Abstract
Excessive application of nitrogen (N) fertilizer increases the risk of soil NO3−-N leaching in fluvial soil, threatening soil and groundwater quality and safety. Enhancing soil carbon (C) by returning straw to the field can efficiently improve soil quality. The process of increasing C/N by straw returning to regulate soil nitrogen transformation and mitigate NO3−-N leaching, and the ecological threshold of straw application rate in fluvial soil need to be further explored. This study aims to research a series of soil C/N ratio treatments (including no straw, CK; C/N of 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 and 40), which were set up by adding straw at different application rates, and to investigate the underlying process of increasing C/N ratio by incorporating straw to mitigate NO3−-N leaching. As the soil C/N ratio increased, the total soil nitrogen showed a fluctuating increase with the highest value in S40 treatment (increased by 358 mg kg−1), while the NO3−-N leaching amount reached the lowest value at the C/N ratio of 20, with an average reduction of 45% (decreased by 29.3 mg kg−1). Increasing soil C/N ratio significantly increased soil microbial biomass, cellulase, urease and N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase activities while it decreased the net N mineralization rate, ammonification rate and nitrification rate. Principal component analysis showed that the NO3−-N leaching was positively correlated with the ammonification rate, nitrification rate and net N mineralization rate, and negatively correlated with the abundances of bacteria, fungi and nitrogen-fixing genes (nifH) (p < 0.01). Structural equation model analysis showed that straw-regulated C/N, dissolved organic N and soil fungi were the most important factors affecting NO3−-N leaching, followed by the ammonification rate. Overall, increasing soil C/N by adding straw could enhance soil microbial biomass (especially fungi) and enzyme activities to promote soil N storage and reduce net N mineralization, ammonification and nitrification to decrease NO3−-N leaching.
1. Introduction
Excessive N application leads to eutrophication of watershed water and nitrate pollution of groundwater primarily through surface runoff and soil percolation [1,2]. In China, the amount of chemical N fertilizer applied for agricultural use in 2023 by 1.6 × 107 tons (https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/2024/indexch.htm, accessed on 9 October 2025), and the N fertilizer loss rate at the current farmland management level is between 40 and 50% [3]. The fluvial soils are the primary soil type in North China, which is one of the most important grain-producing areas. The parent material of fluvial soils is alluvium from the Yellow River, which has a loose texture, good aeration and permeability, making it easier for NO3−-N to form and accumulate [4]. Fluvial soils, with their low cation exchange capacity and weak adsorption capacity for NO3−-N, combined with NO3−-N sharing the same negative charge as soil particles, result in NO3−-N having strong mobility and a tendency to accumulate and leach into deeper soil layers [4,5]. Excessive nitrogen application and concentrated precipitation in the summer maize season are prone to NO3−-N leaching [5]. Compared with terrestrial soils, agricultural soils have a lower mean C/N ratio, resulting in the accumulation and leaching of nitrate in agricultural soils under heavy rainfall [6]. Reducing the leaching loss of NO3−-N in fluvial soils is crucial for mitigating the adverse environmental impacts caused by N fertilization in agroecosystems, and it has positive significance for improving the environment and promoting sustainable development.
Crop straw (e.g., wheat, maize, sawdust) is an abundant and renewable carbon resource; returning straw to the field is commonly conducted in China to improve soil quality [7]. Straw incorporation could regulate soil N transformation through exogenous organic C inputs, regulating soil stoichiometric ratio, improving soil physical structure, and change microbial turnover [6,8]. Straw returning reduces the leaching loss of NO3−-N in leachate by increasing soil water-holding capacity, slowing leachate leakage and enhancing nitrogen sequestration in the soil [9,10]. Adding sawdust can stimulate microbial nitrate immobilization [11]. The combined application of straw and denitrifying bacteria agents could reduce soil nitrate leaching by promoting microbial nitrate assimilation [4]. However, Ren et al. [12] demonstrated that straw incorporation only decreased gross rates of mineralization and nitrification compared to straw removal at 150 kg N ha−1 per season, presenting a contrasting trend at 250 kg N ha−1 per season. Therefore, the ecological threshold of C/N ratio application for enhancing nitrogen sequestration and reducing nitrate nitrogen leaching remains to be studied. Soil microorganisms constitute an active nitrogen pool in the soil. Bacteria and fungi, while participating in nitrogen storage and mineralization, can also effectively regulate soil enzyme activities. Soil enzymes are key catalysts for soil biochemical processes. Among them, decomposing enzymes (e.g., urease, protease) mainly regulate soil mineralization processes (e.g., N-acetyl-β-D-glucosidase, NAG), nitrification functional enzymes (e.g., Ammonia Monooxygenase) are involved in soil nitrification and almost all nitrogen fixation processes in soil depend on Nitrogenase.
Soil C/N ratio reflect the coordinated changes in soil C and N pools and is an important indicator of the ecosystem’s C sequestration potential and N sustainability [6]. Soil C/N ratio was negatively related to gross nitrification rates and positively correlated with the abundance changes in 18S rRNA, nifH and AOA genes [13,14]. The process of increasing C/N by straw returning to regulate soil nitrogen transformation and mitigate NO3−-N leaching and the ecological threshold of straw application rate in fluvial soil needs to be further explored. Cheng et al. [15] used meta-analysis and demonstrated that soil microbial NO3− immobilization was enhanced when C/N ratio was >18, and not affected when the C/N ratio was <18. Therefore, this study explored the regulatory patterns of soil C/N adjusted by straw addition on nitrogen transformation and nitrogen leaching in fluvial soil.
The purpose of this study is (1) to explore the dynamic characteristics of nitrogen transformation and distribution in fluvial soil by increasing C/N; and (2) to clarify the ecological threshold of straw application rate for enhancing N sequestration and minimizing NO3−-N leaching. We hypothesized that (1) adding straw can reduce nitrogen leaching in the fluvial soil, (2) adding straw can increase microbial N storge and reduce soil net nitrogen mineralization and nitrification, and the (3) incorporation straw to increase the C/N ratio can enhance soil enzyme activity and improve soil inorganic nitrogen transformation. The soil 15N tracer technique can distinguish between fertilizer-derived nitrogen and native soil nitrogen, quantify the entire transformation process of nitrogen in the soil–crop system, and precisely determine the sources and fates of nitrogen [16]. In this study, the fertilizer 15N isotope tracing technique was used to clarify the distribution dynamics of N fertilizer in the soil, and a structural equation model was constructed to analyze the key factors affecting NO3−-N leaching from fluvial soils. The results could provide insightful support for optimizing sustainable farmland management to mitigate agricultural N loss and improve the ecosystem environment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Soil
The original fluvial soil was collected from agricultural fields to conduct soil incubation experiment. The collection site was in Yuanyang County (35°03′56″ N, 113°56′24″ E), Xinxiang City, Henan Province. This region has a semi-arid continental monsoon climate, characterized by an average annual temperature of 14 °C and annual precipitation of approximately 600 mm. The soil in this area is Yellow River alluvial soil, a type of fluvial soil, with a sandy loam texture. The cropping system was an annual rotation of summer maize and winter wheat. The soil properties were pH 8.60, soil organic C 4.50 g kg−1, total N 0.46 g kg−1, available N (AN) 54.4 mg kg−1, available phosphorus (AP) 23.5 mg kg−1, available potassium (AK) 155 mg kg−1 and soil C/N 9.87. Wheat straw: total N 4.48 g kg−1, organic C 367 g kg−1, and C/N ratio 82.0.
2.2. Experimental Design
A series of buckets (diameter: 22 cm, height: 25 cm, volume: 9.5 L) containing 2 kg dry soil (<2 mm) was prepared. A C/N ratio gradient was set up by adding wheat straw at seven application rates including no straw (CK), C/N 15 (S15, 16.0 g dry straw bucket−1), C/N 20 (S20, 34.2 g bucket−1), C/N 25 (S25, 55.7 g bucket−1), C/N 30 (S30, 81.6 g bucket−1), C/N 35 (S35, 113 g bucket−1) and C/N 40 (S40, 153 g bucket−1). There were four replications for each treatment. Wheat straw was pre-composted with brown sugar and ammonium sulfate, where the amounts of the two additives were calculated as 1% of the wheat straw weight, with water added until the water content was saturated, and then it was composted for 45 d. Wheat straw was dried and clipped into 2 cm size and mixed evenly into the soil. Fertilizers were applied at local recommended rates, including 210 kg N hm−2 (0.897 g per buckets, ammonium sulfate with 15% 15N abundance), P 120 kg hm−2 (0.717 g per buckets, calcium superphosphate) and K 90 kg hm−2 (0.382 g per buckets, potassium chloride). During the culture period, the water was weighed and replenished to maintain the soil water content at 60% of the maximum field capacity (maintained at a moisture content of 11%). The greenhouse temperature was 10/20 °C (night/day), and light hours were 12/12 h (night/day).
After 90 days incubation, 500 g of soil samples from each treatment was collected, meshed (<2 mm) uniformly and divided into three parts: 100 g soil was air-dried for determining soil total N content and 15N abundance; 100 g fresh soil was stored at −80 °C and used for N functional genes abundance; 300 g fresh soil was used to determine the soil inorganic N, microbial biomass, enzymes and the transform rates of C and N. After sampling, simulated rainfall was conducted and the leachate was collected. A circle of Vaseline was evenly applied to the junction where the soil surface meets the cylinder wall to prevent leaching water from leaking along the cylinder wall. The 2L deionized water (equivalent to the local average maximum rainfall 20 mm, 1990–2020) was added to each treatment. Then, the volume of the soil leaching solution was collected to determine inorganic N content and isotopic composition of NH4+ and NO3− in the leachate. The residual straw was collected, wash and dried for the determination of 15N abundance.
2.3. Soil and Leachate Properties Analysis
Soil pH (active pH) was determined in a soil–distilled water mixture (1:2.5; CO2 removed) with a pH probe (METTLER-TOLEDO, Zurich, Switzerland). AN was determined using the alkali hydrolysis–diffusion separation followed by acid-base titration method. AP was determined by sodium bicarbonate extraction-colorimetry. AK was determined by ammonium acetate extraction-flame photometry. Soil total N was digested with a catalyst (Selenium powder–copper sulfate–potassium sulfate = 1:10:100) and H2SO4 and analyzed by Kjeldahl [17]. NH4+-N and NO3−-N were extracted with 2 mol·L−1 KCl solution, followed by determination via continuous-flow analysis using an Auto Analyzer 3 (SEAL Analytical GmbH, Norderstedt, Germany) [18]. The dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) were determined with a C/N element Analyzer (multiN/C 3100, Analytik Jena AG, Jena, Germany) after extraction with 0.5 mol·L−1 K2SO4 at a soil water ratio of 1:5 [17]. The isotopic composition of NH4+ and NO3− in the leachate was assessed via stable isotope ratio mass spectrometry (Elementar Analysensysteme Hanau, GmbH, Langenselbold, Germany) [19].
2.4. Soil Microbial Biomass
Soil microbial biomass carbon (MBC) and nitrogen (MBN) were determined using a chloroform fumigation and direct extraction method [20,21]. The value to calculate biomass from the C and N determinations (KEC and KEN) was 0.45 and 0.53, respectively [22]. For each column, a 20 g sample of fresh soil was taken, both from chloroform-fumigated and non-fumigated treatments. These samples were directly extracted with 0.5 M K2SO4. The C and N concentrations in the extracts were analyzed using a C/N element analyzer (Multi N/C 3100, Analytik Jena, Jena, Germany).
2.5. Soil Enzyme Activities
Five soil enzyme activities were measured to assess microbial influences on soil C and N cycling processes. Sucrase activity was estimated by determining the products of glucose after incubation with 15 mL sucrose solution (8%), 5 mL phosphate buffer (pH = 5.5) and 0.1 mL toluene at 37 °C for 1 day. Sucrase activity was determined using an Ultraviolet Spectrophotometer (Q-6, Shanghai Metash Instruments Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) at 508 nm. Catalase activity was measured according to the back titration of residual H2O2 method [23]. For NAG activity, 1.0 g fresh soil was mixed with 1 mL 0.01 M 4-nitrophenyl-N-a cetyl-β-D-glucopyranoside solution and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h. The reaction was then terminated by adding 1 mL 0.5 M CaCl2 and 4 mL 0.5 M NaOH. After filtration, the concentration of the product p-nitrophenol was determined using the colorimetric method with a UV-VIS spectrophotometer (UV-1700, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) [24]. Urease activity was determined by incubating a mixture of 5.0 g moist soil and 2.5 mL of 80 mM urea solution at 37 °C for 2 h [25]. The released ammonium was extracted using 50 mL of KCl solution and measured at 690 nm with a digital UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Biotek ELx800, Winooski, VT, USA). Urease activity was expressed as μg ammonium g−1 soil 2 h−1. The activity of cellulase was determined using the Filter Paper Assay (FPA) [26].
2.6. Soil C and N Transformation Rates
A fresh sample of 10.00 g of dry soil was weighed in a triangular flask, 0.5 mL of 0.044 mol·L−1 (NH4)2SO4 solution was added and the mixture was incubated in dark ventilated conditions for 7 days. During this period, the soil moisture was kept at 50% of the maximum field water holding capacity. After 7 days, 50 mL of 2 mol·L−1 KCl solution was added, shaken for one hour and the mixture was filtered. Then the NH4+ and NO3− in the extracts were determined by continuous-flow analysis with an Auto Analyzer 3 (SEAL Analytical GmbH, Norderstedt, Germany) [16], and soil N transformation rates were calculated from the inorganic N content of the soil before and after incubation [27,28].
Net nitrification rate = (Post-incubation NO3−-N concentration − Pre-incubation NO3−-N concentration)/7 d
Net ammonification rate = (Post-incubation NH4+-N concentration − Pre-incubation NH4+-N concentration)/7 d
Net N mineralization rate = [Post-incubation (NO3−-N+NH4+-N) concentration − Pre-incubation (NO3−-N+NH4+-N) concentration]/7 d
The fresh soil, equivalent to 20 g of dry soil, was weighed and placed in a breathing bottle. A mixture of 120 mg of glucose and talcum powder with a ratio of 1:4 was added. The centrifuge tube with holes containing 10 mL 0.1 mol·L−1 NaOH solution was placed in the bottle. The breathing bottle was sealed and incubated at 25 °C for two hours under dark conditions. After incubation, 2 mL of 1 mol·L−1 BaCl2 and two drops of phenolphthalein indicator were added. The mixture was titrated with 0.05 mol·L−1 HCl solution. Soil C mineralization rate was calculated as the rate of soil respiration producing CO2 [29].
2.7. Soil 16S rRNA, 18S rRNA and N Functional Genes
The soil DNA was extracted from 0.5 g of soil according to the instructions of an EZNA TM Soil DNA Kit (Omega Bio-Tek, Inc., Norcross, GA, USA). qPCR analysis was performed on a Roche LightCycler 480 RealTime PCR Machine (Roche Applied Science, Basel, Switzerland). The primer sets and thermal cycling conditions are shown in Tables S1 and S2 [30,31,32,33,34,35]. The PCR mixture contained 1 μL DNA template, 10 μL SYBR Premix Ex Taq (TaKaRa, Dalian, China), 0.4 μM of each primer and Milli-Q water to a final volume of 20 μL. Melting curve analysis was performed to check the specificity of PCR products at the end of each qPCR run. The standard curve of each functional gene was constructed as previously described. The amplification efficiencies were 86–93%, with R values ranging from 0.992 to 0.999 [36].
2.8. Statistical Analysis
We assessed the main effect of C/N ratio input levels via one-way ANOVA. Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD) among different treatments at the 5% level was employed. All statistical analyses were executed using the Origin 8.5, and SPSS Statistics 26. To investigate the relationships among various soil indicators under different C/N ratio input conditions, we conducted principal component analysis using Canoco 4.5. Furthermore, to investigate the contributions of straw-based C/N regulation, soil DON, bacterial and fungal population, nifH gene, net ammonification rate, net nitrogen mineralization rate, net nitrification rate and soil nitrate nitrogen to nitrate leaching, a structural equation model was conducted using IBM SPSS Amos 21.
3. Results
3.1. NH4+-N and NO3−-N in Soil and Leachate
The one-way ANOVA results showed that as the C/N ratio increased, the NO3−-N content in soil decreased from 90.46 mg kg−1 to 7.43 mg kg−1 and reached its lowest value when the C/N ratio was 20 (Figure 1a). These suggest that increasing the soil C/N ratio could reduce soil NO3−-N accumulation.
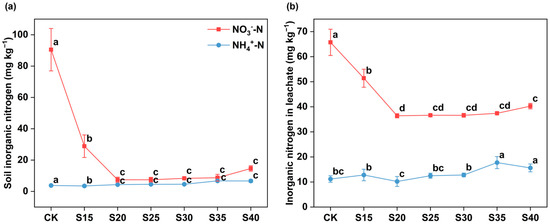
Figure 1.
The content of inorganic nitrogen in soil (a) and leachate (b) under different C/N ratio treatments. The error bars represent the standard errors of the mean of four replicates. Different letters above the lines indicate significant differences based on the LSD test (p < 0.05).
The lowest value of NO3−-N in leachate was observed at a C/N ratio of 20, with an average reduction of 45% (decreased by 29.3 mg kg−1) (Figure 1b). The NH4+-N content in the leachate was significantly increased in S35 and S40 treatments (p < 0.05). Inorganic N in the leachate was predominantly present as NO3−-N. As the C/N ratio increased, the NH4+-N content in the leachate increased, while the NO3−-N content decreased. When the C/N ratio was 35, the proportion of NO3−-N in the leachate was the lowest, accounting for 68% (Figure S2).
3.2. Soil Total N, Microbial Biomass N and Labeled Fertilizer 15N Distribution
Compared to the CK, soil total N content exhibited a fluctuating increase with the soil C/N ratio increasing, with the highest value in S40 treatment (increased by 358 mg kg−1) (Figure 2a). Meanwhile, soil MBN and the ratio of soil MBN to TN were significantly increased in treatments S35 and S40. Labeled fertilizer N in the CK treatment had a loss accounting for 41% (with 9% leached into water) (Figure 2b). Compared with the CK treatment, increasing the soil C/N ratio reduced both fertilizer N emission loss and leaching loss. Soil total 15N abundance was significantly increased in S15 and S20 treatments, with the lowest nitrogen loss proportion (4%) at a C/N ratio of 20. When the C/N ratio was higher than 25, although the proportion of labeled N loss from fertilizer decreased, soil 15N abundance was lower than that in the CK treatment because the straw 15N abundance increased significantly (Figure 2b).
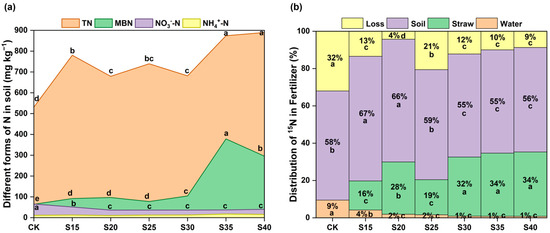
Figure 2.
The content of different N forms in soil (a) and the distribution ratio of fertilizer 15N (b) under different C/N ratio treatments. The leached water was only determined for NO3−-N and NH4+-N. Loss was calculated as 100% minus the percentage of 15N in soil, straw and water. TN, Total nitrogen; MBN, Microbial biomass N; NO3−-N, Nitrate nitrogen; NH4+-N, Ammonium nitrogen. Different letters above the area chart indicate significant differences based on the LSD test (p < 0.05).
3.3. Soil Dissolved Organic C and N and Their Related Transformation Rates
Compared to the CK treatment, elevating the C/N ratio led to a significant increase in soil DOC content (p < 0.05, Figure 3a), and the highest value was observed at a C/N ratio of 40. Increasing the soil C/N ratio significantly increased soil dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) content (p < 0.05; Figure 3c). Soil DON content increased significantly with increasing C/N ratio and reached a maximum at a C/N ratio of 20, followed by a decreasing trend at C/N ratios of 35 and 40.
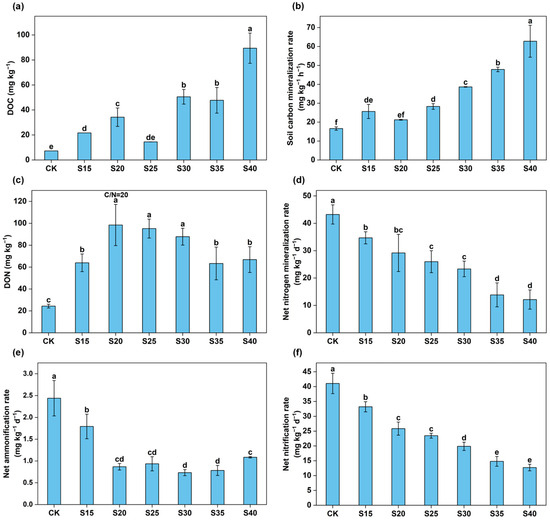
Figure 3.
The content of soil dissolved organic carbon (DOC) (a) and soil carbon mineralization rate (b) under different C/N ratio treatments. The responses of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) (c), net nitrogen mineralization rate (d), net ammonification rate (e), and net nitrification rate (f) to different C/N ratio treatments. The error bars represent the standard errors of the mean of quadruplicate samples. Different letters above the columns indicate significant differences based on the LSD test (p < 0.05).
Soil C mineralization rate significantly increased with increasing C/N ratio (p < 0.05), with the highest value observed in the S40 treatment (Figure 3b). Increasing the C/N ratio substantially reduced the soil net nitrogen mineralization rate and net nitrification rate, with the lowest values showed in the S40 treatment (Figure 3d,f). Soil net ammonification decreased markedly between C/N 15 and 20 but stabilized at C/N 20 to 40 (Figure 3e). Simultaneously, the trend in net ammonification rates paralleled the dynamics of soil NO3−-N, suggesting that increasing C/N ratios could decrease net ammonification rates, thereby minimizing nitrification rates and mitigating NO3−-N leaching.
3.4. Soil Microbial Biomass C and Abundance of N-Functional Genes
Compared to the CK treatment, soil MBC content significantly increased at C/N 25 and 35 (p < 0.05; Figure 4a). Both soil bacterial and fungal populations were significantly enhanced by increasing C/N ratios (p < 0.05), with a greater degree of increase in fungi (Figure 4b,c).
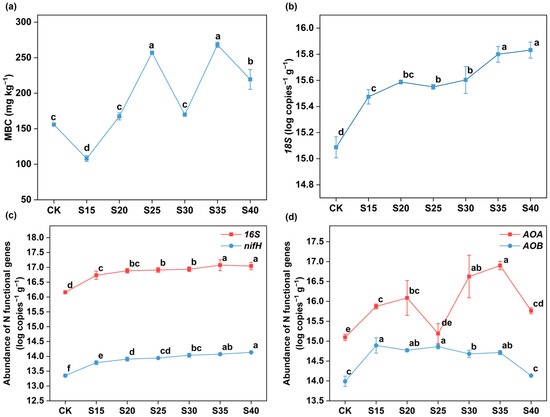
Figure 4.
The responses of soil microbial biomass carbon (MBC) (a), fungal 18S rRNA genes (b), bacterial 16S rRNA genes and nitrogen-fixing genes (nifH) (c) and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and archaea (AOA) genes (d) to different C/N ratio treatments. The error bars represent the standard errors of the mean of quadruplicate samples. Different letters above the lines indicate significant differences based on the LSD test (p < 0.05).
The abundance of the nifH significantly increased as soil C/N ratios rose (p < 0.05; Figure 4c). Similarly, AOA gene abundance significantly increased in treatments S15, S20, S30, S35 and S40, with the highest value in the S35 treatment (Figure 4d). AOB gene abundance exhibited a significant increase in the treatments S15, S20, S25, S30 and S35 (p < 0.05, Figure 4d).
3.5. Soil Enzyme Activities Related to C and N Transformations
Compared to the control, a significant increase in soil cellulase activity was observed at C/N ratios of 35 and 40 (p < 0.05; Figure 5a). Sucrase activity was significantly increased as C/N ratios increased, with the highest value observed at C/N 35, followed by a notable decrease at C/N 40 (Figure 5b). Straw incorporation significantly increased soil catalase activity, showing significant enhancement at C/N ratios of 15–25, followed by a decline at ratios of 30–40 (Figure 5c). Elevated soil C/N ratios markedly increased urease activity (p < 0.05), reaching the maximum level at a C/N ratio of 35 (Figure 5d). N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase activity showed a significant increase with rising C/N ratios, exhibiting a pronounced enhancement at C/N ratios of 15 and 20, followed by a gradual decline at C/N ratios of 25–40 (Figure 5e).
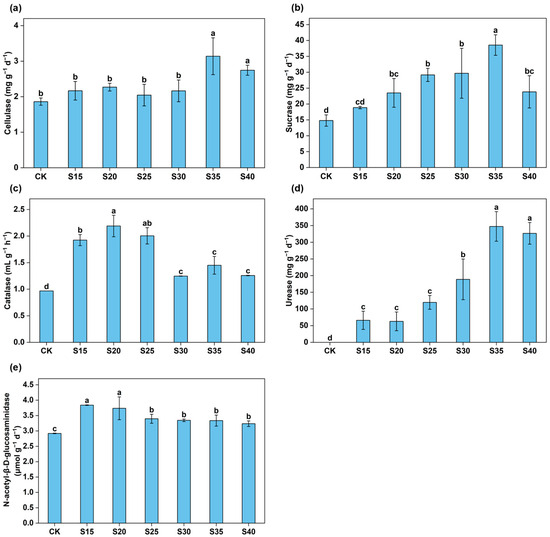
Figure 5.
The responses of cellulase (a), sucrase (b), catalase (c), urease (d), and N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (e) activities to different C/N ratio treatments. The error bars represent the standard errors of the mean of quadruplicate samples. Different letters above the columns indicate significant differences based on the LSD test (p < 0.05).
3.6. Principal Component Analysis of Soil Indicators
The principal component analysis (PCA) results revealed the differences among various soil indicators under different C/N ratio management levels. The first and second axes explained 54.0% and 18.0% of the variation, respectively (Figure 6).
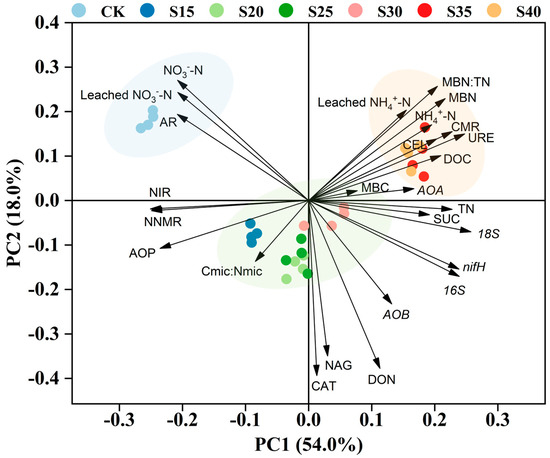
Figure 6.
Under different C/N ratio treatments, the principal component analysis (PCA) of soil indicators. NO3−-N, Nitrate Nitrogen; AR, Ammonification rate; NIR, Nitrification rate; NNMR, Net nitrogen mineralization rate; AOP, Ammonia oxidation potential; Cmic:Nmic, Microbial biomass carbon-to-nitrogen ratio; CAT, Catalase; SUC, Sucrase; TN, Total nitrogen; URE, Urease; CEL, Celluiase; CMR, Carbon mineralization rate.
Relative to straw addition, NO3−-N, leached NO3−-N, and the ammonification rate were significantly higher under the CK treatment. Soil NO3−-N and leached NO3−-N were significantly negative correlated with bacteria, fungi, nifH, AOA and AOB (p < 0.01). Straw incorporation significantly decreased the ammonia oxidation potential, soil net nitrogen mineralization rate and soil nitrification rate, with the lowest values in the S35 and S40 treatments. At the C/N ratios of 25 and 30, catalase activity, N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase activity, and soil DON content significantly increased. At the C/N ratios of 35 and 40, there were significant increases in soil cellulase activity, urease activity, DOC, carbon mineralization rate, MBN, MBN:TN, leached NH4+-N, and NH4+-N content. The NO3−-N content in soil leachate was significantly positively correlated with soil NO3−-N, ammonification rate, nitrification rate, net nitrogen mineralization rate, and negatively correlated with soil bacteria, fungi and nifH. Additionally, nitrification rate was significantly negatively correlated with C mineralization rate, urease activity, sucrase activity, MBN, TN and DON (p < 0.05).
3.7. Structural Equation Modeling of Key Factors Affecting NO3−-N Leaching
A variety of fitting test results showed that the structural equation model (SEM) of the effect of increasing soil C/N ratio on soil NO3−-N leaching has a good fit (χ2 = 14.319, df = 18, χ2/df = 0.795, p = 0.708, GFI = 1.00, RMSEA = 0.00), which could accurately represent the direct and indirect effects between variables (Figure 7a). The SEM could explain 94% of the variance in soil leached NO3−-N. Regarding the total effects, straw-regulated C/N, DON and soil fungi were the most important factor affecting NO3−-N leaching, followed by the ammonification rate (Figure 7b). Although the C/N ratio did not directly affect leached NO3−-N, it strongly explained the variation in the ammonification rate, which directly contributed to the decrease in soil NO3−-N leaching. Meanwhile, nitrification was reduced by indirectly influencing fungi, DON, bacteria and nifH. Straw-regulated C/N was significantly negatively correlated with the ammonification rate and net nitrogen mineralization rate and positively correlated with fungi abundance (p < 0.01). The DON content was significantly negatively correlated with the ammonification rate and leached NO3−-N and significantly positively correlated with nifH and bacterial abundance (p < 0.05).
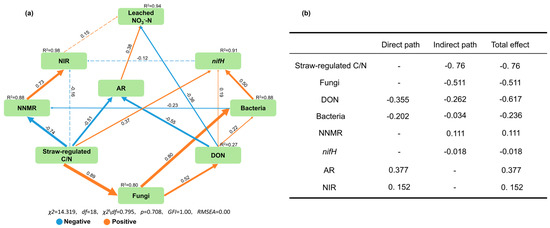
Figure 7.
Structural equation modeling describing the direct and indirect effects of soil key indicators on nitrate leaching (a). The orange and blue arrows indicate significant positive and negative effects (p < 0.05), respectively, whereas dashed arrows indicate nonsignificant relationships. Values adjacent to arrows represent standardized path coefficients. The width of arrows is proportional to the strength of path coefficients. R2 donates the proportion of variance explained. The contribution of each variable to NO3−-N leaching by the direct, indirect and total effect (b). AR, Ammonification rate; NIR, Nitrification rate; NNMR, Net nitrogen mineralization rate.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Straw-Increased C/N Ratio on Enhancing Soil N Storage and Minimizing N Losses
Straw addition significantly increased the soil TN content, indicating increased N storage (Figure 2a). Heterotrophic microorganisms serve as the dominant drivers of biogeochemical cycles. Their growth and activity were primarily limited by C in soils with both relatively low (grassland, ca. 4% soil C) and high (forest, ca. 13% soil C) organic matter content [37]. Our study found that straw addition significantly increased MBC content, along with the abundance of fungi, bacteria, and nifH genes (Figure 4). These results indicated that straw return could promote the growth of heterotrophic microorganisms including N-fixers, which collectively benefits the immobilization of soil inorganic N [37,38]. It also significantly elevated the ratio of soil MBN to total N, indicating microbial N pool expansion. Rong and Zhang [4,39] also reported that straw addition supplies ample C sources to soil microorganisms, markedly enhancing microbial biomass C and N, fungal and bacterial abundances and microbial reproduction, thereby promoting N immobilization.
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) plays an important role in the soil biological activity and transport of nutrients in soils. DOM can arise from the dissolution of plant residues during microbial transformation, while soil microbes consume DOM and convert it into intrinsically recalcitrant compounds [40]. DON is one of the most important components of DOM, which plays an important role in soil biological activity, pedogenesis and transport of pollutants in soils [41]. Straw addition increased DON contents (Figure 3). The SEM suggests that the straw-regulated C/N, DON, and soil fungi were the most important drivers of leached NO3−-N (Figure 7a). There are two distinct DON pools in soils: the low molecular-weight pool has a fast turnover rate and it mainly consists of free amino acids and proteins, whereas the high molecular-weight pool comprises humic substances and turnover very slowly [42]. An increase in DON can accelerate the turnover of the active N pool, inhibit ammonification, and decrease NO3−-N leaching. Fungi exhibit stronger decomposition capacity. We found that straw addition significantly increased fungal abundance, and there was a significant positive correlation between DON and fungi (Figure 4b and Figure 6). Fungi has a wider C/N range than bacteria, excelling in decomposing recalcitrant organic materials (e.g., cellulose), whereas bacteria primarily degrade labile fraction [43]. This suggests that increasing the soil C/N ratio promotes fungi growth to increase soil DON content. Bacteria could use inorganic N and low molecular-weight amino acids and protein for growth [44]. Straw addition increased the abundance of bacteria and N-fixer, those positively correlated with soil DON (Figure 6). Other studies have also found that the application of compound glutamic acid liquid granules can have significant slow-release effects and nitrogen retention capacity by enhancing the accumulation of MBN and DON [45]. The rapid growth of fungi can promote the decomposition of complex organic matter into dissolved organic N, providing an effective N source for bacterial (N-fixer) growth and thereby enhance nitrogen retention.
Fu et al. [46] demonstrated that microbial-derived C, particularly fungal necromass C, exceeds plant-derived C and constitutes the dominant contributor to soil C stocks. They further identified that TN was significantly positive correlated with fungal necromass C accumulation. Our results similarly showed a significantly positive correlation between fungal abundance and TN (Figure 6). Therefore, we speculated that straw addition could reduce NO3−-N leaching by promoting microbial growth (especially fungi), accelerating the turnover of the active N pool and increasing soil microbial N storage (Figure 8a). When the C/N ratio was 20, fertilizer N storage in soil was at its maximum, and gas–liquid losses were minimized (Figure 2b and Figure 8b). Simultaneously, the soil NO3−-N accumulation and leaching decreased to the minimum level when the C/N ratio was 20 (Figure 1). Thus, we speculated that the ecological threshold of straw application rate in fluvial soil was at a C/N ratio of 20 for enhancing N sequestration and minimizing NO3−-N leaching.
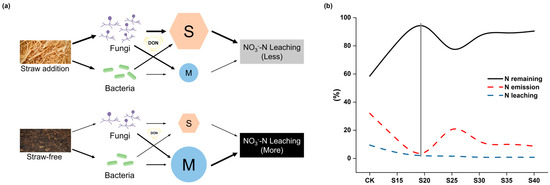
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of N sequestration mediated by straw incorporation. The arrow weight indicates impact magnitude (a). “M” and “S” represent N mineralization and N storage, respectively, their sizes represent the N flux of each process. The storage and air–liquid losses of fertilizer N in the soil (b). When the C/N ratio was 20, the storage of fertilizer N was maximized while its air–liquid losses were minimized. The N leaching consists of only NO3−-N and NH4+-N. The gray auxiliary line perpendicular to the horizontal axis indicates the maximum value of remaining fertilizer N and the minimum value of fertilizer N emissions.
4.2. Effects of Increasing C/N Ratio on C and N Transformation Enzymes
Enzymes have been considered particularly critical, as they catalyze the rate-limiting steps of decomposition and nutrient mineralization [37]. Increasing the C/N ratios significantly increased activities of catalase, cellulase, sucrase, urease and soil N-acetyl-β-D-glucosidase, which were all significantly positively correlated with TN and negatively correlated with leached NO3−-N (Figure 6), indicating that straw addition could activate complex C and N to promote soil N sequestration by increasing soil enzyme activities. Soil NAG enzyme activity is often used as a biological indicator for assessing nitrogen availability. Microorganisms could enhance the synthesis and secretion of NAG enzyme to obtain N sources by releasing NH4+-N through deacetylation under N limitation [47,48]. Catalase could scavenge H2O2 to provide a stable microenvironment for microbial growth, thereby enabling them to efficiently assimilate inorganic N (such as NH4+, NO3−) and reducing the risk of N loss [48,49]. Meanwhile, catalase could reduce the damage of H2O2 to soil colloids, maintain their ability to adsorb NH4+, and reduce ammonia volatilization loss [50]. There were significant increases in catalase, soil N-acetyl-β-D-glucosidase and soil DON, which was consistent with the increased fertilizer 15N at the C/N ratios of 15 and 20 (Figure 2b and Figure 6). These suggested that straw applied at C/N ratios of 15 and 20 could enhance activities of catalase and NAG enzymes to increase soil inorganic N availability. Straw applied at a C/N ratio of 40 showed the highest increase in soil total N, DOC and soil C mineralization rate, while soil DON, catalase and NAG enzymes predominantly increased at C/N ratio of 20. These indicated different optimal C-N stoichiometric ratios for C and N turnover in fluvial soil.
4.3. Effects of Increasing the C/N Ratio on N Transformation Rates
Soil net N mineralization, net ammonification and nitrification rates decreased as the C/N ratio increased, which helped minimize NO3−-N accumulation and loss. The soil net ammonification rate decreased rapidly at C/N ratios of 15 and 20, reaching its lowest value at a C/N ratio of 20. This trend in the change in ammonification rate was consistent with that in soil NO3−-N concentration (Figure 1 and Figure 3e), indicating that straw C input could suppress the ammonification rate to reduce soil NO3−-N accumulation. Previous studies found that when soil carbon input is relatively high, the nitrogen mineralization rate is inhibited due to insufficient nitrogen availability for microorganisms [13]. Additionally, increased C input significantly enhanced microbial N storage and reduced net mineralization (Figure 2a and Figure 3d). Nitrification rate decreased with the increase in straw addition (Figure 3f), which might be due to the increase in organic carbon in soil and the decrease in nitrification substrate (NH4+), thus reducing the nitrification rate [13]. Interestingly, we found that straw addition increased the abundance of AOA and AOB, indicating that it might promote the first step of soil autotrophic nitrification [51]. Xue [52] also observed that organic fertilizer application notably boosted the gene abundance of AOA and AOB, which significantly correlated with soil total nitrogen. Gene abundance does not necessarily reflect process rates, and high organic C input could suppress autotrophic nitrification even if AOA and AOB abundance increases [53,54]. The entire process by which straw addition suppresses soil nitrification via the regulation of soil microorganisms needs to be further investigated. Therefore, straw incorporation could mitigate soil NO3−-N accumulation and leaching through reducing soil net N mineralization and nitrification process (Figure 8a). The results of this study have certain guiding significance for field management practices in terms of optimizing straw returning strategies and improving soil quality and environmental safety. Moreover, this study failed to the short-term experimental results may not reflect the long-term impacts on soil nitrogen cycling and nitrate nitrogen leaching. The applicability of our results needs to be further verified in complex field environments.
5. Conclusions
This study revealed that increasing the soil C/N ratio by straw incorporation significantly increased soil N storage while substantially decreased NO3−-N leaching in fluvial soil. The ecological threshold of straw application rate in fluvial soil was at a C/N ratio of 20 for enhancing N sequestration and minimizing NO3−-N leaching. Straw applied at C/N ratios of 15 and 20 could enhance activities of catalase and NAG enzymes to increase soil inorganic N availability. Increasing the C/N ratio by adding straw could reduce NO3−-N leaching by promoting microbial growth (especially fungi), increasing soil DON, microbial N storage and reducing the net N mineralization and nitrification. This could support efforts to lower agricultural non-point source N pollution and promote sustainable agricultural production. Built on these findings, field experiments could be further explored the ecological processes that ensure crop safety production and reduce N losses.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy15102371/s1, Figure S1: Schematic diagram of the leaching device used in this experiment. The device was designed using a bucket with a diameter of 22 cm, a height of 25 cm and holes with a diameter of 0.5 cm that were evenly distributed at the bottom of the column to collect the leachate; Figure S2: The proportion of inorganic nitrogen in leachate under different C/N ratio treatments; Table S1: Primers used for real-time quantitative PCR; Table S2: qPCR amplification system and amplification.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.Z. and P.Z.; data curation, Y.H., C.Z. and W.Z.; formal analysis, W.Z., P.Z., Y.H. and C.Z.; investigation, Y.H. and C.Z.; validation, Y.H. and C.Z.; methodology, W.Z. and P.Z.; visualization, S.Q., Y.Z. and F.S.; supervision, W.Z., P.Z., S.Q., Y.Z. and F.S.; funding acquisition, W.Z. and P.Z., writing-original draft preparation, Y.H. and C.Z.; writing-review and editing, W.Z. and P.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFD1700900) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41907084).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to my fellow group members and teachers for their insightful advice and encouragement throughout the research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ascott, M.J.; Gooddy, D.C.; Wang, L.; Stuart, M.E.; Lewis, M.A.; Ward, R.S.; Binley, A.M. Global patterns of nitrate storage in the vadose zone. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yang, J.L.; Zhao, X.R.; Yang, S.H.; Mulder, J.; Dörsch, P.; Zhang, G.L. Nitrate leaching and N accumulation in a typical subtropical red soil with N fertilization. Geoderma 2022, 407, 115559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.T. The concept and meanings of nitrogen fertilizer availability ratio-Discussing misunderstanding of traditional nitrogen use efficiency. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2014, 51, 921–933. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, J.T.; Di, H.J.; Han, L.L.; Li, P.P.; Shen, J.P.; Han, B.; Zhang, L.M. The effects and mechanisms of deep straw incorporation and denitrifying bacterial agents on mitigating nitrate leaching and N2O emissions in four soil types in the North China Plain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 366, 108958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Ju, X.T.; Yang, H. Nitrate leaching in a winter wheat-summer maize rotation on a calcareous soil as affected by nitrogen and straw management. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Sun, T.R.; Pan, Z.Z.; Lv, J.; Peňuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Xiao, K.Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, Y.G. Rethinking organic carbon sequestration in agricultural soils from the elemental stoichiometry perspective. Glob. Change Biol. 2025, 31, e70319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, R.; Guo, R.; Yang, Q.X.; Naseer, M.A.; Sun, B.P.; Wang, L.L.; Zhang, J.; Ren, X.L.; Chen, X.L.; Jia, Z.K. Can straw recycling achieve sustainable agriculture at the smallholder level? A case in a semi-arid region. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 439, 140859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manevski, K.; Børgesena, C.D.; Li, X.X.; Andersen, M.N.; Zhang, X.Y.; Abrahamsend, P.; Hu, C.S.; Hansen, S. Optimising crop production and nitrate leaching in China: Measured and simulated effects of straw incorporation and nitrogen fertilisation. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 80, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.X.; Nicoullaud, B.; Rochette, P.; Grossel, A.; Hénault, C.; Cellier, P.; Richard, G. A regional experiment suggests that soil texture is a major control of N2O emissions from tile-drained winter wheat fields during the fertilization period. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 60, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Gong, H.Q.; Wei, Y.Q.; Xu, T.; Li, J.; Ding, G.C. Promoting agricultural waste-driven denitrification and nitrogen sequestration with nano-enabled strategy. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 401, 130746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.X.; Elrys, A.S.; Zhang, H.M.; Tu, X.S.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J.B.; Cai, Z.C. How does organic amendment affect soil microbial nitrate immobilization rate? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 173, 108784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, J.B.; Mu, L.; Xin, X.; Yun, Y.; Zhu, A.; Ge, S. Effects of straw management and N levels on gross nitrogen transformations in fluvo-aquic soil of the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 944, 173652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, G.; Bengtson, P.; Månsson, K. Gross nitrogen mineralization-, immobilization-, and nitrification rates as a function of soil C/N ratio and microbial activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.W. Changes of microbial population and N-cycling function genes with depth in three Chinese paddy soils. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Chang, S.X.; Wang, S. The quality and quantity of exogenous organic carbon input control microbial NO3− immobilization: A meta analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangir, M.M.R.; Fenton, O.; Carolan, R.; Harrington, R.; Johnston, P.; Zaman, M.; Richards, K.G.; Müller, C. Application of 15N tracing for estimating nitrogen cycle processes in soils of a constructed wetland. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.L.; Willett, V.B. Experimental evaluation of methods to quantify dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.F.; Liu, Y.Z.; Mo, C.Y.; Jiang, Z.H.; Yang, J.P.; Lin, J.D. Microbial mechanism of biochar addition on nitrogen leaching and retention in tea soils from different plantation ages. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.S.; Qiu, W.H. The potential for N2O emission and nitrate leaching in seasonally open solar greenhouses during the summer fallow: A 15N tracer study. Soil Use Manag. 2016, 32, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Rouland, C.; Benedetti, M.; Li, F.B.; Pando, A.; Lavelle, P.; Dai, J. Microbial biomass, enzyme and mineralization activity in relation to soil organic C, N and P turnover influenced by acid metal stress. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass-C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, D.S.; Brookes, P.C.; Powlson, D.S. Measuring soil microbial biomass. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Sleutel, S.; Buchan, D.; De Neve, S.; Cai, D.X.; Gabriels, D.; Jin, J.Y. Changes of soil enzyme activities under different tillage practices in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 104, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.T.; Wang, R.Z.; Wang, S.D.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.G.; Zhu, B.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Jiang, Y. Microbial Immobilization Shapes the Non-Linear Response of Allochthonous Nitrogen Retention to Grassland Acidification Within Soil Aggregates. Glob. Change Biol. 2025, 31, e70229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeler, E.; Gerber, H. Short-term assay of soil urease activity using colorimetric determination of ammonium. Biol. Fert. Soils 1988, 6, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.P.; Hong, J.; Ye, X. Biofuels: Methods and Protocols, 1st ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 213–231. [Google Scholar]
- Trap, J.; Bureau, F.; Akpa-Vinceslas, M.; Decaens, T.; Aubert, M. Changes in humus forms and soil N pathways along a 130-year-old pure beech forest chronosequence. Ann. For. Sci. 2011, 68, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trap, J.; Bureau, F.; Vinceslas-Akpa, M.; Chevalier, R.; Aubert, M. Changes in soil N mineralization and nitrification pathways along a mixed forest chronosequence. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2009, 258, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleuss, P.; Widding, M.; Heintz-Buschart, A.; Guhr, A.; Martin, S.; Kirkman, K.; Spohn, M. Stoichiometric controls of soil carbon and nitrogen cycling after long-term nitrogen and phosphorus addition in a mesic grassland in South Africa. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, C.; Dou, Z.X.; Ji, D.G. Independent and combined effects of oxytetracycline and antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli O157: H7 on soil microbial activity and partial nitrification processes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 98, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.J.; Yeom, J.K.; Kim, J.S.; Han, J.W.; Lim, H.S.; Park, H.; Hyun, S.H.; Park, W.J. Change in gene abundance in the nitrogen biogeochemical cycle with temperature and nitrogen addition in Antarctic soils. Res. Microbiol. 2011, 162, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poly, F.; Ranjard, L.; Nazaret, S.; Gourbiere, F.; Monrozier, L.J. Comparison of nifH gene pools in soils and soil microenvironments with contrasting properties. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotthauwe, J.; Witzel, K.; Liesack, W. The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: Molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 4704–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.D.; Cunliffe, M. Multi-year assessment of coastal planktonic fungi reveals environmental drivers of diversity and abundance. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2118–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, T.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Fang, Z.Y.; Huang, Q.W.; Zhang, R.F.; Li, R.; Shen, B.; Shen, Q.R. Effects of organic-inorganic compound fertilizer with reduced chemical fertilizer application on crop yields, soil biological activity and bacterial community structure in a rice-wheat cropping system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coci, M.; Nicol, G.W.; Pilloni, G.N.; Schmid, M.; Kamst-van Agterveld, M.P.; Bodelier, P.L.E.; Laanbroek, H.J. Quantitative assessment of ammonia-oxidizing bacterial communities in the epiphyton of submerged macrophytes in shallow lakes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoph, R.; Johannes, R.; Hans, S. Can enzymatic stoichiometry be used to determine growth-limiting nutrients for microorganisms?—A critical assessment in two subtropical soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 128, 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.T.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.J.; Li, Z.P.; Gao, Y.J. Long-Term Effects of potassium fertilization and wheat straw return on cropland soil fertility and microorganisms in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Agronomy 2025, 15, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Q.L.; Li, R.N.; Huang, S.W.; Tang, J.W.; Zhang, Y.C.; Wang, L.Y. Soil microbial characteristics and yield response to partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with organic amendments in greenhouse vegetable production. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 1432–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Q.; Liu, Z.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Duan, Z.; Song, X. Effects of intercropping on composition and molecular diversity of soil dissolved organic matter in apple orchards: Different roles of bacteria and fungi. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 382, 109509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, B. Seasonal and inter-annual variation of leaching of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen under long-term manure application in an acidic clay soil in subtropical China. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 146, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Shannon, D.; Murphy, V.; Farrar, D. Role of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) in soil N cycling in grassland soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Q.; Chen, L.; Jia, Z.J.; Zhang, C.Z.; Ma, D.H.; Li, F.; Zhang, J.B.; Li, D.M.; Han, X.R.; Cai, Z.J.; et al. Multiple long-term observations reveal a strategy for soil pH-dependent fertilization and fungal communities in support of agricultural production. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 293, 106837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mélodie, D.; Pascale, C. Small bacterial and phagic proteins: An updated view on a rapidly moving field. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 39, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.M.; Liu, J.; Yu, H.J.; Yu, J.; Qi, G.C.; Wang, D. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer types on enzyme activities and bacterial communities related to the nitrogen cycle in soda saline-alkaline paddy rhizosphere soil. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2025, 38, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.R.; Chen, H.; Ma, Z.B.; Liang, G.; Chadwick, D.R.; Jones, D.L.; Wanek, W.; Wu, L.; Ma, Q. Fungal necromass carbon dominates global soil organic carbon storage. Glob. Change Biol. 2025, 31, e70413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Vitousek, P.M. Soil C:N:P stoichiometry and the coupling of C and nutrient cycling. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 727–737. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.L.; Murphy, D.V.; Ryder, M.H. Influence of soil catalase activity on microbial nitrogen assimilation. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 157, 567–575. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.L.; Zhang, P.P.; Wang, L.F.; Ma, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.Y. Interaction of Nitrogen and Phosphorus on Wheat Yield, N Use Efficiency and Soil Nitrate Nitrogen Distribution in the North China Plain. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2020, 14, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, H. Catalase protects soil colloids from hydrogen peroxide damage and reduces ammonia volatilization. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 357–364. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.L.; Zeng, Z.Q.; Tian, D.H.; Wang, J.S.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, F.Y.; Zhang, R.Y.; Chen, W.N.; Luo, Y.Q.; Niu, S.L. Global patterns and controlling factors of soil nitrification rate. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 4147–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, P.; Peng, C.; Ling, N.; Shen, Q.R. Quantitative and compositional responses of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria to long-term field fertilization. Sci Rep. 2016, 6, 28981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.L.; Rengel, Z.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Li, H.B.; Zhang, A.P. Ammonia-oxidizing archaea bacteria (AOB) and comammox drive the nitrification in alkaline soil under long term biochar and N fertilizer applications. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 193, 105124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, R.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, G.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, L.; Shen, F.; Jie, X.; Liu, S. Variations in Soil Nitrogen Availability and Crop Yields under a Three-Year Annual Wheat and Maize Rotation in a Fluvo-Aquic Soil. Plants 2023, 12, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).