Abstract
Long-term positioning tests can systematically reveal the evolution characteristics of soil fertility and crop productivity, and reflect the spatiotemporal changes in soil quality and their driving factors. While soil microorganisms mediating nutrient cycling are crucial for maintaining crop productivity and the long-term resilience of agricultural ecosystems, how prolonged use of different fertilization strategies affects their functional capacity remains insufficiently understood. In this study, we applied metagenomic sequencing to investigate how three fertilization treatments, namely (i) N0 receiving only phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) fertilizers, (ii) N250 receiving conventional urea + P and K, and (iii) F250 receiving humic acid urea + P and K, influence soil microbial communities, functional genes related to C and N cycling, and associated soil properties in a long-term field experiment. The F250 treatment significantly increased average annual yields of wheat and maize to 7166.21 kg hm−2 and 8309.96 kg hm−2, respectively. These values were 148.66% and 73.47% higher than those under N0, and 8.22% and 11.64% higher than those under N250. Compared with N0, both N250 and F250 signally augmented soil nitrate, ammonium, total nitrogen (TN), and soil organic carbon (SOC), altered microbial community composition, and enhanced the relative abundance of genes engaged in C fixation and methane oxidation. Both treatments also promoted denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA). Relative to N250, F250 specifically enriched the beneficial bacterial genus Pedobacter, further increased the abundance of the C fixation gene pccA, and markedly upregulated the DNRA gene nrfA. Soil TN and SOC were identified as the key environmental factors regulating microbial community structure and the functional potential of C and N cycling pathways. Collectively, our findings provide a mechanistic understanding of how long-term application of humic acid urea enhances crop productivity by modulating the genetic potential of soil microorganisms in biogeochemical cycles, offering a biological foundation for optimizing fertilization strategies in sustainable agriculture.
1. Introduction
The cultivation of high-yielding crop varieties, combined with irrigation and the application of chemical fertilizers and other agrochemicals, is a well-established strategy for enhancing crop productivity [1]. Among nitrogen (N) fertilizers, urea is the most widely used globally due to its high N concentration, rapid nutrient release, favorable storage and handling properties, ease of application, and broad adaptability across diverse cropping systems [2,3]. However, a considerable share of the N released from urea often remains unutilized by crops, leading to environmental concerns such as surface water eutrophication and the degradation of groundwater and air quality [4]. While improvements in fertilization practices can mitigate these issues, the development of green, high-efficiency urea formulations offers a more direct approach to enhancing nutrient use efficiency and crop yields without requiring changes to existing farming practices, while also helping to reduce the environmental burden associated with N losses. Consequently, several advanced urea products have been developed, including polymer-coated slow-release urea, urea stabilized with biochemical inhibitors, and urea–formaldehyde-based fertilizers [5,6]. Among these, humic acid-urea has gained particular attention because it not only improves fertilizer N use efficiency [4] but also enhances soil quality and increases crop yields [7]. Furthermore, its production cost is lower than that of coated controlled-release urea, which has contributed to its widespread adoption as the leading modified N fertilizer globally and delivered substantial benefits across food security, economic viability, and environmental sustainability [8]. Nevertheless, existing research has largely emphasized the short-term effects of humic acid fertilizers on nutrient use efficiency and yield maintenance, with limited data on the long-term impacts of humic acid-urea application [9,10]. Long-term field experiments offer a valuable opportunity to investigate the microbial mechanisms through which humic acid influences soil health and crop productivity [11,12].
Carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) cycles constitute fundamental biogeochemical processes that govern the transformation of organic and inorganic substances in soil and mediate the exchange of gases between the soil and the atmosphere [12]. Soil C and N are critical determinants of soil quality and crop productivity, and their dynamics directly influence the stability and functioning of agricultural ecosystems; consequently, the C and N cycles hold particular importance in agroecological contexts [13]. These cycles encompass a suite of tightly coupled microbial-driven processes, including organic matter decomposition, C and N mineralization and immobilization, methane metabolism, nitrification, and denitrification [14]. Extensive research has examined how humic acid application affects soil microbial communities. For instance, Li et al. [12] documented that humic acid fertilizers reduced the abundance of fungal pathogens, while augmenting the proportions of Basidiomycota and Mortierellomycota, fungal groups commonly associated with plant growth promotion. Other research has shown that, at specific concentrations, humic acid can increase the abundance of beneficial bacteria (e.g., Bradyrhizobium) while suppressing potentially harmful taxa (Xanthobacteraceae), thereby enhancing the structural stability of bacterial and fungal co-occurrence networks [15]. Despite these advances, few studies have investigated how humic acid urea influences the functional potential of microbial genes engaged in soil C, N, and phosphorus (P) cycling.
Metagenomics is a microbial research method that analyzes the total DNA extracted directly from environmental samples. By combining high-throughput sequencing with functional gene annotation, it allows researchers to examine the composition of microbial communities, their evolutionary relationships, metabolic capabilities, functional activities, and how they respond to environmental conditions [16]. Research using this approach has proven that chemical fertilization increases the abundance of genes associated with methane oxidation but exerts minimal influences on those linked to C degradation and fixation in soil [17]. In addition, chemical fertilization markedly raises the overall abundance of genes linked to denitrification, assimilatory nitrate reduction, and dissimilatory nitrate reduction [18]. The application of organic amendments or biofertilizers, by contrast, leads to a pronounced decline in the prevalence of genes responsible for breaking down both easily degradable and more persistent carbon compounds, such as chi and xylH, while enhancing the abundance of genes engaged in N transformation. These include GDH1, GDH2, ureA, glnA, and arcC, which participate in N mineralization and assimilation, as well as nrfA, napB, and napC, which are linked to dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA) [19]. These results highlight the value of metagenomics in monitoring shifts in microbial functional genes during C and N cycling. Applying this method to uncover shifts in gene abundance after humic acid application can offer direct insight into how soil fertility supports the long-term health and sustainability of agricultural systems [17].
In this study, we combined metagenomic analysis with statistical methods to measure the abundance of functional genes associated with microbial C and N cycling in soil and to assess potential shifts in metabolic activity under long-term fertilization. The study pursued three objectives: (i) to explore the effects of different fertilization on the crop productivity and soil chemical properties, (ii) to evaluate the long-term impacts of various fertilization regimes on microbial diversity and the genetic capacity for C and N cycling, (iii) to identify the dominant microbial taxa harboring key functional genes engaged in C and N transformations and examine how these genes are linked to soil properties, and (iv) to investigate the interconnections among functional genes that drive C and N cycling processes in soil.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Site
The field trial was initiated in 2015 at the Modern Agricultural Research and Development Base of the Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences (34°47′45″ N, 113°40′18″ E), situated in Yuanyang County, Henan Province, China. The site lies within the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain and belongs to a typical warm temperate continental monsoon climate. The region accumulates approximately 4700 °C in effective annual temperature, with a mean annual air temperature of 14.5 °C and average yearly precipitation of 615.1 mm. This area exemplifies the winter wheat-summer maize cropping system commonly implemented throughout northern China. Prior to the experiment, the soil at the site exhibited the following baseline chemical characteristics: pH 8.34 ± 0.04, total nitrogen (TN) 0.74 ± 0.10 g/kg, soil organic matter (SOM) 11.8 ± 0.12 g/kg, available phosphorus (AP) 26.5 ± 2.95 mg/kg, and available potassium (AK) 147 ± 16.84 mg/kg.
2.2. Experimental Design and Soil Sampling
Three different nitrogen application levels were set, while the application amounts of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers were the same: (i) no N fertilizer (N0), (ii) conventional urea at a rate of 250 kg N ha−1 year−1 (N250), and (iii) humic acid urea at the same N rate of 250 kg ha−1 year−1 (F250). Treatments were organized in a randomized complete block arrangement, with each plot measuring 48 m2 (6 m × 8 m) and every treatment replicated four times, resulting in a total of 12 plots. Detailed information on fertilizer application rates, composition, and sources is provided in Table A1.
Crop yield was assessed annually by collecting plant samples at physiological maturity for both wheat and maize. In June 2024, soil samples were taken from each plot at a depth ranging from 0 to 20 cm. Ten soil cores per plot were taken following an “S”-shaped sampling pattern to ensure representativeness. Soil cores collected from each plot were thoroughly mixed to create a single composite sample, yielding one sample per plot. Visible plant debris, stones, and root fragments were removed, and the soil was gently sieved (2 mm mesh) before subsampling. The processed soil was then used for DNA extraction as well as the analysis of physicochemical and microbiological properties.
The following soil parameters were measured: organic C (SOC), total N (TN), microbial biomass C (MBC) and N (MBN), available P (AP) and K (AK), ammonium (NH4+-N) and nitrate (NO3−-N), as well as the activities of six extracellular enzymes, namely α-1,4-glucosidase (AG), β-1,4-glucosidase (BG), β-D-cellobiosidase (CBH), β-1,4-xylosidase (XYL), β-1,4-N-acetyl-glucosaminidase (NAG), and leucine aminopeptidase (LAP). All analytical methods are described in Text A1.
2.3. Soil DNA Extraction and Sequencing of Bacterial and Fungal Communities
Genomic DNA was isolated from 0.50 g of fresh, homogenized soil per sample using the FastDNA® SPIN Kit (MP Biomedicals, Illkirch, France), combined with mechanical cell disruption carried out on the FastPrep-24 instrument (MP Biomedicals, Irvine, CA, USA). Amplification was performed targeting the V4 hypervariable region of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene and the ITS2 region of fungi. 515F (5′-GCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA-3′) and 806R → (5′-GGACTACVSGGGTATCTAAT-3′) were chosen in bacterial and the amplicon length was 291 bp. ITS3F → (5′-GCATCGATGAAGAACGCAGC-3′) and ITS4 (5′-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3′) were chosen in fungi and the amplicon length was 350 bp. Each sample was amplified in triplicate using TransStart FastPfu DNA Polymerase to ensure technical consistency. Following PCR, amplicons were purified and subjected to paired-end sequencing, and analyzed with an Illumina Miseq PE 300 platform (Majorbio Bio-Pharm Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Raw sequencing reads were processed using FLASH to merge overlapping paired-end reads and with Trimmomatic to eliminate adapter sequences and excise low-quality nucleotides. Read pairs were merged only when they overlapped by at least 12 nucleotides with 100% identity in the overlapping region. Putative chimeric sequences were identified and removed before subsequent analysis. The classium-sklearn (Naive Bayes) method was used to conduct taxonomic analysis on the representative sequences of Amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) to obtain the classification level of ASVs. The sequence reads ranged from 38,334 to 74,758 per sample. We annotated and aligned sequenced rRNA against Silva (Release 138, http://www.arb-silva.de, accessed on 16 July 2025) and Unite (Release 9.0 https://unite.ut.ee, accessed on 18 July 2025) databases, respectively. In total, we had 897,096 rarified 16S sequence reads and 460,008 ITS sequence reads, which resulted in 14,167 bacterial ASVs and 2995 fungal ASVs, respectively. The raw sequencing reads has been archived in the NCBI following the accession numbers: PRJNA1343905 for bacterial communities and PRJNA1340503 for the fungal communities.
2.4. Metagenomic Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
Metagenomic libraries were sequenced using the Illumina HiSeq 4000 system (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA), generating paired-end reads of 150 bp in length. Each sample yielded between 6.00 and 10.0 Gbp of raw sequence data. Raw reads were initially processed for quality control with Fastp v0.20.0 (https://github.com/OpenGene/fastp, accessed on 22 July 2025), which trimmed adapter sequences and discarded low-quality reads failing to meet the following thresholds: length < 50 bp, mean Phred quality score < 20, or inclusion of ambiguous (N) nucleotides. Contigs were generated from high-quality reads via MEGAHIT v1.1.2 (https://github.com/voutcn/megahit, accessed on 25 July 2025) using an optimized k-mer setting, followed by prediction of open reading frames (ORFs) with Prodigal v2.6.3 (https://github.com/hyattpd/Prodigal, accessed on 26 July 2025). ORFs shorter than 100 nucleotides were excluded; the remaining were translated into protein sequences and clustered at 95% identity and 90% coverage using CD-HIT v4.6.1 (http://www.bioinformatics.org/cd-hit/, accessed on 28 July 2025) to construct a nonredundant gene catalog [20]. We mapped clean reads from each sample to the nonredundant gene catalog using SOAPaligner v2.2.1 (https://github.com/ShujiaHuang/SOAPaligner, accessed on 6 August 2025) to estimate gene abundances and annotated the catalog by aligning predicted protein to KEGG (version 94.2, http://www.genome.jp/kegg/, accessed on 10 August 2025) with DIAMOND v0.8.35 (https://github.com/bbuchfink/diamond, accessed on 12 August 2025) using blastp. Functional genes linked to C and N cycling were identified based on their annotation to key C/N transformation pathways and consistent detection in all metagenomes. Their taxonomic origins were inferred by aligning encoded proteins to the NCBI nonredundant (NR) database using DIAMOND (blastp mode) [21]. Raw reads of metagenomics have been deposited in the NCBI under the accession PRJNA1344279.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Treatment effects on crop yield, soil properties, and microbial relative abundance were analyzed using factorial ANOVA, followed by least significant difference (LSD) post hoc tests (p < 0.05). Analyses were implemented in SPSS (v26.0; IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). To visualize variation in microbial community structure among treatments, principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) was conducted using Bray–Curtis dissimilarity as the distance metric. Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) effect size (LEfSe) was carried out in R with the ‘ggtree’ package, applying a minimum LDA score threshold of 3; only taxa meeting or exceeding this threshold were considered potential biomarker species. Redundancy analysis (RDA) was employed to assess the extent to which soil environmental variables shaped microbial community structure. To quantify changes in functional gene abundance due to fertilization, log2-fold changes (LFCs) between treatment groups were estimated using the apeglm shrinkage estimator implemented in the DESeq2 v1.48.2 R package. Differential abundance of functional genes was statistically assessed via Wilcoxon rank-sum tests on DESeq2 median ratios, with p values corrected for false discovery rate (FDR) at a significance level of p < 0.05 [17]. The Kruskal–Wallis test (a nonparametric approach) was applied to identify significant variation in the relative abundance (≥0.1%) of microbial taxa across treatments. Associations between soil physicochemical characteristics and either microbial taxa or functional genes were examined using the Mantel test, implemented with the “ggcor” R package. Additionally, Spearman’s rank correlation was employed to investigate linkages between individual soil variables and specific microbial taxa or functional genes.
3. Results
3.1. Response of Crop Yield and Soil Chemical Properties to Fertilization Regimes
Crop yields across all treatments exhibited distinct temporal patterns. Yields under the N250 and F250 treatments generally increased over time, whereas those under the N0 treatment remained relatively stable, with occasional declines in certain years (Figure 1A,C). The annual yield growth rate in the N0 treatment decreased over the study period, while both N250 and F250 treatments exhibited significantly higher rates (p < 0.05). However, the growth rates between N250 and F250 did not differ significantly (Figure 1A,C). The average annual yields of wheat and maize were highest under the F250 treatment, reaching 7166.21 kg ha−1 and 8309.96 kg ha−1, respectively, followed by the N250 treatment. Both fertilized treatments yielded significantly more than the unfertilized N0 control (p < 0.01; Figure 1B,D). Moreover, the F250 treatment produced markedly higher yields than N250 (p < 0.05), with increases of 8.22% for wheat and 11.64% for maize (Figure 1B,D).
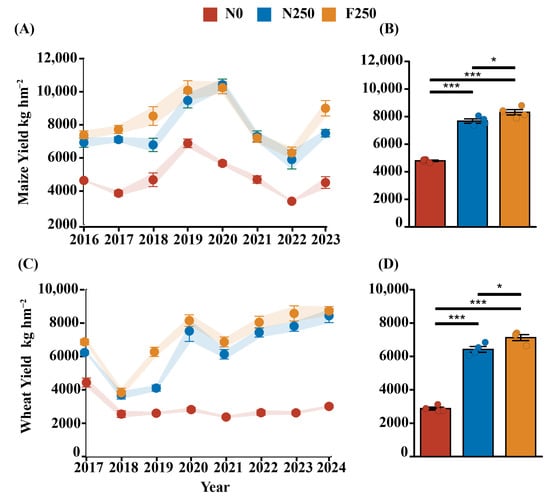
Figure 1.
The changing trends of crop yields ((A): corn; (C): wheat) and the annual average yields ((B): corn; (D): wheat) under long-term different fertilization treatments. The error lines in the bar chart are standard errors. Significance levels: * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001.
Long-term fertilization also induced notable changes in soil chemical properties (Figure A1). Relative to the N0 treatment, both N250 and F250 significantly increased soil concentrations of NO3−-N, NH4+-N, SOC, and TN (p < 0.05), but led to pronounced reductions in AP and AK (p < 0.05). Although all measured soil chemical parameters were numerically higher under F250 than under N250, the differences were not statistically significant except for NH4+-N and MBC, which were significantly greater in the F250 treatment. Collectively, these results indicate that long-term application of humic acid urea not only prominently enhances crop productivity but also improves key soil nutrient indicators, as demonstrated in Figure 1 and Figure A1.
3.2. Response of Microbial Communities to Fertilization Regimes
Across all treatments, the bacterial community was primarily dominated by Pseudomonadota at the phylum level, with average relative abundances of 23.31% (N0), 23.32% (N250), and 22.62% (F250). Other dominant bacterial phyla included Acidobacteriota (14.99%, 12.46%, and 15.27%), Actinomycetota (10.00%, 12.25%, and 11.38%), and Bacteroidota (8.43%, 9.65%, and 8.99%) (Figure 2A). Compared to the N0 treatment, N250 substantially elevated the relative abundance of Actinomycetota and Bacillota, whereas F250 resulted in a pronounced reduction in Myxococcota (Figure 2A). Among fungi, Ascomycota was the predominant phylum, accounting for 72.90% (N0), 79.42% (N250), and 80.57% (F250) of the fungal community. F250 increased the relative abundance of Ascomycota by 10.52% relative to N0 (p < 0.05; Figure 2B). PCoA analysis based on amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) revealed clear separation among the microbial communities of the three treatments for both bacteria and fungi, indicating that long-term fertilization significantly shaped community composition (Figure 2C,D). Redundancy analysis (RDA) further showed that AK, AP, and TN were the primary soil properties driving shifts in bacterial community structure, whereas SOC, AP, and TN were the predominant drivers shaping fungal community composition (Figure 2E,F).
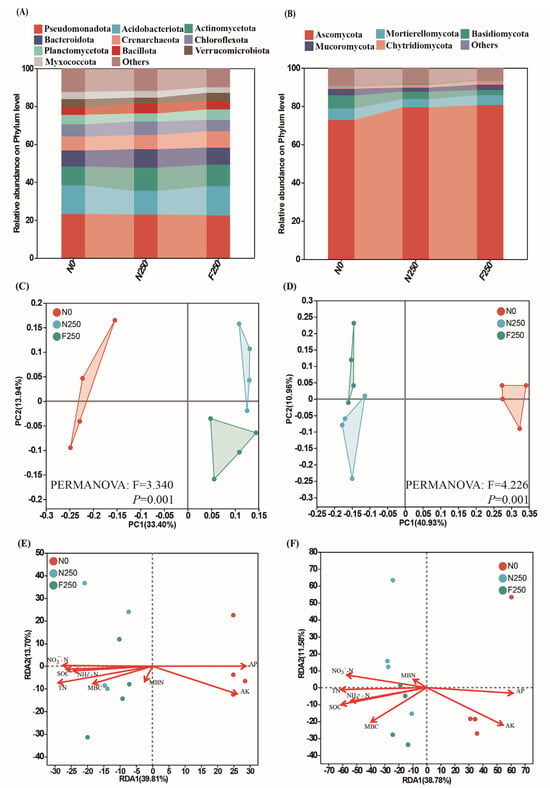
Figure 2.
Shifts in soil microbial communities under long-term fertilization. Relative abundance of bacterial (A) and fungal (B) taxa at the phylum level. Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) of bacterial (C) and fungal (D) communities based on Bray–Curtis dissimilarity. Redundancy analysis (RDA) linking bacterial (E) and fungal (F) community composition to soil nutrient variables.
LEfSe analysis (LDA > 3; p < 0.05) identified treatment-specific microbial taxa across taxonomic levels (Figure 3). Among bacteria, 106 taxa differed significantly among treatments: 51 biomarker taxa were enriched in N0, 42 in N250, and 13 in F250 (Figure 3A). Notably, the genus Sphingomonas was significantly enriched under N0, Bacillus under N250, and Pedobacter under F250. In the fungal community, 98 taxa showed significant differences across treatments, with 50, 28, and 20 biomarkers identified in N0, N250, and F250, respectively (Figure 3B). At the genus level, Ramophialophora was signally enriched in N0, Trichocladium in N250, and Schizothecium in F250 (Figure 3B).
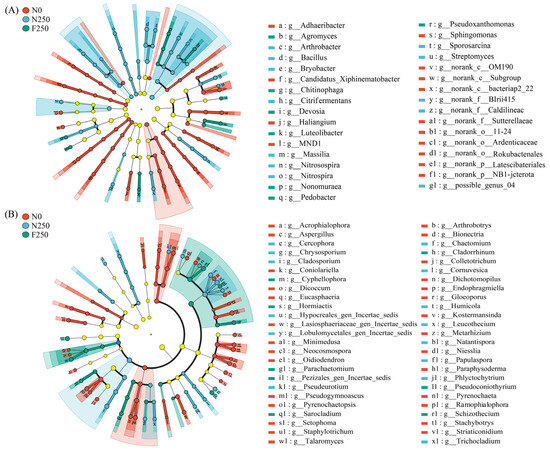
Figure 3.
LEfSe cladograms identifying microbial taxa significantly enriched in each fertilization treatment (LDA score > 3, p < 0.05) for bacteria (A) and fungi (B). Concentric rings represent taxonomic ranks from phylum (outermost) to genus (innermost).
3.3. Influence of Fertilizer Application on Microbial Taxa Driving C Cycling Processes
Functional genes associated with the C cycle and exhibiting a relative abundance exceeding 1% were classified into four categories: other carbohydrate metabolism, C fixation, methane metabolism, and serine and threonine metabolism (Figure 4A). The highest normalized abundance was observed for genes involved in central carbohydrate metabolic pathways, followed by those related to C fixation (Figure 4A). Within central carbohydrate metabolism, genes linked to the citrate cycle and glycolysis were more abundant than those associated with the pentose phosphate pathway. In the C fixation category, genes participating in the reductive citrate cycle and the dicarboxylate-hydroxybutyrate cycle displayed the highest abundances (Figure 4A). The Wilcoxon rank-sum test revealed that long-term fertilization substantially altered the abundance of key functional genes involved in C cycling (Figure 4B). Both N250 and F250 treatments resulted in significantly higher abundances of pccA and pmoA and observably lower abundances of frdA/B and porA/B relative to N0. Furthermore, the N250 treatment markedly increased gpm abundance compared with N0. The F250 treatment further elevated pccA levels and induced a more pronounced decline in frdA/B and porA/B relative to N250 (Figure 4B). Compared with N0 treatment, N250 treatment and F250 treatment significantly increased the activities of AG, BG, CBH and XYL enzymes in the soil (Figure A2). Compared with the N250 treatment, there was no significant difference in soil enzyme activities in the F250 treatment. Except for the AG enzyme activity which was higher than that in the N250 treatment, the activities of other enzymes were all lower than those in the N250 treatment.
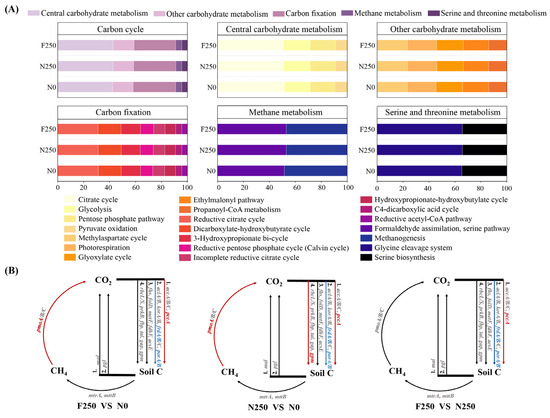
Figure 4.
Functional potential of soil microbial communities in C cycling. (A) Relative abundance of C cycling genes grouped by metabolic pathway under each fertilization treatment. (B) Differential abundance of C cycling genes across treatments based on metagenomic analysis. Red indicates significantly higher gene abundance in the former treatment, blue indicates significantly lower abundance, and gray denotes no significant difference.
Taxonomic assignment of C-cycling genes indicated that Pseudomonadota was the predominant phylum across all fertilization treatments, contributing an average of 26.08% of annotated sequences, followed by Actinomycetota (25.99%) and Acidobacteriota (10.48%) (Figure A3A). Compared with the unfertilized N0 treatment, both fertilized treatments enhanced the relative contribution of Actinomycetota while reducing that of Acidobacteriota and Candidatus Rokubacteria. Notably, Pseudomonadota abundance was notably higher under the F250 treatment than under N250 (Figure A3B).
3.4. Influence of Fertilizer Application on Microbial Taxa Driving N Cycling Processes
Functional genes associated with N cycling were categorized into seven pathways: N fixation, denitrification, nitrification, assimilatory nitrate reduction (ANRA), dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA), complete nitrification, and nitrate assimilation (Figure 5A). Among these pathways, denitrification-related genes exhibited the highest abundance across all treatments, followed by those linked to ANRA, complete nitrification, nitrate assimilation, and DNRA (Figure 5A). Wilcoxon rank-sum tests uncovered that prolonged fertilization significantly altered the abundance of key N-cycling genes (Figure 5B). Relative to the N0 treatment, both N250 and F250 substantially elevated the abundances of nirB, nirK, and norB, genes encoding enzymes that catalyze critical steps in denitrification and DNRA. The F250 treatment further enhanced the abundance of nrfA (a key DNRA gene) compared with both N0 and N250. In contrast, F250 led to a pronounced decline in nifD and nifK, genes essential for N fixation, relative to the N0 treatment (Figure 5B).
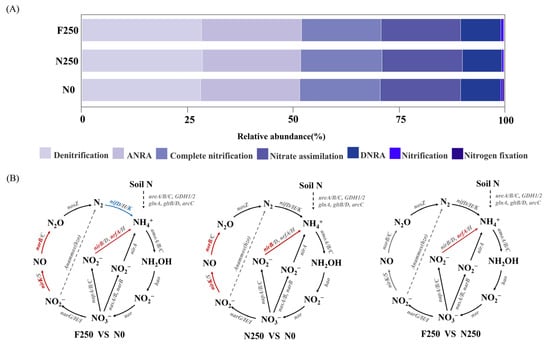
Figure 5.
Functional potential of soil microbial communities in N cycling. (A) Relative abundance of N cycling genes categorized by metabolic pathway. (B) Differential abundance of N cycling genes among fertilization treatments. Color coding follows the same convention as in Figure 4.
According to the Taxonomic profiling of N-cycling genes, it was evident that Actinomycetota and Pseudomonadota were the predominant phyla, followed by Acidobacteriota, Nitrososphaerota, and Candidatus Rokubacteria, which together accounted for 71.29% to 72.66% of all annotated sequences (Figure A5A). Compared with N0, both N250 and F250 significantly enriched Actinomycetota while reducing the abundance of Acidobacteriota and Candidatus Rokubacteria (Figure A5B). Notably, Pseudomonadota displayed a much lower abundance under N250 than under either N0 or F250, suggesting a differential response of this key N-cycling phylum to conventional versus humic acid-enhanced urea.
3.5. Relationship Between Microbial Functional Genes and Soil Nutritional Variables
The Mantel test revealed that soil TN and SOC were the primary environmental drivers shaping the functional profiles of microbial communities associated with C and N cycling under different fertilization treatments (Figure 6). Although both factors exerted strong overall influences, their associations with specific functional genes varied across metabolic pathways. Heatmap-based correlation analysis demonstrated that TN and SOC were significantly and positively correlated (p < 0.05) with genes involved in C fixation, including accB, pccA, fhs, folD, metF, and tal. A similar positive relationship was observed between these soil properties and pmoA/B, key genes in methane oxidation. In the N cycle, TN and SOC also exhibited significant positive correlations with a broad suite of functional genes. These included genes associated with N degradation (GDH2, glnA, arcC, gltB), denitrification (norB, nirK, narG/H), DNRA (napA, nirB/D), ANRA (narB, nirA), and nitrification (amoA/B, hao) (Figure 7). At the taxonomic level, Actinomycetota showed extremely strong positive associations with both TN and SOC in the context of C and N cycling processes (p < 0.01). In contrast, Acidobacteriota and Candidatus Rokubacteria displayed significant negative correlations with these soil nutrients (p < 0.05) (Figure 8).
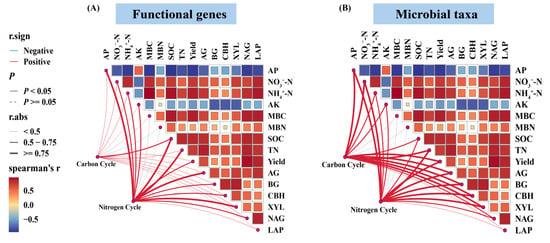
Figure 6.
Environmental drivers of microbial functional genes (A) and taxa (B) involved in C and N cycling. Spearman correlation coefficients between soil properties and gene/taxon abundances are shown as a color gradient. Mantel test results are represented by edges connecting environmental factors to genes or taxa; edge width reflects the Mantel r statistic, and edge color indicates statistical significance.
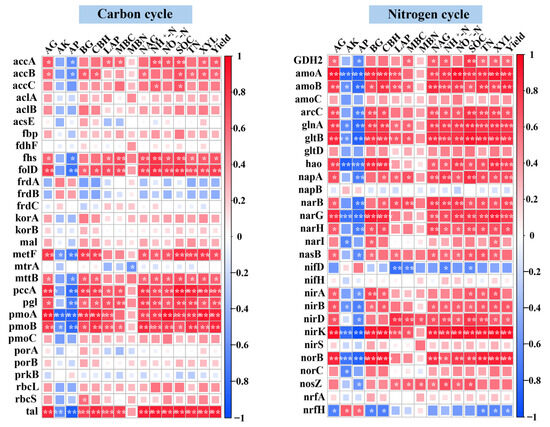
Figure 7.
Spearman correlation heatmap showing associations between soil properties and abundances of C and N cycling genes. Significance levels: * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
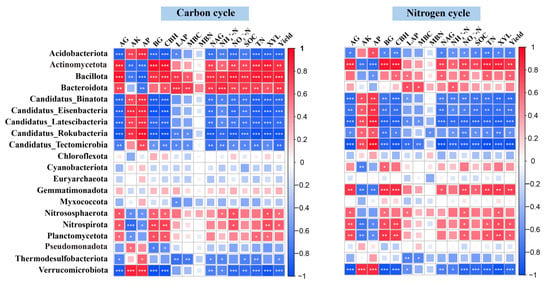
Figure 8.
Spearman correlation heatmap depicting relationships between soil properties and relative abundances of microbial taxa involved in C and N cycling. Significance levels: * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
4. Discussion
4.1. Humic Acid Significantly Increases Crop Yields and Soil Chemical Properties
Soil chemical properties are fundamental determinants of soil fertility [22]. The use of humic acid-based fertilizers has been proven to enhance soil nutrient availability, improve fertility, and indirectly influence microbial activity, ultimately contributing to higher crop yields [18]. In the present study, long-term use of humic acid urea (F250) markedly increased both crop productivity and key soil nutrient indicators, including NO3−-N, NH4+-N, SOC, MBC, and TN, compared with both the unfertilized control (N0) and conventional urea (N250) (Figure 1 and Figure A1). These improvements likely stem from the ability of humic acid to enhance nutrient retention and slow the release of nitrogen, thereby improving nutrient use efficiency and supporting sustained plant growth [23]. Our results are consistent with those of Kong et al. [24], who found that humic acid urea increased maize and wheat yields while improving N use efficiency through reduced N losses and prolonged nutrient release. In line with this mechanism, we observed that F250 significantly elevated soil NH4+-N levels relative to N250, and also increased NO3−-N content (Figure A1). This effect may be ascribed to the capacity of humic acid to suppress urease activity, thereby slowing urea hydrolysis, moderating the rate of ammonium production, and reducing the risk of subsequent nitrification and N loss through leaching or volatilization [25]. Previous studies have also reported that repeated application of humic acid fertilizers over multiple years can increase soil AP and AK compared with conventional urea [12], and that AP levels under humic acid treatment can exceed those in unfertilized controls [24]. However, in our experiment, both N250 and F250 treatments resulted in significantly lower AP and AK concentrations than the N0 treatment (p < 0.05), with no distinct difference between the two fertilized treatments (Figure A1). This apparent discrepancy may be related to site-specific factors such as soil texture, initial nutrient status, or long-term imbalances in nutrient inputs and crop removal.
4.2. Humic Acid Significantly Alters Microbial Community Composition
Soil microorganisms are integral components of agroecosystems, playing critical roles in the mineralization, transformation, and availability of soil nutrients [26]. The distinct nutrient regimes established by different fertilization practices in this study led to pronounced shifts in microbial community structure. Our results confirmed that Pseudomonadota, Actinomycetota, Acidobacteriota, and Bacteroidota are the predominant bacterial phyla, consistent with their widespread prevalence in terrestrial ecosystems [27] (Figure 2A). While N250 prominently enriched the relative abundance of Actinomycetota and Bacillota relative to N0 (p < 0.05), the F250 treatment did not produce statistically significant alterations in these taxa. This aligns with previous observations that chemical nitrogen fertilization favors Actinomycetota, a group often associated with oligotrophic conditions and capable of producing extracellular enzymes that degrade complex organic matter [28]. In contrast, Bacillota, typically considered copiotrophic, tend to respond positively to N inputs [18] and contribute to the decomposition of readily available organic substrates during N cycling [29]. Interestingly, while some studies report that humic acid application increases Bacillota abundance [12], our results show no such enrichment under F250. Additionally, Myxococcota exhibited a significant decline under F250 relative to N0. Given that prior work links Myxococcota abundance to high levels of available N and organic matter [30,31], the reduction observed here supports the notion that humic acid urea moderates N availability, thereby altering the ecological niche for this group. Among fungi, Ascomycota, Mortierellomycota, and Basidiomycota were the dominant phyla (Figure 2B). Both Ascomycota and Basidiomycota are well-known decomposers in soil ecosystems [32]. Most members of Ascomycota are saprophytic, and their abundance often correlates with SOM content [18]. Humic acid is recognized to stimulate microbial and enzymatic activity, accelerating organic matter mineralization and nutrient release [33]. Consistent with this, Ascomycota exhibited the greatest relative abundance under F250, with intermediate levels in N250 and the lowest in N0.
These community-level patterns were further corroborated by LEfSe analysis, which identified treatment-specific biomarkers from phylum to genus (Figure 3). The genus Sphingomonas was enriched in N0, aligning with findings by Li et al. [18]. Sphingomonas is known to promote plant health through N fixation and antagonism against soil-borne pathogens [34]. In the N250 treatment, Bacillus, a member of Bacillota, was markedly enriched. Bacillus species contribute to soil fertility and plant growth and participate in key N transformations, including N fixation and denitrification [35]. Under F250, the genus Pedobacter was notably enriched. Pedobacter has been shown to suppress pathogenic fungi such as Fusarium acuminatum and compete with dominant saprophytes like Chaetomium globosum, thereby enhancing crop yield and stress tolerance [36]. Collectively, these results indicate that long-term fertilization regimes differentially shape the enrichment of beneficial versus potentially detrimental microorganisms. The distinct microbial assemblages fostered by humic acid urea likely contribute to improved soil microecological balance, which in turn supports higher crop productivity and overall soil quality.
4.3. Humic Acid Significantly Alters the C Fixation Process
Soil C pools are critical for maintaining soil fertility, productivity, and biodiversity, and they play a key role in stabilizing soil structure and enhancing C sequestration [37]. N inputs from chemical fertilizers can shift the soil N status, thereby influencing C turnover dynamics [38]. However, in the present study, long-term fertilization did not exert an observable impact on the abundance of functional genes associated with C degradation (Figure 4B), a finding consistent with earlier reports by Su et al. [39] and Yu et al. [40]. This muted response may stem from prolonged fertilization-induced shifts in the composition of dominant microbial taxa, reduced metabolic efficiency in carbohydrate processing, or constrained expression of relevant catabolic genes [41,42]. To further assess microbial activity related to C cycling, we quantified the activities of four extracellular enzymes, e.g., AG, BG, CBH, XYL, which are widely recognized as sensitive indicators of soil organic C decomposition [43] (Figure A2). Both N250 and F250 treatments markedly enhanced the activities of all four enzymes against the N0 control. Although enzyme activities were slightly higher under N250 than F250, the difference was not statistically significant. This pattern may reflect the elevated availability of inorganic N under conventional urea application, which increases microbial demand for C to maintain cellular stoichiometric balance [44]. In contrast, the F250 treatment simultaneously increased SOC, potentially satisfying microbial C demands more effectively and moderating the need for heightened enzyme production, thereby resulting in comparable, though slightly lower, enzyme activities relative to N250.
Notably, the F250 treatment signally altered the abundance of genes associated with C fixation compared with both N0 and N250 (Figure 4B), suggesting that humic acid urea exerts a stronger influence on microbial C assimilation pathways than conventional urea. Additionally, both N250 and F250 significantly increased pmoA abundance, which encodes the particulate methane monooxygenase enzyme central to methane oxidation, relative to N0, although the two fertilized treatments did not differ significantly. This contrasts with findings from rice paddy studies, where chemical N application often suppresses methane-oxidizing microbes [45,46]. However, in dryland agricultural systems like the one studied here, methane fluxes are typically negligible or even negative [40], indicating that methane cycling plays a minor role in overall C dynamics.
4.4. The Application of Humic Acid Exerts a Significant Influence on the N Cycle
In this study, genes associated with denitrification constituted the largest functional group within the N cycle (Figure 5A). Denitrification is a key microbial process that converts NO3− or NO2− into gaseous N oxides (NO, N2O, N2), thereby contributing to atmospheric N loss [47]. Relative to the N0 control, both N250 and F250 treatments markedly elevated the abundance of denitrification-related genes, particularly nirK and norB (Figure 5B). This aligns with previous findings that elevated availability of C and N substrates stimulates denitrifying microbial activity [48]. Beyond denitrification, fertilization regimes also markedly influenced genes involved in DNRA. Specifically, the F250 treatment significantly enhanced the abundance of nrfA, a key DNRA gene, compared with both N0 and N250 (Figure 5B). This indicates that humic acid urea promotes the DNRA pathway more effectively than conventional urea. DNRA plays a critical role in retaining N in the soil by reducing mobile nitrate to ammonium (NH4+), which is less prone to leaching and more readily taken up by crops [19]. By favoring DNRA over complete denitrification, humic acid urea may help mitigate both nitrate leaching and emissions of the potent greenhouse gas N2O. Thus, enhancing DNRA represents a promising strategy to simultaneously sustain high crop productivity and mitigate environmental N losses [49]. N fixation, the biological conversion of atmospheric N2 into bioavailable ammonia, also responded to fertilization [50]. The F250 treatment substantially reduced the abundance of N fixation genes (nifD/K) compared with N0. This suppression is likely due to the ample supply of inorganic N under fertilized conditions, which alleviates the need for energetically costly biological N fixation [51]. In the N0 treatment, the absence of external N inputs creates a strong selective pressure for diazotrophic microbes, leading to higher expression of nif genes. Our observation is consistent with prior studies showing that improved N availability suppresses the abundance and activity of N-fixing microorganisms by satisfying microbial N demands and downregulating nifH/K/D expression [52,53].
4.5. Interconnections Among Soil Properties, Microbial Communities and Functional Genes: Tight Coupling of C and N Cycles Driven by TN and SOC
The functional potential of soil microbial communities is closely linked to their taxonomic composition [17]. In this study, bacteria were the primary contributors to C and N cycling processes, whereas archaea and fungi played comparatively minor roles (Figure A3 and Figure A5), consistent with prior reports [19]. At the phylum level, the microbial taxa associated with C, N, and P cycling showed substantial overlap, suggesting that dominant bacterial groups function as generalist taxa capable of participating in multiple biogeochemical pathways [54,55]. Specifically, Pseudomonadota, Actinomycetota, Acidobacteriota, and Candidatus Rokubacteria emerged as key generalists in our system. This corroborates the findings of Gonzalez-Pimentel et al. [56], who identified these same phyla as central players in diverse metabolic processes, including methanotrophy, sulfur and N transformations, and CO2 fixation. According to the oligotrophic-copiotrophic framework [57], the enrichment of functional genes under fertilization likely reflects the proliferation of microbial taxa adapted to nutrient-rich conditions. Pseudomonadota and Actinomycetota are typically classified as copiotrophs with high metabolic versatility and nutrient acquisition capacity, while Acidobacteriota and Candidatus Rokubacteria often exhibit traits intermediate between oligotrophs and copiotrophs but can respond positively to organic inputs [18,19,41]. Notably, Bacteroidota, a phylum generally regarded as copiotrophic due to its rapid response to labile organic substrates [58], also showed significant enrichment following humic acid urea application. Functional annotation further revealed that Bacteroidota contributed meaningfully to both C and N cycling genes, with clear treatment-dependent differences. This suggests that Bacteroidota may actively support the decomposition of organic matter and N transformation processes in humic acid-amended soils, thereby enhancing overall nutrient cycling efficiency.
Crucially, soil TN and SOC emerged as the strongest environmental predictors driving variation in both microbial community structure and functional gene profiles associated with C and N cycling (Figure 6). This reflects the fundamental stoichiometric coupling between C and N in terrestrial ecosystems: increased N availability influences the synthesis and breakdown of SOM, while C availability governs microbial energy supply for N transformations [17]. As key limiting macronutrients, TN and SOC directly regulate microbial growth, enzyme production, and the rates of organic matter decomposition and nutrient mineralization [41,59]. Previous studies have shown that soil TN and SOC levels strongly linked to the abundance of genes mediating denitrification, DNRA, and ANRA, highlighting their central role in modulating N pathway selection [18]. This relationship was further corroborated by Hu et al. [17], who reported a highly significant association (p < 0.01) between TN, SOC, and the collective activity of C-N cycling genes. In summary, a dynamic interplay exists among soil chemical properties, microbial community composition, and the functional genetic potential for biogeochemical cycling. This tripartite relationship enables the soil ecosystem to maintain functional stability while adapting to long-term fertilization practices.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrates that N fertilization significantly enhances soil chemical properties, reshapes microbial community structure, and modulates key processes in the C and N cycles, ultimately influencing crop productivity. Specifically, the adoption of humic acid urea markedly augmented wheat and maize yields, improved soil fertility, and enriched beneficial microbial taxa. It also enhanced the genetic potential for C fixation and methane oxidation, while promoting the expression of genes involved in denitrification and DNRA. Among the measured soil properties, TN and SOC emerged as the dominant environmental drivers regulating microbial functional profiles in C and N cycling. Meanwhile, the functional genes of these two cycles were found to be tightly coupled. These findings elucidate the mechanisms underlying C and N transformation in agricultural soils and reveal how functional microorganisms respond to long-term humic acid urea application. By linking fertilization practices to microbial-mediated biogeochemical processes, this work provides a scientific foundation for advancing sustainable agroecosystem management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.L., X.S., Q.Z., Y.C. and S.D.; methodology, X.S., Q.Z. and Y.C.; validation, M.W., K.Y. and K.Z.; formal analysis, M.W. and K.Z.; investigation, T.G., K.Y., S.Z. and K.Z.; resources, P.L., S.H., Q.Z., Y.C., Z.Z., S.S., S.D. and S.Z.; data curation, T.G., M.W., K.Y., P.L., X.X., Z.Z., S.S., S.D., S.Z. and K.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, T.G.; writing—review and editing, M.W., P.L., X.S., S.H., X.X., Q.Z., Z.Z., S.S., S.D. and S.Z.; visualization, M.W. and K.Y.; supervision, T.G., P.L., X.S., S.H., X.X., Q.Z., Y.C., Z.Z., S.S. and S.Z.; project administration, T.G., P.L., X.S. and Y.C.; funding acquisition, S.H. and X.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research and APC was founded by [National Natural Science Foundation of China] grant number [32202603], [Talented Youth Project of Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences] grant number [2024YQ04], [Smart Fertilization Project] grant number [05], and [Science and Technology Research Project of Henan Province] grant number [252102111104].
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in National Center for Biotechnology Information (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) under the accession numbers: PRJNA1343905; PRJNA1340503; and PRJNA1344279.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Amount of nutrient inputs (kg ha−1 year−1).
Table A1.
Amount of nutrient inputs (kg ha−1 year−1).
| Treatment | Winter Wheat | Summer Maize | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | K2O | N | P2O5 | K2O | |
| N0 | 0 | 75 | 60 | 0 | 75 | 60 |
| N250 | 250 | 75 | 60 | 250 | 75 | 60 |
| F250 | 250 | 75 | 60 | 250 | 75 | 60 |
Note: In the N0 treatment, no nitrogen fertilizer was applied. In the N250 treatment, the nitrogen fertilizer was common urea (46% N). In the F250 treatment, it was humic acid urea (46% N). Each treatment uses 12% superphosphate as the phosphorus fertilizer and 50% potassium sulfate as the potassium fertilizer. The fertilizer provided by Henan Xinlianxin Chemicals Group Co., LTD. The amount of fertilizer applied to wheat and corn is the same, and it should be applied as a basal fertilizer to the experimental field at one time before sowing the crops.
Appendix A.1. Analysis of Soil Properties
Soil moisture content was determined by drying 5 g of fresh soil at 105–108 °C for 12 h. Nitrate (NO3−-N) and ammonium (NH4+-N) concentrations were measured using a continuous flow analyzer (SKALAR SAN++, Netherlands). Total nitrogen (TN) was quantified by the Kjeldahl digestion method. Soil organic carbon (SOC) was estimated via wet oxidation with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7). Available phosphorus (AP) was extracted with 0.5 M sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) and analyzed by molybdenum-antimony colorimetry with scandium as a stabilizer. Available potassium (AK) was extracted with 1 M ammonium acetate and determined using a flame photometer [60]. Microbial biomass carbon (MBC) and nitrogen (MBN) were assessed by the chloroform fumigation-extraction method [28]. Activities of soil extracellular enzymes were measured using a fluorometric microplate assay [61].
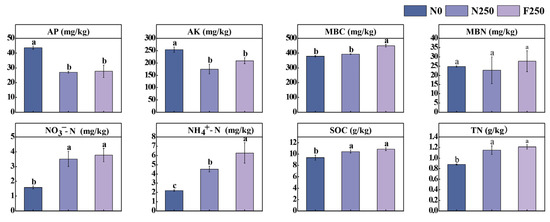
Figure A1.
Effects of long-term fertilization on soil chemical properties. Bars labeled with different letters indicate significant differences among treatments (p < 0.05).
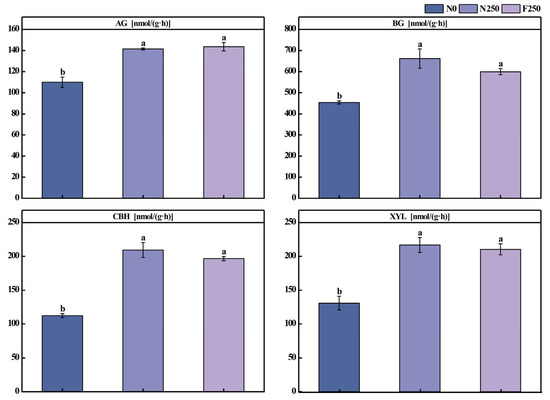
Figure A2.
Effects of long-term fertilization on the activities of C-cycling-related soil enzymes. Bars labeled with different letters indicate significant differences among treatments (p < 0.05). AG: α-1,4-glucosidase, BG: β-1,4-glucosidase, CBH: β-D-cellobiosidase, XYL: β-1,4-xylosidase.
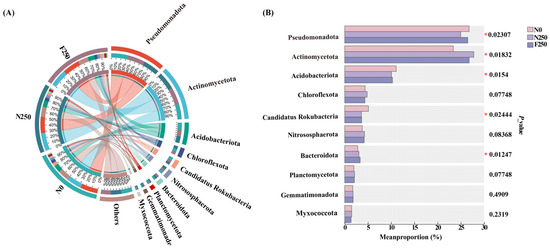
Figure A3.
Relative abundance of microbial taxa (>0.1%) associated with C-cycling genes at the phylum level (A) and pairwise comparisons among fertilization treatments (B). Asterisks denote significant differences: p < 0.05.
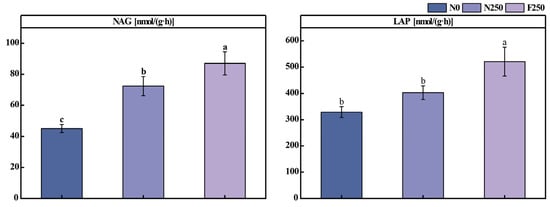
Figure A4.
Effects of long-term fertilization on the activities of N-cycling-related soil enzymes. Bars labeled with different letters indicate significant differences among treatments (p < 0.05). NAG: β-1,4-N-acetyl-glucosaminidase, LAP: leucine aminopeptidase.
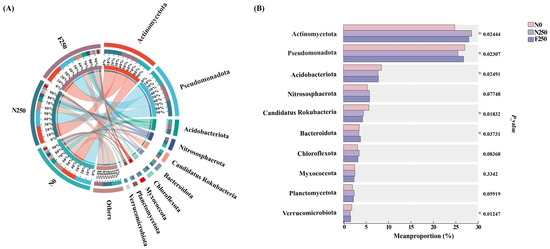
Figure A5.
Relative abundance of microbial taxa (>0.1%) associated with N-cycling genes at the phylum level (A) and pairwise comparisons among fertilization treatments (B). Asterisks denote significant differences: p < 0.05.
References
- Zhu, Z.L.; Chen, D.L. Nitrogen fertilizer use in China-Contributions to food production, impacts on the environment and best management strategies. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2002, 63, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Chen, X.; Lu, D.; Wang, H. Long-acting mechanisms of concentrated urea application-High urea concentrations are biological inhibitors. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 182, 104723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lei, F.; Li, D.; Yang, H.; Luo, W.; Zhu, Z.; Hu, X.; Lin, Q. Evaluation of nitrogen release characteristics and enhanced efficiency of a novel synthetic slow-release nitrogen fertilizer. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 5671–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Lin, H.; Gao, W.; Li, M. The effects of humic acid urea and polyaspartic acid urea on reducing nitrogen loss compared with urea. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 4425–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; Fugice, J.; Singh, U.; Lewis, T.D. Development of fertilizers for enhanced nitrogen use efficiency–Trends and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Yuan, L. Innovation and industrial development of green efficiency fertilizers in China. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2023, 29, 2143–2149. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Xu, M.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Yuan, L.; Zhao, B. Humic acid urea enhanced productivity and reduced active nitrogen loss in summer maize-winter wheat cropping system: A field lysimeter experiment. Field Crops Res. 2024, 319, 109656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, L.; Li, Y.; Wen, Y.; Xu, J.; Hu, S.; Zhao, B. Humic acids incorporated into urea at different proportions increased winter wheat yield and optimized fertilizer-nitrogen fate. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mekser, H.K.A.; Mohamed, Z.E.O.M.; Ali, M.A. Influence of humic acid and some micronutrients on yellow corn yield and quality. World Appl. Sci. J. 2014, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- García, A.C.; Santos, L.A.; Izquierdo, F.G.; Rumjanek, V.M.; Castro, R.N.; dos Santos, F.S.; de Souza, L.G.A.; Berbara, R.L.L. Potentialities of vermicompost humic acids to alleviate water stress in rice plants (Oryza sativa L.). J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 136, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampong, K.; Thilakaranthna, M.S.; Gorim, L.Y. Understanding the role of humic acids on crop performance and soil health. Front. Agron. 2022, 4, 848621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fang, F.; Wei, J.; Wu, X.; Cui, R.; Li, G.; Zheng, F.; Tan, D. Humic acid fertilizer improved soil properties and soil microbial diversity of continuous cropping peanut: A three-year experiment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, J.P.; McCulley, R.L.; Burke, I.C. Carbon fluxes, nitrogen cycling, and soil microbial communities in adjacent urban, native and agricultural ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2005, 11, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, H.M.; Mueller, R.C.; Lori, M.; Mayer, J.; Mäder, P.; Hartmann, M. Organic cropping systems alter metabolic potential and carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycling capacity of soil microbial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 203, 109737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, R.; Hei, J.; Li, Y.; Al Farraj, D.A.; Noor, F.; Wang, S.; He, X. Effects of humic acid fertilizer on the growth and microbial network stability of Panax notoginseng from the forest understorey. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, L.D.F.; Westmann, C.A.; Lovate, G.L.; de Siqueira, G.M.V.; Borelli, T.C.; Guazzaroni, M.E. Metagenomic approaches for understanding new concepts in microbial science. Int. J. Genom. 2018, 2018, 2312987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Gu, H.; Liu, J.; Wei, D.; Zhu, P.; Cui, X.A.; Zhou, B.; Chen, X.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; et al. Metagenomics reveals divergent functional profiles of soil carbon and nitrogen cycling under long-term addition of chemical and organic fertilizers in the black soil region. Geoderma 2022, 418, 115846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, H.; Han, M.; Yang, L. Soil metagenomics reveals the effect of nitrogen on soil microbial communities and nitrogen-cycle functional genes in the rhizosphere of Panax ginseng. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1411073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Hu, Q.; Mao, W.; Yang, Z.; Chen, H.; Sun, L.; Zhai, M. Metagenomics insights into the functional profiles of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles in a walnut orchard under various regimes of long-term fertilisation. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 148, 126887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahram, M.; Hildebrand, F.; Forslund, S.K.; Anderson, J.L.; Soudzilovskaia, N.A.; Bodegom, P.M.; Palme, J.B.; Anslan, S.; Coelho, L.P.; Harend, H.; et al. Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome. Nature 2018, 560, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Fish, J.A.; Gilman, M.; Sun, Y.; Brown, C.T.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Xander: Employing a novel method for efficient gene-targeted metagenomic assembly. Microbiome 2015, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, J.M.; Morales, B.; Lima, E.M.; de Bastos, F.; Morales, C.A.S.; de Araújo, E.F. Soil morphological, physical and chemical properties affecting Eucalyptus spp. productivity on Entisols and Ultisols. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 226, 105563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.; Khattak, R.A.; Sarir, M.S. Effect of different levels of lignitic coal derived humic acid on growth of maize plants. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2002, 33, 3567–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, B.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhu, T.; Ming, Y.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Wang, F.; Jiao, S.; Shi, L.; et al. The application of humic acid urea improves nitrogen use efficiency and crop yield by reducing the nitrogen loss compared with urea. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Yuan, Q.; Yuan, H. Changes of chemical properties of humic acids from crude and fungal transformed lignite. Fuel 2006, 85, 2402–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Six, J. Soil structure and microbiome functions in agroecosystems. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Ye, J.; Wang, H.; He, H. Soil metagenomic analysis on changes of functional genes and microorganisms involved in nitrogen-cycle processes of acidified tea soils. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 998178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Tang, S.; Zhou, J.; Wanek, W.; Gregory, A.S.; Ge, T.; Marsden, K.A.; Chadwick, D.R.; Liang, Y.; Wu, L.; et al. Long-term manure and mineral fertilisation drive distinct pathways of soil organic nitrogen decomposition: Insights from a 180-year-old study. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 207, 109840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Yang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Ye, J.; Wang, X.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Feng, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H. Microbial taxa distribution is associated with ecological trophic cascades along an elevation gradient. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yang, Z.; Yang, N.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, J.; et al. Wheat Yield, N Use Efficiency, Soil Properties, and Soil Bacterial Community as Affected by Long-Term Straw Incorporation and Manure Under Wheat–Summer Maize Cropping System in Southern Shanxi Province, China. Plants 2025, 14, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kpalari, D.F.; Mounkaila Hamani, A.K.; Hui, C.; Sogbedji, J.M.; Liu, J.; Le, Y.; Kama, R.; Gao, Y. Soil bacterial community and greenhouse gas emissions as responded to the coupled application of nitrogen fertilizer and microbial decomposing inoculants in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedling stage under different water regimes. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, F.; Bouziri, L.; Nicolardot, B.; Ranjard, L. Impact of wheat straw decomposition on successional patterns of soil microbial community structure. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wu, J.; Qu, X.; Li, J. Effects of organic wastes on structural characterizations of humic acid in semiarid soil under plastic mulched drip irrigation. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruczyńska, A.; Kuźniar, A.; Podlewski, J.; Słomczewski, A.; Grządziel, J.; Marzec-Grządziel, A.; Gałązka, A.; Wolińska, A. Bacteroidota structure in the face of varying agricultural practices as an important indicator of soil quality—A culture independent approach. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 342, 108252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, X.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q. A novel carbon-nitrogen coupled metabolic pathway promotes the recyclability of nitrogen in composting habitats. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 381, 129134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Cao, M.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Han, L.; Cai, Y.; Shi, X.; Ma, L.; Abdellah, Y.A.Y.; et al. Artificial Endosymbiosis of Pedobacter sp. DDGJ Boosts the Growth Potential, Stress Resistance and Productivity of Morchella Mushrooms. Microb. Biotechnol. 2025, 18, e70197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil health and carbon management. Food Energy Secur. 2016, 5, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Li, Z.; Wakelin, S.A.; Yu, W.; Liang, Y. Mineral fertilizer alters cellulolytic community structure and suppresses soil cellobiohydrolase activity in a long-term fertilization experiment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 55, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.Q.; Ding, L.J.; Xue, K.; Yao, H.Y.; Quensen, J.; Bai, S.J.; Wei, W.X.; Wu, S.J.; Jizhong Zhou Tiedje, J.M.; Zhu, Y.G. Long-term balanced fertilization increases the soil microbial functional diversity in a phosphorus-limited paddy soil. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Luo, S.; Xu, X.; Gou, Y.; Wang, J. The soil carbon cycle determined by GeoChip 5.0 in sugarcane and soybean intercropping systems with reduced nitrogen input in South China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 155, 103653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Fu, Y.; Li, P.; Qiao, J.; Li, H.; Wu, L.; Wang, B.; Lu, S. Exploring the effects of different fertilizer application durations on the functional microbial profiles of soil carbon and nitrogen cycling by using metagenomics in Paulownia plantations in a subtropical zone. Eur. J. For. Res. 2024, 143, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Jeffries, T.C.; Trivedi, C.; Anderson, I.C.; Lai, K.; McNee, M.; Flower, K.; Singh, B.P.; Minkey, D.; et al. Soil aggregation and associated microbial communities modify the impact of agricultural management on carbon content. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 3070–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, S.; Li, J.; Chen, J.I.; Wang, G.; Mayes, M.A.; Dzantor, K.E.; Hui, D.; Luo, Y. Soil extracellular enzyme activities, soil carbon and nitrogen storage under nitrogen fertilization: A meta-analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 101, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Q.; Zheng, M.; Su, Y.; Xiao, K.; Wang, K.; Li, D. Responses of soil microbial resource limitation to multiple fertilization strategies. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, M.; Shrestha, P.M.; Frenzel, P.; Conrad, R. Effect of nitrogen fertilization on methane oxidation, abundance, community structure, and gene expression of methanotrophs in the rice rhizosphere. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.M.; He, J.Z. Immediate effects of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium amendments on the methanotrophic activity and abundance in a Chinese paddy soil under short-term incubation experiment. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.N.; Schwaner, G.W.; Cumming, J.R.; Driscoll, T.P. Metagenomic reconstruction of nitrogen and carbon cycling pathways in forest soil: Influence of different hardwood tree species. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 156, 108226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Wu, J.; Li, C.; Yan, X.; Zhu, R.; Zhu, B.; et al. Effect of fertilization regimes and seasonal change on nosZ-denitrifying bacterial community in a double-rice paddy field. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, C.B.; Kumar, U.; Kaviraj, M.; Minick, K.J.; Mishra, A.K.; Singh, J.S. DNRA: A short-circuit in biological N-cycling to conserve nitrogen in terrestrial ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Xiao, C.; Xie, Y. Shedding light on the role of chemical bond in catalysis of nitrogen fixation. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Tan, W.; Tang, S.; Ling, Q.; Tang, C.; Qin, P.; Luo, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, F.; Li, Y. Metagenomics reveals taxon-specific responses of soil nitrogen cycling under different fertilization regimes in heavy metal contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rütting, T.; Boeckx, P.; Müller, C.; Klemedtsson, L. Assessment of the importance of dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium for the terrestrial nitrogen cycle. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 1779–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, J.; Wei, D.; Zhou, B.; Chen, X.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. Long-term application of nitrogen, not phosphate or potassium, significantly alters the diazotrophic community compositions and structures in a Mollisol in northeast China. Res. Microbiol. 2019, 170, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriswasdi, S.; Yang, C.C.; Iwasaki, W. Generalist species drive microbial dispersion and evolution. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ni, K.; Shi, Y.; Yi, X.; Ji, L.; Wei, S.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Ma, Q.; et al. Metagenomics reveals N-induced changes in carbon-degrading genes and microbial communities of tea (Camellia sinensis L.) plantation soil under long-term fertilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Pimentel, J.L.; Martin-Pozas, T.; Jurado, V.; Miller, A.Z.; Caldeira, A.T.; Fernandez-Lorenzo, O.; Sanchez-Moral, S.; Saiz-Jimenez, C. Prokaryotic communities from a lava tube cave in La Palma Island (Spain) are involved in the biogeochemical cycle of major elements. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Liu, G.; Chen, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Ai, S.; Wei, D.; Li, D.; Ma, B.; Tang, C.; et al. Long-term nutrient inputs shift soil microbial functional profiles of phosphorus cycling in diverse agroecosystems. ISME J. 2020, 14, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannoni, S.J.; Cameron Thrash, J.; Temperton, B. Implications of streamlining theory for microbial ecology. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1553–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Peng, Y.; Abbott, B.W.; Biasi, C.; Wei, B.; Zhang, D.; Jun Wang Yu, J.; Li, F.; Wang, G.; Kou, D.; et al. Phosphorus rather than nitrogen regulates ecosystem carbon dynamics after permafrost thaw. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 5818–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agric Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 25–106. [Google Scholar]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Saiya-Cork, K.; Long, T.; Osgood, M.P.; Neher, D.A.; Zak, D.R.; Norby, R.J. Soil microbial activity in a Liquidambar plantation unresponsive to CO2-driven increases in primary production. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2003, 24, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).