Quantitative Source Apportionment and Source-Oriented Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Soils: A Case Study of Yutian County in the Southern Margin of Tarim Basin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
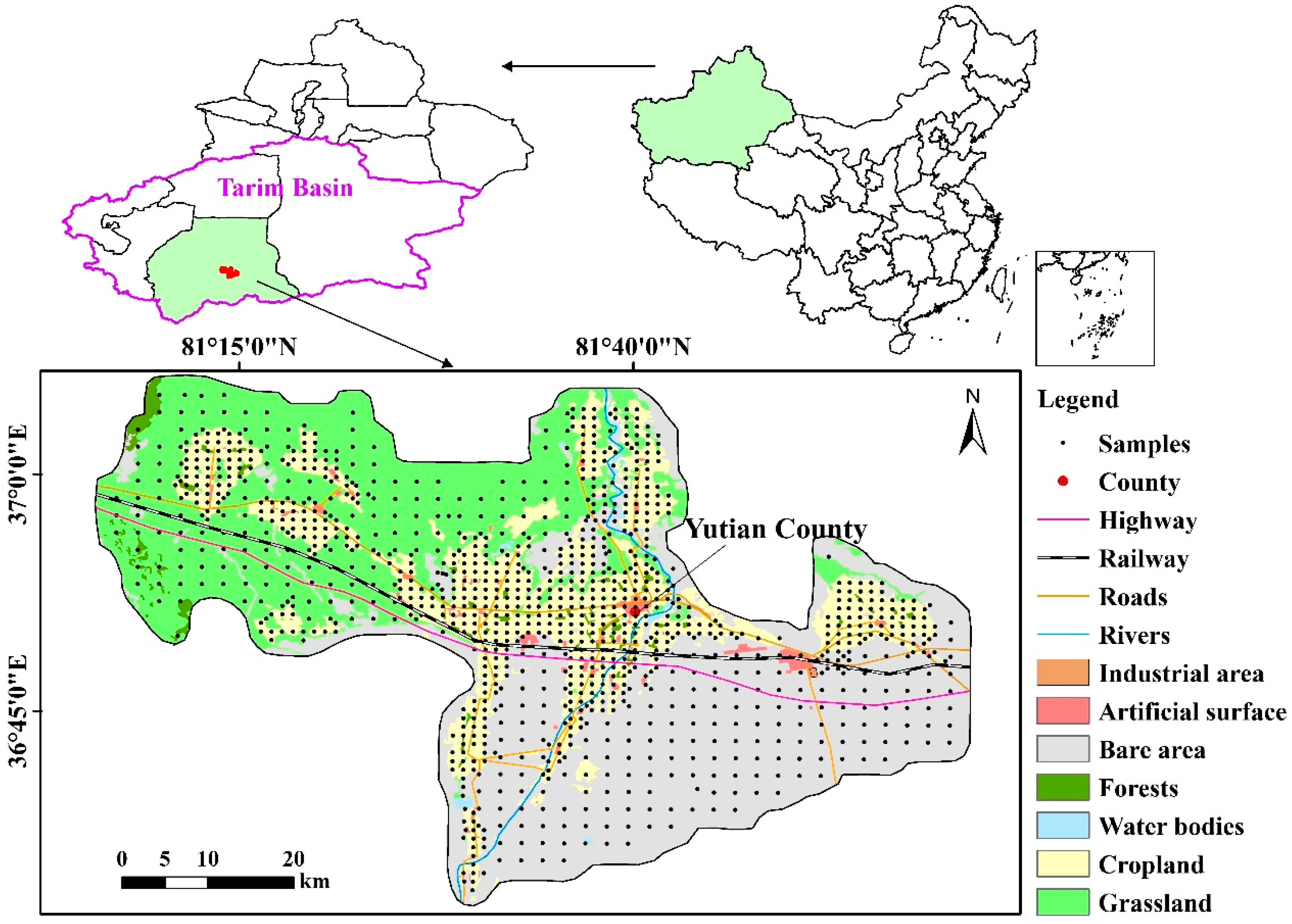
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Treatment
2.3. Self-Organizing Map (SOM)
2.4. Positive Matrix Factorization
2.5. Health Risk Assessment Based on Pollution Sources
2.6. Monte Carlo Model
3. Results and Discussion
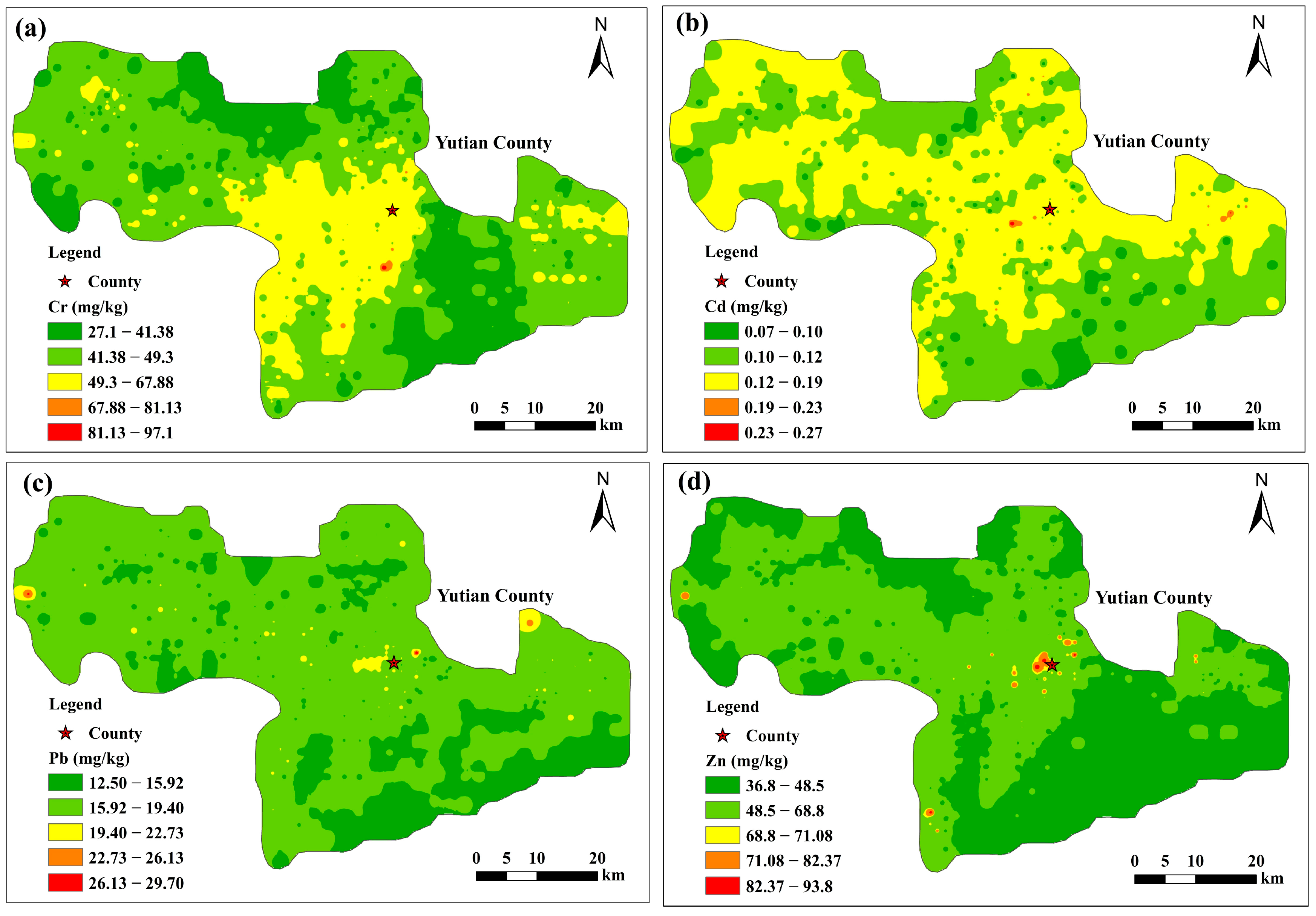
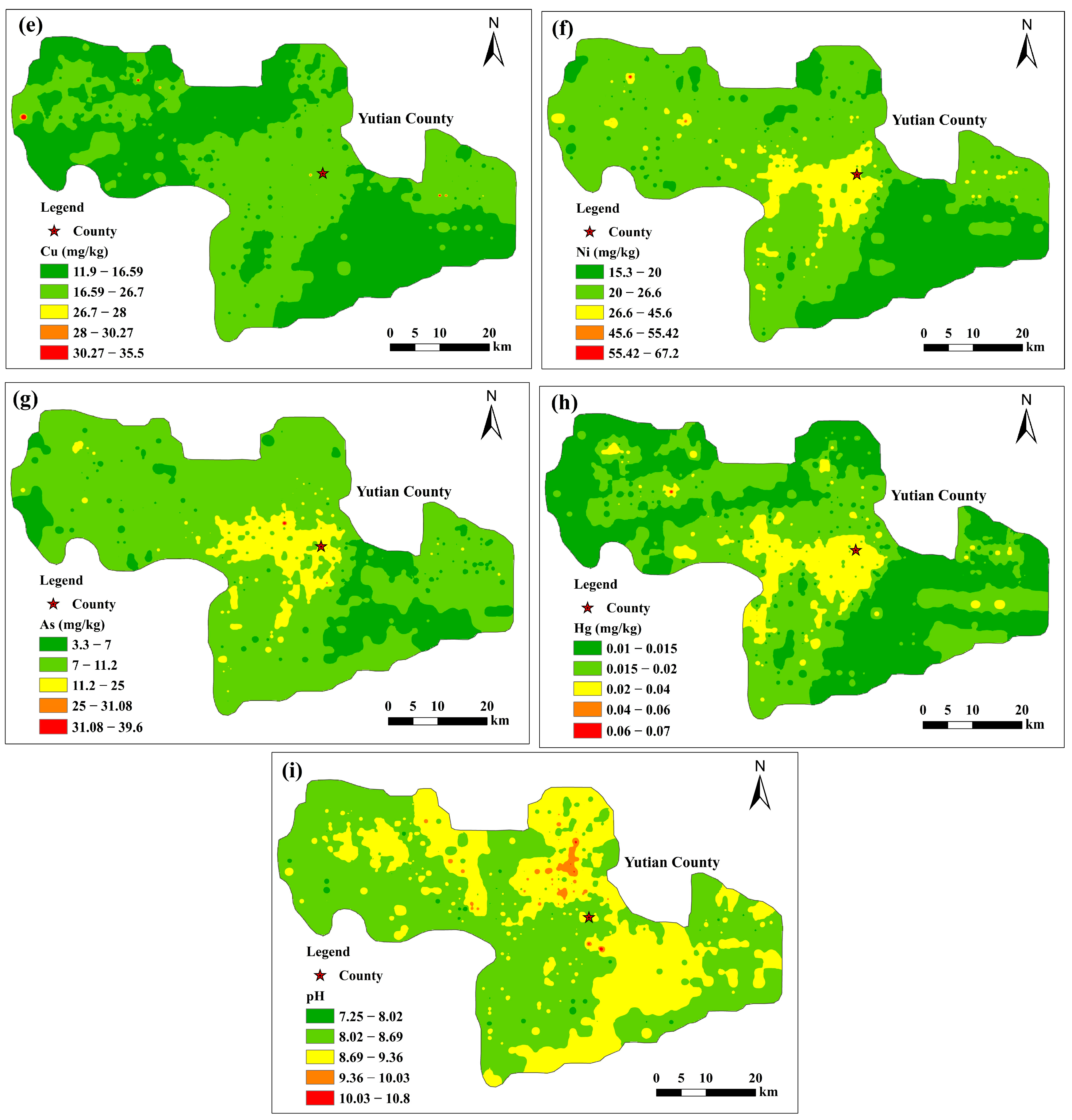
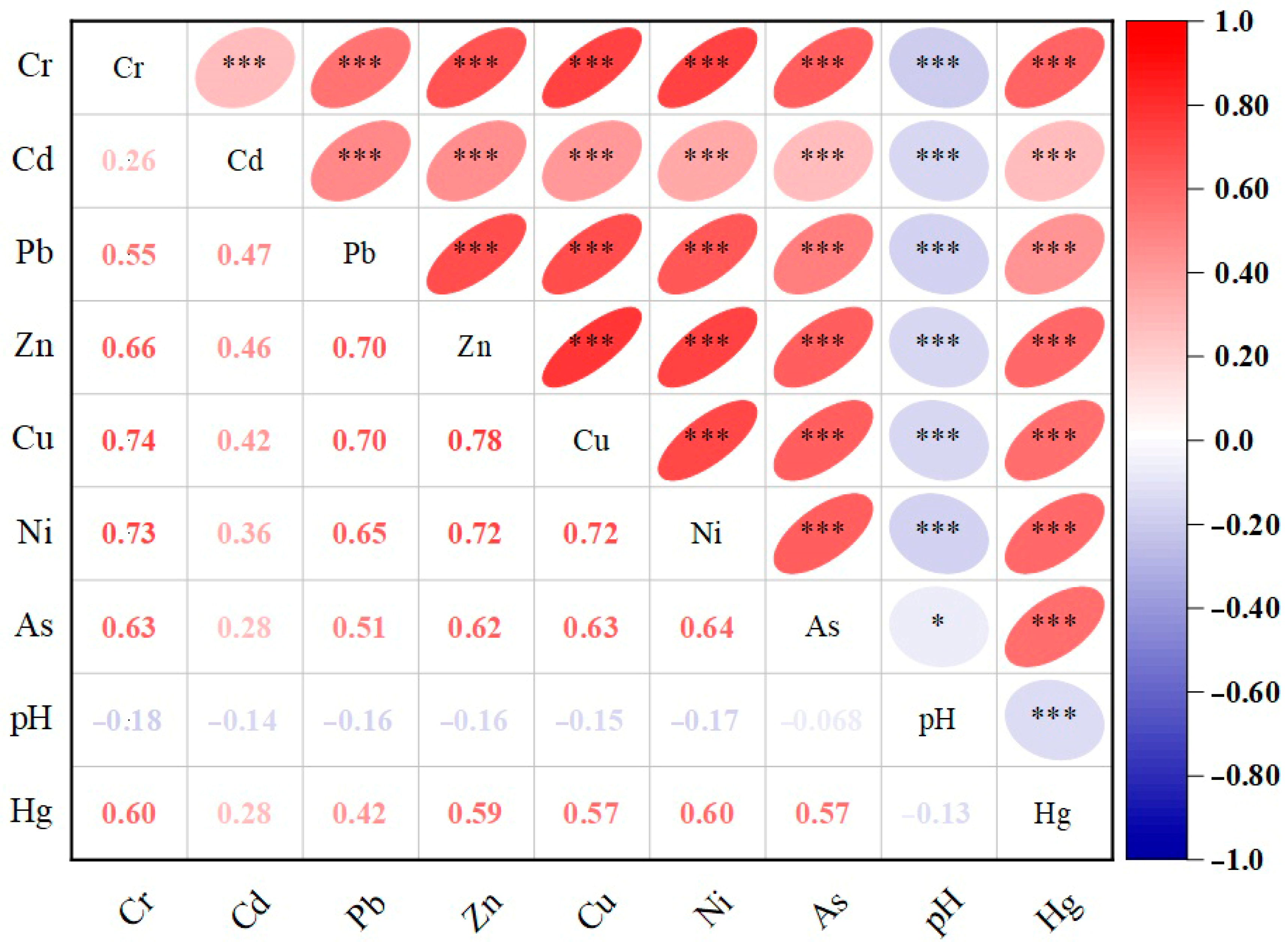
3.1. Concentrations and Distribution of Soil Heavy Metals
| Cr | Cd | Pb | Zn | Cu | Ni | As | Hg | a pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 27.10 | 0.07 | 12.50 | 36.80 | 11.90 | 15.30 | 3.30 | 0.01 | 7.25 |
| Max | 97.10 | 0.27 | 29.70 | 93.80 | 35.50 | 67.20 | 39.60 | 0.07 | 10.80 |
| Mean | 47.73 | 0.13 | 17.00 | 52.30 | 17.83 | 23.21 | 9.15 | 0.02 | 8.64 |
| Median | 46.50 | 0.12 | 16.80 | 51.40 | 17.20 | 22.30 | 8.50 | 0.02 | 8.61 |
| Standard deviation | 7.70 | 0.02 | 1.46 | 8.61 | 2.85 | 4.12 | 2.62 | 0.01 | 0.38 |
| Coefficient of variation (%) | 16.14 | 18.52 | 8.56 | 16.45 | 16.00 | 17.75 | 28.58 | 30.27 | 4.37 |
| Soil background in Xinjiang [55] | 49.30 | 0.12 | 19.40 | 68.80 | 26.70 | 26.60 | 11.20 | 0.02 | - |
| b Soil environmental screening standard value (GB 15618-2018) | 250.00 | 0.60 | 170.00 | 300.00 | 100.00 | 190.00 | 25.00 | 3.40 | |
| Mean value of Weining County, Guizhou Province [32] | 167.43 | 5.69 | 109.26 | 314.99 | 137.81 | 77.12 | 22.59 | 0.12 | 5.67 |
| Mean value of Baoqing County, Heilongjiang Province [33] | 70.8 | 0.08 | 25.49 | 65.16 | 25.03 | 30.61 | - | 0.04 | 6.35 |
| Mean value of Anqing City, Anhui Province [50] | 59.51 | 0.34 | 46.01 | 90.02 | 25.73 | - | 12.91 | 0.32 | - |
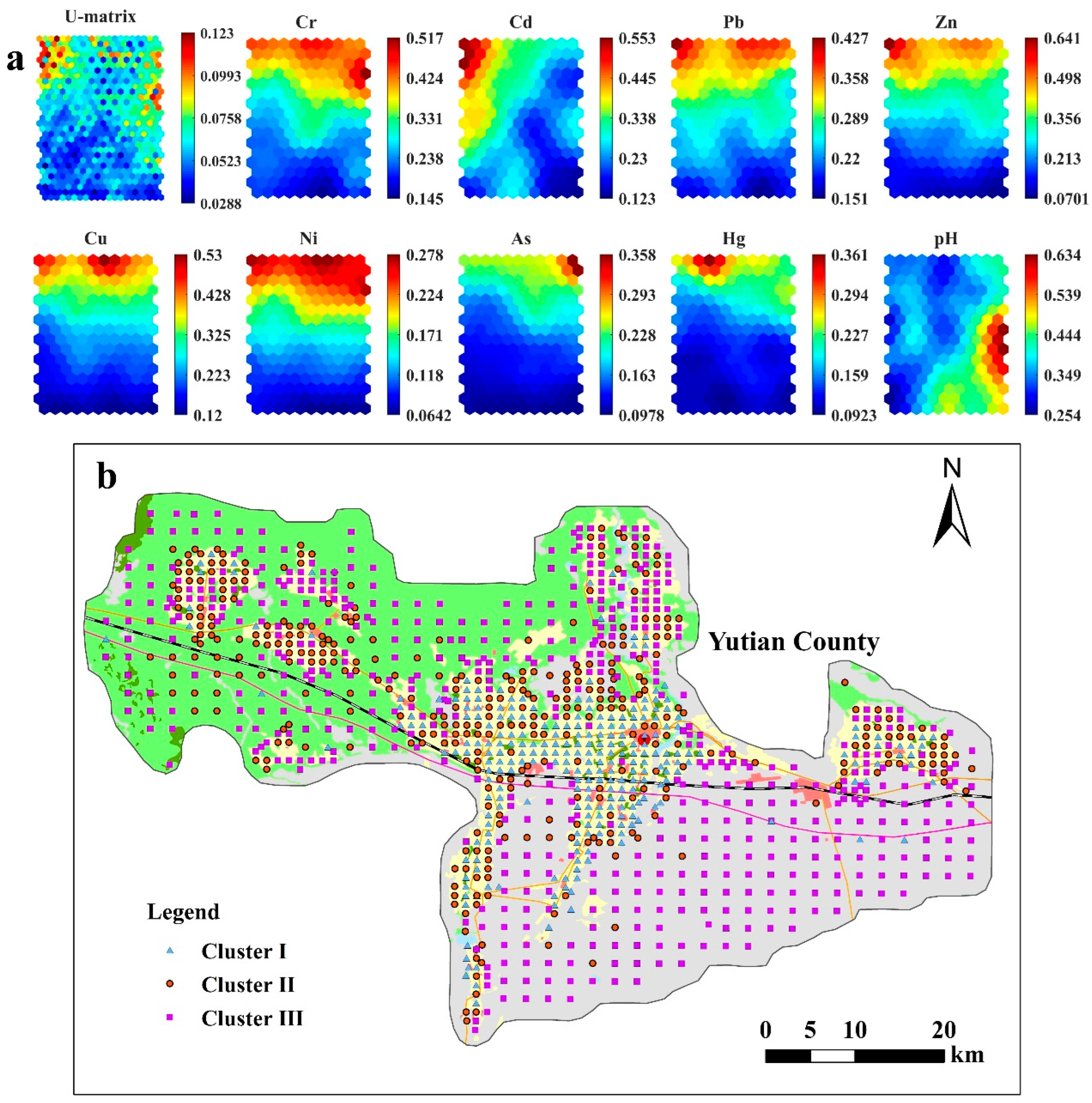
3.2. SOM Results
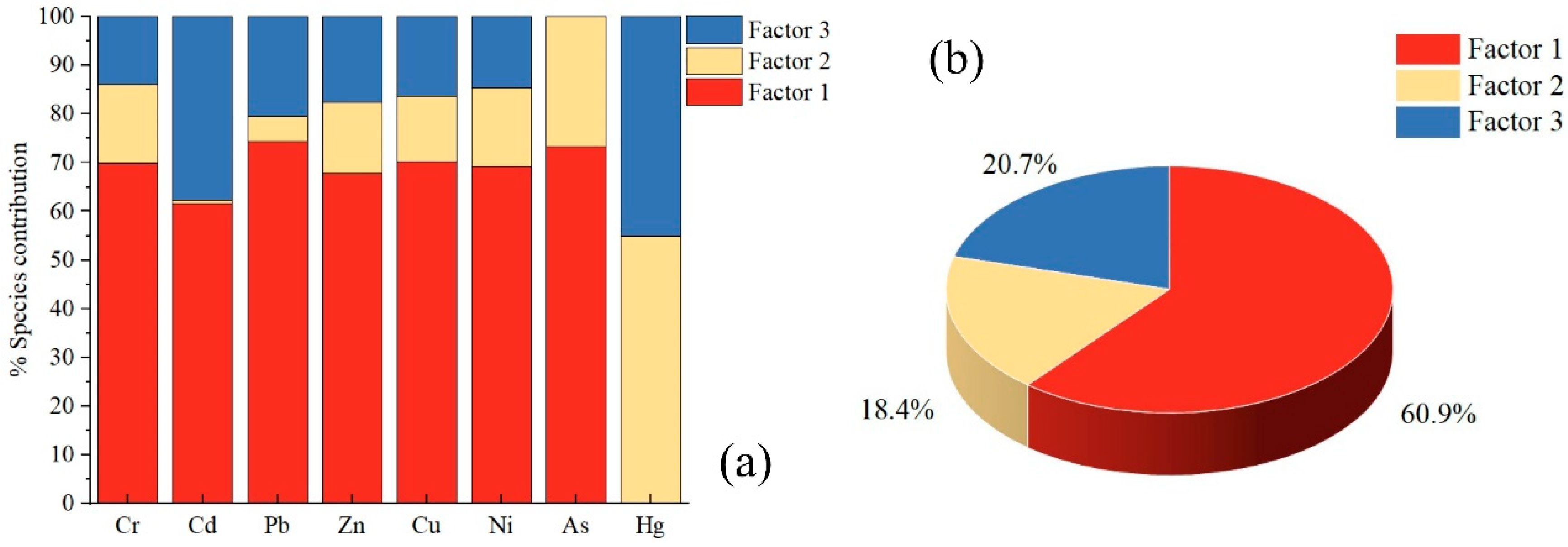
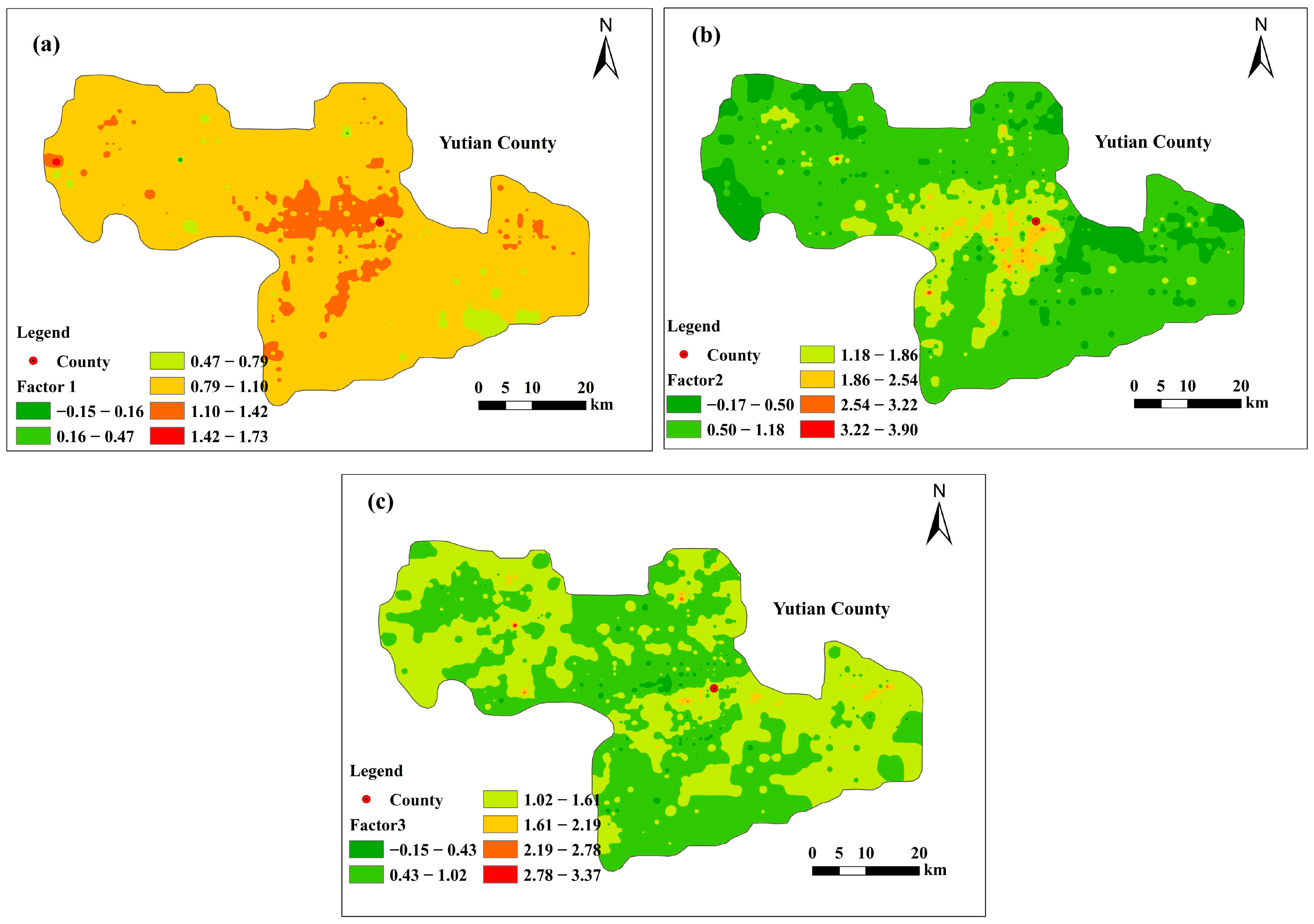
3.3. Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metal
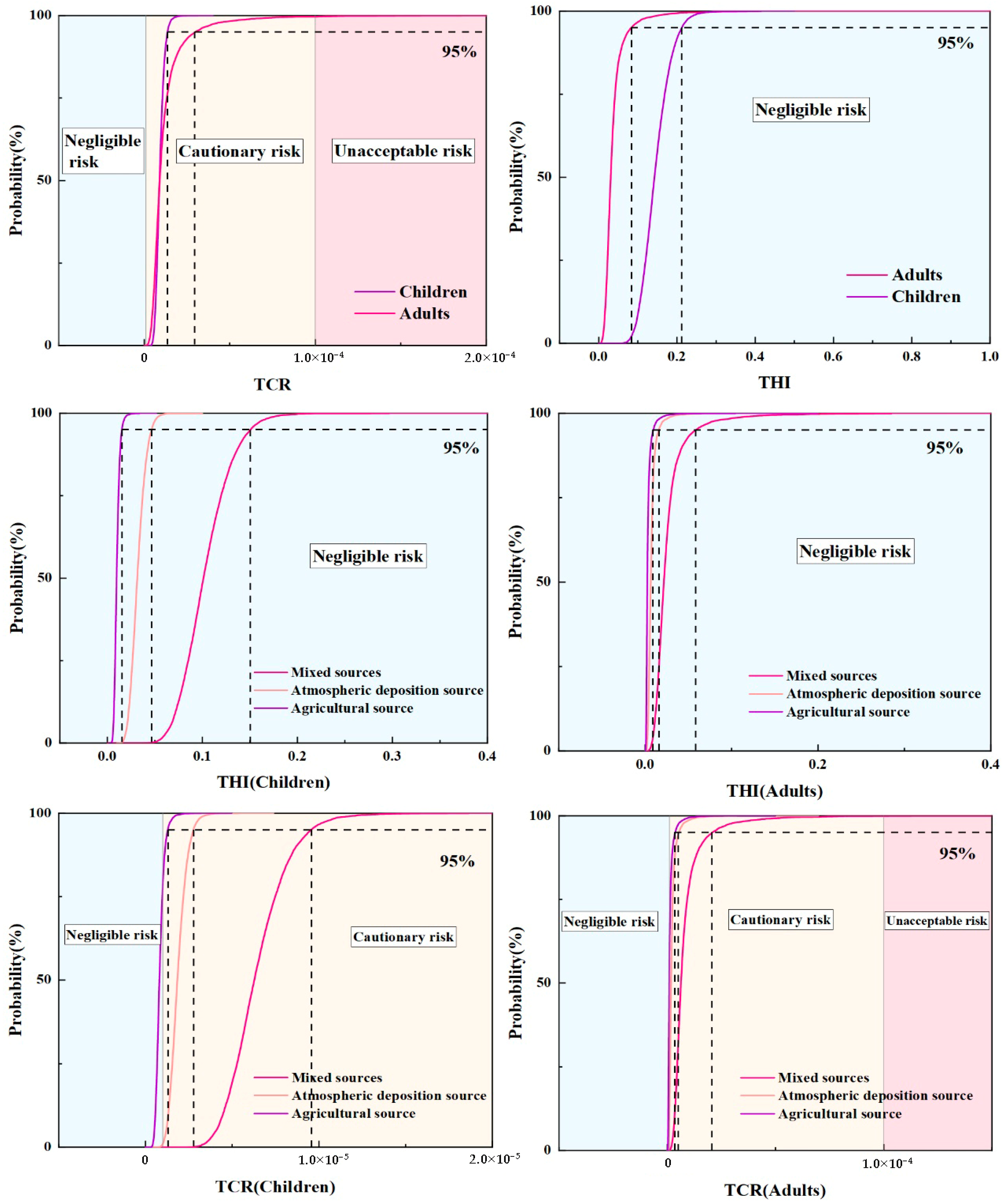
3.4. Health Risk Evaluation of Pollution Sources Based on Monte Carlo Simulation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, G.; Niu, Z.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Xiang, P. Soil heavy metal pollution and food safety in China: Effects, sources and removing technology. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.S. Multivariate receptor models and robust geostatistics to estimate source apportionment of heavy metals in soils. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, M.; Darvishiyan, M.; Momeni, M.; Eslami, H.; Fallahzadeh, R.A.; Zarei, A. Ecological risk assessment of trace elements (TEs) pollution and human health risk exposure in agricultural soils used for saffron cultivation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Feng, W.; Wang, S.; Chen, L.; Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, D. Farmland heavy metals can migrate to deep soil at a regional scale: A case study on a wastewater-irrigated area in China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 281, 116977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.M.; Hu, W.Y.; Wang, H.F.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.K.; Huang, B. Spatial distribution, ecological risk and sources of heavy metals in soils from a typical economic development area, Southeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.B.; Hu, X.Y.; Wang, T.; Sun, M.X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.X. Non-inverted U-shaped challenges to regional sustainability: The health risk of soil heavy metals in coastal China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Q.; Li, Z.Y.; Lu, X.N.; Duan, Q.N.; Huang, L.; Jun, B.J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.T.; Wang, P.; Shi, H.Y.; Zhuang, C.W.; Deng, Y.R.; Yang, X.J.; Xiao, R.B. Quantitative source apportionment and driver identification of soil heavy metals using advanced machine learning techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Lei, S.; Bian, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Gan, Y. Geographic distribution of heavy metals and identification of their sources in soils near large, open-pit coal mines using Positive Matrix Factorization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.Y.; Chen, X.; Xie, F.Z.; Zhang, Z.H.; Ma, T.Q.; Dong, X.; Zheng, L.G. Combining APCS-MLR model to evaluate the distribution and sources of rare earth elements in a large catchment. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.B.; Cheng, J.L.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Shi, Z. Pollution assessment and source apportionment of soil heavy metals in a coastal industrial city, Zhejiang, Southeastern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, C.L.; Zereini, F.; Püttmann, W. Metal and metalloid accumulation in cultivated urban soils: A medium-term study of trends in Toronto, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.R.; Zhang, J.R.; Shen, W.J.; Wang, J.; Li, X.Y. Machine learning can identify the sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil: A case study in northern Guangdong Province, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 246, 114192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Guo, G.H.; Zhang, D.G.; Lei, M. An integrated method for source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils and model uncertainty analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licen, S.; Astel, A.; Tsakovski, S. Self-organizing map algorithm for assessing spatial and temporal patterns of pollutants in environmental compartments: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q.; Lin, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X. Machine learning based on the graph convolutional self-organizing map method increases the accuracy of pollution source identification: A case study of trace metal (loid)s in soils of Jiangmen City, south China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 250, 114467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Shen, Z.J.; Wang, Y.M.; Mei, N.; Li, C.X.; Liu, Y.J.; Ma, W.B.; Zhang, C.; Wang, D.Y. Tracing and quantifying the source of heavy metals in agricultural soils in a coal gangue stacking area: Insights from isotope fingerprints and receptor models. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.T.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.Y.; Lei, K.G.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Zheng, D.F.; Fang, X.Q.; Cao, Y. Heavy metal contamination risk assessment and correlation analysis of heavy metal contents in soil and crops. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Chen, Z.W.; Li, Y.Y.; Ding, K.B.; Liu, W.S.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.Q.; Zhang, M.Y.; Baker, A.J.M.; Yang, W.J.; et al. Factors influencing heavy metal availability and risk assessment of soils at typical metal mines in Eastern China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, M.; Gündüz, K.; Sünbül, M.R. Pollution status, potential sources and health risk assessment of arsenic and trace metals in agricultural soils: A case study in Malatya province, Turkey. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.M.; Liu, S.; Song, L.; Wu, C.S.; Yang, B.; Lu, H.Z.; Wang, X.; Zakari, S. Contamination and source-specific risk analysis of soil heavy metals in a typical coal industrial city, central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.L.; Liu, Y.F.; Liu, Q.; Gui, D.W.; Cui, B.C.; Chen, X.N.; Abd, S.K. Spatial distribution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in soils of Southern Xinjiang oases. Env. Monit Assess 2025, 197, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.W.; Xue, J.P.; Cai, J.X.; Zhang, Y.C.; Li, F.X.; Zha, X.H.; Fang, G.D. The spatial distribution and influencing factors of heavy metals in soil in Xinjiang, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ/T 166-2004; The Technical Specification for Soil Environmental Monitoring. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2004.
- DZ/T 0258-2014; Specification of Multi-Purpose Regional Geochemical Survey (1:250,000). Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Kohonen, T. Self-organized formation of topologically correct feature maps. Biol. Cybern. 1982, 43, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.R.; Wang, G.C.; Rao, Z.; Liao, F.; Shi, Z.M.; Huang, X.J.; Chen, X.L.; Yang, Y. Deciphering spatial pattern of groundwater chemistry and nitrogen pollution in Poyang Lake Basin (eastern China) using self-organizing map and multivariate statistics. J. Clean. Profuction 2021, 329, 129697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souid, F.; Telahigue, F.; Agoubi, B.; Kharroubi, A. Isotopic behavior and self-organizing maps for identifying groundwater salinization processes in Jerba Island, Tunisia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain Bhuiyan, M.A.; Chandra Karmaker, S.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Rakib, M.A.; Saha, B.B. Enrichment, sources and ecological risk mapping of heavy metals in agricultural soils of dhaka district employing SOM, PMF and GIS methods. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Liang, T.; Guo, Q.; Guan, Y.; Rinklebe, J. Elucidating the differentiation of soil heavy metals under different land uses with geographically weighted regression and self-organizing map. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Ren, B.Z. Analyzing topsoil heavy metal pollution sources and ecological risks around antimony mine waste sites by a joint methodology. Ecol. Indicators. 2023, 154, 110761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Liu, H.Y.; Meng, W.; Liu, N.T.; Wu, P. Accumulation and source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils based on GIS, SOM and PMF: A case study in superposition areas of geochemical anomalies and zinc smelting, Southwest China. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.Y.; Kong, F.P.; Liu, X.J.; Dai, L.J.; Liu, H.B.; He, J.B.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.Q. An integrated approach for quantifying trace metal sources in surface soils of a typical farmland in the three rivers plain, China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 337, 122614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesanto, J.; Alhoniemi, E. Clustering of the self-organizing map. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2000, 11, 586–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, G.H.; Li, K.; Zhang, D.G.; Lei, M. Quantitative source apportionment and associated driving factor identification for soil potential toxicity elements via combining receptor models, SOM, and geo-detector method. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.L.; Bouldin, D.W. A cluster separation measure. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1979, 1, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Environmentrics 1994, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Kong, L.; Jiang, D.; Wei, J.; Cao, S.; Li, X.; Zheng, L.; Deng, S. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of chemicals of concern in soil, water and sediment at a large strontium slag pile area. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 304, 114228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, T.; Li, J.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Shaheen, S.M.; Antoniadis, V.; Bolan, N.; Rinklebe, J. Integrated assessment of the impact of land use types on soil pollution by potentially toxic elements and the associated ecological and human health risk. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 299, 118911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US EPA. Positive Matrix Factorization Model for Environmental Data Analyses. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Office of Research and Development. 2014. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/air-research/positive-matrix-factorization-model-environmental-data-analyses#overview (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Zeng, J.; Han, G.; Yang, K. Assessment and sources of heavy metals in suspended particulate matter in a tropical catchment, northeast Thailand. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Banerjee, S.; Prajapati, J.; Mandal, J.; Mukherjee, A.; Bhattacharyya, P. Pollution and health risk assessment of mine tailings contaminated soils in India from toxic elements with statistical approaches. Chemosphere 2023, 324, 138267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Exposure Factors Handbook, final ed.; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; [EPA/600/R-09/052F].
- Jiang, H.H.; Cai, L.M.; Hu, G.C.; Wen, H.H.; Luo, J.; Xu, H.Q.; Chen, L.G. An integrated exploration on health risk assessment quantification of potentially hazardous elements in soils from the perspective of sources. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.R.; Su, H.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, J.J.; Liu, K.; Xie, X.F.; Jia, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.C.; Wang, G.M.; et al. A Monte Carlo simulation-based health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils of the tropical region in southern China. Environ. Geochem Health 2024, 46, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Song, L.T.; Yao, Z.P.; Meng, F.S.; Teng, Y.G. Characterization and source apportionment of heavy metals in the sediments of Lake Tai (China) and its surrounding soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Chang, Q. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils and identification of main influencing factors in a typical industrial park in northwest China. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Teng, Y.G.; Lu, S.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, J.S. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Teng, Y.G.; Lu, S.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.S. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of trace metals in surface soils of Beijing metropolitan, China. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.X.; Zhao, M.L.; Huang, J.L.; Liu, Y.F.; Wu, Y.Y.; Cai, B.Y.; Han, Z.W.; Huang, H.H.; Fan, Z.Q. Determination of priority control factors for the management of soil trace metal(loid)s based on source-oriented health risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshunsanya, S.O. Introductory chapter: Relevance of soil pH to agriculture. In Soil pH for Nutrient Availability and Crop Performance; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Y.; Peng, T.; Xue, S.W. Mechanisms of plant saline-alkaline tolerance. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 281, 153916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brautigan, D.J.; Rengasamy, P.; Chittleborough, D.J. Aluminium speciation and phytotoxicity in alkaline soils. Plant Soil 2012, 360, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, J.A.; Jansen, B.; Kalbitz, K.; Faz, A.; Martínez-Martínez, S. Salinity increases mobility of heavy metals in soils. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Zhou, J.L.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Wang, S.T.; Du, J.Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Zeng, Y.Y.; Wei, X. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of agricultural land in the Southern Margin of Tarim Basin in Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2021, 31, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.; Oldoni, H.; Silva, W.A.; Martins, R.L.; Bassoi, L.H. Temporal variation and spatial distribution of relative indices of leaf chlorophyll in grapevine cv. chardonnay. Eng. Agric. 2019, 39, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.M.; Wang, X.X.; Cui, G.N.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.F.; Li, B.; Yao, Z.L. Source apportionment and ecological and health risk mapping of soil heavy metals based on PMF, SOM, and GIS methods in Hulan River Watershed, Northeastern China. Environ. Monit Assess 2022, 194, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.R.; Li, J.B.; Wang, Y.Z.; Huang, P.C.; He, X.M. Evaluation and source analysis of heavy metal pollution in grassland soils under different management modes in Altay, Xinjiang. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.J.; Wang, M.Y.; Gao, X.; Zhu, H.W.; Zhang, Y. Environmental capacity simulation and source analysis of toxic metals in soils of Wucaiwan mining area, Xinjiang, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abliz, A.; Shi, Q.D.; Abulizi, A. Contamination status and health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in the northern slope of eastern Tianshan Mountains industrial belt in Xinjiang, northwest China. Forests 2023, 13, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baishan, K.; Wang, X.M.; Huang, X.Y.; Eziz, M. Health risk assessment and source analysis of toxic element pollution in cultivated soils of the Weigan and Kuqa Rivers oasis in Xinjiang, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 32, 3501–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.B.; Shi, J.B.; Feng, X.B. Mercury pollution in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3672–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirrone, N.; Cinnirella, S.; Feng, X.; Finkelman, R.B.; Friedli, H.R.; Leaner, J.; Mason, R.; Mukherjee, A.B.; Stracher, G.B.; Streets, D.G.; et al. Global mercury emissions to the atmosphere from anthropogenic and natural sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5951–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality-Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Shokr, M.S.; Abdellatif, M.A.; EIBehairy, R.A.; Abdelhameed, H.H.; EIBaroudy, A.A.; Mohamed, E.S.; Rebouh, N.Y.; Ding, Z.L.; Abuzaid, A.S. Assessment of potential heavy metal contamination hazards based on GIS and multivariate analysis in some mediterranean zones. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamoud, A.M.; Halder, B.; Shakir, H.S.; Yaseen, Z.M. Soil heavy metal contamination analysis: A representative case study in New Zealand. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; Shi, Y.; Guo, G.L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Su, Y.Q.; Zhang, C. Spatial distribution prediction of soil as in a large-scale arsenic slag contaminated site based on an integrated model and multi-source environmental data. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebonye, N.M.; Eze, P.N.; John, K.; Gholizadeh, A.; Dajčl, J.; Drábek, O.; Němeček, K.; Borůvka, L. Self-organizing map artificial neural networks and sequential Gaussian simulation technique for mapping potentially toxic element hotspots in polluted mining soils. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 222, 106680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruvka, L.; Vacek, O.; Jehlicka, J. Principal component analysis as a tool to indicate the origin of potentially toxic elements in soils. Geoderma 2005, 128, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Kausar, D.; Akhter, G.; Shah, M.H. Evaluation of the mobility and pollution index of selected essential/toxic metals in paddy soil by sequential extraction method. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Z.; Su, L.; Liu, M. Quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in cultivated soil and associated model uncertainty. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 215, 112150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Ghosh, S.; Jha, S.; Kumar, S.; Mondal, G.; Sarkar, D.; Datta, R.; Mukherjee, A.; Bhattacharyya, P. Assessing pollution and health risks from chromite mine tailings contaminated soils in India by employing synergistic statistical approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, X.F.; Lou, Z.H.; Xiao, R.; Ren, Z.Q.; Lv, X.N. Source analysis and source-oriented risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils of different cultivated land qualities. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 341, 130942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Guo, D.K.; Liu, K.; Meng, H.; Zheng, Y.J.; Yuan, F.Q.; Zhu, G.H. Levels, sources, and spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils from a typical coal industrial city of Tangshan, China. Catena 2019, 175, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.H.; Chen, S.Q.; Li, K.; Lei, M.; Ju, T.N.; Tian, L.Y. Determining the priority control sources of heavy metals in the roadside soils in a typical industrial city of North China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šajn, R.; Halamić, J.; Peh, Z.; Galović, L.; Alijagić, J. Assessment of the natural and anthropogenic sources of chemical elements in alluvial soils from the Drava River using multivariate statistical methods. J. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 110, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Z.X.; Su, L.M. Pollution characteristics, spatial distributions, and source apportionment of heavy metals in cultivated soil in Lanzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Geng, X.; Zhao, M.; Sun, T.; Fan, Z. Health risk assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in park soils of the largest megacity in China by using Monte Carlo simulation coupled with Positive matrix factorization model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Wang, F.; Xu, C.; Pan, N.; Lin, J.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Y.; Luo, H. Source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil based on PMF: A case study in Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Lu, X.W.; Yu, B.; Fan, X.Y.; Wang, L.Q.; Lei, K.; Yang, Y.F.; Zuo, L.; Rinklebe, J. Spatial distribution, risk estimation and source apportionment of potentially toxic metal(loid)s in resuspended megacity street dust. Environ. Int. 2022, 160, 107073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.W.; Liu, N.T.; Li, X.M.; Zeng, S.F.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.Y. Understanding heavy metal accumulation in roadside soils along major roads in the Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.; Rose, N.L.; Myllyvirta, L.; Haberle, S.; Lintern, A.; Yuan, J.J.; Sinclair, D.; Holley, C.; Zawadzki, A.; Sun, R.Y. Mercury atmospheric emission, deposition and isotopic fingerprinting from major coal-fired power plants in Australia: Insights from palaeo-environmental analysis from sediment cores. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.C.; Yu, H.H.; Ye, T.R.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Yuan, G.L.; Albanese, S. Geostatistical mapping and quantitative source apportionment of potentially toxic elements in top- and sub-soils: A case of suburban area in Beijing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wei, D.; Zhu, Y.G. An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2524–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.F.; Shao, S.; Ni, H.; Fu, Z.Y.; Hu, L.S.; Zhou, Y.; Min, X.X.; She, S.F.; Chen, S.C.; Huang, M.X.; et al. Current status, spatial features, health risks, and potential driving factors of soil heavy metal pollution in China at province level. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 114961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltas, H.; Sirin, M.; Gökbayrak, E.; Ozcelik, A.E. A case study on pollution and a human health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils around Sinop province Turkey. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.F.; Li, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, T.Q.; Wang, J.N.; Liu, T.T. Review of soil heavy metal pollution in China: Spatial distribution, primary sources, and remediation alternatives. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 181, 106261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.P.; Wang, L.; Yan, M.J.; Ma, B.; Cao, R.X. Source apportionment of soil heavy metals based on multivariate statistical analysis and the PMF model: A case study of the Nanyang Basin, China. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 33, 103537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.G.; Korna, R.; Fan, J.R.; Ke, W.S.; Lou, W.; Wang, J.T.; Zhu, F. Spatial distribution, environmental risks, and sources of potentially toxic elements in soils from a typical abandoned antimony smelting site. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 127, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, W.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, J.; Wang, S.; Du, J.; Hu, L.; Shan, R.; Zhang, L. Quantitative Source Apportionment and Source-Oriented Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Soils: A Case Study of Yutian County in the Southern Margin of Tarim Basin, China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122721
Fan W, Zhou J, Zheng J, Wang S, Du J, Hu L, Shan R, Zhang L. Quantitative Source Apportionment and Source-Oriented Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Soils: A Case Study of Yutian County in the Southern Margin of Tarim Basin, China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(12):2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122721
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Wei, Jinlong Zhou, Jianghua Zheng, Songtao Wang, Jiangyan Du, Lina Hu, Ruiqi Shan, and Lizhong Zhang. 2025. "Quantitative Source Apportionment and Source-Oriented Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Soils: A Case Study of Yutian County in the Southern Margin of Tarim Basin, China" Agronomy 15, no. 12: 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122721
APA StyleFan, W., Zhou, J., Zheng, J., Wang, S., Du, J., Hu, L., Shan, R., & Zhang, L. (2025). Quantitative Source Apportionment and Source-Oriented Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Soils: A Case Study of Yutian County in the Southern Margin of Tarim Basin, China. Agronomy, 15(12), 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122721






