Breeding Evaluation of Potato Hybrids for Late Blight Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
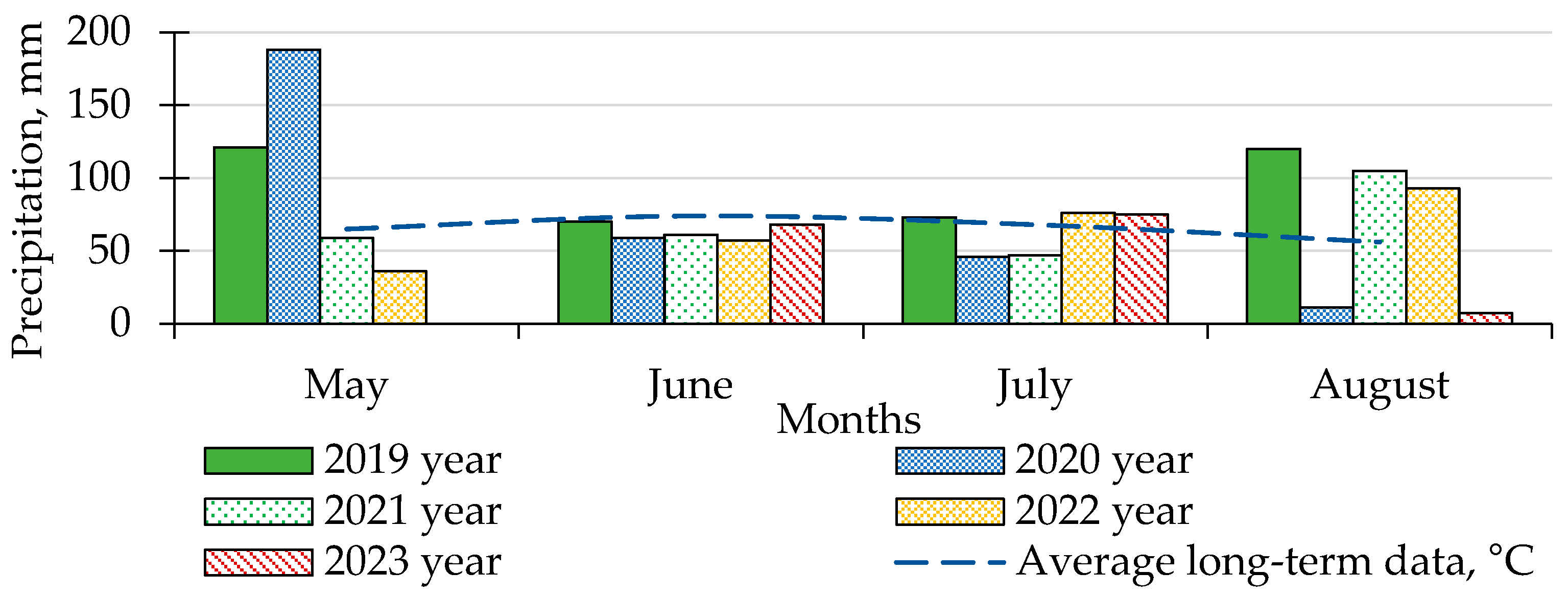
2.1. Description of Experimental Site and Characterization of Climate and Soil
2.2. Plant Materials
2.3. Trial Design and Management
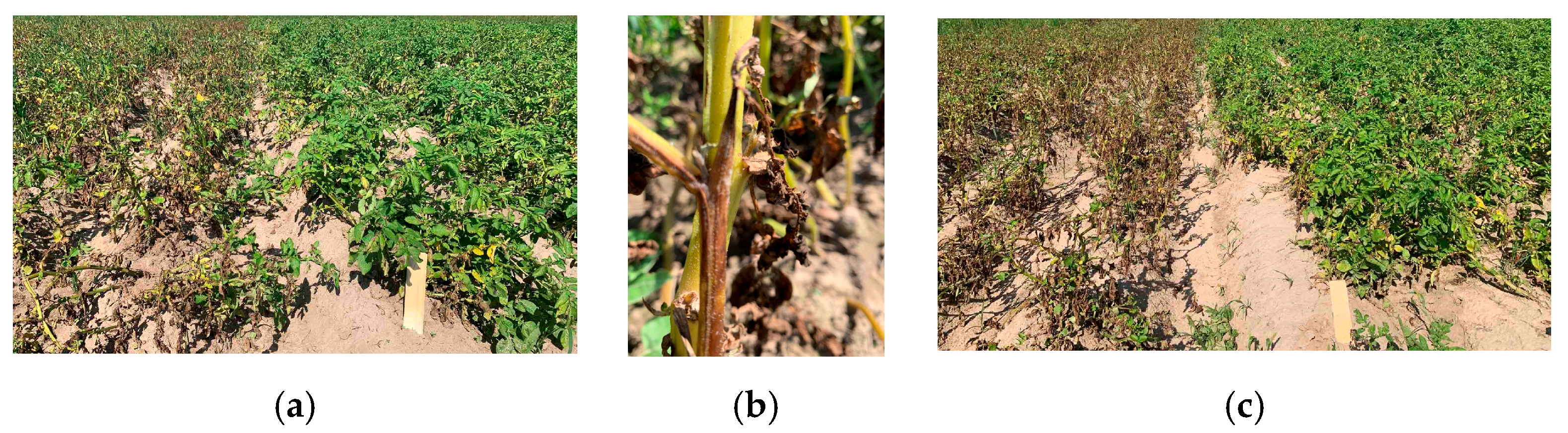
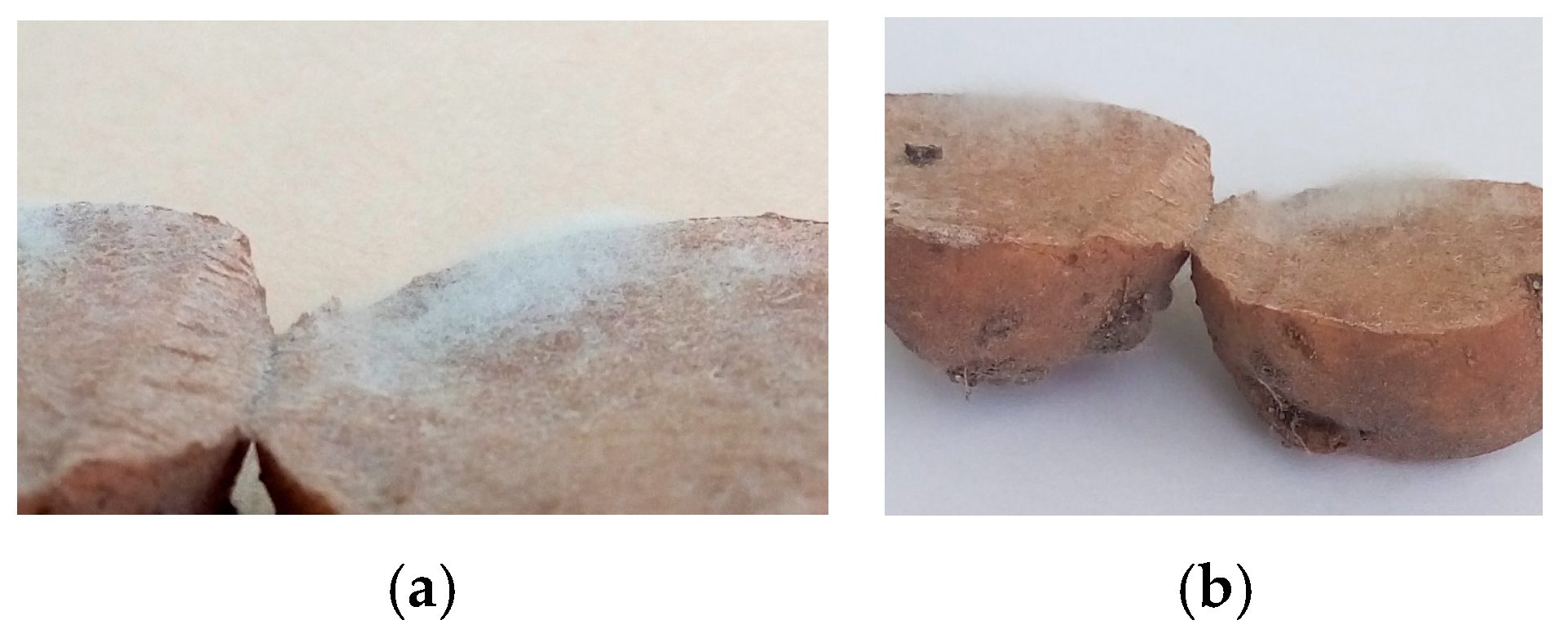
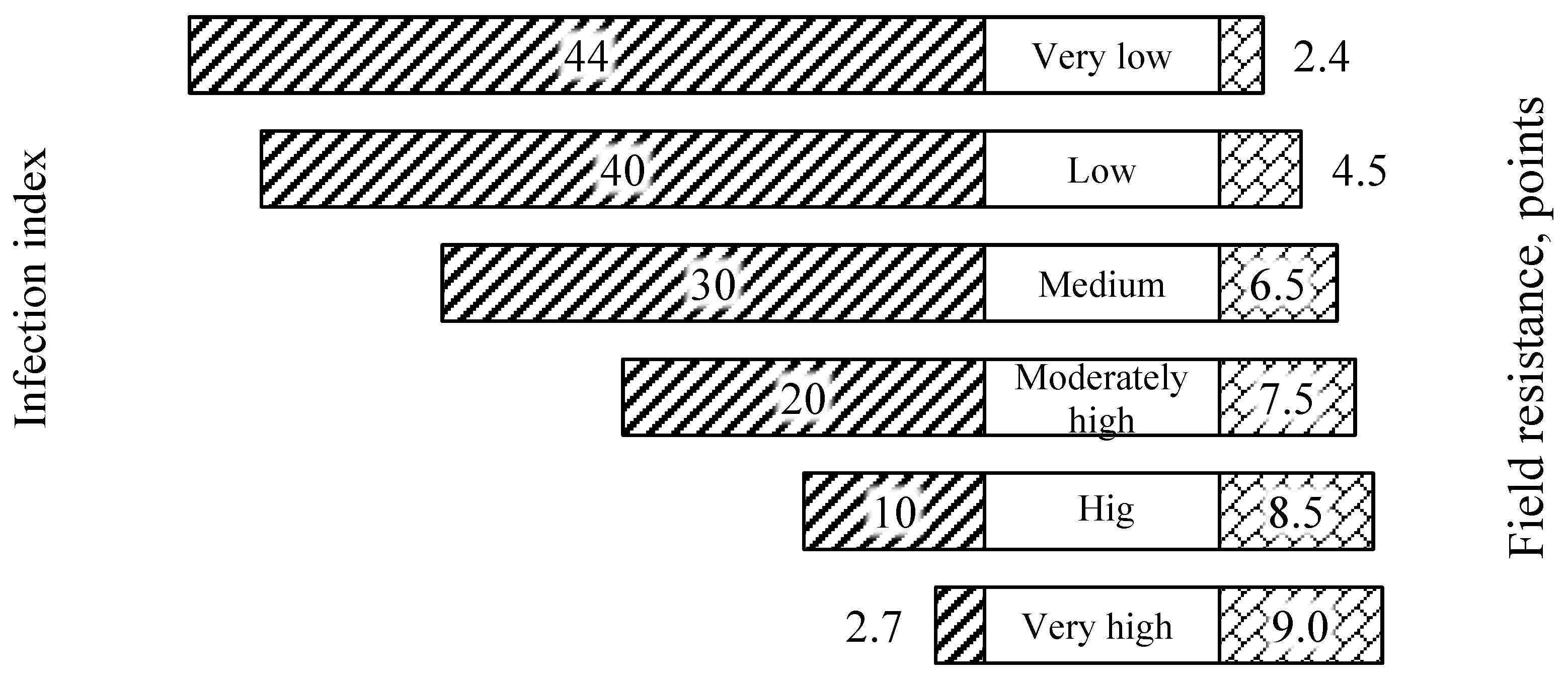
2.4. Data Collection
- a1, a2, a3—the diameter of the affected leaf surface, mm;
- b1, b2, b3—scores of fungal sporulation on the affected leaf surface (0–4);
- n1, n2, n3—the incubation period of the disease manifestation on the leaves, days.
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Influence of Weather Conditions on the Development of Late Blight
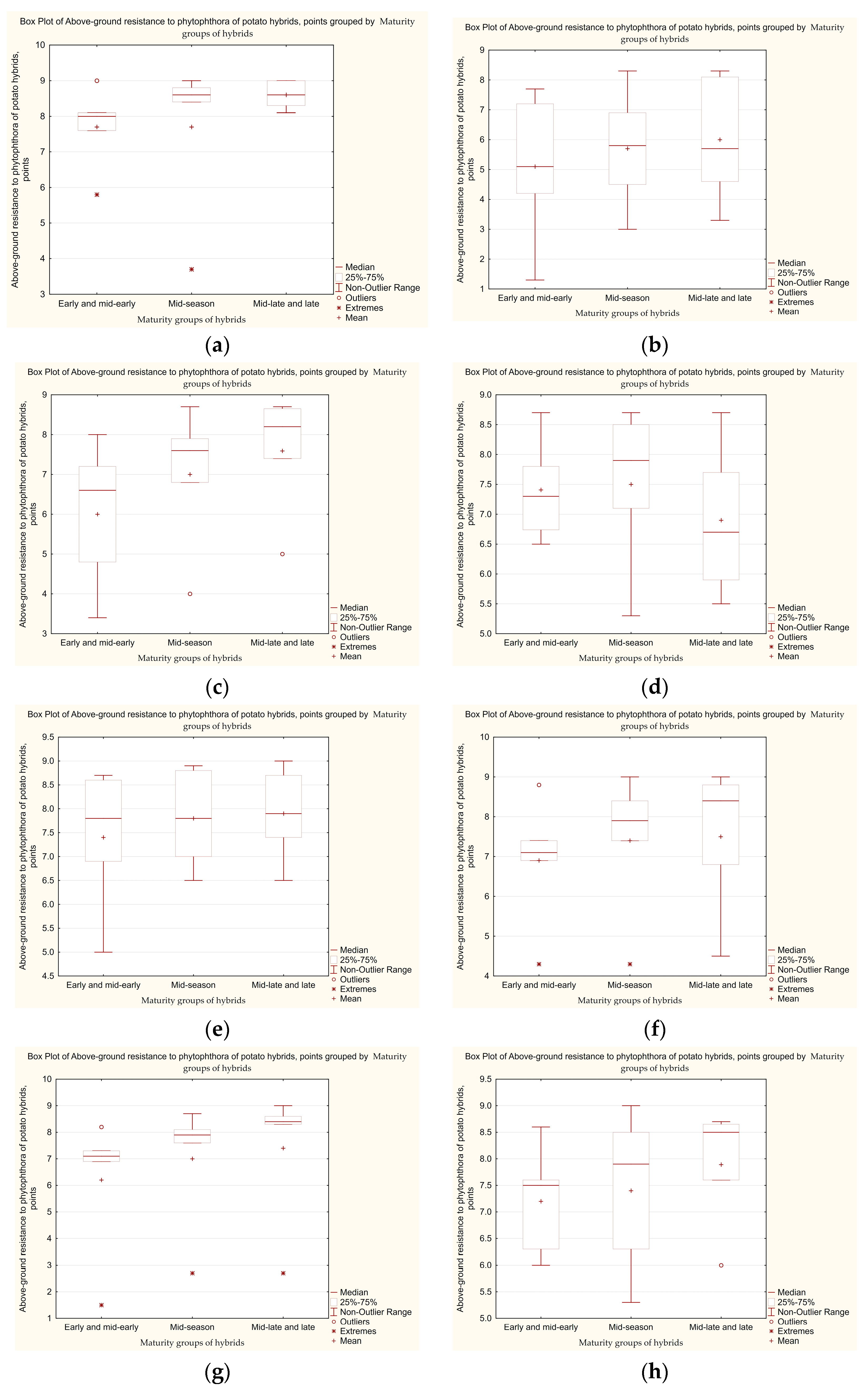
3.2. Laboratory Analysis of Late Blight Development on Leaves of Potato Hybrids of Different Maturity
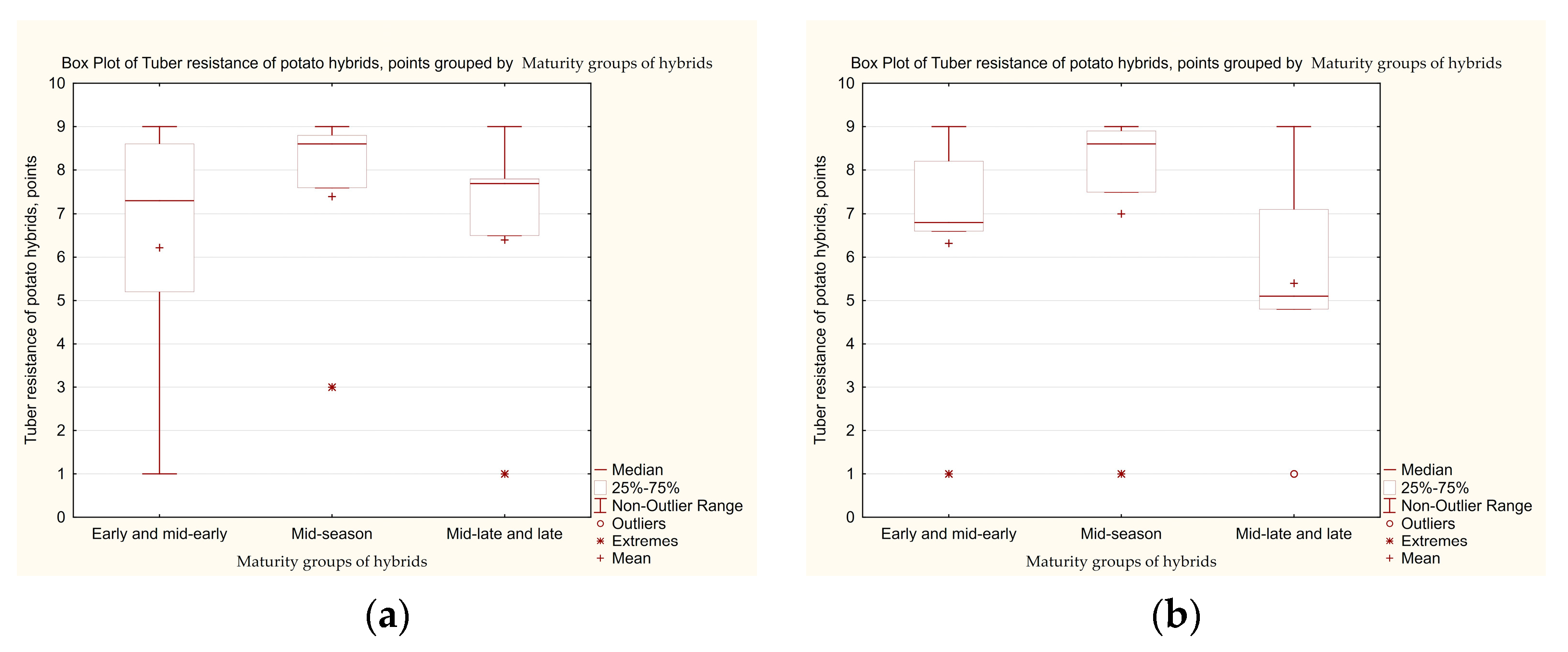
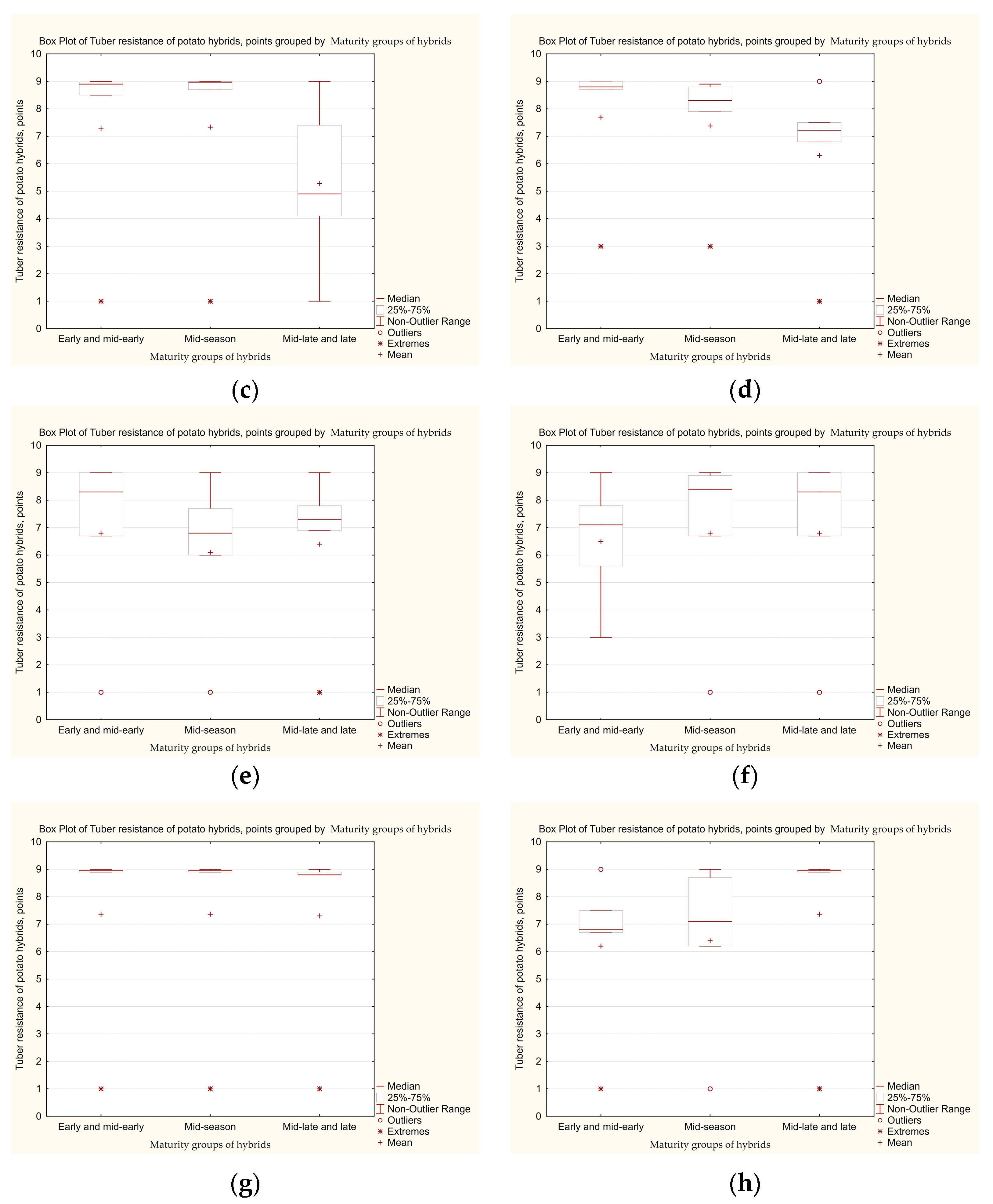
3.3. Determination of the Level of Tolerance of Potato Hybrid Tubers to Late Blight, Taking into Account the Influence of Genetic Factors Related to the Maturity Group
3.4. Analysis of Heritability of Late Blight Resistance Trait in Potato Hybrids
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Song, S.; Xie, S.; Kang, F. Study on starch content detection and visualization of potato based on hyperspectral imaging. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 4420–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsedaley, B. Late Blight of Potato (Phytophthora infestans) Biology, Economic Importance and its Management Approaches. J. Biol. Agric. Healthc. 2014, 4, 215–225. [Google Scholar]
- Bulgakov, V.; Holovach, I.; Ruzhylo, Z.; Fedosiy, I.; Ihnatiev, Y.; Olt, J. Theory of oscillations performed by tools in spiral potato separator. Agron. Res. 2020, 18, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zhou, S. Potato late blight caused by Phytophthora infestans: From molecular interactions to integrated management strategies. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 3456–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimsteine, G. Phytophthora infestans Populations in Latvia. Proc. Latv. Acad. Sci. Sect. B Nat. Exact Appl. Sci. 2008, 62, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domazakis, E.; Lin, X.; Aguilera-Galvez, C.; Wouters, D.; Bijsterbosch, G.; Wolters, P.J.; Vleeshouwers, V.G.A.A. Effectoromics-based identification of cell surface receptors in potato. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1578, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Duan, S.; Xu, J.; Zheng, J.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; Li, B.; Li, G.; Jin, L. Late blight resistance evaluation and genome-wide assessment of genetic diversity in wild and cultivated potato species. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 710468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynov, V.; Chizhik, V. Genetics of pathogen–host interaction by the example of potato late blight disease. Russ. J. Genet. 2020, 56, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taktaev, B.; Podberezko, I.; Janse, L. Field Evaluation of Ukrainian Potato Varieties for Resistance to Fungal and Bacterial Pathogens in the Polissya Area of Ukraine. Res. Agric. Sci. 2024, 55, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgakov, V.; Pascuzzi, S.; Ivanovs, S.; Ruzhylo, Z.; Fedosiy, I.; Santoro, F. A new spiral potato cleaner to enhance the removal of impurities and soil clods in potato harvesting. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonets, T.; Furdyha, M. Characteristics of potato varieties according to adaptability parameters researched in the forest zone of Ukraine. AgroLife Sci. J. 2022, 11, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilchuk, R.; Zaviriukha, P.; Andrushko, O.; Kosylovych, H.; Holiachuk, Y. Creation of potato hybrids (Solanum tuberosum) progeny with high field resistance against phytophotorosis. Sci. Horiz. 2023, 26, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzyńska, K.; Trawczyński, C.; Pietraszko, M. Environmental and Agronomical Factors Limiting Differences in Potato Yielding between Organic and Conventional Production System. Agriculture 2023, 13, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, W.; Wharton, P.; Hammerschmidt, R.; Abuel Samen, F.; Douches, D. Late Blight. In Michigan State University Extension Bulletin E–2945; Michigan State University: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2013; Available online: https://archive.lib.msu.edu/DMC/extension_publications/e2945/E2945-2004.PDF (accessed on 21 February 2025).
- Aboltins, A.; Rucins, A.; Bobos, I.; Fedosiy, I.; Komar, O.; Zavadska, O.; Zavgorodniy, V. Evaluation of Productivity and Morphological Variability of Asparagus Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp. subsp. sesquipedalis (L.) Verdc.) Cultivars Intended for Vegetable Production. Agronomy. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedosiy, I.; Bobos, I.; Zavadska, O.; Komar, O.; Tonkha, O.; Furdyha, M.; Olt, J. Research into properties of blue melilot and fenugreek cultivated using different sowing times. Agron. Res. 2022, 20, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondus, R.; Kharchenko, Y.; Furdyga, M.; Mishchenko, L.; Podhaietsky, A.; Hordienko, V.; Hordienko, O.; Koval, V. Polymorphism of the available potato gene pool for resistance to abiotic and biotic factors of the environment and its practical use. J. V.N. Karazin Kharkiv Natl. Univ. Ser. Biol. 2022, 38, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadska, O.; Bobos, I.; Fedosiy, I.; Podpryatov, G.; Olt, J. Studying the storage and processing quality of the carrot taproots (Daucus carota) of various hybrids. Agron. Res. 2020, 18, 2271–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluchowska, P.; Śliwka, J.; Yin, Z. Late blight resistance genes in potato breeding. Planta 2022, 255, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgakov, V.; Kuvachov, V.; Nozdrovický, L.; Findura, P.; Smolinskyi, S.; Ihnatiev, Y. The study of movement of the wide span tractor-based field machine unit with power method of its control. Acta Technol. Agric. 2018, 21, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shandil, R.K.; Chakrabarti, S.K.; Singh, B.P.; Sharma, S.; Sundaresha, S.; Kaushik, S.K.; Bhatt, A.K.; Sharma, N.N. Genotypic background of the recipient plant is crucial for conferring RB gene mediated late blight resistance in potato. BMC Genet. 2017, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilchuk, R.; Ilchuk, Y.; Koval, A.; Mialkovsky, R.; Holovatiuk, R. Analysis of potato source material-main stage of selection work. Ukr. J. Ecol. 2021, 11, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Nasr-Esfahani, M. An IPM plan for early blight disease of potato Alternaria solani sorauer and A. alternata (Fries.) Keissler. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2022, 55, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, T.; Saville, A.; Myers, K.; Tewari, S.; Cooke, D.E.L.; Tripathy, S.; Fry, W.E.; Ristaino, J.B.; Guha Roy, S. Large sub-clonal variation in Phytophthora infestans from recent severe late blight epidemics in India. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pysarenko, N.; Furdyha, M.; Zakharchuk, N.; Hordiienko, V. Resistance status of potato varieties to early blight under changing climate conditions in Polissia, Ukraine. Sci. Prog. Innov. 2025, 28, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossei, J.; Uptmoor, R.; Thieme, R.; Nachtigall, M.; Hammann, T. Insights into the genetic basis of the pre-breeding potato clones developed at the Julius Kühn Institute for high and durable late blight resistance. Plant Genet. Resour. 2021, 19, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, H.S.; Jansky, S.H.; Halterman, D.A. Screening of Wild Potatoes Identifies New Sources of Late Blight Resistance. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogozina, E.V.; Beketova, M.P.; Muratova, O.A.; Kuznetsova, M.; Khavkin, E.E. Stacking resistance genes in multiparental interspecific potato hybrids to anticipate late blight outbreaks. Agronomy 2021, 11, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogozina, E.V.; Gurina, A.A.; Chalaya, N.A.; Zoteyeva, N.M.; Kuznetsova, M.A.; Beketova, M.P.; Muratova, O.A.; Sokolova, E.A.; Drobyazina, P.E.; Khavkin, E.E. Diversity of Late Blight Resistance Genes in the VIR Potato Collection. Plants 2023, 12, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiha, T.K.; Rahman, M.A.; Islam, S.; Jalal, N.; Islam, A.; Nahiyan, A.S.M. Exploring potato diversity: A comprehensive genetic and phenotypic analysis of quantitative and qualitative traits. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2024, 60, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keijzer, P.; van Bueren, E.T.L.; Engelen, C.J.M.; Hutten, R.C.B. Breeding late blight resistant potatoes for rganic farming–a collaborative model of participatory plant breeding: The Bioimpuls project. Potato Res. 2021, 65, 349–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek, K.; Jupe, F.; Witek, A.I.; Baker, D.; Clark, M.D.; Jones, J.D. Accelerated cloning of a potato late blight-resistance gene using RenSeq and SMRT sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Han, Z.; Lu, Y.; Han, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; He, H. Expression and analysis of StNR and StNiRs, key enzyme genes of nitrogen assimilation in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) with different nitrogen efficiencies. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, S.; Verma, M.R.; Dubey, R.K.; Desmukh, M.R.; Verma, D.; Govindakrishnan, P.M.; Satpathy, P.C.; Singh, D.; Kumar, S.; Khaiwal, R.; et al. Genotype by Environment Interaction and Yield Stability of Potato Cultivars under Tropical Conditions. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2018, 20, 583–595. [Google Scholar]
- Peymani, N.; Golparvar, A.R.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.; Mahmoudi, E.; Shams, M. Candidate marker genes and enzymes for selection of potato with resistance to early blight, caused by Alternaria alternata. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2022, 1, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghislain, M.; Byarugaba, A.A.; Magembe, E.; Njoroge, A.; Rivera, C.; Rom’an, M.L.; Tovar, J.C.; Gamboa, S.; Forbes, G.A.; Kreuze, J.F.; et al. Stacking three late blight resistance genes from wild species directly into African highland potato varieties confers complete field resistance to local blight races. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobos, I.; Komar, O.; Fedosiy, I.; Havrys, I.; Retman, M. Research on the impact of planting schemes on the trait variability of Vigna varieties (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp. subsp. sesquipedalis (L.) Verdc.). Sci. Horiz. 2024, 27, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkha, O.; Menshov, O.; Bykova, O.; Pikovska, O.; Fedosiy, I. Magnetic methods application for the physical and chemical properties assessment of Ukraine soil. In Proceedings of the XIV International Scientific Conference “Monitoring of Geological Processes and Ecological Condition of the Environment”, Kyiv, Ukraine, 10–13 November 2020; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Bunnik, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pysarenko, N.; Zakharchuk, N.; Furdyha, M.; Oliinyk, T. Influence of weather conditions in Central Polissia, Ukraine, on the expression of quality indicators in potato cultivars of different maturity groups. Sci. Horiz. 2024, 27, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, W.E.; Apple, A.E.; Bruhn, J.A. Evaluation of potato late blight forecasts modified to incorporate host resistance and fungicide weathering. Phytopathology 1983, 73, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angmo, D.; Sharma, S.P.; Kalia, A. Breeding strategies for late blight resistance in potato crop: Recent developments. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 7879–7891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Esse, H.P.; Reuber, T.L.; van der Does, D. Genetic modification to improve disease resistance in crops. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katembo, A.V.; Katswangene, P.K.; Odimba, D.O.; Wallis, N.Z. Potato Breeding for Late Blight Resistance in Central and East Africa. Eur. J. Agric. Food Sci. 2024, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Viquez-Zamora, M.; den Uil, D.; Sinnige, J.; Kruyt, H.; Vossen, J.; van Heusden, S. Introgression of genes for resistance against Phytophthora infestans in diploid potato. Am. J. Potato Res. 2020, 97, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfouze, H.A.; El-Sayed, O.E. Comparative analysis of late blight resistance R genes and their coding proteins in some potato genotypes. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2022, 58, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckerstorfer, M.F.; Engelhard, M.; Heissenberger, A.; Simon, S.; Teichmann, H. Plants developed by new genetic modification techniques—Comparison of existing regulatory frameworks in the EU and non-EU countries. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Li, W.; Dawson, I.G.; Clark, B.; Chen, S.; Frewer, L.J. Consumer responses to genetically modified food in China: The influence of existing general attitudes, affect and perceptions of risks and benefits. Food Qual. Prefer. 2022, 99, 104543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiszewska, M.; Sobkowiak, S.; Stefańczyk, E.; Śliwka, J. Population structure of Phytophthora infestans from a single location in Poland over a long period of time in context of weather conditions. Microb. Ecol. 2021, 81, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puidet, B.; Koppel, M.; Kiiker, R. Genetic Diversity and Reproduction Trends of Phytophthora infestans in Estonia: EU_41_A2 Detected without an Indication of Clonal Reproduction. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwiczewska, M.; Janiszewska, M.; Yin, Z.; Śliwka, J. Populations of Phytophthora infestans in northern and eastern Europe. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2025, 171, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, W.A.; Parry, F.A.; Bhat, B.A. Potato late blight disease prediction using meteorological parameters in Northern Himalayas of India. J. Agrometeorol. 2021, 23, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, R.S.; Yuvaraj, M.; Sharmila, R.; Jagathjothi, N.; Saranya, M.; Suganthi, N.; Sivaji, M. Effects of Climate Change on Plant Diseases. In Plant Quarantine Challenges Under Climate Change Anxiety; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 183–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuley, I.K.; Hansen, J.G. Characterization of the level and type of resistance of potato varieties to late blight (Phytophthora infestans). Phytopathology 2022, 112, 1917–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastelo, M.; Bastos, C.; Ortiz, R.; Blas, R. Environmental impact and phenotypic stability in potato clones resistant to late blight Phytophthora infestans (Mont) de Bary, resilient to climate change in Peru. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0318255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown-Donovan, K.M.; Porter, G.A.; Tan, E.H. Late blight resistance profiles of elite potato germplasm in the United States. Am. J. Potato Res. 2021, 98, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.A.; Ukladov, E.O.; Golubeva, T.S. Phytophthora infestans: An overview of methods and attempts to combat late blight. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, K.B.; Park, S.J.; Park, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; Shin, S.Y.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, H.S. Editing of StSR4 by Cas9-RNPs confers resistance to Phytophthora infestans in potato. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 997888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berindean, I.V.; Taoutaou, A.; Rida, S.; Ona, A.D.; Stefan, M.F.; Costin, A.; Muntean, L. Modern Breeding Strategies and Tools for Durable Late Blight Resistance in Potato. Plants 2024, 13, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Nie, J.; Wu, J.; Qi, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Tian, Z. Regulation of potato late blight resistance genes by different promoters and translation regulators. Hortic. Adv. 2025, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, S.; Bhardwaj, V.; Bairwa, A.; Dalamu; Sharma, S.; Sharma, A.K.; Kumar, V. Genome-wide association mapping and genomic prediction for late blight and potato cyst nematode resistance in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1211472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
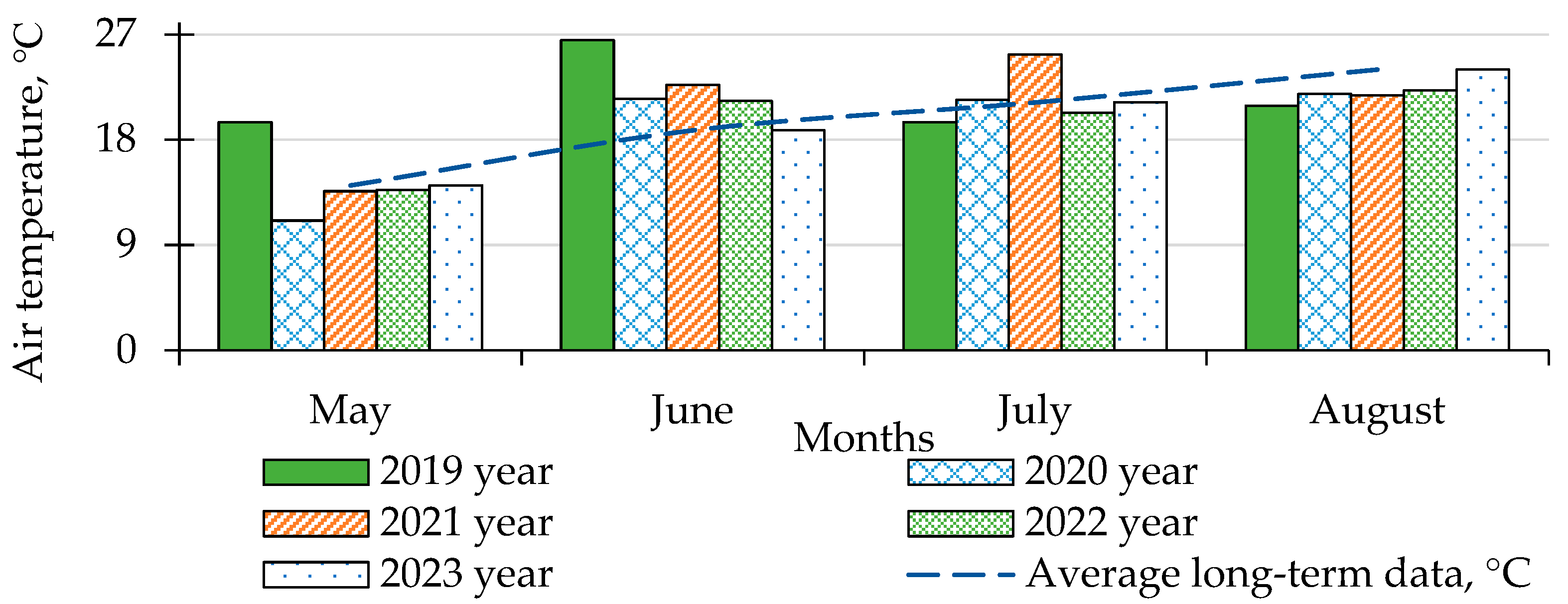


| Set of Combinations | Female ♀ | Male ♂ |
|---|---|---|
| 15.47/62 | Mezhyrichka 11/ | Belarusian 3 |
| Early | Late | |
| Not stable | stand | |
| 15.7/15 | Dobrochin/ | Well |
| Average growth | Late | |
| Not a brush | stand | |
| 11.29/70 | Slavyanka/ | Flood |
| Mid-ripening | Early | |
| stand | Not stable | |
| 14.10-5 | Heather/ | Milovice |
| Early | late | |
| medium-strength | stand | |
| 13.36c40 | Stream/ | 09.202c.79 |
| Early | Late | |
| medium-strength | resistant | |
| 15.27/9 | Innovator/ | Gourmet |
| Mid-ripening | Mid-ripening | |
| stand | stand | |
| 15.10/10 | Fantasy/ | Verdi |
| Average growth | Mid-ripening | |
| medium-strength | medium-strength | |
| 15.5/12 | Verkhovyna/ | Unita |
| Mid-ripening | Mid-ripening | |
| stand | stand | |
| 15.2/1 | Bellarosa/ | Fantasy |
| Early | Average growth | |
| Not stable | medium-strength | |
| 15.18/8 | Temptation/ | Verdi |
| Mid-ripening | Mid-ripening | |
| Not stable | stand | |
| 13.62/78 | Kalynivska/ | Aria |
| Medium-late | early | |
| stand | not stable | |
| 12.30/3 | Mozart/ | Glow |
| Mid-ripening | Late | |
| medium-strength | stand | |
| 12.24/14 | Kuroda/ | Shchedryk |
| Medium-late | early | |
| stand | medium-strength | |
| 12.10/40 | Virinea/ | Stream |
| Mid-ripening | Early | |
| stand | medium-strength | |
| 15.1/22 | Neighbourhood/ | Podolia |
| Mid-ripening | early | |
| stand | not stable | |
| 14.16/16 | Shchedryk/ | Bellarosa |
| early | early | |
| medium-strength | not stable | |
| 12.9/78 | Orchid/ | Fun |
| Mid-ripening | Mid-ripening | |
| stand | stand | |
| 24.12|6 | Kuroda/ | Shchedryk |
| Medium-late | early | |
| stand | medium-strength | |
| 12/2914 | 04/21c31/ | Bellarosa |
| early | early | |
| resistant | not stable | |
| 13.55/2 | Chervona Ruta/ | Bellarosa |
| Medium-late | early | |
| stand | not stable |
| Maturity Groups of Hybrids | Year of Study | Number of Samples | Hybrids with Resistance, % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High (8–9 Points) | Low (1–3 Points) | |||||||
| Assessment: | Assessment: | |||||||
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | |||
| First set of hybrids | ||||||||
| Early and mid-early | 2019 | 125 | 100 | 41.2 | - | 0 | 17.5 | - |
| 2020 | 118 | 73.8 | 26.2 | 0 | 2.5 | 23.8 | 99.1 | |
| Mid-season | 2019 | 144 | 100 | 68.7 | 25.8 | 0 | 0 | 16.1 |
| 2020 | 139 | 94.7 | 50.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 4.6 | 92.5 | |
| Mid-late and late | 2019 | 126 | 100 | 88.1 | 30.3 | 0 | 0 | 8.0 |
| 2020 | 122 | 99.2 | 62.3 | 0 | 0 | 0.8 | 90.9 | |
| Second set of hybrids | ||||||||
| Early and mid-early | 2020 | 91 | 95.3 | 39.6 | 4.8 | 0 | 13.1 | 67.8 |
| 2021 | 73 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 82.2 | |
| Mid-season | 2020 | 138 | 100 | 64.0 | 13.7 | 0 | 1.6 | 29.8 |
| 2021 | 113 | 98.2 | 96.5 | 1.8 | 0 | 0 | 64.7 | |
| Mid-late and late | 2020 | 84.7 | 79.8 | 31.7 | 0 | 0 | 9.4 | |
| 2021 | 100 | 98.1 | 7.1 | 0 | 0 | 21.2 | ||
| Third set of hybrids | ||||||||
| Early and mid-early | 2021 | 81 | 100 | 96.2 | 5.2 | 0 | 0 | 76.8 |
| 2022 | 81 | 98.8 | 84 | 14.8 | 0 | 0 | 40.7 | |
| Mid-season | 2021 | 117 | 100 | 95.7 | 12.4 | 0 | 0 | 53.8 |
| 2022 | 117 | 99.1 | 89.8 | 27.4 | 0 | 0 | 29.9 | |
| Mid-late and late | 2021 | 248 | 100 | 98.3 | 15.2 | 0 | 0 | 34.8 |
| 2022 | 243 | 99.6 | 93.4 | 27.2 | 0 | 0 | 17.3 | |
| Fourth set of hybrids | ||||||||
| Early and mid-early | 2022 | 139 | 92.6 | 56.4 | 9.3 | 0 | 5.7 | 43.8 |
| 2023 | 125 | 100 | 100 | 4.0 | 0 | 0 | 50.4 | |
| Mid-season | 2022 | 196 | 98.7 | 82.0 | 8.4 | 0 | 1.2 | 48.3 |
| 2023 | 196 | 100 | 99.5 | 6.1 | 0 | 0 | 29.6 | |
| Mid-late and late | 2022 | 241 | 100 | 79.6 | 15.4 | 0 | 0 | 35.2 |
| 2023 | 201 | 100 | 100 | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 8.5 | |
| Maturity Groups of Hybrids | Year of Study | Number of Samples | Min–Max | Average Resistance Score | Distribution of Hybrids, %, by Leaf Resistance Score, Points | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 1 | |||||
| First set of hybrids | ||||||||||
| Early and mid-early | 2019 | 125 | 5–9 | 7.7 ± 0.52 a | 2.9 | 58.3 | 26.9 | 12.2 | 0 | 0 |
| 2020 | 118 | 1.3–7.7 | 5.1 ± 1.14 a | 0.0 | 2.6 | 23.5 | 64.3 | 6.1 | 3.5 | |
| Mid-season | 2019 | 144 | 3.7–9.0 | 7.7 ± 1.0 a | 8.8 | 63.2 | 21.0 | 7.0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2020 | 139 | 3.0–8.3 | 6.3 ± 0.92 a | 0 | 12.3 | 42.1 | 44.7 | 0.9 | 0 | |
| Mid-late and late | 2019 | 126 | 5.3–9.0 | 8.0 ± 0.18 a | 21.5 | 59.5 | 15.7 | 3.3 | 0 | 0 |
| 2020 | 122 | 3.3–8.3 | 6.6 ± 0.97 a | 0 | 15.7 | 47.1 | 37.2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Second set of hybrids | ||||||||||
| Early and mid-early | 2020 | 91 | 3.4–8 | 6.0 ± 0.83 a | 0 | 8.6 | 42.8 | 48.6 | 0 | 0 |
| 2021 | 73 | 6.7–8.7 | 7.4 ± 0.39 a | 2.8 | 31.5 | 65.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Mid-season | 2020 | 138 | 4.0–8.7 | 7.0 ± 0.80 a | 0.9 | 36.3 | 45.2 | 17.6 | 0 | 0 |
| 2021 | 113 | 5.3–8.7 | 7.5 ± 0.61 a | 1.9 | 53.9 | 42.3 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Mid-late and late | 2020 | 223 | 5.0–8.7 | 7.6 ± 0.68 a | 3.1 | 51.6 | 41.4 | 3.9 | 0 | 0 |
| 2021 | 156 | 6.7–8.7 | 7.9 ± 0.58 a | 7.1 | 85.8 | 7.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Third set of hybrids | ||||||||||
| Early and mid-early | 2021 | 81 | 5.0–8.7 | 7.4 ± 0.68 a | 4.0 | 29.4 | 65.3 | 1.3 | 0 | 0 |
| 2022 | 81 | 4.3–8.8 | 6.9 ± 0.73 a | 4.0 | 24.0 | 56.0 | 16.0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Mid-season | 2021 | 117 | 6.5–8.9 | 7.8 ± 0.47 a | 10.4 | 33.1 | 51.9 | 7.5 | 0 | 0 |
| 2022 | 117 | 4.3–9.0 | 7.4 ± 0.81 a | 7.5 | 72.2 | 16.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Mid-late and late | 2021 | 248 | 6.5–9.0 | 7.9 ± 0.45 a | 11.6 | 72.2 | 16.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2022 | 243 | 4.5–9.0 | 7.5 ± 0.84 a | 8.5 | 35.5 | 52.6 | 3.4 | 0 | 0 | |
| Fourth set of hybrids | ||||||||||
| Early and mid-early | 2022 | 139 | 1.5–8.2 | 6.2 ± 1.19 a | 0 | 13.9 | 43.5 | 41.7 | 0 | 0.9 |
| 2023 | 125 | 6.0–8.7 | 7.2 ± 0.47 a | 2.8 | 39.8 | 50.9 | 6.5 | 0 | 0 | |
| Mid-season | 2022 | 196 | 2.7–8.7 | 7.0 ± 1.08 a | 4.7 | 31.9 | 38.4 | 24.4 | 0.6 | 0 |
| 2023 | 196 | 5.3–9.0 | 7.4 ± 0.69 a | 5.8 | 52.9 | 39.5 | 1.7 | 0 | 0 | |
| Mid-late and late | 2022 | 241 | 2.7–9.0 | 7.4 ± 1.18 a | 10.1 | 46.3 | 34.0 | 9.0 | 0.5 | 0 |
| 2023 | 201 | 6.0–8.7 | 7.9 ± 0.51 a | 2.1 | 82.4 | 14.9 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | |
| Maturity Groups of Hybrids | Year of Study | Number of Samples | Min–Max | Average Resistance Score | Distribution of Hybrids, %, by Tuber Resistance Scores | Hybrids that Combine High (8–9 Points) Leaf and Tuber Resistance, % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 1 | ||||||
| First set of hybrids | |||||||||||
| Early and mid-early | 2019 | 26 | 1–9 | 6.2 ± 1.46 a | 26.9 | 19.2 | 11.5 | 11.5 | 26.9 | 3.9 | 40.0 |
| 2020 | 1–9 | 6.3 ± 1.40 a | 42.3 | 11.5 | 0 | 15.4 | 23.1 | 7.7 | 0.0 | ||
| Mid-season | 2019 | 30 | 3–9 | 7.4 ± 1.12 a | 46.7 | 23.3 | 10.0 | 0 | 20.0 | 0 | 41.91 |
| 2020 | 1–9 | 7.0 ± 1.52 a | 53.3 | 10.0 | 6.7 | 6.7 | 20.0 | 3.3 | 0.0 | ||
| Mid-late and late | 2019 | 40 | 1–9 | 6.4 ± 1.40 a | 22.5 | 27.5 | 15.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 0 | 48.76 |
| 2020 | 1–9 | 5.4 ± 1.33 a | 20.0 | 15.0 | 10.0 | 15.0 | 30.0 | 10.0 | 2.04 | ||
| Second set of hybrids | |||||||||||
| Early and mid-early | 2020 | 38 | 1–9 | 7.3 ± 1.42 a | 60.5 | 10.5 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 21.2 | 2.6 | 3.41 |
| 2021 | 3–9 | 7.7 ± 1.17 a | 73.7 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 18.5 | 0 | 2.27 | ||
| Mid-season | 2020 | 33 | 1–9 | 7.4 ± 1.51 a | 60.8 | 6.1 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 6.1 | 9.0 | 24.30 |
| 2021 | 3–9 | 7.4 ± 1.10 a | 57.7 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 6.1 | 18.2 | 0 | 16.67 | ||
| Mid-late and late | 2020 | 26 | 1–9 | 5.3 ± 1.38 a | 38.4 | 0 | 7.8 | 7.8 | 23.0 | 23.0 | 25.50 |
| 2021 | 1–9 | 6.3 ± 1.37 a | 42.3 | 15.4 | 15.4 | 19.1 | 7.8 | 7.8 | 28.57 | ||
| Third set of hybrids | |||||||||||
| Early and mid-early | 2021 | 26 | 1–9 | 6.8 ± 1.50 a | 50.0 | 11.6 | 3.8 | 7.7 | 26.9 | 0 | 24.0 |
| 2022 | 3–9 | 6.5 ± 1.03 a | 76.9 | 0 | 0 | 3.8 | 7.7 | 11.6 | 22.58 | ||
| Mid-season | 2021 | 37 | 1–9 | 6.1 ± 1.36 a | 43.3 | 5.4 | 5.4 | 10.8 | 29.7 | 5.4 | 30.7 |
| 2022 | 1–9 | 6.8 ± 1.50 a | 59.5 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 8.1 | 21.6 | 5.4 | 35.0 | ||
| Mid-late and late | 2021 | 42 | 1–9 | 6.4 ± 1.39 a | 50.0 | 4.8 | 4.8 | 7.1 | 28.5 | 4.8 | 51.21 |
| 2021 | 1–9 | 6.8 ± 1.51 a | 50.0 | 16.7 | 0.0 | 2.4 | 28.5 | 2.4 | 17.54 | ||
| Fourth set of hybrids | |||||||||||
| Early and mid-early | 2022 | 43 | 1–9 | 7.6 ± 1.59 a | 76.7 | 0.0 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 14.0 | 4.7 | 14.75 |
| 2023 | 1–9 | 6.2 ± 1.36 a | 51.1 | 2.3 | 4.7 | 7.0 | 18.6 | 16.3 | 5.45 | ||
| Mid-season | 2022 | 51 | 1–9 | 7.7 ± 1.57 a | 74.5 | 3.9 | 0.0 | 5.9 | 11.8 | 3.9 | 28.9 |
| 2023 | 1–9 | 6.4 ± 1.44 a | 52.9 | 2.0 | 3.9 | 7.8 | 23.5 | 9.8 | 21.2 | ||
| Mid-late and late | 2022 | 36 | 1–9 | 7.3 ± 1.55 a | 72.2 | 0 | 0 | 2.8 | 19.4 | 5.6 | 42.79 |
| 2023 | 1–9 | 7.6 ± 1.59 a | 72.2 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 8.3 | 5.6 | 8.3 | 30.0 | ||
| Set of Combinations | Origin | Number of the First-Year Seedlings, pcs | Number of Late Blight-Resistant Hybrids with Leaf Resistance of 8–9 Points, % | Number of Hybrids That Combine High (8–9 Points) Leaf and Tuber Resistance, % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Including Early | Total | Including Early | |||
| 15.47/62 | Mezhirichka 11/Belarusian 3 | 562 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0 | 0 |
| 15.7/15 | Dobrochin/Krinitsa | 824 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0 | 0 |
| 11.29/70 | Slovyanka/Povin | 40 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| 14.10-5 | Veresivka/Milovitsa | 613 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| 13.36c40 | Strumok/09.202s.79 | 2800 | 0.11 | 0 | 0.11 | 0 |
| 15.27/9 | Innovator/Gurman | 481 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| 15.10/10 | Fantasiya/Verdi | 822 | 0.48 | 0 | 0.12 | 0 |
| 15.5/12 | Verkhovyna/Unita | 670 | 0.59 | 0.29 | 0 | 0 |
| 15.2/1 | Bellarosa/Fantasiya | 1070 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| 15.18/8 | Spokusa/Verdi | 106 | 1.88 | 0 | 1.88 | 0 |
| 13.62/78 | Kalynivska/Aria | 550 | 1.09 | 0 | 0.54 | 0 |
| 12.30/3 | Mozart/Zarevo | 600 | 1.0 | 0 | 0.33 | 0 |
| 12.24/14 | Kuroda/Shchedrik | 3500 | 0.17 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 12.10/40 | Virinea/Strumok | 200 | 4.0 | 0.50 | 2.0 | 0.50 |
| 15.1/22 | Okolitsa/Podolia | 694 | 0.57 | 0.14 | 0.57 | 0.14 |
| 14.16/16 | Shchedryk/Bellarosa | 584 | 0.34 | 0 | 0.34 | 0 |
| 12.9/78 | Orkhideya/Zabava | 763 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.26 | 0.13 |
| 12/2416 | Kuroda/Shchedrik | 810 | 0.24 | 0 | 0.24 | 0 |
| 12/2914 | 04/21c31/Bellarosa | 158 | 3.79 | 0.63 | 3.79 | 0.63 |
| 13.55/2 | Chervona ruta/Bellarosa | 410 | 0.48 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rucins, A.; Aboltins, A.; Furdyha, M.; Zakharchuk, N.; Oliynik, T.; Fedosiy, I.; Komar, O. Breeding Evaluation of Potato Hybrids for Late Blight Resistance. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102431
Rucins A, Aboltins A, Furdyha M, Zakharchuk N, Oliynik T, Fedosiy I, Komar O. Breeding Evaluation of Potato Hybrids for Late Blight Resistance. Agronomy. 2025; 15(10):2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102431
Chicago/Turabian StyleRucins, Adolfs, Aivars Aboltins, Mykola Furdyha, Natalya Zakharchuk, Tetyana Oliynik, Ivan Fedosiy, and Oleksandr Komar. 2025. "Breeding Evaluation of Potato Hybrids for Late Blight Resistance" Agronomy 15, no. 10: 2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102431
APA StyleRucins, A., Aboltins, A., Furdyha, M., Zakharchuk, N., Oliynik, T., Fedosiy, I., & Komar, O. (2025). Breeding Evaluation of Potato Hybrids for Late Blight Resistance. Agronomy, 15(10), 2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102431






