A GWR Approach to Determine Factors Controlling Soil Se in Fujian Province
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Processing
2.3. Sample Analysis and Quality Control
2.4. Computer Software and Data Transformation
3. Spatial Analysis
3.1. Hotspot Analysis
3.2. Geographically Weighted Regression
4. Results and Discussion
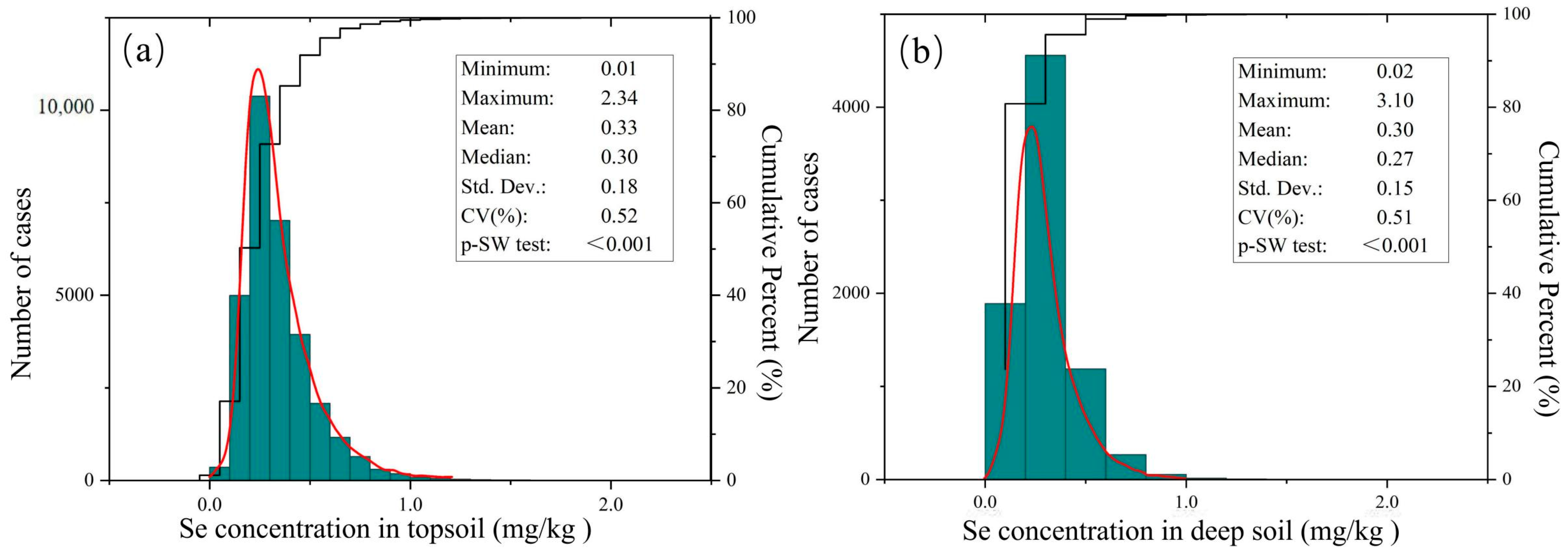
4.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Se
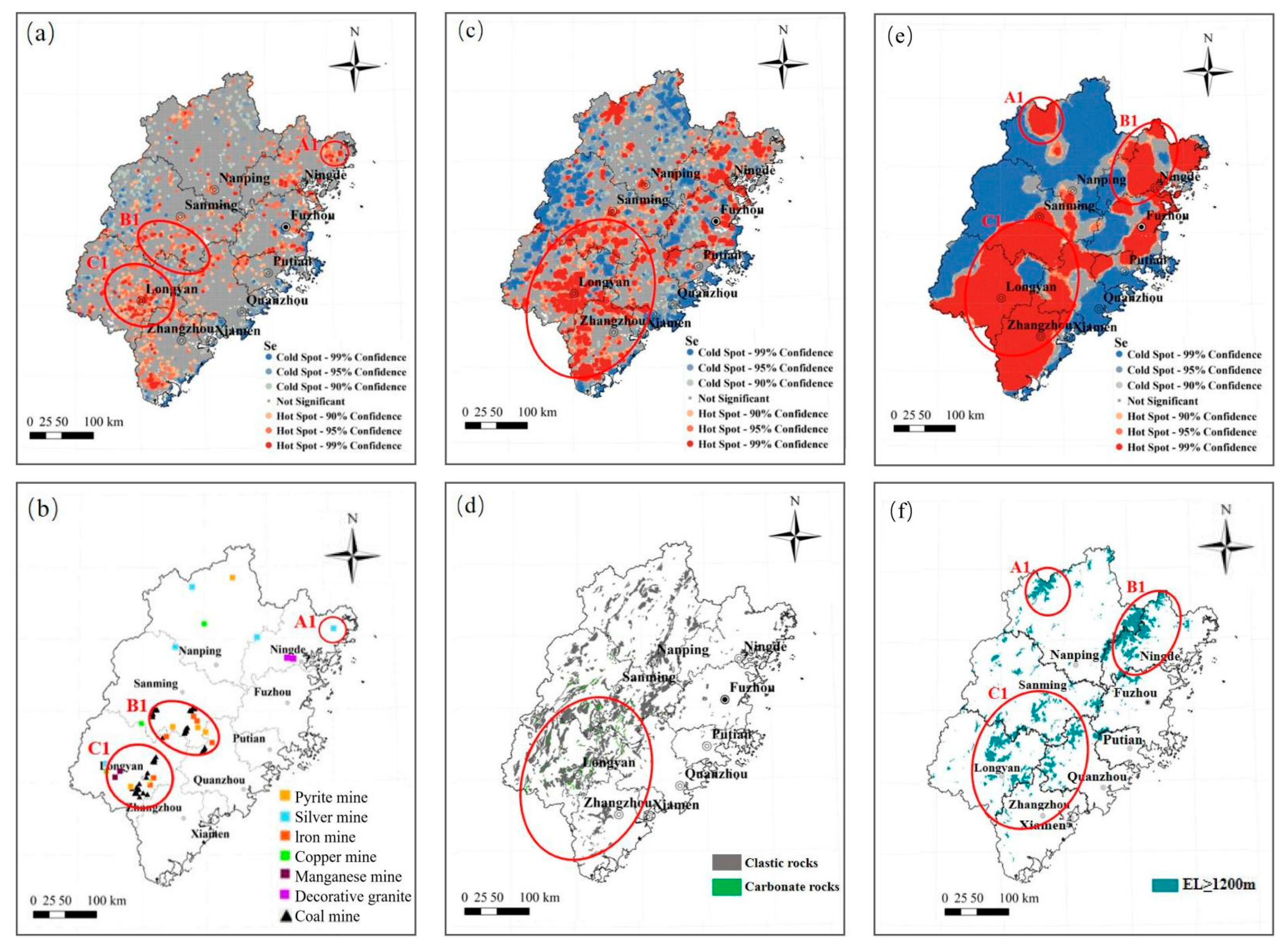
4.2. Soil Se Hotspot Analysis
4.3. Soil Se Geographically Weighted Regression
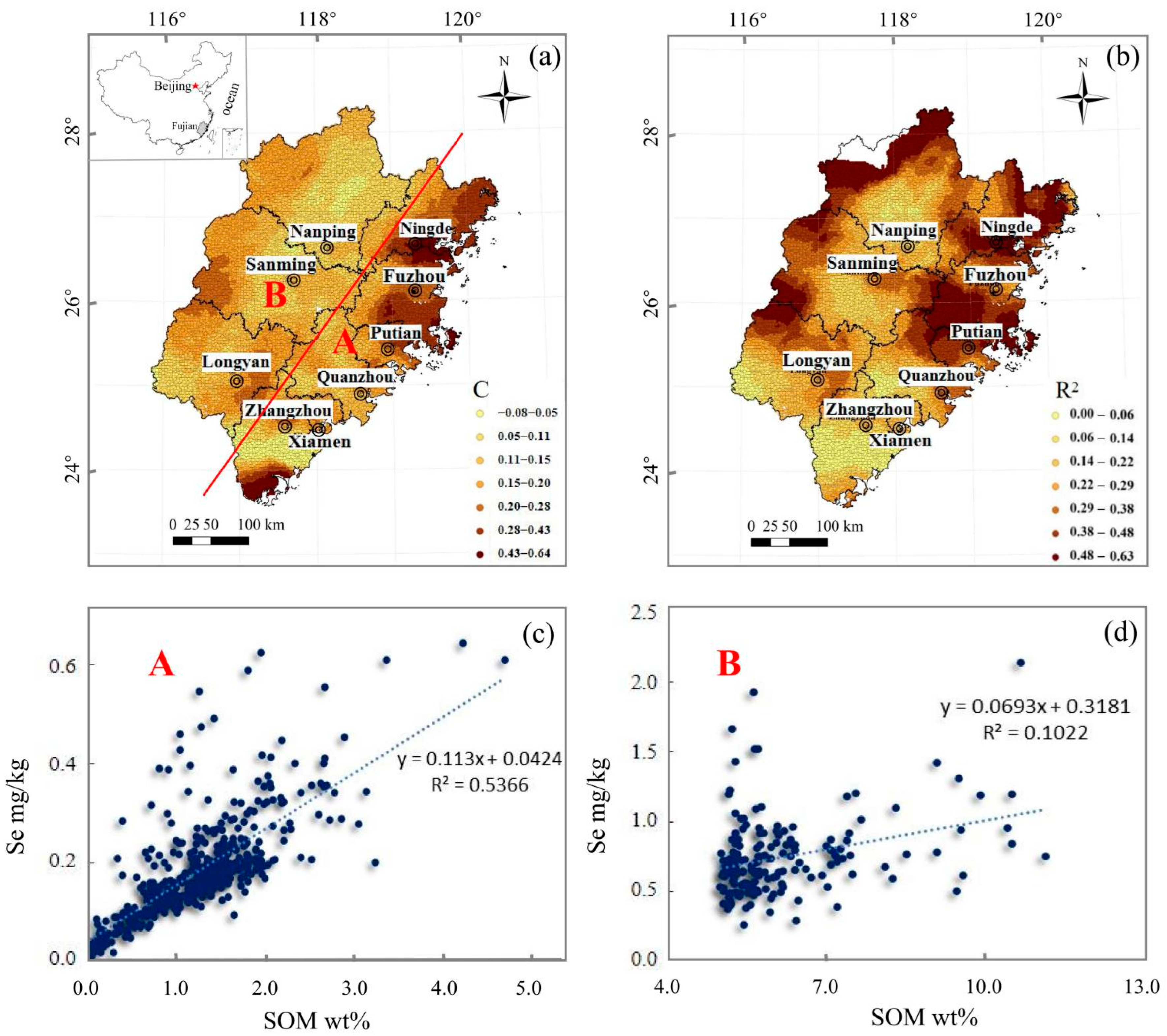
4.3.1. Soil Se and Organic Matter
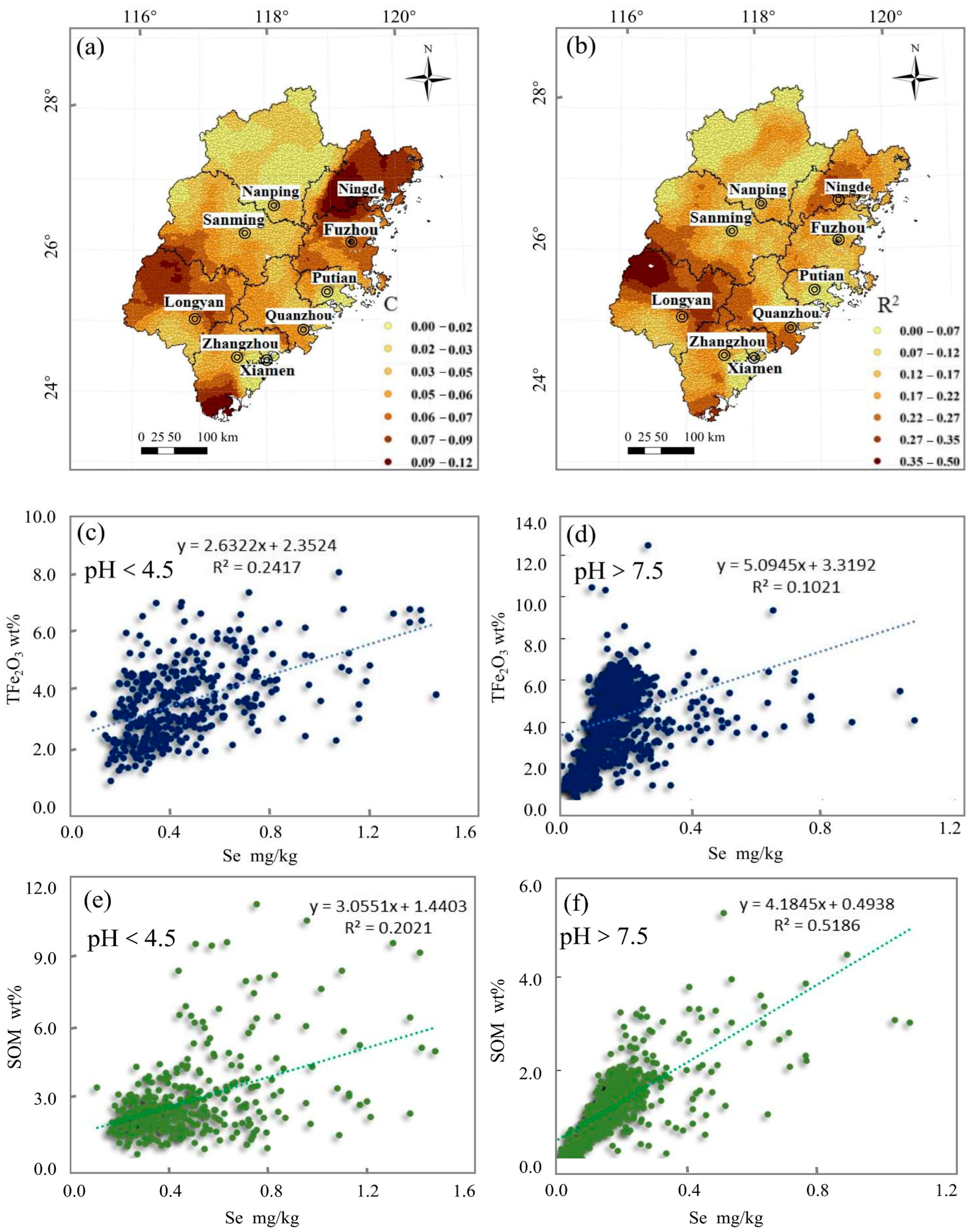
4.3.2. Soil Se and pH
4.3.3. Soil Se and TFe2O3
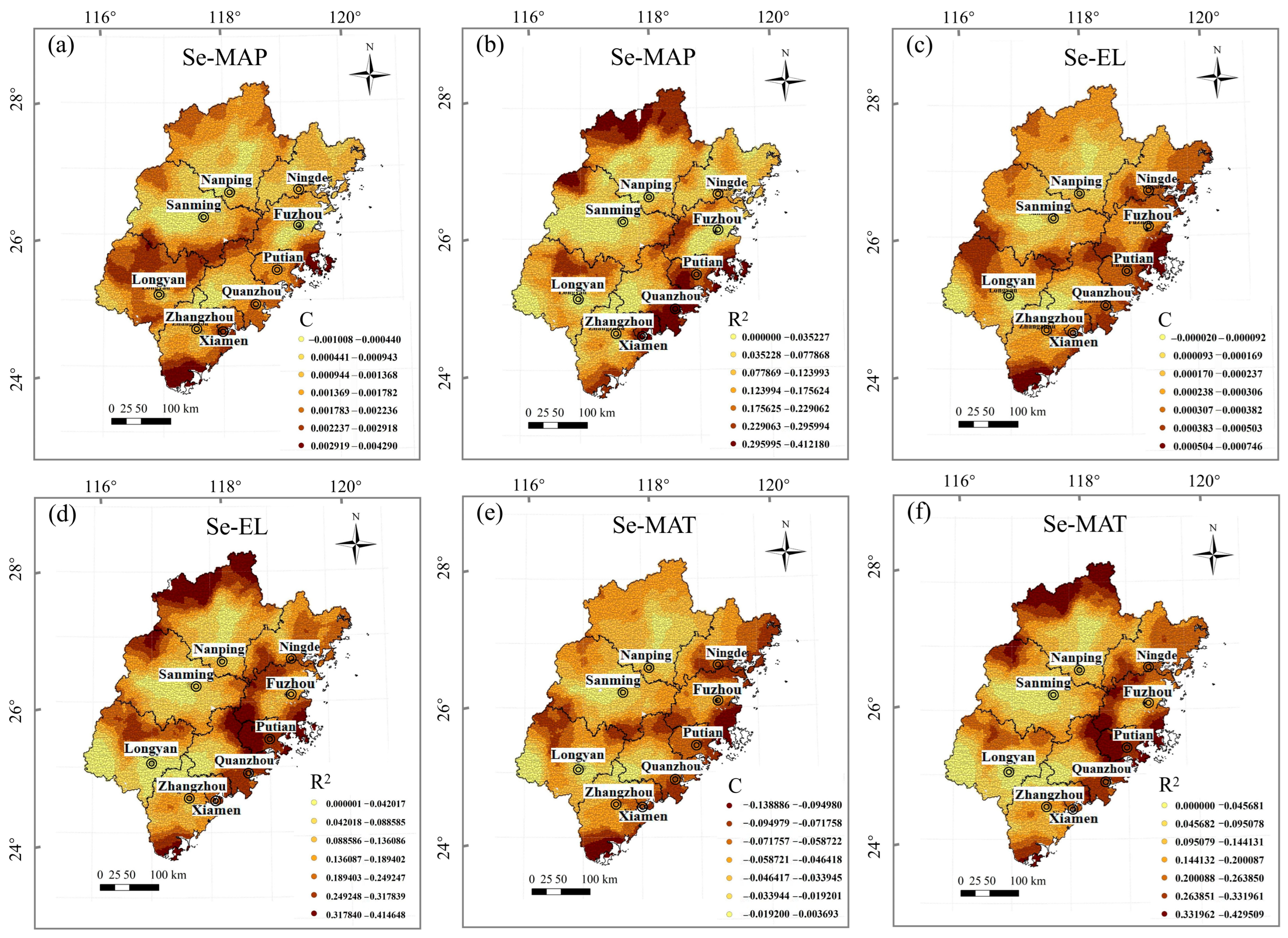
4.3.4. Soil Se and Environmental Factors
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hilal, T.; Killam, B.; Grozdanović, M.; Dobosz-Bartoszek, M.; Loerke, J.; Bürger, J.; Mielke, T.; Copeland, P.R.; Simonovi, M.; Spahn, C.M.T. Structure of the mammalian ribosome as it decodes the selenocysteine UGA codon. Science 2022, 376, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różewicz, M.; Bartosiewicz, B. Circulation of Selenium in the Environment. Environ. Prot. Nat. Resour. 2021, 32, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zhu, W.; Wang, W.; Li, R.; Hou, S.; Wang, D.; Yang, L. Selenium in soil and endemic diseases in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 284, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, R. A Medical Mystery in Middle China. Science 2009, 324, 1378–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieliszek, M.; Błażejak, S. Selenium: Significance, and outlook for supplementation. Nutrition 2013, 29, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fordyce, F. Selenium geochemistry and health. Ambio 2007, 36, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Liu, J. Selenium content characteristics of surface soil and rice seed in Fujian province and prediction of selenium-enriched production areas. Rock Miner. Anal. 2025, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.; Yang, J.; Wu, H.; Fu, Y.; Gao, J.; Tang, S.; Ma, S. Distribution of soil selenium and its relationship with parent rocks in Chengmai County, Hainan Island, China. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 136, 105147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, B.; Xu, K.; Zheng, D.; Tian, J. Distribution of Se in the rocks, soil, water and crops in Enshi County, China. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 122, 104707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Winkel, L. Multi-scale factors and processes controlling selenium distributions in soils. In Selenium in Plants: Molecular, Physiological, Ecological and Evolutionary Aspects; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Winkel, L.; Johnson, C.; Lenz, M.; Grundl, T.; Leupin, O.; Amin, M.; Charlet, L. Environmental selenium research: From microscopic processes to global understanding. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiles, C.; Mora, C.; Driese, S. Pedogenic iron-manganese nodules in Vertisols: A new proxy for paleoprecipitation? Geology 2001, 29, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, J.; Farics, É.; Szabó, P.; Sajó, I. Fe-Al phosphate microcrystals in pedogenic goethite pisoliths. Minerals 2020, 10, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsten, M.; Mikutta, R.; Vogel, C.; Thompson, A.; Mueller, C.; Kimaro, D.; Bergsm, H.; Feger, K.; Kalbitz, K. Iron oxides and aluminous clays selectively control soil carbon storage and stability in the humid tropics. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5076. [Google Scholar]
- Porras, R.; Hicks Pries, C.; McFarlane, K.; Hanson, P.; Torn, M. Association with pedogenic iron and aluminum: Effects on soil organic carbon storage and stability in four temperate forest soils. Biogeochemistry 2017, 133, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Liao, X.; Wang, J.; Chang, K. Effects of topography and soil properties on soil selenium distribution and bioavailability (phosphate extraction): A case study in Yongjia County, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clístenes, W.; Fernando, B.; Adelazil, B.; Biondi, C.; Lins, S.; Agenor, B. Geopedology-climate interactions govern the spatial distribution of selenium in soils: A case study in northeastern Brazil. Geoderma 2021, 399, 115119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shand, C.; Eriksson, J.; Dahlin, A.; Lumsdon, D. Selenium concentrations in national inventory soils from Scotland and Sweden and their relationship with geochemical factors. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 121, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DZ/T 0258-2014; Specification of Multi-Purpose Regional Geochemical Survey (1:250000). Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- DZ/T 0295-2016; Specification of Land Quality Geochemical Assessment. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Li, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Yu, T.; Wu, T.; Zhuo, X.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Lin, K.; et al. Spatially varying relationships of soil Se concentration and rice Se concentration in Guangxi, China: A geographically weighted regression approach. Chemosphere 2023, 343, 140241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Wang, L.; Rishe, N. v-TerraFly: Large scale distributed spatial data visualization with autonomic resource management. J. Big Data 2014, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Yang, Z.; Yu, T.; Xia, X.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, G. Geochemical Parameters of Soils in China; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Luo, L.; Xu, W.; Ledwith, V. Use of local Moran’s I and GIS to identify pollution hotspots of Pb in urban soils of Galway, Ireland. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 398, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Croot, P.; Zhang, C. Discovering hidden spatial patterns and their associations with controlling factors for potentially toxic elements in topsoil using hot spot analysis and K-means clustering analysis. Environ. Int. 2021, 151, 106456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Geng, W.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, X. Use of geographically weighted regression (GWR) to reveal spatially varying relationships between Cd accumulation and soil properties at field scale. Land 2022, 11, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazina, T.; Sun, Y.; Voegelin, A.; Lenz, M.; Berg, M.; Winkel, L. Terrestrial selenium distribution in China is potentially linked to monsoonal climate. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Hou, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, J. Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium and influencing factors of spatial distribution in Ninghua area, Fujian province. Rock Miner. Anal. 2025, 44, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Dinh, Q.; Wang, M.; Tran, T.; Zhou, F.; Wang, D.; Zhai, H.; Peng, Q.; Xue, M.; Du, Z.; Bauelos, G. Bioavailability of selenium in soil-plant system and a regulatory approach. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 49, 443–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, A.; Katz, M.; Wang, T.; Platero-Prats, A.; Chapman, K.; Hupp, J.; Farha, O. High efficiency adsorption and removal of selenate and selenite from water using metal-organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7488–7494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favorito, J.; Grossl, P.; Davis, T.; Eick, M.; Hankes, N. Soil-plant-animal relationships and geochemistry of selenium in the Western Phosphate Resource Area (United States): A review. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 128959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Zhang, H.; Huang, F.; Feng, X. Understanding the translocation and bioaccumulation of cadmium in the Enshi seleniferous area, China: Possible impact by the interaction of Se and Cd. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Man, N.; Wang, S.; Liang, D.; Liu, J. Selenite adsorption and desorption in main Chinese soils with their characteristics and physicochemical properties. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadis, V.; Levizou, E.; Shaheen, S.M.; Ok, Y.S.; Sebastian, A.; Baum, C.; Prasad, M.N.V.; Wenzel, W.W.; Rinklebe, J. Trace elements in the soil-plant interface: Phytoavailability, translocation, and phytoremediation–a review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 171, 621–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, Y.; Hornick, J.; Istasse, L.; Dufrasne, I. Selenium in the environment, metabolism and involvement in body functions. Molecules 2013, 18, 3292–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.M.; Ali, R.A.; Abowaly, M.E.; Rabie, A.E.-M.A.; El Abbasy, N.E.; Rinklebe, J. Assessing the mobilization of As, Cr, Mo, and Se in Egyptian lacustrine and calcareous soils using sequential extraction and biogeochemical microcosm techniques. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 191, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Doolittle, J.; Woodard, H. Selenite adsorption and desorption in selected South Dakota soils as a function of pH and other oxyanions. Soil Sci. 2011, 176, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Cicchella, D.; Liu, T.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, B.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X. Origin, distribution and enrichment of selenium in oasis farmland of Aksu, Xinjiang, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 223, 106723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, J.; Abdelouas, A.; Ribet, S.; Grambow, B. Sorption of selenite in a multi-component system using the “dialysis membrane” method. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 2524–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Li, Z.; Zhe, Y.; Huang, J.; Liang, D. Selenate adsorption and desorption in 18 kinds of Chinese soil with their physicochemical properties. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 3160–3168. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.; Bailey, E.H.; Arshad, M.; Ahmed, S.; Watts, M.; Young, S. Fate of selenium in biofortification of wheat on calcareous soil: An isotopic study. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 3643–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Q.; Gu, W.; Wang, K.; Du, X. A review of geological characteristics and selenium enrichment in Se-bearing volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. Int. Geol. Rev. 2024, 67, 1306–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhou, W.; Shang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Z.; Tang, D.; Cui, H.; Liao, C.; Yu, D. Spatial distribution and enrichment characteristics of selenium in paddy soil and rice around the Dongting Lake. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 359, 124552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; Yang, H.; Jin, L.; Hu, H. Release characteristics of arsenic, selenium, lead and transformation of minerals during ashing process of coal. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2022, 50, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audrey, L.; Florence, M.; Dominic, L.; Raoul-Marie, C. Influence of temperature on selenium mobility under contrasting redox conditions: A sediment flow-through reactor experiment. Biogeochemistry 2025, 168, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Indicators | Unit | Analysis Method | Detection Limit | RSD% | RE% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Se | mg/kg | AFS | 0.01 | 7.56 | 0.0104 | −0.42 |
| pH | - | ISE | 0.1 | 1.26 | 0.0049 | −0.84 |
| SOM | % | VOL | 0.05 | 2.98 | 0.0156 | −1.45 |
| TFe2O3 | % | XRF | 0.01 | 2.73 | 0.0112 | 0.40 |
| P | mg/kg | XRF | 8 | 3.15 | 0.0090 | −1.12 |
| Content Classification | Total Se in Soil | Area/Square Kilometers (in Ten Thousand) | Proportion/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| deficient | <0.125 | 0.3 | 2.4 |
| marginal | 0.125~0.175 | 0.9 | 7.7 |
| sufficient | 0.175~0.40 | 7.8 | 62.8 |
| rich | 0.40~3 | 3.4 | 27.1 |
| excessive | >3 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Cai, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, J. A GWR Approach to Determine Factors Controlling Soil Se in Fujian Province. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112560
Wang Y, Cai J, Liu J, Yang Z, Zhao X, Liu X, Li Z, Liu J. A GWR Approach to Determine Factors Controlling Soil Se in Fujian Province. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112560
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ying, Junliang Cai, Jiufen Liu, Zhongfang Yang, Xiaofeng Zhao, Xiaohuang Liu, Ziqi Li, and Jia Liu. 2025. "A GWR Approach to Determine Factors Controlling Soil Se in Fujian Province" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112560
APA StyleWang, Y., Cai, J., Liu, J., Yang, Z., Zhao, X., Liu, X., Li, Z., & Liu, J. (2025). A GWR Approach to Determine Factors Controlling Soil Se in Fujian Province. Agronomy, 15(11), 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112560








