Effects of Mung Bean Residue Return and Biochar Amendment Combined with Reduction in Inorganic Fertilizer on Rice Yield and Nutrient Uptake: A Case Study in Mekong Delta, Vietnam
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Description
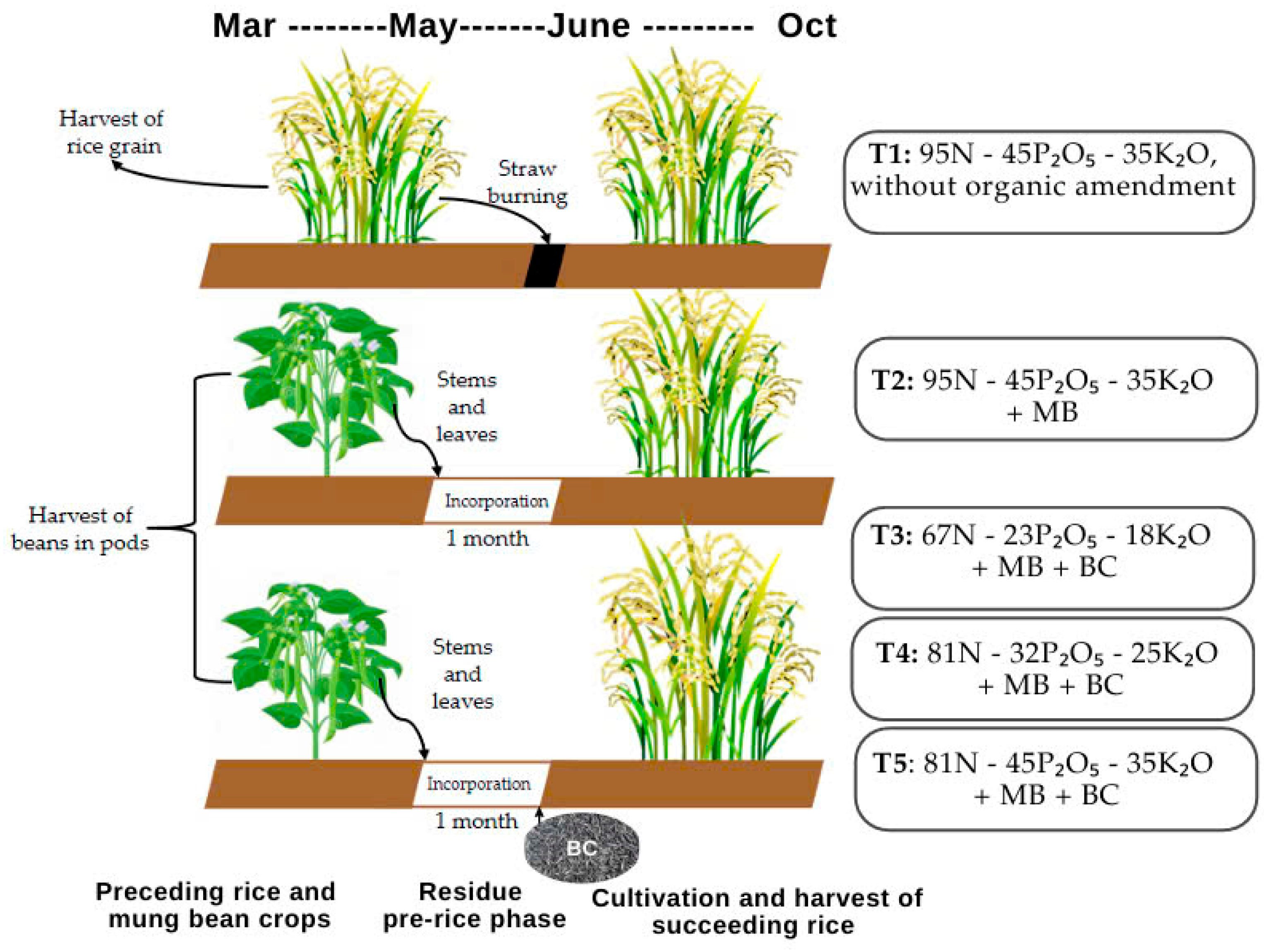
2.2. Experimental Designs
2.2.1. Preceding Rice and Mung Bean Crops
2.2.2. Residue Management During Pre-Rice Phase
2.2.3. Cultivation and Harvest of Succeeding Rice in SA
2.3. Soil and Plant Sampling
2.3.1. Soil Sampling
2.3.2. Plant Sampling
2.4. Analysis of Physical and Chemical Properties of Soil and Plant
2.5. Calculation of N, P, and K Accumulation in Rice Grain, Straw, and Total Biomass
2.6. Calculation of N, P, and K Balance
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Residue Management (Straw Burning and Mung Bean Residue Incorporation) in Spring–Summer Crop on the Soil Chemical Properties
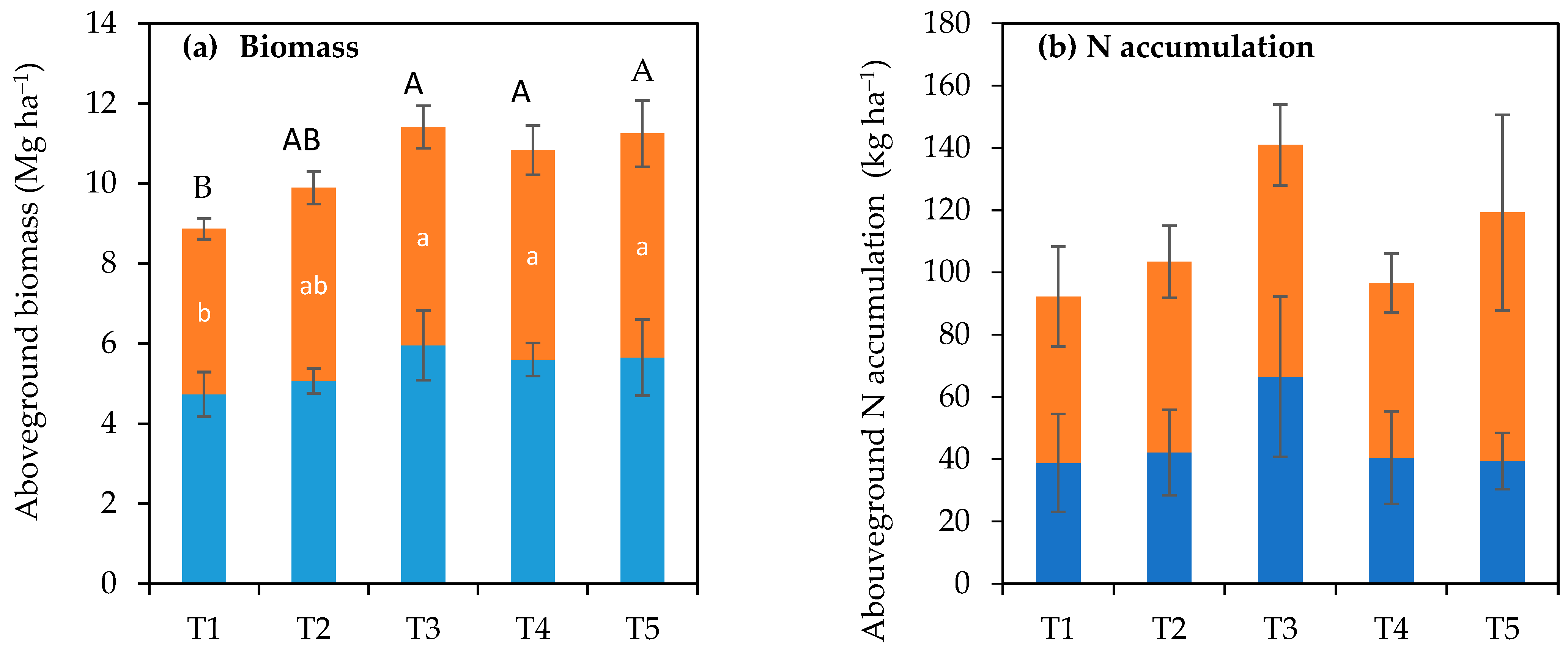
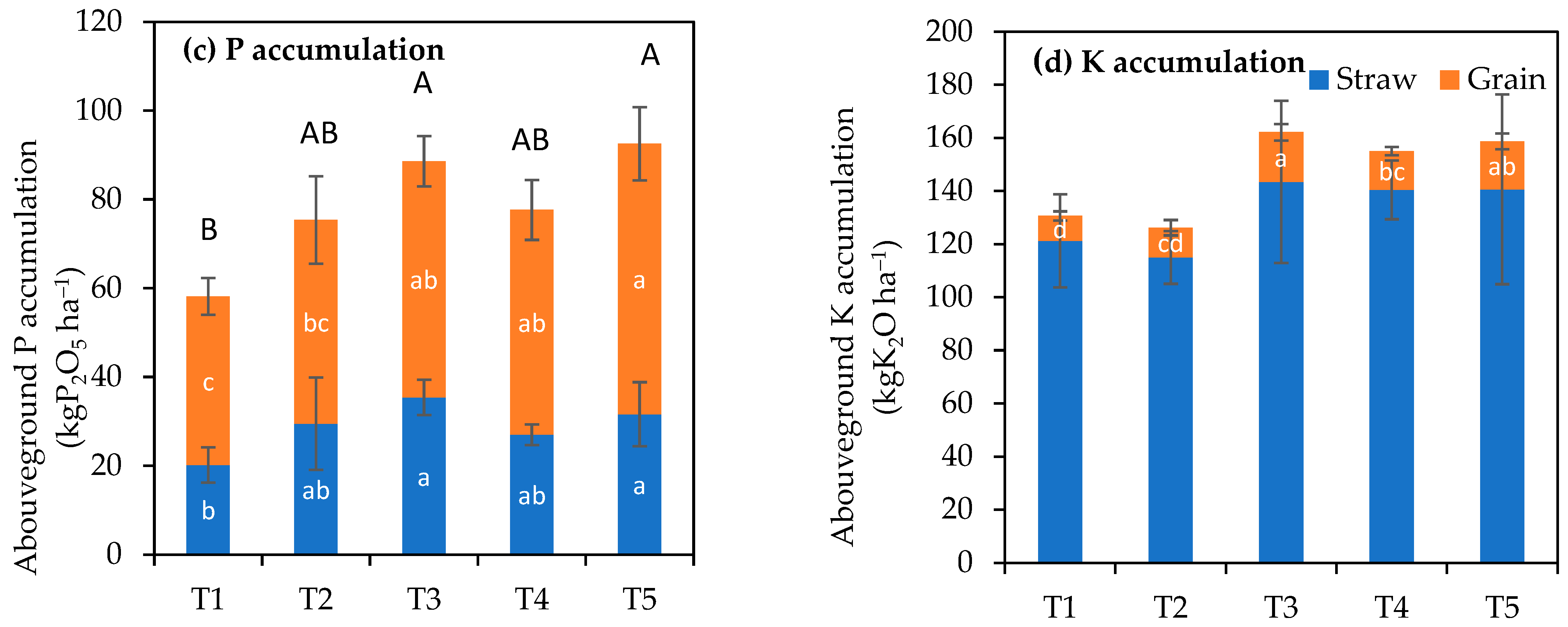
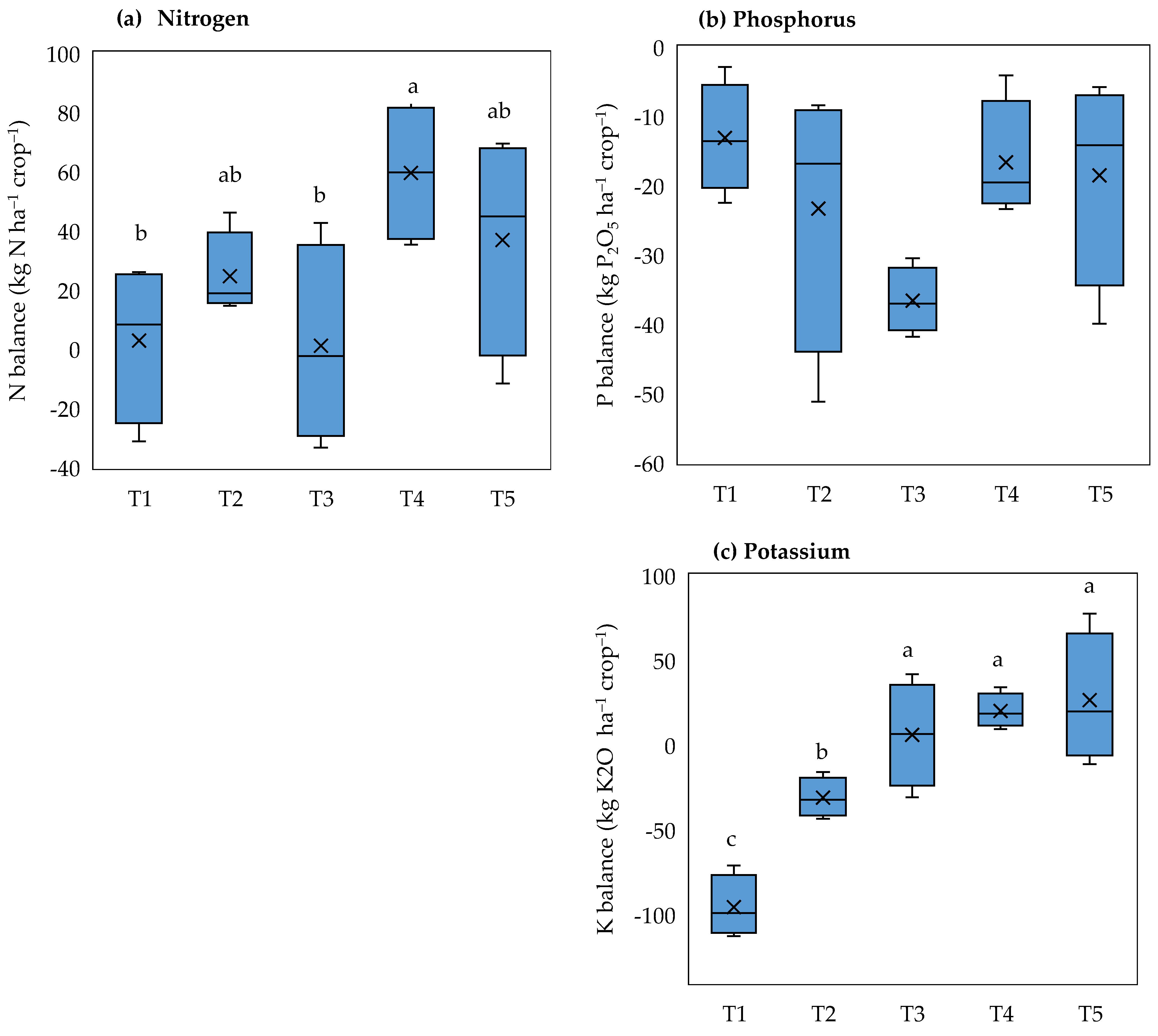
3.2. Effects of Co-Incorporation of Mung Bean Residue and Rice Husk Biochar on Rice Grain and Straw Yields, Nutrient Accumulation, and Nutrient Balance in the Rice Crop in Summer–Autumn
3.3. Effects of Co-Incorporation of Mung Bean and Rice Husk Biochar on Chemical Properties of Soil at the Harvest of Rice Crop in Summer–Autumn
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of Rice Yield to Mung Bean Residue Return and Rice Husk Biochar Amendment Combined with Reducing Inorganic Fertilizer
4.2. Response of Nutrient Accumulation and Apparent Balance to Mung Bean Residue Return and Rice Husk Biochar Amendment Combined with Reducing Inorganic Fertilizer on Sustainable Agricultural Practice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thang, T.C.; Khoi, D.K.; Thiep, D.H.; Tinh, T.V.; Pede, V.O. Assessing the Potential of Climate Smart Agriculture in Large Rice Field Models in Vietnam; CCAFS Working Paper; CCAFS: Frederiksberg, Denmark, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Linh, T.B.; Sleutel, S.; Vo Thi, G.; Le Van, K.; Cornelis, W.M. Deeper tillage and root growth in annual rice-upland cropping systems result in improved rice yield and economic profit relative to rice monoculture. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 154, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassman, K.G.; Pingali, P.L. Intensification of irrigated rice systems: Learning from the past to meet future challenges. Geojournal 1995, 35, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobermann, A.; Cruz, P.C.S.; Cassman, K.G. Fertilizer inputs, nutrient balance, and soil nutrient-supplying power in intensive, irrigated rice systems. I. Potassium uptake and K balance. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 1996, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Niu, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Yuan, L.; Xie, J. Potassium nutrition of crops under varied regimes of nitrogen supply. Plant Soil 2010, 335, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Gao, S.; Lu, Y.; Liao, Y.; Nie, J.; Cao, W. Co-incorporation of green manure and rice straw improves rice production, soil chemical, biochemical and microbiological properties in a typical paddy field in southern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh, T.T.D.; Khoi, C.M.; Sinh, N.V.; Dung, T.V.; Phuong, N.T.K.; My, H.M.T.; Toyota, K. Enhancing soil quality in intensive rice cultivation through short-term growth of green manure and its incorporation combined with rice husk or its ash: A laboratory incubation study. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Gutierrez, J.; Kim, P.J. Considering winter cover crop selection as green manure to control methane emission during rice cultivation in paddy soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 161, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorup-Kristensen, K.; Magid, J.; Jensen, L.S. Catch crops and green manures as biological tools in nitrogen management in temperate zones. Adv. Agron. 2003, 79, 227–302. [Google Scholar]
- Kaewpradit, W.; Toomsan, B.; Cadisch, G.; Vityakon, P.; Limpinuntana, V.; Saenjan, P.; Jogloy, S.; Patanothai, A. Mixing groundnut residues and rice straw to improve rice yield and N use efficiency. Field Crops Res. 2009, 110, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Cao, W.; Bai, J.; Xu, C.; Zeng, N.; Gao, S.; Rees, R.M.; Dou, F. Co-incorporation of rice straw and leguminous green manure can increase soil available nitrogen (N) and reduce carbon and N losses: An incubation study. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odhiambo, J.J. Potential use of green manure legume cover crops in smallholder maize production systems in Limpopo province, South Africa. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Mureithi, J.; Gachene, C.; Ojiem, J. The role of green manure legumes in smallholder farming systems in Kenya: The legume research network project. Trop. Subtrop. Agroecosystems 2003, 1, 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Amano, T.; Shiraiwa, T. Nitrogen use efficiency and recovery from N fertilizer under rice-based cropping systems. Aust. J. Crop. Sci. 2009, 3, 336–351. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.; Sofian-Azirun, M.; Boyce, A. Response of nitrogen fertilizer and legume residues on biomass production and utilization in rice-legume rotation. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2013, 23, 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Sangwan, P.; Dhankhar, R.M.V.; Bidra, S. Utilization of rice husk and their ash: A review. Res. J. Chem. Environ. Sci. 2013, 1, 126–129. [Google Scholar]
- Asadi, H.; Ghorbani, M.; Rezaei-Rashti, M.; Abrishamkesh, S.; Amirahmadi, E.; Chengrong, C.; Gorji, M. Application of rice husk biochar for achieving sustainable agriculture and environment. Rice Sci. 2021, 28, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, N.T.K.; Khoi, C.M.; Ritz, K.; Linh, T.B.; Minh, D.D.; Duc, T.A.; Sinh, N.V.; Linh, T.T.; Toyota, K. Influence of rice husk biochar and compost amendments on salt contents and hydraulic properties of soil and rice yield in salt-affected fields. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh, D.T.T.; Khoi, C.M.; Ritz, K.; Van Sinh, N.; Phuong, N.T.K.; My, H.M.T.; Linh, T.B.; Minh, D.D.; Linh, T.T.; Toyota, K. Effects of rice husk biochar and compost amendments on soil phosphorus fractions, enzyme activities, and rice yields in salt-affected acid soils in the Mekong Delta, Viet Nam. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, E.; Vaneeckhaute, C. Greenhouse gas emissions from inorganic and organic fertilizer production and use: A review of emission factors and their variability. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, G.W.; Bauder, J.W. Particle-size analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 383–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, R.B.; Reinsch, T.G. Bulk density and linear extensibility. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 201–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, R.R.; Islam, K.R.; Stine, M.A.; Gruver, J.B.; Samson-Liebig, S.E. Estimating active carbon for soil quality assessment: A simplified method for laboratory and field use. Am. J. Altern. Agric. 2003, 18, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houba, V.; Van der Lee, J.; Novozamsky, I. Soil Analysis Procedures; Other Procedures (Soil and Plant Analysis, Part 5B); Department of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, Wageningen Agricultural University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1995; 217p. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, R.H.; Kurtz, L.T. Determination of total, organic, and available forms of phosphorus in soils. Soil Sci. 1945, 59, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillman, G.; Sumpter, E. Modification to the compulsive exchange method for measuring exchange characteristics of soils. Soil Res. 1986, 24, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Guo, J.; Fang, F.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, L. Inventory of apparent nitrogen and phosphorus balance and risk of potential pollution in typical sloping cropland of purple soil in China—A case study in the Three Gorges Reservoir region. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 106, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, X.; Liao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Nie, J.; Cao, W. Co-incorporation of rice straw and green manure benefits rice yield and nutrient uptake. Crop. Sci. 2019, 59, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Shah, F.; Zhou, C. Combining rice straw biochar with leguminous cover crop as green manure and mineral fertilizer enhances soil microbial biomass and rice yield in South China. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 778738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, D.; Babu, S.; Qureshi, A.A.; Murthy, I. Enhancing nutrient-use efficiency in crop production—A review. Indian J. Agron. 2007, 52, 261–274. [Google Scholar]
- Mbuthia, L.W.; Acosta-Martínez, V.; DeBruyn, J.; Schaeffer, S.; Tyler, D.; Odoi, E.; Mpheshea, M.; Walker, F.; Eash, N. Long term tillage, cover crop, and fertilization effects on microbial community structure, activity: Implications for soil quality. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 89, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, M.S.; Khera, T.S.; Doran, J.W.; Singh, K.; Singh, B. Yields and nitrogen dynamics in a rice–wheat system using green manure and inorganic fertilizer. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Xu, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Tu, C.; Amonette, J.E.; Cadisch, G.; Yong, J.W.H.; Hu, S. Impact of biochar application on nitrogen nutrition of rice, greenhouse-gas emissions, and soil organic carbon dynamics in two paddy soils of China. Plant Soil. 2013, 370, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, K.T.; Okazaki, K.; Ookawa, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Ohwaki, Y. Influence of rice-husk biochar and Bacillus pumilus strain TUAT-1 on yield, biomass production, and nutrient uptake in two forage rice genotypes. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, C.J.; Fitzgerald, J.D.; Hipps, N.A. Potential mechanisms for achieving agricultural benefits from biochar application to temperate soils: A review. Plant Soil 2010, 337, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, I.; Wang, P.; Mei, Q.; Huang, Y. Effects of different straw biochars on soil organic carbon, nitrogen, available phosphorus, and enzyme activity in paddy soil. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunil, T.K.; Virdia, H.M.; Patel, K.G.; Ragi, S.; Chowdhury, M.; Kumar, P.; Elbagory, M.; Omara, A.E.-D.; Salem, A.; Elbeltagi, A.; et al. Effect of summer legume residue incorporation and fertilizer regimes on rice growth, yield, and nutrient uptake. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1467201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, T.E.; Sohi, S.P. Establishing release dynamics for plant nutrients from biochar. GCB Bioenergy 2013, 5, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.-K.; Shinogi, Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Choi, B. Utilization of biochar impregnated with anaerobically digested slurry as slow-release fertilizer. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2014, 177, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, N.M.; Janssen, B.H.; Oenema, O.; Dobermann, A. Comparison of partial and complete soil K budgets under intensive rice cropping in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 116, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatments | Total N (kg N ha−1) | Total P (kg P2O5 ha−1) | Total K (kg K2O ha−1) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inorg. | MB | RHB | Total | Inorg. | MB | RHB | Total | Inorg. | MB | RHB | Total | |
| T1 | 95 | 0 | 0 | 95 | 45 | 0 | 0 | 45 | 35 | 0 | 0 | 35 |
| T2 | 95 | 28 | 0 | 128 | 45 | 7 | 0 | 52 | 35 | 60 | 0 | 95 |
| T3 | 67 | 28 | 47 | 142 | 23 | 7 | 22 | 52 | 18 | 60 | 90 | 168 |
| T4 | 81 | 28 | 47 | 156 | 32 | 7 | 22 | 61 | 25 | 60 | 90 | 175 |
| T5 | 81 | 28 | 47 | 156 | 45 | 7 | 22 | 74 | 35 | 60 | 90 | 185 |
| Crops | Time | pHH2O (1:5) | EC (1:5) | Labile C | P Bray 2 | Inorganic N | Exchangeable K | Exchangeable Ca |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mS cm−1 | g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | cmolc kg−1 | cmolc kg−1 | |||
| Rice | 1st | 4.53 | 0.64 | 0.97 | 19.0 | 27.0 | 0.07 | 6.2 |
| 2nd | 4.50 | 0.64 | 0.97 | 19.1 | 27.6 | 0.07 | 6.3 | |
| T-test | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Mung bean | 1st | 4.88 | 0.59 | 0.95 | 19.4 | 26.5 | 0.09 | 6.8 |
| 2nd | 4.80 | 0.57 | 0.94 | 17.1 | 17.5 | 0.20 | 6.6 | |
| T-test | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | *** | ns |
| Treatment | pH (H2O) | EC (1:5) | Labile C | Bray 2 P | Inorganic N | Exchangeable K | Exchangeable Ca |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mS cm−1 | g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | cmolc kg−1 | cmolc kg−1 | ||
| T1 | 5.08 ± 0.10 | 0.23 ± 0.05 | 1.01 ± 0.15 | 12.7 ± 5.6 | 27.5 ± 4.0 | 0.183 ± 0.028 | 6.37 ± 0.44 |
| T2 | 5.13 ± 0.10 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 1.12 ± 0.06 | 16.5 ± 7.9 | 29.1 ± 5.0 | 0.134 ± 0.008 | 6.43 ± 0.37 |
| T3 | 5.13 ± 0.26 | 0.30 ± 0.10 | 1.05 ± 0.05 | 16.5 ± 5.9 | 32.4 ± 4.2 | 0.199 ± 0.041 | 6.23 ± 0.25 |
| T4 | 5.28 ± 0.22 | 0.22 ± 0.04 | 1.03 ± 0.06 | 16.0 ± 5.4 | 28.1 ± 2.0 | 0.130 ± 0.027 | 6.11 ± 0.20 |
| T5 | 5.10 ± 0.32 | 0.29 ± 0.14 | 1.08 ± 0.06 | 14.2 ± 4.1 | 28.6 ± 1.6 | 0.162 ± 0.012 | 6.33 ± 0.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Linh, D.T.T.; Khoi, C.M.; Dung, T.V.; Khanh, T.H.; Sinh, N.V.; Phuong, N.T.K.; My, H.M.T.; Toyota, K. Effects of Mung Bean Residue Return and Biochar Amendment Combined with Reduction in Inorganic Fertilizer on Rice Yield and Nutrient Uptake: A Case Study in Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Agronomy 2025, 15, 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020278
Linh DTT, Khoi CM, Dung TV, Khanh TH, Sinh NV, Phuong NTK, My HMT, Toyota K. Effects of Mung Bean Residue Return and Biochar Amendment Combined with Reduction in Inorganic Fertilizer on Rice Yield and Nutrient Uptake: A Case Study in Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Agronomy. 2025; 15(2):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020278
Chicago/Turabian StyleLinh, Doan Thi Truc, Chau Minh Khoi, Tran Van Dung, Tran Huynh Khanh, Nguyen Van Sinh, Nguyen Thi Kim Phuong, Huynh Mach Tra My, and Koki Toyota. 2025. "Effects of Mung Bean Residue Return and Biochar Amendment Combined with Reduction in Inorganic Fertilizer on Rice Yield and Nutrient Uptake: A Case Study in Mekong Delta, Vietnam" Agronomy 15, no. 2: 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020278
APA StyleLinh, D. T. T., Khoi, C. M., Dung, T. V., Khanh, T. H., Sinh, N. V., Phuong, N. T. K., My, H. M. T., & Toyota, K. (2025). Effects of Mung Bean Residue Return and Biochar Amendment Combined with Reduction in Inorganic Fertilizer on Rice Yield and Nutrient Uptake: A Case Study in Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Agronomy, 15(2), 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020278






