin hydrogel supported nZVI: Immobilization mechanisms and long-term simulation. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yan, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Andom, O.; Li, Z. Microplastics alter cadmium accumulation in different soil-plant systems: Revealing the crucial roles of soil bacteria and metabolism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 474, 134768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, L.; Cheng, Z.; Yao, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wang, L.; Sun, H. LDPE microplastics affect soil microbial communities and nitrogen cycling. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Ippolito, J.A.; Noerpel, M.; Scheckel, K.G.; Yan, J. Nutrient alterations following biochar application to a Cd-contaminated solution and soil. Biochar 2021, 3, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, M.; Lu, X.; Meng, Z.; Liu, J.; Mo, X. Biochar addition can negatively affect plant community performance when altering soil properties in saline-alkali wetlands. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1347658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zu, M.; Li, R.; Zuo, J.; Tao, J. Soil properties, microbial diversity, and changes in the functionality of saline-alkali soil are driven by microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 446, 130712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zheng, H.; Wang, X. Effects of soil amendments on fractions and stability of soil organic matter in saline-alkaline paddy. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 112993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillig, M.C.; Leifheit, E.; Lehmann, J. Microplastic effects on carbon cycling processes in soils. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Piao, J.; Miao, S.; Che, W.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Shiraiwa, T.; Tanaka, T.; Taniyoshi, K.; Hua, S.; et al. Long-term effects of biochar one-off application on soil physicochemical properties, salt concentration, nutrient availability, enzyme activity, and rice yield of highly saline-alkali paddy soils: Based on a 6-year field experiment. Biochar 2024, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.N.; Xu, C.-Y.; Tahmasbian, I.; Che, R.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wallace, H.M.; Bai, S.H. Effects of biochar on soil available inorganic nitrogen: A review and meta-analysis. Geoderma 2017, 288, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.L.; Meyer, K.M.; Garcia-Jaramillo, M.; Weidman, C.S.; Stewart, C.E.; Wanzek, T.; Grusak, M.A.; Watts, D.W.; Novak, J.; Trippe, K.M. Towards predicting biochar impacts on plant-available soil nitrogen content. Biochar 2022, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sima, J.; Zhao, L.; Mašek, O.; Cao, X. Indispensable role of biochar-inherent mineral constituents in its environmental applications: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manasa, M.R.K.; Katukuri, N.R.; Darveekaran Nair, S.S.; Haojie, Y.; Yang, Z.; Guo, R.b. Role of biochar and organic substrates in enhancing the functional characteristics and microbial community in a saline soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 269, 110737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Machado, A.A.; Lau, C.W.; Kloas, W.; Bergmann, J.; Bachelier, J.B.; Faltin, E.; Becker, R.; Görlich, A.S.; Rillig, M.C. Microplastics Can Change Soil Properties and Affect Plant Performance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6044–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Yang, J.; Guo, Y.; Wu, X.; Tian, Y.; Li, H.; Awasthi, M.K. Pollution control in biochar-driven clean composting: Emphasize on heavy metal passivation and gaseous emissions mitigation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-H.; Wang, H.-Y.; Kuo, J.; Lo, S.-L. Adsorption and desorption characteristics of heavy metals onto conventional and biodegradable plastics. Chemosphere 2023, 333, 138920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Hou, J.; Dang, Q.; Cui, D.; Xi, B.; Tan, W. Decrease in bioavailability of soil heavy metals caused by the presence of microplastics varies across aggregate levels. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, C.; Yang, X.; Niazi, N.K.; Xu, X.; Wen, Y.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S.; Xu, S.; Wang, H. Impact of sugarcane bagasse-derived biochar on heavy metal availability and microbial activity: A field study. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; He, J.; Chen, Q.; He, F.; Wei, T.; Jia, H.; Guo, J. Marked changes in biochar’s ability to directly immobilize Cd in soil with aging: Implication for biochar remediation of Cd-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 73856–73864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, T.; Chang, S.X.; Jiang, X.; Song, Y. Biochar increases soil microbial biomass but has variable effects on microbial diversity: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 749, 141593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilliam, R.S.; Glanville, H.C.; Wade, S.C.; Jones, D.L. Life in the ‘charosphere’—Does biochar in agricultural soil provide a significant habitat for microorganisms? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Niu, L.; Su, A.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y. Sustained and efficient remediation of biochar immobilized with Sphingobium abikonense on phenanthrene-copper co-contaminated soil and microbial preferences of the bacteria colonized in biochar. Biochar 2023, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.Y.; Yi, T.; Song, X.P.; Liu, H.; Yang, H.J.; Huang, J.G. Mobilization of recalcitrant phosphorous and enhancement of pepper P uptake and yield by a new biocontrol and bioremediation bacterium Burkholderia cepacia CQ18. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Liu, J.; Ma, W.; Gao, X. Remediation of cadmium-contaminated soil by biochar-loaded nano-zero-valent iron and its microbial community responses. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Liu, J.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. Changes of bacterial community compositions after three years of biochar application in a black soil of northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 113, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Singh, B.P.; Li, G.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, X. Biochar application constrained native soil organic carbon accumulation from wheat residue inputs in a long-term wheat-maize cropping system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 252, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Shao, L.; Lü, F. Removal of Copper (II) by Biochar Mediated by Dissolved Organic Matter. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Lee, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Long-term effects of biochar amendment on rhizosphere and bulk soil microbial communities in a karst region, southwest China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 140, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussud, C.; Hudec, C.; George, M.; Fabre, P.; Higgs, P.; Bruzaud, S.; Delort, A.-M.; Eyheraguibel, B.; Meistertzheim, A.-L.; Jacquin, J.; et al. Colonization of Non-biodegradable and Biodegradable Plastics by Marine Microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquin, J.; Cheng, J.; Odobel, C.; Pandin, C.; Conan, P.; Pujo-Pay, M.; Barbe, V.; Meistertzheim, A.-L.; Ghiglione, J.-F. Microbial Ecotoxicology of Marine Plastic Debris: A Review on Colonization and Biodegradation by the “Plastisphere”. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Bai, S.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Tang, L.; Dasgupta, S.; Tang, Y.; Peng, X. Volcanic ash inputs enhance the deep-sea seabed metal-biogeochemical cycle: A case study in the Yap Trench, western Pacific Ocean. Mar. Geol. 2020, 430, 106340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Mu, C.; Lin, X.; Ma, W.; Wu, H.; Si, D.; Ge, C.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, L.; Li, H.; et al. Foliar Application of Nanoparticles Reduced Cadmium Content in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Grains via Long-Distance “Leaf–Root–Microorganism” Regulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 6900–6912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.Y.; Xie, L.L.; Jin, D.C.; Mi, B.B.; Wang, D.H.; Li, X.F.; Dai, X.Z.; Zou, X.X.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Y.Q.; et al. Bacterial community response to cadmium contamination of agricultural paddy soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 139, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, Q.; Gong, G.; Wang, G.; Guo, X.; Xu, X. Effects of soil chemical properties and fractions of Pb, Cd, and Zn on bacterial and fungal communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Shao, T.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Sun, Q.; Long, X.; Yue, Y.; Gao, X.; Rengel, Z. Effects of planting L. on soil properties and microbial community in saline-alkali soil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2951–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Gupta, V.V.S.R.; Degryse, F.; McLaughlin, M.J. Abundance and diversity of sulphur-oxidising bacteria and their role in oxidising elemental sulphur in cropping soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Wen, C.; Yan, C. Meta-analysis reveals the combined effects of microplastics and heavy metal on plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Tang, Y.; Khan, K.Y.; Son, Y.; Jung, J.; Qiu, X.; Zhao, X.; Iqbal, B.; Stoffella, P.J.; Kim, G.-J.; et al. The toxicological effect on pak choi of co-exposure to degradable and non-degradable microplastics with oxytetracycline in the soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 268, 115707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, P.; Zhao, S.; Shi, H.; Zhu, Y.; Teng, Y.; Jiang, G.; Liu, S. Combined effects of microplastics and cadmium on the soil-plant system: Phytotoxicity, Cd accumulation and microbial activity. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 121960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.; Pan, X.; Zhang, W.; Dong, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ran, J.; Zhou, D.; Li, G.; Zheng, Z. Remediation of Coastal Wetland Soils Co-Contaminated with Microplastics and Cadmium Using Spartina alterniflora Biochar: Soil Quality, Microbial Communities, and Plant Growth Responses. Agronomy 2025, 15, 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040877
Shi J, Pan X, Zhang W, Dong J, Zhao Y, Ran J, Zhou D, Li G, Zheng Z. Remediation of Coastal Wetland Soils Co-Contaminated with Microplastics and Cadmium Using Spartina alterniflora Biochar: Soil Quality, Microbial Communities, and Plant Growth Responses. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040877
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Jing, Xiangyu Pan, Weizhen Zhang, Jing Dong, Yu Zhao, Jiao Ran, Dan Zhou, Guo Li, and Zheng Zheng. 2025. "Remediation of Coastal Wetland Soils Co-Contaminated with Microplastics and Cadmium Using Spartina alterniflora Biochar: Soil Quality, Microbial Communities, and Plant Growth Responses" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040877
APA StyleShi, J., Pan, X., Zhang, W., Dong, J., Zhao, Y., Ran, J., Zhou, D., Li, G., & Zheng, Z. (2025). Remediation of Coastal Wetland Soils Co-Contaminated with Microplastics and Cadmium Using Spartina alterniflora Biochar: Soil Quality, Microbial Communities, and Plant Growth Responses. Agronomy, 15(4), 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040877






