Genetic Variation and Assessment of Seven Salt-Tolerance Genes in an Indica/Xian Rice Population
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Germplasms and Genotyping Analysis
2.2. Plant Growth Conditions
2.3. Phenotypic Assessment of Salt Tolerance
2.4. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.5. Protein Structure Predication
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of ST Genes in 550 Indica/Xian Rice Accessions
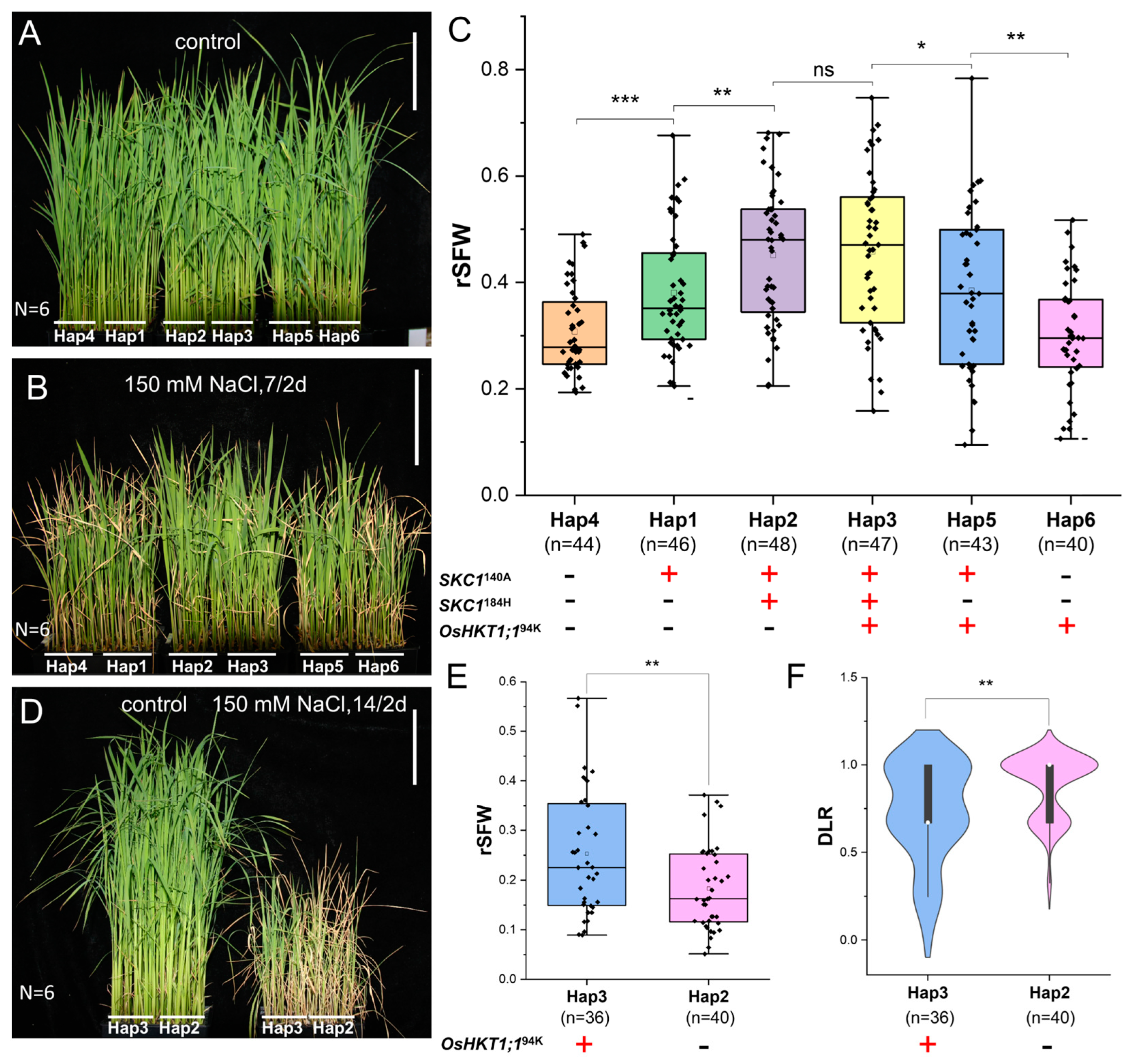
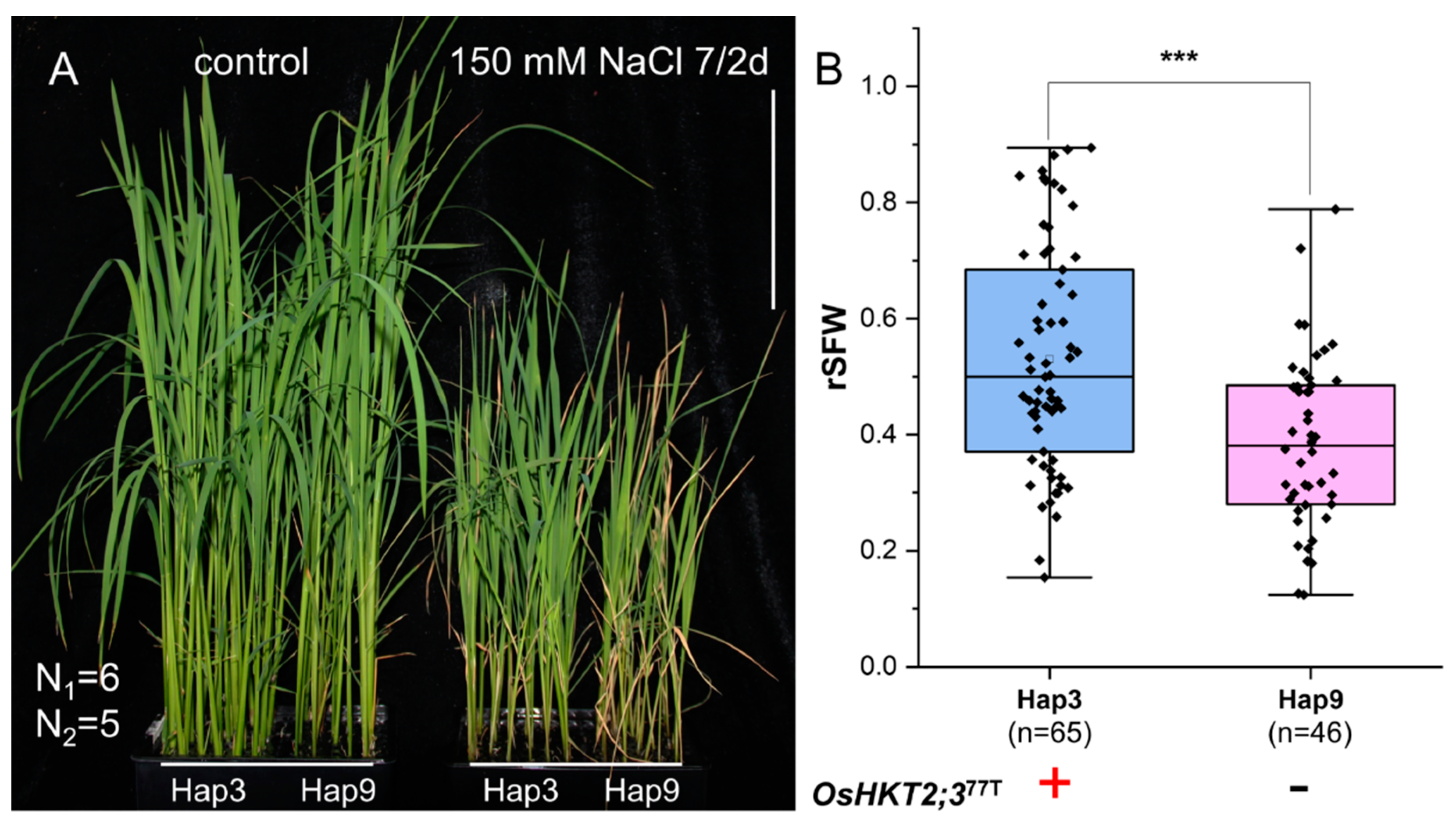
3.2. Assessment of the Functions of Three OsHKT Family Genes
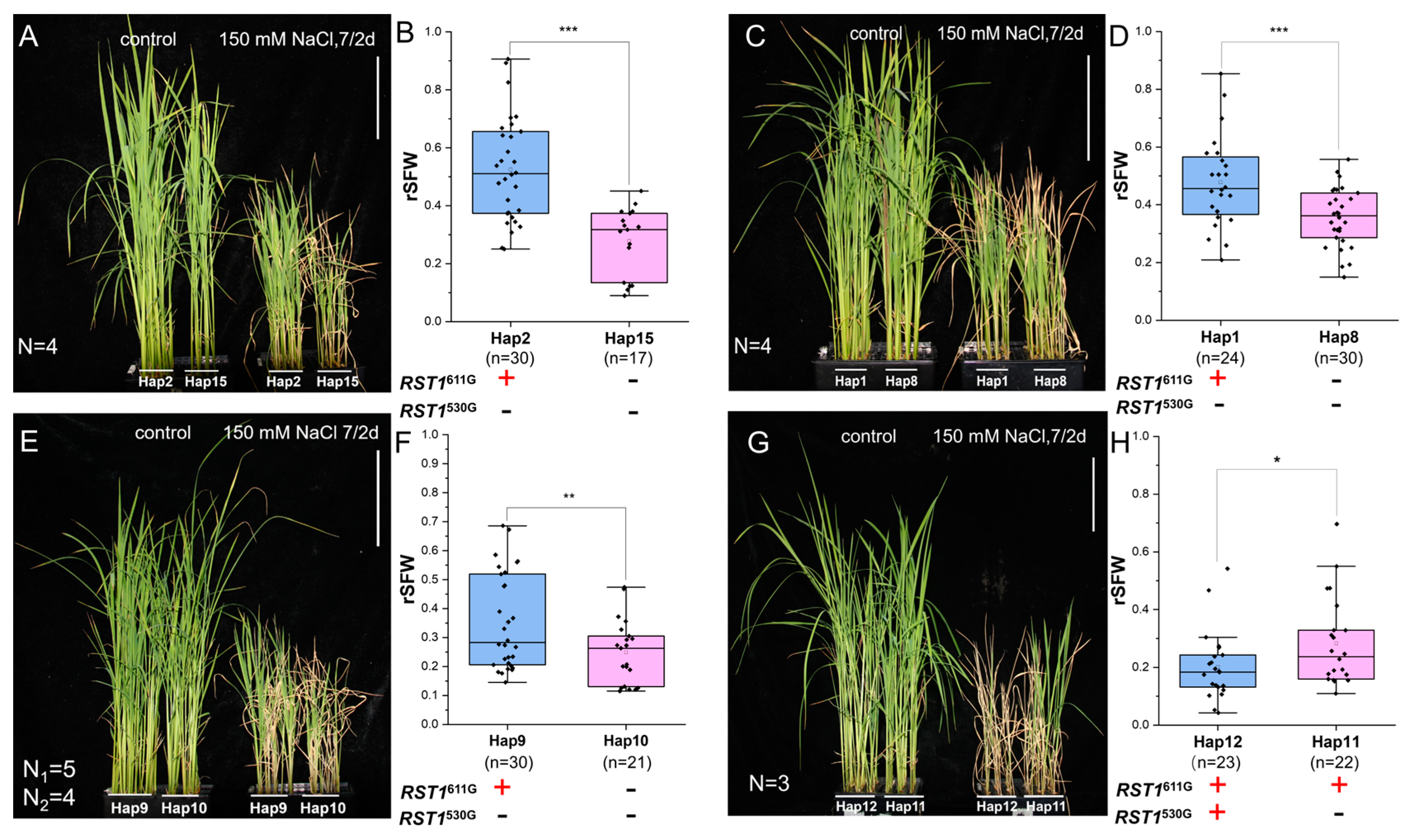
3.3. Functional Evaluation of RST1
3.4. Evaluation of Salt Tolerance of OsWRKY53173G
4. Discussion
4.1. Cloned ST Genes Broadly Distributed in Indica/Xian Rice Accessions
4.2. Two Haplotypes of SKC1 Synergistically Regulate Salt Tolerance
4.3. Genetic Analysis of Natural Variations Assists in the Exploration of the Mechanism of ST
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CSSL | Chromosome segment substitution line (CSSL) |
| DLR | Dead leaf rate |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association study |
| EMS | Ethyl methanesulfonate |
| Haps | Haplotypes |
| HKT | High-affinity K+ transporter |
| MAS | Marker-assisted selection |
| NILs | Near-isogenic lines |
| qRT–PCR | Quantitative real-time PCR |
| QTL | Quantitative trait locus |
| rSFW | Relative shoot fresh weight |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| ST | Salt tolerance |
References
- Negrão, S.; Courtois, B.; Ahmadi, N.; Abreu, I.; Saibo, N.; Oliveira, M.M. Recent updates on salinity stress in rice: From physiological to molecular responses. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2011, 30, 329–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmans, J.W.; Qureshi, A.S.; Kisekka, I.; Munns, R.; Grattan, S.R.; Rengasamy, P.; Ben-Gal, A.; Assouline, S.; Javaux, M.; Minhas, P.S.; et al. Critical knowledge gaps and research priorities in global soil salinity. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 169, pp. 1–191. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Mao, B.; Yuan, D.; Chu, C.; Duan, M. Salt tolerance in rice: Physiological responses and molecular mechanisms. Crop J. 2022, 10, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global predictions of primary soil salinization under changing climate in the 21st century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Mo, J.; Zhou, H.; Shen, X.; Xie, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, S. Comparative transcriptome analysis of gene responses of salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive rice cultivars to salt stress. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.; Jan, R.; Asif, S.; Farooq, M.; Jang, Y.H.; Kim, E.G.; Kim, N.; Kim, K.M. Exogenous melatonin induces salt and drought stress tolerance in rice by promoting plant growth and defense system. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Kota, S.; Flowers, T.J. Salt tolerance in rice: Seedling and reproductive stage QTL mapping come of age. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 3495–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapagain, S.; Pruthi, R.; Singh, L.; Subudhi, P.K. Comparison of the genetic basis of salt tolerance at germination, seedling, and reproductive stages in an introgression line population of rice. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmavathi, G.; Bangale, U.; Rao, K.N.; Balakrishnan, D.; Arun, M.N.; Singh, R.K.; Sundaram, R.M. Progress and prospects in harnessing wild relatives for genetic enhancement of salt tolerance in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1253726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.; Tiwari, S.; Kumar, N.; Sinha, S.; Krishnamurthy, S.L.; Singh, R.; Kalia, S.; Singh, N.K.; Rai, V. QTLs and genes for salt stress tolerance: A journey from seed to seed continued. Plants 2024, 13, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J. Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2001, 6, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deinlein, U.; Stephan, A.B.; Horie, T.; Luo, W.; Xu, G.; Schroeder, J.I. Plant salt-tolerance mechanisms. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Song, C.; Zhu, J.K.; Shabala, S. Mechanisms of plant responses and adaptation to soil salinity. Innovation 2020, 1, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Gao, J.; Li, L.; Cai, X.; Huang, W.; Chao, D.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Z.; Luan, S.; Lin, H. A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.I.; Yamaji, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Okubo, K.; Ueno, H.; Costa, A.; Tanoi, K.; Matsumura, H.; Fujii-Kashino, M.; Horiuchi, T.; et al. OsHKT1;5 mediates Na+ exclusion in the vasculature to protect leaf blades and reproductive tissues from salt toxicity in rice. Plant J. 2017, 91, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platten, J.D.; Egdane, J.A.; Ismail, A.M. Salinity tolerance, Na+ exclusion and allele mining of HKT1;5 in Oryza sativa and O. glaberrima: Many sources, many genes, one mechanism? BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Nan, N.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.J.; Hwang, I.; Liu, B.; Xu, Z.Y. A DNA methylation reader-chaperone regulator-transcription factor complex activates OsHKT1;5 expression during salinity stress. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 3535–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkataraman, G.; Shabala, S.; Véry, A.A.; Hariharan, G.N.; Somasundaram, S.; Pulipati, S.; Sellamuthu, G.; Harikrishnan, M.; Kumari, K.; Shabala, L.; et al. To exclude or to accumulate? Revealing the role of the sodium HKT1;5 transporter in plant adaptive responses to varying soil salinity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 169, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Ma, J.; Wei, H.; Xiao, F.; Wang, Y.; Jahan, N.; Hazman, M.; Qian, Q.; Shang, L.; Guo, L. Combining GWAS, genome-wide domestication and a transcriptomic analysis reveals the loci and natural alleles of salt tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 912637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Jing, W.; Xiao, L.; Jin, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhang, W. The rice high-affinity potassium transporter1;1 is involved in salt tolerance and regulated by an MYB-type transcription factor. Plant Physiol. 2015, 168, 1076–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfatih, A.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Jan, S.U.; Zhang, Z.S.; Xia, J.Q.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Nazish, T.; Wu, J.; Zhao, P.X.; et al. Nitrate-responsive OsMADS27 promotes salt tolerance in rice. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 100458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; He, H.; Chen, D.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, C.; et al. Uncovering key salt-tolerant regulators through a combined eQTL and GWAS analysis using the super pan-genome in rice. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, nwae043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Hu, Y.; Vannozzi, A.; Wu, K.; Cai, H.; Qin, Y.; Mullis, A.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, L. The WRKY transcription factor family in model plants and crops. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2018, 36, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.H.; Anand, S.; Singh, B.; Bohra, A.; Joshi, R. WRKY transcription factors and plant defense responses: Latest discoveries and future prospects. Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, C.; Xuan, W.; An, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, B.; Chi, W.; Chen, G.; Ge, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Genome-wide association studies identify OsWRKY53 as a key regulator of salt tolerance in rice. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Jing, W.; Cao, C.; Sun, M.; Chi, W.; Zhao, S.; Dai, J.; Shi, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, B.; et al. Transcriptional repressor RST1 controls salt tolerance and grain yield in rice by regulating gene expression of asparagine synthetase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2210338119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Khan, N.U.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, X.; Tang, F.; Wang, F.; Li, Z. Genetic basis and identification of candidate genes for salt tolerance in rice by GWAS. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garciadeblás, B.; Senn, M.E.; Bañuelos, M.A.; Rodríguez-Navarro, A. Sodium transport and HKT transporters: The rice model. Plant J. 2003, 34, 788–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Fang, J.; Wu, X.; Dong, L. Na+/K+ balance and transport regulatory mechanisms in weedy and cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) under salt stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Singh, B.; Panda, K.; Singh, B.P.; Singh, N.; Misra, P.; Rai, V.; Singh, N.K. Association of SNP haplotypes of HKT family genes with salt tolerance in Indian wild rice germplasm. Rice 2016, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafalski, A. Applications of single nucleotide polymorphisms in crop genetics. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002, 5, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Mauleon, R.; Hu, Z.; Chebotarov, D.; Tai, S.; Wu, Z.; Li, M.; Zheng, T.; Fuentes, R.R.; Zhang, F.; et al. Genomic variation in 3010 diverse accessions of Asian cultivated rice. Nature 2018, 557, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.H.; Li, J.H.; Huang, X.C.; Li, S.; Gao, W.J. Advance of SNP analysis based on whole genome resequencing in crop gene mapping. Agri. Food Sci. 2015, 51, 1400–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Norton, G.J.; Price, A.H. Genome-wide association mapping for salt tolerance of rice seedlings grown in hydroponic and soil systems using the Bengal and Assam Aus panel. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 576479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Hu, K.; Zhao, J.; Guo, F.; Shan, W.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; Feng, Z.; Chen, Z.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis for salt-induced phenotypic and physiologic responses in rice at seedling and reproductive stages. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 822618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shohan, M.U.S.; Sinha, S.; Nabila, F.H.; Dastidar, S.G.; Seraj, Z.I. HKT1;5 transporter gene expression and association of amino acid substitutions with salt tolerance across rice genotypes. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 101420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Jia, Y.; Xu, X.; Fu, P.; Zhou, J.; Yang, G. Structural insights into the Oryza sativa cation transporters HKTs in salt tolerance. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2024, 66, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B.; Wang, T.; Luo, Y.; Xu, D.; Li, L.; Diao, Y.; Gao, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zheng, X. Genome-wide association study identified novel candidate loci/genes affecting lodging resistance in rice. Genes 2021, 12, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Feng, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Mao, S.; Zhang, H.; Huang, W.; Liu, H.; Feng, S.; Chu, Z. Investigation of imidazolinone herbicide resistance gene with KASP markers for Japonica/Geng rice varieties in the Huanghuaihai Region of China. Plants 2024, 13, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Niu, Y.; Yang, C.; Liang, Y.; Xu, J. Screening of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes for salinity tolerance and dissecting determinants of tolerance mechanism. Plants 2024, 13, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Y.; Yu, Y.; Mao, S.; Wu, T.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, K.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Chu, Z. Comparative transcriptomic profiling of the two-stage response of rice to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola interaction with two different pathogenic strains. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 347. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, H.; Tamiru, M.; Abe, A.; Yoshida, K.; Uemura, A.; Yaegashi, H.; Obara, T.; Oikawa, K.; Utsushi, H.; Kanzaki, E.; et al. MutMap accelerates breeding of a salt-tolerant rice cultivar. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, K.S.; Meng, L.; Guo, L.; Leng, Y.; Ye, G. Advances in sensing, response and regulation mechanism of salt tolerance in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soda, N.; Kushwaha, H.R.; Soni, P.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Pareek, A. A suite of new genes defining salinity stress tolerance in seedlings of contrasting rice genotypes. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2013, 13, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, R.; Mendioro, M.S.; Diaz, G.Q.; Gregorio, G.B.; Singh, R.K. Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with yield and yield components under reproductive stage salinity stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Genet. 2013, 92, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, F.; Deng, P.; Jing, W.; Zhang, W. Characterization and mapping of a salt-sensitive mutant in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2013, 55, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yang, B.; He, Y.; Zhan, C.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Z. A quantitative trait locus, qSE3, promotes seed germination and seedling establishment under salinity stress in rice. Plant J. 2019, 97, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, L.; Zhang, W.; Zou, T.; Du, Q.; Ma, X.; Cui, D.; Han, B.; Zhang, Q.; Han, L. Integrating linkage mapping and comparative transcriptome analysis for discovering candidate genes associated with salt tolerance in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1065334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Wang, H.; Yin, X.; Wang, F.; Hu, S.; Liu, W.; Chen, L.; Dai, X.; Liang, M. Identification of salt tolerance related candidate genes in ‘Sea Rice 86’ at the seedling and reproductive stages using QTL-Seq and BSA-Seq. Genes 2023, 14, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.M.; Takamatsu, T.; Baslam, M.; Kaneko, K.; Itoh, K.; Harada, N.; Sugiyama, T.; Ohnishi, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Takagi, H.; et al. Salt tolerance improvement in rice through efficient SNP marker-assisted selection coupled with speed-breeding. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mickelbart, M.V.; Hasegawa, P.M.; Bailey-Serres, J. Genetic mechanisms of abiotic stress tolerance that translate to crop yield stability. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrão, S.; Almadanim, M.C.; Pires, I.S.; Abreu, I.A.; Maroco, J.; Courtois, B.; Gregorio, G.B.; McNally, K.L.; Oliveira, M.M. New allelic variants found in key rice salt-tolerance genes: An association study. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2013, 11, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wei, X.; Sang, T.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, C.; Lu, T.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Genome-wide association studies of 14 agronomic traits in rice landraces. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, X.; Li, C.; Wang, A.; Zhao, Q.; Li, W.; Guo, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhu, C.; et al. Genome-wide association study of flowering time and grain yield traits in a worldwide collection of rice germplasm. Nat. Genet. 2011, 44, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, K.; Yamamoto, E.; Aya, K.; Takeuchi, H.; Lo, P.C.; Hu, L.; Yamasaki, M.; Yoshida, S.; Kitano, H.; Hirano, K.; et al. Genome-wide association study using whole-genome sequencing rapidly identifies new genes influencing agronomic traits in rice. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivabharathi, R.C.; Rajagopalan, V.R.; Suresh, R.; Sudha, M.; Karthikeyan, G.; Jayakanthan, M.; Raveendran, M. Haplotype-based breeding: A new insight in crop improvement. Plant Sci. 2024, 34, 112129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Nie, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; et al. A wild rice CSSL population facilitated identification of salt tolerance genes and rice germplasm innovation. Physiol. Plant. 2024, 176, e14301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| SNP Alleles | Base Type (S/T) 1 | Homozygous (S) | Heterozygous | Homozygous (T) | Percentages of T (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STG5I12S | A/C | 30 | 9 | 511 | 92.91 |
| SKC1P140A | C/G | 95 | 19 | 436 | 79.27 |
| SKC1R184H | G/A | 358 | 18 | 174 | 31.63 |
| OsHKT1;1L94K | G/A | 428 | 13 | 109 | 19.82 |
| OsHKT2;3I77T | T/C | 56 | 7 | 487 | 88.55 |
| OsWRKY53A173G | C/G | 37 | 4 | 509 | 92.55 |
| OsSTL1P298S | G/A | 0 | 0 | 550 | 100 |
| RST1A530G | C/G | 504 | 11 | 35 | 6.36 |
| RST1E611G | A/G | 32 | 2 | 516 | 93.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Y.; Wang, T.; Wen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Diao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Feng, W.; Chu, Z. Genetic Variation and Assessment of Seven Salt-Tolerance Genes in an Indica/Xian Rice Population. Agronomy 2025, 15, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030570
Cheng Y, Wang T, Wen Y, Zheng X, Liu H, Chen X, Diao Y, Hu Z, Feng W, Chu Z. Genetic Variation and Assessment of Seven Salt-Tolerance Genes in an Indica/Xian Rice Population. Agronomy. 2025; 15(3):570. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030570
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Yuanhang, Tao Wang, Yeying Wen, Xingfei Zheng, Haifeng Liu, Xiangsong Chen, Ying Diao, Zhongli Hu, Wenjie Feng, and Zhaohui Chu. 2025. "Genetic Variation and Assessment of Seven Salt-Tolerance Genes in an Indica/Xian Rice Population" Agronomy 15, no. 3: 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030570
APA StyleCheng, Y., Wang, T., Wen, Y., Zheng, X., Liu, H., Chen, X., Diao, Y., Hu, Z., Feng, W., & Chu, Z. (2025). Genetic Variation and Assessment of Seven Salt-Tolerance Genes in an Indica/Xian Rice Population. Agronomy, 15(3), 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030570







