Maize Seed Damage Identification Method Based on Improved YOLOV8n
Abstract
1. Introduction
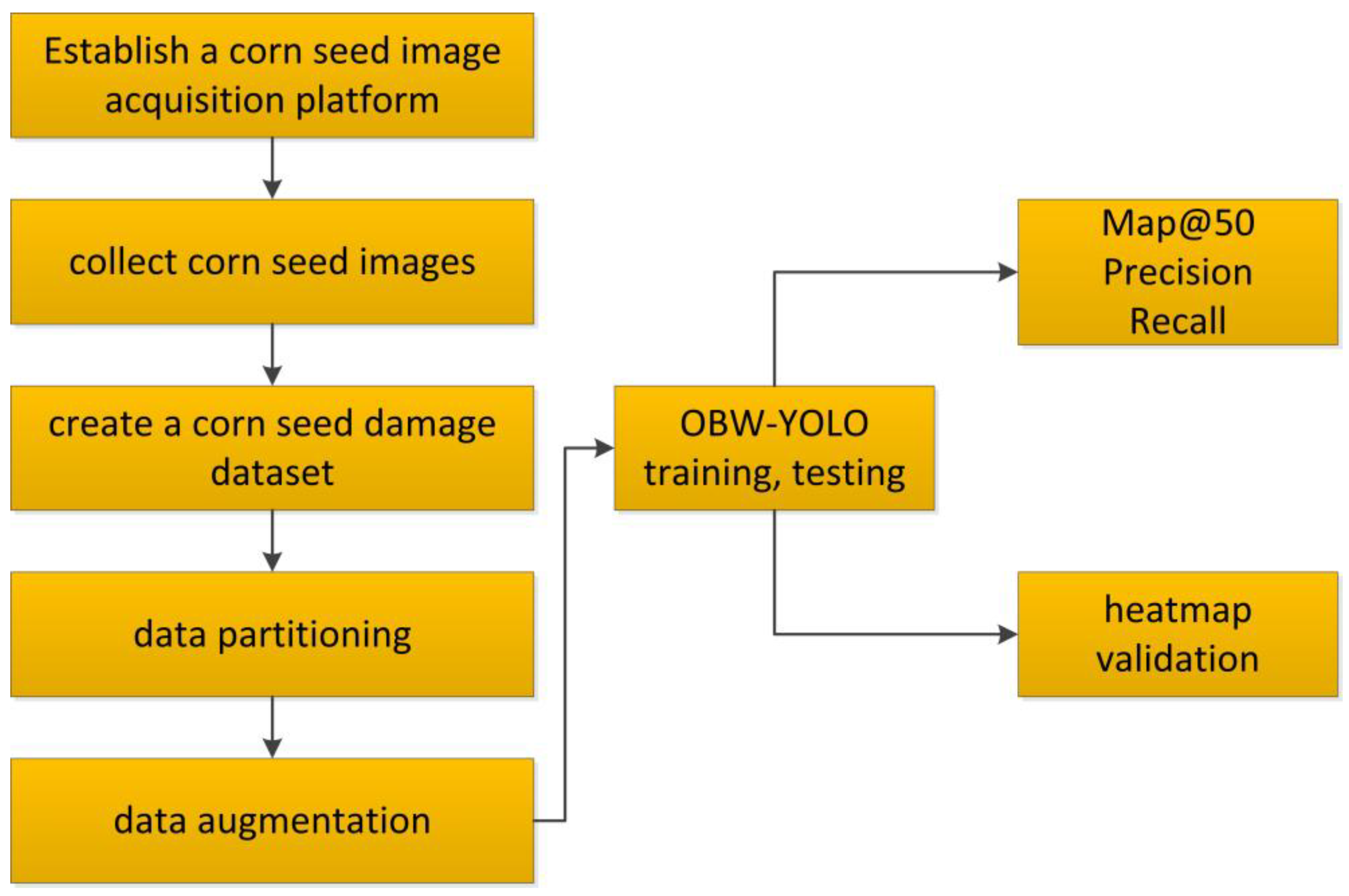
2. Materials and Methods
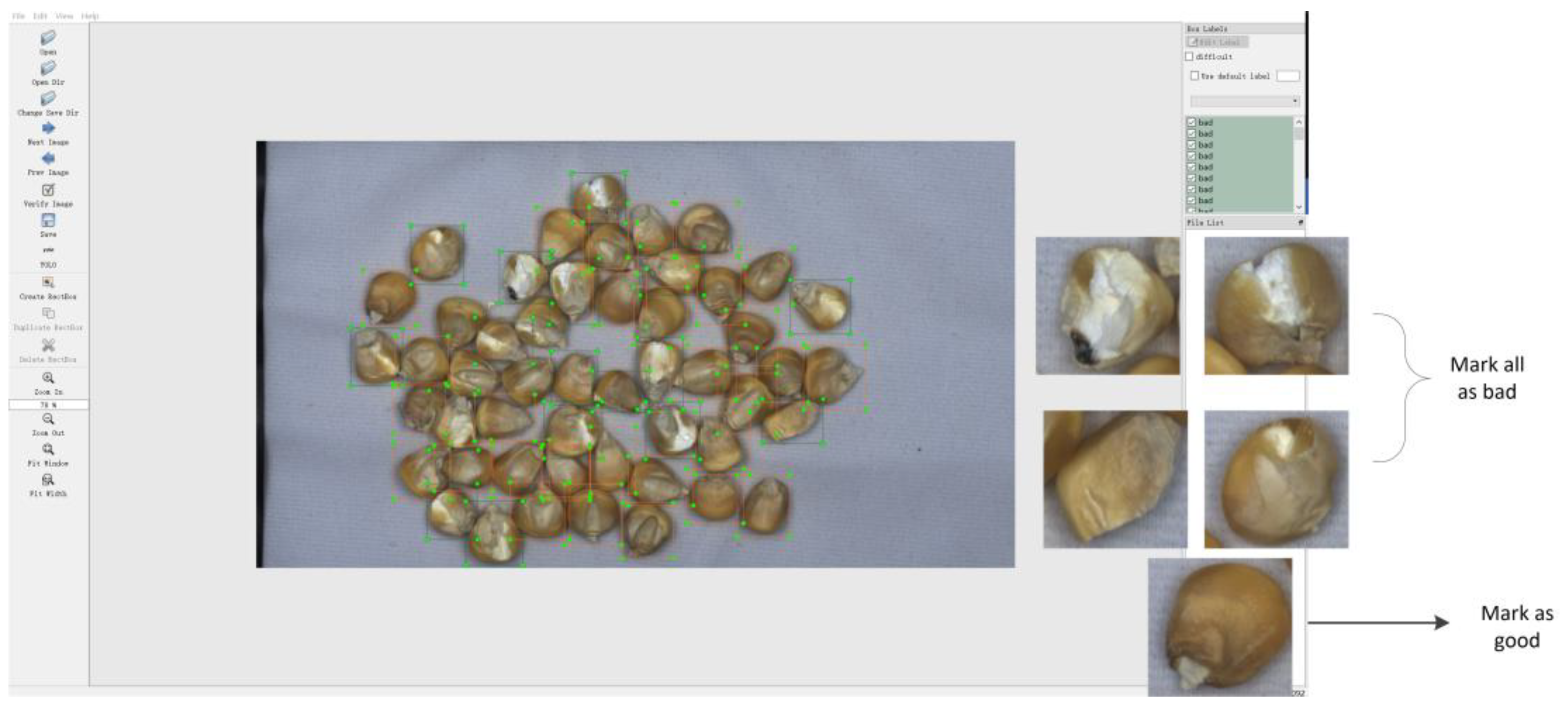
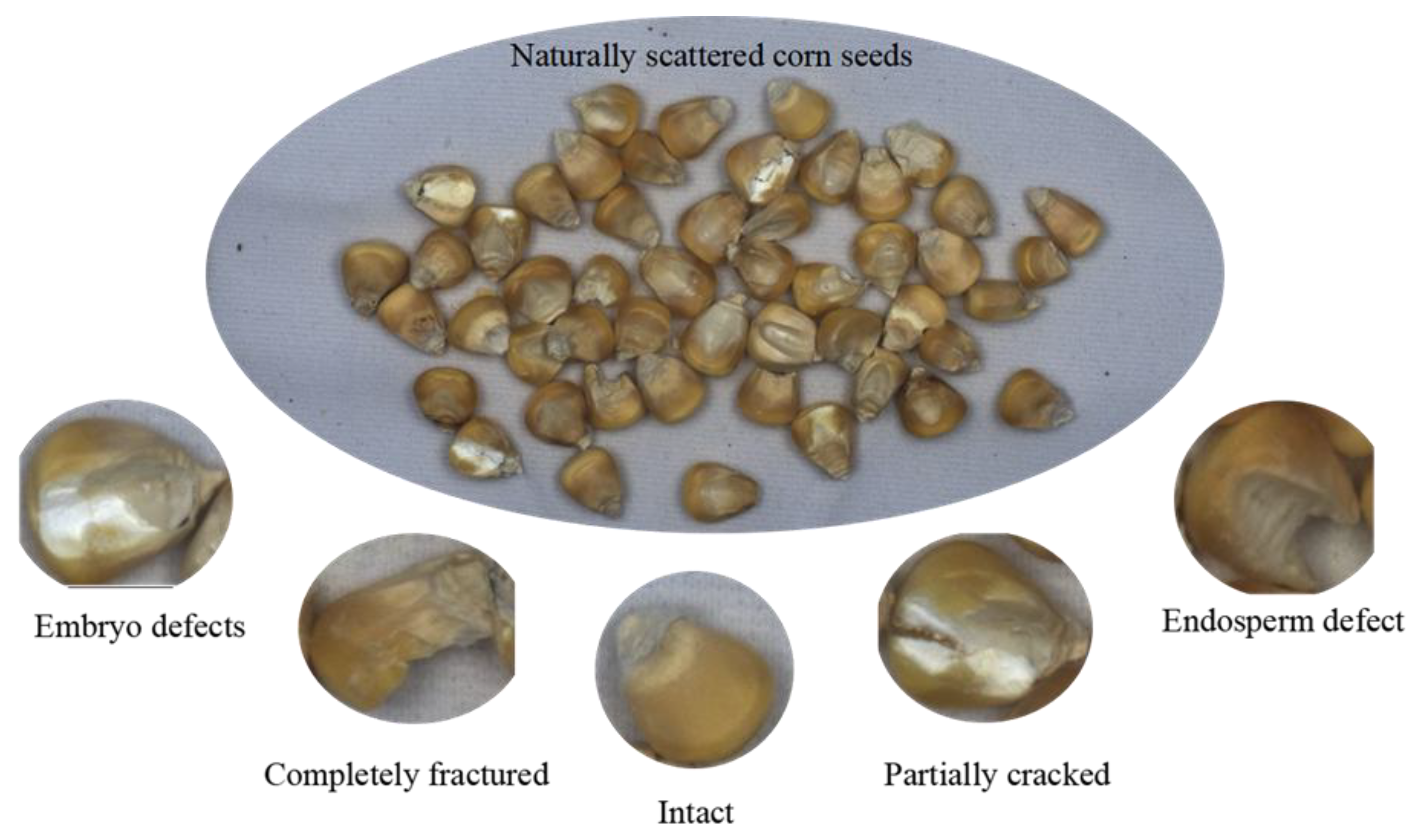
2.1. Development of a Cracked Maize Seed Dataset
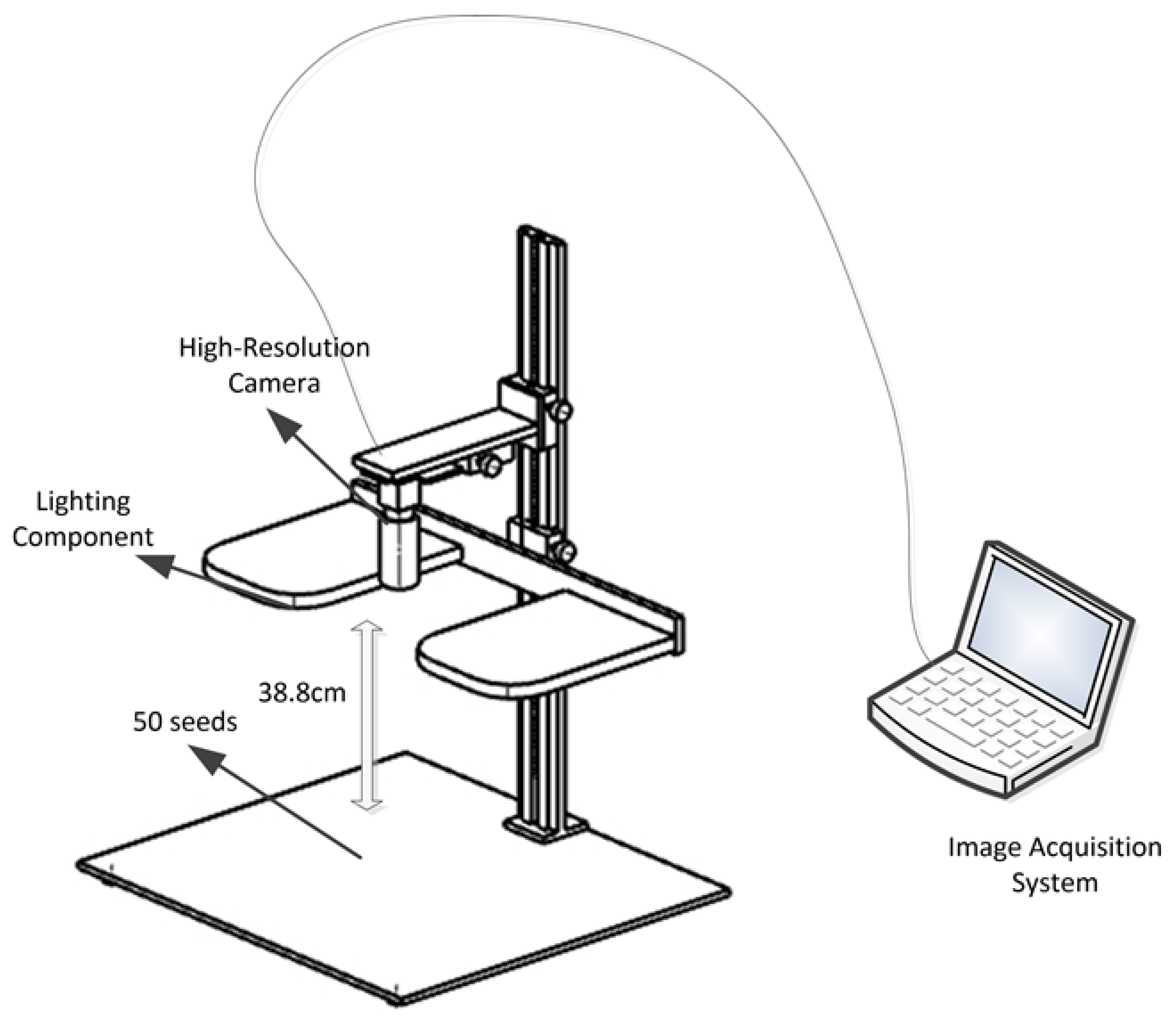
2.1.1. Image Acquisition
- (1)
- Adjustable Camera Platform: A custom-designed platform that supports fine-tuning of camera height, ensuring precise adjustment of the shooting angle. The adjustable height range is from 10 cm to 50 cm.
- (2)
- Lighting Component: The system consists of two LED lights, both from the brand RL and model RL-11, with a color temperature range from 2700 K to 5500 K. These lights provide uniform illumination to optimize image quality. The LED lights are manufactured in Shaoxing, China, by Shaoxing Creative Imaging Equipment Co., Ltd.
- (3)
- High-resolution Camera: Equipped with a 20-megapixel area scan camera, model MV-CS200-10UC by Hikvision, along with a 2000-pixel adjustable zoom lens for brightness control, ensuring high-precision image capture. The equipment manufactured by Hikvision in Hangzhou, China.
- (4)
- Image Acquisition System: A computer running Hikvision image acquisition software MSV-4.1.0, used for real-time image data capture and processing.
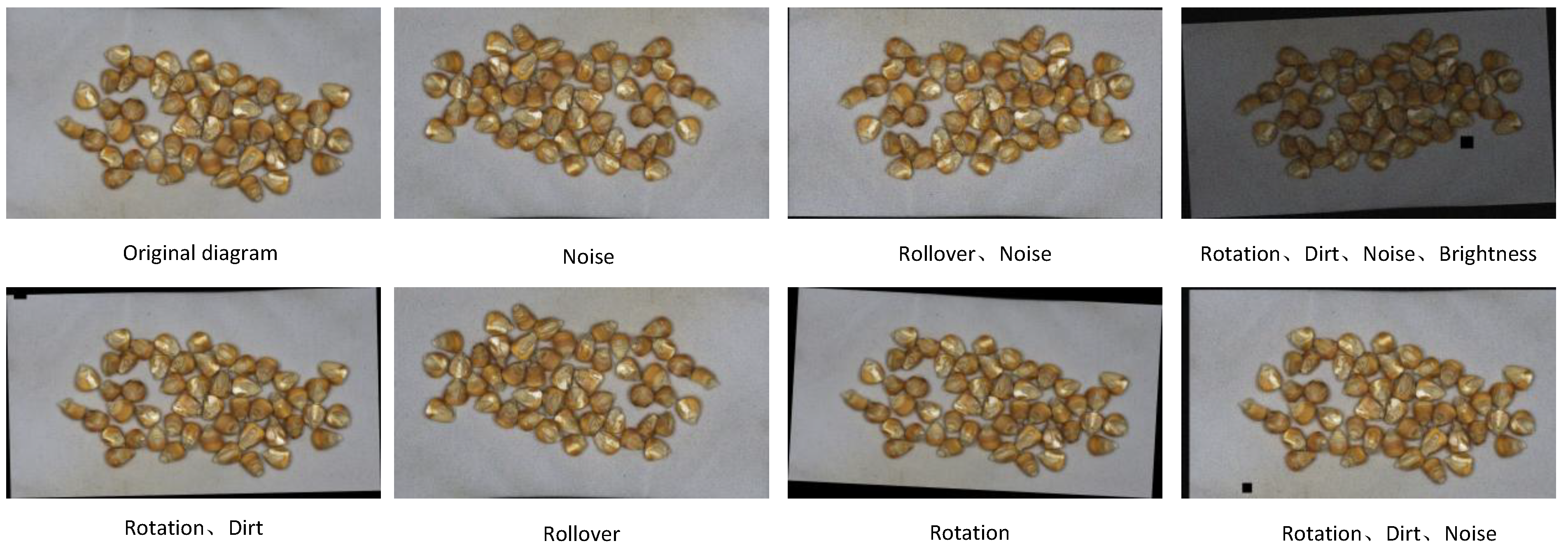
2.1.2. Data Enhancement
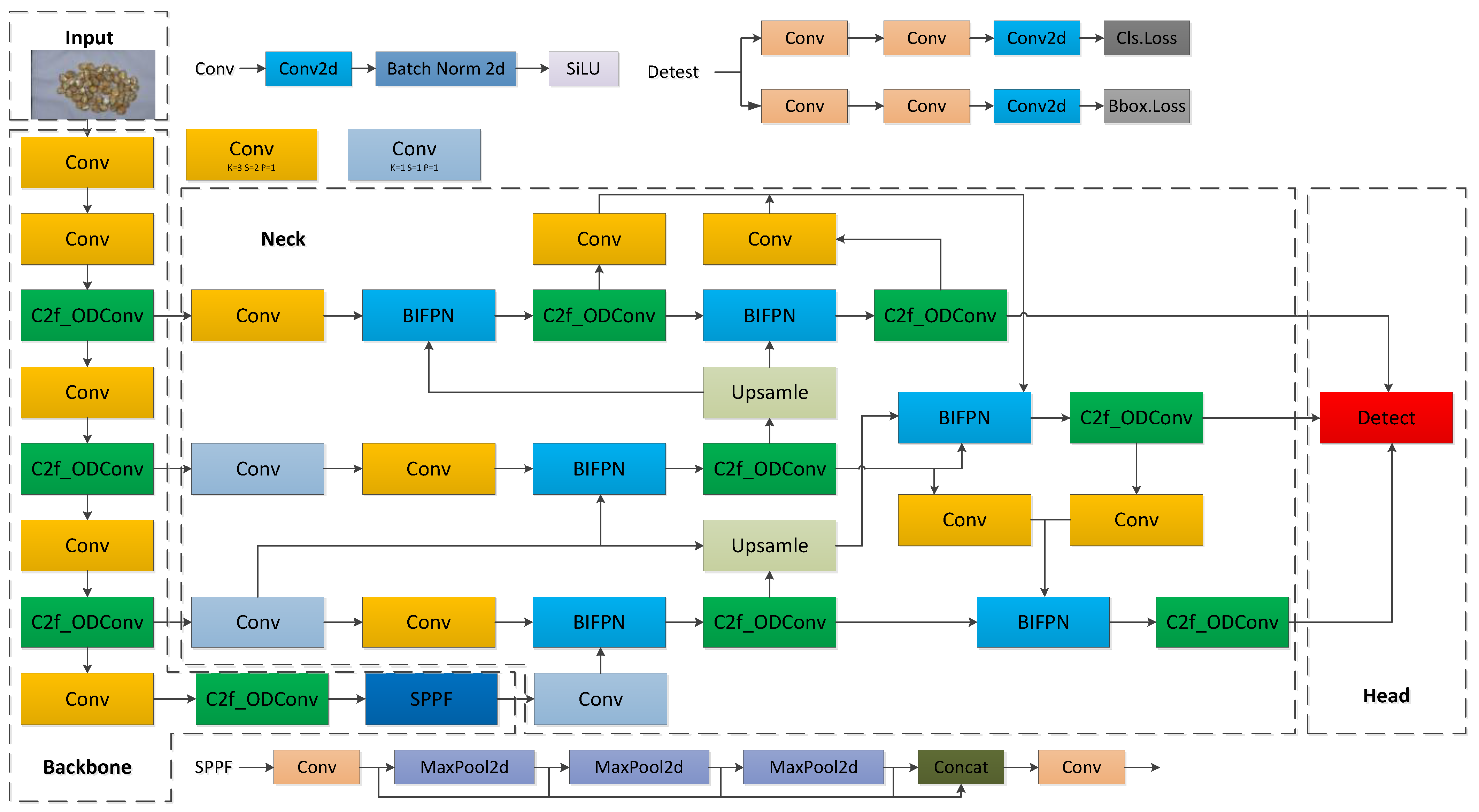
2.2. The Network Structure of OWB-YOLO
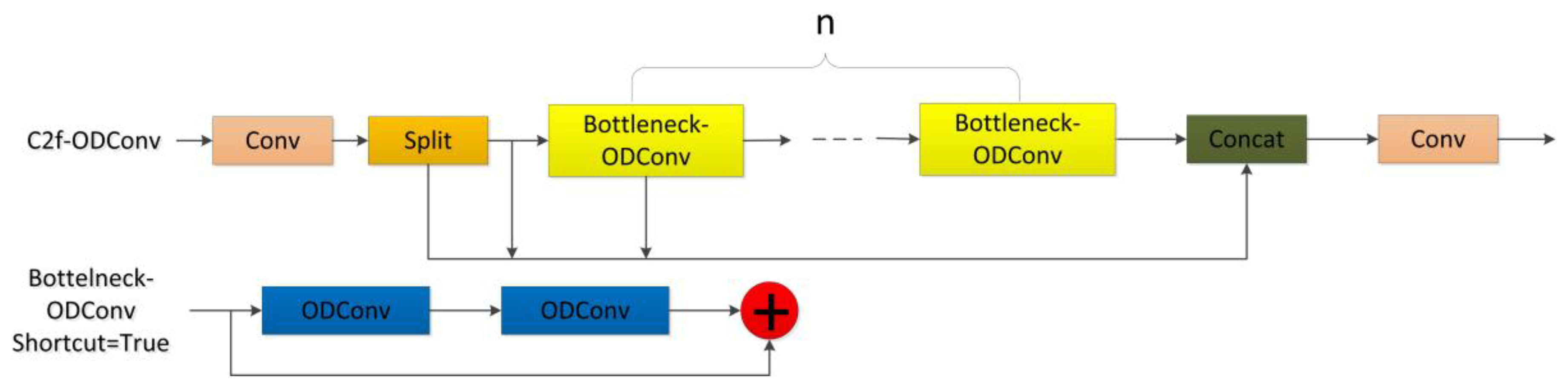
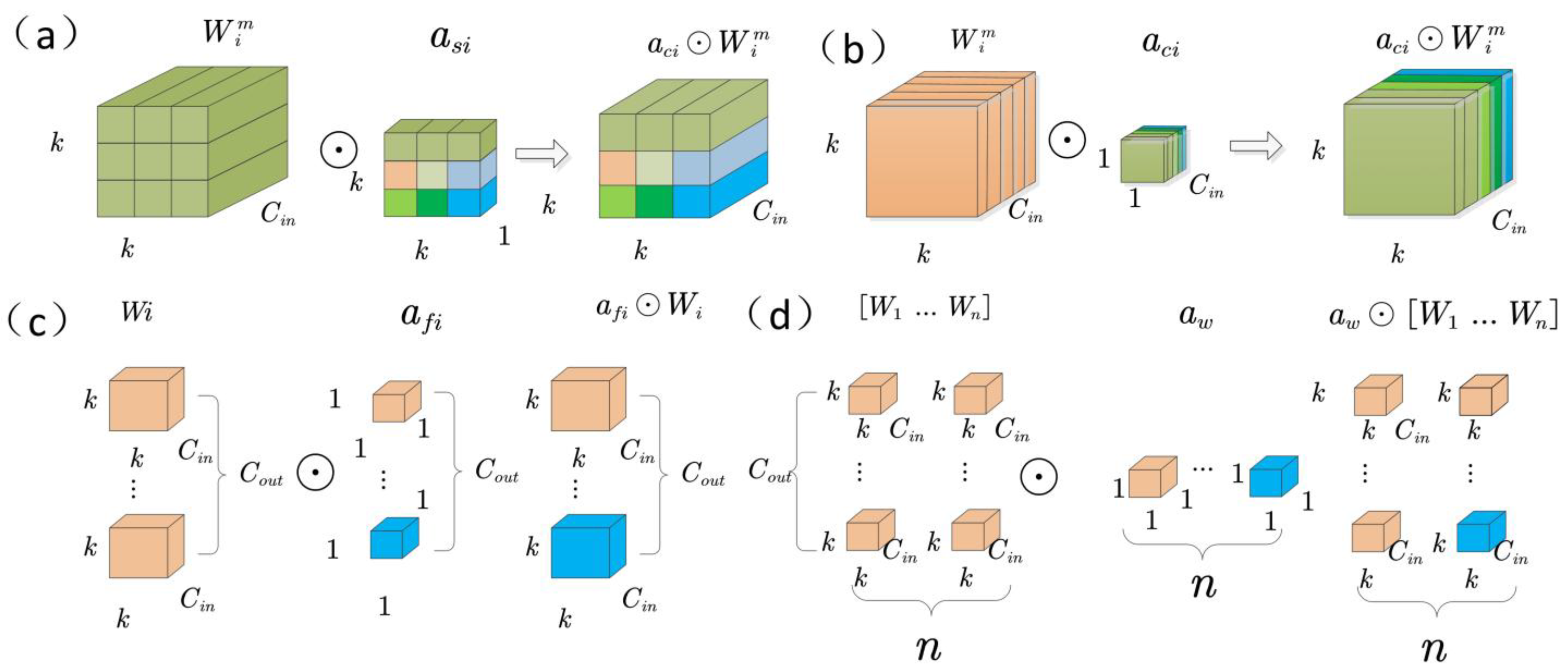
2.2.1. C2f-ODConv Attention Mechanism
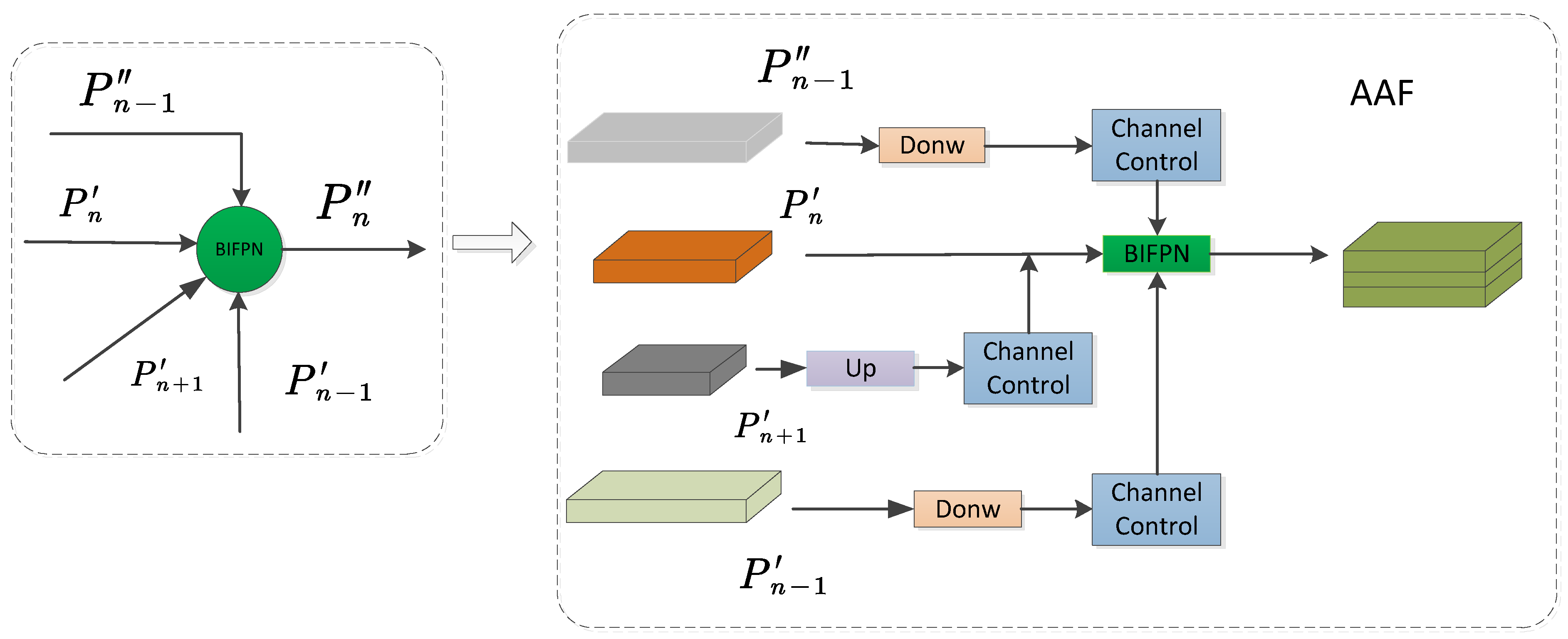
2.2.2. Neck Network Improvement

2.2.3. Loss Function Improvement
3. Experiment
3.1. Experimental Configuration
3.2. Experiment Parameters Setting
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
4. Results and Analysis
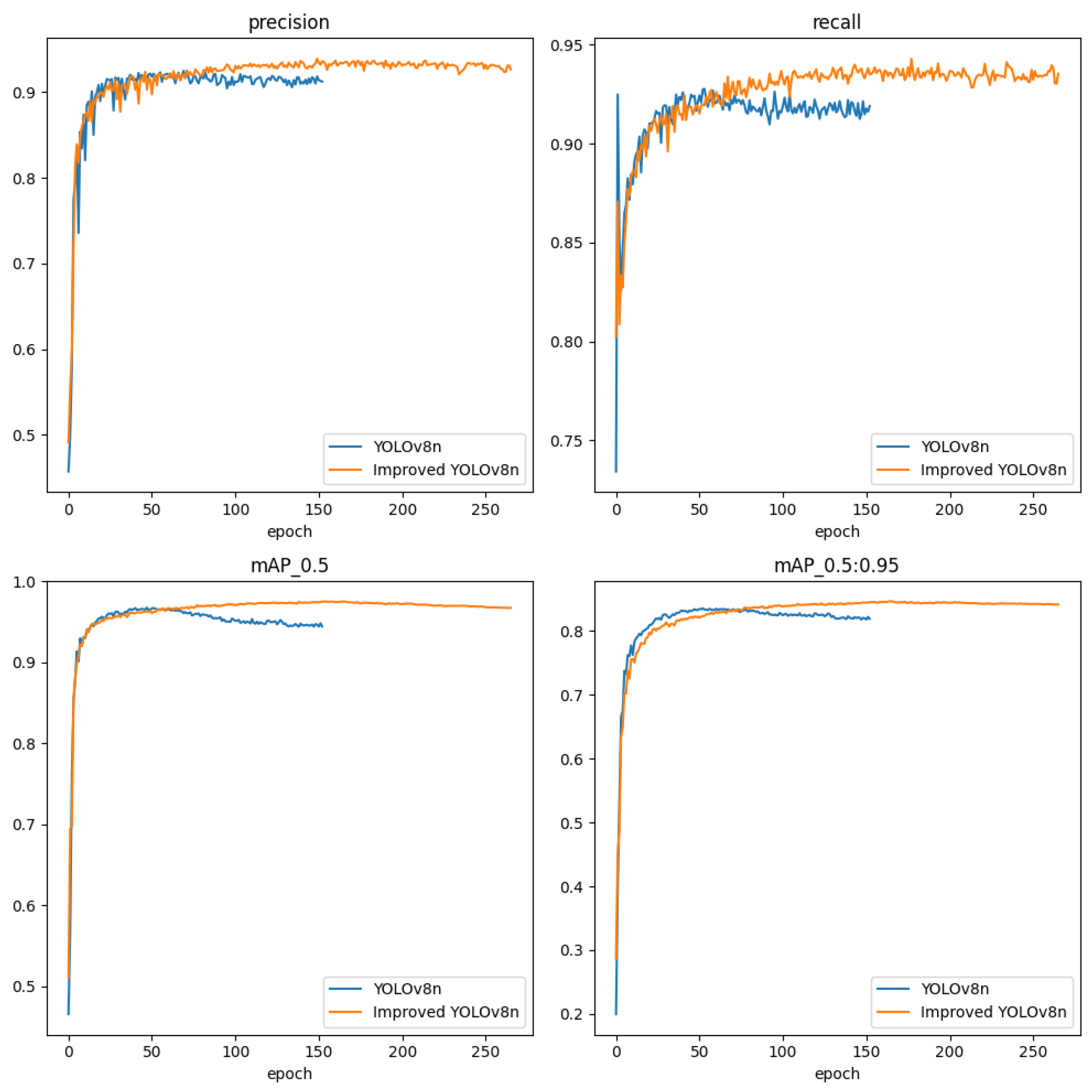
4.1. Comparison of Improvement Methods Effectiveness
4.2. Ablation Experiment
4.3. Comparison Experiments of Different Models
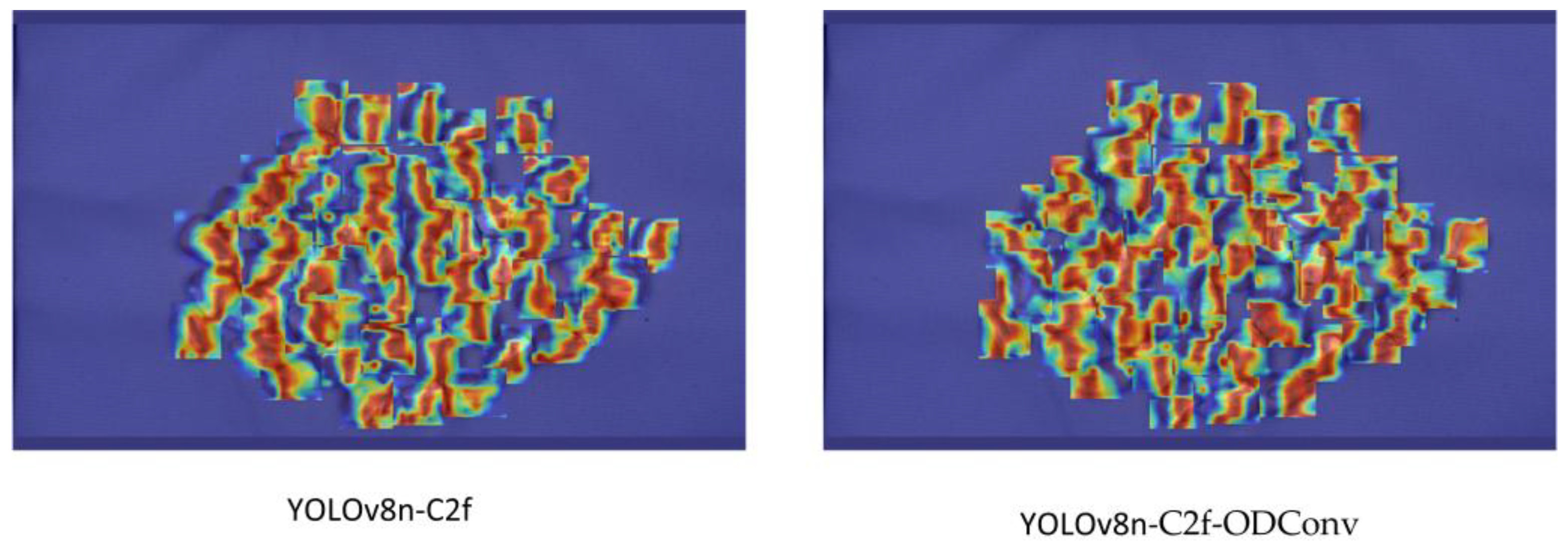
4.4. Model Feature Visualization
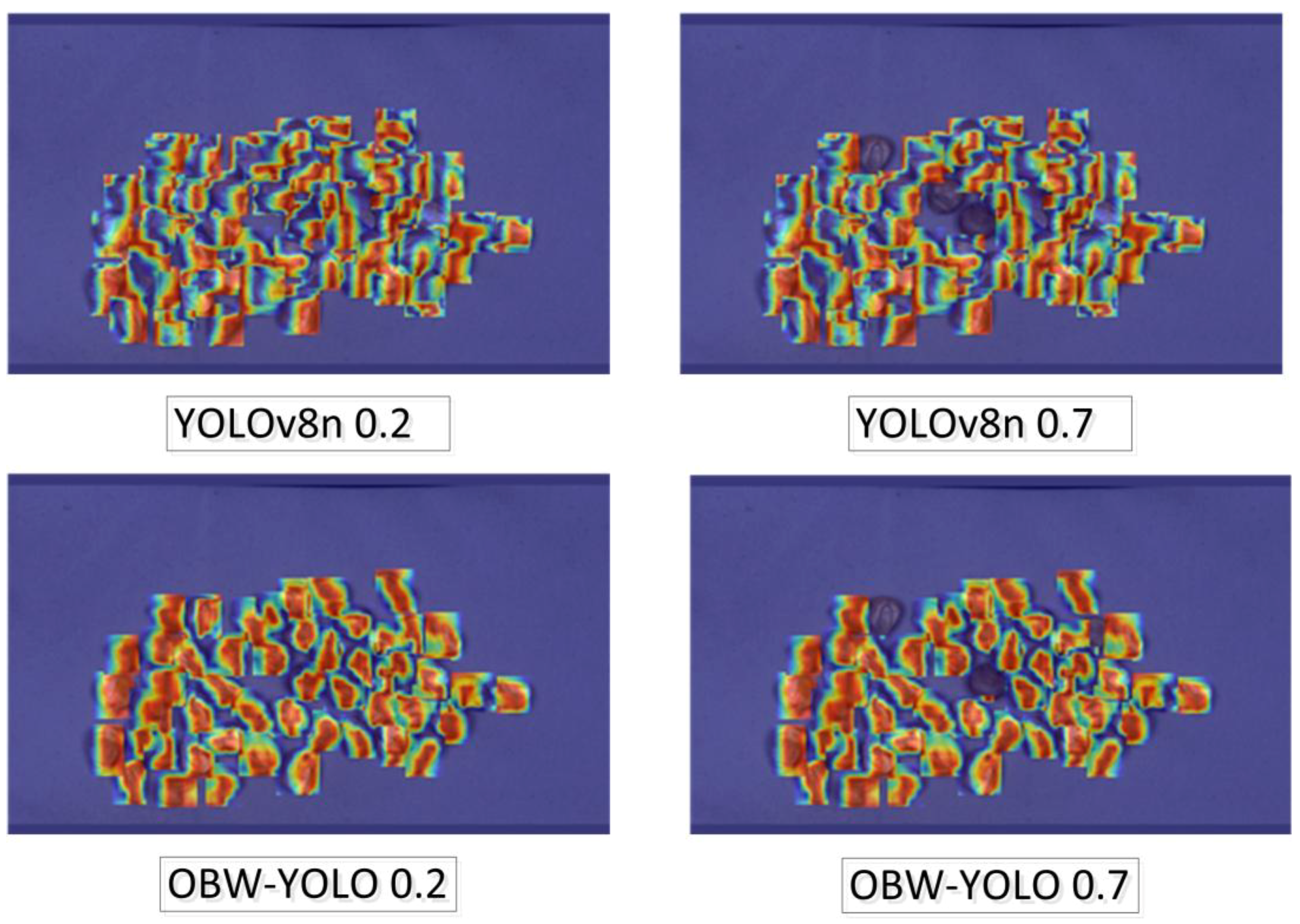
4.5. Algorithm Validation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, P.; Yue, X.; Gu, Y.; Yang, T. Assessment of maize seed vigor under saline-alkali and drought stress based on low field nuclear magnetic resonance. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 220, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Xu, M.; Xu, K.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Yang, R.; Chen, Q.; Yang, S. CSGD-YOLO: A Corn Seed Germination Status Detection Model Based on YOLOv8n. Agronomy 2025, 15, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, K.-L.; Li, L.-J.; Yang, L.-M.; Wang, J.-H.; Qun, S. Selection for high quality pepper seeds by machine vision and classifiers. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 1999–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urena, R.; Rodrıguez, F.; Berenguel, M. A machine vision system for seeds quality evaluation using fuzzy logic. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2001, 32, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granitto, P.M.; Navone, H.D.; Verdes, P.F.; Ceccatto, H. Weed seeds identification by machine vision. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2002, 33, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Medeiros, A.D.; Pereira, M.D.; Soares, T.; Noronha, B.G.; Pinheiro, D.T. Computer vision as a complementary method to vigour analysis in maize seeds. J. Exp. Agric. Int. 2018, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X. Design and Experimental Analysis on Device of Corn Seeds, Double-Sided Damage Detection Based on Machine Vision. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University of Technology, Zibo, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Ning, Y.; Wu, X.; Cheng, W.; Bin, L. Design and Experiment of Online Maize Single Seed Detection and Sorting Device. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-Q.; Zheng, P.; Xu, S.-t.; Wu, X. Object detection with deep learning: A review. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 3212–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, C.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C. Design and experiment of online cottonseed quality sorting device. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 210, 107870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Niu, W.; Yan, Y.; Ma, S.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chang, R.; Song, H. Detection of Broken Hongshan Buckwheat Seeds Based on Improved YOLOv5s Model. Agronomy 2023, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Xu, X.; Liang, A.; Yun, Y.; Li, L.; Hao, F.; Bai, J.; Ma, D. Research on a Lightweight Method for Maize Seed Quality Detection Based on Improved YOLOv8. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 32927–32937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, R.; Karkee, M. Yolo11 and vision transformers based 3d pose estimation of immature green fruits in commercial apple orchards for robotic thinning. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.19846. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, T.; Guo, S.; Feng, S.; Yao, W.; Lan, Y. Yolo-based uav technology: A review of the research and its applications. Drones 2023, 7, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Tao, R.; Liu, Y. SMC-YOLO: A High-Precision Maize Insect Pest-Detection Method. Agronomy 2025, 15, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Tang, Z.; Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; Si, Y.; Lu, M.; Panoutsos, G. Real-time object detection and robotic manipulation for agriculture using a yolo-based learning approach. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Bristol, UK, 25–27 March 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Joshua, C.J. Nanobot-Assisted Pollination for Sustainable Agriculture: A Review of Image Classification and Deep Learning Techniques with YOLO, SLAM, and MATLAB. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 189902–189925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X. A Full-View Detection Method for Maize Grain Based on Multi-Mirror Reflection Imaging Principle and the Tpfm-Sdpf-Yolo Model. Preprint 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Zhong, M. A method for maize pest detection based on improved YOLO-v9 model. In Proceedings of the 2024 7th International Conference on Computer Information Science and Application Technology (CISAT), Hangzhou, China, 12–14 July 2024; pp. 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Lin, Y.; Lin, G.; Su, P.; Huang, S.; Meng, X.; Liu, P.; Yan, J. Real-time detection and counting of wheat spikes based on improved YOLOv10. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solawetz, J.; Francesco. What Is YOLOv8? The Ultimate Guide. 2023. Available online: https://roboflow.com/ (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Tong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yu, R. Wise-IoU: Bounding box regression loss with dynamic focusing mechanism. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.10051. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhou, A.; Yao, A. Omni-dimensional dynamic convolution. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.07947. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Guan, Q.; Zhao, K.; Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Long, H.; Tang, Y. Multi-branch Auxiliary Fusion YOLO with Re-parameterization Heterogeneous Convolutional for Accurate Object Detection. In Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision (PRCV); Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 492–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xiao, Y.; Zong, W.; Song, B. Detecting chestnuts using improved lightweight YOLOv8. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng 2024, 40, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 12993–13000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Ren, D.; Liu, W.; Ye, R.; Hu, Q.; Zuo, W. Enhancing geometric factors in model learning and inference for object detection and instance segmentation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 52, 8574–8586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezatofighi, H.; Tsoi, N.; Gwak, J.; Sadeghian, A.; Reid, I.; Savarese, S. Generalized intersection over union: A metric and a loss for bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. Focal and efficient IOU loss for accurate bounding box regression. Neurocomputing 2022, 506, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xu, Y. Mpdiou: A loss for efficient and accurate bounding box regression. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.07662. [Google Scholar]
- Gevorgyan, Z. SIoU loss: More powerful learning for bounding box regression. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.12740. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Stoken, A.; Borovec, J.; Kwon, Y.; Michael, K.; Tao, X.; Fang, J.; Lorna; Zeng, Y.; et al. Ultralytics YOLOv5. 2020. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/7347926 (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Wang, C.-Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Yeh, I.H.; Liao, H.Y.M. Yolov9: Learning what you want to learn using programmable gradient information. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.13616. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. Yolov10: Real-time end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14458. [Google Scholar]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. Yolov11: An overview of the key architectural enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradova, K.; Dibrov, A.; Myers, G. Towards interpretable semantic segmentation via gradient-weighted class activation mapping (student abstract). In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 13943–13944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Model | P | R | mAP@0.5 | Map@0.95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIoU | 0.93 | 0.933 | 0.971 | 0.845 |
| WIoU | 0.934 | 0.934 | 0.976 | 0.848 |
| DIoU | 0.933 | 0.932 | 0.973 | 0.846 |
| GIoU | 0.929 | 0.932 | 0.972 | 0.845 |
| EIou | 0.932 | 0.932 | 0.971 | 0.844 |
| MpdIoU | 0.928 | 0.933 | 0.972 | 0.845 |
| SIoU | 0.922 | 0.934 | 0.970 | 0.843 |
| Model | P | R | mAP@0.5 | mAP@0.5:0.95 | GFLOPs | Params/M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 0.915 | 0.93 | 0.963 | 0.836 | 8.1 | 6.2 |
| Backbone Replacement | 0.917 | 0.922 | 0.964 | 0.836 | 6.7 | 6.4 |
| Neck Replacement | 0.923 | 0.926 | 0.965 | 0.833 | 7.1 | 6.3 |
| Complete Replacement | 0.927 | 0.932 | 0.969 | 0.841 | 5.7 | 6.5 |
| C2f-ODConv | BIMAFPN | WIoU | P | R | mAP@0.5 | mAP@0.5:0.95 | GFLOPs | Params/M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.915 | 0.93 | 0.964 | 0.836 | 8.1 | 6.2 | |||
| √ | 0.927 | 0.932 | 0.969 | 0.841 | 5.7 | 6.5 | ||
| √ | 0.923 | 0.926 | 0.967 | 0.838 | 7.4 | 4.6 | ||
| √ | 0.919 | 0.931 | 0.963 | 0.834 | 8.1 | 6.2 | ||
| √ | √ | 0.932 | 0.933 | 0.974 | 0.848 | 5.4 | 4.8 | |
| √ | √ | 0.927 | 0.932 | 0.97 | 0.842 | 5.7 | 6.5 | |
| √ | √ | 0.928 | 0.925 | 0.965 | 0.839 | 7.4 | 4.6 | |
| √ | √ | √ | 0.936 | 0.934 | 0.976 | 0.848 | 5.4 | 4.8 |
| Model | P | R | mAP@0.5 | mAP@0.5:0.95 | GFLOPs | Params/M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv3n-tiny | 0.898 | 0.92 | 0.953 | 0.792 | 12.9 | 16.6 |
| YOLOv5s | 0.932 | 0.894 | 0.962 | 0.815 | 15.8 | 14.4 |
| YOLOV7-tiny | 0.926 | 0.925 | 0.963 | 0.813 | 13.0 | 12.3 |
| YOLOv8n | 0.915 | 0.93 | 0.966 | 0.836 | 8.1 | 6.2 |
| YOLOv9n | 0.922 | 0.926 | 0.967 | 0.841 | 8.2 | 18.1 |
| YOLOv10n | 0.924 | 0.924 | 0.962 | 0.832 | 8.2 | 2.7 |
| YOLOv11n | 0.921 | 0.922 | 0.961 | 0.833 | 6.3 | 2.6 |
| YOLOv8-OBW | 0.936 | 0.934 | 0.976 | 0.848 | 5.4 | 4.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Wang, B.; Ru, S.; Yang, R.; Wu, J. Maize Seed Damage Identification Method Based on Improved YOLOV8n. Agronomy 2025, 15, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030710
Yang S, Wang B, Ru S, Yang R, Wu J. Maize Seed Damage Identification Method Based on Improved YOLOV8n. Agronomy. 2025; 15(3):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030710
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Songmei, Benxu Wang, Shaofeng Ru, Ranbing Yang, and Jilong Wu. 2025. "Maize Seed Damage Identification Method Based on Improved YOLOV8n" Agronomy 15, no. 3: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030710
APA StyleYang, S., Wang, B., Ru, S., Yang, R., & Wu, J. (2025). Maize Seed Damage Identification Method Based on Improved YOLOV8n. Agronomy, 15(3), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030710






