Research on Soil Water Leakage and Water Use Efficiency Based on Coupling Biochar and Management Measures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Laboratory Experiment
2.3. Field Experiment
2.4. HYDRUS-AquaCrop
2.4.1. HYDRUS-2D Model and Its Parameters
2.4.2. AquaCrop Model and Its Parameters
2.4.3. HYDRUS-AquaCrop Coupling Model
2.4.4. Simulated Scenarios
- (1)
- To explore the synergistic effect of biochar and irrigation methods on soil water loss, two irrigation methods and five biochar application rates were set. The irrigation methods included conventional irrigation and drip irrigation. The biochar application levels were 0 kg·m−2 (CI, DI), 1.5 kg·m−2 (BCI1.5, BDI1.5), 3 kg·m−2 (BCI3, BDI3), 4.5 kg·m−2 (BCI4.5, BDI4.5), and 6 kg·m−2 (BCI6, BDI6). This simulation was completed with the HYDRUS-2D model.
- (2)
- In this paper, the Pearson-III curve was used to analyze the rainfall frequency from 1980 to 2018. Rainfall data is sourced from the China Meteorological Information Center (http://data.cma.cn/ (accessed on 4 July 2023)). The wet, normal, and dry years are 1983, 1992, and 2010, with 532.8 mm, 420.5 mm, and 334.6 mm of rainfall during the rice growth period, respectively. In three typical years, the responses of crop water consumption (ET), yield (Y), and water use efficiency (WUE = Y/ET) to the synergistic effects of irrigation methods (M), biochar (B), and irrigation amounts (I) were investigated. There were two irrigation methods (M), five biochar application levels (B), and six irrigation amount levels (I) in this study. M and B were identical to (1), and irrigation amounts (I) were 0, 60, 120, 180, 240, 300, and 360 mm. This simulation was completed with the HYDRUS-AquaCrop coupling model.
3. Results
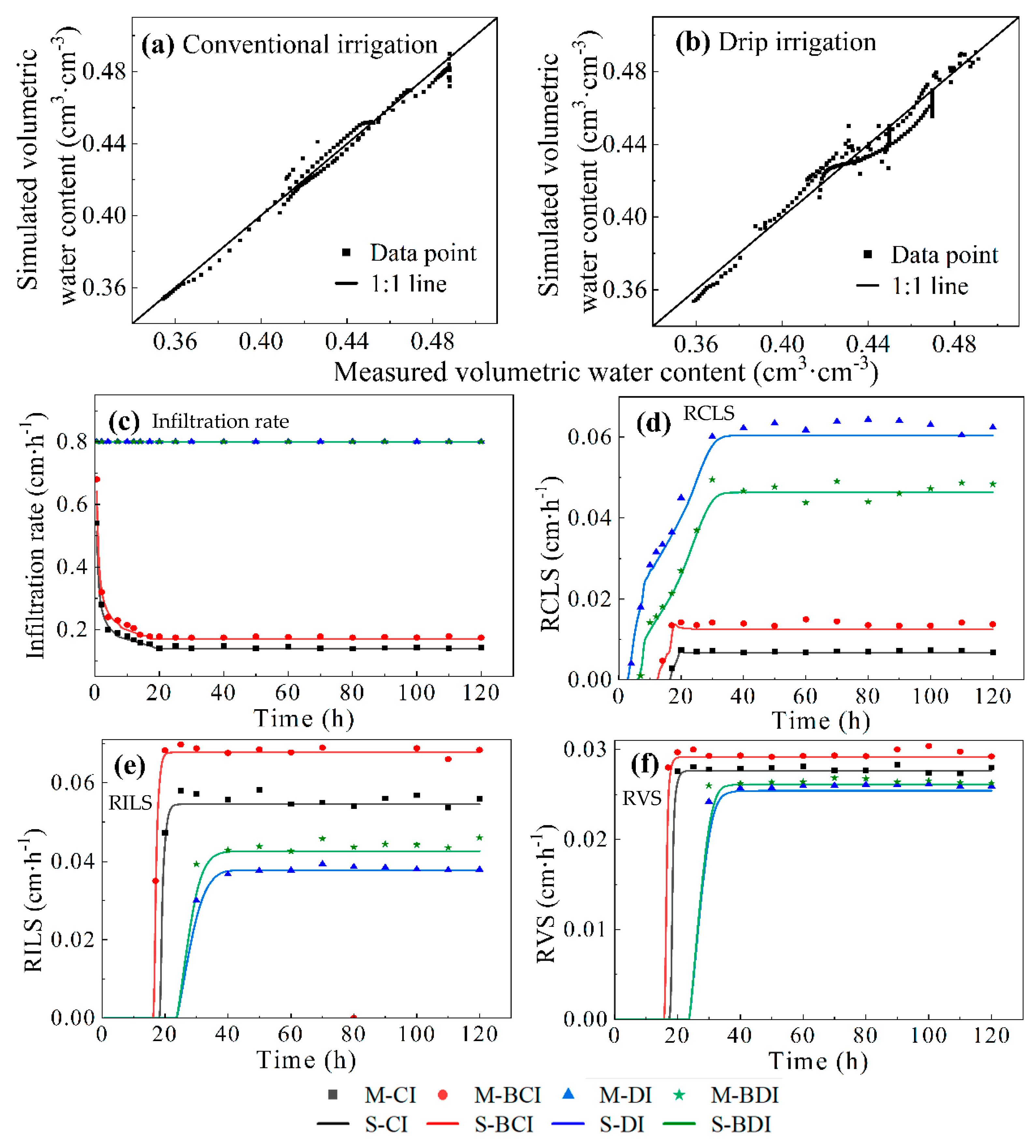
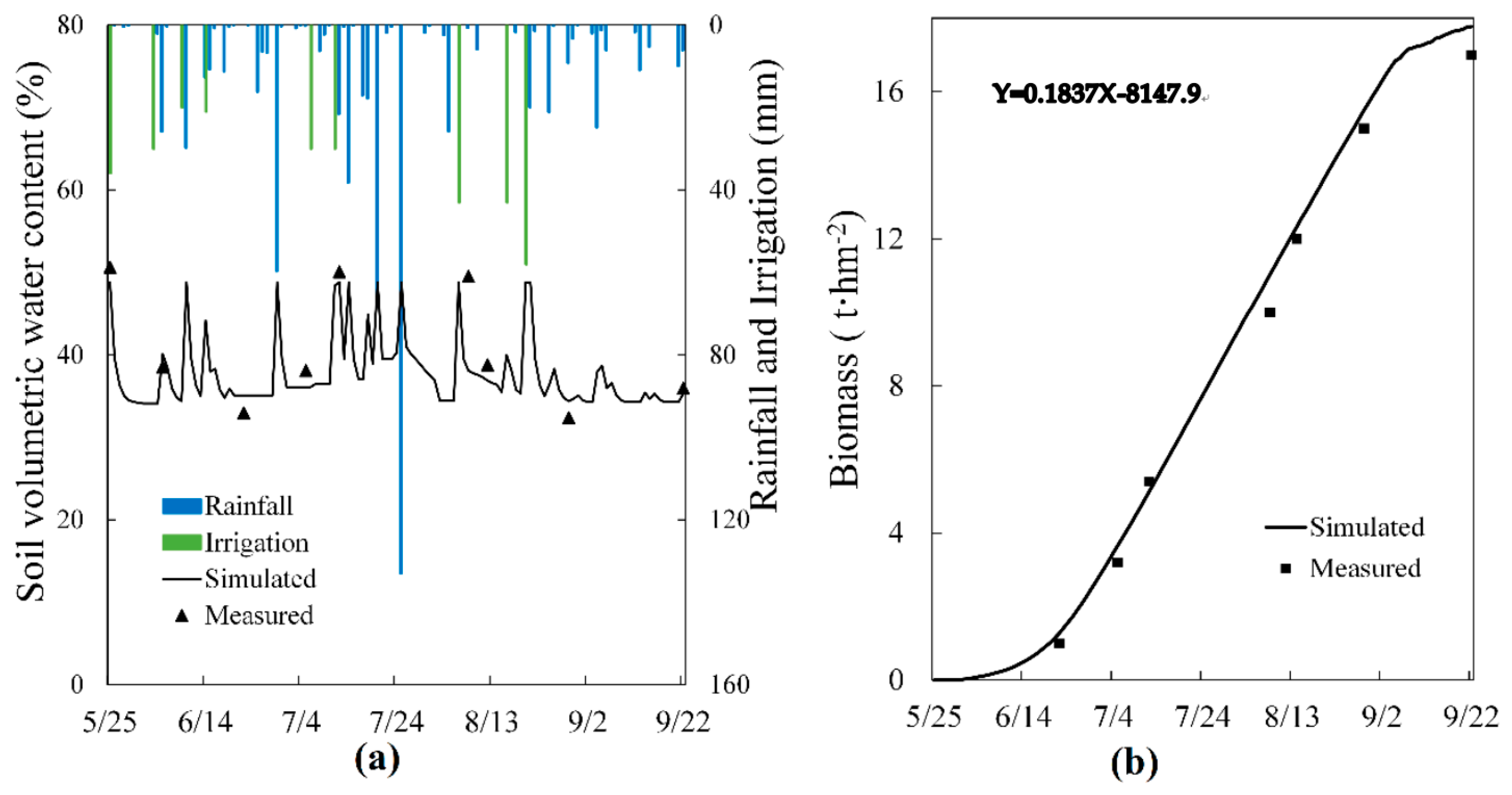
3.1. Model Validation
3.1.1. HYDRUS-2D Model
3.1.2. AquaCrop Model
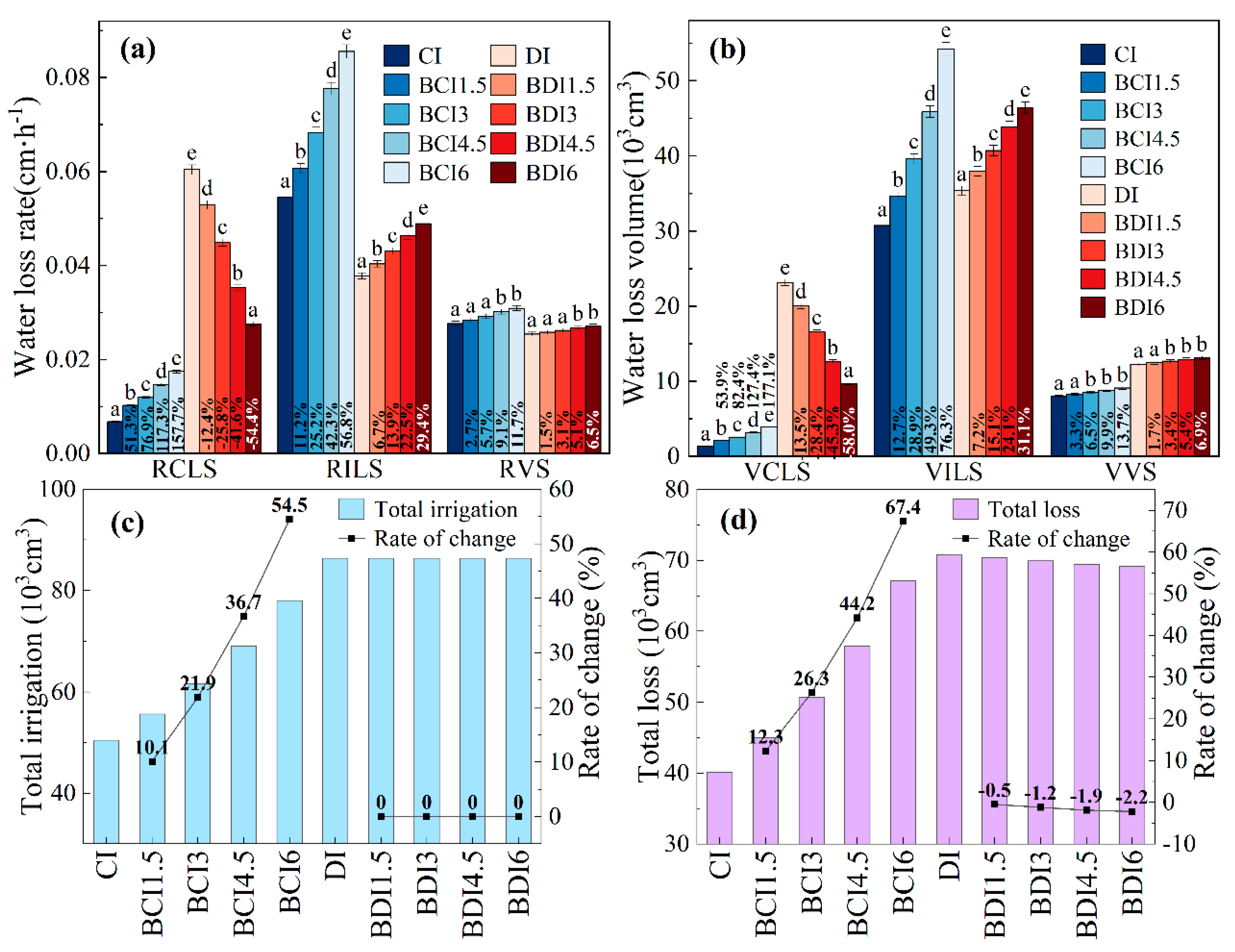
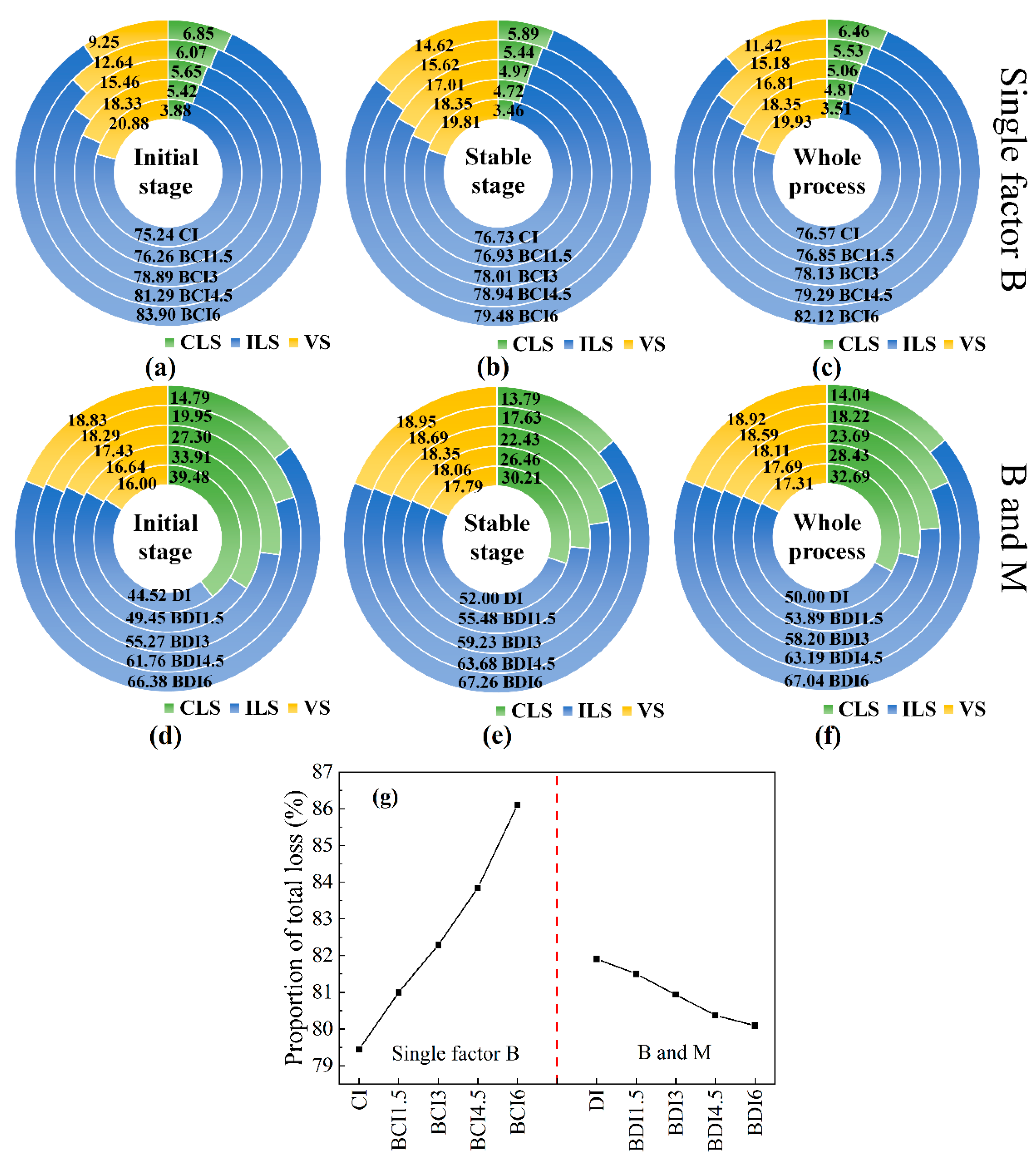
3.2. Response of Soil Water Loss to the Coupling Effect of B and M
3.2.1. Rate and Amount of Water Loss
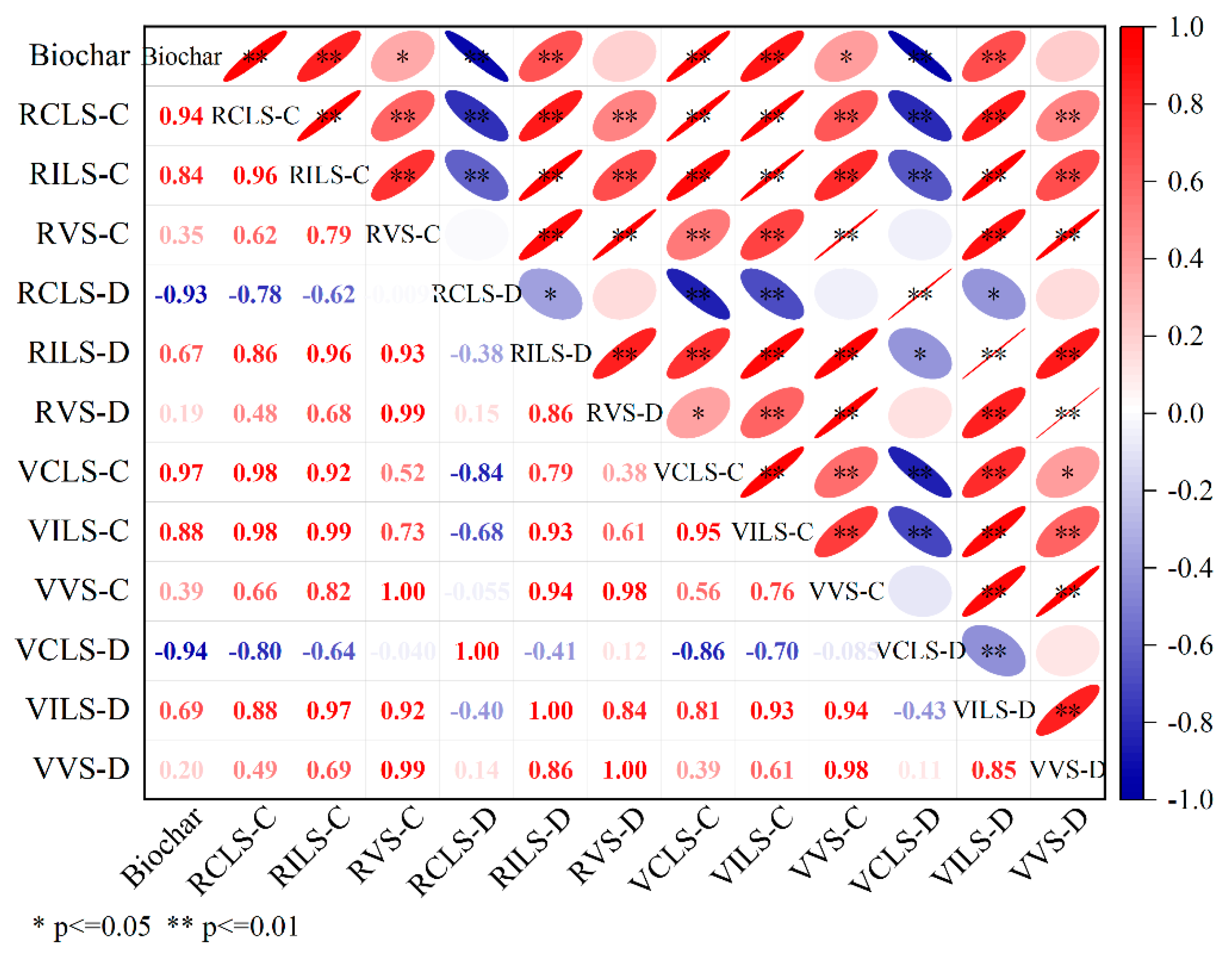
3.2.2. Correlation and Effect Analysis
3.3. Responses of Farmland Water Use Efficiency to Multiple Factors (B, M, I)
3.3.1. Water Consumption, Yield, and Water Use Efficiency
3.3.2. Path Analysis and Effect Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in Soil Water Loss
4.2. Changes in Water Use Efficiency of Farmland
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, H.; Qi, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Geng, M. Synergistic effects of crop residue and microbial inoculant on soil properties and soil disease resistance in a Chinese Mollisol. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Han, X.; Yan, J.; Zou, W.; Wang, E.; Lu, X.; Chen, X. Keystone microbiomes revealed by 14 years of field restoration of the degraded agricultural soil under distinct vegetation scenarios. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; You, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, X.; Su, Y. Dibutyl phthalate alters the metabolic pathways of microbes in black soils. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Zhao, H.; Li, H.; Li, T.X.; Hou, R.J.; Liu, D.; Ji, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yu, P.F. Effects of biochar application during different periods on soil structures and water retention in seasonally frozen soil areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Meng, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Ma, X.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, G.; Zhang, J.; et al. Soil aggregates stability and storage of soil organic carbon respond to cropping systems on Black Soils of Northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrol, V.; Ben-Hur, M.; Verheijen, F.G.A.; Keizer, J.J.; Martins, M.A.S.; Tenaw, H.; Tchehansky, L.; Graber, E.R. Biochar effects on soil water infiltration and erosion under seal formation conditions: Rainfall simulation experiment. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 2709–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.; Quicker, P. Properties of biochar. Fuel 2018, 217, 240–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangi-Abriz, S.; Torabian, S.; Qin, R.; Noulas, C.; Lu, Y.; Gao, S. Biochar effects on yield of cereal and legume crops using meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Kurian, J.; Raghavan, V. Biochar influences on agricultural soils, crop production, and the environment: A review. Environ. Rev. 2016, 24, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Z.; Wei, Z.H.; Ma, Y.Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, F.L. Effects of biochar amendment and reduced irrigation on growth, physiology, water-use efficiency and nutrients uptake of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) on two different soil types. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 144769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partovi, Z.; Ramezani Etedali, H.; Kaviani, A. Effects of applying biochar and straw on nitrate leaching and maize yield production. Water Environ. J. 2021, 35, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, M.; Zhang, J. Effects of adding biochar of different particle sizes on hydro-erosional processes in small scale laboratory rainfall experiments on cultivated loessial soil. Catena 2019, 173, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-G.; Gu, C.-M.; Zhang, R.-H.; Ibrahim, M.; Zhang, G.-S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R.-Q.; Chen, F.; Liu, Y. The benefic effect induced by biochar on soil erosion and nutrient loss of slopping land under natural rainfall conditions in central China. Agr. Water Manage. 2017, 185, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H. Biochar and Soil Physical Properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 687–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.L.; de Moraes, M.T.; Cerri, C.E.P.; Cherubin, M.R. Biochar Amendment Enhances Water Retention in a Tropical Sandy Soil. Agriculture 2020, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Xing, X.; Bordoloi, S. Water retention models for soils mixed with waste residues: Application of the modified van-Genuchten and Brooks-Corey models. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2020, 12, 5059–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoloi, S.; Garg, A.; Sreedeep, S.; Peng, L.; Mei, G.X. Investigation of cracking and water availability of soil-biochar composite synthesized from invasive weed water hyacinth. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosharrof, M.; Uddin, M.K.; Jusop, S.; Sulaiman, M.F.; Shamsuzzaman, S.M.; Haque, A.N.A. Changes in Acidic Soil Chemical Properties and Carbon Dioxide Emission Due to Biochar and Lime Treatments. Agriculture 2021, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaiman, Z.M.; Shafi, M.I.; Beamont, E.; Anawar, H.M. Poultry Litter Biochar Increases Mycorrhizal Colonisation, Soil Fertility and Cucumber Yield in a Fertigation System on Sandy Soil. Agriculture 2020, 10, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faloye, O.T.; Alatise, M.O.; Ajayi, A.E.; Ewulo, B.S. Effects of biochar and inorganic fertiliser applications on growth, yield and water use efficiency of maize under deficit irrigation. Agr. Water Manag. 2019, 217, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Lan, Y.; Li, S.; Meng, J.; Xu, Z.; Tang, L. Interactive effects of straw-derived biochar and N fertilization on soil C storage and rice productivity in rice paddies of Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, B.; Ambus, P.; Zhang, Y.; Hansen, V.; Lin, Z.; Shen, D.; Liu, G.; Bei, Q.; Zhu, J.; et al. Carbon footprint of rice production under biochar amendment—A case study in a Chinese rice cropping system. GCB Bioenergy 2016, 8, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food Security: The Challenge of Feeding 9 Billion People. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Fukuta, Y.; Obara, M.; Tomita, A.; Ishimaru, T.; Sasaki, K.; Fujita, D.; Kobayashi, N. Two Novel QTLs for the Harvest Index that Contribute to High-Yield Production in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice 2021, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesari de Maria, S.; Rienzner, M.; Facchi, A.; Chiaradia, E.A.; Romani, M.; Gandolfi, C. Water balance implications of switching from continuous submergence to flush irrigation in a rice-growing district. Agr. Water Manag. 2016, 171, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Shao, D.; Gu, W.; Liu, H. Field analysis of water and nitrogen fate in lowland paddy fields under different water managements using HYDRUS-1D. Agr. Water Manag. 2015, 150, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yao, Y.; Shao, C.; Li, Y.; Fisher, J.B.; Cheng, J.; Chen, J.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Shang, K.; et al. A novel TIR-derived three-source energy balance model for estimating daily latent heat flux in mainland China using an all-weather land surface temperature product. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 323, 109066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Shao, D.; Fang, L.; Yang, X.; Chen, S.; Gu, W. Modelling percolation and lateral seepage in a paddy field-bund landscape with a shallow groundwater table. Agr. Water Manag. 2019, 214, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.N.A.; Uddin, M.K.; Sulaiman, M.F.; Amin, A.M.; Hossain, M.; Abd Aziz, A.; Mosharrof, M. Impact of Organic Amendment with Alternate Wetting and Drying Irrigation on Rice Yield, Water Use Efficiency and Physicochemical Properties of Soil. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Ma, F.; Yang, R.; Chen, L.; Jia, B.; Cui, J.; Fan, H.; Wang, X.; Li, L. Rice Performance and Water Use Efficiency under Plastic Mulching with Drip Irrigation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 83103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Hou, J.; Zhang, H.; Meng, C.; Zhang, X.; Wei, C. Low Soil Temperature Inhibits Yield of Rice Under Drip Irrigation. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 19, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Chen, L. Analysis of advantage and prospects for rice drip irrigation under plastic film cultivation development in China. China Rice 2012, 18, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Shao, D.; Li, S.; Wang, B. Response of Rice Water Requirement to Groundwater Depths and Irrigations Simulation in Cold Region of Northeast China. J. Irrig. Drain. 2019, 38, 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Shao, D.; Ji, B.; Gu, W.; Yao, M. Biochar effects on soil properties, water movement and irrigation water use efficiency of cultivated land in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šimůnek, J.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Šejna, M. Development and Applications of the HYDRUS and STANMOD Software Packages and Related Codes. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangenuchten, M.T. A Closed Equation for Predicting the Hydraulic Condictivity of Unsatured Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steduto, P.; Hsiao, T.C.; Raes, D.; Fereres, E. AquaCrop-The FAO Crop Model to Simulate Yield Response to Water: I. Concepts Underlying Principles. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raes, D.; Steduto, P.; Hsiao, T.C.; Fereres, E. AquaCrop-The FAO Crop Model to Simulate Yield Response to Water: II. Main Algorithms and Software Description. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, D.; Mohanty, B.P.; Lesikar, B.J. Impact of the Linked Surface Water-Soil Water-Groundwater System on Transport of E. coli in the Subsurface. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, D.; Rathke, S.; Laird, D.; Cruse, R.; Hatfield, J. Impacts of fresh and aged biochars on plant available water and water use efficiency. Geoderma 2017, 307, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glab, T.; Palmowska, J.; Zaleski, T.; Gondek, K. Effect of biochar application on soil hydrological properties and physical quality of sandy soil. Geoderma 2016, 281, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallin, I.L.; Douglas, P.; Doerr, S.H.; Bryant, R. The effect of addition of a wettable biochar on soil water repellency. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Xu, C.; Ma, R.; Tu, K.; Yang, J.; Zhao, S.; Yang, M.; Zhang, F. Biochar application driven change in soil internal forces improves aggregate stability: Based on a two-year field study. Geoderma 2021, 403, 115276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.R.; Patel, A.K.; Jaisi, D.P.; Adhikari, S.; Lu, H.; Khanal, S.K. Environmental application of biochar: Current status and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darzi-Naftchali, A.; Karandish, F.; Simunek, J. Numerical modeling of soil water dynamics in subsurface drained paddies with midseason drainage or alternate wetting and drying management. Agr. Water Manag. 2018, 197, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.; Sudhishri, S.; Das, T.K.; Singh, M.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Dass, A.; Khanna, M.; Sharma, V.K.; Dwivedi, N.; Kumar, M. Water balance in direct-seeded rice under conservation agriculture in North-western Indo-Gangetic Plains of India. Irrig. Sci. 2018, 36, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.S.; Cordery, I.; Iacovides, I. Improved indicators of water use performance and productivity for sustainable water conservation and saving. Agr. Water Manag. 2012, 108, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shao, D.; Xu, B. Indoor experiment and simulation of soil water two-dimensional movement of the paddy fields in the northeast frigid of China. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2018, 49, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen, F.G.A.; Zhuravel, A.; Silva, F.C.; Amaro, A.; Ben-Hur, M.; Keizer, J.J. The influence of biochar particle size and concentration on bulk density and maximum water holding capacity of sandy vs sandy loam soil in a column experiment. Geoderma 2019, 347, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, R.; Ravi, K.; Garg, A. Influence of biochar on the soil water retention characteristics (SWRC): Potential application in geotechnical engineering structures. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 204, 104713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; You, C. Biochar Effect on Water Evaporation and Hydraulic Conductivity in Sandy Soil. Pedosphere 2016, 26, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H. Biochar and Water Quality. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faloye, O.T.; Alatise, M.O.; Ajayi, A.E.; Ewulo, B.S. Synergistic effects of biochar and inorganic fertiliser on maize (zea mays) yield in an alfisol under drip irrigation. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 174, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Shan, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Zhu, T. Mitigating the global warming potential of rice paddy fields by straw and straw-derived biochar amendments. Geoderma 2021, 396, 115081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Tang, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Ge, T.; Jones, D.L.; Wu, J. Contrasting effects of straw and straw-derived biochar amendments on greenhouse gas emissions within double rice cropping systems. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 188, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.N.; Sun, X.; Ding, J.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, J. Biochar improved rice yield and mitigated CH4 and N2O emissions from paddy field under controlled irrigation in the Taihu Lake Region of China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 200, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Bouman, B.A.M.; Feng, L.P.; Tuong, T.P.; Lu, G.A.; Wang, H.Q.; Feng, Y.H. Exploring options to grow rice using less water in northern China using a modelling approach—II. Quantifying yield, water balance components, and water productivity. Agr. Water Manag. 2007, 88, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.; Gao, Y.; Lin, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, D. Effects of Biochar on Water Requirement Regulation and Yield of Tomato under Different Groundwater Tables. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2019, 50, 250–258. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Qu, Z.; Ding, Y.; Yang, W.; Ma, G.; Li, Z. The Effects of Soil Amendment with Straw Biochar on Water and Salt Dynamics as Well as Water Use Efficiency of Corn under Different Irrigations. J. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 39, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, M.; Jin, Q.; Lu, X.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Zhong, H.Z.; Gao, Y. Growth, Water Use, and Nitrate-N-15 Uptake of Greenhouse Tomato as Influenced by Different Irrigation Patterns, N-15 Labeled Depths, and Transplant Times. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.F.; Bian, R.J.; Pan, G.X.; Cui, L.Q.; Hussain, Q.; Li, L.Q.; Zheng, J.W.; Zheng, J.F.; Zhang, X.H.; Han, X.J.; et al. Effects of biochar amendment on soil quality, crop yield and greenhouse gas emission in a Chinese rice paddy: A field study of 2 consecutive rice growing cycles. Field Crops Res. 2012, 127, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Wei, G.; Wei, C. Effect of salinity and soil temperature on the growth and physiology of drip-irrigated rice seedlings. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 63, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | CL + B (0~20 cm) | CL (0~20 cm) | PL (20~35 cm) | IL (35~90 cm) | Biochar (B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand mass fraction (%) | 11.62 ± 0.35 | 10.22 ± 0.28 | 8.86 ± 0.23 | 8.09 ± 0.19 | - |
| Silt mass fraction (%) | 56.74 ± 3.21 | 57.33 ± 3.45 | 58.68 ± 3.66 | 58.87 ± 3.68 | - |
| Clay mass fraction (%) | 31.64 ± 1.58 | 32.44 ± 1.64 | 32.46 ± 1.67 | 33.04 ± 1.78 | - |
| Bulk density (g·cm−3) | 1.10 ± 0.016 | 1.20 ± 0.01 | 1.40 ± 0.02 | 1.35 ± 0.018 | - |
| Organic matter content (g·kg−1) | 4.53 ± 0.06 | 4.14 ± 0.03 | - | - | - |
| pH value | 7.35 ± 0.09 | 6.40 ± 0.07 | - | - | 9.14 ± 0.1 |
| C mass fraction (%) | - | - | - | - | 68.60 ± 3.12 |
| H mass fraction (%) | - | - | - | - | 2.13 ± 0.18 |
| N mass fraction (%) | - | - | - | - | 1.28 ± 0.13 |
| S mass fraction (%) | - | - | - | - | 0.67 ± 0.05 |
| Ash content (%) | - | - | - | - | 25.18 ± 3.96 |
| Particle size range (mm) | - | - | - | - | 1.5-2.0 |
| Rate | RMSE (cm·h−1) | R2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI | BCI | DI | BDI | CI | BCI | DI | BDI | |
| Infiltration rate | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0 | 0 | 0.897 | 0.871 | 1 | 1 |
| RCLS | 0.17 | 0.28 | 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.910 | 0.849 | 0.826 | 0.856 |
| RILS | 0.36 | 0.42 | 0.12 | 0.30 | 0.823 | 0.801 | 0.885 | 0.786 |
| RVS | 0.22 | 0.33 | 0.22 | 0.27 | 0.869 | 0.839 | 0.843 | 0.816 |
| Soil Layer | θr (cm3·cm−3) | θs (cm3·cm−3) | a | n | Ks (cm·h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL + B (0~20 cm) | 0.0903 | 0.5021 | 0.0087 | 1.5254 | 0.1221 |
| CL (0~20 cm) | 0.0911 | 0.4879 | 0.0083 | 1.5447 | 0.0965 |
| PL (20~35 cm) | 0.0868 | 0.4544 | 0.0079 | 1.517 | 0.3921 |
| IL (35~90 cm) | 0.0888 | 0.4696 | 0.0081 | 1.4127 | 0.5029 |
| Model Parameter | Description | Recommended Value | Calibration Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CC0 | Initial canopy cover (%) | 0.1–1.5 | 3.76 |
| CCx | Maximum canopy cover (%) | 66–100 | 95 |
| CGC | Canopy expansion (%) | 8.6–16 | 11.2 |
| CDC | Canopy decline (%) | 6.5–12.1 | 8.4 |
| RDmax | Maximum effective rooting depth (m) | 0.35–0.65 | 0.6 |
| RDmin | Minimum effective rooting depth (m) | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| KcTr | Crop transpiration coefficient | 1.05–1.20 | 1.1 |
| WUE | Normalized biomass water productivity (g·m−2) | 12–23 | 19 |
| HI0 | Harvest Index (%) | 30–56 | 42 |
| Tmin | Minimum effective temperature (°C) | 10 | 10 |
| Tmax | Maximum effective temperature (°C) | 30 | 30 |
| Regression Equation | Path Coefficient | R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | I | M | ||
| ET_W = 413.026 + 0.135B + 0.043I − 5.614M | 0.018 | 0.322 ** | −0.177 ** | 0.368 |
| ET_N = 429.576 + 0.117B + 0.025I − 11.143M | 0.015 | 0.180 ** | −0.334 ** | 0.379 |
| ET_D = 368.902 − 0.508B + 0.148I − 8.746M | −0.038 | 0.631 ** | −0.155 ** | 0.651 |
| Y_W = 7.265 + 0.202B + 0.002I + 0.031M | 0.843 ** | 0.006 | 0.030 | 0.844 |
| Y_N = 6.813 + 0.188B + 0.001I + 0.026M | 0.841 ** | −0.055 | 0.027 | 0.843 |
| Y_D = 5.193 + 0.170B + 0.005I + 0.159M | 0.440 ** | 0.731 ** | 0.097 | 0.858 |
| WUE_W = 1.761 + 0.048B + 0.001I + 0.032M | 0.815 ** | −0.182 ** | 0.130 * | 0.845 |
| WUE_N = 1.586 + 0.043B + 0.001I + 0.048M | 0.806 ** | −0.154 ** | 0.210 ** | 0.847 |
| WUE_D = 1.462 + 0.042B + 0.011I + 0.058M | 0.599 ** | 0.527 ** | 0.195 ** | 0.821 |
| ET (mm) | Y (t·hm−2) | WUE (kg·m−3) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ET_W | ET_N | ET_D | Y_W | Y_N | Y_D | WUE_W | WUE_N | WUE_D | |
| Main Effects | |||||||||
| B | ns | ns | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| I | ** | ** | *** | ns | * | *** | ** | ** | *** |
| M | ** | *** | ** | * | * | ** | ** | *** | *** |
| Interaction Effects | |||||||||
| B×I | ns | ns | * | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| B×M | ns | ns | *** | * | * | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| I×M | ns | * | ** | ns | ns | *** | ns | * | ** |
| B×I×M | ns | ns | * | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Dong, W.; Shao, D.; Liu, L.; Huang, J.; Qin, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, M.; Ma, L. Research on Soil Water Leakage and Water Use Efficiency Based on Coupling Biochar and Management Measures. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112614
Wang H, Dong W, Shao D, Liu L, Huang J, Qin J, Yang X, Zhang R, Zhu M, Ma L. Research on Soil Water Leakage and Water Use Efficiency Based on Coupling Biochar and Management Measures. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112614
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, He, Wei Dong, Dongguo Shao, Luguang Liu, Jie Huang, Jianan Qin, Xiaowei Yang, Rui Zhang, Mei Zhu, and Linhua Ma. 2025. "Research on Soil Water Leakage and Water Use Efficiency Based on Coupling Biochar and Management Measures" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112614
APA StyleWang, H., Dong, W., Shao, D., Liu, L., Huang, J., Qin, J., Yang, X., Zhang, R., Zhu, M., & Ma, L. (2025). Research on Soil Water Leakage and Water Use Efficiency Based on Coupling Biochar and Management Measures. Agronomy, 15(11), 2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112614






