Agricultural Waste for Remediation of Neonicotinoid Pollution: Mechanisms and Environmental Effects of Multi-Site Adsorption of Dinotefuran on Rice Husk Biochar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of RHB
2.3. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.3.1. Adsorption Kinetics
2.3.2. Adsorption Isotherms
2.3.3. Adsorption Thermodynamics
2.3.4. Influence of Environmental Factors
2.4. Reusability Performance
2.5. Characterization
2.6. Density Functional Theory (DFT) Calculation
2.7. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of RHB
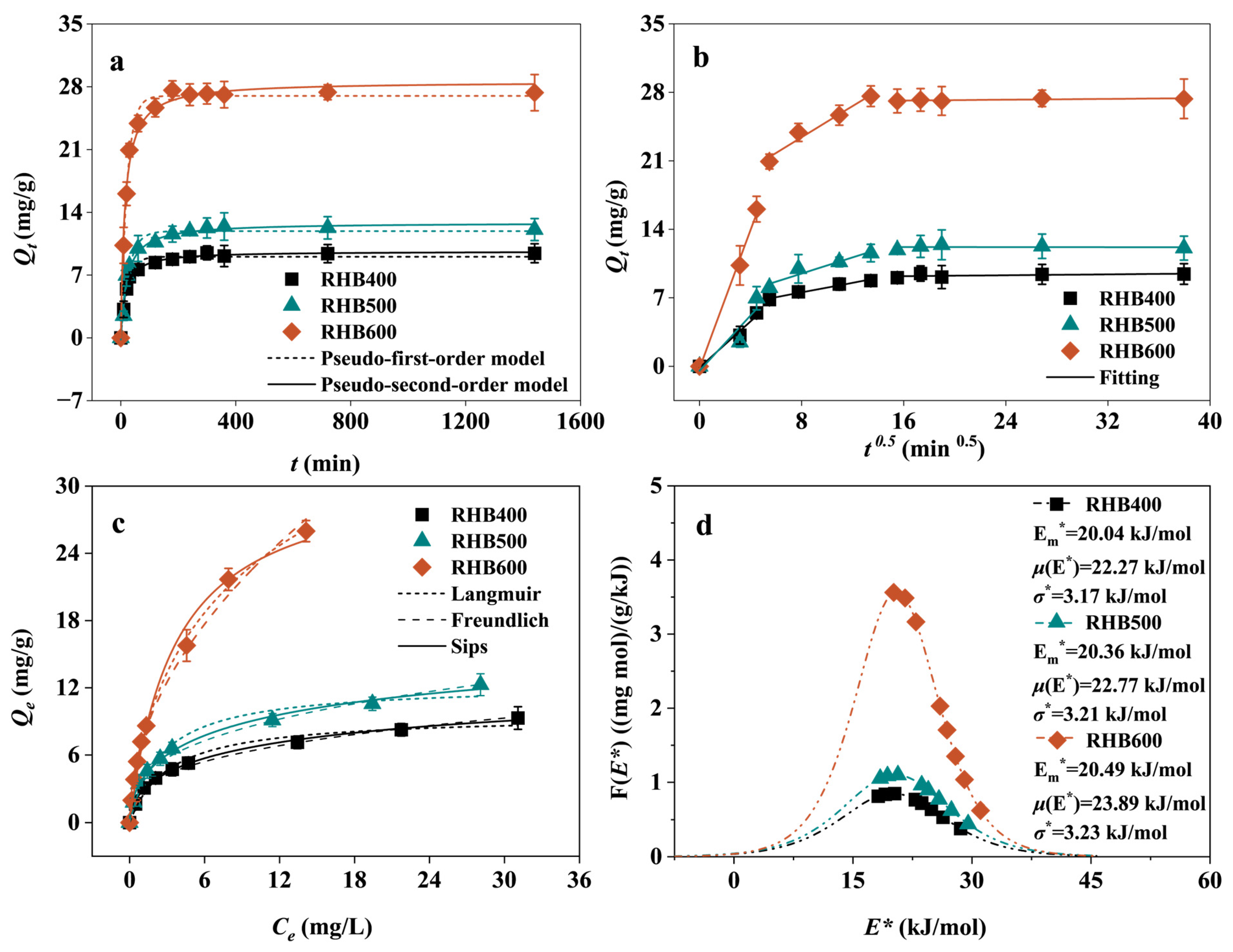
3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
3.3. Analysis of Isothermal Adsorption Results
3.3.1. Adsorption Isotherm
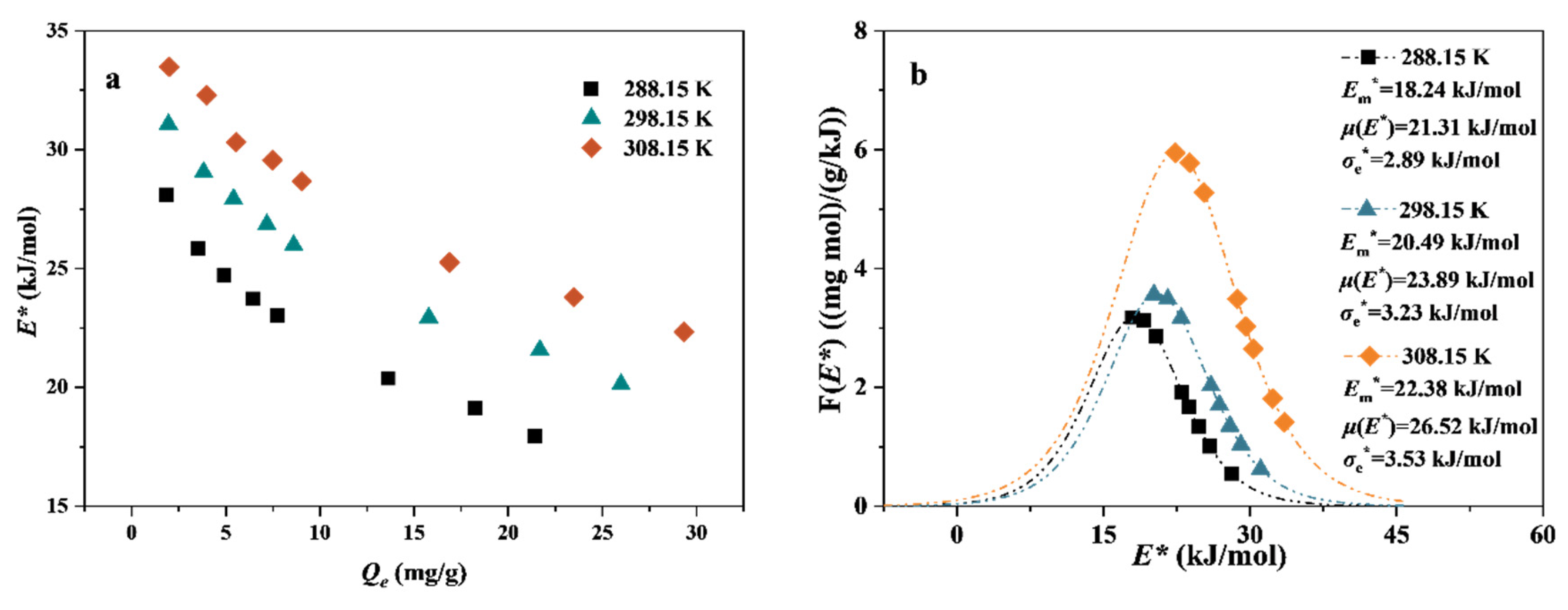
3.3.2. Site Energy Distribution Theory
3.4. Adsorption Thermodynamics
3.5. Influence of Individual Environmental Factors
3.5.1. Ionic Strength
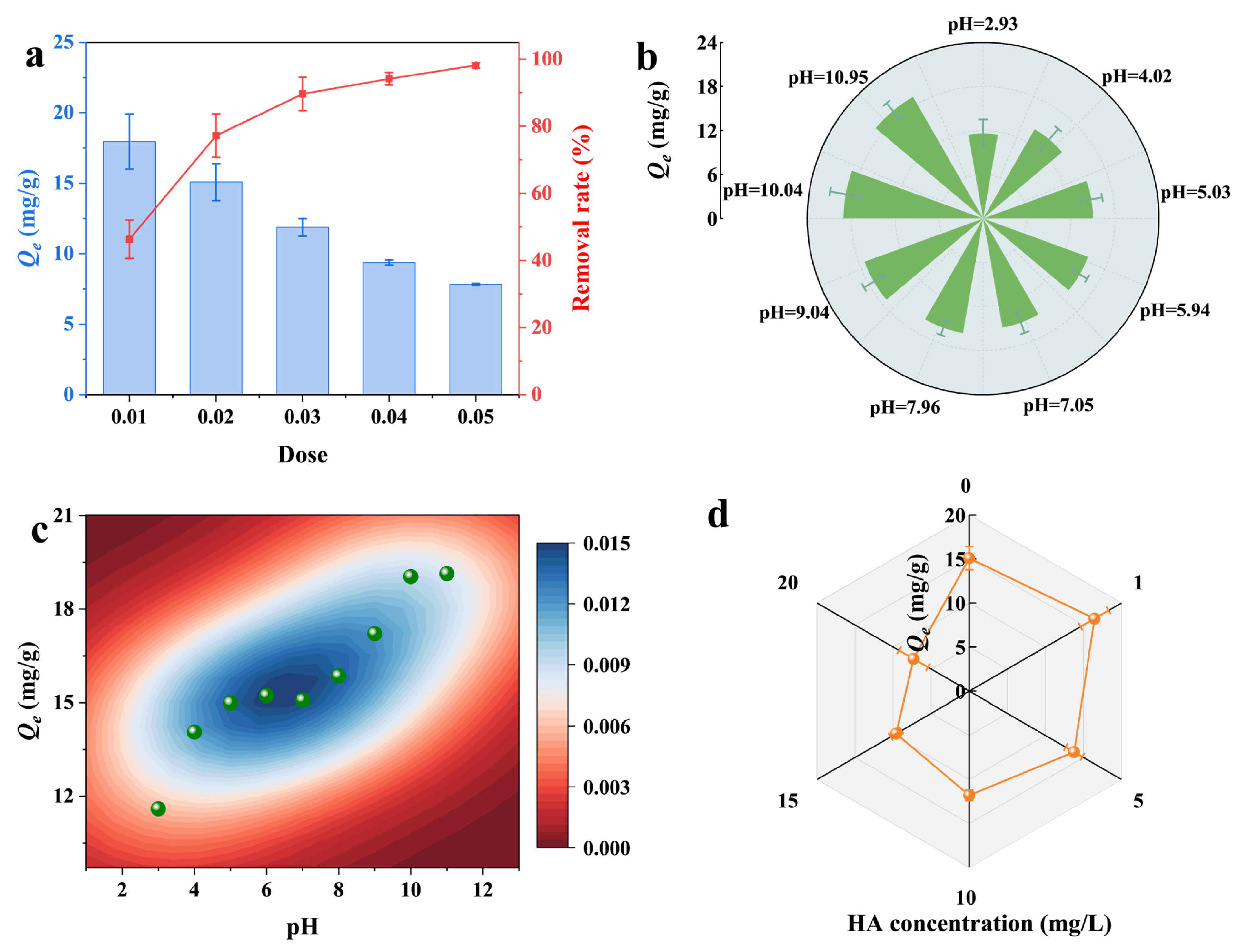
3.5.2. Adsorbent Dosage
3.5.3. Solution pH
3.5.4. HA Concentration
3.5.5. Co-Existing Anions
3.5.6. Co-Existing Cations
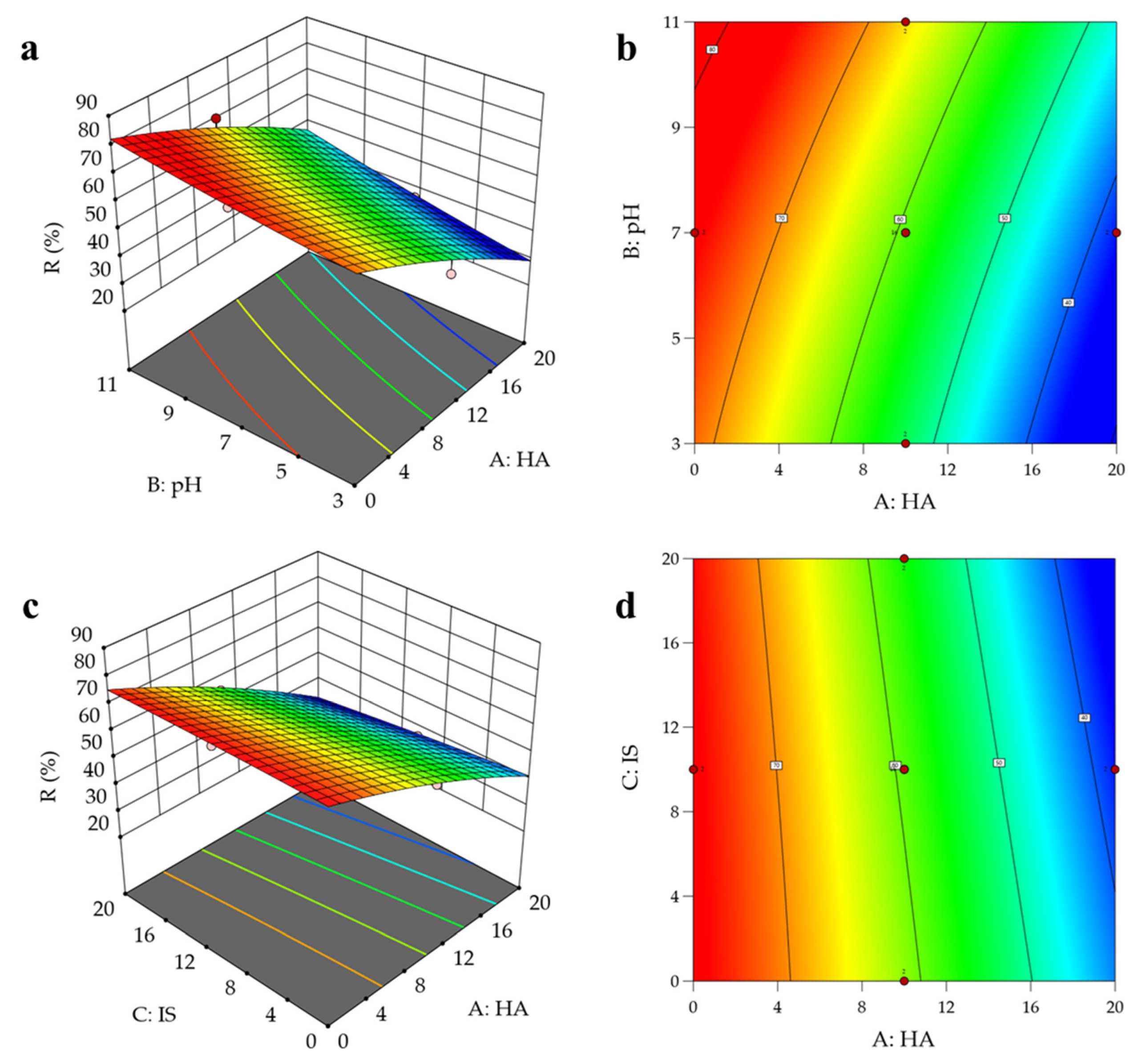
3.6. Interactive Effects of Combined Environmental Factors
3.6.1. RSM Analysis
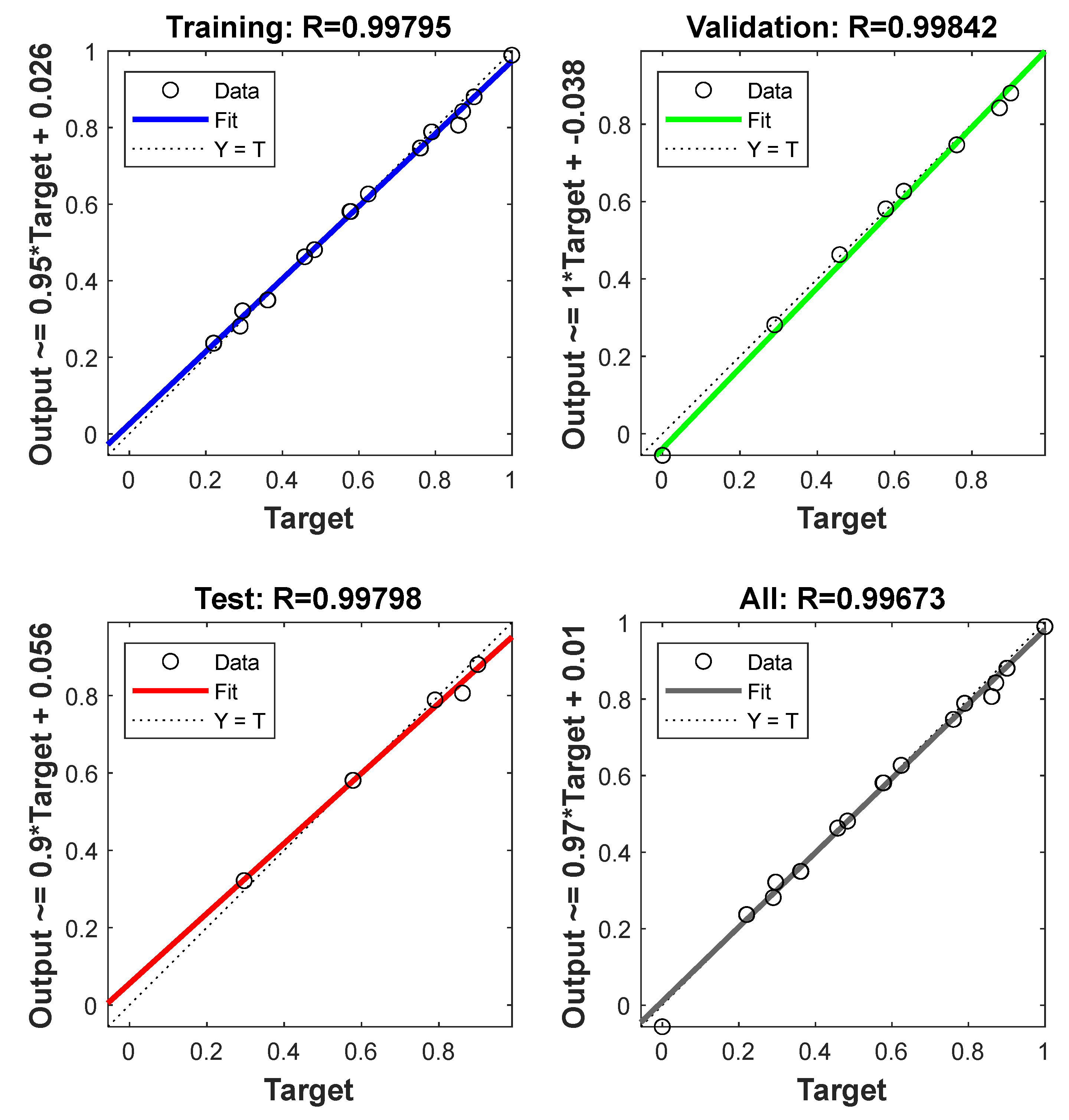
3.6.2. ANN Analysis
3.6.3. Comparison and Validation of RSM and ANN
3.7. Reusability of RHB600
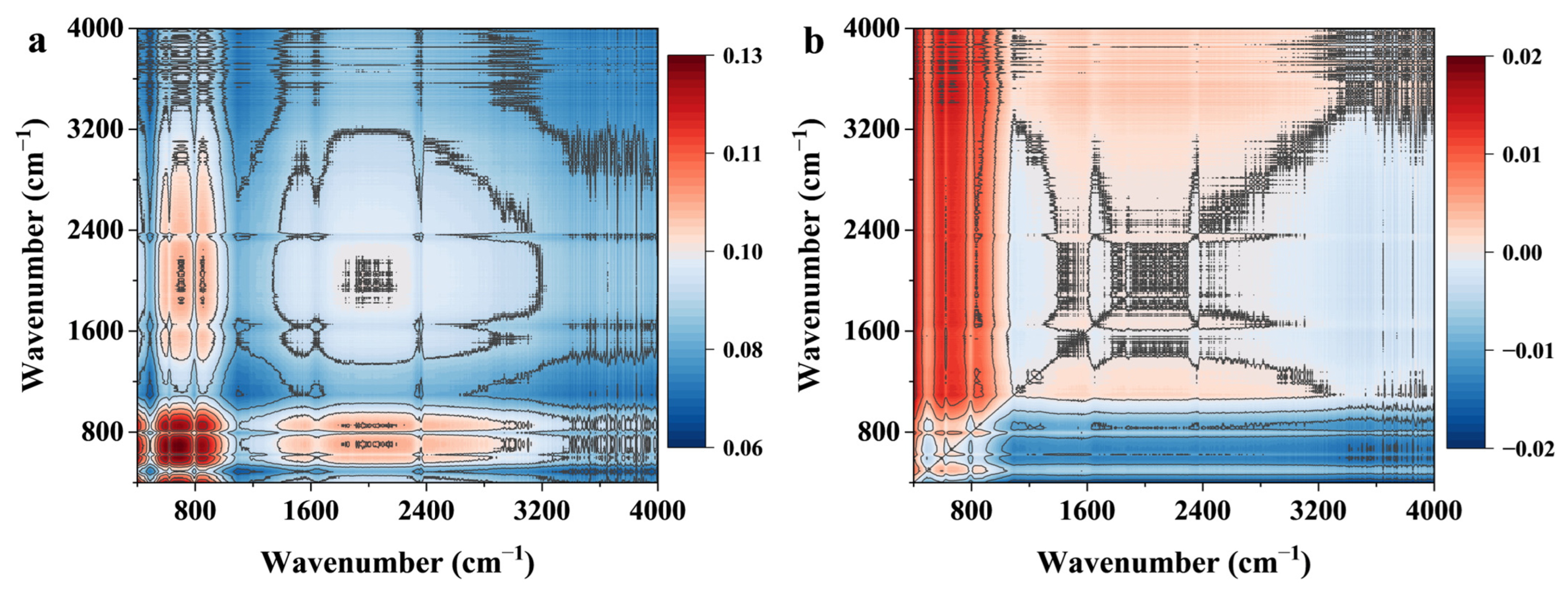
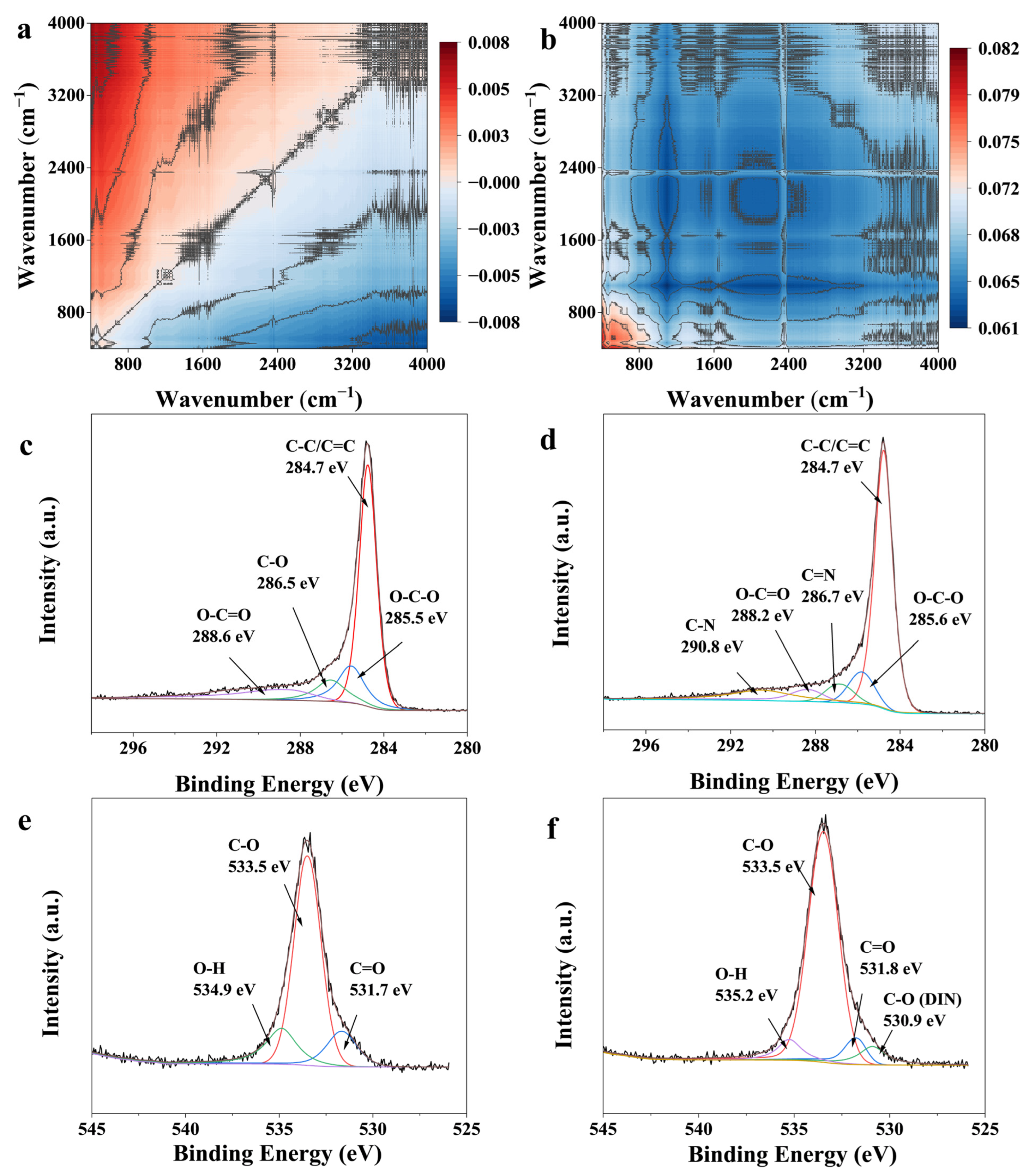
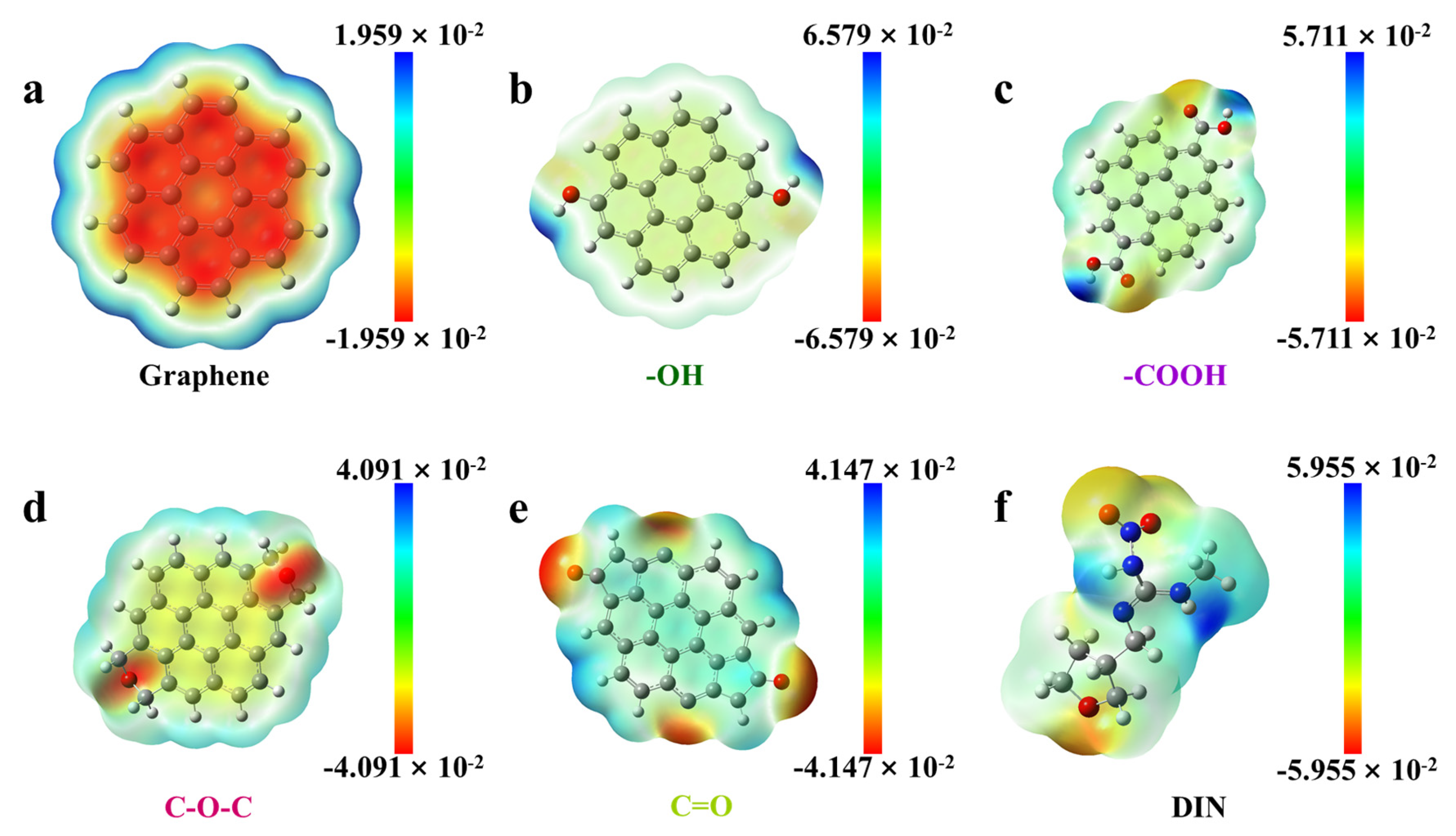
3.8. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
5. Environmental Implications and Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RHB | Rice husk biochar |
| RHB400 | Rice husk biochar pyrolyzed at 400 °C |
| RHB500 | Rice husk biochar pyrolyzed at 500 °C |
| RHB600 | Rice husk biochar pyrolyzed at 600 °C |
| NEOs | Neonicotinoid insecticides |
| DIN | Dinotefuran |
| SSA | Specific surface area |
| PV | Pore volume |
| 2D-COS | Two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy |
| SED | Site energy distribution |
References
- Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, W.-J.; Wu, S.; Lei, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, W.; Mishra, S.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. Environmental occurrence, toxicity concerns, and biodegradation of neonicotinoid insecticides. Environ. Res. 2023, 218, 114953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsafran, M.; Rizwan, M.; Usman, K.; Saleem, M.H.; Jabri, H.A. Neonicotinoid insecticides in the environment: A critical review of their distribution, transport, fate, and toxic effects. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Shen, X.; Lv, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. Bioaccumulation, transformation and toxicity of imidacloprid and dinotefuran in Eisenia fetida under single and binary exposure scenarios. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 111, 104570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Cao, J.; Li, Q.; Yan, Y. Occurrence; source, and risk assessment of neonicotinoid insecticides in the Huai River, China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 122068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Yan, Y. Residues of neonicotinoid insecticides in artificial waterways of the Eastern Route of the South-to North water diversion project, China: Implications for environmental risks and human health. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhang, S.; Covaci, A.; Xia, X. Urban sewage discharge of neonicotinoids and their transformation products threatens aquatic organisms. Water Res. 2025, 268, 122740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, C.A.; Mineau, P.; Devries, J.H.; Sanchez-Bayo, F.; Liess, M.; Cavallaro, M.C.; Liber, K. Neonicotinoid contamination of global surface waters and associated risk to aquatic invertebrates: A review. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, S.; Ito, M.; Nagasawa, S.; Morohashi, M.; Ohno, M.; Todate, Y.; Kose, T.; Kawata, K. Runoff and Degradation of Aerially Applied Dinotefuran in Paddy Fields and River. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 94, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Cui, W.; Wei, D.; Yu, S.; Lu, Z.; Quan, Z. An integrated assessment and spatial-temporal variation analysis of neonicotinoids in pollen and honey from noncrop plants in Zhejiang, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, I.; Soran, M.-L.; Stegarescu, A.; Opriş, O. Devrinol and triadimefon removal from aqueous solutions using CNT-COOH/MnO2/Fe3O4 nanocomposite. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2022, 19, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Zhou, L. Photolysis of fungicide triadimefon: A combined experimental and theoretical investigation on homolytic CO and CN bonds dissociation mechanisms. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 436, 114402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Z.-H.; Yan, L.; Dong, F.-X.; Qian, W.; Deng, Q.-H.; Kong, L.-J.; Yang, J.-W.; Lei, Z.-X.; Du, J.-J.; Chu, W. Degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol by a novel iron based system and its synergism with Cd(II) immobilization in a contaminated soil. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Lv, J.; Hough, R.; Fu, Q.; An, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ke, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.-F. Recent advances and prospects of neonicotinoid insecticides removal from aquatic environments using biochar: Adsorption and degradation mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 939, 173509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Dai, J.; Zhu, Z.; Huo, P.; Yan, Y.; Li, C. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor arrays combined with machine learning for simultaneous determination of three neonicotinoid insecticides. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2025, 111789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajermoun, N.; Haddioui, L.; Bard, A.; Laghrib, F.; Farahi, A.; Lahrich, S.; Bakasse, M.; Saqrane, S.; Abderrahim El Mhammedi, M. Environmental and human health impacts of neonicotinoid insecticides: A review. Pedosphere 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Yang, M.; Chen, H.; Tian, X. Straw and its biochar differently affect soil bacteria community composition, co-occurrence network and function in Cd-contaminated soil. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šunta, U.; Prosenc, F.; Trebše, P.; Bulc, T.G.; Kralj, M.B. Adsorption of acetamiprid, chlorantraniliprole and flubendiamide on different type of microplastics present in alluvial soil. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Qiu, L.; Wang, L. Investigation into adsorption characteristics and mechanism of atrazine on nano-MgO modified fallen leaf biochar. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, F.M.; Undabeytia, T.; Jaworski, M.; Morillo, E.; Sánchez, R. Organo-montmorillonites as adsorbent materials for thiophanate-methyl removal: Adsorption-desorption studies and technological applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, P.; Manna, M.S.; Nag, S. A critical review on green synthesis and modification techniques of biochar: Comparison of efficacies towards adsorption capacities. Biomass Bioenergy 2025, 198, 107859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Xia, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Shao, P. Biochar and effective microorganisms promote Sesbania cannabina growth and soil quality in the coastal saline-alkali soil of the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foong, S.Y.; Chan, Y.H.; Chin, B.L.F.; Lock, S.S.M.; Yee, C.Y.; Yiin, C.L.; Peng, W.; Lam, S.S. Production of biochar from rice straw and its application for wastewater remediation—An overview. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apolloni, F.; Menegazzo, F.; Bittencourt, C.; Signoretto, M. Hazelnut shells and rice husks activated biochars for the adsorption of atrazine and terbuthylazine. Next Energy 2025, 7, 100291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, B.; Hallajisani, A.; Tavakoli, O. Super-effective biochar adsorbents from Co-pyrolysis of rice husk and sewage sludge: Adsorption performance, advanced regeneration, and economic analysis. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2025, 29, 102046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ren, D.; Zhang, X.; Tang, K.; Zhang, X. Adsorption characteristic of Cd2+ on the nano-hydroxyapatite/biochar hybrid materials derived from rice husk and eggshells. Desalin. Water Treat. 2023, 287, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, M.; Yan, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.-W. Removal of neonicotinoid pesticides by adsorption on modified Tenebrio molitor frass biochar: Kinetics and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 297, 121506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yao, X.-W.; Diao, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, M.-L.; Feng, N.-J.; Qian, W.; Zhou, X.-H.; Guo, P.-R.; Kong, L.-J.; et al. Simultaneous removal of triadimefon and dinotefuran by a new biochar-based magnesium oxide composite in water: Performances and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 336, 126213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Guo, J.; Zhou, Q.; Fang, F. Adsorption characteristics of nitrite on natural filter medium: Kinetic, equilibrium, and site energy distribution studies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Che, N.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, C. Copper Nanoparticle Loading and F Doping of Graphene Aerogel Enhance Its Adsorption of Aqueous Perfluorooctanoic Acid. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 7073–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, T.; Sathasivan, A. Dissolved organic carbon concentration changes in surface drinking water sources, treatment challenges and potential solutions—A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 76, 108188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wan, B.; Mansor, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Kappler, A.; Feng, X. Co-sorption of metal ions and inorganic anions/organic ligands on environmental minerals: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zong, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, H.; Kong, Y.; Ma, J.; Ding, L. Efficient removal of cadmium by salts modified-biochar: Performance assessment, theoretical calculation, and quantitative mechanism analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 361, 127717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantou, G.; Wang, J.J.; Zhou, B.; Lee, J.-M.; Park, J.-H. Toxicological fate of biochar according to feedstock and pyrolysis temperature. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 236, 122094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, G.; Singh, R.P.; Deepak, K.; Nayak, P.P.; venkadeshwaran, K.; Tiwari, A.; Sahoo, J.; Priya, K. Continuous pyrolysis of rice husk for sustainable biochar production and carbon sequestration: Recent advances and techno-economic perspectives. Results Eng. 2025, 27, 106991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, K.H.H.; Mustafa, F.S.; Karim, M.A.H.; Hama, S. Biochar-based catalysts: An efficient and sustainable approach for water remediation from organic pollutants via advanced oxidation processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 390, 126245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Maniruzzaman, M.; ealam, N.; Mahmud, P.; Khatun, S.; Hossain, M.K.; Hossain, M.I.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Alam, M.A.; Al-amin, M.; et al. Adsorptive removal of toxic heavy metal and dyes from wastewater by rice husk (lignocellulosic biomass) derived activated biochar: A fixed-bed column adsorption study. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2025, 9, 100698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, T.; Chen, C.; Liu, J.; Mei, M.; Xie, J.; Li, J. Study on adsorption of Direct Red 23 by biochar derived from co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and rice husk waste: Optimization, isotherm, kinetic, thermodynamic and mechanisms. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 221, 378–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, C.; Song, J.; Dai, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Q.; Dai, L. Removal of Cl- from contaminated acid by resin adsorption: Kinetics, isothermal model, approximate site energy distribution and adsorption mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, J.; Koprivica, M.; Ercegović, M.; Simić, M.; Dimitrijević, J.; Bugarčić, M.; Trifunović, S. Synthesis and Application of FeMg-Modified Hydrochar for Efficient Removal of Lead Ions from Aqueous Solution. Processes 2025, 13, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguyal, F.; Sarmah, A.K. Site energy distribution analysis and influence of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on sulfamethoxazole sorption in aqueous solution by magnetic pine sawdust biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Q. Immobilization of laccase on biochar for the remediation of organic pollutants: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 322, 146778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Shi, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, M.; Guo, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y. Comparison of the binding interactions of 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase inhibitor herbicides with humic acid: Insights from multispectroscopic techniques, DFT and 2D-COS-FTIR. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.T.; Hossen, M.F.; Kudrat-E-Zahan, M.; Asraf, M.A.; Zakaria, C.M.; Hayatullah; Rana, M.S. Effect of temperature and time on purity, morphology and phase transformations of silica from rice husk. Chem. Inorg. Mater. 2025, 5, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Gui, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Li, B.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Chen, H. Effect of biomass components’ interaction on the pyrolysis reaction kinetics and small-molecule product release characteristics. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2023, 173, 106039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yan, W.; Liu, X.; Hu, T.; Xiong, Y.; Tian, S.; Feng, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Z. Rice husk waste-derived super-biochar with the max surface area and Philic-CO2 textural structure: Boosting effect and mechanism of post-desilication. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Rui, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, J. Biomass pyrolysis characterisation based on machine learning: Identification of key factors affecting biochar stability. Biomass Bioenergy 2025, 203, 108293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Chiew, C.H.; Guo, S.-R.; Li, L.; Lim, L.Y.; Ong, P.Y.; Wong, K.Y.; Li, C.; Varbanov, P.S.; Lee, C.T. Prediction of biochar physicochemical properties based on biomass initial conditions and pyrolysis process supported by data-driven multiple linear regression model. Energy 2025, 340, 139304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Liu, D.; Bian, Z.; Yang, F.; Gao, H.; Arvola, L. Identifying degradation mechanism of dissolved and particular organic matter by novelty hetero-2D-COS during petrochemical wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 71, 107299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, S.; Qi, Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; He, L.; Li, P.; Qi, X.; Gao, F.; Ding, Y.; et al. An efficient, green and sustainable potassium hydroxide activated magnetic corn cob biochar for imidacloprid removal. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Che, N.; Gao, B.; Li, C. Electrochemical adsorption of perfluorooctanoic acid on a novel reduced graphene oxide aerogel loaded with Cu nanoparticles and fluorine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, A.; Zhu, S.; Shang, C.; Yang, Z.; Cao, L.; Bai, M. Adsorption behavior of neonicotinoid pesticides on typical soil minerals. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Chen, Z.; Shen, J.; Yan, P.; Kang, J.; Wang, B.; Zhao, S.; Shen, Y.; Li, Y. In situ construction of ZnFe-layered double oxides on biochar for improving interfacial adsorption-catalysis of ozone achieves efficient water purification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2026, 380, 135358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, K.; Hu, X.; He, Q.; Yan, J.; Xue, Y. Cadmium removal by MgCl2 modified biochar derived from crayfish shell waste: Batch adsorption, response surface analysis and fixed bed filtration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Ishii, A.; Kamijo, T. Influence of ionic strength and temperature on adsorption of tetrakis-N-methylpyridyl porphyrin onto mesoporous silica. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 655, 130262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ma, J.; Zhang, M.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Yuan, S.; Li, K.; Zhou, T.; Lv, R.; et al. Calcium carbonate self fixed crayfish shell composite biochar for removing tetracycline from water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 711, 136371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Hu, X.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Huang, H.; Wang, R.; Zhou, D.; Yuan, J.; Chen, L. Application and functionalization of toxic waste sludge-derived biochar for efficient phosphate separation from aqueous media: Toxicity diminution, robust adsorption, and inner mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, C.; Sarkar, B.; Bhatnagar, A.; Bolan, N.; Yang, X.; Meng, J.; Liu, Z.; et al. Insights into simultaneous adsorption and oxidation of antimonite [Sb(III)] by crawfish shell-derived biochar: Spectroscopic investigation and theoretical calculations. Biochar 2022, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, E.; Kumar, S.; Verma, C.; Sarkar, S.; Maji, P.K. A comprehensive review on technological advances of adsorption for removing nitrate and phosphate from waste water. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, F.; Anbia, M.; Sepehrian, M. Recent advances in removal of inorganic anions from water by chitosan-based composites: A comprehensive review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 320, 121230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, M.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y. Adsorption of microplastics on aquifer media: Effects of the action time, initial concentration, ionic strength, ionic types and dissolved organic matter. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yan, H.; Tan, W.; Zhu, G. Influence of Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, and Fe3+ on filterability and settleability of drilling sludge. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geysels, B.; Hiemstra, T.; Vermeer, A.W.P.; Groenenberg, J.E. A mechanistic surface complexation model for glyphosate adsorption to ferrihydrite in competition with phosphate. Water Res. 2026, 288, 124634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Jabbarzadeh, A. Enhancing metal surface adsorption and tribological performance of water-based ionic liquid lubricants: The role of amino acid types. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 713, 163711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, R.; Peighambardoust, S.J.; Mohammadi, R.; Omidvar, M.; Sorial, G.A.; Ramavandi, B. Influence of chitosan and magnetic iron nanoparticles on chromium adsorption behavior of natural clay: Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference modeling. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, V.M.; Rajković, K.M.; Stojičević, S.S.; Veličković, D.T.; Nikolić, N.Č.; Lazić, M.L.; Karabegović, I.T. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of total polyphenolic compounds from chokeberries by response surface methodology and artificial neural network. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 160, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisz, O.; Hulicka, G.; Tobiszewski, M.; Bocian, S. Performance evaluation of green and conventional solvents in reversed-phase liquid chromatography based on the separation of non-polar and polar substances. Green Chem. 2024, 27, 3020–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Wu, X.; Chen, P.; Zhao, Z.; Fan, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Xue, J.; Wang, Y. New insights into the interactions between humic acid and three neonicotinoid pesticides, with multiple spectroscopy technologies, two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy analysis and density functional theory. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Aswad, A.F.; Aly, M.I.; Fouad, M.R.; Badawy, M.E.I. Adsorption and thermodynamic parameters of chlorantraniliprole and dinotefuran on clay loam soil with difference in particle size and pH. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2019, 54, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, S.; Yutronic, N.; Jara, P. Magnetic β-Cyclodextrin Nanosponges for Potential Application in the Removal of the Neonicotinoid Dinotefuran from Wastewater. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, P.; Yan, N.; Ren, Y.; Liang, X.; Guo, X. Adsorption of neonicotinoid insecticides by mulch film-derived microplastics and their combined toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 177238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Adsorbent | pH | SSA (m2/g) | PV (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) | Ash (%) | Element Content (%) | Atomic Ratio | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | N | O | H/C | O/C | (O + N)/C | ||||||
| RHB400 | 9.81 | 22.04 | 0.0663 | 15.31 | 35.42 | 52.38 | 3.37 | 0.68 | 8.15 | 0.0643 | 0.1556 | 0.1686 |
| RHB500 | 10.03 | 28.37 | 0.1082 | 7.87 | 40.61 | 44.67 | 2.41 | 0.52 | 11.79 | 0.0540 | 0.2639 | 0.2756 |
| RHB600 | 10.29 | 38.41 | 0.1206 | 4.08 | 42.39 | 41.02 | 2.19 | 0.44 | 13.96 | 0.0534 | 0.3403 | 0.3510 |
| Index | RSM | ANN | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | Checking | Training | Checking | |
| R2 | 0.9751 | 0.9908 | 0.9916 | 0.9942 |
| MSE | 2.3492 | 0.6842 | 0.7867 | 0.4341 |
| SSE | 1.5327 | 0.8272 | 0.8870 | 0.6589 |
| ARE | 1.9539 | 1.2760 | 1.1096 | 0.7652 |
| Proposed Mechanism | Experimental Evidence | Key Observations and Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Pore Filling | SSA Analysis | Increase in SSA and microporosity with pyrolysis temperature (RHB400 to RHB600) correlates with enhanced adsorption capacity. |
| Adsorption Kinetics | The intra-particle diffusion model indicates that pore diffusion is a rate-controlling step. | |
| π–π Interaction | FTIR & 2D-COS | Enhancement of aromatic C=C (1600 cm−1) band; Its response after C–O in 2D-COS suggests a synergistic role following initial anchoring. |
| XPS | Appearance of new C=N and C–N peaks in the C1s spectrum after adsorption, confirming the proximity of DIN’s aromatic rings to the biochar surface. | |
| DFT (ESP Analysis) | Complementary negative ESP regions on RHB600′s aromatic basal planes and DIN’s furan ring facilitate electron donor-acceptor interactions. | |
| Hydrogen Bonding | FTIR & 2D-COS | Synchronous increase in O–H, C=O, C–O bands with DIN concentration; The earliest response of C–O and Si–O–Si in 2D-COS identifies them as key initial hydrogen-binding sites. |
| XPS | Shifts in the binding energy of O–C=O (C1s) and O–H (O1s) peaks after adsorption, indicating strong polar interactions. | |
| DFT (ESP Analysis) | Strong directional complementarity between positive ESP hydrogen atoms of RHB600′s –OH/–COOH and negative ESP oxygen atoms of DIN’s NO2 and C=O groups. | |
| Lewis Acid-Base Interaction | XPS & FTIR | Shifts in binding energy and band intensity related to oxygen and nitrogen-containing groups suggest electron transfer. |
| 2D-COS | The early response of Si–O–Si and Si–OH groups suggest the involvement of mineral components in coordination. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Jiang, X.; Lu, T.; Ma, J. Agricultural Waste for Remediation of Neonicotinoid Pollution: Mechanisms and Environmental Effects of Multi-Site Adsorption of Dinotefuran on Rice Husk Biochar. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122746
Liu L, Jiang X, Lu T, Ma J. Agricultural Waste for Remediation of Neonicotinoid Pollution: Mechanisms and Environmental Effects of Multi-Site Adsorption of Dinotefuran on Rice Husk Biochar. Agronomy. 2025; 15(12):2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122746
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Longfei, Xinyu Jiang, Tianyu Lu, and Jinzhao Ma. 2025. "Agricultural Waste for Remediation of Neonicotinoid Pollution: Mechanisms and Environmental Effects of Multi-Site Adsorption of Dinotefuran on Rice Husk Biochar" Agronomy 15, no. 12: 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122746
APA StyleLiu, L., Jiang, X., Lu, T., & Ma, J. (2025). Agricultural Waste for Remediation of Neonicotinoid Pollution: Mechanisms and Environmental Effects of Multi-Site Adsorption of Dinotefuran on Rice Husk Biochar. Agronomy, 15(12), 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122746






