Abstract
The Jianghuai region in China is well known for its high-quality and high-yielding maize production, but there is inadequate analysis about the N management in this region (especially the topdressing ratio). To evaluate the suitable topdressing ratio for maize nitrogen application, the effects of different nitrogen topdressing ratios on soil nitrogen and summer maize growth were studied in 2022–2023. In each treatment, a total of 250 kg N/hm2 was applied, i.e., 50 kg N/hm2 was applied as the base fertilizer, and the rest of the nitrogen fertilizer (200 kg N/hm2) was applied at the jointing and filling stages at different ratios, including 3:7 (60 and 140 kg N/hm2 were applied at the jointing and filling stages, respectively, T1 treatment), 7:3 (T2 treatment), and 1:1 (CK treatment). Compound fertilizer (N:P:K = 18%:12%:5%) was used as the base fertilizer, and urea was used as the topdressing fertilizer. The results showed that in 2022 (dry year), compared with values in the T1 treatment, the nitrate-nitrogen accumulation in the 0–100 cm soil layer at maize harvest under the T2 and CK treatments decreased by 33.8% and 14.7%, respectively; compared with values in CK treatment, the T2 treatment could significantly increase the ear length of maize by 9.4%. In 2023 (wet year), compared with values in the T1 treatment, the 100-grain weight, maize yield, N partial factor productivity (NPFP), and N uptake efficiency (NUPE) of T2 treatment significantly increased by 13.4%, 17.2%, 20.1%, and 21.5%, respectively; compared with values in the CK treatment, ear length, maize yield, and NPFP of T2 treatment significantly increased by 6.15%, 14.0%, and 15.8%, respectively. Therefore, for this study, a topdressing ratio of 7:3 between the jointing and filling stages (T2 treatment) was beneficial to reduce nitrogen accumulation in dry years and increase maize yield and nitrogen partial factor productivity in wet years.
1. Introduction
Nitrogen is one of the essential elements for crop growth and yield formation [1], and nitrogen fertilizer can effectively improve crop yield [2]. Maize, a crucial food crop that is widely grown and consumed around the world [3], is one of the primary crops that heavily rely on nitrogen fertilizer. The nitrogen applied to maize accounts for 17.8% of global nitrogen fertilizer usage [4]. However, as the nitrogen fertilizer application rate increases, the crop yield initially rises and then plateaus [5]. Despite this, many farmers in China still tend to apply nitrogen fertilizer excessively to ensure high crop yields, which has led to a significant decline in nitrogen utilization efficiency, resulting in substantial resource wastage and environmental pollution [6]. The nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) of grain production systems in China stands at only 30% or less, which is 50–80% lower than the global average [7]. More than 45% of applied nitrogen is lost through various means, such as leaching, denitrification, and runoff [8]. Nitrate leaching accounts for more than 10% of the total input of nitrogen fertilizers [9]. This leached nitrate-nitrogen can contaminate groundwater resources and pose serious threats not only to the environment but also to human health [10]. Therefore, it is very important to determine the rational application of nitrogen.
The demand for nitrogen fertilizer varies at different stages of maize growth [11], and the timing and amount of nitrogen application are two important factors that affect soil nitrogen accumulation and leaching, crop yield, and nitrogen use efficiency [12,13,14]. For example, Lu et al. [15] found that split-N fertilization significantly reduced nitrate-nitrogen leaching by 7.3–32.4% and increased maize yield by 10.6–34.4% compared with values in treatments with single fertilization in Northwest China. Zheng et al. [16] reported that compared with N1 (topdressing at the jointing stage) and N3 (topdressing at the tasseling stage) treatments, the spring maize yield, N use efficiency, and N uptake in N2 (topdressing at the belling stage) treatment significantly increased by 12.1% and 24.7%, 26.4% and 38.9%, and 10.0% and 16.0%, respectively. Fu et al. [17] found that reduced or no topdressing at the jointing stage decreased the maize yield in Northeast China. Ma et al. [18] found that, for all the N application rates, the N recovery efficiency and dry matter yield of forage maize in treatments with a basal/topdressing ratio of 2:8 were higher than those in treatments with a basal/topdressing ratio of 4:6 for normal rainfall years, while the results (dry matter yield) were the opposite for dry years. However, Nafziger and Rapp [19] found that the application of a portion of N fertilizer to later vegetative stages (tasseling) did not affect the maize yield compared with values in treatment with single fertilization (around sowing) in Perry County, IL, USA. Liu et al. [20] reported that the water condition could affect the optimal N rate for maize in Northwest China; the recommended N rates for the rainy and drought seasons were 211 and 126 kg N hm−2, respectively. Du et al. [21] reported that, compared with a N application of 200 kg N hm−2, a N application rate of 160 kg N hm−2 significantly reduced annual N2O emissions by 24% without decreasing in maize yields. Generally, delaying topdressing can increase inorganic nitrogen accumulation in the soil profile (0–60 cm) [16], and nitrogen leaching can increase if the topdressing at the early stage (jointing) is higher than half of the total topdressing [17]. The difference in results is mainly due to the varied climate and soil conditions [22,23].
The Jianghuai region of China is well known for its high-quality and high-yielding maize production. However, due to the overuse of nitrogen fertilizer in this area, a large amount of nitrogen accumulates in the soil and tends to move downward with rainfall, which poses a potential threat to groundwater security [24]. Currently, most of the studies on the N management of maize in China have been conducted in North China Plain and Northeast and Northwest China [25], while there is inadequate analysis of the N management in Jianghuai (especially the reasonable topdressing ratio). The climate (especially the rainfall) in this region is different from that in North China Plain and Northeast and Northwest China, so it is necessary to conduct research on nitrogen fertilizer management in this region. We hypothesized that the fertilizer requirement for maize varies at different growth stages and the topdressing amount of fertilizer at different growth stages may affect the soil nitrate content and crop growth. Therefore, this study aims to explore the effects of different topdressing ratios on soil nitrate distribution, crop growth, yield, and nitrogen use efficiency.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Information
Experiments using different topdressing ratios for maize were carried out from June 2022 to October 2023 at the Agricultural Soil and Water Experimental Station (119°26′ E, 32°24′ N, about 10 m above sea level) of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou City, Jiangsu Province, China. The area has a subtropical monsoon humid climate with average annual sunshine of 2140 h. The average annual precipitation is 1016.69 mm, the average frost-free period is 220 days, and the mean annual temperature is about 14.8 °C. The temperature and rainfall during the whole growing period of summer maize in 2022 and 2023 are shown in Figure 1. The total precipitation in the 2022 maize season was 281.2 mm, and the amount of precipitation in June (the last 5 days), July, August, September, and October was 6.6 mm, 130.42 mm, 32.8 mm, 16.4 mm, and 95 mm, respectively. The total precipitation in the 2023 maize season was 851.9 mm, and the amount of precipitation in June, July, August, September, and October (the first 15 days) was 2.8 mm, 541.07 mm, 165.41 mm, 127.2 mm, and 15.4 mm, respectively. Based on the daily precipitation data of Yangzhou from 1994 to 2023 [26], the precipitation frequency of the 2022 and 2023 maize seasons was 87.10% and 9.68%, respectively, so the 2022 and 2023 summer maize seasons could be considered as a drought season and wet season, respectively [27]. The physical and chemical properties of the soil in the test field are shown in Table 1.

Figure 1.
Air temperature and rainfall during the maize growing season in (a) 2022 and (b) 2023.

Table 1.
The soil physical properties of the experimental field.
2.2. Experimental Design
Three treatments were compared in this study. In each treatment, a total of 250 kg N/hm2 was applied: 50 kg N/hm2 was applied as the base fertilizer, and the rest of the nitrogen fertilizer (200 kg N/hm2) was applied as topdressing at the jointing and filling stages with three different ratios, namely 3:7 (60 and 140 kg N/hm2 were applied at the jointing and filling stages, respectively), 7:3 (140 and 60 kg N/hm2 were applied at the jointing and filling stages, respectively), and 1:1 (100 and 100 kg N/hm2 were applied at the jointing and filling stages, respectively). The three ratios are referred to as the T1, T2, and CK treatments, respectively (Table 2). For the convenience of mechanical operation, each plot was relatively large (e.g., 6 m × 10 m). The coefficients of variation for soil nutrients and texture before the experiment were 2.3–10.0%, belonging to weak variability. Considering the weak variability in soil and the relatively large area of each plot, each treatment was repeated three times, and these plots were laid out in a completely randomized design in this study. Summer maize (Zea mays L.) was used in this experiment, and the variety was Jiangyu 403. Before sowing, 280 kg/hm2 of three-nutrient compound fertilizer (N:P:K = 18%:12%:5%) and 562.5 kg/hm2 of potassium dihydrogen phosphate (N:P:K = 0%:5%:34%) were applied for each treatment. Urea was used as the topdressing fertilizer. The planting density of maize was 8 plants /m2. The maize was sown in late June and harvested in late October.

Table 2.
The experimental treatments.
2.3. Sampling, Measurement, and Calculations
2.3.1. Soil Moisture Content
The soil samples were taken every 14 days during the whole growth period of the crop. Soil samples (0–100 cm) were collected using a soil auger at 20 cm increments. During sampling in each plot, the soil samples were taken using the 5-point sampling method, and then, the soil samples on the same diagonal were mixed into one sample, so there were three soil samples for each plot. The soil moisture content was determined using the oven-drying method.
2.3.2. Soil Nitrate-Nitrogen
Soil samples for the NO3–N measurements were collected before sowing and each topdressing and at maize harvest. Soil samples (0–100 cm) were collected using a soil auger at 20 cm increments. The 5-point sampling method was used for soil sampling in each plot to ensure sampling uniformity and sufficient quantity of samples. The soil samples were extracted using the KCl solution extraction method, and the nitrate-nitrogen content in the soil was determined with ultraviolet spectrophotometry [28].
2.3.3. Crop Growth Index
The growth index of summer maize mainly included plant height, leaf area, and dry biomass. Considering sampling uniformity and sufficient quantity of samples, the 5-point sampling method was also used for plant samples in each plot. Five maize plants were selected for each plot to measure the growth index. The leaf area index (LAI) was calculated according to Equation (1) [29].
where LAI is the plant leaf area index; represents the planting density (plant/m2); L represents the leaf length (cm); B represents the width of the leaf (cm); represents the correction factor (0.735 for maize).
2.3.4. Determination of Crop Yield
The yield factors of summer maize were cob length, cob diameter, 100-grain weight, and grain yield. At harvest, samples within 5 m2 (35 plants) were collected for each replicate to determine maize grain yield and yield factors (15 m2 for each treatment). The collected maize samples were threshed and dried under natural air conditions until the moisture content of the maize grain reached about 14%.
2.3.5. Determination of Plant Nitrogen
The N uptake of the maize plants was determined with their total aboveground biomass and N concentration. When the summer maize was harvested, 5 whole plant samples were taken from each plot to determine the N concentration. The samples were dried in the oven at 105 °C for 30 min and then dried at 75 °C to constant weight. After grinding, the samples were digested and boiled with H2SO4–H2O2, and the total nitrogen concentration of the plants was measured using the Kjeldahl method [30].
2.3.6. Nitrogen Use Efficiency Index
The nitrogen partial factor productivity (NPFP), nitrogen uptake efficiency (NUPE), and nitrogen utilization efficiency (NUTE) were calculated according to Equations (2)–(4) [31].
where Yield is the maize grain yield (kg hm−2); Nuptake represents the nitrogen uptake of the maize plants (kg hm−2); and Nrate represents the fertilizer level (kg hm−2).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Data analysis was performed using Microsoft Excel 2022 and statistical analysis was performed using SPSS Statistics 26.0. Considering the weak variability in soil and the relatively large area of each plot, higher number of samples would be desirable, so these soil and plant samples could meet the sample requirement for statistical analysis of field experiments. For soil nitrate-nitrogen, growth indexes, yield indicators, yield, and fertilizer use efficiency, a one-way analysis of variance was performed to compare the differences in mean value among all treatments using the least significant difference (LSD) method at a 5% level.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Water Change
The soil water content of different treatments during the growth period of summer maize is presented in Figure 2, which shows that the soil water content of different treatments was similar, so the average water content of the three treatments was used to discuss the changes in soil water content during the whole growth period.
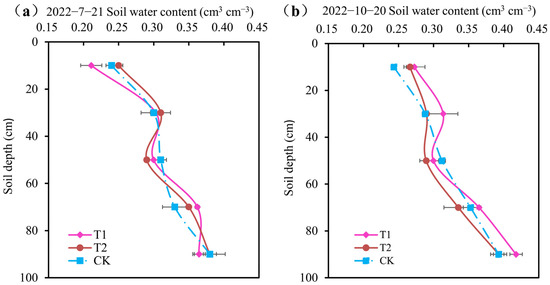
Figure 2.
Soil water content for different treatments.
The changes in soil water content during the growth period of the summer maize are shown in Figure 3. In 2022, the soil water content at 0–60 cm and 60–100 cm varied from 0.17 to 0.30 cm3 cm−3 and 0.31 to 0.40 cm3 cm−3, respectively. In 2023, the soil water content at 0–60 cm and 60–100 cm varied from 0.28 to 0.36 cm3 cm−3 and 0.28 to 0.41 cm3 cm−3, respectively. In the whole growth period of the maize, the soil water content in the 0–60 cm soil layer in 2022 was generally lower than that in 2023, and the soil water content for 60–100 cm in 2022 was similar to that in 2023.
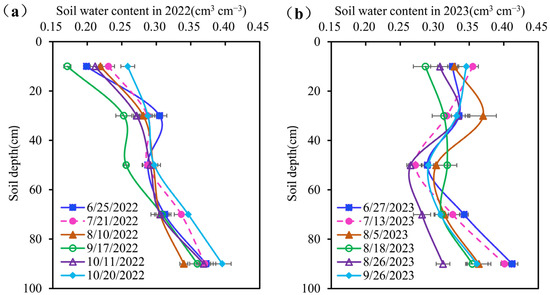
Figure 3.
Soil water content at different times (the soil water content in 2022 and 2023 were shown in (a) and (b), respectively).
Figure 3a shows that there was a great difference in 0–60 cm soil water content between 17 September 2022 and the other dates; there was little difference in 0–60 cm soil water content in June, July, and August; compared with that on 10 August, the soil water content in the 0–60 cm soil layer on 17 September decreased greatly; and compared with that on 17 September, the soil water content in the 0–60 cm soil layer on 11 and 20 October increased greatly. Figure 3b shows that, in 2023, compared with that on 13 July, the soil water content in the 20–60 cm soil layer on 5 August increased greatly. Compared with that on 5 August, the soil water content in the 0–40 cm soil layer on 18 August decreased greatly.
3.2. Effects of Different Treatments on Soil Nitrate-Nitrogen
Figure 4 shows the soil nitrate-nitrogen under different treatments in different periods. The initial value of soil nitrate-nitrogen in 2022 is shown in Figure 4a. Figure 4b shows the soil nitrate-nitrogen in each treatment before the first topdressing, indicating that there was little difference in soil nitrate-nitrogen between the different treatments, which was due to using the same amount of base fertilizer. Compared with the mean values of all the treatments on 27 June, the nitrate-nitrogen in the 0–20 cm and 20–40 cm soil layers on 1 August increased by 62.6% and 74.4%, respectively. There was a non-significant difference in nitrate-nitrogen in the soil layers below 40 cm (p > 0.05), indicating that the applied fertilizer N did not migrate to soil below 40 cm at this stage. Figure 4c shows the distribution of soil nitrate-nitrogen in each treatment before the second topdressing, indicating that compared with values in the T1 treatment, the nitrate-nitrogen concentrations in the top 20 cm soil layer of the T2 and CK treatments were 56.6% and 60.8% higher, respectively. Figure 4d shows the distribution of nitrate-nitrogen in the soil of the different treatments at the summer maize harvest; it reveals that there was no significant difference in the nitrate-nitrogen in the 0–20 cm soil layer between the different treatments (p > 0.05). In the 20–60 cm soil layer, the highest soil nitrate-nitrogen concentration was obtained in the T1 treatment, followed by the CK treatment, and the lowest was observed in the T2 treatment. In the soil layer below 60 cm, the nitrate-nitrogen was similar for all treatments. Compared with the mean initial values of each soil layer (Figure 4a), the mean nitrate-nitrogen in the 0–20, 20–20, and 40–60 cm soil layers at the summer maize harvest (Figure 4d) increased by 161.1%, 304.8%, and 272.3%, respectively. There was little change in soil nitrate-nitrogen concentrations in the 60-100 cm soil layer during the 2022 summer maize season, indicating that nitrate-nitrogen was not washed into the deep soil layer (below 60 cm) in 2022.
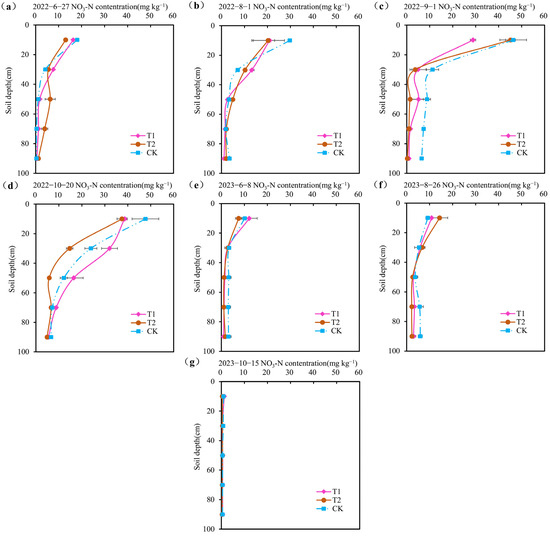
Figure 4.
Soil nitrate-nitrogen content at different times.
Figure 4e shows the initial value of soil nitrate-nitrogen in 2023. Figure 4f shows the distribution of nitrate-nitrogen in each treatment before the second topdressing in 2023, revealing that compared with values in the T2 treatment, the nitrate-nitrogen concentrations in the top 20 cm soil layer of the T1 and CK treatments decreased by 24.0% and 35.9%, respectively. Figure 4g shows the distribution of nitrate-nitrogen in soil under different treatments at the maize harvest in 2023. The concentrations of nitrate-nitrogen in 0–100 cm soil under different treatments were similar to each other and at a very low level (0.33–1.35 mg kg−1).
Figure 5 shows the amount of nitrate-nitrogen in the 0–100 cm soil layer under each treatment at the summer maize harvest. It shows that, in 2022, compared with the value in the T1 treatment (314.5 kg hm−2), the nitrate-nitrogen accumulation in the 0–100 cm soil layer under the T2 (208.4 kg hm−2) and CK (268.3 kg hm−2) treatments was significantly decreased by 33.8% and 14.7%, respectively (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference in soil nitrate-nitrogen accumulation among different treatments at the summer maize harvest in 2023 (p > 0.05), and the values were all at a low level (6.54–13.2 kg hm−2). Compared with the values in 2022, the nitrate-nitrogen accumulation in the 0–100 cm soil layer under each treatment at the maize harvest in 2023 decreased by 95.5–96.9%. This indicates that nitrate-nitrogen could accumulate in the 0–100 cm soil layer under low rainfall (282.2 mm) conditions, while soil nitrate-nitrogen may leach out of the 0–100 cm soil layer under high rainfall (851.8 mm) conditions.
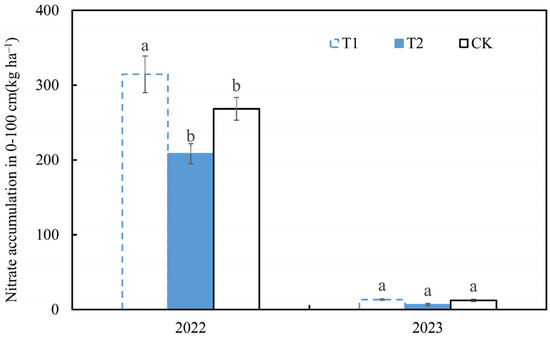
Figure 5.
Soil nitrogen accumulation after harvest of summer maize. The different lowercase letters indicate there was a significant difference among the three treatments for each year (p < 0.05).
3.3. Effects of Different Treatments on Growth Indexes of Summer Maize
Figure 6 shows the variation in summer maize growth indexes with time under different treatments. It shows that there were no significant (p > 0.05) differences in plant height, leaf area index, and dry aboveground biomass among the different treatments in 2022. In 2023 (except the leaf area index on 5 August), there were also no significant (p > 0.05) differences in the three indexes among the different treatments. On 5 August 2023, compared with the CK treatment, the T2 treatment significantly increased the leaf area index of maize by 53.9% (p < 0.05).
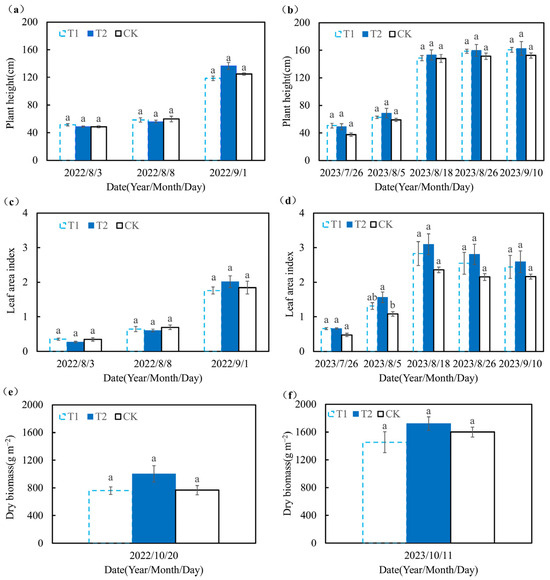
Figure 6.
Growth index of summer maize in 2022 and 2023 (the plant height of maize in 2022 and 2023 were shown in (a) and (b), respectively; the leaf area index of maize in 2022 and 2023 were shown in (c) and (d), respectively; the dry biomass of maize in 2022 and 2023 were shown in (e) and (f), respectively). The different lowercase letters indicate there was a significant difference among the three treatments for each time (p < 0.05).
Compared with the average values of the three treatments in 2022, the average leaf area index of summer maize at the jointing stage (8 August 2022; 5 August 2023) and filling stage (1 September 2022, and 26 August 2023) in 2023 increased by 108.6% and 33.6%, respectively; the average plant height at the jointing and filling stages in 2023 increased by 9.3% and 23.6%, respectively; the average dry aboveground biomass at harvest in 2023 increased by 88.6%.
3.4. Effects of Different Treatments on Summer Maize Yield
The yield indicators of summer maize under different treatments are presented in Table 3, which shows that there were no significant effects of different treatments on cob diameter, 100-grain weight, and yield of maize in 2022 (p > 0.05); compared with values in the CK treatment, the T2 treatment in 2022 significantly increased the cob length of maize by 9.4% (p < 0.05).

Table 3.
Indicators of output.
In 2023, there were significant effects of different treatments on cob diameter, 100-grain weight, cob length, and yield of maize (p < 0.05), e.g., compared with the value in the T1 treatment, the 100-grain weight of maize in the T2 and CK treatments significantly increased by 13.4% and 7.33%, respectively (p < 0.05); compared with the value in the CK treatment, the cob length of maize in the T2 treatment significantly increased by 6.15% (p < 0.05); compared with the values in the T1 and CK treatments, the T2 treatment significantly increased the maize yield by 17.2% and 14.0 % (p < 0.05).
Compared with the values in the same treatment in 2022, the 100-grain weight and cob diameter in 2023 decreased by 9.7–22.8% and 7.2–8.6%, respectively; the cob length in 2023 increased by 3.2–6.4%; the yields in 2023 decreased by 8.92–11.8%. This indicated that the growth status of maize during the reproductive growth stage in 2023 was worse than that in 2022.
3.5. Effects of Different Nitrogen Application Treatments on Nitrogen Use Efficiency
The fertilizer use efficiency of summer maize under different treatments is presented in Table 4. It shows that the treatments had no significant effects on the N uptake, NPFP, NUPE, and NUTE of maize in 2022.

Table 4.
Fertilizer use efficiency.
In 2023, the NPFP of the maize in the T2 treatment was significantly increased by 15.8% and 20.1% compared with the values in the CK and T1 treatment, respectively (p < 0.05); compared with the T1 treatment, N uptake by the maize plants in the T2 and CK treatments was increased by 21.5% and 22.2%, respectively; compared with the T1 treatment, the NUPE under the T2 and CK treatments was increased by 21.5% and 22.2%, respectively; compared with the CK treatment, the NUTE of the T1 and T2 treatments increased by 20.9% and 20.8%, respectively; there were no significant differences in N uptake, NUPE, and NUTE among the different treatments.
Compared with the values in the same treatment in 2022, the NPFP and NUTE in 2023 decreased by 9.2–13.9% and 60.3–67.8%, respectively, while the NUPE in 2023 increased by 123.1–173.4%.
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Water Change During the Experimental Period
The different treatments had little effect on soil water content during the growth period of summer maize because the water supply (rainfall) for all treatments was the same. Li et al. [28] also found that there was little difference in soil water content among all the fertilizer treatments as they used the same water supply for each. The water content in the 0–60 cm soil layer was mostly affected by rainfall, evapotranspiration, and root uptake [32]. The total amount of rainfall during maize season in 2022 and 2023 was 281.2 mm and 851.9 mm, respectively, so the higher rainfall in 2023 led to higher water content in the 0–60 cm soil layer compared with the values in 2022. The soil layer below 60 cm in this field was often affected by the shallow groundwater, and the groundwater table depth of the experimental field during the whole growth period of maize varied within 1.2–1.5 m, so the soil water content for 60–100 cm in 2022 was similar to that in 2023.
Generally, low water supply led to low soil water content. Ning et al. [33] found that soil water content at the filling stage increased compared with values at the jointing stage due to several heavy bursts of rainfall during the filling stage, while the soil water content at the maize harvest decreased compared with values at the filling stage due to the low rainfall. In this study, the low soil water content in the 0–60 cm soil layer on September 17th was mainly due to the low rainfall (33.7 mm) from 10 August to 17 September 2022. The low rainfall (29 mm) from 5 August to 18 August 2023 also led to a decrease in soil water content in the 0–40 cm soil layer from 5 August to 18 August. High water supply often led to high soil water content; compared with that on 17 September 2023, the high rainfall (96.6 mm) from 17 September to 11 October had led to the higher soil water content in the 0–60 cm soil layer on 11 October. The higher soil water content in the 20–60 cm soil layer on 5 August 2023 was mostly due to the high rainfall (316.0 mm) from 14 July to 4 August.
4.2. Effects of Different Treatments on Soil Nitrate-Nitrogen
The soil nitrate-nitrogen was often affected by fertilizer application, water supply, crop uptake, and so on. The soil nitrate-nitrogen concentration often increased with the increase in the fertilizer application rate [33]. In this study, the nitrate-nitrogen concentration in the top 20 cm soil layer of the T2 and CK treatments on 1 September 2022 (before the second topdressing) was higher than that in the T1 treatment, which was due to the relatively higher nitrogen application level in the T2 and CK treatments in the first topdressing; compared with the value in the T2 treatment, the decrease in the nitrate-nitrogen concentration in the top 20 cm soil layer of the T1 and CK treatments on 26 August 2023 (before the second topdressing) may be mostly due to the relatively higher N fertilizer application level in the T2 treatment in the first topdressing.
The soil nitrate-nitrogen concentration was often affected by the time of fertilizer application. Lu et al. [34] reported that delaying the application time of fertilizer increased the soil nitrogen concentration in the upper soil layer at crop harvest. The amounts of N fertilizer for all treatments were the same, while there were great differences in soil nitrate-nitrogen concentration in the 20–60 cm soil layer on 20 October 2022 (at maize harvest); the highest value was obtained in the T1 treatment, followed by the CK treatment, and the lowest was observed in the T2 treatment; meanwhile, compared with the value in the T2 treatment, the nitrate-nitrogen accumulation in the 0–100 cm soil layer at the maize harvest in 2022 under the T1 and CK treatments was significantly increased, indicating that the application time of fertilizer greatly affected the soil nitrate-nitrogen concentration and accumulation in 2022. Gu et al. [35] believed that applying topdressing at the right time could reduce the risk of soil pollution. The maize plant requires more nitrogen during the jointing stage [35], and applying topdressing before the peak absorption period can help reduce the loss of soil nitrate-nitrogen [13]. In our study, increasing the nitrogen fertilizer application level during the jointing stage (T2 treatment) significantly reduced the soil nitrate-nitrogen concentration at the maize harvest in 2022.
Previous studies have revealed that the downward movement of soil water through the soil profile was the primary reason for nitrate leaching [28], so the water supply would greatly affect the soil nitrate-nitrogen [33,34]. Lu et al. [34] found that the soil nitrate-nitrogen in the 0–60 cm soil layer followed the order of (full irrigation) FI < (deficit irrigation) DI < (rain-fed) RF, while the soil nitrate-nitrogen in the 60–120 cm soil layer followed the order of RF < DI < FI. In this study, the 2022 summer maize season was a drought season, and the amount of total rainfall in the 2022 summer maize season was only 281.2 mm (the maximum single rainfall was only 43.3 mm). There were differences in soil nitrate-nitrogen concentration among the different treatments only in the 0–60 cm soil layer, while there was little change in soil nitrate-nitrogen concentrations in the 60–100 cm soil layer during the 2022 summer maize season, indicating that nitrate-nitrogen was not washed into the deep soil layer (below 60 cm) in 2022. Li et al. [28] also found that there was no nitrate-nitrogen leaching out of the 0–60 cm soil layer during the winter wheat season when each irrigation depth was less than 40 mm. The 2023 summer maize season was a wet season, and the amount of total rainfall in the 2023 summer maize season was 851.9 mm. The concentrations of nitrate-nitrogen in the 0–100 cm soil layer at the maize harvest in 2023 under different treatments were similar to each other and at a very low level (0.33–1.35 mg kg−1), possibly due to the high nitrogen leaching caused by the high rainfall (851.9 mm) in the 2023 maize season.
Compared with values at the maize harvest in 2022 (208.4–314.5 kg hm−2), the nitrate- nitrogen accumulation in the 0–100 cm soil layer under each treatment at the maize harvest in 2023 (6.54–13.2 kg hm−2) decreased by 95.5–96.9%. This indicates that nitrate-nitrogen could accumulate in the 0-100 cm soil layer under low rainfall (282.2 mm, dry year) conditions, while the amount of nitrate-nitrogen in the 0–100 cm soil layer was low under high rainfall (851.8 mm, wet year) conditions. Yang et al. [36] found that the highest nitrate-nitrogen accumulation was observed in dry years, followed by normal rainfall years, and the lowest was observed in wet years. Our results were comparable with those of Yang et al. The differences between the two years were due to the following reasons: the low depth of soil nitrate-nitrogen migration [28] and low level of crop nitrogen uptake (Table 4) [36] in the dry years resulted in the nitrogen accumulation in the 0–100 cm soil layer [37], while the high water supply improved the crop nitrogen uptake and the depth of soil water leaching. The results in this study also indicated that the soil nitrate-nitrogen in the 0–100 cm soil layer was mostly affected by fertilizer treatments in the dry year, while the high water supply could decrease the effects of fertilizer treatments on soil nitrate-nitrogen, so the water supply should be considered when developing fertilizer management.
4.3. Effects of Different Treatments on Growth of Summer Maize and Nitrogen Use Efficiency
The growth of maize was affected by water supply and nitrogen supply [38]: both water stress and nitrogen stress had adverse effects on the growth of maize plants [39,40]. Yang et al. [41] found that the plant height and leaf area index of maize decreased with the increase in the degree of drought stress. Ran et al. [38] reported that N stress reduced the final biomass and grain yield by 12.3% and 18.7%, respectively. In this study, the low rainfall in 2022 (only 282.2 mm, dry year) led to water stress on the maize, which may have reduced its nitrogen demand [40], so there were no significant (p > 0.05) differences in plant height, leaf area index, dry aboveground biomass, yield indicator, and yields among the different treatments in 2022. Li et al. [42] found that rainfall intensity had a significant impact on fertilizer loss, and high rainfall led to a decrease in soil nitrogen content. In 2023, there were heavy bursts of rainfall on 21–22 August (112.6 mm) and 12–13 September (67.8 mm), which could have led to large nitrogen leaching, resulting in a similar soil nitrogen concentration in the 0–100 cm soil layer (Figure 4) among the different treatments, so there were almost no significant (p > 0.05) differences in plant height, leaf area index, and dry aboveground biomass among the different treatments during the summer maize season in 2023 (except 5 August).
In this study, the values of the growth indexes (Figure 6) in 2023 were higher than those in 2022, while the values of yield indicators and yield (Table 3) in 2023 were almost lower than those in 2022, which indicated that the growth status of the maize during the vegetative growth stage in 2023 was better than that in 2022, while the growth status of the maize during the reproductive growth stage in 2023 was worse than that in 2022. This could be due to the following: the amount of precipitation in August 2022 was only 32.8 mm, which may have led to severe water stress and then caused adverse affects on the growth of the maize plants during the vegetative stage, while the adequate rainfall in 2023 was able to meet the water demand for maize growth, so the growth indexes in 2023 were higher than those in 2022. Mushore et al. [43] reported that high rainfall may lead to low soil nitrogen content, which is not conducive to yield formation, making extreme rainfall one of the main threats to maize production [44]. In 2023, the heavy bursts of rainfall on 21–22 August (112.6 mm) and 12–13 September (67.8 mm) could have led to low soil nitrate-nitrogen in the 0–100 cm soil layer for all treatments (Figure 4), which might have placed severe nitrogen stress on the maize, so the growth status of the maize during the reproductive growth stage in 2023 was worse than that in 2022.
In 2022, there were no significant differences in maize yield among the three treatments, but the yield in the T2 treatment was higher than that in the T1 and CK treatments by 11.6–13.5%. In 2023, compared with values in the T1 and CK treatments, the maize yield in the T2 treatment significantly increased by 17.2% and 14.0 % (p < 0.05). This indicated that the higher application rate of N fertilizer in the first topdressing in the T2 treatment could increase the yield under these experimental conditions (water stress in 2022 and nitrogen stress in 2023). This could be because topdressing at the jointing stage improves crop growth in the vegetative stage, which could enhance resistance to water and nitrogen stress. Gu et al. [35] also found that topdressing at the jointing stage had significant effects on maize grain yield and yield composition.
Water stress (especially in the vegetative stage) in 2022 had serious adverse effects on the vegetative growth of the maize plants [45], subsequently reducing their nitrogen uptake [46]. Ran et al. [38] reported that water stress reduced aboveground N uptake and seed N uptake by 25.7% and 42.9%, respectively, while the adequate rainfall in 2023 was able to meet the water demand of maize growth, increasing the nitrogen uptake of the maize plants (Table 4), so the NUPE of the summer maize under each treatment in the wet year (2023) was much higher than that in the dry year (2022). Wang et al. [47] also found that the nitrogen accumulation of maize plants with adequate water supply was significantly higher than that of maize plants treated with an inadequate water supply. The demand for nitrogen fertilizer for maize varies at different growth stages, and precise nitrogen application can make effective use of nitrogen fertilizer [48]. This study showed that under the same nitrogen application level, the application of high-nitrogen fertilizer at the jointing stage (T2 treatment) could significantly increase NPFP.
5. Conclusions
This study examined the effects of different nitrogen topdressing ratios on soil nitrogen and summer maize growth. The results show that a topdressing ratio between the jointing and filling stages of 7:3 can reduce soil nitrogen accumulation in a dry year (2022) and increase maize yield and N partial productivity in a wet year (2023). Based on this study, the recommended topdressing ratio between the jointing and filling stages is 7:3 (both dry and wet years) when considering the summer maize yield, nitrogen use efficiency, and soil nitrate-nitrogen accumulation, and the water supply should be considered when developing N fertilizer management.
Author Contributions
Y.L. designed the experiments and wrote the paper; Y.C. conducted field test and data collection; Y.O. and J.W. conducted data analysis and article writing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, granted number: 52409073.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, G.; Gou, Z.; Tian, G.; Sima, W.; Zhou, J.; Bo, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Q. Study on the effectiveness and mechanism of a sustainable dual slow-release model to improve N utilization efficiency and reduce N pollution in black soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 168033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; van Grinsven, H.J.M.; van Loon, M.P.; Doelman, J.C.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Lassaletta, L. Costs and benefits of synthetic nitrogen for global cereal production in 2015 and in 2050 under contrasting scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.R.; Cao, Y.B.; Shi, Y.T.; Qin, F.; Jiang, C.F.; Yang, S.H. Genetic and molecular exploration of maize environmental stress resilience: Toward sustainable agriculture. Mol. Plant. 2023, 16, 1496–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladha, J.K.; Tirol-Padre, A.; Reddy, C.K.; Cassman, K.G.; Verma, S.; Powlson, D.S.; van Kessel, C.; Richter, D.D.; Chakraborty, D.; Pathak, H. Global nitrogen budgets in cereals: A 50-year assessment for maize, rice, and wheat production systems. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, J.W.; Liu, P.; Zhao, B.; Dong, S.T. Increased plant density and reduced N rate lead to more grain yield and higher resource utilization in summer maize. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 2515–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Wang, G.Y.; Muhammad, I.; Chi, Y.X.; Zeeshan, M.; Nasar, J.; Zhou, X.B. Interactive Effects of Melatonin and Nitrogen Improve Drought Tolerance of Maize Seedlings by Regulating Growth and Physiochemical Attributes. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, N.; Zhang, Y.P.; Li, Y.; Luo, J.F.; Gao, X.H.; Jing, Y.P.; Bo, L.J. Water pollution risk from nitrate migration in the soil profile as affected by fertilization in a wheat-maize rotation system. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 210, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Liu, X.D.; Hua, Z.L.; Xue, H.Q.; Mei, S.C.; Wang, P.; Wang, S.W. Comparison of Nitrogen Loss Weight in Ammonia Volatilization, Runoff, and Leaching Between Common and Slow-Release Fertilizer in Paddy Field. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.S.; Kou, C.L.; Wang, Q. Optimal Fertilizer Application Reduced Nitrogen Leaching and Maintained High Yield in Wheat-Maize Cropping System in North China. Plants 2022, 11, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingraham, P.A.; Salas, W.A. Assessing nitrous oxide and nitrate leaching mitigation potential in US corn crop systems using the DNDC model. Agric. Syst. 2019, 175, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagdeep, S.; Varinderpal, S. Chlorophyll meter based precision nitrogen management in spring maize. J. Plant Nutr. 2022, 46, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, A.; Rahimikhoob, A.; Ebrahimian, H.; Varavipour, M. Simulation of nitrogen uptake and distribution under furrows and ridges during the maize growth period using HYDRUS-2D. Irrig Sci. 2019, 37, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, D.; Nelson, K.A. Polymer-coated urea rates, timings, and ratio combinations with non-coated urea for corn. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 1072–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.D.; Cheng, H.; Dai, H.C.; Zhang, H.; Ai, J.J.; Liu, K.C.; Li, Z.X.; Zamanian, K.; Qian, X. Nitrogen uptake and utilization of two maize hybrids with contrasting nitrogen use efficiencies depending on fertilization amount. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2023, 69, 2202–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.S.; Hu, T.T.; Zhang, B.C.; Wang, L.; Yang, S.H.; Fan, J.L.; Yan, S.C.; Zhang, F.C. Nitrogen fertilzier management effects on soil nitrate leaching, grain yield and economic benefit of summer maize in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 247, 106739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ji, J.; Liu, S. Effect of topdressing time on spring maize yield and nitrogen utilization in black soil of northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.X.; Wang, J.D.; Gong, S.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, C.J.; Mo, Y. Optimization of irrigation and fertilization of drip-irrigated corn in the chernozem area of north-east China based on the CERES-Maize model. Irrig Drain. 2020, 69, 714–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Jiang, C.; Shou, N.; Gao, W.; Yang, X. An Optimized Nitrogen Application Rate and Basal Topdressing Ratio Improves Yield, Quality, and Water- and N-use Efficiencies for Forage Maize (Zea mays L.). Agronomy 2023, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafziger, E.D.; Rapp, D. Corn yield response to late-split nitrogen fertilizer. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.Z.; Fan, Z.; Yan, Z.N.; Ren, X.L.; Zhao, X.N.; Zhang, J.J.; Chen, X.L. Evaluation of N nutrition and optimal fertilizer rate for ridge-furrow mulched maize based on critical N dilution curve under different water conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 296, 108801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.L.; Lu, Y.; Guo, S.L.; Wang, R.; Song, X.T.; Ju, X.T. Enhanced efficiency nitrogen fertilizers (EENFs) can reduce nitrous oxide emissions and maintain high grain yields in a rain-fed spring maize cropping system. Field Crops Res. 2024, 312, 109408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Irmak, S. Comparative ananlyses of variable and fixed rate irrigation and nitrogen management for maize in different soil types: Part I. impact on soil-water dynamics and crop evapotranspiration. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Lin, X.M.; Lun, F.; Zeng, R.Y.; Sassenrath, G.F.; Pan, Z.H. Nitrogen fertilizer use and climate interactions: Implications for maize yields in Kansas. Agric. Syst. 2024, 220, 104079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.-B.; Xu, J.-L.; Li, Y.-S. Provenance of groundwater solute and its controlling factors in Yancheng area. Huanjing Kexue 2022, 43, 1908–1919. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.C.; Meng, F.C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Gao, Q.; Yan, L. Optimum management strategy for improving maize water productivity and partial factor productivity for nitrogen in China: A meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Meteorological Data Network. National Meteorological Information Center—China Meteorological Data. Available online: http://data.cma.cn (accessed on 21 August 2024).
- Shan, Y.Y.; Li, G.; Tan, S.; Su, L.J.; Sun, Y.; Mu, W.Y.; Wang, Q.J. Optimizing the Maize Irrigation Strategy and Yield Prediction under Future Climate Scenarios in the Yellow River Delta. Agronomy 2023, 13, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Huang, G. The Effect of Nitrogen Rates on Yields and Nitrogen Use Efficiencies during Four Years of Wheat–Maize Rotation Cropping Seasons. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 2076–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochieng’, I.O.; Ranjan, S.; Seleiman, M.F.; Padhan, S.R.; Psiwa, R.; Sow, S.; Wasonga, D.O.; Gitari, H.I. Increasing rainwater use efficiency, gross return, and grain protein of rain-fed maize under nitrate and urea nitrogen forms. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2023, 51, 13293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.H.; Fu, P.X.; Cheng, G.G.; Lu, W.P.; Lu, D.L. Delaying application time of slow-release fertilizer increases soil rhizosphere nitrogen content, root activity, and grain yield of spring maize. Crop J. 2022, 10, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasar, J.; Zhao, C.J.; Khan, R.; Gul, H.; Gitari, H.; Shao, Z.; Abbas, G.; Haider, I.; Iqbal, Z.; Ahmed, W.; et al. Maize-soybean intercropping at optimal N fertilization increases the N uptake, N yield and N use efficiency of maize crop by regulating the N assimilatory enzymes. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1077948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.T.; Irmak, S. Maize response to coupled irrigation and nitrogen fertilization under center pivot, subsurface drip and surface (furrow) irrigation: Soil-water dynamics and crop evapotranspiration. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 267, 107634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.F.; Chen, H.Q.; Qin, A.Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Duan, A.W.; Wang, X.P.; Liu, Z.D. Optimizing irrigation and N fertigation regimes achieved high yield and water productivity and low N leaching in a maize field in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 301, 108945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.S.; Xiang, Y.Z.; Fan, J.L.; Zhang, F.C.; Hu, T.T. Sustainable high grain yield, nitrogen use efficiency and water productivity can be achieved in wheat-maize rotation system by changing irrigation and fertilization strategy. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 258, 107177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.T.; Ding, M.Q.; Lu, W.P.; Lu, D.L. Nitrogen topdressing at the jointing stage affects the nutrient accumulation and translocation in rainfed waxy maize. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 657–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Feng, G.; Adeli, A.; Tewolde, H.; Qu, Z. Simulated long-term effect of wheat cover crop on soil nitrogen losses from no-till corn-soybean rotation under different rainfall patterns. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Wang, G.Y.; Khan, K.; Yang, L.; Chi, Y.X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.B. Irrigation combines with nitrogen application to optimize soil carbon and nitrogen, increase maize yield, and nitrogen use efficiency. Plant Soil. 2024, 16, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.J.; Ran, H.; Ma, L.F.; Jennings, S.A.; Yu, T.G.; Deng, X.; Yao, N.; Hu, X.T. Quantifying water productivity and nitrogen uptake of maize under water and nitrogen stress in arid Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 285, 108370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Y.; Zhou, G.S.; He, Q.J.; Zhou, H.L. Quantitative Response of Maize Vcmax25 to Persistent Drought Stress at Different Growth Stages. Water 2021, 13, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Ding, R.S.; Du, T.S.; Kang, S.Z.; Tong, L.; Li, S.E. Stomatal conductance drives variations of yield and water use of maize under water and nitrogen stress. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 268, 107651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.M.; Li, Y.R. Effects of water stress and fertilizer stress on maize growth and spectral identification of different stresses. Spectroc. Acta Pt A-Molec. Biomolec. Spectr. 2023, 297, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.A.; Ma, F.; Wang, J.; Qiu, P.P.; Zhang, N.; Guo, W.W.; Xu, J.Z.; Dai, T.Y. Study on the Mechanism of Rainfall-Runoff Induced Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss in Hilly Slopes of Black Soil Area, China. Water 2023, 15, 3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushore, T.; Manatsa, D.; Pedzisai, E.; Muzenda-Mudavanhu, C.; Mushore, W.; Kudzotsa, I. Investigating the implications of meteorological indicators of seasonal rainfall performance on maize yield in a rain-fed agricultural system: Case study of Mt. Darwin District in Zimbabwe. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 129, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guan, K.Y.; Schnitkey, G.D.; DeLucia, E.; Peng, B. Excessive rainfall leads to maize yield loss of a comparable magnitude to extreme drought in the United States. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 2325–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, M.C.; Kemanian, A.R.; Mortensen, D.A. Cover crop effects on maize drought stress and yield. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 311, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirisuntornlak, N.; Ullah, H.; Sonjaroon, W.; Arirob, W.; Anusontpornperm, S.; Datta, A. Effect of seed priming with silicon on growth, yield and nutrient uptake of maize under water-deficit stress. J. Plant Nutr. 2021, 44, 1869–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Janz, B.; Engedal, T.; de Neergaard, A. Effect of irrigation regimes and nitrogen rates on water use efficiency and nitrogen uptake in maize. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillaci, C.; Tadiello, T.; Acutis, M.; Perego, A. Reducing Topdressing N Fertilization with Variable Rates Does Not Reduce Maize Yield. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).