The Optimal Cyanobacterial Sludge Incorporation Balances Nutrient Retention and NH3 Emission Reduction During Composting with Chicken Manure and Wheat Straw
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Measurement
2.3.1. Sample Collection
2.3.2. Composting Temperature, pH, EC, GI and CEC
2.3.3. Compost Nutrient Content
2.3.4. Microcystin and Heavy Metal Content of Compost Products
2.3.5. NH3 Volatilization from Composting
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
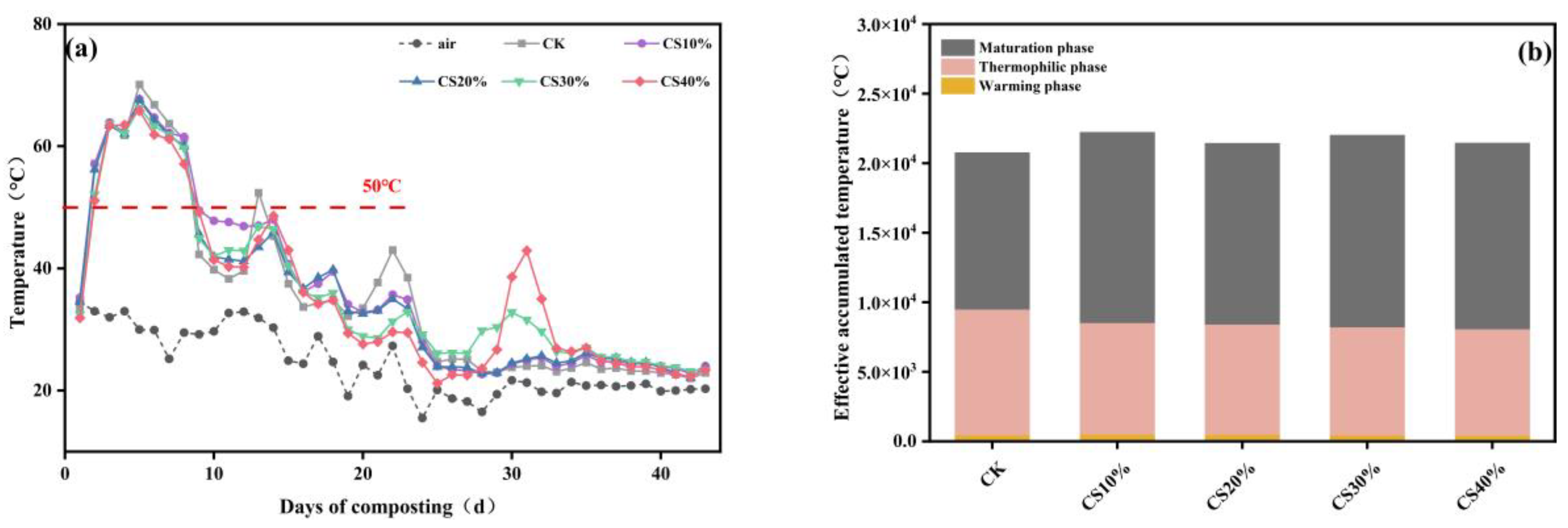
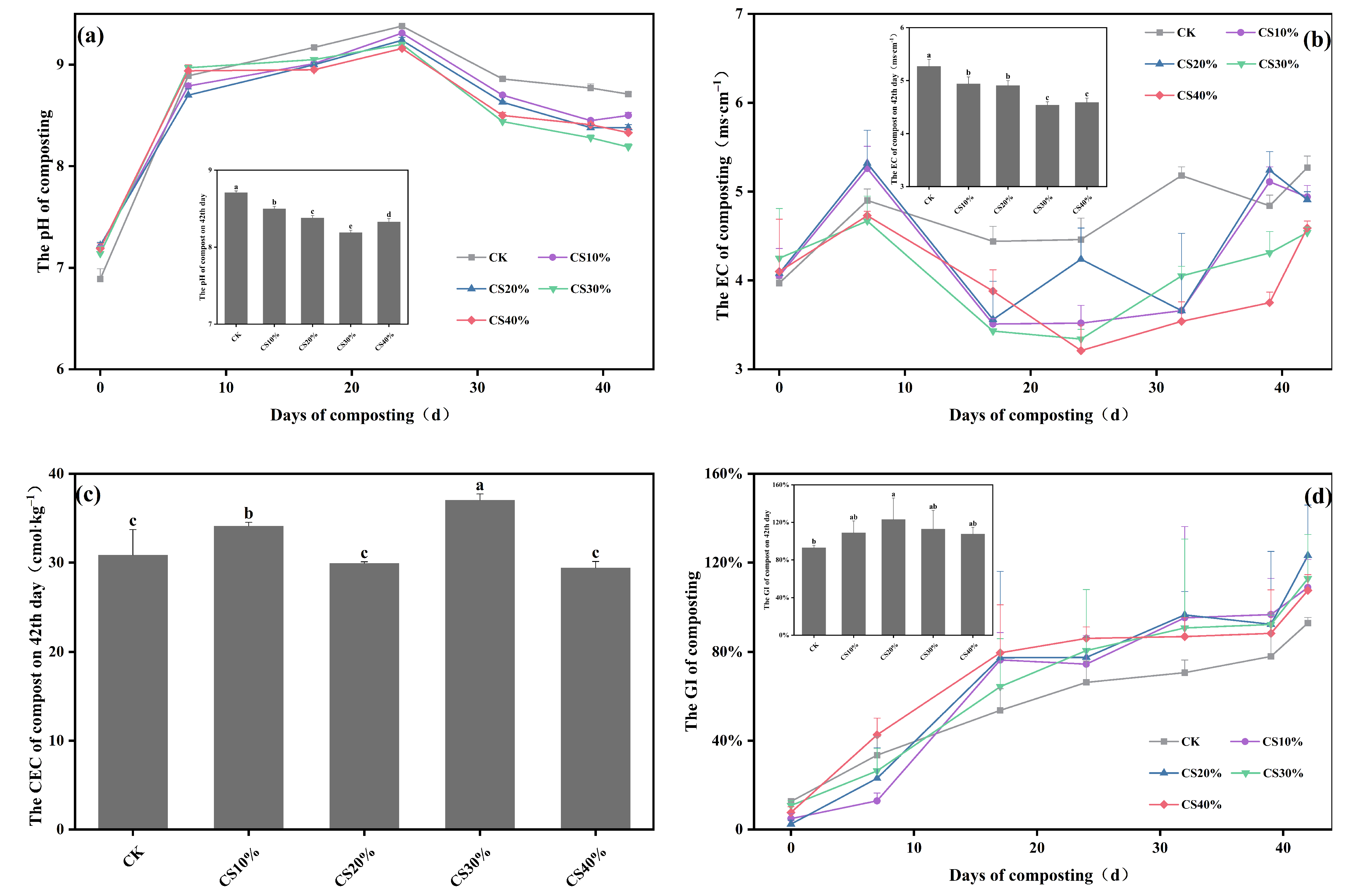
3.1. Dynamics in Maturation Parameters During Composting
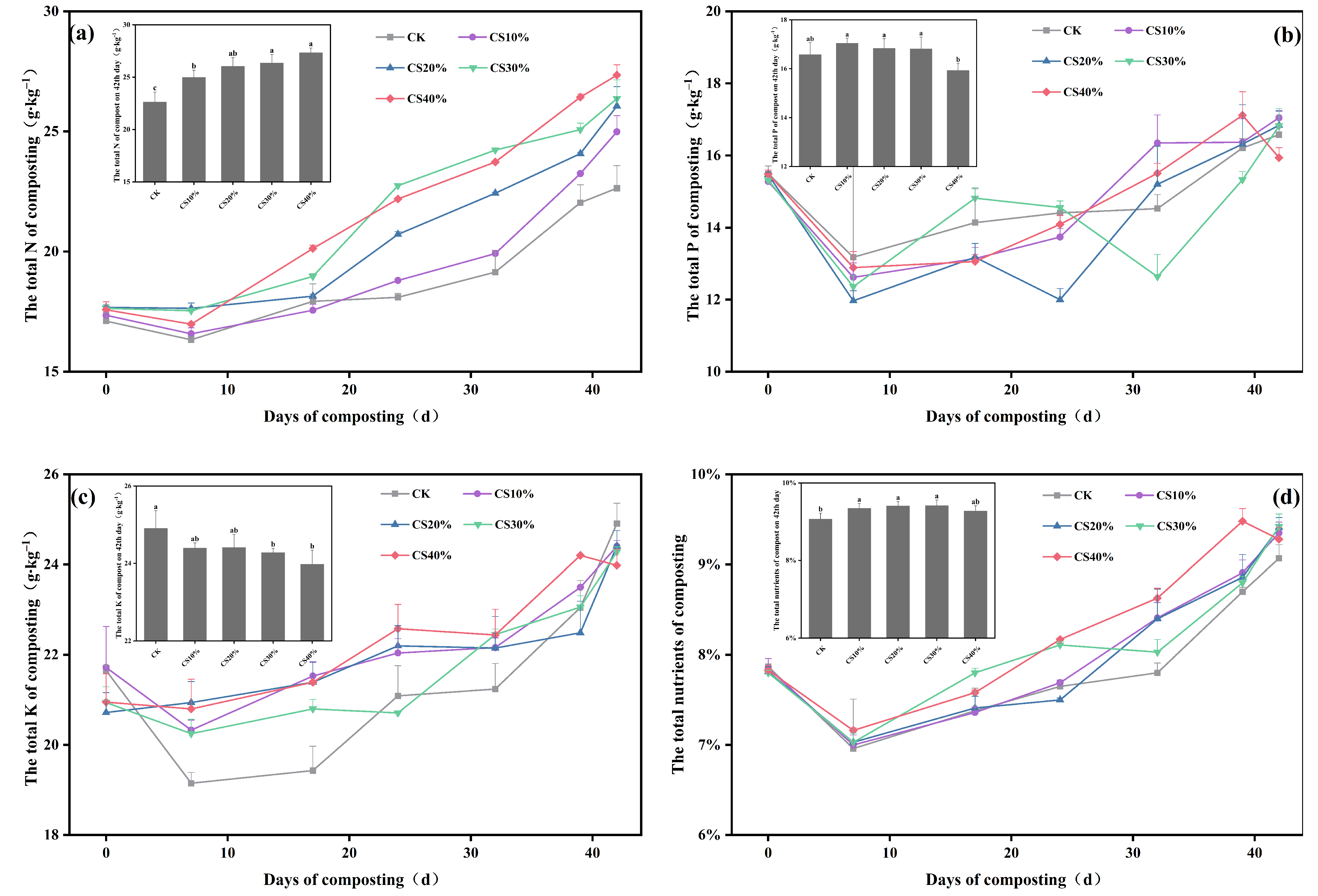
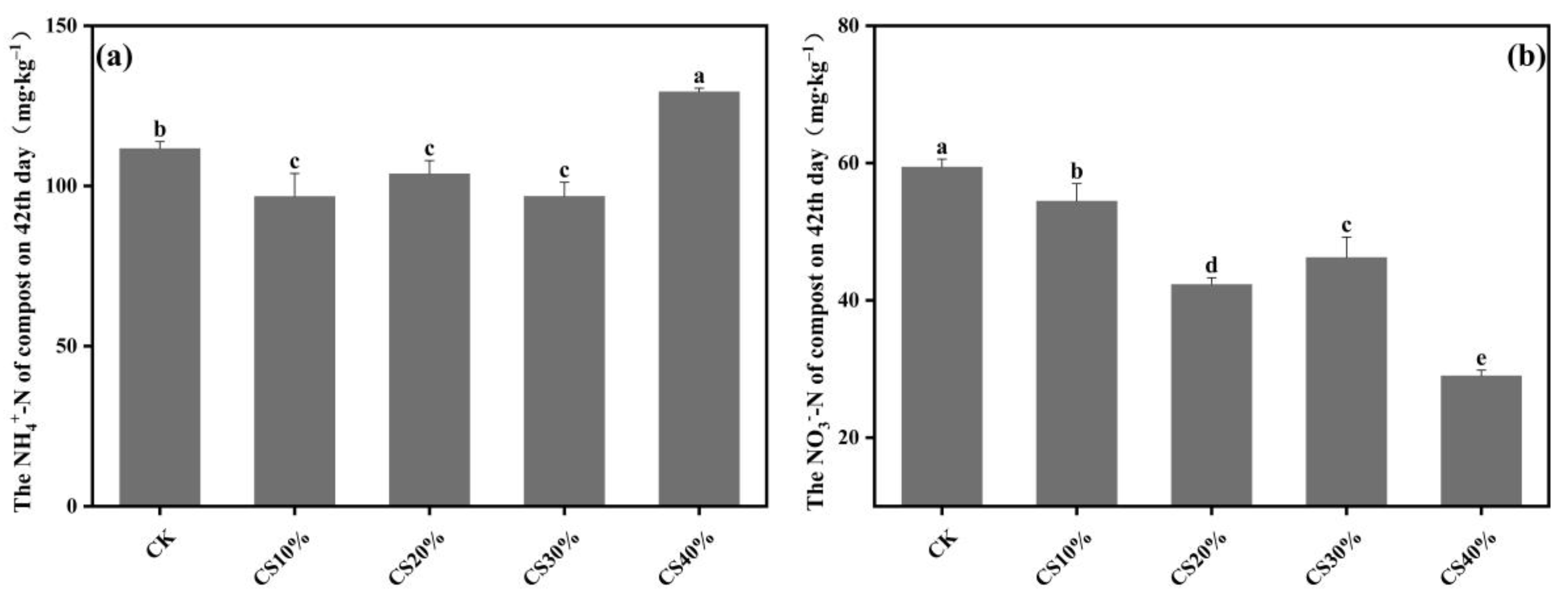
3.2. Dynamics in N, P, and K Content During Composting
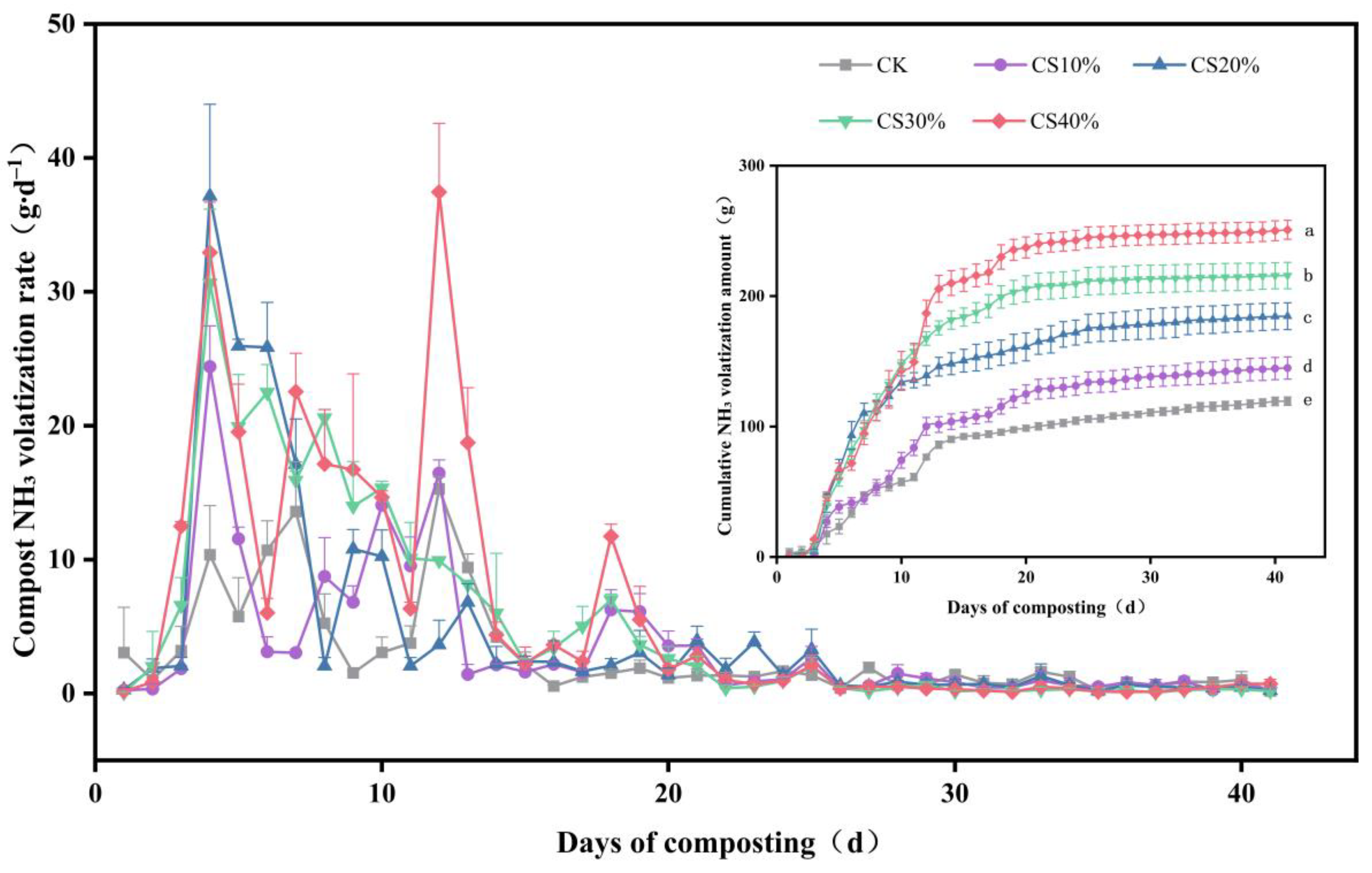
3.3. NH3 Volatilization During Composting
3.4. Safety of Compost Products
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of CS Addition on Maturation Parameters During Composting
4.2. Effect of CS Addition on Nutrient Retention During Composting
4.3. Effects of CS Addition on NH3 Volatilization During Composting
4.4. Effects of CS Addition on the Safety of Compost Products
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, M.; Duan, H.; Shi, X.; Yu, Y.; Kong, F. Contributions of Meteorology to the Phenology of Cyanobacterial Blooms: Implications for Future Climate Change. Water Res. 2012, 46, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Huang, T.; Zhu, L.; Hu, J.; Ma, S.; Sun, Q.; Chen, K. Effect of Cyanobacterial Bloom Proliferation on Antibiotic Resistance Genes in the Sediments of a Eutrophic Lake. Environ. Res. 2025, 278, 121717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zuo, J.; Grossart, H.-P.; Dai, G.; Liu, J.; Song, L.; Gan, N. Evaluating Microcystinase A-Based Approach on Microcystins Degradation during Harvested Cyanobacterial Blooms. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 348, 123878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Wang, C.; Zhou, J.; Cong, H.; Gao, Y.; Cai, W.; Feng, S.; Zhang, C. Feedstock Optimization with Low Carbon to Nitrogen Ratio during Algal Sludge Aerobic Composting: Quality and Gaseous Emissions. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 416, 131811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Y.; Wang, C.; Cong, H.; Feng, S. Contributions of the Bacterial Communities to the Microcystin Degradation and Nutrient Transformations during Aerobic Composting of Algal Sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, H.; Ding, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Ding, Y. Research Progress on Influencing Factors on Compost Maturity and Cyanobacteria Toxin Degradation during Aerobic Cyanobacteria Composting: A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 70635–70657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, M.; Bian, B.; Yang, Z.; Yang, W.; Zhang, L. Full-Scale Thermophilic Aerobic Co-Composting of Blue-Green Algae Sludge with Livestock Faeces and Straw. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 142079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piash, M.I.; Itoh, T.; Abe, K.; Iwabuchi, K. Superior Nutrient Recovery and Release by Chicken Manure-Derived Biochar over Hydrochar and Compost for Soil Fertilization. Geoderma Reg. 2025, 40, e00906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, L.; Wang, D.; Lin, J.; Yan, Y.; Liu, H.; Cai, M.; Yang, X.; Li, Q. Role of Carbon Bioavailability in Enhancing Carbon Sequestration and Humification in Black Soldier Fly Larvae Body and Frass during Chicken Manure Composting. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 37, 104036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Jing, Y.; Fu, N.; Wang, Y.; Qin, D.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Wan, J. New Insight into Bacterial Communities of Chicken Manure Composting under Increased Carbon to Nitrogen Ratios: Spatial Heterogeneity in Diversity, Networks, and Assembly Processes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Clarke, W.; Pratt, S. Composting of Waste Algae: A Review. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunwande, G.A.; Osunade, J.A.; Adekalu, K.O.; Ogunjimi, L.A.O. Nitrogen Loss in Chicken Litter Compost as Affected by Carbon to Nitrogen Ratio and Turning Frequency. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7495–7503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, C.; Wang, X.; Hai, L. Increased Abundance of Nitrogen Transforming Bacteria by Higher C/N Ratio Reduces the Total Losses of N and C in Chicken Manure and Corn Stover Mix Composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, H.; Powlson, D.; Min, J.; Shi, W. Rice Production, Nitrous Oxide Emission and Ammonia Volatilization as Impacted by the Nitrification Inhibitor 2-Chloro-6-(Trichloromethyl)-Pyridine. Field Crops Res. 2015, 173, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Ren, J. Simulated NH4-N Deposition Inhibits CH4 Uptake and Promotes N2O Emission in the Meadow Steppe of Inner Mongolia, China. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kithome, M.; Paul, J.W.; Bomke, A.A. Reducing Nitrogen Losses during Simulated Composting of Poultry Manure Using Adsorbents or Chemical Amendments. J. Environ. Qual. 1999, 28, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, W.; Li, G.; Wang, K.; Gong, X. Performance of Phosphogypsum and Calcium Magnesium Phosphate Fertilizer for Nitrogen Conservation in Pig Manure Composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, R.; Cheng, J.; He, T.; Fu, T. Potential of Combined Reactor and Static Composting Applications for the Removal of Heavy Metals and Antibiotic Resistance Genes from Chicken Manure. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 356, 120592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, G.; Wei, X.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Bao, S.; Wang, S.; Zhu, L.; Xi, B.; Tan, W. Effect of Aqueous Phase from Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sewage Sludge on Heavy Metals and Heavy Metal Resistance Genes during Chicken Manure Composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 471, 134398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, M.; Kumar, L.; Shah, M.P.; Bharadvaja, N. Algal Bioremediation of Heavy Metals: An Insight into Removal Mechanisms, Recovery of by-Products, Challenges, and Future Opportunities. Energy Nexus 2022, 7, 100129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, R.; Guieysse, B. Algal–Bacterial Processes for the Treatment of Hazardous Contaminants: A Review. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2799–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Cheng, Y.; Li, T.; Sun, H.; Xue, L.; Cui, H.; Feng, Y.; Yang, L.; Chu, Q. Co-application of Biogas Slurry and Hydrothermal Carbonization Aqueous Phase Substitutes Urea as the Nitrogen Fertilizer and Mitigates Ammonia Volatilization from Paddy Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Chen, S.; Zhu, N.; Jeyakumar, P.; Wang, J.; Xie, W.; Feng, Y. Hydrothermal Carbonization Aqueous Phase Promotes Nutrient Retention and Humic Substance Formation during Aerobic Composting of Chicken Manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 385, 129418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Schuchardt, F.; Shen, Y.; Li, G.; Li, C. Impact of Struvite Crystallization on Nitrogen Losses during Composting of Pig Manure and Cornstalk. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Sun, X.; Sun, H.; Feng, Y.; Gong, X.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, J.; Xue, L. Effects of Biochar and Wood Vinegar Co-application on Composting Ammonia and Nitrous Oxide Losses and Fertility. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 412, 131388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Evolution of Physicochemical Properties and Bacterial Community in Aerobic Composting of Swine Manure Based on a Patent Compost Tray. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bartos, J.M.; Boggs, B.L.; Falls, J.H.; Siegel, S.A. Determination of Phosphorus and Potassium in Commercial Inorganic Fertilizers by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry: Single-Laboratory Validation. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhao, H.; Li, H.; Cai, Q.; Mo, C.; Wong, M.; Li, Q. High Ecological and Human Health Risks from Microcystins in Vegetable Fields in Southern China. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 1315-2023; Soil and Sediment—Determination of 19 Total Metal Elements—Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Ren, X.; Wang, Q.; Awasthi, M.K.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z. Improvement of Cleaner Composting Production by Adding Diatomite: From the Nitrogen Conservation and Greenhouse Gas Emission. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 286, 121377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, B.; Karmegam, N.; Awasthi, M.K.; Chang, S.W.; Selvi, P.K.; Balachandar, R.; Chinnappan, S.; Azelee, N.I.W.; Munuswamy-Ramanujam, G. Valorization of Food Waste and Poultry Manure through Co-composting Amending Saw Dust, Biochar and Mineral Salts for Value-Added Compost Production. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Ou, Y.-L.; Lin, J.-G. Co-composting of Green Waste and Food Waste at Low C/N Ratio. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, T.; Ying, Y.; Yao, X. Effects of Different Additives on the Chemical Composition and Microbial Diversity during Composting of Camellia Oleifera Shell. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 330, 124990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, F.; Zhang, G.; Qin, R.; Li, X.; Xiao, R. Nutrient Transformations during Composting of Pig Manure with Bentonite. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 121, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, R.; Li, J. Current Research Scenario for Microcystins Biodegradation—A Review on Fundamental Knowledge, Application Prospects and Challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Zang, B.; Li, Y. Effect of Spent Mushroom Substrate as a Bulking Agent on Gaseous Emissions and Compost Quality during Pig Manure Composting. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 12398–12406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Cui, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Song, W. Enhancing Compost Quality through Biochar and Oyster Shell Amendments in the Co-composting of Seaweed and Sugar Residue. Chemosphere 2024, 366, 143500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wei, Y.; Kou, J.; Han, Z.; Shi, Q.; Liu, L.; Sun, Z. Improve Spent Mushroom Substrate Decomposition, Bacterial Community and Mature Compost Quality by Adding Cellulase during Composting. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 299, 126928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Awasthi, M.K.; Jiang, Y.; Li, R.; Ren, X.; Zhao, J.; Shen, F.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z. Evaluation of Medical Stone Amendment for the Reduction of Nitrogen Loss and Bioavailability of Heavy Metals during Pig Manure Composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Kalamdhad, A.S. Assessment of Bioavailability and Leachability of Heavy Metals during Rotary Drum Composting of Green Waste (Water Hyacinth). Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, H.; Ni, J.-Q.; Zhuo, G.; Chen, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhen, G. Effect of Municipal Sludge-Based Biochar Produced at Different Pyrolysis Temperatures on Humification and Oxytetracycline Degradation of Pig Manure Composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, T.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Li, G. Effects of External Additives: Biochar, Bentonite, Phosphate, on Co-composting for Swine Manure and Corn Straw. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 125927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, M.P.; Alburquerque, J.A.; Moral, R. Composting of Animal Manures and Chemical Criteria for Compost Maturity Assessment. A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5444–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Yin, J.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Li, G.; Cui, Z.; Yuan, J. Applicability and Limitation of Compost Maturity Evaluation Indicators: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 489, 151386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guo, X.; Zhao, T.; Li, T. Green Waste Composting with Bean Dregs, Tea Residue, and Biochar: Effects on Organic Matter Degradation, Humification and Compost Maturity. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, A.; Li, G.; Wei, Y.; He, S.; Lin, Z.; Shen, X.; Wang, Q. Effect of Different Components of Single Superphosphate on Organic Matter Degradation and Maturity during Pig Manure Composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Awasthi, M.K.; Syed, A.; Bahkali, A.H. Effect of Cyanobacteria Biochar Addition on Humification, Fungal Dynamics and Its Mechanism of Action in Pig Manure Composting. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karak, T.; Sonar, I.; Paul, R.K.; Das, S.; Boruah, R.K.; Dutta, A.K.; Das, D.K. Composting of Cow Dung and Crop Residues Using Termite Mounds as Bulking Agent. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, G.; Ma, R.; Kong, Y.; Yuan, J. Selection of Sensitive Seeds for Evaluation of Compost Maturity with the Seed Germination Index. Waste Manag. 2021, 136, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, M.; Awasthi, M.K.; Chen, H.; Awasthi, S.K.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, Z. Measurement of Cow Manure Compost Toxicity and Maturity Based on Weed Seed Germination. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Huang, H.; Li, R.; Shen, F.; Lahori, A.H.; Wang, P.; Guo, D.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, S.; et al. Effect of Biochar Amendment on Greenhouse Gas Emission and Bio-Availability of Heavy Metals during Sewage Sludge Co-Composting. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, G.; Li, W.; Tan, W.; Bao, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhu, L.; Chen, L.; Xi, B. Effect of the Aqueous Phase from the Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sewage Sludge as a Moisture Regulator on Nitrogen Retention and Humification during Chicken Manure Composting. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 470, 144398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.W.-C.; Fung, S.O.; Selvam, A. Coal Fly Ash and Lime Addition Enhances the Rate and Efficiency of Decomposition of Food Waste during Composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3324–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Yuan, X.; Cui, Z. Co-Composting of the Biogas Residues and Spent Mushroom Substrate: Physicochemical Properties and Maturity Assessment. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 276, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haouas, A.; El Modafar, C.; Douira, A.; Ibnsouda-Koraichi, S.; Filali-Maltouf, A.; Moukhli, A.; Amir, S. Evaluation of the Nutrients Cycle, Humification Process, and Agronomic Efficiency of Organic Wastes Composting Enriched with Phosphate Sludge. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 302, 127051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Kuroda, K.; Waki, M.; Yasuda, T. Effects of Struvite Formation and Nitratation Promotion on Nitrogenous Emissions Such as NH3, N2O and NO during Swine Manure Composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 1468–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, C. Industrial-Scale Composting of Swine Manure with a Novel Additive-Yellow Phosphorus Slag: Variation in Maturity Indicators, Compost Quality and Phosphorus Speciation. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 384, 129356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, X.F.; Luo, M.; Dong, H.Y.; Li, S.B.; Li, M.C.; Kang, J. Variations of N-P-K Contents in Livestock and Livestock Manure Composting. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2021, 19, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, O.; Das, A.; Yu, C.; Hu, Z. Nitrifying Bacterial Growth Inhibition in the Presence of Algae and Cyanobacteria. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2010, 107, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chadwick, D.; Zhang, D.; Li, G.; Chen, S.; Luo, W.; Du, L.; He, S.; Peng, S. Effects of Aeration Rate on Maturity and Gaseous Emissions during Sewage Sludge Composting. Waste Manag. 2016, 56, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Sun, H.; Sun, X.; Gong, X.; Bian, R.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Xue, L.; Feng, Y. Co-Amendment of Dicyandiamide with Waste Carbonization Products into Composting: Enhanced Fertility, Reduced Gas Emission and Increased Economic Benefits. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 471, 143379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Feng, D. Biochar, Phosphate, and Magnesium Oxide in Seaweed and Cornstarch Dregs Co-Composting: Enhancing Organic Matter Degradation, Humification, and Nitrogen Retention. Waste Manag. 2024, 187, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Chen, Q.; Quan, H.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, T. Combined Treatment for Chicken Manure and Kitchen Waste Enhances Composting Effect by Improving pH and C/N. Waste Biomass Valor 2025, 16, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiland, F.; Klamer, M.; Lind, A.-M.; Leth, M.; Bååth, E. Influence of Initial C/N Ratio on Chemical and Microbial Composition during Long Term Composting of Straw. Microb. Ecol. 2001, 41, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, H. The Effects of Apple Pomace, Bentonite and Calcium Superphosphate on Swine Manure Aerobic Composting. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.J.; Zhou, Y.-F. Comparison of the Chemical, Physical and Microbial Properties of Composts Produced by Conventional Composting or Vermicomposting Using the Same Feedstocks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 10763–10772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ye, C.; Gao, B.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Ding, K.; Li, H.; Ren, K.; Chen, S.; Wang, W.; et al. Applying Struvite as a N-Fertilizer to Mitigate N2O Emissions in Agriculture: Feasibility and Mechanism. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Shangguan, Y.; Yang, G.; Liu, X. Degradation Performance and Mechanism of Microcystins in Aquaculture Water Using Low-Temperature Plasma Technology. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 347, 123744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, H. Influence of Biochar on Heavy Metals and Microbial Community during Composting of River Sediment with Agricultural Wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, J.; Ghosh, U.; Kalamdhad, A.S.; Khwairakpam, M.; Singh, J. Transformation of Elemental Toxic Metals into Immobile Fractions in Paper Mill Sludge through Rotary Drum Composting. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 101, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, S.; Hafidi, M.; Merlina, G.; Revel, J.-C. Sequential Extraction of Heavy Metals during Composting of Sewage Sludge. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Gao, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zuo, H.; Wei, Z. Roles of Different Humin and Heavy-Metal Resistant Bacteria from Composting on Heavy Metal Removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 296, 122375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, N.; Baruah, P.P. Cyanobacteria as a Potent Platform for Heavy Metals Biosorption: Uptake, Responses and Removal Mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 11, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yi, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Nie, Y.; Luo, M.; Wang, Q.; et al. Improved Humification and Cr (VI) Immobilization by CaO2 and Fe3O4 during Composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 413, 131479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Tested Materials | Moisture | Organic Matter | Total N | Total P | Total K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | (g kg−1) | ||||
| CS | 23.4 | 410.2 | 74.1 | 109.8 | 17.5 |
| Chicken manure | 10.5 | 345.9 | 76.0 | 32.7 | 8.8 |
| Wheat Straw | 3.7 | 647.7 | 7.2 | 8.7 | 178.5 |
| Treatments | Chicken Manure | Wheat Straw | Struvite | CS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5.4 | 3.6 | 0.27 | – |
| CS10% | 4.86 | 3.6 | 0.27 | 0.54 |
| CS20% | 4.32 | 3.6 | 0.27 | 1.08 |
| CS30% | 3.78 | 3.6 | 0.27 | 1.62 |
| CS40% | 3.24 | 3.6 | 0.27 | 2.16 |
| Treatments | Microcystins Content (μg kg−1) | Degradation Rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microcystin–RR | Microcystin–LR | Microcystin–RR | Microcystin–LR | |
| CS10% | 52.7 ± 27.6 b | 33.5 ± 13.6 b | 35.7% | 30.2% |
| CS20% | 57.7 ± 13.2 b | 39.1 ± 0.2 b | 65.9% | 59.3% |
| CS30% | 50.5 ± 7.9 b | 31.9 ± 3.3 b | 79.5% | 77.9% |
| CS40% | 123.7 ± 2.4 a | 75.4 ± 2.9 a | 62.3% | 60.7% |
| Treatments | As | Cd | Cr | Hg | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg kg−1) | |||||
| NY/T | ≤15 | ≤3 | ≤150 | ≤2 | ≤50 |
| CK | 1.53 ± 0.01 a | 1.14 ± 0.03 a | 35.00 ± 0.70 c | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 6.48 ± 0.01 a |
| CS10% | 1.00 ± 0.02 b | 0.60 ± 0.02 b | 29.40 ± 0.30 e | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 4.58 ± 0.04 b |
| CS20% | 1.09 ± 0.15 b | 0.41 ± 0.02 c | 39.30 ± 0.80 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 4.26 ± 0.12 c |
| CS30% | 0.91 ± 0.07 cd | 0.24 ± 0.01 d | 37.85 ± 0.65 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 4.12 ± 0.00 d |
| CS40% | 0.82 ± 0.04 d | 0.25 ± 0.00 d | 32.85 ± 0.35 d | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 4.26 ± 0.12 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Y.; Sun, H. The Optimal Cyanobacterial Sludge Incorporation Balances Nutrient Retention and NH3 Emission Reduction During Composting with Chicken Manure and Wheat Straw. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102429
Liu Y, Chen Y, Chen Y, Feng Y, Sun H. The Optimal Cyanobacterial Sludge Incorporation Balances Nutrient Retention and NH3 Emission Reduction During Composting with Chicken Manure and Wheat Straw. Agronomy. 2025; 15(10):2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102429
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yifei, Yudong Chen, Ying Chen, Yanfang Feng, and Haijun Sun. 2025. "The Optimal Cyanobacterial Sludge Incorporation Balances Nutrient Retention and NH3 Emission Reduction During Composting with Chicken Manure and Wheat Straw" Agronomy 15, no. 10: 2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102429
APA StyleLiu, Y., Chen, Y., Chen, Y., Feng, Y., & Sun, H. (2025). The Optimal Cyanobacterial Sludge Incorporation Balances Nutrient Retention and NH3 Emission Reduction During Composting with Chicken Manure and Wheat Straw. Agronomy, 15(10), 2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102429






