Biodegradable Film Mulching Increases Soil Respiration: A Two-Year Field Comparison with Polyethylene Film Mulching in a Semi-Arid Region of Northern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Field Experimental Design
2.3. Measurement of Soil Temperature and Soil Moisture
2.4. Determination of Soil CO2 Concentration
2.5. Determination of Soil Respiration and Its Components
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Volumetric Water Content
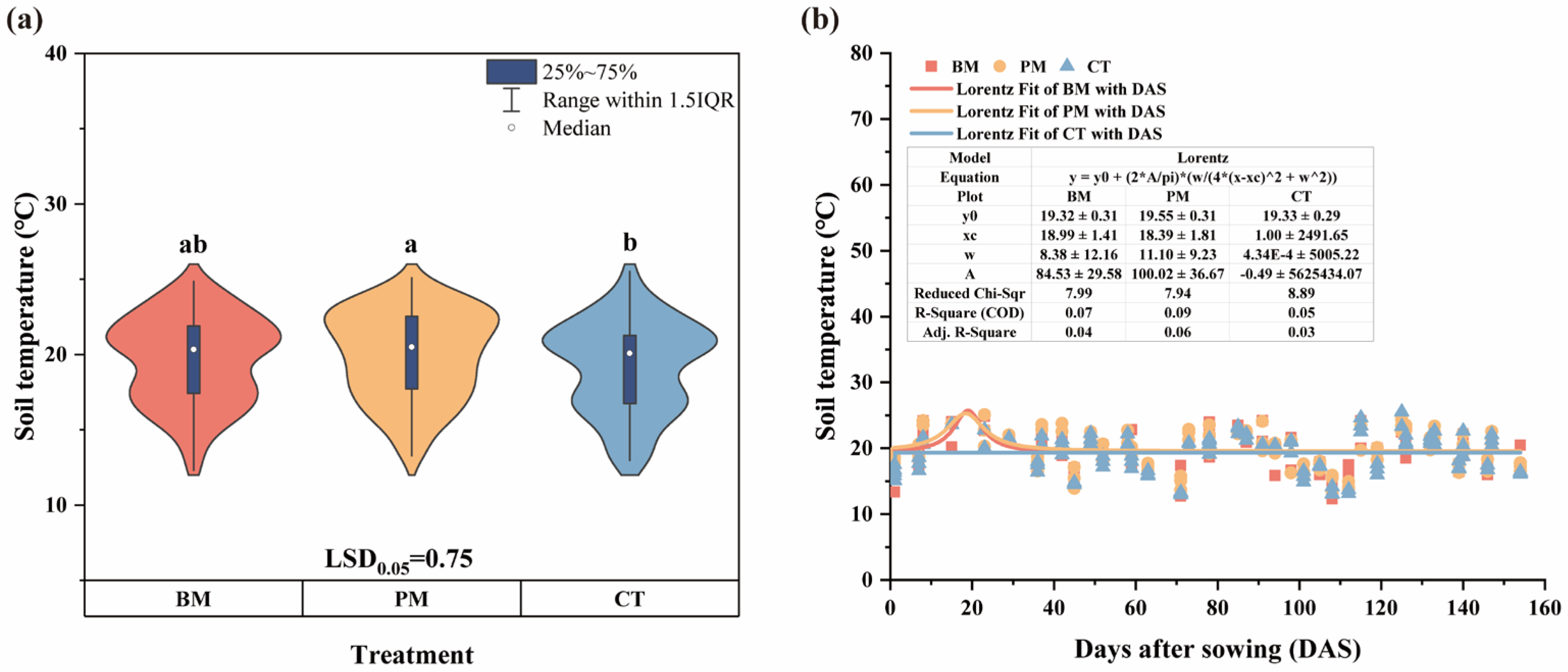
3.2. Soil Temperature Under Different Mulching Treatments
3.3. Soil CO2 Concentration
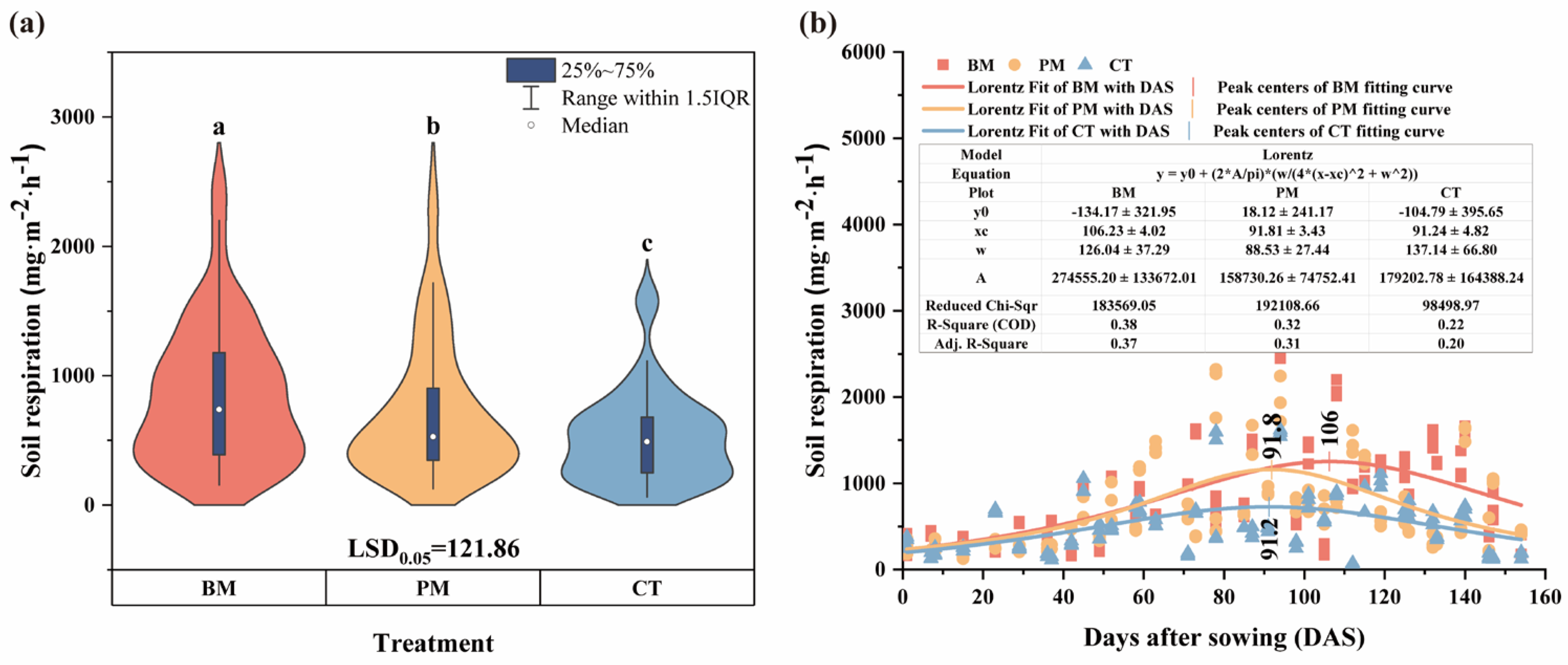
3.4. Soil Respiration
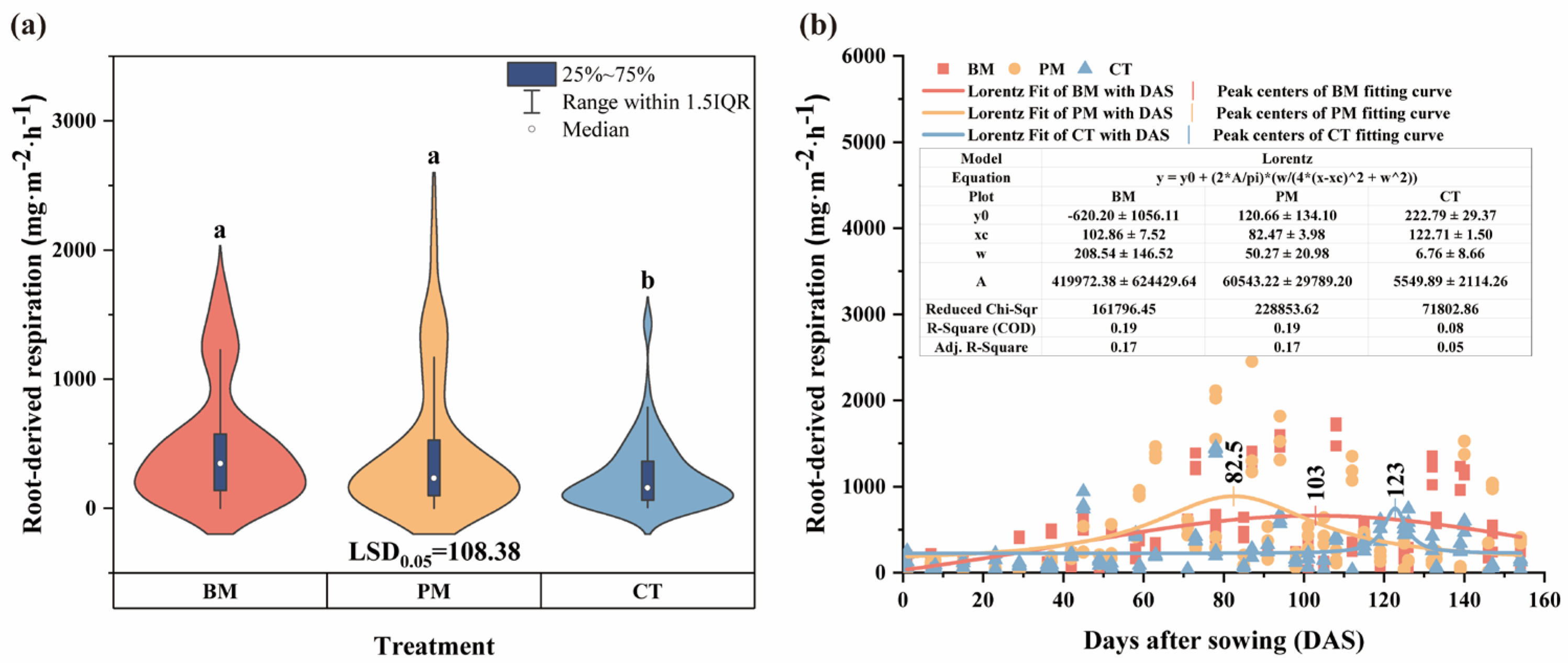
3.5. Root-Derived Respiration
3.6. Non-Root-Derived Respiration
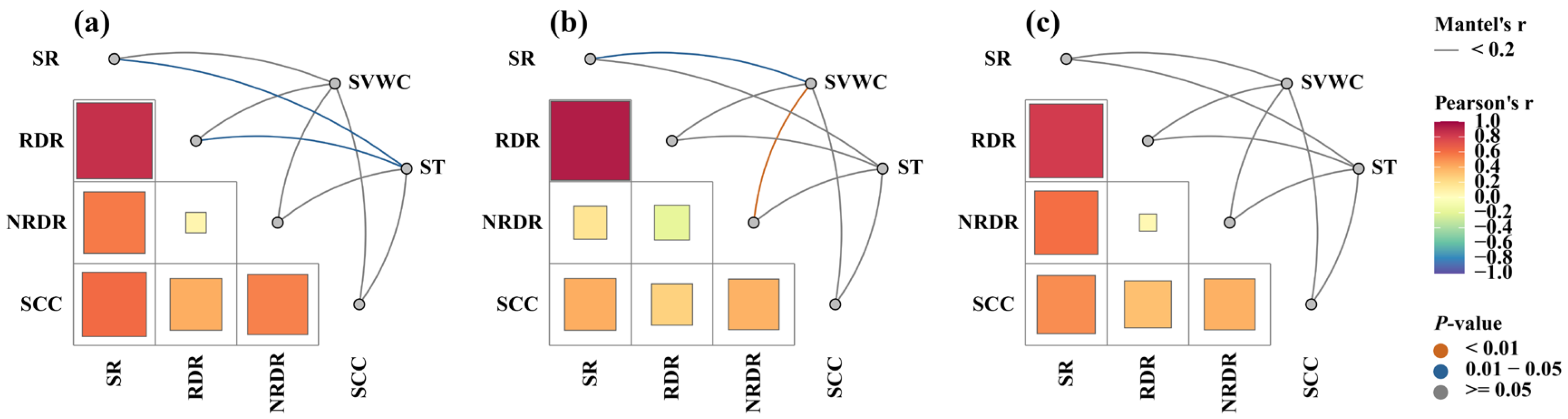
3.7. Relationships Between Soil Respiration Components and Environmental Factors
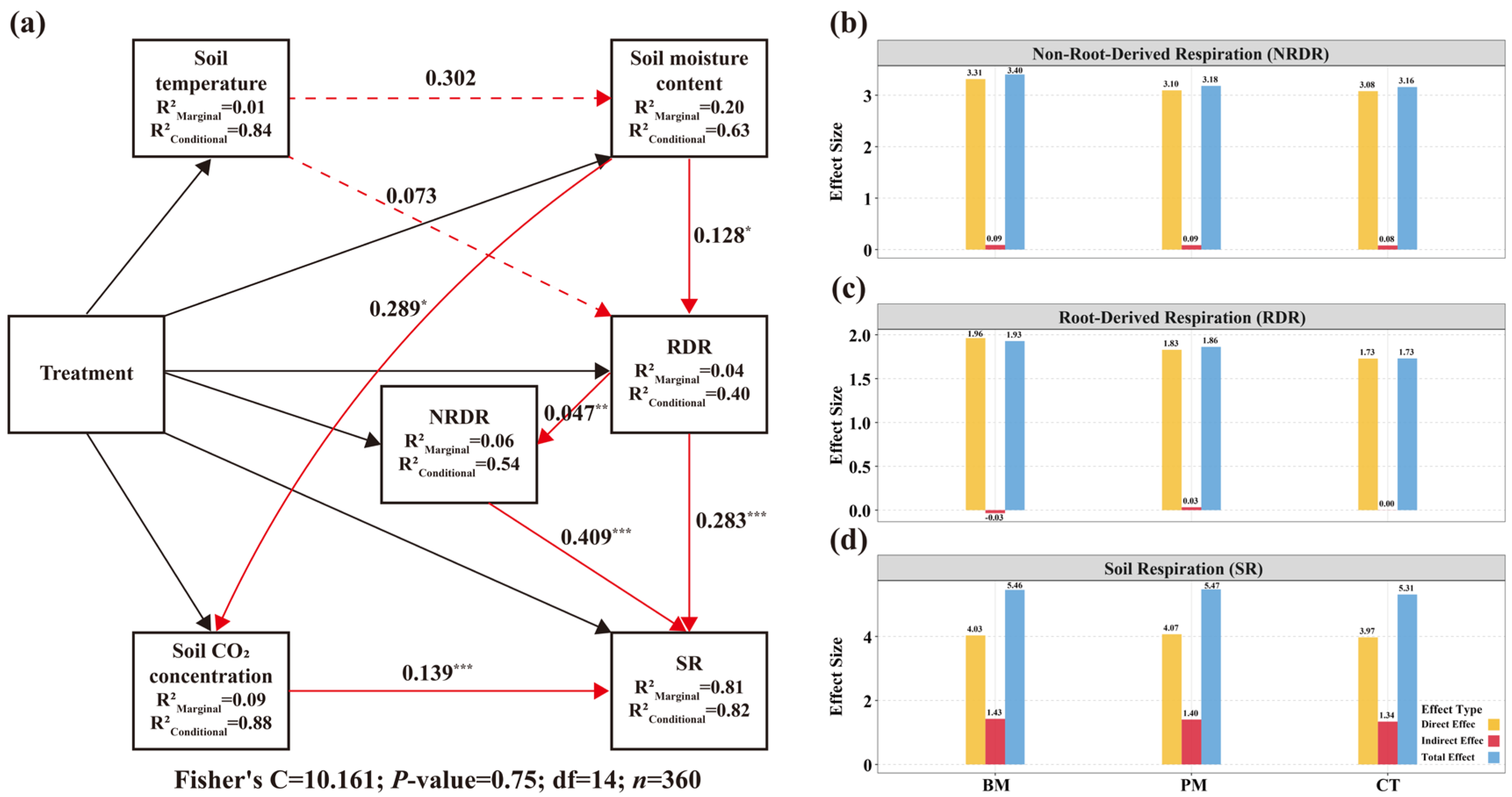
3.8. Structural Equation Modeling of Treatment Effects on Soil Respiration Components
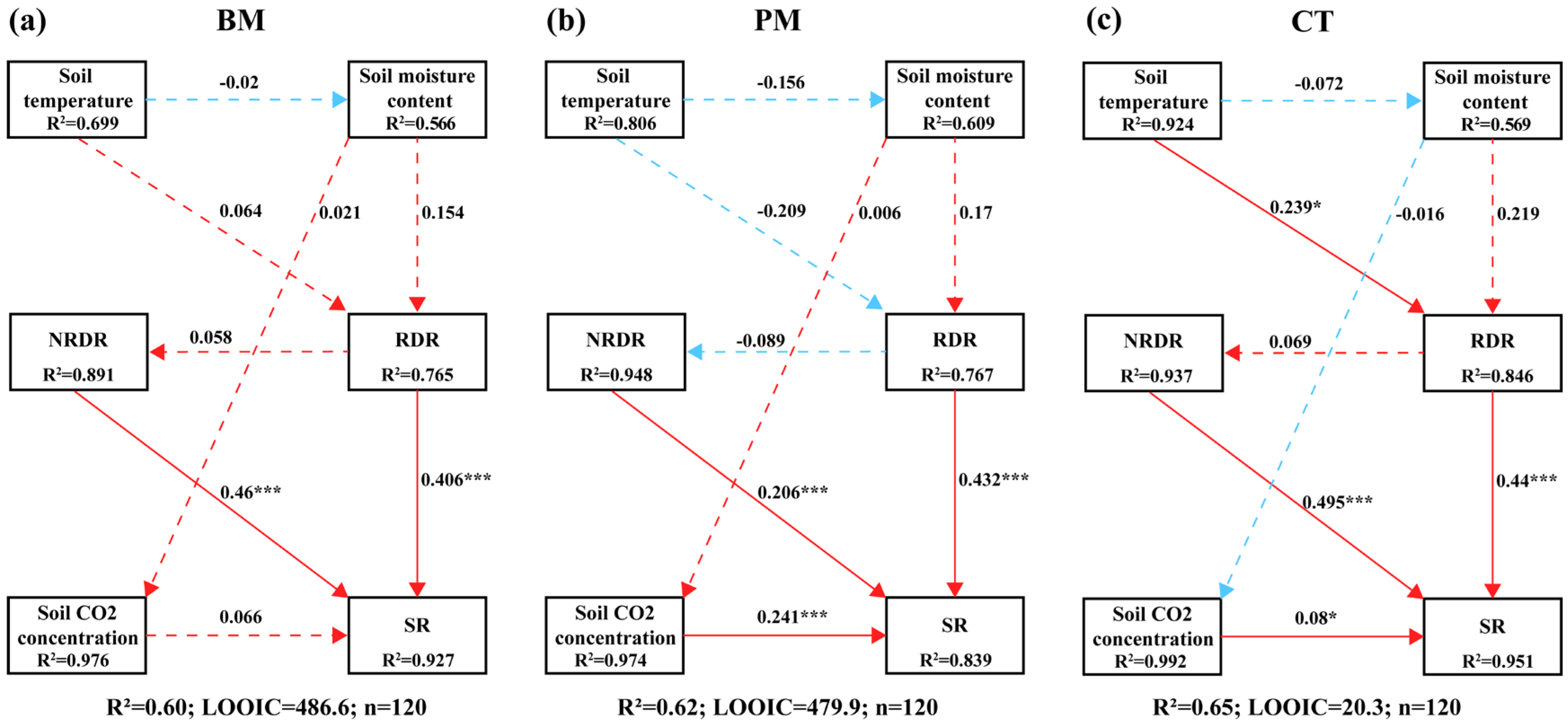
3.9. Pathway Differentiation Across Treatments: SEM-Based Insights
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Mulch Treatments on Soil Hydrothermal Conditions and CO2 Concentrations
4.2. Mechanistic Responses of Soil Respiration and Its Components to Different Mulching Treatments
4.3. Environmental Drivers and Pathway Regulation of Soil Respiration Components Under Different Mulching Treatments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, D.; Li, H.; Wang, E.; He, W.; Hao, W.; Yan, C.; Li, Y.; Mei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; et al. An overview of the use of plastic-film mulching in China to increase crop yield and water-use efficiency. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1523–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Chen, L.; Qu, H.; Wang, Y.; Misselbrook, T.; Jiang, R. Impacts of plastic film mulching on crop yields, soil water, nitrate, and organic carbon in northwestern China: A meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 202, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Yan, C.; Liu, Q.; Ding, W.; Chen, B.; Li, Z. Effects of plastic mulching and plastic residue on agricultural production: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; He, W.; Turner, N.C. Plastic-film mulch in Chinese agriculture: Importance and problems. World Agric. 2014, 4, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ren, S.; Xu, W.; Liang, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Jones, D.L.; Chadwick, D.R.; et al. Effects of plastic residues and microplastics on soil ecosystems: A global meta-analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanayaka, S.; Zhang, H.; Semple, K.T. Environmental fate of microplastics and common polymer additives in non-biodegradable plastic mulch applied agricultural soils. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanale, C.; Galafassi, S.; Di Pippo, F.; Pojar, I.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. A critical review of biodegradable plastic mulch films in agriculture: Definitions, scientific background and potential impacts. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 170, 117391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin-LaHue, D.; Ghimire, S.; Yu, Y.; Scheenstra, E.J.; Miles, C.A.; Flury, M. In-field degradation of soil-biodegradable plastic mulch films in a Mediterranean climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzyakov, Y. Sources of CO2 efflux from soil and review of partitioning methods. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 425–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Larionova, A.A. Root and rhizomicrobial respiration: A review of approaches to estimate respiration by autotrophic and heterotrophic organisms in soil. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2005, 168, 503–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, P.J.; Edwards, N.T.; Garten, C.T.; Andrews, J.A. Separating root and soil microbial contributions to soil respiration: A review of methods and observations. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 115–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Shi, F.; Guan, F. Effects of plastic mulching on soil CO2 efflux in a cotton field in northwestern China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, T.; Schaeffer, S.; Li, S.; Fu, S.; Pei, J.; Li, H.; Zhuang, J.; Radosevich, M.; Wang, J. Carbon fluxes from plants to soil and dynamics of microbial immobilization under plastic film mulching and fertilizer application using 13C pulse-labeling. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 80, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuello, J.P.; Hwang, H.Y.; Gutierrez, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, P.J. Impact of plastic film mulching on increasing greenhouse gas emissions in temperate upland soil during maize cultivation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 91, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, Y.; García-Palacios, P.; Cao, J.; Dacal, M.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Xia, J.; Niu, S.; Yang, H.; et al. Differential responses of carbon-degrading enzyme activities to warming: Implications for soil respiration. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 4816–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, R.; Liu, G.; Yue, M.; Wang, G.; Peng, C.; Wang, K.; Gao, X. Soil temperature, microbial biomass and enzyme activity are the critical factors affecting soil respiration in different soil layers in Ziwuling Mountains, China. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1105723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, P.D.; Marin, M.; Bending, G.D.; George, T.S.; Collins, C.D.; Otten, W. Building soil sustainability from root–soil interface traits. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Min, J.; Ju, S.; Zeng, X.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Shaheen, S.M.; Bolan, N.; Rinklebe, J.; et al. Possible hazards from biodegradation of soil plastic mulch: Increases in microplastics and CO2 emissions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, F.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Zhao, C.; Ding, R.; Yang, B.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z. Soil respiration in response to biotic and abiotic factors under different mulching measures on rain-fed farmland. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 232, 105749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Meler, M.A.; Taneva, L.; Trueman, R.J. Plant respiration and elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration: Cellular responses and global significance. Ann. Bot. 2004, 94, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Krohn, C.; Franks, A.E.; Wang, X.; Wood, J.L.; Petrovski, S.; McCaskill, M.; Batinovic, S.; Xie, Z.; Tang, C. Elevated atmospheric CO2 alters the microbial community composition and metabolic potential to mineralize organic phosphorus in the rhizosphere of wheat. Microbiome 2022, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Wang, G.; Xue, K.; Yang, Y.; Xie, J.; Yu, H.; Bai, S.; Liu, F.; He, Z.; Ning, D.; et al. Stimulation of soil respiration by elevated CO2 is enhanced under nitrogen limitation in a decade-long grassland study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 33317–33324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, N.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Uwiragiye, Y.; Fallah, N.; Crowther, T.W.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; et al. Degradable film mulching increases soil carbon sequestration in major Chinese dryland agroecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Yao, Z.; Yan, C.; Liu, Q.; Ding, X.; He, W. Maize yield reduction is more strongly related to soil moisture fluctuation than soil temperature change under biodegradable film vs. plastic film mulching in a semi-arid region of northern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 287, 108351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhou, X. Soil Respiration and the Environment; Academic Press: London, UK, 2006; pp. 257–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, G.P.; Hutchinson, G.L. Enclosure-based measurement of trace gas exchange: Application and sources of error. In Biogenic Trace Gases: Measuring Emissions from Soil and Water; Matson, P.A., Harris, R.C., Eds.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1995; pp. 14–51. [Google Scholar]
- Abduwaiti, A.; Liu, X.; Yan, C.; Xue, Y.; Jin, T.; Wu, H.; He, P.; Bao, Z.; Liu, Q. Testing biodegradable films as alternatives to plastic-film mulching for enhancing the yield and economic benefits of processed tomato in Xinjiang Region. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglam, M.; Sintim, H.Y.; Bary, A.I.; Miles, C.A.; Ghimire, S.; Inglis, D.A.; Flury, M. Modeling the effect of biodegradable paper and plastic mulch on soil moisture dynamics. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 193, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, S.; Geza, M.; Xu, S.; Sexton, P.; Graham, C. Assessment and HYDRUS (2D/3D) simulation of soil moisture dynamics under contrasting tillage management in rainfed cropping systems. Vadose Zone J. 2025, 24, e70028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Shao, R.; Xue, Y.; Ying, H.; Yin, Y.; Cui, Z.; Yang, Q. Water productivity of irrigated maize production systems in northern China: A meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 234, 106119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacuzzi, N.; Tortorici, N.; Alaimo, F.; Cozzolino, E.; Sarno, M.; Mori, M.; Tuttolomondo, T. Biodegradable mulching films affect soil temperature and agronomic performance of open field eggplant in hot-arid environments. Ital. J. Agron. 2024, 19, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhao, W.; Yang, R.; Feng, H. Soil temperature modeling in topsoil with plastic film mulching and low spring temperatures. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 66, 1936–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Ye, H.; Li, W.; Zong, R.; Tian, X. Effects of different plastic mulching film on soil hydrothermal status and water utilization by spring maize in Northwest China. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 774833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandopadhyay, S.; Martin-Closas, L.; Pelacho, A.M.; DeBruyn, J.M. Biodegradable plastic mulch films: Impacts on soil microbial communities and ecosystem functions. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandopadhyay, S.; Sintim, H.Y.; DeBruyn, J.M. Soil microbial communities associated with biodegradable plastic mulch films in two agroecosystems. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 587074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Stahr, K.; Zhao, X.; Jia, H. Plastic mulching increased soil CO2 concentration and emissions from an oasis cotton field in Central Asia. Soil Use Manag. 2016, 32, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Martín, L.; Almira, M.J.; Estrela-Muriel, L.; Tolrà, R.; Rubio, L.; Poschenrieder, C.; Busoms, S. A role for root carbonic anhydrase βCA4 in the bicarbonate tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana. Physiol. Plant. 2024, 176, e70026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierbaumer, S.; Nattermann, M.; Schulz, L.; Zschoche, R.; Erb, T.J.; Winkler, C.K.; Tinzl, M.; Glueck, S.M. Enzymatic conversion of CO2: From natural to artificial utilization. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 5702–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Horwath, W.R.; Dorodnikov, M.; Blagodatskaya, E. Review and synthesis of the effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on soil processes: No changes in pools, but increased fluxes and accelerated cycles. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 128, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceron-Chafla, P.; Kleerebezem, R.; Rabaey, K.; van Lier, J.B.; Lindeboom, R.E. Direct and indirect effects of increased CO2 partial pressure on the bioenergetics of syntrophic propionate and butyrate conversion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12583–12592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Min, W.; Flury, M.; Gunina, A.; Lv, J.; Li, Q.; Jiang, R. Impact of long-term conventional and biodegradable film mulching on microplastic abundance, soil structure and organic carbon in a cotton field. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 356, 124367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Tao, H.; Yao, H.; Zhao, C. Assessment of the effect of plastic mulching on soil respiration in the arid agricultural region of China under future climate scenarios. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 256, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.M.; Li, X.G.; Javaid, M.M.; Ashraf, M.; Zhang, F. Ridge-furrow plastic film mulching farming for sustainable dryland agriculture on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 3284–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Shen, Y.; Yue, S. Film mulching affects root growth and function in dryland maize–soybean intercropping. Field Crops Res. 2021, 271, 108240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Friedel, J.K.; Stahr, K. Review of mechanisms and quantification of priming effects. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.A.; Finley, B.K.; Mau, R.L.; Schwartz, E.; Dijkstra, P.; Bowker, M.A.; Hungate, B.A. The soil priming effect: Consistent across ecosystems, elusive mechanisms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 140, 107617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaramitaro, V.; Piacenza, E.; Paliaga, S.; Cavallaro, G.; Badalucco, L.; Laudicina, V.A.; Chillura Martino, D.F. Exploring the feasibility of polysaccharide-based mulch films with controlled ammonium and phosphate ions release for sustainable agriculture. Polymers 2024, 16, 2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliaga, S.; Badalucco, L.; Ciaramitaro, V.C.; Chillura Martino, D.F.; Gelsomino, A.; Kandeler, E.; Marhan, S.; Laudicina, V.A. Fertilizer-enriched bio-based mulch films increase nitrogen and phosphorus availability and stimulate soil microbial biomass and activity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 211, 106159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Li, S.; Lu, J.; Penn, C.J.; Wang, Q.W.; Lin, G.; Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J.; Wang, J.; Rillig, M.C. Consequences of 33 years of plastic film mulching and nitrogen fertilization on maize growth and soil quality. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 9174–9183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wu, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z. Continuous years of biodegradable film mulching enhances the soil environment and maize yield sustainability in the dryland of northwest China. Field Crops Res. 2022, 288, 108698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florez-Sarasa, I.; Fernie, A.R.; Gupta, K.J. Does the alternative respiratory pathway offer protection against the adverse effects resulting from climate change? J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, R.; Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Ullah, R.; Zhang, F. Plastic film mulching regulates soil respiration and temperature sensitivity in maize farming across diverse hydrothermal conditions. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Li, X.; Shi, H.; Yan, J.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y. Assessment and modeling of maize evapotranspiration and yield with plastic and biodegradable film mulch. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 307, 108474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Rillig, M.C.; Bing, H.; Cui, Q.; Qiu, T.; Cui, Y.; Peñuelas, J.; Liu, B.; Bian, S.; Monikh, F.A.; et al. Microplastic pollution promotes soil respiration: A global-scale meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Terminel, M.L.; Flores-Rentería, D.; Sánchez-Mejía, Z.M.; Rojas-Robles, N.E.; Sandoval-Aguilar, M.; Chávez-Vergara, B.; Robles-Morua, A.; Garatuza-Payan, J.; Yépez, E.A. Soil respiration is influenced by seasonality, forest succession and contrasting biophysical controls in a tropical dry forest in northwestern Mexico. Soil Syst. 2022, 6, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondéjar, R.; Tláskal, V.; Větrovský, T.; Štursová, M.; Toscan, R.; da Rocha, U.N.; Baldrian, P. Metagenomics and stable isotope probing reveal the complementary contribution of fungal and bacterial communities in the recycling of dead biomass in forest soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Bazhabaike, M.; Zhou, M.; Yin, T. Biodegradable Film Mulching Increases Soil Respiration: A Two-Year Field Comparison with Polyethylene Film Mulching in a Semi-Arid Region of Northern China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112631
Liu X, Wang D, Bazhabaike M, Zhou M, Yin T. Biodegradable Film Mulching Increases Soil Respiration: A Two-Year Field Comparison with Polyethylene Film Mulching in a Semi-Arid Region of Northern China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112631
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaowei, Dejun Wang, Mahepali Bazhabaike, Mingdong Zhou, and Tao Yin. 2025. "Biodegradable Film Mulching Increases Soil Respiration: A Two-Year Field Comparison with Polyethylene Film Mulching in a Semi-Arid Region of Northern China" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112631
APA StyleLiu, X., Wang, D., Bazhabaike, M., Zhou, M., & Yin, T. (2025). Biodegradable Film Mulching Increases Soil Respiration: A Two-Year Field Comparison with Polyethylene Film Mulching in a Semi-Arid Region of Northern China. Agronomy, 15(11), 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112631





