The Impact of Climate Change on Chorthippus dubius (Zubovski, 1898) Distribution in Alpine Grassland—A Case Study in the Qilian Mountain National Park, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
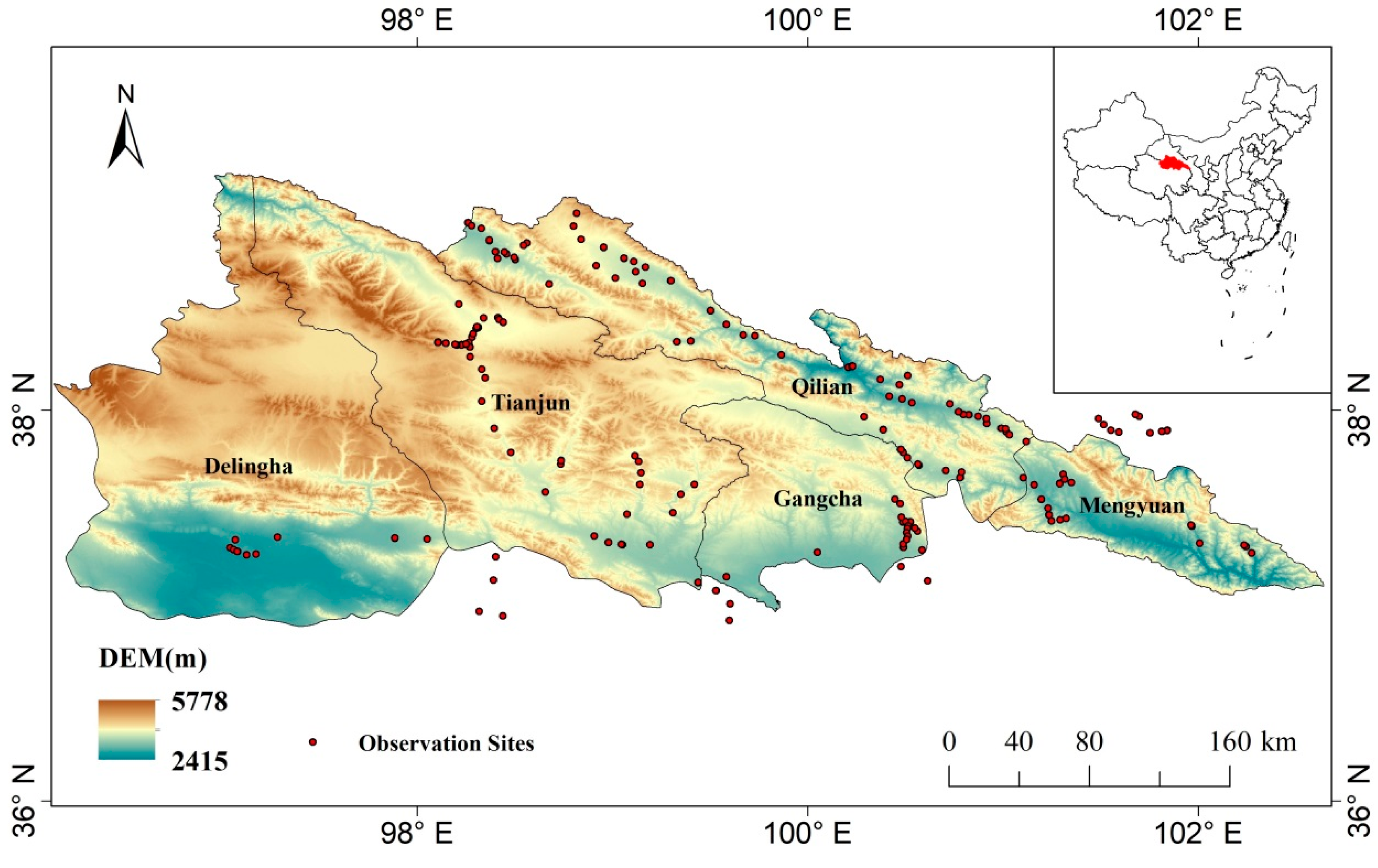
2.1. Study Area
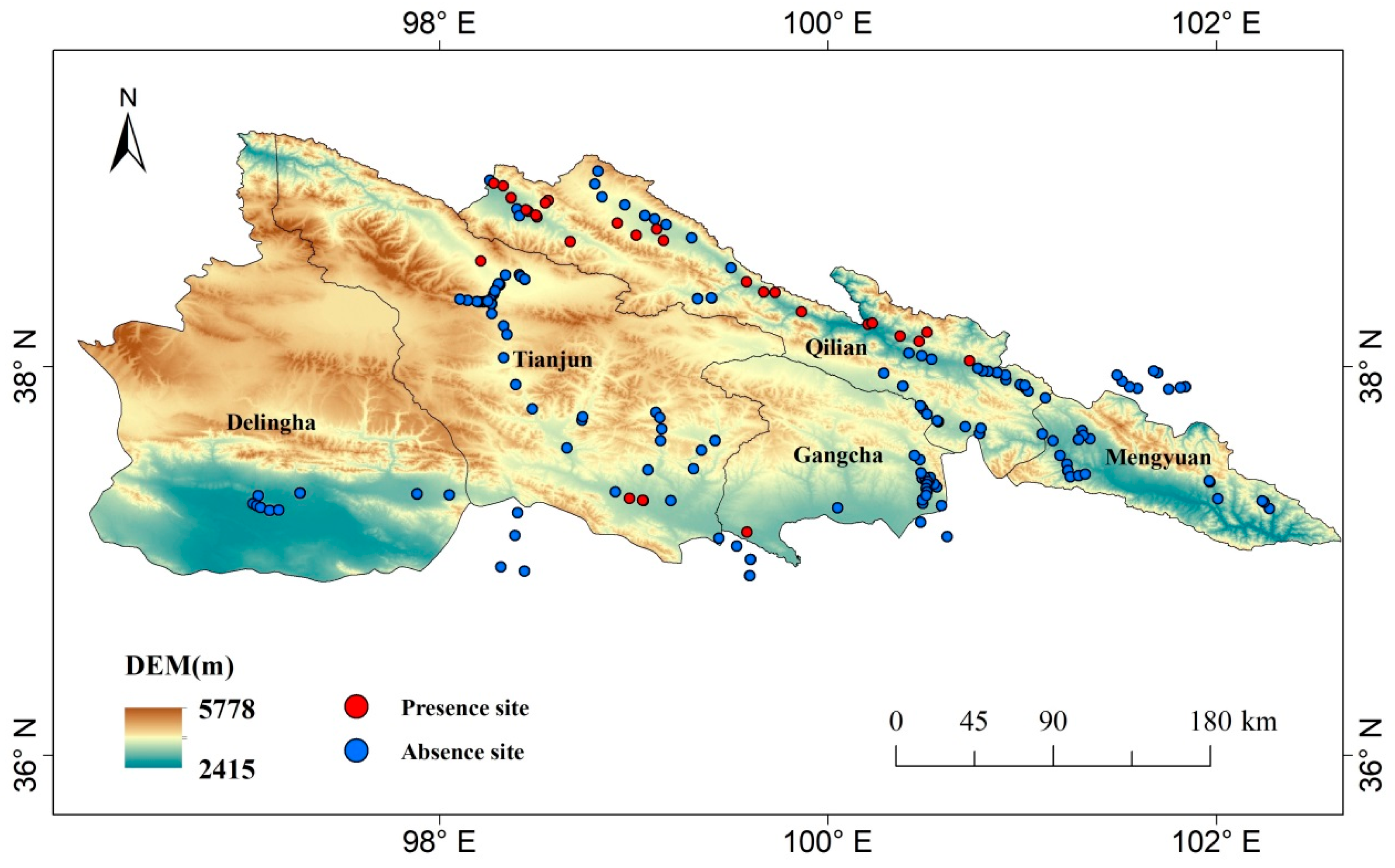
2.2. Field Observation
2.3. Environmental Factors and Data Preprocessing
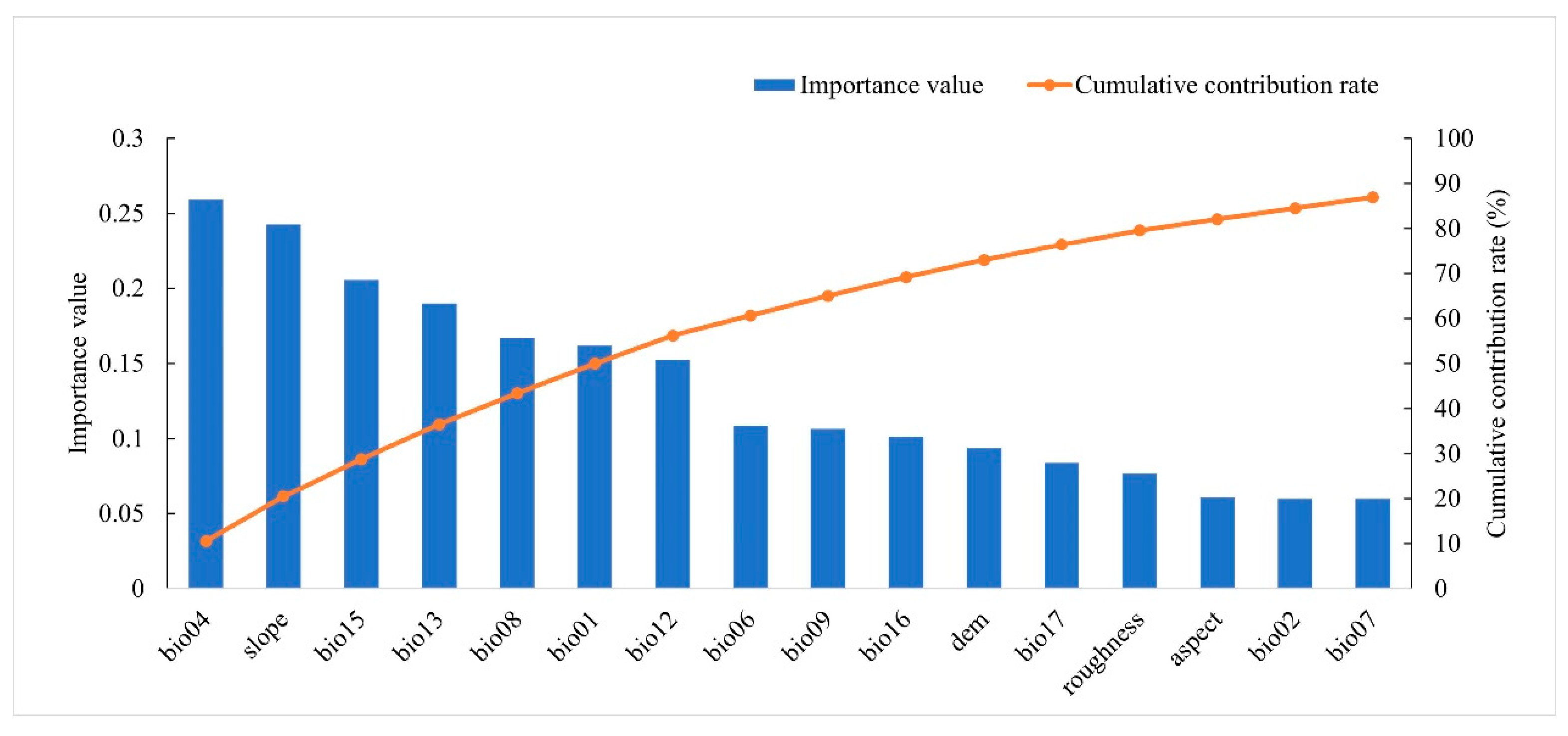
2.4. Selection of Environmental Factors
2.5. Construction of Ecological Niche Models
2.6. Simulation of C. dubius Distribution Probability in Different Climate Scenarios
3. Results
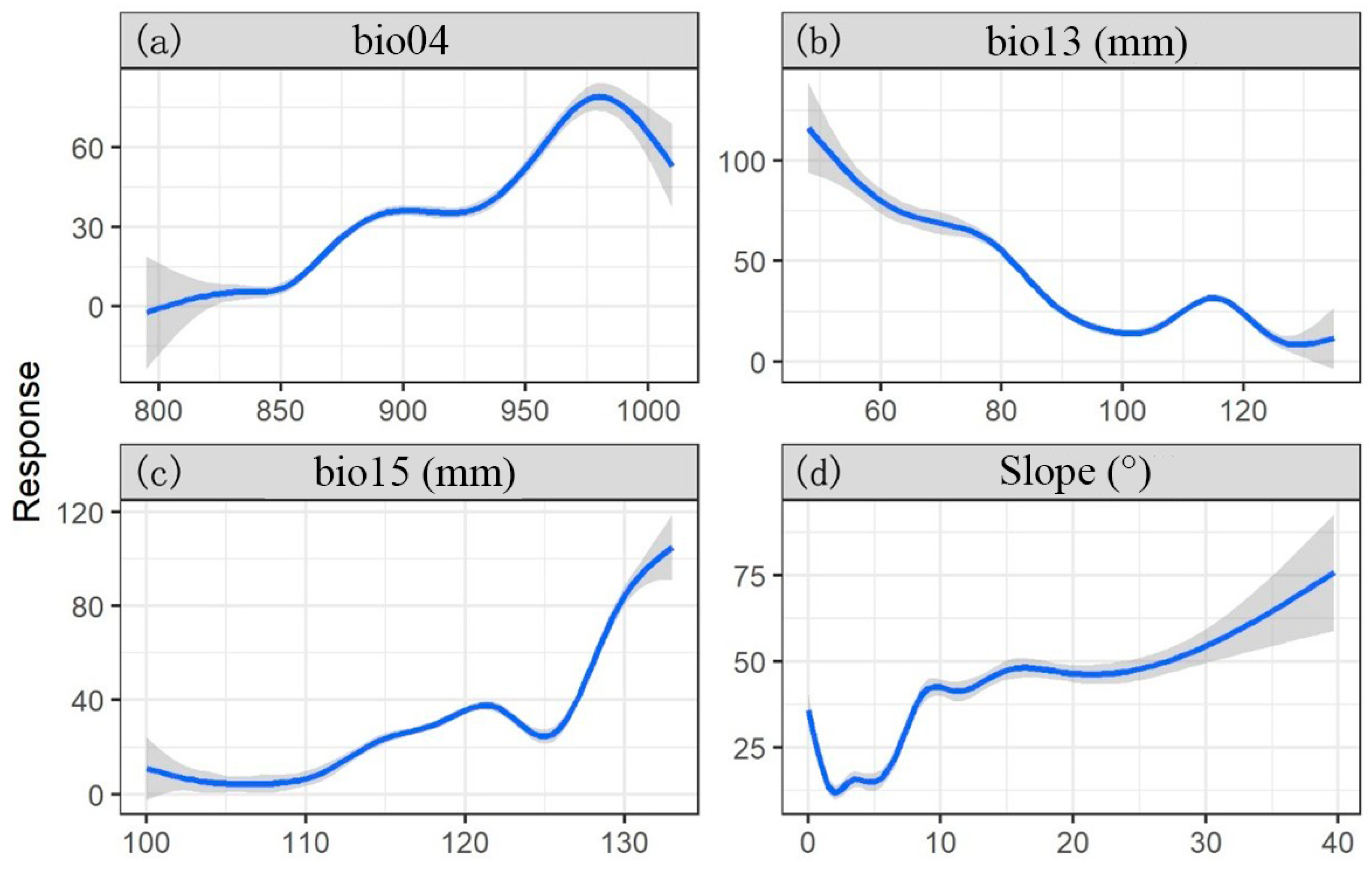
3.1. Main Distribution and Influencing Factors of C. dubius
3.2. Optimal Ecological Niche Model
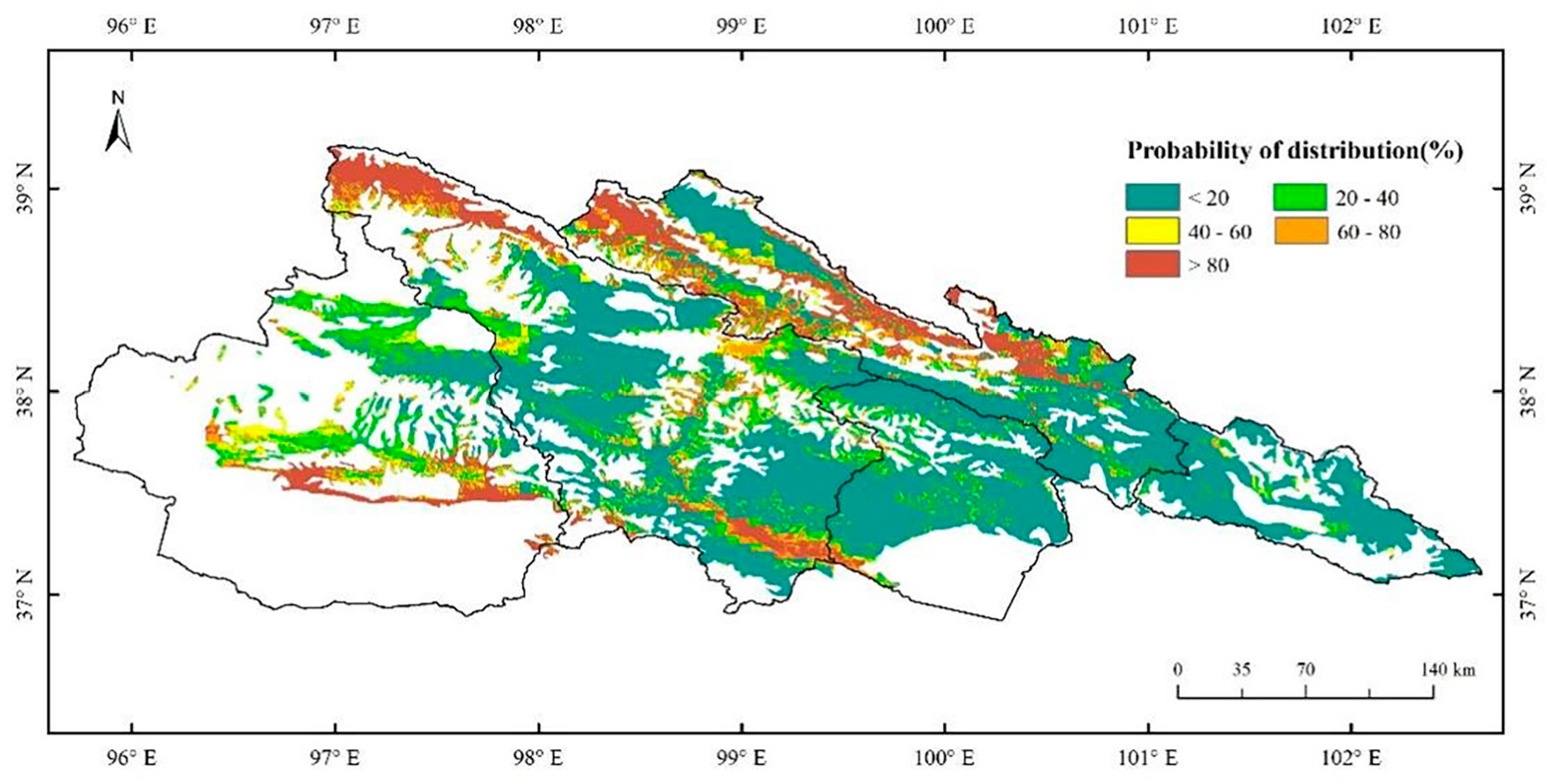
3.3. Spatial Distribution of C. dubius Presence Probability in the Current Situation
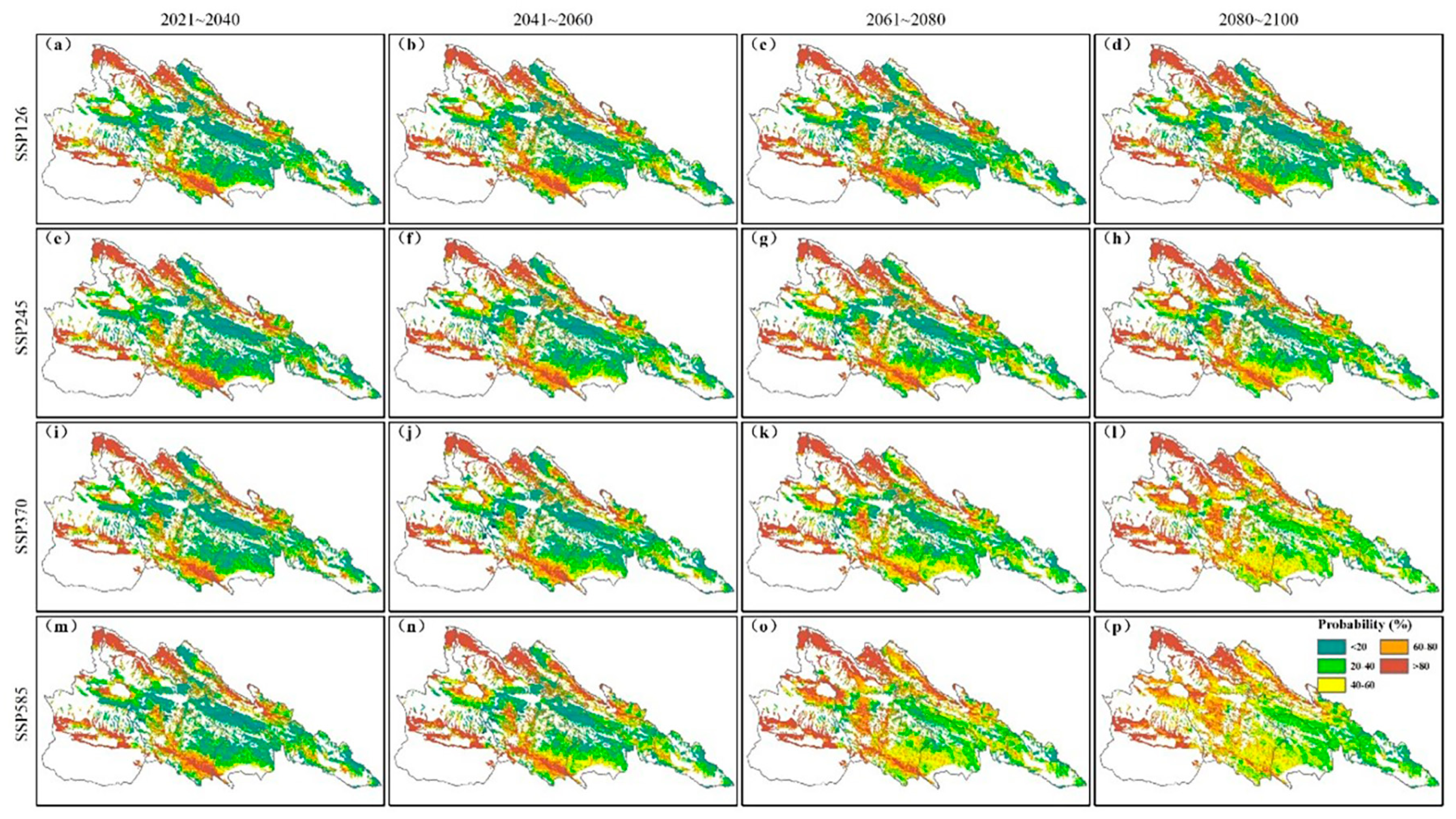
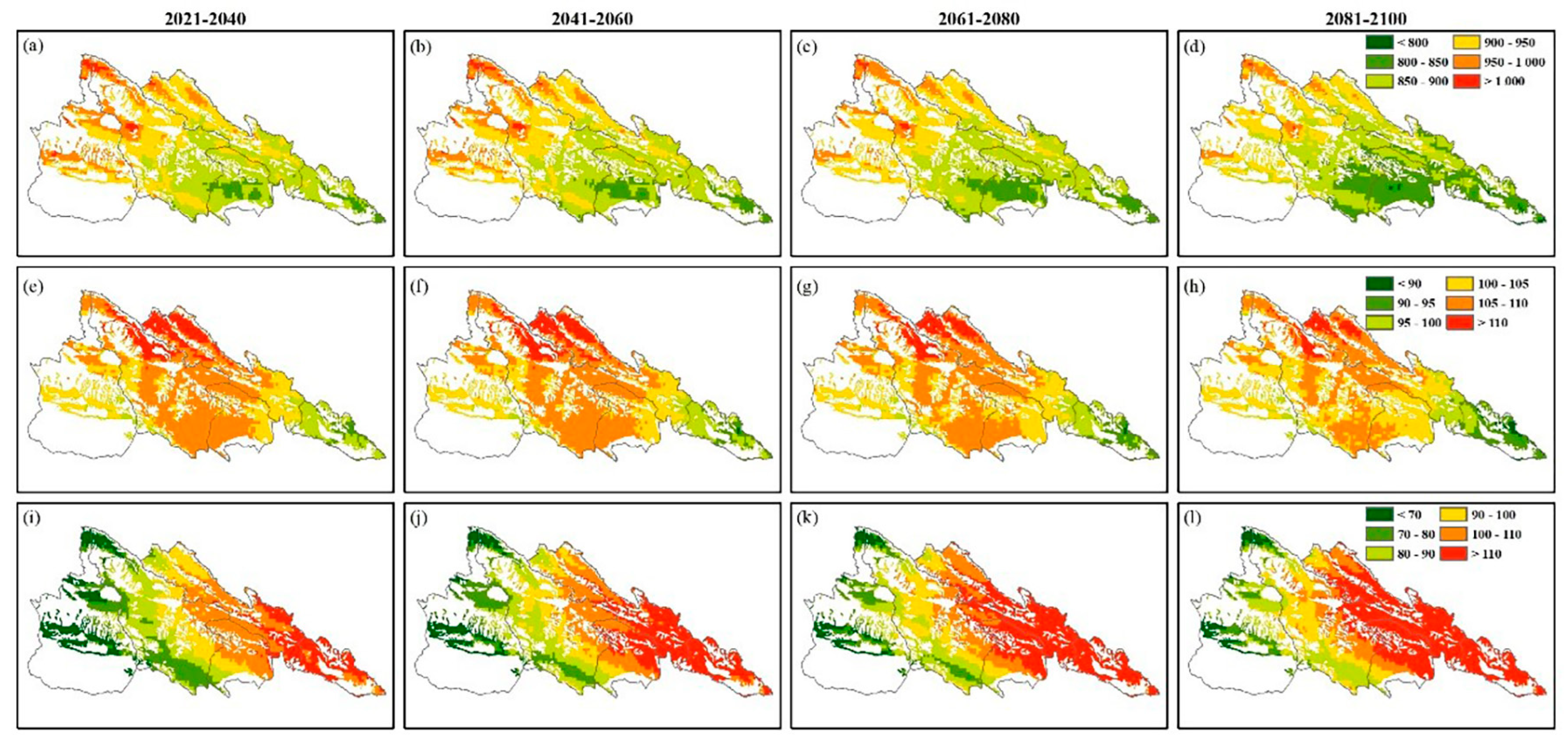
3.4. Temporal and Spatial Dynamics Variation in C. dubius Presence Probability in Different Climate Scenarios
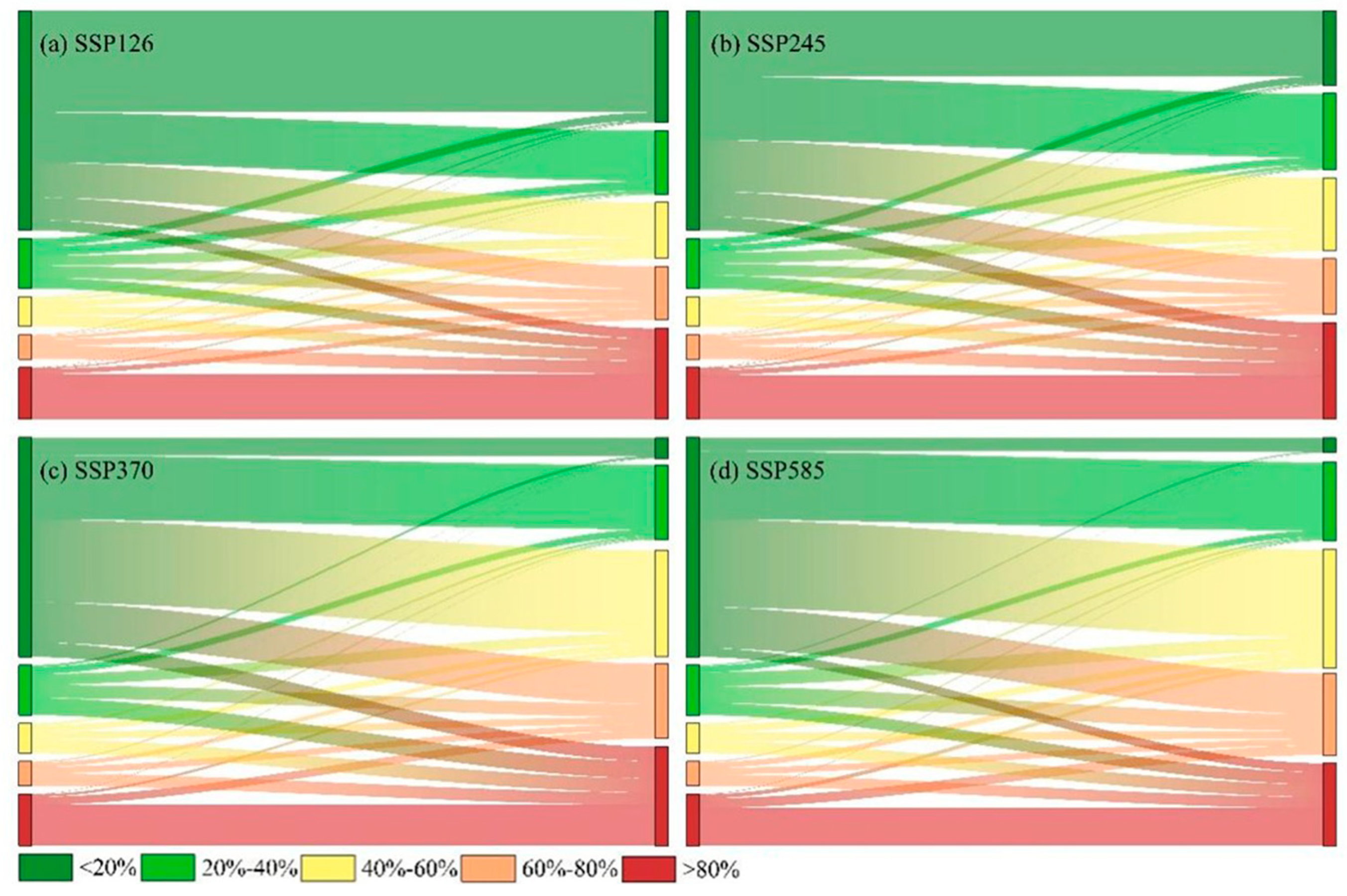
3.5. Transition in C. dubius Presence Probability Under Climate Change
4. Discussion
4.1. Distribution and Influenced Factors of C. dubius
4.2. Limitations and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ciancio, A.; Mukerji, K.G. (Eds.) Integrated Management of Arthropod Pests and Insect Borne Diseases; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Krall, S. Desert Locusts in Africa: A Disaster? Disasters 1995, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veran, S.; Simpson, S.J.; Sword, G.A.; Deveson, E.; Piry, S.; Hines, J.E.; Berthier, K. Modeling spatiotemporal dynamics of outbreaking species: Influence of environment and migration in a locust. Ecology 2015, 96, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Du, G.; Wang, G. The occurring and control situation of grasshopper in the grassland of China (review). Acta Agrestia Sin. 2014, 22, 929–934. [Google Scholar]
- Le Gall, M.; Overson, R.; Cease, A. Corrigendum: A global review on locusts (Orthoptera: Acrididae) and their interactions with livestock grazing practices. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1154640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, W.; Ye, H.; Lu, L. Study on the identification of habitat suitability areas for the dominant locust species Dasyhippus barbipes in Inner Mongolia. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hao, S.; Kang, L. Effects of soil temperature and moisture on the development and survival of grasshopper eggs in inner mongolian grasslands. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 727911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, B.; Gayen, A.; Haque, S.M.; Das, A. Influence of climate on desert locust (Schistocerca gregaria Forskål, 1775) Plague and migration prediction in tropics. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symmons, P.M.; Cressman, K. Desert Locust Guidelines: Biology and Behaviour; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2001; Volume 42. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Han, M.; Yuan, X.; Hou, Y.; Qin, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, X.; Klein, J.A.; Zhu, B. Warming has a minor effect on surface soil organic carbon in alpine meadow ecosystems on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 1618–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miehe, G.; Schleuss, P.-M.; Seeber, E.; Babel, W.; Biermann, T.; Braendle, M.; Chen, F.; Coners, H.; Foken, T.; Gerken, T.; et al. The Kobresia pygmaea ecosystem of the Tibetan highlands—Origin, functioning and degradation of the world’s largest pastoral alpine ecosystem: Kobresia pastures of Tibet. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 754–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, Q.; Hao, Y.; Xia, A.; Liu, W.; Hu, R.; Cui, X.; Xue, K.; Song, X.; Xu, C.; Ding, B.; et al. Quantitative assessment of the impact of physical and anthropogenic factors on vegetation spatial-temporal variation in Northern Tibet. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, T.; Zhao, W.; Feng, S.; Hua, T. Plant community traits respond to grazing exclusion duration in alpine meadow and alpine steppe on the Tibetan plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 863246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavaleta, E.S.; Shaw, M.R.; Chiariello, N.R.; Mooney, H.A.; Field, C.B. Additive effects of simulated climate changes, elevated CO2, and nitrogen deposition on grassland diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 7650–7654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Li, R.; Tian, L.; Zhang, T. Effect of grazing exclusion on ecosystem respiration among three different alpine grasslands on the central Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S. Remote Sensing Monitoring and Prediction of Grasshopper in Qinghai Lake; Shanghai Science and Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Lecoq, M.; Latchininsky, A.; Hunter, D. Locust and grasshopper management. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2019, 64, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, A.N.; Prather, C.M.; Branson, D.H.; Pennings, S.C. Effects of grasshoppers on prairies: Herbivore composition matters more than richness in three grassland ecosystems. J. Anim. Ecol. 2018, 87, 1727–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, L.I.; Ullah, H.; Zhang, Z. IPM-Biological and integrated management of desert locust. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 3467–3487. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, R.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, B.; Lv, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, W.; Ning, T.; Gui, J.; et al. Climate background, relative rate, and runoff effect of multiphase water transformation in Qilian Mountains, the third pole region. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Li, Z.; Feng, Q.; Li, Z.; Gui, J.; Li, Y. Ecological conservation pattern based on ecosystem services in the Qilian Mountains, northwest China. Environ. Dev. 2023, 46, 100834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.Y.; Yu, H.Y.; Chen, W.; Li, M.; Yi, S.H.; Meng, B.P. Predicting inhabitable areas for locust based on field observation and multi-environmental factors in alpine grassland—A case study in the Qilian Mountain National Park, China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1149952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Feng, Q.; Adamowski, J.F.; Alizadeh, M.R.; Yin, Z.; Wen, X.; Zhu, M. The role of climate change and vegetation greening on the variation of terrestrial evapotranspiration in northwest China’s Qilian Mountains. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Nawaz, Z. Predicting the impacts of climate change, soils and vegetation types on the geographic distribution of Polyporus umbellatus in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tang, Z.; Wang, B.; Kan, H.; Sun, Y.; Qin, Y.; Meng, B.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Lv, Y.; et al. A 250 m annual alpine grassland AGB dataset over the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau (2000–2019) in China based on in situ measurements, UAV photos, and MODIS data. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 821–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, T. An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branson, D.H.; Sergeev, M. Relationships between Plant Diversity and Grasshopper Diversity and Abundance in the Little Missouri National Grassland. Psyche-J. Entomol. 2010, 2011, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cease, A.J.; Elser, J.J.; Fenichel, E.P.; Hadrich, J.C.; Harrison, J.F.; Robinson, B.E. Living with locusts: Connecting soil nitrogen, locust outbreaks, livelihoods, and livestock markets. Bioscience 2015, 65, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joern, A. Disturbance by fire frequency and bison grazing modulate grasshopper assemblages in tallgrass prairie. Ecology 2005, 86, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvarov, B. Grasshoppers and locusts. In A Handbook of General Acridology, Behaviour, Ecology, Biogeography, Population Dynamics; Centre for Overseas Pest Research: London, UK, 1997; Volume 2, pp. 1–613. [Google Scholar]
- Nishide, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Tanaka, S. The hatching time of Locusta migratoria under outdoor conditions: Role of temperature and adaptive significance. Physiol. Entomol. 2017, 42, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressman, K. Current methods of desert locust forecasting at FAO. EPPO Bull. 1996, 26, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, D. A possible relationship between outbreaks of the oriental migratory locust (Locusta migratoria manilensis Meyen) in China and the El Niño episodes. Ecol. Res. 1999, 14, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.M.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.H. The responses of grasshoppers and their natural enemies to soil humidity and slope in Mahuang Mountain. Ningxia 2016, 43, 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, R.; Xie, B.-Y.; Li, D.-M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Use of MODIS data to monitor the oriental migratory locust plague. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 104, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhao, L.; Huang, W. Monitoring of Desert Locust in Africa and Asia; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hamuda, E.; Glavin, M.; Jones, E. A survey of image processing techniques for plant extraction and segmentation in the field. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 125, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamuda, E.; Mc Ginley, B.; Glavin, M.; Jones, E. Improved image processing-based crop detection using Kalman filtering and the Hungarian algorithm. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 148, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X. Grasshopper detection method based on machine vision. Agric. Eng. 2008, 24, 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, O.L.P.; Svenning, J.; Olsen, K.; Dupont, S.; Garner, B.H.; Iosifidis, A.; Price, B.W.; Høye, T.T. Species-level image classification with convolutional neural network enables insect identification from habitus images. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemoto, N.; Terada, K.; Takashina, Y.; Nakano, A. High-precision Classification of Small Insects with Similar Color and Shape Using Image Processing. Electron. Commun. Jpn. 2017, 100, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, E.R., Jr.; Rondon, S.I. Detection of potato beetle damage using remote sensing from small unmanned aircraft systems. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 026013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuba, N.; Kawamura, K.; Yasuda, T.; Lim, J.; Yoshitoshi, R.; Kurokawa, Y.; Maeda, T. Counting of Pennisetum alopecuroides at heading stage in a grazed pasture using images from an unmanned aerial vehicle. Grassl. Sci. 2020, 66, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Environment Variables | Code | Variable |
|---|---|---|
| Climate variables | bio01 | Annual Mean Temperature |
| bio02 | Mean Diurnal Range | |
| bio04 | Temperature Seasonality | |
| bio06 | Min Temperature of Coldest Month | |
| bio07 | Temperature Annual Range | |
| bio08 | Mean Temperature of Wettest Quarter | |
| bio09 | Mean Temperature of Driest Quarter | |
| bio12 | Annual Precipitation | |
| bio13 | Precipitation of Wettest Month | |
| bio15 | Precipitation Seasonality | |
| bio16 | Precipitation of Wettest Quarter | |
| bio17 | Precipitation of Driest Quarter | |
| Topographic variables | dem | Digital Elevation Model |
| slop | Slope | |
| aspe | Aspect | |
| Other variables | roughness | Surface Roughness |
| Model | Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Kappa | TSS | ROC | |
| GLM | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.92 |
| GBM | 0.84 | 0.87 | 0.97 |
| CTA | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.86 |
| SRE | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.68 |
| FDA | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.93 |
| MARS | 0.78 | 0.80 | 0.90 |
| RF | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.98 |
| Period | Probability (%) | Proportion of Area (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSP126 | SSP245 | SSP370 | SSP585 | ||
| 2021–2040 | <20 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.33 |
| 20–40 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | |
| 40–60 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 | |
| 60–80 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | |
| >80 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.22 | |
| 2041–2060 | <20 | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.24 |
| 20–40 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.19 | |
| 40–60 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.17 | |
| 60–80 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.15 | |
| >80 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.25 | |
| 2061–2080 | <20 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.08 |
| 20–40 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.19 | |
| 40–60 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.25 | |
| 60–80 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.19 | |
| >80 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.29 | |
| 2081–2100 | <20 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.06 | 0.04 |
| 20–40 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.21 | |
| 40–60 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.31 | |
| 60–80 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.22 | |
| >80 | 0.24 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.22 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Yao, C.; Ji, G.; Xu, W.; Yi, S.; Meng, B. The Impact of Climate Change on Chorthippus dubius (Zubovski, 1898) Distribution in Alpine Grassland—A Case Study in the Qilian Mountain National Park, China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2728. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122728
Wang Y, Yu H, Yao C, Ji G, Xu W, Yi S, Meng B. The Impact of Climate Change on Chorthippus dubius (Zubovski, 1898) Distribution in Alpine Grassland—A Case Study in the Qilian Mountain National Park, China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(12):2728. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122728
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yu, Hongyan Yu, Chuang Yao, Guohui Ji, Wenbo Xu, Shuhua Yi, and Baoping Meng. 2025. "The Impact of Climate Change on Chorthippus dubius (Zubovski, 1898) Distribution in Alpine Grassland—A Case Study in the Qilian Mountain National Park, China" Agronomy 15, no. 12: 2728. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122728
APA StyleWang, Y., Yu, H., Yao, C., Ji, G., Xu, W., Yi, S., & Meng, B. (2025). The Impact of Climate Change on Chorthippus dubius (Zubovski, 1898) Distribution in Alpine Grassland—A Case Study in the Qilian Mountain National Park, China. Agronomy, 15(12), 2728. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122728




