Legacy Effects of Long-Term Brackish Groundwater Irrigation on Bacterial Communities in Wheat Rhizosphere and Yield Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Design and Soil Sampling
2.2. Analysis of Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.3. Soil DNA Extraction and Sequence Processing
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
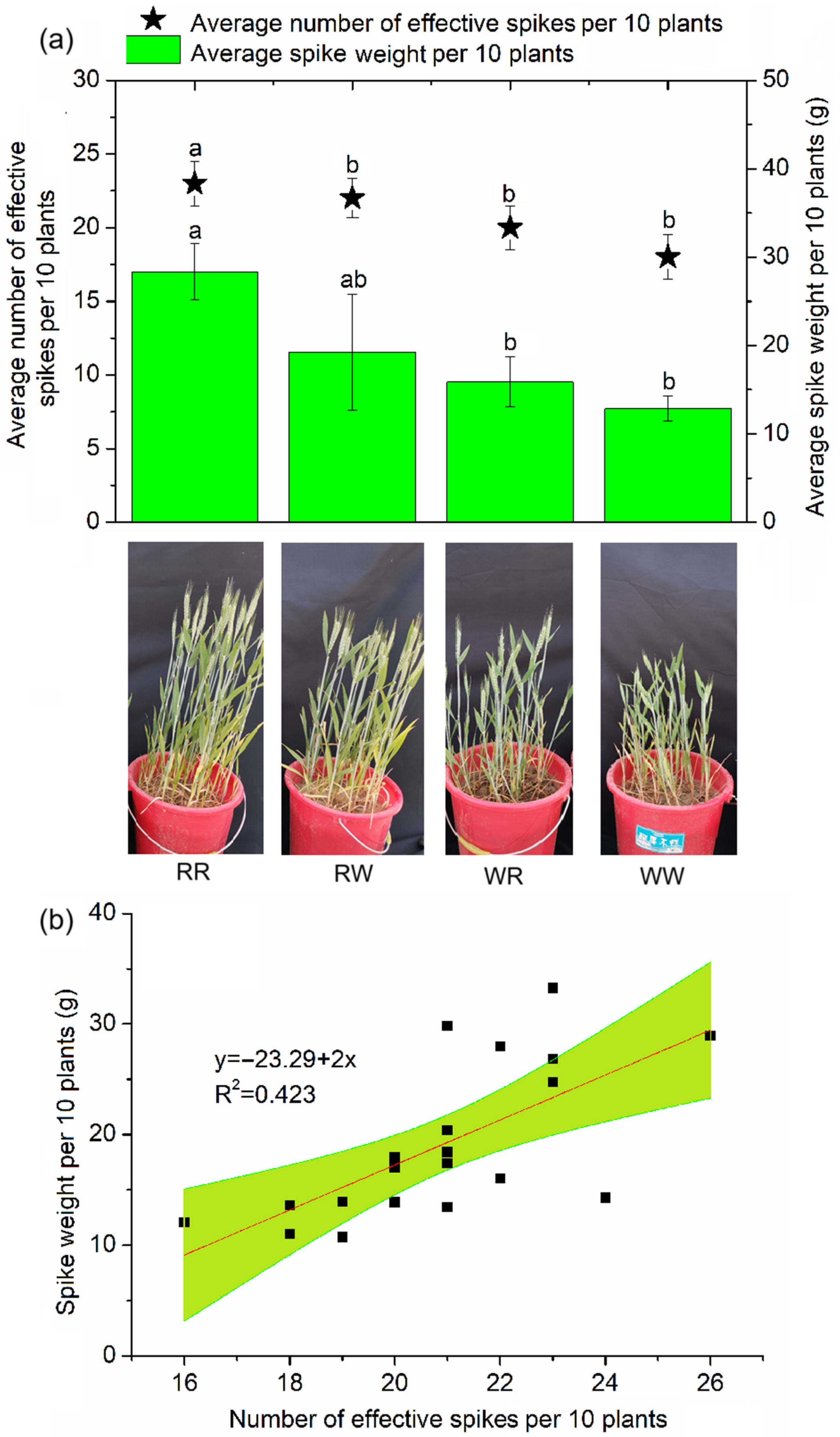
3.1. Effect of Irrigation Regimes on the Number and Weight of Wheat Spikes
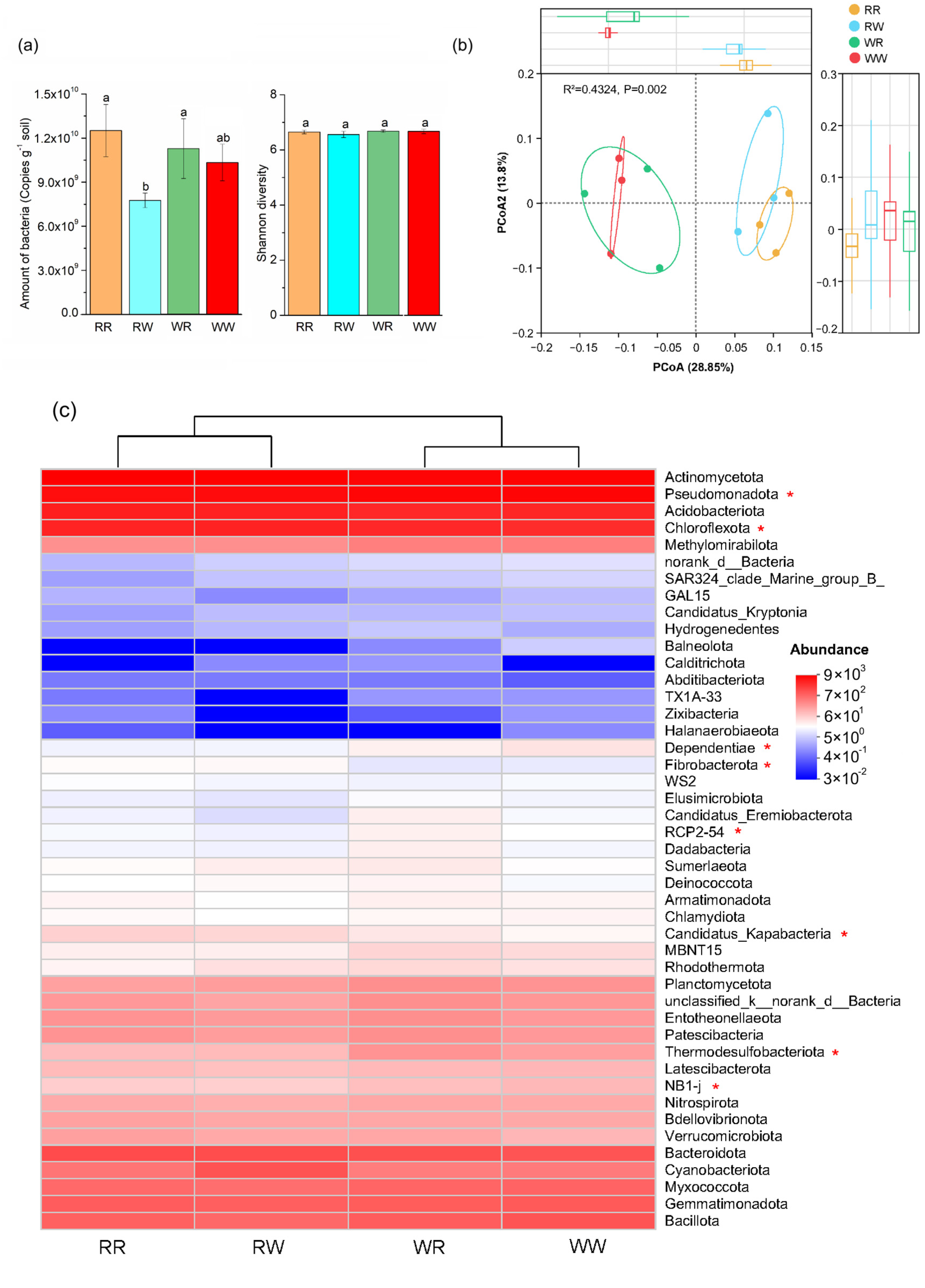
3.2. Effect of Irrigation Regimes on Bacterial Numbers, Diversity, and Community Structure
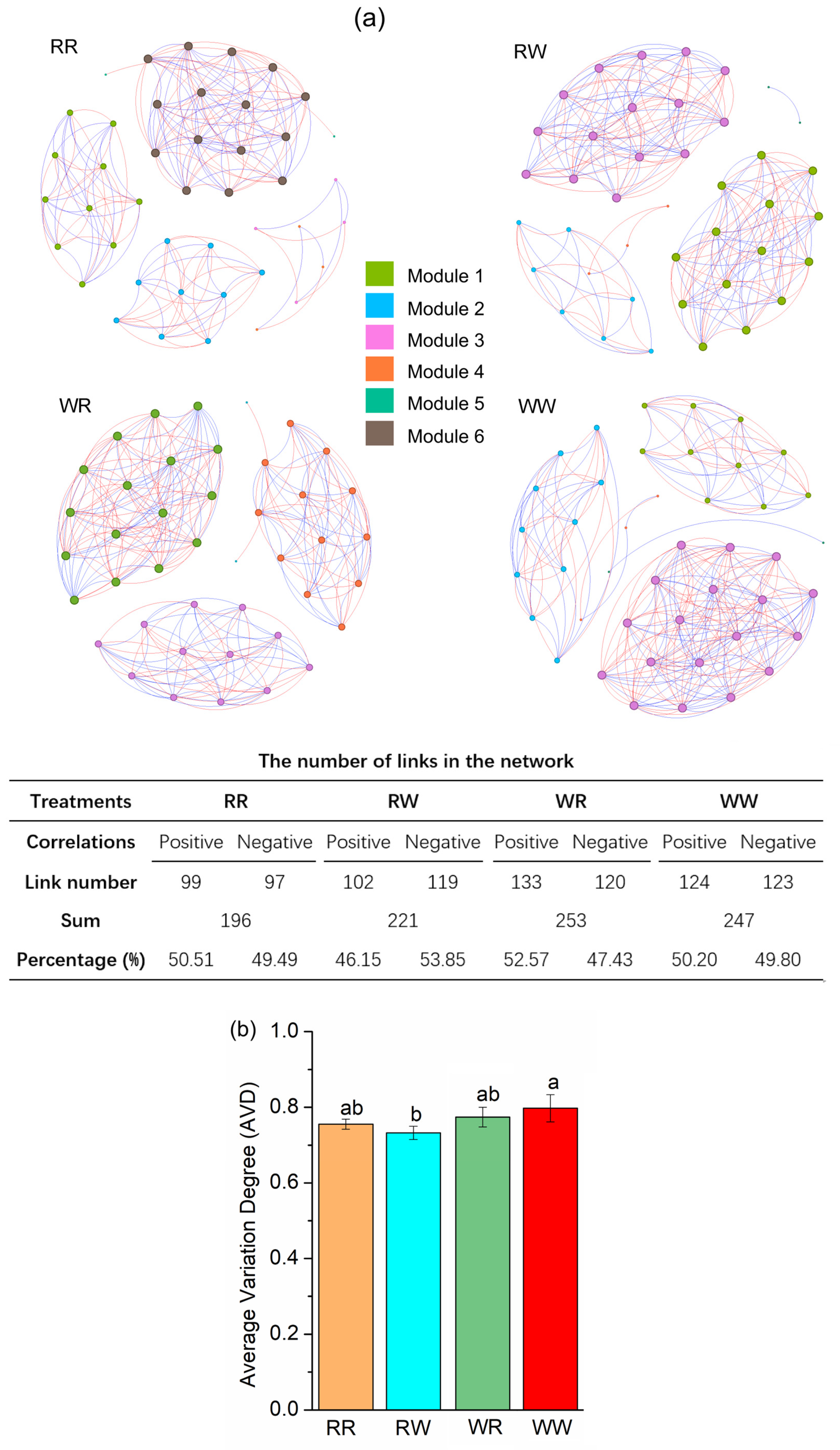
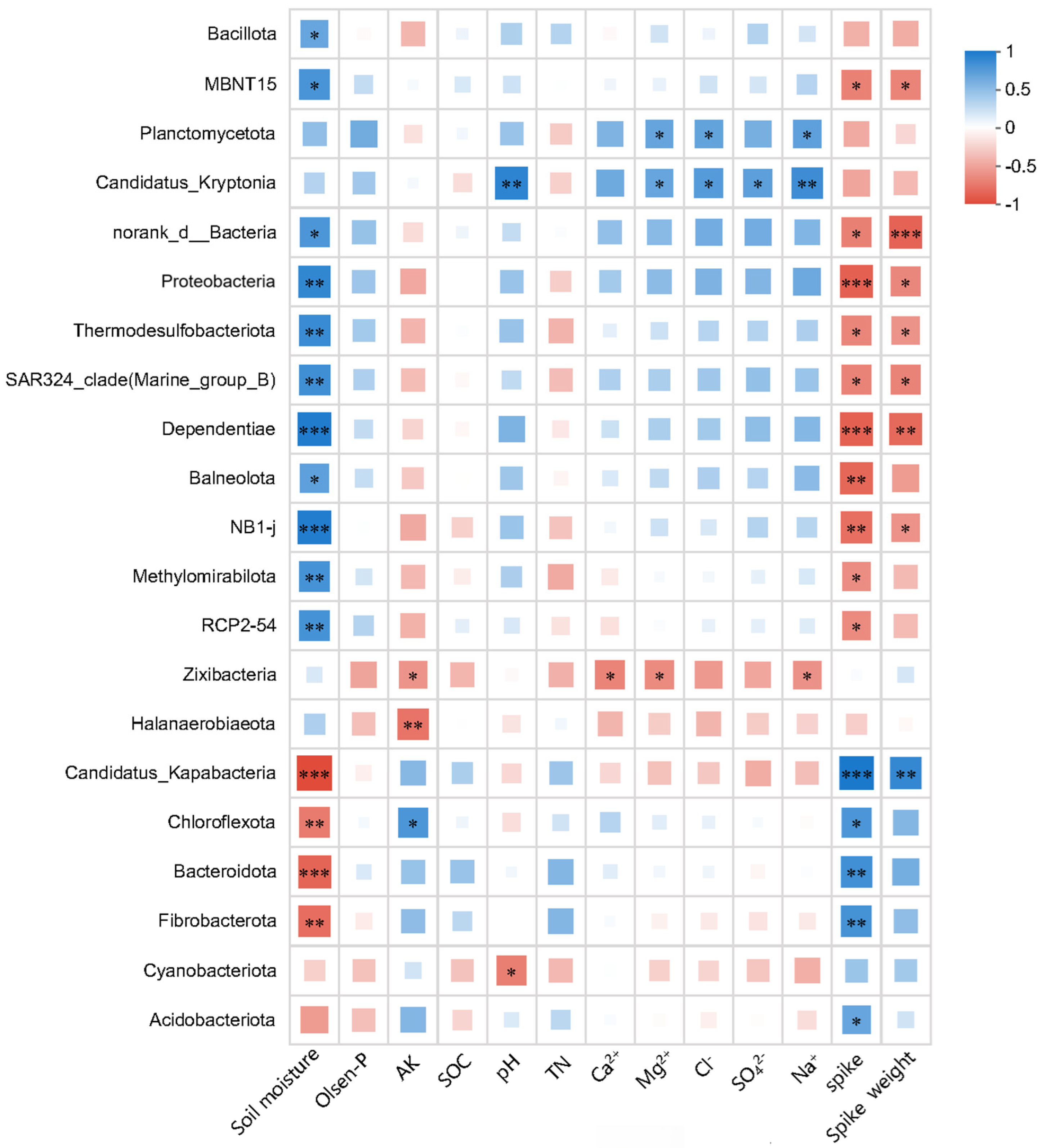
3.3. Effect of Irrigation Regimes on Bacterial Composition Associations
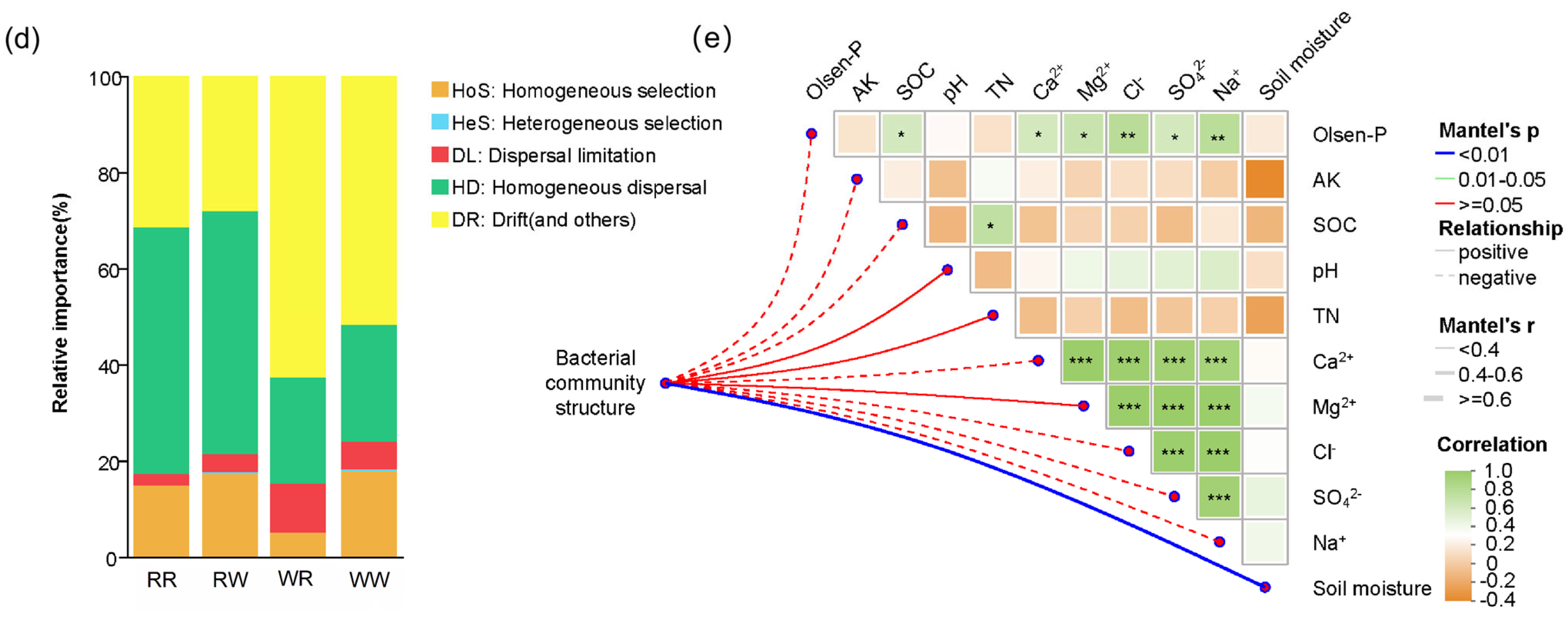
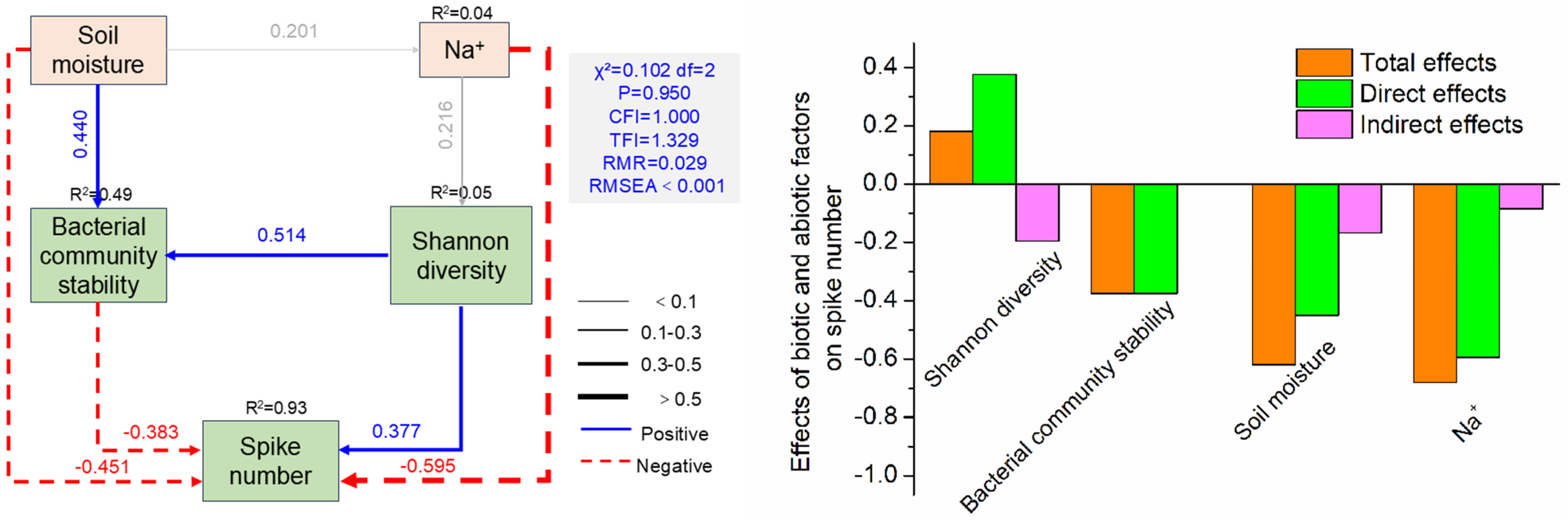
3.4. The Contribution of Biotic and Abiotic Factors to Spike Number
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Irrigation Regimes on Wheat Yield Traits
4.2. Legacy Effect of Long-Term Brackish Groundwater Irrigation on Bacterial Community
4.3. Potential Roles of Bacterial Communities in Wheat Yield Traits
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Shao, L.; Sun, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X. Responses of yield and water use efficiency to irrigation amount decided by pan evaporation for winter wheat. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 129, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, G.; Yao, R.; Yu, S. Impact of irrigation volume and water salinity on winter wheat productivity and soil salinity distribution. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 149, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Cao, H.; Kang, S.; Du, T.; Tong, L.; Kang, J.; Gao, J.; Ding, R. Agronomic measures improve crop yield and water and nitrogen use efficiency under brackish water irrigation: A global meta-analysis. Agric. Syst. 2025, 226, 104304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; Li, D.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B. Brackish water irrigation-induced recruitment of specific consortium determines microbial resistance that facilitates crop yield in a field experiment. Pedosphere 2024, 35, 820–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucci, G.; Lacolla, G.; Boari, F.; Mastro, M.A.; Cantore, V. Effect of water salinity and irrigation regime on maize (Zea mays L.) cultivated on clay loam soil and irrigated by furrow in Southern Italy. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 222, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Awais, M.; Bashir, R.; Ahmad, S.R.; Anwar-ul-Haq, M.; Senousy, H.H.; Iftikhar, M.; Anjum, M.U.; Ramzan, S.; Alharbi, S.A.; et al. Assessment of wheat productivity responses and soil health dynamics under brackish ground water. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Farsi, S.; Nawaz, A.; Rehman, A.; Nadaf, S.; Al Sadi, A.; Siddique, K.; Farooq, M. Effects, tolerance mechanisms and management of salt stress in lucerne (Medicago sativa). Crop Pasture Sci. 2020, 71, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Testerink, C. Root dynamic growth strategies in response to salinity. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 45, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isla, R.; Aragues, R. Yield and plant ion concentrations in maize (Zea mays L.) subject to diurnal and nocturnal saline sprinkler irrigations. Field Crops Res. 2010, 116, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhu, C.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z. Evaluation and application of the AquaCrop model in simulating soil salinity and winter wheat yield under saline water irrigation. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, C.; Yan, Z.; Shao, L.; Chen, S.; Niu, J.; Zhang, X. Effects of long-term saline water irrigation on soil salinity and crop production of winter wheat-maize cropping system in the North China Plain: A case study. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 303, 109060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, L.; Ochman, D.; Huang, C.W.; Domec, J.C.; Schwartz, N.; Hartzell, S. Translating soil salinity to agricultural salt stress: Key salt-tolerance mechanisms for agrohydrologic models. iScience 2025, 28, 113139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, K.; Gao, X.; Ai, X.; Chen, G.; Guo, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, L. Effect of irrigation with magnetized and ionized water on yield, nutrient uptake and water-use efficiency of winter wheat in Xinjiang, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 308, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Feng, S.; Huo, Z.; Ji, Q. Effects of deficit irrigation with saline water on soil water-salt distribution and water use efficiency of maize for seed production in arid Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.Z.; Park, B.J.; Lee, Y.T. Effect of salinity stress on bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of wheat microgreen extract under organic cultivation conditions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Shi, Y.; Cui, X.; Yue, P.; Li, K.; Liu, X.; Tripathi, B.M.; Chu, H. Salinity is a key determinant for soil microbial communities in a desert ecosystem. mSystems 2019, 4, e00225-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; Zhai, H.L.; Xu, H.Y.; Song, W.Z.; Liu, M.; Dong, X.F.; Sun, W.; Ma, J.Y. Different salt stress types regulated rhizosphere rare bacterial communities through root exudates and soil physicochemical properties. Plant Soil 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Kumar, R. Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, P.; Jin, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, M.; Wu, L.; Lan, S. Microbial community composition and interactions in saline biocrusts: Insights into cyanobacterial inoculation for soil restoration. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 212, 106225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; La, S.; Zhang, X.; Gao, L.; Tian, Y. Salt-induced recruitment of specific root-associated bacterial consortium capable of enhancing plant adaptability to salt stress. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2865–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakar, M.; Rajguru, B.; Thakkar, J.; Bhatt, V.; Shri, M.; Warghane, A. Impact of salt-induced chemo-signal on rhizomicrobiome-plant interaction. J. Crop. Health 2025, 77, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Joshi, M. Microbial strategies for enhancing wheat and rice resilience to drought, salinity, and heat stress. Rhizosphere 2025, 34, 101108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardoim, P.R.; Van Overbeek, L.S.; Berg, G.; Pirttilä, A.M.; Compant, S.; Campisano, A.; Döring, M.; Sessitsch, A. The hidden world within plants: Ecological and evolutionary considerations for defining functioning of microbial endophytes. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2015, 79, 293–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierer, N. Embracing the unknown: Disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Jin, M.; Wang, R.; Chen, J.; Guo, S. Reduced co-occurrence and ion-specific preferences of soil microbial hub species after ten years of irrigation with brackish water. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 199, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, C.; Ning, S.; Cao, C.; Li, K.; Dang, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Impacts of long-term saline water irrigation on soil properties and crop yields under maize-wheat crop rotation. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 286, 108383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis—Part 2, Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 2nd ed.; Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 539–579. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M. Nitrogen-total. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Chemical Methods—Part 3; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; p. 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Qiu, H.; Hu, Y.; Wei, X.; Chen, X.; Ge, T.; Wu, J.; Su, Y. Cellulose and lignin regulate partitioning of soil phosphorus fractions and alkaline phosphomonoesterase encoding bacterial community in phosphorus-deficient soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2019, 55, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.N.S.; Kavitha, P.; Chari, M.S.; Reddy, M.S. Comparison of extraction methods to assess potassium availability for rice growing soils of canal ayacut of Kurnool district. Asian J. Soil Sci. 2016, 11, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jin, M.; Šimůnek, J.; van Genuchte, M.T. Evaluation of mulched drip irrigation for cotton in arid Northwest China. Irrig. Sci. 2014, 32, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Liu, J.; Boorboori, M.R.; Li, D.; Chen, S.; Ma, X.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, H. Effect of biochar application rate on changes in soil labile organic carbon fractions and the association between bacterial community assembly and carbon metabolism with time. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Lai, Y.; Shi, L.D.; Wang, K.D.; Dai, Y.J.; Liu, Y.W.; Ma, F.; Rittmann, B.E.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, H.P. Nitrate effects on chromate reduction in a methane-based biofilm. Water Res. 2017, 115, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; Volume 3, pp. 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Yuan, M.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Y.; Arkin, A.P.; Firestone, M.K.; Zhou, J. A quantitative framework reveals ecological drivers of grassland microbial community assembly in response to warming. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, D.; Coughlan, J.; Mullen, M. Structural equation modelling: Guidelines for determining model fit. Electron. J. Bus. Res. Methods 2008, 6, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Gilliham, M. Salinity tolerance of crops—What is the cost? New Phytol. 2015, 208, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.; Hasnain, Z.; Danish, S.; Battaglia, M.L.; Fahad, S.; Ansari, M.J.; Alharbi, S.A. Modulations of wheat growth by selenium nanoparticles under salinity stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hendawy, S.; Tahir, M.U.; Hu, Y.; Al-Suhaibani, N. Evaluating the Necessity of a Control Treatment for Assessing Salt Tolerance in Wheat Genotypes Based on Agro-Physiological Traits in Real-Field Conditions. Plants 2025, 14, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Shi, C.; Wang, P.; Chang, S.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Li, S.; Hu, T.; Ru, Z. Optimizing Wheat Planting Density by Adjusting Population Structure and Stabilizing Stem Strength to Achieve High and Stable Yields. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liao, Y.; Liu, W. High nitrogen application rate and planting density reduce wheat grain yield by reducing filling rate of inferior grain in middle spikelets. Crop J. 2020, 9, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xin, C.; Haider, F.U.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, P.; Li, X. Rhizobacteria mitigate salinity stress in maize by modulating photosynthesis, antioxidant defense, and rhizosphere microbial diversity. Plant Stress 2025, 15, 100781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seixas, A.F.; Quendera, A.P.; Sousa, J.P.; Silva, A.F.; Arraiano, C.M.; Andrade, J.M. Bacterial response to oxidative stress and RNA oxidation. Front. Genet. 2022, 12, 821535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, V.; Verma, M.K.; Gupta, S.; Mandhan, V.; Chauhan, N.S. Metagenomic profiling of soil microbes to mine salt stress tolerance genes. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlden, A.; Timms-Wilson, T.M.; Day, M.J.; Bailey, M.J. Influence of plant developmental stage on microbial community structure and activity in the rhizosphere of three field crops. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 65, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Waghmode, T.R.; Sun, R.; Kuramae, E.E.; Hu, C.; Liu, B. Root-associated microbiomes of wheat under the combined effect of plant development and nitrogen fertilization. Microbiome 2019, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlemper, T.R.; Leite, M.F.A.; Lucheta, A.R.; Shimels, M.; Bouwmeester, H.J.; van Veen, J.A.; Kuramae, E.E. Rhizobacterial community structure differences among sorghum cultivars in different growth stages and soils. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinneny, J.R. Developmental responses to water and salinity in root systems. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 35, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhou, J.; Sui, N. Mechanisms of salt tolerance in halophytes: Current understanding and recent advances. Open Life Sci. 2018, 13, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, M.S.; Wassmann, R.; Bueno, C.; Heinz Rennenberg, H. Impact of root exudates of different cultivars and plant development stages of rice (Oryza sativa L.) on methane production in a paddy soil. Plant Soil 2001, 230, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, D.; Coleman-Derr, D. Drought stress and root-associated bacterial communities. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 8, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achtenhagen, J.; Goebel, M.O.; Miltner, A.; Woche, S.K.; Kästner, M. Bacterial impact on the wetting properties of soil minerals. Biogeochemistry 2015, 122, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chialva, M.; Ghignone, S.; Cozzi, P.; Lazzari, B.; Bonfante, P.; Abbruscato, P.; Lumini, E. Water management and phenology influence the root-associated rice field microbiota. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Sun, R.; Tian, Y.; Guo, K.; Sun, H.; Liu, X.; Chu, H.; Liu, B. Long term phytoremediation of coastal saline soil reveals plant species specific patterns of microbial community recruitment. mSystems 2020, 5, e00741-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Gong, H.; Li, J.; Hou, R.; Sun, Z.; Ouyang, Z. Microbes with high–abundance attributes dominate the prokaryote communities of saline–alkali soil and construct more complex networks in the plant rhizosphere. Geoderma 2023, 439, 116684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Zhu, Y.G.; Wang, J.T.; Singh, B.; Han, L.L.; Shen, J.P.; Li, P.P.; Wang, G.B.; Wu, C.F.; Ge, A.H.; et al. Host selection shapes crop microbiome assembly and network complexity. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, K.; Li, K.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Jin, Y.; He, X. Assembly, network and functional compensation of specialists and generalists in poplar rhizosphere under salt stress. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2025, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Ren, Y.; Xiong, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Miao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R. Specialized metabolic functions of keystone taxa sustain soil microbiome stability. Microbiome 2021, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, L.W.; Kuramae, E.E.; Navarrete, A.A.; Van Veen, J.A.; Tsai, S.M. Taxonomical and functional microbial community selection in soybean rhizosphere. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Weisenhorn, P.; Gilbert, J.A.; Chu, H. Wheat rhizosphere harbors a less complex and more stable microbial co-occurrence pattern than bulk soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudent, M.; Dequiedt, S.; Sorin, C.; Girodet, S.; Nowak, V.; Duc, G.; Salon, C.; Maron, P.A. The diversity of soil microbial communities matters when legumes face drought. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Whalen, J.K. A new perspective on functional redundancy and phylogenetic niche conservatism in soil microbial communities. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Loreau, M.; Huang, M.; Niu, M.; Schöb, C.; Zhou, R.; Lin, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, H.; Chen, J. Increased diversity by cushion plants enhances alpine community productivity and stability. New Phytol. 2025, 248, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Li, Z.; Gao, X.; Wu, L.; Lan, J.; Peng, W. Effects of subsurface drip irrigation on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) growth and soil microbial community structures in arid and semi-arid areas of northern China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 159, 103859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, Z.; Mehrabadi, M.; Fazli, M.; Khalesro, S.; Abedi, R.; Mokhtassi-Bidgoli, A. Enhancing tolerance of wheat cultivars to metribuzin stress through bioremediation with Pseudomonas spp. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichorst, S.A.; Kuske, C.R.; Schmidt, T.M. Influence of plant polymers on the distribution and cultivation of bacteria in the phylum Acidobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezgui, C.; Trinsoutrot-Gattin, I.; Benoit, M.; Laval, K.; Riah-Anglet, W. Linking changes in the soil microbial community to C and N dynamics during crop residue decomposition. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 3039–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Carrión, V.J. Importance of Bacteroidetes in host–microbe interactions and ecosystem functioning. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, H.; Tian, G.; Liu, J.; He, S.; Li, D. Legacy Effects of Long-Term Brackish Groundwater Irrigation on Bacterial Communities in Wheat Rhizosphere and Yield Performance. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122732
Qiu H, Tian G, Liu J, He S, Li D. Legacy Effects of Long-Term Brackish Groundwater Irrigation on Bacterial Communities in Wheat Rhizosphere and Yield Performance. Agronomy. 2025; 15(12):2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122732
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Husen, Guangli Tian, Jieyun Liu, Shuai He, and Dongwei Li. 2025. "Legacy Effects of Long-Term Brackish Groundwater Irrigation on Bacterial Communities in Wheat Rhizosphere and Yield Performance" Agronomy 15, no. 12: 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122732
APA StyleQiu, H., Tian, G., Liu, J., He, S., & Li, D. (2025). Legacy Effects of Long-Term Brackish Groundwater Irrigation on Bacterial Communities in Wheat Rhizosphere and Yield Performance. Agronomy, 15(12), 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122732





