New Insights into the Regulatory Non-Coding RNAs Mediating Rice–Brown Planthopper Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
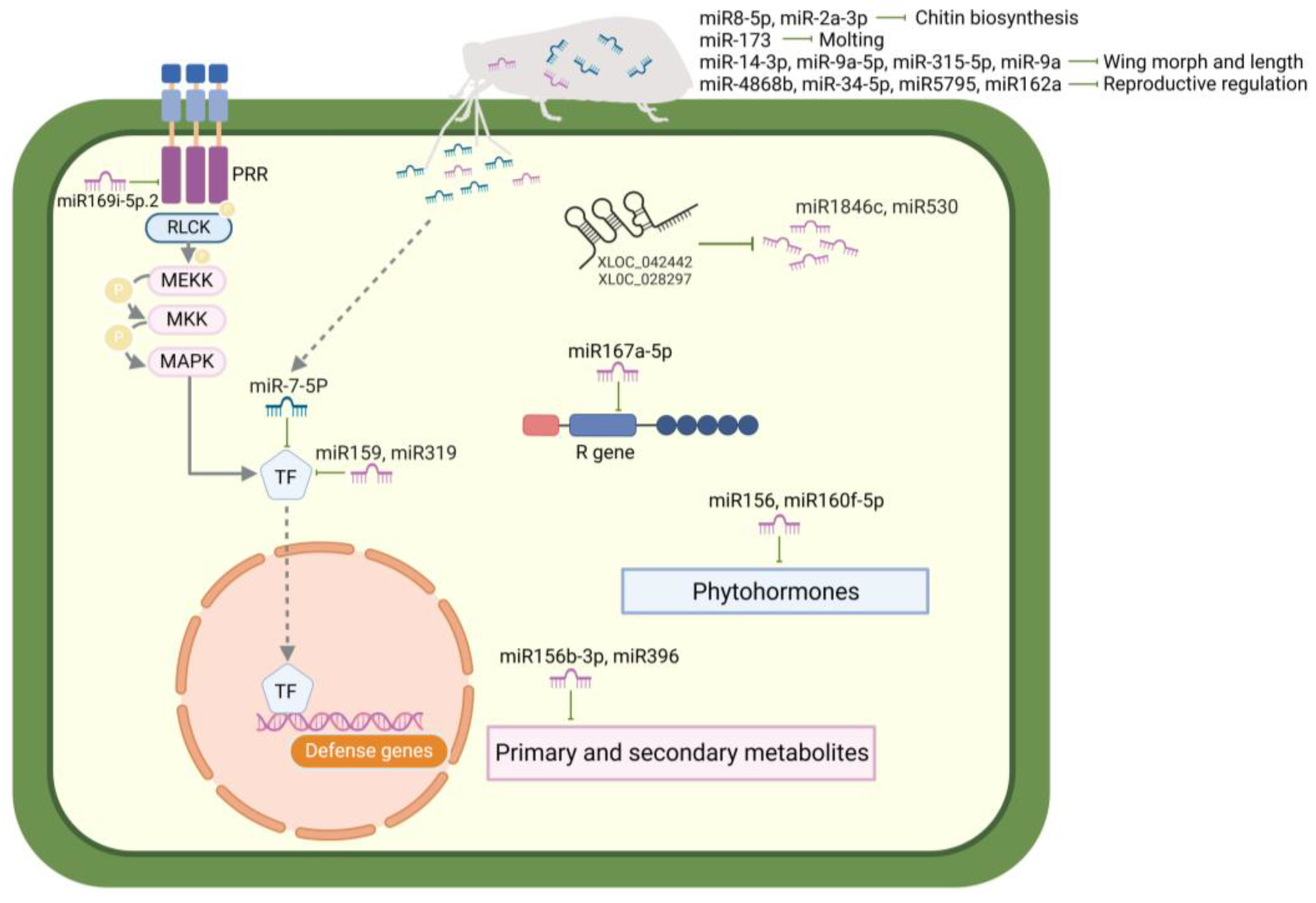
2. Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Rice–BPH Interactions
2.1. Roles of ncRNAs in the BPH Resistance of Rice
2.1.1. Rice miRNAs Involved in BPH Resistance
2.1.2. Rice lncRNAs and circRNAs Involved in BPH Resistance
2.2. Roles of ncRNAs in the Adaptation of BPHs to Rice
2.2.1. BPH miRNAs Involved in Development, Adaptation, and Reproduction
2.2.2. lncRNAs Involved in the Adaptation, Fecundity, and Virulence of BPHs
2.3. Cross-Kingdom Interactions Between Rice and BPHs Mediated by ncRNAs
2.3.1. Rice-Derived miRNAs Targeting BPH
| ncRNA | Species | Target(s) | Function in BPH Resistance | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XLOC_042442 | Oryza sativa | miR1846c | Function as ceRNAs by sponging miR1846c | Sequencing and experimental validation | [29] |
| XLOC_028297 | Oryza sativa | miR530 | Function as ceRNAs by sponging miR530 | Sequencing and experimental validation | [29] |
| miR160f-5p | Oryza sativa | ARF16 | Negatively regulates ARF16, influencing auxin signaling pathways | Sequencing | [31] |
| miR167a-5p | Oryza sativa | NB-ARC | Negatively regulates NB-ARC, involved in disease resistance | Sequencing | [31] |
| miR156b-3p | Oryza sativa | GDSL | Negatively regulates GDSL-like lipase | Sequencing | [32] |
| miR169i-5p.2 | Oryza sativa | LRR | Negatively regulates leucine-rich repeat family protein | Sequencing | [32] |
| miR5795 | Oryza sativa | NlVg | Mediates the fecundity of BPH by inhibiting vitellogenin (NlVg) expression in BPH | Sequencing | [34] |
| miR156 | Oryza sativa | SPLs | Mediates JA/JA-Ile biosynthesis, negatively regulating BPH resistance | Transgenic validation | [36] |
| miR396 | Oryza sativa | OsGRF8 | Negatively regulates BPH resistance through flavonoid biosynthesis | Transgenic validation | [38] |
| miR159 | Oryza sativa | OsGAMYBL2 | Regulates OsGAMYBL2-GS3 pathway, enhancing BPH resistance | Transgenic validation | [39] |
| miR319 | Oryza sativa | OsPCF5 | Regulates miR319-OsPCF5-OsMYB30C pathway, mediating BPH resistance | Transgenic validation | [40] |
| miR162a | Oryza sativa | NlTOR | Mediates cross-kingdom RNAi, regulating BPH reproduction | Transgenic validation | [74] |
| miR-8-5p | Nilaparvata lugens | NlTre-2 | Regulates chitin biosynthesis | Sequencing and experimental validation | [52] |
| miR-2a-3p | Nilaparvata lugens | NlPAGM | Regulates chitin biosynthesis | Sequencing and experimental validation | [52] |
| miR-173 | Nilaparvata lugens | NlFtz-F1 | Regulates molting by targeting the transcription factor NlFtz-F1 within the 20E pathway | Sequencing and experimental validation | [53] |
| miR-14-3p | Nilaparvata lugens | NlInRs | Modulates the wing morph of BPHs | Sequencing | [54] |
| miR-9a-5p | Nilaparvata lugens | NlInRs | Modulates the wing morph of BPHs | Sequencing | [54] |
| miR-315-5p | Nilaparvata lugens | NlInRs | Modulates the wing morph of BPHs | Sequencing | [54] |
| miR-9a | Nilaparvata lugens | NlUbx | Regulates wing length in BPHs | Experimental validation | [55] |
| miR-4868b | Nilaparvata lugens | NlGS | Modulates reproductive capacity in BPHs | Experimental validation | [62] |
| miR-34-5p | Nilaparvata lugens | NLHR4, NlCp-1, NlSPATA20 | Is involved in reproductive regulation | Sequencing | [63] |
| miR-7-5P | Nilaparvata lugens | OsbZIP43 | Weakens rice immune responses | Experimental validation | [73] |
2.3.2. BPH-Derived miRNAs Targeting Rice
2.4. Integration of Multi-Omics Data for Clarifying Rice–BPH Interactions
2.5. Practical Implications and Potential Technical or Economic Challenges
2.5.1. Practical Implications of ncRNA-Based Pest Control
2.5.2. Technical Challenges in the Application of RNAi for Pest Control
2.5.3. Economic Challenges and Regulatory Considerations
3. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, B.; Chen, R.; Guo, J.; He, G. Current understanding of the genomic, genetic, and molecular control of insect resistance in rice. Mol. Breed. 2020, 40, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Ali, J.; Zhou, S.; Ren, G.; Xie, H.; Xu, J.; Yu, X.; Zhou, F.; Peng, S.; Ma, L.; et al. From Green Super Rice to green agriculture: Reaping the promise of functional genomics research. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, L.; He, G. Genetic and molecular understanding of host rice resistance and Nilaparvata lugens adaptation. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2021, 45, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Deng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Guo, J.; Qiu, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; et al. Rice functional genomics: Decades’ efforts and roads ahead. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 33–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, H.; Guan, W.; Guo, Q.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Peng, Y.; Shan, J.; Gao, M.; Shi, S.; et al. A tripartite rheostat controls self-regulated host plant resistance to insects. Nature 2023, 618, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Wang, H.; Zha, W.; Wu, Y.; Liu, K.; Xu, D.; He, G.; Zhou, L.; You, A. Recent Advances in the Genetic and Biochemical Mechanisms of Rice Resistance to Brown Planthoppers (Nilaparvata lugens Stål). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapranov, P.; Cheng, J.; Dike, S.; Nix, D.A.; Duttagupta, R.; Willingham, A.T.; Stadler, P.F.; Hertel, J.; Hackermüller, J.; Hofacker, I.L.; et al. RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription. Science 2007, 316, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolittle, W.F. Is junk DNA bunk? A critique of ENCODE. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5294–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariel, F.; Romero-Barrios, N.; Jégu, T.; Benhamed, M.; Crespi, M. Battles and hijacks: Noncoding transcription in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarfard, S.; Ghorbani, A.; Karbanowicz, T.P.; Lim, Z.X.; Saedi, M.; Fariborzi, N.; McTaggart, A.R.; Izadpanah, K. Regulatory non-coding RNA: The core defense mechanism against plant pathogens. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 359, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu Lakshmi Bavithra, C.; Murugan, M.; Pavithran, S.; Naveena, K. Enthralling genetic regulatory mechanisms meddling insecticide resistance development in insects: Role of transcriptional and post-transcriptional events. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1257859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Ma, C.; Peng, R.; Xie, M. Insights into the role of non-coding RNAs in the development of insecticide resistance in insects. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1429411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cech, T.R.; Steitz, J.A. The noncoding RNA revolution—Trashing old rules to forge new ones. Cell 2014, 157, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, K.V.; Mattick, J.S. The rise of regulatory RNA. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.-W.; Huang, K.; Yang, C.; Kang, C.-S. Non-coding RNAs as regulators in epigenetics. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.; Xu, J.; Tang, H.; Li, P.; Yu, B.; Liu, Q. The roles of small RNAs in rice-brown planthopper interactions. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1326726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Feng, M.; Kolliopoulou, A.; Taning, C.N.; Sun, J.; Swevers, L. What are the functional roles of piwi proteins and piRNAs in insects? Insects 2023, 14, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verduci, L.; Strano, S.; Yarden, Y.; Blandino, G. The circ RNA–micro RNA code: Emerging implications for cancer diagnosis and treatment. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csorba, T.; Questa, J.I.; Sun, Q.; Dean, C. Antisense COOLAIR mediates the coordinated switching of chromatin states at FLC during vernalization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16160–16165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šečić, E.; Kogel, K.-H.; Ladera-Carmona, M.J. Biotic stress-associated microRNA families in plants. J. Plant Physiol. 2021, 263, 153451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Li, Y.; Wai, W.K.H.; Yin, J.; Zhu, Y. The bioinformatic tools, characteristics, biological functions and molecular mechanisms associated with plant circular RNA. New Crops 2024, 2, 100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Li, P.; Mei, H.; Wang, D.; Sun, J.; Yang, C.; Hao, L.; Cao, S.; Chu, C.; Hu, S.; et al. Fine-tuning of MiR528 accumulation modulates flowering time in rice. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, A.; Izadpanah, K.; Peters, J.R.; Dietzgen, R.G.; Mitter, N. Detection and profiling of circular RNAs in uninfected and maize Iranian mosaic virus-infected maize. Plant Sci. 2018, 274, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Xu, M.; Ito, H.; Cai, J.; Ma, X.; Qin, J.; Yu, D.; Meng, Y. Deciphering the non-coding RNA-level response to arsenic stress in rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Signal. Behav. 2019, 14, 1629268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Chung, H. New and emerging mechanisms of insecticide resistance. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2024, 63, 101184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hao, L.; Li, D.; Zhu, L.; Hu, S. Long non-coding RNAs and their biological roles in plants. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y. Plant noncoding RNAs: Hidden players in development and stress responses. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 35, 407–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Dou, W.; Taning, C.N.T.; Smagghe, G.; Wang, J.-J. Regulatory roles of microRNAs in insect pests: Prospective targets for insect pest control. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 70, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zha, W.; Qiu, D.; Guo, J.; Liu, G.; Li, C.; Wu, B.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Hu, L.; et al. Comprehensive identification and characterization of lncRNAs and circRNAs reveal potential brown planthopper-responsive ceRNA networks in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1242089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadarajah, K.K.; Abdul Rahman, N.S.N. The Role of Non-Coding RNA in Rice Immunity. Agronomy 2021, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lv, W.; Hu, L.; Rao, W.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, L.; He, Y.; He, G. Identification and analysis of brown planthopper-responsive microRNAs in resistant and susceptible rice plants. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Wu, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, H.; Zhu, L.; Chen, R.; He, G.; Du, B. A combined microRNA and transcriptome analyses illuminates the resistance response of rice against brown planthopper. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, S.; Yuan, S.-Y.; Lai, F.-X.; Wang, W.-X.; Fu, Q.; Wan, P.-J. Identification and analysis of miRNAs in IR56 rice in response to BPH infestations of different virulence levels. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Sun, J.; Su, Q.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W. Screening of Brown Planthopper Resistant miRNAs in Rice and Their Roles in Regulation of Brown Planthopper Fecundity. Rice Sci. 2022, 29, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Geng, M.; Xue, Y.; Yu, Q.; Lu, B.; Liu, M.; Shao, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; et al. Combined miRNA and mRNA sequencing reveals the defensive strategies of resistant YHY15 rice against differentially virulent brown planthoppers. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1366515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Han, J.; Zhou, G.; Xu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Shi, M.; Guo, C.; Wu, G. Silencing of miR156 confers enhanced resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Planta 2018, 248, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Q.; Bian, W.; Erb, M.; Lou, Y. Prioritizing plant defence over growth through WRKY regulation facilitates infestation by non-target herbivores. Elife 2015, 4, e04805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Tan, J.; Zhou, C.; Yang, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, S.; Sun, S.; Miao, X.; Shi, Z. The OsmiR396-OsGRF8-OsF3H-flavonoid pathway mediates resistance to the brown planthopper in rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Yang, G.; Miao, X.; Shi, Z. OsmiR159 Modulate BPH Resistance Through Regulating G-Protein γ Subunit GS3 Gene in Rice. Rice 2023, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; Zhu, M.; Miao, X.; Shi, Z. OsmiR319-OsPCF5 modulate resistance to brown planthopper in rice through association with MYB proteins. BMC Biol. 2024, 22, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Muhammad, S.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, N.; Qin, B.; Qiu, Y.; Du, Z.; Ulhassan, Z.; Zhou, W.; et al. Comparative transcriptome-wide identification and differential expression of genes and lncRNAs in rice near-isogenic line (KW-Bph36-NIL) in response to BPH feeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1095602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ma, X.; Zhao, L.; Lai, X.; Chen, J.; Lang, X.; Han, Q.; Wan, X.; Li, C. Comprehensive transcriptomic analysis of three varieties with different brown planthopper-resistance identifies leaf sheath lncRNAs in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.-H.; Wang, Y.-X.; Xiao, J.; Jia, Y.-F.; Liu, F.; Wang, W.-X.; Wei, Q.; Lai, F.-X.; Fu, Q.; Wan, P.-J. Defense Regulatory Network Associated with circRNA in Rice in Response to Brown Planthopper Infestation. Plants 2024, 13, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 2011, 146, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, C.L.; Black, W.C.; Hess, A.M.; Foy, B.D. Comparative genomics of small RNA regulatory pathway components in vector mosquitoes. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Vernooy, S.Y.; Guo, M.; Hay, B.A. The Drosophila microRNA Mir-14 suppresses cell death and is required for normal fat metabolism. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, C.; Sharma, S.; Meghwanshi, K.K.; Patel, S.; Mehta, P.; Shukla, N.; Do, D.N.; Rajpurohit, S.; Suravajhala, P.; Shukla, J.N. Long Non-Coding RNAs in Insects. Animals 2021, 11, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.; Mannaa, M.; Hewedy, O.; Ali, M.G.; Jung, H.; Seo, Y.S. Versatile Roles of Microbes and Small RNAs in Rice and Planthopper Interactions. Plant Pathol. J. 2022, 38, 432–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, W.W.; Zhu, Z.R. The microRNA pathway core genes are indispensable for development and reproduction in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Mol. Biol. 2023, 32, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, W.; Zhou, L.; Li, S.; Liu, K.; Yang, G.; Chen, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, P.; Hussain, S.; You, A. Characterization and comparative profiling of the small RNA transcriptomes in the Hemipteran insect Nilaparvata lugens. Gene 2016, 595, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liang, Z.; Liang, Y.; Pang, R.; Zhang, W. Conserved microRNAs miR-8-5p and miR-2a-3p modulate chitin biosynthesis in response to 20-hydroxyecdysone signaling in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, T.C.; Pang, R.; Yue, X.Z.; Hu, J.; Zhang, W.Q. Genome-wide screening and functional analysis reveal that the specific microRNA nlu-miR-173 regulates molting by targeting Ftz-F1 in Nilaparvata lugens. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, A.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Jie, W.; Cao, Z.; Omar, M.A.A.; He, K.; Li, F. Identification and Analysis of MicroRNAs Associated with Wing Polyphenism in the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhao, M.H.; Tian, M.M.; Zhao, J.; Cai, W.L.; Hua, H.X. An InR/mir 9a/NIUbx regulatory cascade regulates wing diphenism in brown planthoppers. Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 1300–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Saha, T.T.; Zou, Z.; Raikhel, A.S. Regulatory pathways controlling female insect reproduction. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 489–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Xu, J.; Bai, H.; Zhu, F.; Palli, S.R. Juvenile hormone regulates vitellogenin gene expression through insulin-like peptide signaling pathway in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 41924–41936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyria, J.; Orchard, I.; Lange, A.B. The involvement of insulin/ToR signaling pathway in reproductive performance of Rhodnius prolixus. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 130, 103526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.G.; Raikhel, A.S. The small GTPase Rheb is a key component linking amino acid signaling and TOR in the nutritional pathway that controls mosquito egg development. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ye, Y.-Z.; Ogihara, M.H.; Takeshima, M.; Fujinaga, D.; Liu, C.-W.; Zhu, Z.; Kataoka, H.; Bao, Y.-Y. Functional analysis of ecdysteroid biosynthetic enzymes of the rice planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 123, 103428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moure, U.A.E.; Tan, T.; Sha, L.; Lu, X.; Shao, Z.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H. Advances in the immune regulatory role of non-coding RNAs (miRNAs and lncRNAs) in insect-pathogen interactions. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 856457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Li, T.; Chen, J.; Dong, Y.; Qiu, J.; Kang, K.; Zhang, W. Functional screen for microRNAs of Nilaparvata lugens reveals that targeting of glutamine synthase by miR-4868b regulates fecundity. J. Insect Physiol. 2015, 83, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, C.; Chen, M.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, Z. Characterization of MicroRNAs Associated with Reproduction in the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganegoda, G.U.; Li, M.; Wang, W.; Feng, Q. Heterogeneous network model to infer human disease-long intergenic non-coding RNA associations. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2015, 14, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurokawa, R. Long noncoding RNA as a regulator for transcription. Long Non-Coding RNAs 2011, 51, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.J.; Zhang, Q.C.; Georgiev, P.; Ilik, I.A.; Akhtar, A.; Chang, H.Y. Rapid evolutionary turnover underlies conserved lncRNA–genome interactions. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Jing, D.; Tang, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, H.; Duanmu, H.; Cong, Y.; Chen, M.; Ye, X.; Zhou, H.; et al. InsectBase 2.0: A comprehensive gene resource for insects. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1040–D1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, W.; Li, S.; Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, K.; Li, P.; Liu, K.; Yang, G.; Chen, Z.; Shi, S.; et al. Genome-wide identification of long non-coding (lncRNA) in Nilaparvata lugens’s adaptability to resistant rice. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, D.; Hou, B.; Yin, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, F. Genome-wide identification of long noncoding RNA genes and their potential association with fecundity and virulence in rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Rajamani, V.; Reddy, V.S.; Mukherjee, S.K.; Bhatnagar, R.K. Transgenic plants over-expressing insect-specific microRNA acquire insecticidal activity against Helicoverpa armigera: An alternative to Bt-toxin technology. Transgenic Res. 2015, 24, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Weiberg, A.; Lin, F.-M.; Thomma, B.P.; Huang, H.-D.; Jin, H. Bidirectional cross-kingdom RNAi and fungal uptake of external RNAs confer plant protection. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 16151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X. New insight into inter-kingdom communication: Horizontal transfer of mobile small RNAs. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Lu, J.; Lu, H.; Ye, Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; et al. Cross-kingdom RNA interference mediated by insect salivary microRNAs may suppress plant immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2318783121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Cao, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Li, J.-F. Overexpression of an Osa-miR162a Derivative in Rice Confers Cross-Kingdom RNA Interference-Mediated Brown Planthopper Resistance without Perturbing Host Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, L.; Shen, W.; Shi, Q.; Qi, G.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z. Osa-miR162a Enhances the Resistance to the Brown Planthopper via α-Linolenic Acid Metabolism in Rice (Oryza sativa). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 11847–11859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giambruno, R.; Mihailovich, M.; Bonaldi, T. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics to unveil the non-coding RNA world. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, T.; Gao, M.; Ye, M.; Lin, M.; Wu, D.; Guo, J.; Guan, W.; Wang, J.; Yang, K.; et al. Transcriptome and metabolome profiling reveal the resistance mechanisms of rice against brown planthopper. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Zha, W.; Yu, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, H.; Li, P.; Liu, K.; Chen, J.; Yang, G.; et al. Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis provide insight into the resistance response of rice against brown planthopper. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1213257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schutter, K.; Taning, C.N.T.; Van Daele, L.; Van Damme, E.J.; Dubruel, P.; Smagghe, G. RNAi-based biocontrol products: Market status, regulatory aspects, and risk assessment. Front. Insect Sci. 2022, 1, 818037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwokeoji, A.O.; Nwokeoji, E.A.; Chou, T.; Togola, A. A novel sustainable platform for scaled manufacturing of double-stranded RNA biopesticides. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2022, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolge, H.; Kadam, K.; Galande, S.; Lanjekar, V.; Ghormade, V. New frontiers in pest control: Chitosan nanoparticles-shielded dsRNA as an effective topical RNAi spray for gram podborer biocontrol. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 5145–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Liu, S.; Sun, M.; Yu, Q.; Li, C.; Graham, R.I.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, P.; Ren, G. Delivery of methoprene-tolerant dsRNA to improve RNAi efficiency by modified liposomes for pest control. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 13576–13588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devos, Y.; Álvarez-Alfageme, F.; Gennaro, A.; Mestdagh, S. Assessment of unanticipated unintended effects of genetically modified plants on non-target organisms: A controversy worthy of pursuit? J. Appl. Entomol. 2016, 140, 12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.V. Non-coding RNAs in crop genetic modification: Considerations and predictable environmental risk assessments (ERA). Mol. Biotechnol. 2013, 55, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, L.; Wu, Y.; Zha, W.; Zhou, L.; You, A. New Insights into the Regulatory Non-Coding RNAs Mediating Rice–Brown Planthopper Interactions. Agronomy 2025, 15, 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030686
Hu L, Wu Y, Zha W, Zhou L, You A. New Insights into the Regulatory Non-Coding RNAs Mediating Rice–Brown Planthopper Interactions. Agronomy. 2025; 15(3):686. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030686
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Liang, Yan Wu, Wenjun Zha, Lei Zhou, and Aiqing You. 2025. "New Insights into the Regulatory Non-Coding RNAs Mediating Rice–Brown Planthopper Interactions" Agronomy 15, no. 3: 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030686
APA StyleHu, L., Wu, Y., Zha, W., Zhou, L., & You, A. (2025). New Insights into the Regulatory Non-Coding RNAs Mediating Rice–Brown Planthopper Interactions. Agronomy, 15(3), 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030686






