Transport of Phosphorus from Three Fertilizers Through High- and Low-Phosphorus Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fertilizer
2.2. Soil
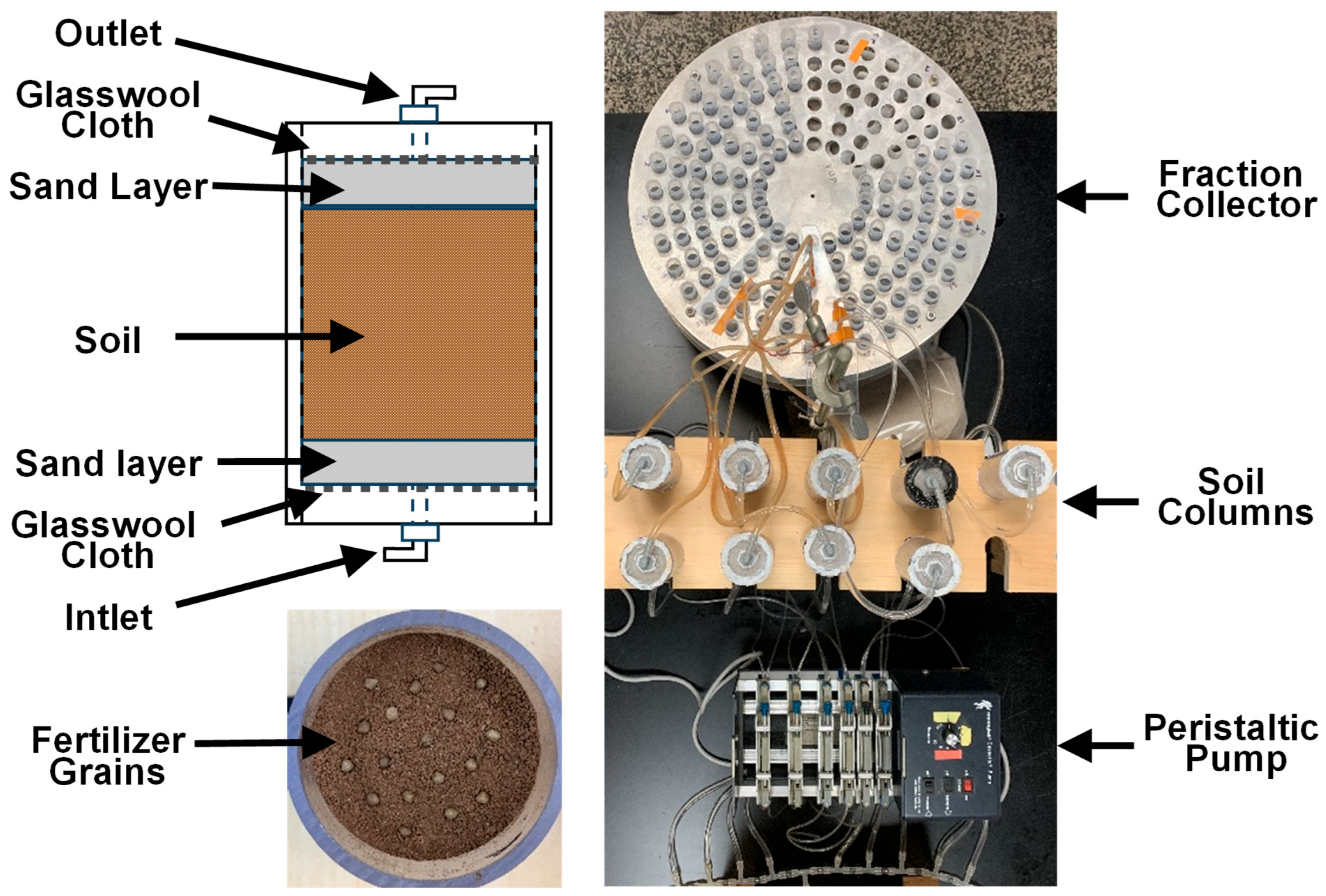
2.3. Column Preparation
2.4. Experimental Procedures
2.4.1. Water Application
2.4.2. Phosphorus Retention in Soil
2.4.3. Outflow Phosphorus Concentration Analysis
2.4.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
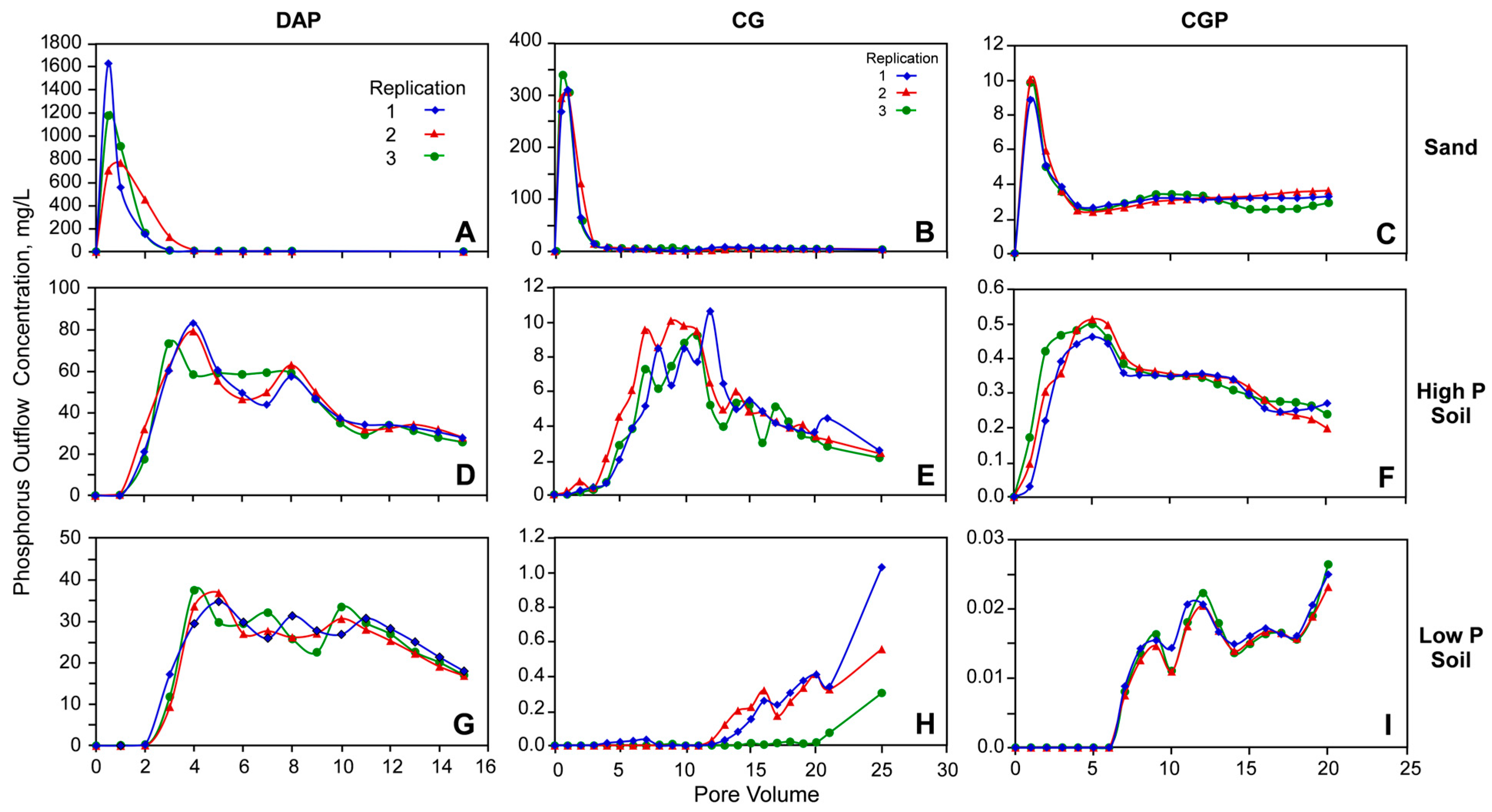
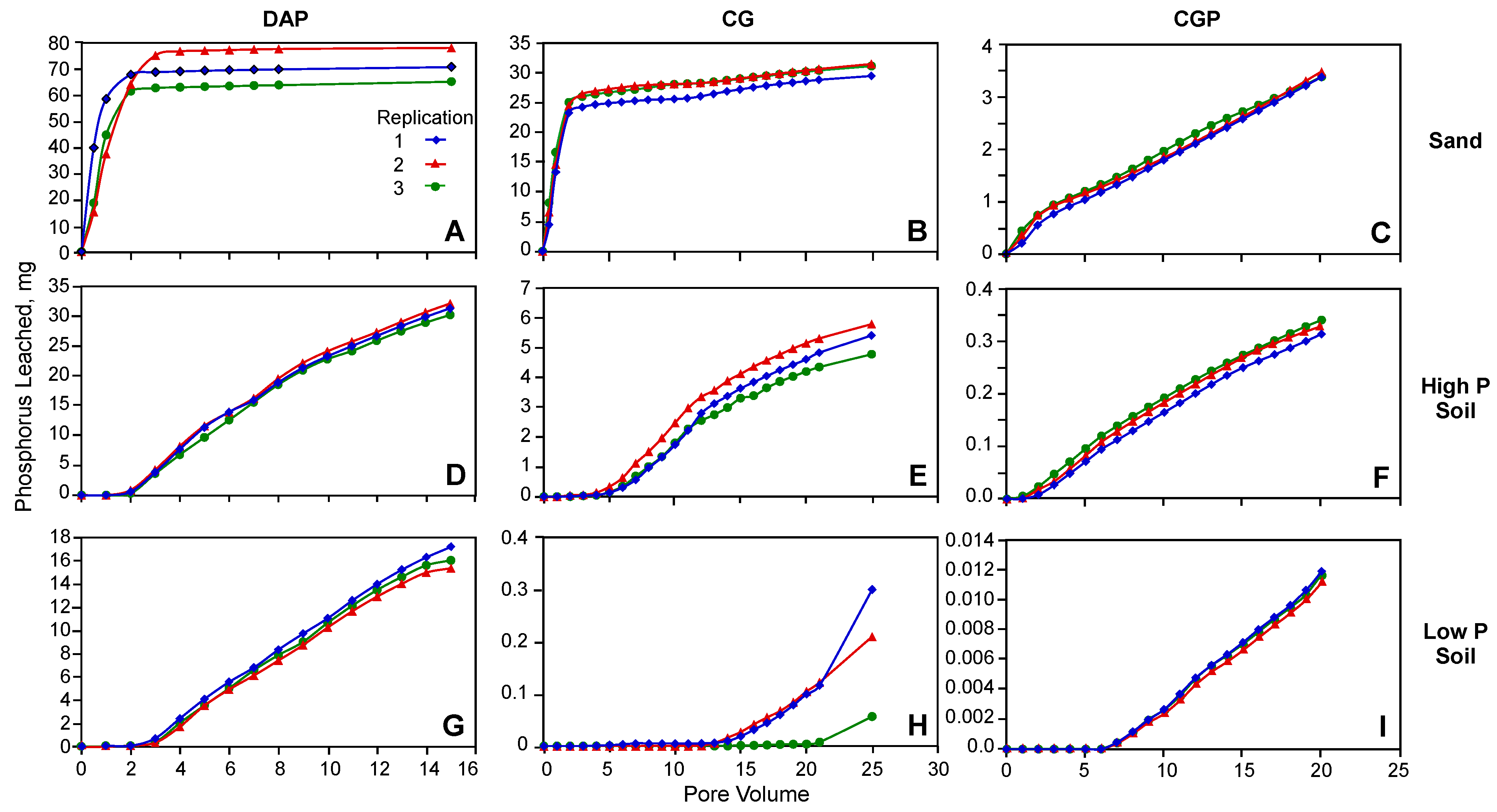
3.1. Solubility of P from Fertilizer Grains
3.2. Phosphorus Retention
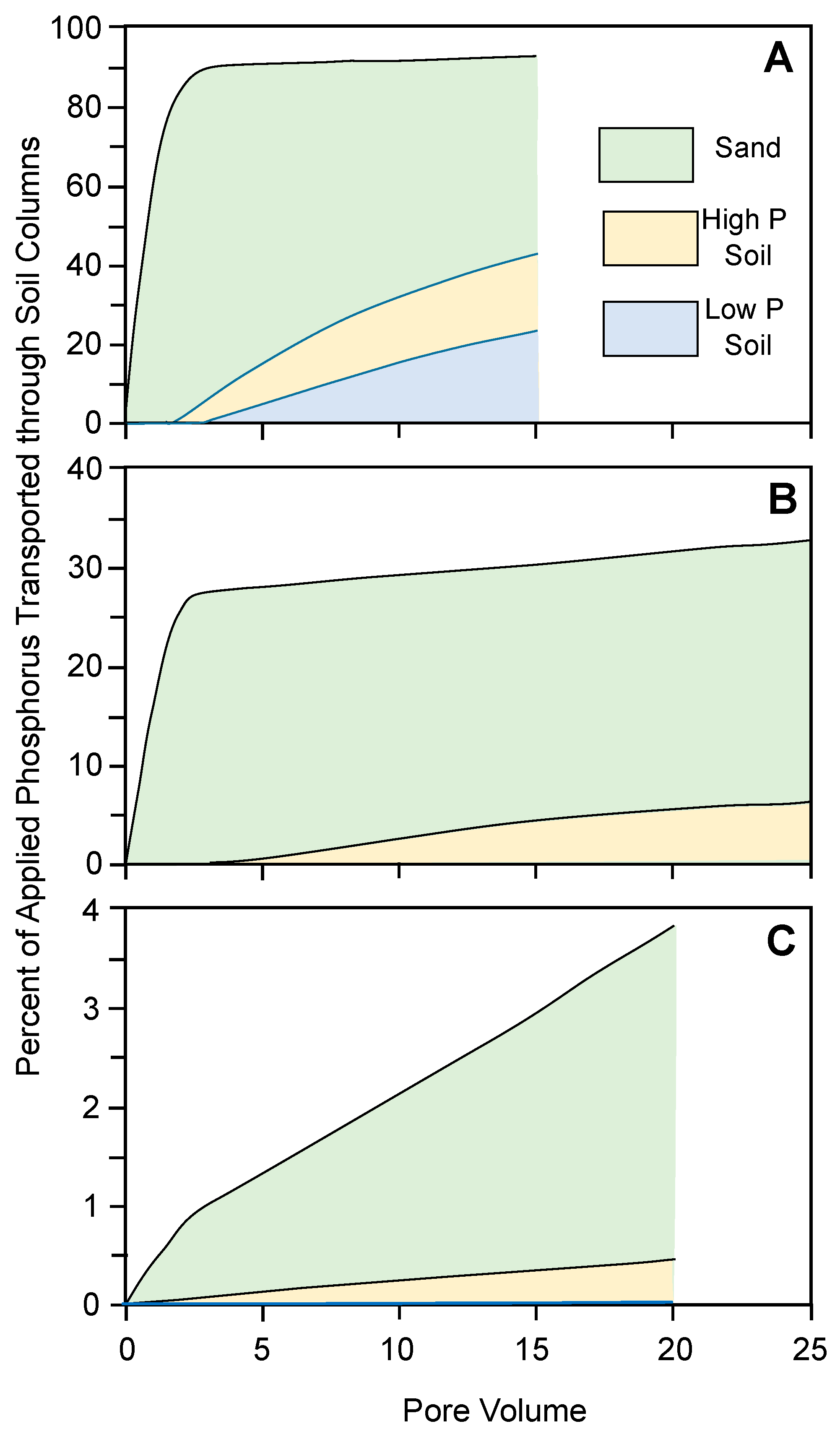
3.3. Phosphorus Transport
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Havlin, J.L.; Tisdale, S.L.; Nelson, W.L.; Beaton, J.D. Soil Fertility and Fertilizers—An Introduction to Nutrient Management, 8th ed.; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, J.H., Jr. Phosphorus bioavailability. In Bioavailability of Nutrients for Animals: Amino Acids, Minerals; Ammerman, C.B., Baker, D.H., Lewis, A.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 257–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veum, T.L. Phosphorus and calcium nutrition and metabolism. In Phosphorus and Calcium Utilization and Requirements in Farm Animals; Vitti, D.M.S.S., Kebreab, E., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2010; pp. 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buol, S.W.; Suthard, R.J.; Graham, R.C.; McDaniel, P.A. Soil Genesis and Classification, 6th ed.; Wiley-Blackwall: Ames, IA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Paz-Ares, J.; Puga, M.I.; Rojas-Triana, M.; Martinez-Hevia, I.; Diaz, S.; Poza-Carrión, C.; Miñambres, M.; Leyva, A. Plant adaptation to low phosphorus availability: Core signaling, crosstalks, and applied implications. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 104–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierzynski, G.M.; McDowell, R.W.; Sims, J.T. Chemistry, cycling, and potential movement of inorganic phosphorus in soils. In Phosphorus: Agriculture and the Environment; Sims, J.T., Sharpley, A.N., Eds.; Agronomy Series No. 46; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 2005; pp. 51–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, K.; Cordell, D.; Mavinic, D. A brief history of phosphorus: From the philosopher’s stone to nutrient recovery and reuse. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippelli, G.M. Phosphate rock formation and marine phosphorus geochemistry: The deep time perspective. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edixhoven, J.D.; Gupta, J.; Savenije, H.H.G. Recent revisions of phosphate rock reserves and resources: A critique. Earth Syst. Dynam. 2014, 5, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.; Bennett, E. A broken biogeochemical cycle. Nature 2011, 478, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Chopra, A.K.; Kumar, A. A review on sewage sludge (biosolids) a resource for sustainable agriculture. Arch. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2017, 2, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; He, Z.L.; Stoffella, P.J. Land application of biosolids in the USA: A review. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2012, 2012, 201462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, B.O.; Smith, S.R. Review of ‘emerging’ organic contaminants in biosolids and assessment of international research priorities for the agricultural use of biosolids. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 226–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, I.L.; Brusseau, M.L.; Prevatt, F.J.; Escobar, B.A. Incidence of Pfas in soil following long-term application of class B biosolids. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzebon, E.A.; Seifert, L. Emerging environmental health risks associated with the land application of biosolids: A scoping review. Environ. Health 2017, 22, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordell, D.; Drangert, J.; White, S. The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Glob. Environ. Change 2009, 19, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich Earth Institute. Fertilizer from Urine, Clean Rivers, Sustainable Farms. 2024. Available online: https://richearthinstitute.org/ (accessed on 7 October 2025).
- Maurer, M.; Pronk, W.; Larsen, T.A. Treatment processes for source-separated urine. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3151–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neal, J.A.; Boyer, T.H. Phosphate recovery using hybrid anion exchange: Applications to source-separated urine and combined wastewater streams. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5003–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendrowski, A.; Boyer, T.H. Phosphate removal from urine using hybrid anion exchange resin. Desalination 2013, 322, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, T.H.; Saetta, D. Opportunities for building-scale urine diversion and challenges for implementation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egle, L.; Rechberger, H.; Zessner, M. Overview and description of technologies for recovering phosphorus from municipal wastewater. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 105, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, A.L.; Fattah, K.P.; Mavinicm, D.S.; Koch, F.A. Optimizing Struvite Production for Phosphate Recovery in WWTP. J. Environ. Eng. 2008, 134, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Piqueres, A.; Ribó, M.; Rodríguez-Carretero, I.; Quiñones, A.; Canet, R. Struvite as a Sustainable Fertilizer in Mediterranean Soils. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilleos, P.; Roberts, K.R.; Williams, I.D. Struvite precipitation within wastewater treatment: A problem or a circular economy opportunity? Heliyon 2022, 8, e09862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, V.; Castillo, R.; Magrí, A.; Holzapfel, E.; Vidal, G. Phosphorus recovery from domestic wastewater: A review of the institutional framework. J. Environ. Manage. 2024, 351, 119812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, M.A.; Romeo-Hall, A.G.; Rooimans, T.M.; Slootweg, J.C. An assessment of the drivers and barriers for the deployment of urban phosphorus recovery technologies: A case study of the Netherlands. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smil, V. Phosphorus in the environment: Natural flows and human interferences. Ann. Rev. Energy Environ. 2000, 25, 53–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, N.J.; Debnath, A.; Sen, A. Investigating the dissolution of soil phosphate. Plant Soil 2023, 490, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syers, J.K.; Johnston, A.E.; Curtin, D. Efficiency of Soil Fertilizer Phosphorus Use: Reconciling Changing Concepts of Soil Phosphorus Behavior with Agronomic Information. FAO Fertilizer and Plant Nutrition Bulletin No. 18. 2008. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome. Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/010/a1595e/a1595e00.htm (accessed on 7 October 2025).
- Kile, L.K.; Gatiboni, L.; Osmond, D.L.; Marshall, A.; Johnson, A.; Duckworth, O.W. Why does overapplication of phosphorus fertilizers occur: Insights from North Carolina farmers. Agriculture 2025, 15, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yan, H.; Xu, S.; Lin, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, D. Moderately deep banding of phosphorus enhanced winter wheat yield by improving phosphorus availability, root spatial distribution, and growth. Soil Till. Res. 2022, 220, 105388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, G.; Bell, M.J.; Kopittke, P.M.; Lombi, E.; Doolette, C.L.; Brunetti, G.; Klysubun, W.; Janke, C.K. Mobility and lability of phosphorus from highly concentrated fertiliser bands. Geoderma 2023, 429, 116248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, G.W.; Hoeft, R.G. Placement methods for improved efficiency of P and K fertilizers: A review. J. Prod. Agric. 1988, 1, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertahi, S.; Bertrand, I.; Ilsouk, M.; Oukarroum, A.; Amjoud, M.B.; Zeroual, Y.; Barakat, A. New generation of controlled release phosphorus fertilizers based on biological macromolecules: Effect of formulation properties on phosphorus release. Int. J. Bio. Macromol. 2020, 143, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weeks, J.J.; Hettiarachchi, G.M. A review of the latest in phosphorus fertilizer technology: Possibilities and pragmatism. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1300–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Pang, J.; Mickan, B.S.; Ryan, M.H.; Jenkins, S.N.; Siddique, K.H.M. Wastewater-derived struvite has the potential to substitute for soluble phosphorus fertiliser for growth of chickpea and wheat. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 3011–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talboys, P.J.; Heppell, J.; Roose, T.; Healey, J.R.; Jones, D.L.; Withers, P.J.A. Struvite: A slow-release fertiliser for sustainable phosphorus management? Plant Soil 2016, 401, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lv, J.; Xie, J.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Tang, C.; Niu, T.; Patience, B.E. Effect of slow-release fertilizer on soil fertility and growth and quality of wintering Chinese chives (Allium tuberm Rottler ex Spreng.) in greenhouses. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerman, J.N.; Zvomuya, F.; Cicek, N.; Flaten, D. Evaluation of manure-derived struvite as a phosphorus source for canola. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 933, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugavel, D.; Rusyn, I.; Solorza-Feria, O.; Kamaraj, S.-K. Sustainable SMART fertilizers in agriculture systems: A review on fundamentals to in-field applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Abdi, D.; Cade-Menun, B.J. Investigation of soil legacy phosphorus transformation in long-term agricultural fields using sequential fractionation, P K-edge XANES and solution P NMR spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2015, 49, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.; Jarvie, H.P.; Buda, A.; May, L.; Spears, B.; Kleinman, P. Phosphorus legacy: Overcoming the effects of past management practices to mitigate future water quality impairment. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 1308–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Q.; MacKenzie, A.F.; Liang, B.C.; Drury, C.F. Soil test phosphorus and phosphorus fractions with long-term phosphorus addition and depletion. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F.; Correll, D.L.; Howarth, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, V.H. Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoshit, M.; Komats, T.; Moldrup, P.; De Jonge, L.W.; Ozak, N.; Fukushima, T. Soil constituent facilitated transport of phosphorus from a high-P surface soil. Soils Found. 2003, 43, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Chapra, S.C.; Wedepohl, R.; Sims, J.T.; Daniel, T.C.; Reddy, K.R. Managing Agricultural Phosphorus for Protection of Surface Waters: Issues and Options. J. Environ. Qual. 1994, 23, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VandeVoort, A.R.; Livi, K.J.; Arai, Y. Reaction conditions control soil colloid facilitated phosphorus release in agricultural Ultisols. Geoderma 2013, 206, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugener, N.M.; Stone, I.P.; Weinke, A.D.; Biddanda, B.A. Out of oxygen: Stratification and loading drove hypoxia during a warm, wet, and productive year in a Great Lakes estuary. J. Great Lakes Res. 2023, 49, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamprath, E.J. Changes in phosphate availability of ultisols with long-term cropping. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1999, 30, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennock, D.J. Designing field studies in soil science. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 84, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selles, F.; Campbell, C.A.; Zentner, R.P.; Curtin, D.; James, D.C.; Basnyat, P. Phosphorus use efficiency and long-term trends in soil available phosphorus in wheat production systems with and without nitrogen fertilizer. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 91, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, S.E.; Arnall, D.B.; Ashford-Kornburger, D.; Brouder, S.M.; Christian, E.; Dobermann, A.; Haefele, S.M.; Haegele, J.; Helmers, M.J.; Jin, V.L.; et al. Field trial guidelines for evaluating enhanced efficiency fertilizers. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2025, 89, e20787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, N.K.; da Costa, J.G.C. Evaluation of common bean genotypes for phosphorus use efficiency. J. Plant Nutr. 2000, 23, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, M.; Ylivainio, K. Methods for testing short- and long-term phosphorus fertilizing efficiency of products with varying solubility. Sci Total Environ. 2024, 922, 170965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauly, D.G.; Nyborg, M.; Malhi, S.S. Controlled-release P fertilizer concept evaluation using growth and P uptake of barley from three soils in a greenhouse. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2002, 82, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombi, E.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Johnston, C.; Armstrong, R.D.; Holloway, R.E. Mobility, solubility and lability of fluid and granular forms of P fertiliser in calcareous and non-calcareous soils under laboratory conditions. Plant Soil 2005, 269, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombi, E.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Johnston, C.; Armstrong, R.D.; Holloway, R.E. Mobility and lability of phosphorus from granular and fluid monoammonium phosphate differs in a calcareous soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierzynski, J.; Hettiarachchi, G.M. Reactions of phosphorus fertilizers with and without a fertilizer enhancer in three acidic soils with high phosphorus-fixing capacity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2018, 82, 1124–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaggs, T.D.; Wilson, G.V.; Shouse, P.J.; Leij, F.J. Solute transport: Experimental methods. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 4. Physical Methods; Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C., Eds.; SSSA Book Series No. 5; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 1381–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Abit, S.M.; Vepraskas, M.J.; Duckworth, O.W.; Amoozegar, A. Dissolution of phosphorus into pore-water flowing through an organic soil. Geoderma 2013, 197–198, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretzschmar, R.; Robarge, W.P.; Amoozegar, A. Influence of natural organic matter on colloid transport through saprolite. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stall, C.; Amoozegar, A.; Lindbo, D.; Graves, A.; Rashash, D. Transport of E. coli in a sandy soil as impacted by depth to water table. J. Environ. Health 2014, 76, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, N.A.; Gatiboni, L.; Osmond, D.; Vann, R.; Kuleasza, S.; Crozier, C.; Hardy, D. Critical soil test values of phosphorus and potassium for soybean and corn in three long-term trials in North Carolina. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2023, 87, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, G.W.; Or, D. Particle-size analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 4. Physical Methods; Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C., Eds.; SSSA Book Series No. 5; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 255–293. [Google Scholar]
- Flint, A.L.; Flint, L.E. Particle density. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 4. Physical Methods; Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C., Eds.; SSSA Book Series No. 5; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 229–240. [Google Scholar]
- Steel, R.G.D.; Torrie, J.H. Principles and Procedures of Statistics; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Elrys, A.H.; Zhang, L.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Liu, Y.; Fu, S.; Yan, J.; Ye, Q.; Wen, D.; Hou, E. The global fate of inorganic phosphorus fertilizers added to terrestrial ecosystems. One Earth 2024, 7, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, K.W.; Williams, M.R.; Macrae, M.L.; Fausey, N.R.; Frankenberger, J.; Smith, D.R.; Kleinman, P.J.A.; Brown, L.C. Phosphorus transport in agricultural subsurface drainage: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 467–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.; Lederer, H.; Kahle, P.; Lennartz, B. Linking transport pathways and phosphorus distribution in a loamy soil: A case study from a North-Eastern German Stagnosol. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, D.K.; Ball, B.; Zhang, T.Q. Accounting for the risks of phosphorus losses through tile drains in a phosphorus index. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 1720–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatiboni, L.C.; Schmitt, D.E.; Cassol, P.C.; Comin, J.J.; Heidemann, J.C.; Brunetto, G.; Nicoloso, R.D. Samples disturbance overestimates phosphorus adsorption capacity in soils under long-term application of pig slurry. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 1262–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, R.; Yang, R.; Wei, H.; Li, Y.; Xiao, H.; Wu, J. Using a simple soil column method to evaluate soil phosphorus leaching risk. Clean Soil Air Water 2013, 41, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, M.; McLaughlin, M. Reactions of phosphate fertilizers and by-products in soils. In Phosphorus: Agriculture and the Environment; Sims, J.T., Sharpley, A.N., Eds.; Agronomy Series No. 46; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 2005; pp. 181–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigon, L.M.L.; Kaiser, D.E.; Feyereisen, G.W. Influence of soil test phosphorus level and leaching volume on phosphorus leaching. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2022, 86, 1280–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, G.S.; Sims, J.T. Managing phosphorus leaching in Mid-Atlantic soils: Importance of legacy sources. Vadose Zone J. 2015, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| P Content | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Textural | Particle | Base | Humic | Water | ||||||||
| Soil | Sand | Silt | Clay | Class | Density | pH | CEC | Saturation | Matter | Extractable | Mehlich III | Total |
| % | g/cm3 | cmol+/kg | % | % | mg/kg | |||||||
| High P | 40.6 | 35.9 | 23.5 | loam | 2.61 | 6.2 | 9.5 | 85 | 0.41 | 0.0 | 150.0 | 1133 |
| Low P | 43.7 | 34.6 | 21.7 | loam | 2.59 | 6.2 | 10.1 | 86 | 0.27 | 0.0 | 12.6 | 665 |
| DAP | CG | CGP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | Mean | StdDev | Mean | StdDev | Mean | StdDev |
| Sand | 9.02 | 1.69 | 66.45 | 3.00 | 96.17 | 0.50 |
| High P | 57.79 | 5.06 | 93.62 | 0.37 | 99.60 | 0.16 |
| Low P | 77.62 | 2.30 | 99.41 | 0.29 | 99.97 | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
DuPlooy, L.; Heitman, J.; Gatiboni, L.; Amoozegar, A. Transport of Phosphorus from Three Fertilizers Through High- and Low-Phosphorus Soils. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102395
DuPlooy L, Heitman J, Gatiboni L, Amoozegar A. Transport of Phosphorus from Three Fertilizers Through High- and Low-Phosphorus Soils. Agronomy. 2025; 15(10):2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102395
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuPlooy, Lily, Joshua Heitman, Luke Gatiboni, and Aziz Amoozegar. 2025. "Transport of Phosphorus from Three Fertilizers Through High- and Low-Phosphorus Soils" Agronomy 15, no. 10: 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102395
APA StyleDuPlooy, L., Heitman, J., Gatiboni, L., & Amoozegar, A. (2025). Transport of Phosphorus from Three Fertilizers Through High- and Low-Phosphorus Soils. Agronomy, 15(10), 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102395






