The Contrasting Ecological Effects of Farmland and Alfalfa Grassland Across Different Planting Scales in the North China Plain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Collection
2.1.1. Study Area
2.1.2. Data Collection and Processing
2.2. Robust Regression
2.3. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
2.3.1. Goal and Scope Definition
2.3.2. Inventory Analysis
2.3.3. Life Cycle Impact Assessment
3. Results
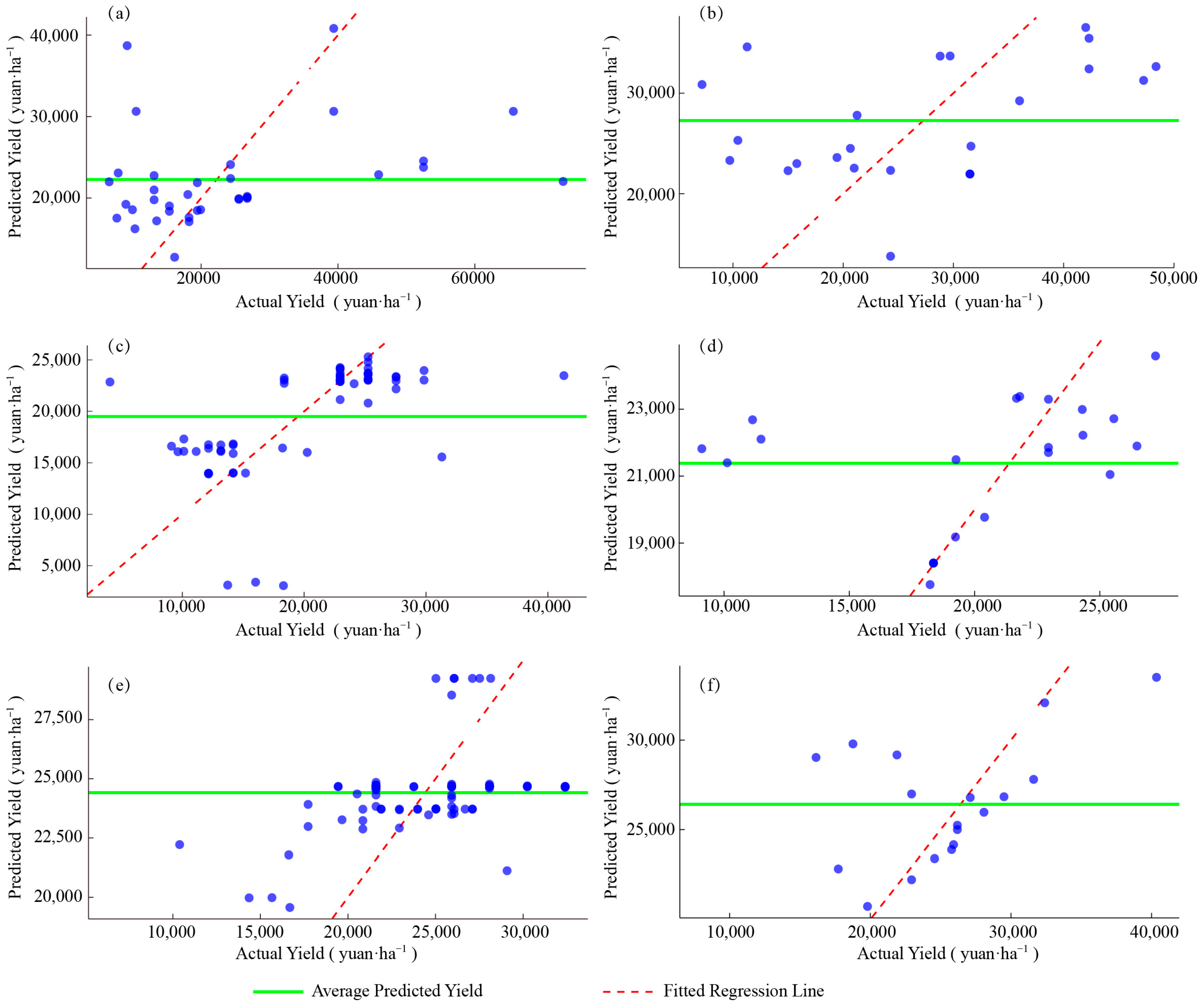
3.1. Predicted Yield Values from Robust Regression
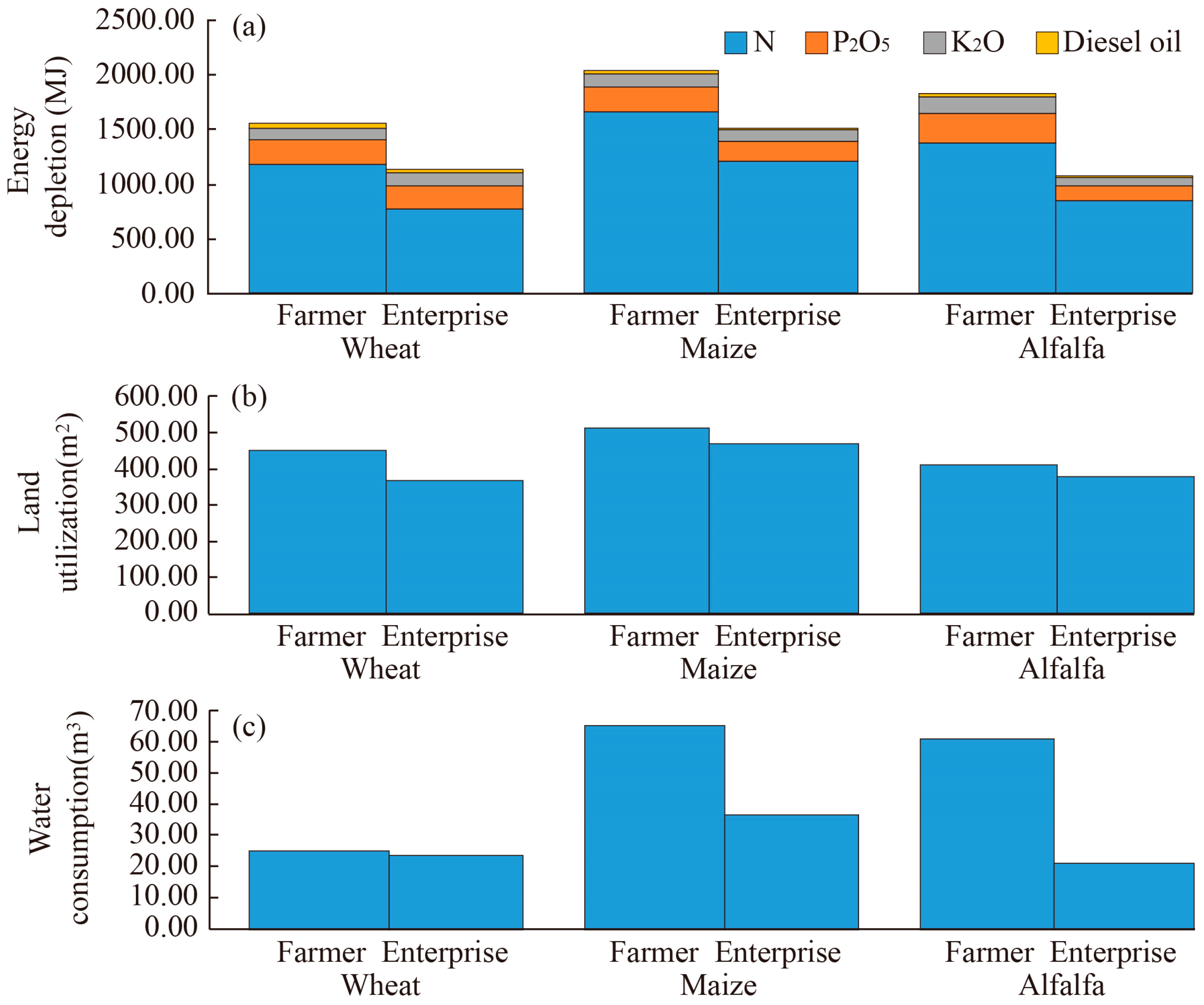
3.2. Resource Consumption
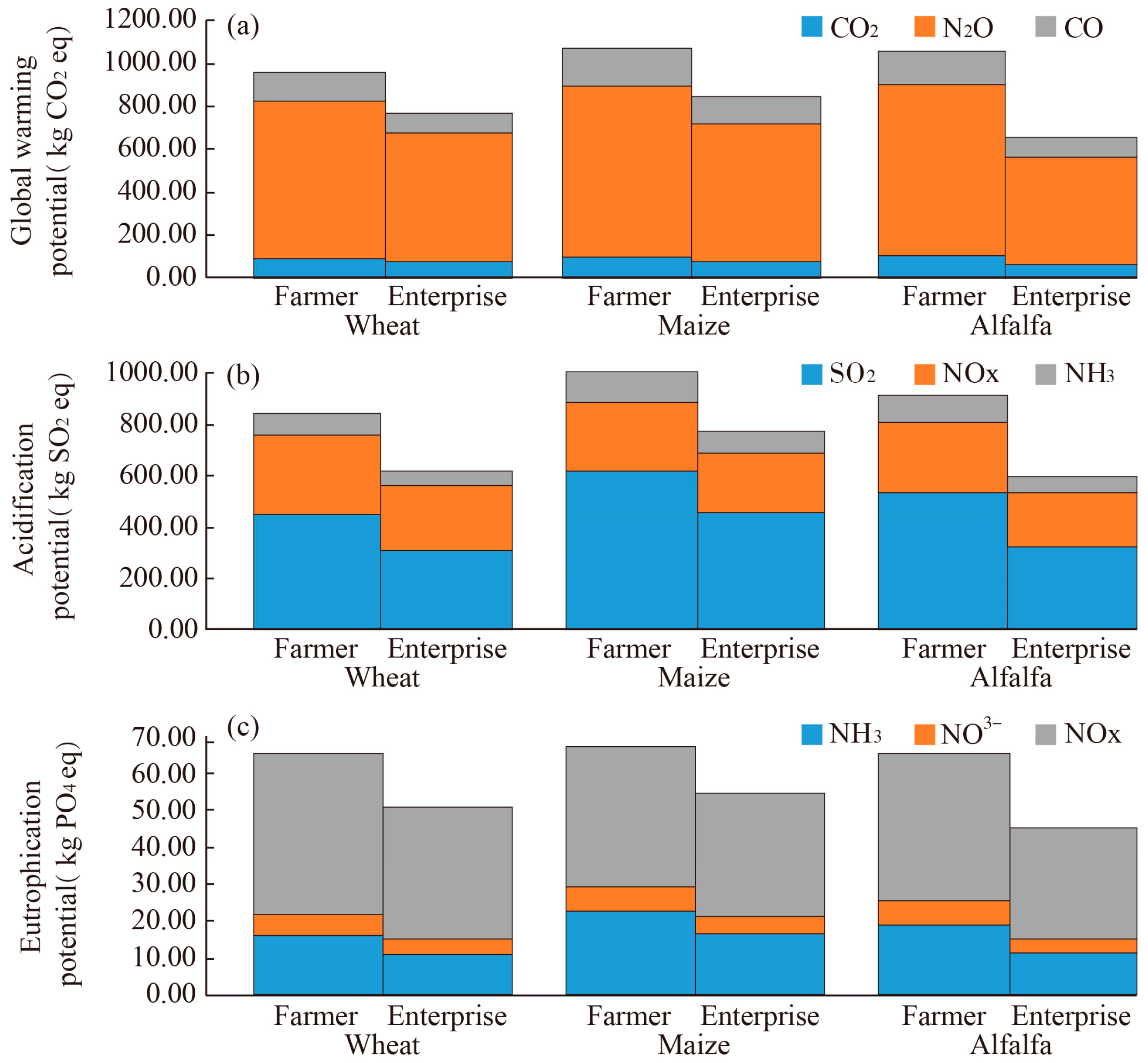
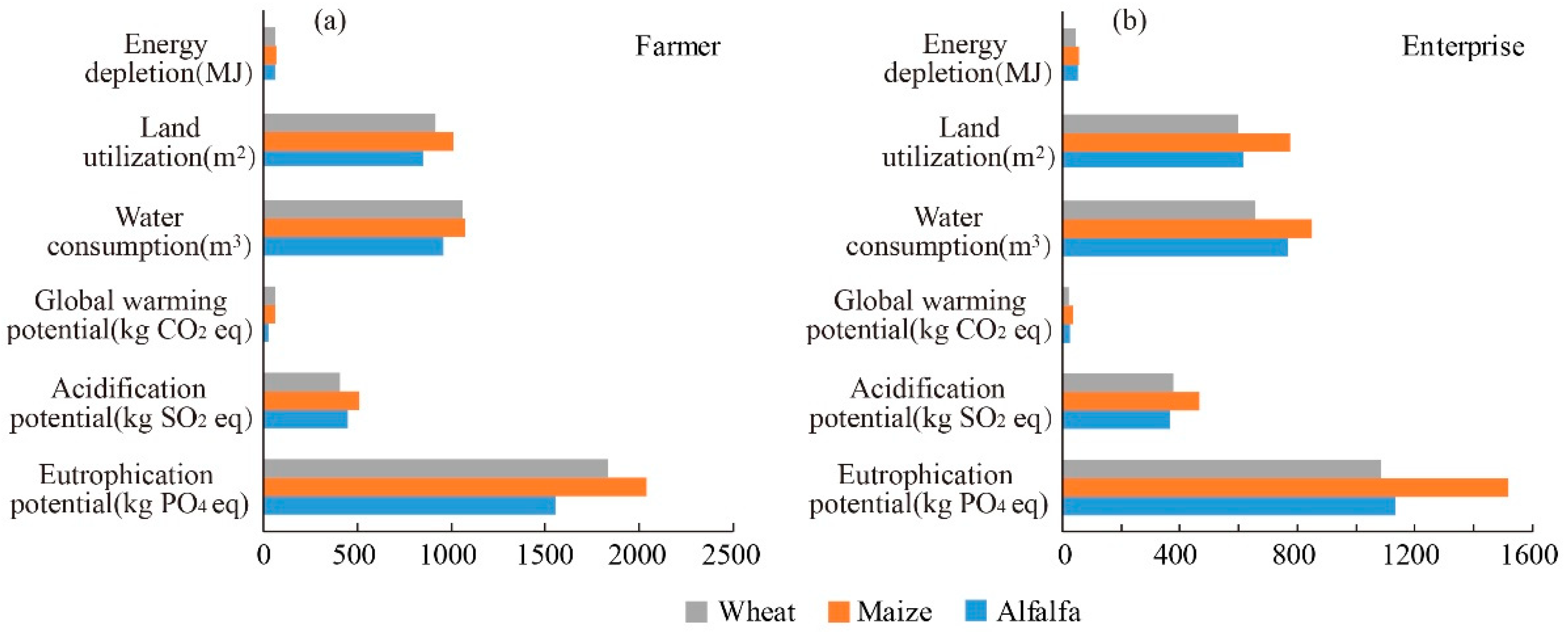
3.3. Environmental Emissions
3.4. Characterization of Environmental Indices
4. Discussion
4.1. Reasons for Differences in Resource Consumption and Environmental Effects
4.2. Similarities and Differences in Environmental Effects at Different Scales
4.3. Optimizing Management and Planting Mode
4.4. The Limitations and Uncertainties of the Research Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| LCA | Life Cycle Assessment |
| LCI | Life Cycle Inventory |
| LCIA | Life Cycle Impact Assessment |
| FU | Functional Unit |
| GY | Grain Yield |
| MS | Material Stage |
| FS | Farming Stage |
| ED | Energy Depletion |
| LU | Land Utilization |
| WC | Water Consumption |
| GW | Global Warming (kg CO2 eq) |
| AC | Acidification (kg SO2 eq) |
| EP | Eutrophication (kg PO4 eq) |
References
- Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Gao, L.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, Z.; Fan, T.; Wei, K.; Huang, L. Nutrient-derived environmental impacts in Chinese agriculture during 1978–2015. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.L.; Liu, C.Y.; Xie, J.N.; Han, L.; Zhang, C.H.; Guo, D.W.; Niu, J.Z.; Jin, H.; McConkey, B.G. Life cycle assessment on agricultural production: A mini review on methodology, application, and challenges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xiong, J.; Du, T.; Ju, X.; Gan, Y.; Li, S.; Xia, L.; Shen, Y.; Pacenka, S.; Steenhuis, T.S.; et al. Diversifying crop rotation increases food production, reduces net greenhouse gas emissions and improves soil health. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Tu, C.; Fu, C.; Luo, Y. The Current Research Progress and Prospects of Cultivated and Grassland Soil Health-A Review. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2022, 59, 625–642. [Google Scholar]
- Köninger, M.; von Velsen-Zerweck, A.; Eiberger, C.; Löffler, C.; Töpper, A.; Visscher, C.; Reckels, B.; Vervuert, I. Nutrient Composition and Feed Hygiene of Alfalfa, Comparison of Feed Intake and Selected Metabolic Parameters in Horses Fed Alfalfa Haylage, Alfalfa Hay or Meadow Hay. Animals 2024, 14, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xia, H.; Qin, X.J. Effect of mixture sowing on biomass allocation in the artificially-planted pastures, Southeastern Tibetan. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Hou, M.; Yang, J.; Ma, G. Effects of Different Previous Crops on Soil Nutrients and Wheat Yield under Phosphorus Scarcity in the North China Plain. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2022, 37, 150–158. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.T.; Tian, H.Q.; Shi, H.; Zhang, J.F.; Wang, X.K.; Pan, S.F.; Yang, J. Increased greenhouse gas emissions intensity of major croplands in China: Implications for food security and climate change mitigation. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 6116–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhashim, R.; Deepa, R.; Anandhi, A. Environmental Impact Assessment of Agricultural Production Using LCA: A Review. Climate 2021, 9, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brentrup, F.; Küsters, J.; Lammel, J.; Barraclough, P.; Kuhlmann, H. Environmental impact assessment of agricultural production systems using the life cycle assessment (LCA) methodology II. The application to N fertilizer use in winter wheat production systems. Eur. J. Agron. 2004, 20, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, R. Revisiting the evaluation of robust regression techniques for crop yield data detrending. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2010, 92, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, Y.; Ren, C.; Ma, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, W. Comparative analysis of three fitting methods of rice trend yield. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2017, 25, 345–355. [Google Scholar]
- Maimaitijiang, M.; Sagan, V.; Sidike, P.; Hartling, S.; Esposito, F.; Fritschi, F.B. Soybean yield prediction from UAV using multimodal data fusion and deep learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Werf, H.M.G.; Knudsen, M.T.; Cederberg, C. Towards better representation of organic agriculture in life cycle assessment. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebitzer, G.; Ekvall, T.; Frischknecht, R.; Hunkeler, D.; Norris, G.; Rydberg, T.; Schmidt, W.P.; Suh, S.; Weidema, B.P.; Pennington, D.W. Life cycle assessment: Part 1: Framework, goal and scope definition, inventory analysis, and applications. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 701–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, W.; Liu, W.; Bao, Y. Life cycle assessment of the winter wheat-summer maize production system on the North China Plain. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2007, 14, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Dale, B.E.; Jenkins, R. Life cycle assessment of corn grain and corn stover in the United States. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2009, 14, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Shao, X.; Tian, S.; Li, H.; Huang, Y. Life cycle assessment comparison of three typical energy utilization ways for corn stover in China. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 152, 106199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, S.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G. Comparative environmental performance of lignocellulosic ethanol from different feedstocks. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zelm, R.; Seroa da Motta, R.d.P.; Lam, W.Y.; Menkveld, W.; Broeders, E. Life cycle assessment of side stream removal and recovery of nitrogen from wastewater treatment plants. J. Ind. Ecol. 2020, 24, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi-Mobtaker, H.; Kaab, A.; Rafiee, S.; Nabavi-Pelesaraei, A. A comparative of modeling techniques and life cycle assessment for prediction of output energy, economic profit, and global warming potential for wheat farms. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 4922–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Luo, Y.T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.T.; Shen, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Shang, S.P. Comparison on environmental impacts of cereal and forage production in the Loess Plateau of China: Using life cycle assessment with uncertainty and variability analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 135094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekvall, T.; Finnveden, G. Allocation in ISO 14041—A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2001, 9, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, H.; Yan, X.M.; Xing, R.; Jiang, A.Y. The empirical effect of agricultural social services on pesticide inputs. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.H.; Serrenho, A.C. Greenhouse gas emissions from nitrogen fertilizers could be reduced by up to one-fifth of current levels by 2050 with combined interventions. Nat. Food 2023, 4, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabathuler, H. LCA History: Centrum voor Milieukunde Leiden (CML): The CML story how environmental sciences entered the debate on LCA. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 1997, 2, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidema, B.P.; Wesnæs, M.S. Data quality management for life cycle inventories—An example of using data quality indicators. J. Clean. Prod. 1996, 4, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleeswijk, A.W.; van Oers, L.F.C.M.; Guinée, J.B.; Struijs, J.; Huijbregts, M.A.J. Normalisation in product life cycle assessment: An LCA of the global and European economic systems in the year 2000. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taki, M.; Soheili-Fard, F.; Rohani, A.; Chen, G.; Yildizhan, H. Life cycle assessment to compare the environmental impacts of different wheat production systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhard, B. Modeling Crop Rotations and Co-Products in Agricultural Life Cycle Assessments; Springer: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Notarnicola, B. Life Cycle Assessment in the Agri-Food Sector: Case Studies, Methodological Issues and Best Practices; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann, I.T.; Moltesen, A. Does it matter which Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) tool you choose?—A comparative assessment of SimaPro and GaBi. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 86, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinée, J. Handbook on life cycle assessment—Operational guide to the ISO standards. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2001, 6, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Breedveld, L.; Huppes, G.; de Koning, A.; van Oers, L.; Suh, S. Normalisation figures for environmental life-cycle assessment: The Netherlands (1997/1998), Western Europe (1995) and the world (1990 and 1995). J. Clean. Prod. 2003, 11, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.M.; Beare, D.J.; Bennett, E.M.; Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Ingram, J.S.I.; Jaramillo, F.; Ortiz, R.; Ramankutty, N.; Sayer, J.A.; Shindell, D. Agriculture production as a major driver of the Earth system exceeding planetary boundaries. Ecol. Soc. 2017, 22, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, J.; Poulter, B.; Sardans, J.; Ciais, P.; van der Velde, M.; Bopp, L.; Boucher, O.; Godderis, Y.; Hinsinger, P.; Llusia, J.; et al. Human-induced nitrogen-phosphorus imbalances alter natural and managed ecosystems across the globe. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.S.; Niu, S.L. A global analysis of soil acidification caused by nitrogen addition. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 024019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Li, Z.H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J.B.; Liu, P.; Li, R.F.; Yang, Q.L.; Dong, S.T.; Zhang, J.W.; Zhao, B. Narrowing Yield Gaps and Enhancing Nitrogen Utilization for Summer Maize (Zea mays L) by Combining the Effects of Varying Nitrogen Fertilizer Input and Planting Density in DSSAT Simulations. Front. Plant. Sci. 2020, 11, 560466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Xu, C.C.; Ridoutt, B.G.; Wang, X.C.; Ren, P.A. Nitrogen and phosphorus losses and eutrophication potential associated with fertilizer application to cropland in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 159, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotz, S.; Gravely, E.; Mosby, I.; Duncan, E.; Finnis, E.; Horgan, M.; LeBlanc, J.; Martin, R.; Neufeld, H.T.; Nixon, A.; et al. Automated pastures and the digital divide: How agricultural technologies are shaping labour and rural communities. J. Rural. Stud. 2019, 68, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Gan, W. Effect of biased reduction targets on agricultural green innovation: An empirical study on the strategy of zero growth in synthetic fertilizer use. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2024, 34, 186–196. [Google Scholar]
- German, L.A.; Hepinstall-Cymerman, J.; Biggs, T.; Parker, L.; Salinas, M. The environmental effects of sugarcane expansion: A case study of changes in land and water use in southern Africa. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 121, 102240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Lin, K.Y.A.; Oh, W.D.; Lisak, G. Metal-organic frameworks for pesticidal persistent organic pollutants detection and adsorption—A mini review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Yang, F.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Q. The impact of green agricultural subsidies on fertilizer reduction and its mechanism: Evidence from pilot policies for organic fertilizer subsidies. Resour. Sci. 2023, 45, 1515–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Zou, Y.; Wanger, T.C.; Zhou, W.W.; Gc, Y.D.; Lu, Y.H. Agro-ecology science relates to economic development but not global pesticide pollution. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 307, 114529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Davis, K.F.; van der Werf, W.; Ritsema, C.J.; Pacenka, S.; Zhang, F.; Siddique, K.H.; Du, T. Diversified crop rotations enhance groundwater and economic sustainability of food production. Food Energy Secur. 2021, 10, e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, Y.X.; Li, H.; Li, S.S.; Wang, X.L.; Chai, H. Difference of Bacterial Community Structure in the Meadow, Maize, and Continuous Cropped Alfalfa in Northeast China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 794848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Portillo, D.G.; Arroyo, B.; Morales, M.B. The adequacy of alfalfa crops as an agri-environmental scheme: A review of agronomic benefits and effects on biodiversity. J. Nat. Conserv. 2022, 69, 126253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liao, W.M.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, H.L. Impact of high standard farmland construction policy on chemical fertilizer reduction: A case study of China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1256028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.M.; Yang, J.Y.; Liu, S.; Hoogenboom, G. An evaluation of the statistical methods for testing the performance of crop models with observed data. Agric. Syst. 2014, 127, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

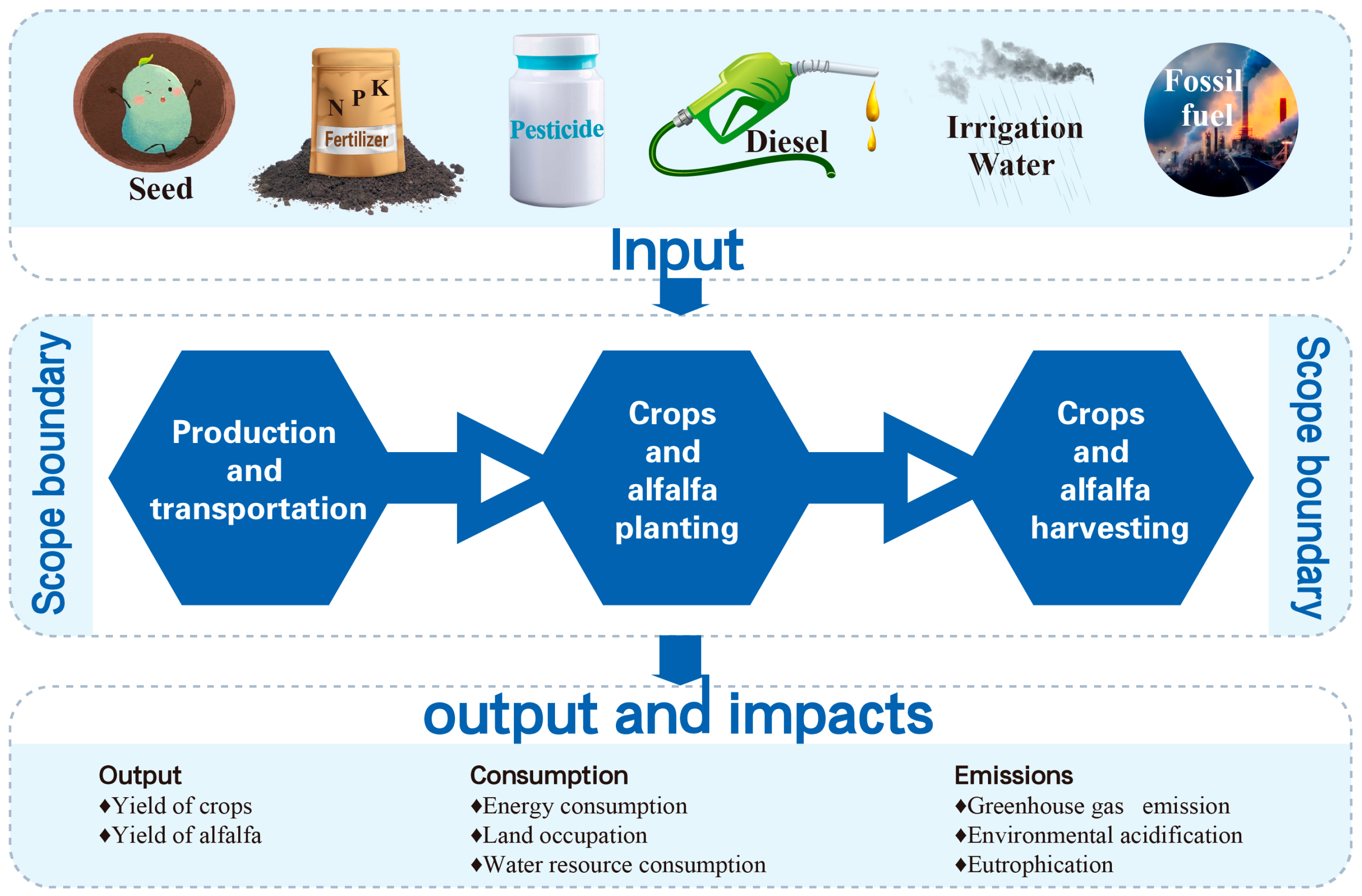
| Inventory | Data Source |
|---|---|
| Raw materials producing | |
| Species, manufacturers, and dosages of fertilizers | Field investigation |
| Species, manufacturers, and dosages of farm chemicals | Field investigation |
| Agricultural film | Literature |
| Seed | Literature |
| Transportation of raw materials | Field investigation |
| Cultivating | |
| Fuel consumption and emission of field-turning machine | Field investigation and the literature |
| Water and electricity consumption of irrigation | Field investigation |
| Emissions of field greenhouse gas | Literature |
| Harvesting | |
| Fuel consumption and emission of harvesting machine | Field investigation and the literature |
| Transportation of products | Field investigation |
| Scale | Crop Type | Land Use (ha) | N (kg/ha/FU) | P2O5 (kg/ha/FU) | K2O (kg/ha/FU) | Pesticide (kg/ha/FU) | Irrigation Water (m3/ha/FU) | Diesel Fuel (kg/ha/FU) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farmer | Wheat | 12.80 | 17.97 | 10.45 | 9.56 | 0.04 | 64.92 | 6.67 |
| Enterprise | 255.35 | 13.05 | 8.47 | 7.99 | 0.02 | 36.41 | 6.22 | |
| Farmer | Maize | 12.87 | 14.88 | 12.97 | 11.62 | 0.04 | 60.85 | 7.36 |
| Enterprise | 240.24 | 9.20 | 6.12 | 5.92 | 0.03 | 20.95 | 6.08 | |
| Farmer | Alfalfa | 40.92 | 12.79 | 10.38 | 8.78 | 0.03 | 24.98 | 8.76 |
| Enterprise | 486.23 | 8.33 | 9.94 | 9.69 | 0.03 | 23.40 | 7.27 |
| Environmental Impact Category | Unit | Reference Value | Weight | Emission and Equivalent Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy depletion | MJ/a | 2,590,457 | 0.15 | |
| Land use | m2 | 5423 | 0.12 | |
| Water depletion | m3 | 8800 | 0.13 | |
| CO2 (1) | ||||
| Global warming | kg CO2 eq | 6869 | 0.12 | CO (2) |
| CH4 (21) | ||||
| N2O (310) | ||||
| SO2 (1) | ||||
| Acidification | kg SO2 eq | 56.26 | 0.14 | NOx (0.7) |
| NH3 (1.88) | ||||
| NH3 (0.35) | ||||
| Eutrophication | kg PO4 eq | 1.88 | 0.12 | NO3-N (0.42) |
| NOx (0.1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Shao, C.; Wang, L.; Xin, X. The Contrasting Ecological Effects of Farmland and Alfalfa Grassland Across Different Planting Scales in the North China Plain. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102432
Zhu X, Li Y, Liu Z, Shao C, Wang L, Xin X. The Contrasting Ecological Effects of Farmland and Alfalfa Grassland Across Different Planting Scales in the North China Plain. Agronomy. 2025; 15(10):2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102432
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xiaoyu, Yutong Li, Zhongkuan Liu, Changliang Shao, Lulu Wang, and Xiaoping Xin. 2025. "The Contrasting Ecological Effects of Farmland and Alfalfa Grassland Across Different Planting Scales in the North China Plain" Agronomy 15, no. 10: 2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102432
APA StyleZhu, X., Li, Y., Liu, Z., Shao, C., Wang, L., & Xin, X. (2025). The Contrasting Ecological Effects of Farmland and Alfalfa Grassland Across Different Planting Scales in the North China Plain. Agronomy, 15(10), 2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102432








