Abstract
Nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) play vital roles in crop growth. However, conventional fertilizers exhibit low utilization efficiency, making them prone to causing resource wastage and water eutrophication. Although metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) have shown great potential for application in controlled-release fertilizers (CRFs), currently reported MOF-based CRFs suffer from low nutrient content, which limits their further application. To address this issue, this study synthesized a series of hierarchically porous MOFs, denoted as MIL-156(X), using sodium acetate as a modulator under hydrothermal conditions. These materials were subsequently loaded with urea and phosphate from aqueous solution to form MOFs-based CRFs (N-P-MIL-156(X)). Results indicate that MIL-156(X) retain microporous integrity while incorporating abundant mesopores. Increasing modulator content reduced particle size and average pore diameter but increased specific surface area and adsorption capacity for urea and phosphate. MIL-156-H (with a high modulator content addition) exhibited the highest adsorption capacity, conforming to Langmuir isotherm and pseudo-second-order kinetics. The adsorption mechanisms of urea and phosphate involved hydrogen bonding and the formation of Ca intra-spherical complexes, respectively. N-P-MIL-156-H contained 10.8% N and 16.3% P2O5, with sustained release durations exceeding 42 days (N) and 56 days (P2O5) in an aqueous solution. Pot trials demonstrated significantly higher nutrient use efficiency (N-44.8%, P2O5-16.56%) and a 12.22% yield increase compared to conventional fertilization (N-35.6%, P2O5-13.32%). Thus, N-P-MIL-156-H-based fertilization significantly promotes rice growth and N/P utilization efficiency, offering a promising strategy for developing controlled-release fertilizers and improving nutrient management.
1. Introduction
Rapid global population growth, accelerated urbanization, and diminishing arable land pose significant threats to food security, creating an urgent need for sustainable and efficient agricultural practices [1,2,3,4]. The agricultural sector heavily relies on chemical fertilizers to meet rising food demands, with annual global consumption increasing from 46 million to 130 million tons over the past three decades and projected to double by 2030 [5]. However, conventional fertilizers suffer from low nutrient use efficiency, leading to substantial environmental degradation [6]. In response, controlled-release fertilizers (CRFs), designed to synchronize nutrient release with crop demands, have emerged as a promising solution.
Currently, the most prevalent CRFs utilize petroleum-based synthetic polymers (e.g., polyolefins, acrylic resins, polysulfone) as coating materials [7,8,9,10]. These CRFs are costly, exhibit inefficient nutrient release, and involve complex, often toxic manufacturing processes [11]. Critically, their non-biodegradability and reliance on non-renewable resources raise serious environmental and energy concerns [12,13]. While bio-based coating materials derived from starch, lignin, cellulose, or chitosan offer environmental benefits, their poor mechanical strength and high hydrophilicity typically result in excessively rapid nutrient release, hindering practical large-scale application [14]. Consequently, the development of advanced material-based CRFs is highly desirable.
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), as prominent porous functional materials, are formed by the self-assembly of metal ions with organic ligands. Owing to their high surface area and porosity, MOFs have been utilized in applications such as fertilizers [5], drug carriers [15], and sensing [16] and food packaging [17]. Previous studies have confirmed the promising nutrient release potential and agronomic efficacy of MOFs as fertilizers. For instance, iron-based MOFs enhanced chlorophyll content, biomass, and enzyme activity in legumes [18], while oxalate-phosphate-amine (OPA-MOFs), when applied as a slow-release fertilizer, significantly promoted wheat growth, nutrient uptake, and grain yield [19]. Urea-loaded core–shell MOF/silica nanocarriers enable a sustained supply of nitrogen to rice plants, thereby leading to improved nitrogen use efficiency and higher grain yield [20]. The application of MOFs in fertilizers necessitates a high nutrient content, which is a fundamental prerequisite. Nevertheless, the relatively low nutrient loading capacities of reported MOFs severely limit their practical utility. Strategies to enhance MOFs loading capacity through structural modification are therefore crucial.
Recently, reducing the particle size of synthesized MOFs has emerged as an attractive strategy to increase target molecule loading capacity. This approach enlarges the specific surface area and pore volume while mitigating internal diffusion limitations due to reduced diffusion pathlength [21]. During MOFs crystallization, particle size is governed by crystal nucleation and growth rates [22]. Modulator additives represent a key method for regulating nucleation kinetics [23]. Previous studies have successfully employed modulators to decrease MOFs particle size, thereby enhancing their adsorption capacity for guest molecules [24]. In our earlier research, hierarchically porous HUiO-66-NH2 was synthesized using MOF-5 as a template, improving its phosphorus removal efficiency from water [25].
Although reducing the particle size of MOFs has proven effective for loading target molecules [24,26], research on enhancing nutrient loading capacity through this approach and subsequently developing CRFs remains unreported. In this study, a series of Ca-based MIL-156(X) MOFs with controlled crystal sizes was synthesized using sodium acetate as a modulator. These MOFs were subsequently loaded with urea and phosphate to create controlled-release N-P-MIL-156(X) fertilizers. The MIL-156(X) structures were thoroughly characterized. The MIL-156(X) adsorption capacities for urea and phosphate were evaluated and the underlying adsorption mechanisms were elucidated. Finally, the nutrient release profiles of N-P-MIL-156(X) were investigated, and their effects on rice (Oryza sativa L.) growth and development were assessed in pot trials. This research aims to demonstrate that tuning MIL-156 crystal size significantly enhances nitrogen and phosphorus loading capacity, and that the resulting N-P-MIL-156(X) fertilizers improve nutrient use efficiency and promote rice growth. This work provides novel perspectives for developing MOF-based slow-release fertilizers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Gallic acid monohydrate (C7H6O5H2O, ≥98.0%), calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2, ≥98.0%), potassium hydroxide (KOH, ≥98.0%), urea (CO(NH2)2, ≥99.0%), potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4, 99.0%) and sodium acetate (CH3COONa, 99.0%). All the reagents, analytical grade, were provided from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
2.2. Synthesis of MIL-156(X)
282 mg (0.0015 mol) of gallic acid monohydrate was added to 15 mL of ultrapure water at 25 °C. Subsequently, Ca(OH)2 (148 mg, 0.002 mol) was dissolved in the resulting solution. A 5 M KOH solution was then added dropwise until the pH reached 14 (≈1200 μL, ≈0.006 mol), followed by the addition of a specified volume of sodium acetate solution (50 mmol/L). The mixture was transferred to a Teflon-lined autoclave and heated in an oven to 120 °C at a ramping rate of 5 °C/min, maintaining this temperature for 24 h. The solid product was isolated by filtration, washed three times with distilled water, and dried at room temperature to yield crystalline MIL-156(X). Based on the volume of sodium acetate added (0.5 mL—low modulator template concentration; 1 mL–medium modulator concentration; 2 mL—high modulator concentration), the synthesized MOFs were designated as MIL-156 L, MIL-156-M, and MIL-156-H, respectively. For comparison, MIL-156 was synthesized using a procedure based on the previously published literature without modulator addition [27].
2.3. Material Characterization
X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectra were collected in the 5−70° range by an X-ray diffractometer (ARL X’TRA, Thermo Electron Corporation, Basel, Switzerland) using CuKα radiation source at 0.02° step size and 5° min−1 scanning rate. The organic groups of samples were examined by Fourier transform infrared attenuated total reflection spectroscopy (FTIR−ATR) (TurDefender FT, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) in the range of 500–4000 cm−1 at a 4 cm−1 resolution. The elemental composition and bond valence structure of samples were explored through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) (K-ALPHA, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). The microstructures were analyzed via scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (JW-BK132, ZEISS Merlin Compact, Oberkochen, Germany) at 10 kV accelerating voltage. Samples were sputter-coated with Au (30 mA, 1 min) prior to imaging. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was performed on a TA TGA5500 analyzer under N2 atmosphere, with a heating rate of 10 °C/min from 40 to 800 °C to assess thermal stability and weight loss profiles. The pore size distribution and specific surface area of the samples were determined by N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms measured on an analyzer (TriStar II 3flex, Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, USA). The samples were activated in a vacuum at 200 °C for 10 h prior to measurement.
2.4. Nutrient Loading Experiments
For adsorption kinetics experiment. Individual stock solutions of urea (100 mg/L) and potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4, 100 mg/L) were prepared. An equal volume of each solution was subsequently combined to yield a mixed nutrient solution. A 20 mL aliquot of this mixed solution was introduced into a 50 mL glass vial, followed by the addition of 10 mg of MIL-156(X). The solution pH was adjusted to 7.0 using 0.1 mol/L NaOH and HCl solutions, as needed. Agitation was performed at 200 rpm and 298 K. Samples were withdrawn from the respective amber vials at predetermined intervals over a 24 h period. Immediately following sampling, each solution was filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane filter. Urea concentration in the supernatant was quantified using the para-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde colorimetric method [28], whereas phosphate concentration was determined employing a UV-2550 spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The adsorption capacity (qt, mg/g) and adsorption rate of MIL-156(X) towards the nutrients were calculated. The nutrient adsorption capacity at time t is defined by Equation (1):
where qt represents the adsorption capacity (mg/g) at time t (min); C0 and Ct denote the initial nutrient concentration and the concentration at time t (min), respectively (mg/L); m is the mass of the adsorbent (g); and V is the volume of the solution (L).
The kinetic adsorption data were fitted to the pseudo-first-order (Equation (2)) and pseudo-second-order (Equation (3)) kinetic models:
Here, qt and qe (mg/g) signify the adsorption capacities for the nutrients (urea and phosphate) at time t (min) and at equilibrium, respectively; k1 (min−1) and k2 (g·mg−1·min−1) are the rate constants for the pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order models, respectively.
Adsorption isotherms were conducted by introducing 20 mL of the mixed nutrient solution, with initial concentrations ranging from 10 to 100 mg/L, into 50 mL glass vials. A constant MIL-156(X) dosage of 10 mg was maintained in each vial. The solution pH was adjusted to 7.0 using 0.1 mol/L NaOH and HCl solutions. The vials were agitated at 200 rpm for 24 h at temperatures of 298 K, 318 K, and 328 K. Post-equilibrium, the solutions were filtered through 0.45 μm membrane filters. The equilibrium concentrations of urea and phosphate in the supernatants were measured, enabling the calculation of the equilibrium adsorption capacity and adsorption rate for MIL-156(X).
Adsorption isotherm models, including Langmuir (Equation (4)) and Freundlich (Equation (5)), were employed to fit the adsorption isotherm results. The nonlinear equations are defined as follows:
where qe (mg/g) is the equilibrium adsorption capacity; qm (mg/g) represents the theoretical maximum (saturation) adsorption capacity; Ce (mg/L) is the equilibrium concentration of the adsorbate in solution; KL (L/mg) is the Langmuir constant related to adsorption affinity; KF is the Freundlich adsorption constant ((mg/g)/(mg/L)n); 1/n is the adsorption index.
2.5. Nutrient Release Characteristics of N-P-MIL-156-H
Three buffer systems were prepared at pH 5.0 (citric acid-sodium citrate buffer solution), pH 7.0 (deionized water), and pH 9.0 (borate buffer solution), respectively. Then, 2 g of the precisely weighed N-P-MIL-156-H was placed in a 150 mL flask and added with 100 mL of the prepared buffer solutions (pH 5.0, 7.0, and 9.0, respectively). After the flask was tightly closed, it was placed at 25 °C for culturing in an incubator. Three parallel experiments were set for each treatment. Afterward, each solution was taken out on days 1, 3, 5, 7, 14, 28, 42, and 56, and added again with 100 mL of the corresponding buffer solution. Then, the urea and phosphate content in each solution was analyzed. The cumulative urea and phosphates release rates were calculated as:
where Ci (mg/mL) denotes the urea/phosphates concentration in the sampling solution on day i (i = 1, 3…56 d), Vi denotes the volume (100 mL) of urea in the sampling solution on day i (i = day 1, 3…56 d), n represents sampling frequency, and m0 (mg) represents the urea/phosphates loading in N-P-MIL-156-H.
The experimental data were fitted and analyzed via zero-order, first-order, Higuchi, and Ritger-Peppas dynamics mathematical models by following equations to explore the nutrient release mechanism of N-P-MIL-156-H [29,30].
zero-order release kinetics model
first-order release kinetics model
Higuchi model
Ritger-Peppas model
where Mt/M∞ is the urea/phosphates release rate (%) at time t, k is the rate constant, and n is the diffusion.
2.6. Application of N-P-MIL-156-H in Rice
Rice was used in pot experiments conducted at Jiangsu Open University, Nanjing, China. A pot with the diameter of 20 cm and the height of 15 cm was loaded 3 kg of air-dried paddy soil (with physicochemical properties listed in Table S1). Four treatments were set: (1) no fertilizer input (CK), (2) conventional fertilization (Urea + Calcium superphosphate + Potassium sulfate) (CF), (3) MIL-156-H treatment, and (4) N-P-MIL-156-H treatment (N—10.8%, P2O5—16.3%, K—5.2%, Ca—10.2%). Three replicate pots were set up for each treatment. The application rate for both Treatment (3) (MIL-156-H) and Treatment (4) (N-P-MIL-156-H) was set at 20 g per pot. To ensure nutrient equivalence for comparison, the total nutrient input in Treatment (2) (CF) was matched to that of Treatment (4). On 12 May 2024, all fertilizers were applied as a single basal dose prior to transplanting. One day after fertilization, 15-day-old rice seedlings (Nanjing 5055) were transplanted into the pots, with nine seedlings planted per pot. All experimental pots were maintained in a greenhouse at a constant temperature of 25 °C with sufficient light exposure and appropriate water management. On 5 July 2024, leaf samples of rice plants were collected during the peak tillering stage for spectra recording by the technique of FTIR photoacoustic spectroscopy (Nicolet 6700, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) matched with a photoacoustic accessory (MTEC 300, MTEC Photoacoustics, Ames, IA, USA) for nitrogen nutrition assessment. The wavenumber range was 4000 to 500 cm−1, and the mirror speed was 0.32 cm s−1 with 4 cm−1 resolution. The rice was harvested on 25 October 2024, and the grain yield, 1000 kernel weight, number of kernels per ear, and aboveground biomass were determined for each treatment. The overground part was harvested and was dried at 105 °C for 30 min, then oven-dried at 80 °C to a constant weight as the dry matter content. The CHN analyzer was used to determine the nitrogen content, the total phosphorus content was determined using the molybdenum antimony colorimetric method (UV-2600, 880 nm). The nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) and phosphorus use efficiency (PUE) were calculated compared to no fertilizer input treatment.
3. Results
3.1. Structural Characterization of MIL-156(X)
Figure 1a presents the PXRD patterns of MIL-156(X). The diffraction peak positions of MIL-156(X) exhibit excellent agreement with the simulated pattern of MIL-156, indicating that the introduction of the modulator exerts no discernible influence on its crystalline structure. This correspondence conclusively demonstrates that MIL-156(X) retains the structural integrity and high crystallinity characteristic of the microporous MIL-156 framework. Figure 1b depicts the microstructure and morphological features of the MIL-156(X) materials. MIL-156 and MIL-156 L exhibit distinct rod-like morphologies; however, the particle size of MIL-156 L is notably smaller than that of MIL-156. With further increase in the modulator concentration, the dimensions of the MOFs are significantly reduced, decreasing from approximately 100 μm for MIL-156 to about 3 μm for MIL-156-H. Moreover, the introduction of the modulator results in a roughened surface texture of the MOFs. The FTIR spectra of MIL-156(X) are shown in Figure 1c. MOF samples display remarkably similar spectral profiles. Characteristic absorption bands corresponding to O-H stretching vibrations of water molecules within the crystal structure are observed at 3646 cm−1 and 3510 cm−1. Peaks arising from C-C and C-O stretching vibrations are evident at 1574 cm−1 and 1436 cm−1, respectively, attributable to aromatic rings and carboxylate moieties. The absorption at 1076 cm−1 is assigned to phenolic hydroxyl groups. Furthermore, the band at 745 cm−1 corresponds to C-H bending vibrations of aromatic compounds, while the peak at 556 cm−1 is ascribed to Ca-O bond vibrations. Thermogravimetric-Derivative Thermogravimetric (TG-DTG) curves for the different samples are presented in Figure 1d. All MOFs demonstrate comparable thermal stability profiles. A pronounced weight loss occurs below 69 °C in MIL-156(X), associated with the liberation of both free and bound water molecules. A significant mass loss event is observed around 685 °C, likely attributed to framework decomposition and the subsequent formation of CaO and K2CO3 [27]. Collectively, these results confirm that while modulator concentration exerts a profound influence on crystal morphology, the fundamental structural integrity of the MIL-156 framework is preserved in MIL-156(X).
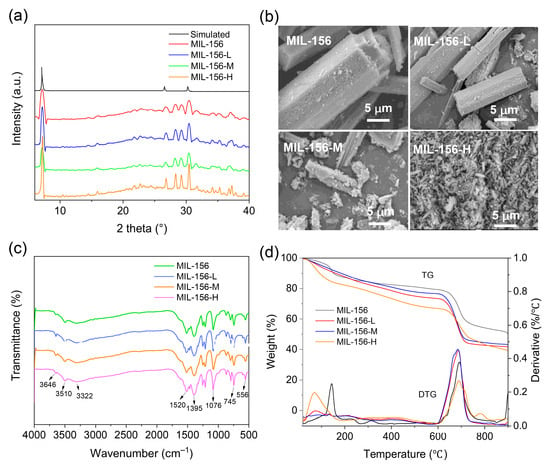
Figure 1.
XRD patterns (a), SEM images (b), FTIR spectra (c), and TG-DTG curves of MIL-156(X) (d).
The specific surface area and pore architecture of MIL-156(X) were investigated using N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms and pore size distribution analysis. As illustrated in Figure 2a, the N2 sorption isotherms of MIL-156(X) exhibit hybrid characteristics of both Type I and Type IV isotherms. At low relative pressures (P/P0 < 0.1), a rapid uptake of nitrogen is observed, indicating the presence of microporous structures on the surface of the material. At higher relative pressures (P/P0 = 0.8 ~ 1.0), a sharp increase in adsorption capacity accompanied by a distinct hysteresis loop in the desorption branch signifies the presence of mesopores. The corresponding pore size distribution profiles for MIL-156(X) clearly reveal a multimodal pore structure encompassing both micropores (<2 nm) and mesopores (2–20 nm), thereby corroborating the existence of a hierarchical porous framework (Figure 2b). According to Table S2, the average pore diameter increases from 3.6 nm for MIL-156-H to 5.2 nm for MIL-156 L. Conversely, the specific surface area decreases from 408 m2/g (MIL-156-H) to 236 m2/g (MIL-156 L). This phenomenon can be rationalized by considering nucleation kinetics. Elevated modulator concentrations accelerate nucleation rates, leading to a higher density of nuclei within the reaction system. Consequently, these numerous nuclei undergo rapid growth under competitive conditions, ultimately yielding smaller crystalline particles [24]. Therefore, as the amount of modulator increases, more depleted mesoporosity occurs in the final form of the material.
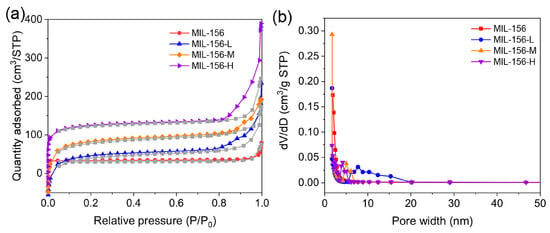
Figure 2.
N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms (a) and pore size distribution curves of MIL-156(X) (b).
3.2. MIL-156(X)’s Loading Experiments on Nutrients
To investigate the influence of modulator dosage on the adsorption capacity for urea and phosphate, the adsorption isotherms of MIL-156(X) were studied. As depicted in Figure 3a,b, the adsorption capacities of MIL-156(X) for both urea and phosphate increased with rising concentrations of the respective adsorbates. To gain deeper insight into the adsorption process, the isotherm data were fitted using the Langmuir and Freundlich models. As shown in Table S3, the Langmuir model exhibited higher R2 values than the Freundlich model, indicating that the adsorption of urea and phosphate onto MIL-156(X) conforms more closely to the Langmuir isotherm model. This suggests monolayer adsorption predominates during the adsorption process. Calculated saturation adsorption capacities derived from the Langmuir model were 193.3, 248.8, 351.5, and 427.6 mg/g for urea, and 101.2, 233.5, 315.7, and 397.6 mg/g for phosphate on MIL-156, MIL-156 L, MIL-156-M, and MIL-156-H, respectively. These results demonstrate that, compared to pristine MIL-156, the mesoporous MIL-156(X) variants exhibit progressively enhanced adsorption capacities for both urea and phosphate as the particle size decreases. A comparative summary of nutrient content in various MOF-type fertilizers is presented in Table 1. As can be seen, previous studies typically utilized MOFs containing only one (N) or two (N, P) nutrients. In contrast, the N-P-MIL-156-H in our study incorporates three nutrients (N, P, and K), with a total nutrient content of 32.3%, which surpasses all previously reported values. This result demonstrates the remarkable nutrient loading capacity of MIL-156-H, a property that is crucial for its application in CRFs.
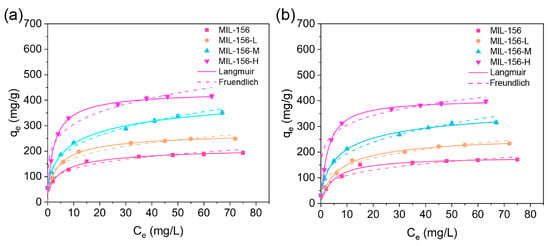
Figure 3.
Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models of MIL-156 (X) for urea (a) and phosphate (b) absorption.

Table 1.
Main parameters of different materials reported in the relevant studies.
Time-dependent adsorption experiments were conducted to assess the adsorption kinetics of urea and phosphate onto MIL-156(X) As shown in Figure 4, within the initial 5 min, MIL-156 achieved adsorption rates of 63.5% and 51.8% for urea and phosphate, respectively. The adsorption rates for both nutrients onto the MIL-156(X) series were significantly increased, particularly within the first 5 min, ultimately reaching adsorption equilibrium around 150 min. Notably, MIL-156-H exhibited the most rapid adsorption kinetics, achieving rates of 93.2% and 90.5% for urea and phosphate within the initial 5 min period. These findings collectively indicate the exceptional nitrogen and phosphorus loading capabilities of MIL-156(X). The kinetic processes governing urea and phosphate adsorption onto MIL-156(X) were further analyzed using Pseudo-first-order and Pseudo-second-order models. The results revealed that the Pseudo-second-order model provided a superior fit (as indicated by higher R2 values) to the time-dependent adsorption data compared to the Pseudo-first-order model. This suggests that the adsorption of urea and phosphate onto MIL-156(X) is predominantly governed by a chemisorption process [25]. Furthermore, the calculated Pseudo-second-order rate constants for urea adsorption were 0.05, 0.011, and 0.025 g·mg−1·min−1 for MIL-156 L, MIL-156-M, and MIL-156-H, respectively. Corresponding values for phosphate adsorption were 0.008, 0.013, and 0.019 g·mg−1·min−1 (Table S4). Clearly, MIL-156-H exhibited markedly higher adsorption rates than the other adsorbents. This indicates rapid diffusion of urea and phosphate to the adsorption sites. The underlying reason lies in the significantly increased specific surface area, which generates numerous additional adsorption sites. Moreover, the reduced particle size shortens the diffusion path length and minimizes internal diffusion limitations [22].
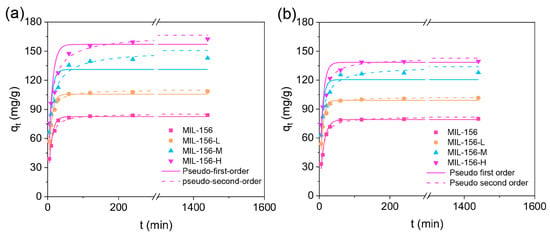
Figure 4.
Adsorption kinetics of MIL-156 (X) for urea (a) and phosphate (b).
3.3. Potential Mechanisms of Urea and Phosphate Loading on MIL-156(X)
To investigate the mechanism of urea and phosphate loading on MIL-156(X), the materials were characterized using FTIR and XPS before and after nutrient loading. Figure 5a presents the FTIR spectra obtained before and after loading. A distinct red shift was observed in the characteristic O-H stretching vibration peak of N-P-MIL-156-H at 3410 cm−1 compared to that of pristine MIL-156 at 3510 cm−1. The appearance of a new peak at 1610 cm−1 in N-P-MIL-156-H, corresponding to the C=O stretching vibration observed at 1682 cm−1 in urea, indicates the successful loading of urea on MIL-156-H. However, a concomitant red shift in the C=O vibration was also noted. These results suggest the formation of strong hydrogen bonds between the OH groups in MIL-156-H and the C=O groups of urea [36]. Following phosphate loading, a prominent peak emerged at 1070 cm−1, attributable to the asymmetric stretching vibration of P-O, signifying successful phosphate loading. Furthermore, an increase in the intensity of the Ca-O vibration at 555 cm−1, assigned to the bending vibration of O-P-O, indicates the occurrence of chemical coordination bonding between Ca and P. XPS analysis was further employed to elucidate the interactions between MIL-156(X) and urea/phosphate. As depicted in Figure 5b, the survey spectrum prior to loading exhibited peaks corresponding to O1s, C1s, K2p, and Ca2p. Subsequent to the adsorption of urea and phosphate, characteristic N1s and P2p peaks emerged, confirming the successful adsorption of both nutrients. The high-resolution P2p XPS spectrum reveals a lower binding energy (133.2 eV) for phosphate-loaded N-P-MIL-156-H compared to that of KH2PO4 (~134.0 eV) (Figure 5c), indicative of chemical bond formation between MIL-156-H and phosphate. Additionally, Figure 5d demonstrates that the Ca2p binding energy of N-P-MIL-156-H shifted to a higher value following phosphate adsorption. This shift arises from the migration of electrons from Ca atoms towards the more electronegative P-O bonds. Moreover, a new peak emerged at 358.4 eV, ascribed to Ca-O-P, providing evidence for the formation of an inner-sphere complex between Ca and phosphorus. This result signifies the participation of Ca-OH groups in phosphate loading via inner-sphere complexation involving Ca and phosphorus. This finding aligns with previous studies which demonstrated that MOFs adsorb phosphate by forming inner-sphere complexes at metal centers (e.g., Zr, Ce) [37,38,39]. The adsorption processes of urea and phosphate by the MIL-156-H are depicted in Figure 5e.
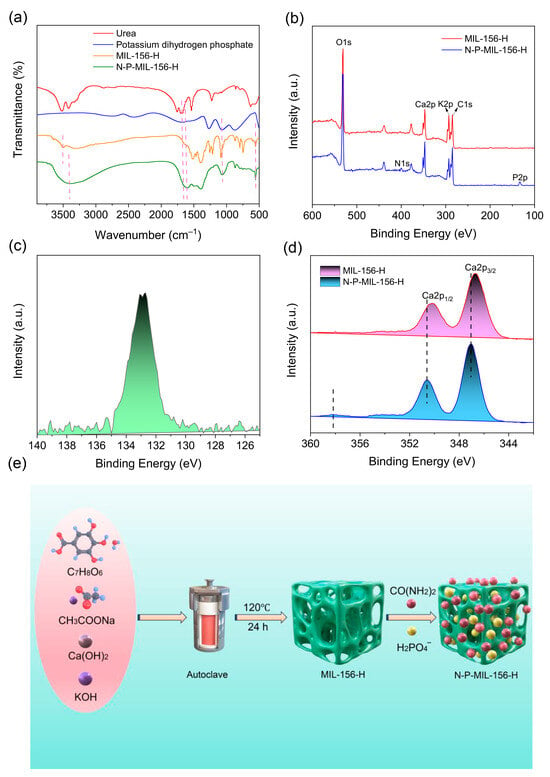
Figure 5.
FTIR spectra of MIL-156-H before and after urea/phosphate loading (a); XPS analysis of MIL-156-H before and after urea/phosphate loading: survey scan (b), P2p (c) and Ca2p (d); schematic diagram of nutrient loading of MIL-156-H (e).
3.4. Nutrient Release Characteristics of N-P-MIL-156-H
To investigate the controlled-release capability of N-P-MIL-156-H for nutrients, the cumulative release rates of nutrients in aqueous solutions under varying pH conditions were measured at 25 °C. At pH 5, the cumulative nitrogen release rate from N-P-MIL-156-H exceeded 88% within 14 days, while at pH 7, it reached 85.2% over 28 days. Under alkaline conditions (pH 9), the nitrogen release rate was further reduced, requiring over 42 days for substantial release. This release duration markedly exceeds that reported for other MOFs [15,33], indicating the controllable nature of the nutrient release process (Figure 6a). These results demonstrate that the release rate of N-P-MIL-156-H is significantly higher under acidic conditions compared to neutral or alkaline environments. This phenomenon is attributed to the formation of strong hydrogen bonds between the amino groups of urea and the hydroxyl groups on MIL-156-H; these hydrogen bonds are readily disrupted under acidic conditions, leading to premature urea release. The cumulative phosphorus release profile (Figure 6b) showed release rates of 42.2%, 48.6%, and 52.7% within 56 days at pH 5, 7, and 9, respectively. This increased phosphate release under alkaline conditions is ascribed to the facilitated desorption of phosphate anions from N-P-MIL-156-H, which aligns with previous research findings [25].
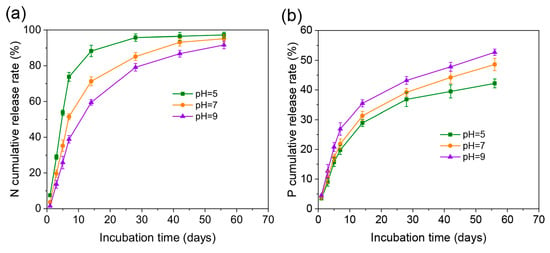
Figure 6.
N (a) and P (b) release curves of N-P-MIL-156-H in aqueous solution.
The nutrient release kinetics of N-P-MIL-156-H were further elucidated by fitting the experimental data to various mathematical models. Analysis of the model parameters revealed that the Higuchi model provided the strongest explanation for the N-P-MIL-156-H release mechanism across different pH conditions, followed by the Ritger-Peppas model (Table S5). The cumulative release profiles indicated an initial rapid urea and phosphate release phase, attributable to diffusion-dominated release mechanisms.
3.5. Application of N-P-MIL-156-H in Rice
A pot experiment was conducted to investigate the effects of N-P-MIL-156-H on rice growth. As shown in Figure 7a, the rice treated with N-P-MIL-156-H flourished particularly well compared with the other three groups. The grain yields under the CK, CF, MIL-156-H, and N-P-MIL-156-H treatments were 81.53, 56.32, 72.65 and 52.78 g per pot, respectively. Compared to the CF treatment, the N-P-MIL-156-H treatment increased grain yield by 12.22% (Table 2), demonstrating excellent fertilizer benefits and outperforming the results reported in previous studies [19,20]. This enhancement is attributed to the controlled release of nutrients from N-P-MIL-156-H, which better matches the nutrient demands of rice at different growth stages, thereby providing a sustained nutrient supply and promoting plant development. As essential nutrients for rice, nitrogen and phosphorus were absent in the MIL-156-H treatment, resulting in a significantly lower yield compared to the CF and N-P-MIL-156-H treatments. Moreover, the N-P-MIL-156-H treatment significantly increased the number of kernels per ear, 1000-kernel weight and aboveground biomass compared to other three treatments, demonstrating a pronounced fertilizer effect. Nutrient use efficiency is a critical indicator for evaluating the benefits of fertilizers. Relative to the nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) (35.6%) and phosphorus use efficiency (PUE) (13.32%) observed under the CF treatment, the N-P-MIL-156-H treatment markedly improved both NUE and PUE, achieving values of 44.8% and 16.56%, respectively. These results indicate that N-P-MIL-156-H can function as an efficient nutrient delivery system for precise nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) management.
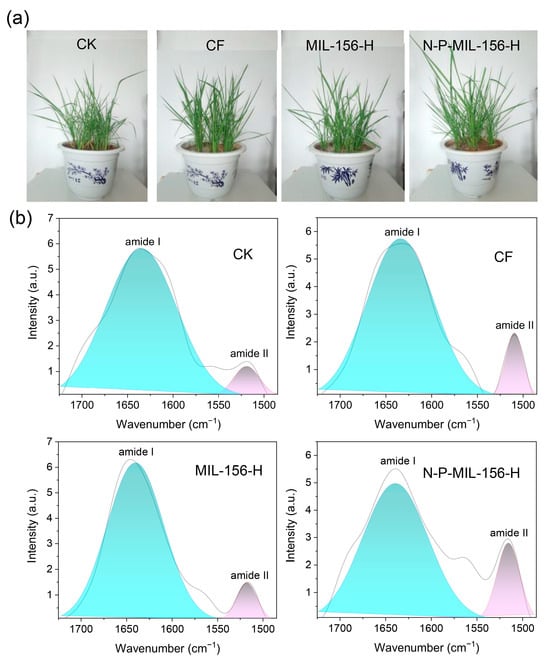
Figure 7.
Growth status of rice (a) and deconvolution of FTIR-PAS spectra for different treatments (b).

Table 2.
Effects of N-P-MIL-156-H application on rice growth.
To further elucidate the nitrogen utilization efficiency in rice, Fourier transform infrared photoacoustic spectroscopy (FTIR-PAS) was employed to probe the nitrogen nutritional status during the tillering stage under different treatments. The results revealed that rice leaves from all four treatments exhibited similar spectral absorption features (Figure S1). The peak observed between 1680 and 1630 cm−1 corresponds to the C=O stretching vibration in amide I, while the minor peak within 1570 to 1510 cm−1 is attributed to the C-N stretching vibration and N-H bending vibration in amide II. Within plant tissues, amides represent the predominant form of nitrogen storage. Consequently, the amide I and amide II bands can be utilized to assess the nitrogen nutritional status of rice [32]. Gaussian deconvolution was subsequently applied to the spectral region of 1700–1500 cm−1 to resolve and fit the peaks, yielding high-resolution, distinct characteristic peaks for amide I and amide II. For a more precise evaluation of rice nitrogen status, the ratio of the characteristic peak intensities of amide II to amide I was calculated. The results showed that the amide II/amide I ratios for the no fertilization (CK), conventional fertilization (CF), MIL-156-H, and N-P-MIL-156-H treatments were 0.20, 0.41, 0.23, and 0.54, respectively (Figure 7b). A higher amide II/amide I ratio signifies an elevated nitrogen nutritional level in rice, indicating that N-P-MIL-156-H promotes greater nitrogen accumulation within the plant. These findings provide preliminary confirmation that N-P-MIL-156-H enhances nitrogen utilization efficiency in rice. Furthermore, the total phosphorus content in rice leaves of the N-P-MIL-156-H treated rice reached 4.1 g/kg, significantly surpassing that of the other three treatments (Figure S2), demonstrating that N-P-MIL-156-H similarly improves phosphorus use efficiency.
4. Discussion
CRFs offer significant advantages in agriculture, including enhanced fertilizer utilization efficiency, reduced environmental stress, lower fertilization costs, and improved crop yield and quality. They represent one of the effective strategies to reconcile the conflict between agricultural production and environmental protection. However, both petroleum-based and bio-based CRFs face challenges such as high costs, potential environmental pollution, limited nutrient types, and a mismatch between nutrient release patterns and crop demands. MOFs, as a novel class of porous materials, have demonstrated great potential in the precise delivery of nutrients. However, the confined pore structures of conventional MOFs often lead to limited nutrient loading capacity. To address this issue, this study employed sodium acetate as a modulator to construct hierarchical porous MOFs (MIL-156(X)) via molecular self-assembly under hydrothermal conditions. The resulting MIL-156(X) achieved high loading efficiency for urea and phosphates, with the nitrogen and phosphorus content in N-P-MIL-156-H reaching 10.6% and 16.5%, respectively. Additionally, N-P-MIL-156-H contained 5.2% K2O, making it a multi-nutrient CRFs that surpasses previously reported MOF-based fertilizers in terms of both nutrient content and diversity. Moreover, the raw materials and synthesis process for N-P-MIL-156-H are environmentally friendly and do not involve toxic reagents, which contributes to sustainable agricultural development. Nevertheless, existing research has elucidated that the release of MOFs into the environment can induce adverse effects on animals, plants, and microorganisms [40,41,42]. As such, the potential ecological risks of applying MOF-based fertilizers to soil, along with their impact on crop growth and metabolism, remain largely unclear and warrant further systematic investigation.
Results from hydroponic experiments indicated that the nutrient release behavior of N-P-MIL-156-H was significantly influenced by pH. However, the release mechanism of N-P-MIL-156-H in soil remains unclear, as soil constitutes an extremely complex system where physical, chemical, and biological factors may collectively affect the structural stability and nutrient release patterns of N-P-MIL-156-H. Furthermore, pot experiments were conducted to evaluate the effects of N-P-MIL-156 on rice growth. The results demonstrated that, compared with conventional fertilization, the N-P-MIL-156 treatment increased rice yield by 12.22%, improved agronomic traits such as grain number per panicle, 1000-grain weight, and above-ground biomass, and enhanced nitrogen use efficiency. Spectroscopic analyses further confirmed that N-P-MIL-156 promoted nitrogen uptake and utilization in rice. It should be noted, however, that pot experiments differ fundamentally from field trials in terms of scale and environmental complexity. Therefore, future research will involve field experiments to further investigate the nutrient release characteristics of N-P-MIL-156-H under real agricultural conditions and its impact on crop growth. These studies will help clarify the applicable conditions for N-P-MIL-156 and provide a scientific basis for its broader application.
5. Conclusions
In summary, a novel MIL-156 MOF with a hierarchically porous structure, designated MIL-156(X), was synthesized via the addition of modulators. MIL-156(X) retains its inherent microporous framework while incorporating substantial mesoporosity. As the modulator concentration increases, the particle size and pore diameter of MIL-156(X) progressively decline, accompanied by an increase in specific surface area. This morphological evolution enhances its adsorption capacity for urea and phosphate. The adsorption processes conform to both the Langmuir isotherm and pseudo-second-order kinetic models. Mechanistically, urea loading involves hydrogen bonding, while phosphate loading occurs via the formation of Ca-inner-sphere complexes. The nutrient release behavior of N-P-MIL-156-H is governed by Fickian diffusion kinetics. Pot experiments demonstrated the positive impact of N-P-MIL-156-H on rice growth, including increased yield, enhanced nitrogen and phosphorus utilization efficiency, and improved agronomic traits, thereby offering a promising strategy for efficient agricultural nutrient management. By engineering MOFs with hierarchical porosity, this approach simultaneously increases nutrient loading capacity, significantly boosts nutrient utilization efficiency, mitigates environmental pollution caused by nitrogen and phosphorus loss, and achieves the dual objectives of promoting agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy15102334/s1, Figure S1: FTIR-PAS spectra of rice leave at different treatments; Figure S2: The total P content of rice leaves at different treatments; Table S1: Soil physical and chemical properties; Table S2: Pore structure parameters calculated from the N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms; Table S3: Parameters of Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models for urea and phosphate adsorption; Table S4: Adsorption kinetics fitting parameters of urea and phosphate by MIL-156(X).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.Z.; Methodology, G.L.; Formal analysis, G.L. and S.L.; Investigation, C.D.; Data curation, R.Z. and F.M.; Writing—original draft, R.Z. and K.W.; Writing—review & editing, F.G. and K.W.; Visualization, F.M.; Supervision, S.L.; Project administration, F.G. and K.W.; Funding acquisition, C.D., F.G. and K.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2024YFD1701004), the Jiangsu Agriculture Science and Technology Innovation Fund (CX(24)3116), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32202613), the Excellent Scientific and Technological Innovation team of Jiangsu Universities (2023) and the Key Laboratory of Modern Agricultural Equipment and Technology (Jiangsu University), Ministry of Education (Project No. MAET202320).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- El-Shal, R.M.; El-Naggar, A.H.; El-Beshbeshy, T.R.; Mahmoud, E.K.; El-Kader, N.I.A.; Missaui, A.M.; Du, D.; Ghoneim, A.M.; El-Sharkawy, M.S. Effect of Nano-Fertilizers on Alfalfa Plants Grown under Different Salt Stresses in Hydroponic System. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhadi, M.; Javed, Q.; Jakubus, M.; Elkouali, M.; Fougrach, H.; Ansar, A.; Ban, S.G.; Ban, D.; Heath, D.; Černe, M. Nanoparticles for Sustainable Agriculture: Assessment of Benefits and Risks. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Wang, H.; Rahman, A.; Abdul Azim, J.; Hussain Memon, W.; Qian, L. Structural Equation Model of Young Farmers’ Intention to Adopt Sustainable Agriculture: A Aase Study in Bangladesh. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2022, 37, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xu, W.; Leng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Ding, H.; Zhou, J.; Cui, L. Review and Research Prospects on Additive Manufacturing Technology for Agricultural Manufacturing. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shaghaleh, H.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Xu, X.; Liu, H. Synthesis of a pH-Responsive Nano-Cellulose/Sodium Alginate/MOFs Hydrogel and its Application in the Regulation of Water and N-Fertilizer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 187, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Gao, B.; Wan, Y.; Li, Y.C.; Zhao, C. Biobased Interpenetrating Network Polymer Composites from Locust Sawdust as Coating Material for Environmentally Friendly Controlled Release Urea Fertilizers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5692–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrencia, D.; Wong, S.K.; Low, D.Y.S.; Goh, B.H.; Goh, J.K.; Ruktanonchai, U.R.; Soottitantawat, A.; Lee, L.H.; Tang, S.Y. Controlled Release Fertilizers: A Review on Coating Materials and Mechanism of Release. Plants 2021, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Guo, Y.; Chen, J. Influence of Transfer Plot Area and Location on Chemical Input Reduction in Agricultural Production: Evidence from China. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, M.; Li, J.; AL-Huqail, A.A.; Hamed, M.A.; Du, D.; EL-Khamisy, R.R. Slow-Released Fertilizers Optimization and Experimental Impacts on Soil Fertility and Wheat- Maize Cropping System. Sci. Agric. 2024, 81, e20230234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Yuan, W.; Li, G.; Petropoulos, E.; Xue, L.; Feng, Y.; Xue, L.; Yang, L.; Ding, Y. Deep Fertilization with Controlled-Release Fertilizer for Higher Cereal Yield and N Utilization in Paddies: The Optimal Fertilization Depth. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 5027–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, Y.C. Biobased Polyurethane, Epoxy Resin, and Polyolefin Wax Composite Coating for Controlled-Release Fertilizer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5380–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumi, N.; Kusube, T.; Nagao, S.; Okochi, H. Accumulation of Microcapsules Derived from Coated Fertilizer in Paddy Fields. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xun, L.; Dong, L.; Duan, J.; Shen, W.; Duan, Z. Nitrogen slow-release behavior of oxamide granules in two different types of paddy soils. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, M.Y.; Sulaiman, S.A. Slow Release Coating Remedy for Nitrogen Loss from Conventional Urea: A Review. J. Control. Release 2016, 225, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Liang, Q.; Abdul, Q.; Rashid, A.; Ren, X.; Ma, H. Preparation technology and preservation mechanism of γ-CD-MOFs biological packaging film loaded with curcumin. Food Chem. 2023, 420, 136142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.J.; Dai, X.L.; Yang, R.Q.; Liu, Z.Y.; Chen, H.L.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, X.N. Fenton-like catalytic MOFs driving electrochemical aptasensing toward tracking lead pollution in pomegranate fruit. Food Control. 2025, 169, 111006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, R.; Ke, L.; Li, J.; Jayan, H.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Zou, X.; Guo, Z. Development of multifunctional metal-organic frameworks (MOFs)-based nanofiller materials in food packaging: A comprehensive review. Trends. Food Sci. Tech. 2024, 154, 104771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhameed, R.M.; Abdelhameed, R.E.; Kamel, H.A. Iron-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks as Fertilizers for Hydroponically Grown Phaseolus Vulgaris. Mater. Lett. 2019, 237, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstoetz, M.; Rose, T.J.; Clark, M.W.; Yee, L.H.; Raymond, C.A.; Vancov, T. Novel Applications for Oxalate-Phosphate-Amine Metal-Organic-Frameworks (OPA-MOFs): Can an Iron-Based OPA-MOF be Used as Slow-Release Fertilizer? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Li, W.; Ma, F.; Gan, F.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, H.; Du, C. Urea-loaded core–shell MOF/silica nanocarriers for continuous nitrogen release to crops. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 11645–11654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Huang, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, T. A general and Facile Strategy for Precisely Controlling the Crystal Size of Monodispersed Metal-Organic Frameworks Via Separating the Nucleation and Growth. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, N.; Biswas, S. Synthesis of Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs): Routes to Various MOF Topologies, Morphologies, and Composites. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 933–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, J.-M.; Jin, L.-N.; Sun, W.-Y. Metal Ion Induced Porous HKUST-1 Nano/ Microcrystals with Controllable Morphology and Size. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 4127–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Yang, B.G.; Wang, F.Y.; Yan, Y.H.; Hong, X.Y.; Xu, H.H.; Xia, M.Z.; Wang, F.Y. Green Synthesis of MOF-808 with Modulation of Particle Sizes and Defects for Efficient Phosphate Sequestration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 300, 121825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Zhang, X.; Du, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, R.; Wang, S.; Guan, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Gan, F. Enhanced Phosphate Removal from Water Via Hierarchically Porous Metal-Organic Frameworks. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, S.; Kim, Y.; Gaikwad, R.; Han, S. Enhanced VOC Adsorption Capacity on MOF Thin Layer with Reduced Particle Size by Cryogrinding and Microwave Method. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, T.; Cooper, L.; Gorman, M.; Lozano-Fernández, T.; Simón-Vázquez, R.; Mouchaham, G.; Marrot, J.; Guillou, N.; Serre, C.; Fertey, P. Crystal Structure Dependent In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Biocompatible Calcium Gallate MOFs. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2813–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Dkhar, D.S.; Chandra, P.; Kayastha, A.M. Watermelon Derived Urease Immobilized Gold Nanoparticles-Graphene Oxide Transducer for Direct Detection of Urea in Milk Samples. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 6357–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.L.; Wang, H.; Chu, H.J.; Li, J.J. Preparation and Characterization of Slow-Release and Water-Retention Fertilizer Based on Starch and Halloysite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.W.; Zhang, G.L.; Dai, Z.Y.; Xiang, Y.B.; Liu, B.; Bian, P.; Zheng, K.; Wu, Z.Y.; Cai, D.Q. Fabrication of Light-Responsively Controlled-Release Herbicide Using a Nanocomposite. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Du, C.; Ma, F.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, J. Optimization of Metal–Organic (citric acid) Frameworks for Controlled Release of Nutrients. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 32270–32277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Shaghaleh, H.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Xu, X.; Liu, H. Synthesis of Bio-Based MIL-100(Fe)@CNF-SA Composite Hydrogel and its Application in Slow-Release N-Fertilizer. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 324, 129274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Xu, X.; Ma, F.; Du, C. Solvent-Free Synthesis of Iron-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) as Slow-Release Fertilizers. Polymers 2021, 13, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Dan, Y.; Tian, D.; Zheng, Y.; Wei, S.; Xiang, D. Facile Fabrication of MOF (Fe)@alginate Aerogel and its Application for a High-Performance Slow-Release N- Fertilizer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindra, P.; Sharma, S.; Sahu, B.K.; Bagdwal, H.; Shanmugam, V.; Singh, M. Targeted Nutrient Application to Tomato Plant with MOF/Zeolite Composite Wrapped with Stimuli-Responsive Biopolymer. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenberg, M.; Loewenschuss, A.; Marcus, Y. An Empirical Correlation Between Stretching Vibration Redshift and Hydrogen Bond Length. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 2699–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J. Facile Design of UiO-66-NH2@La(OH)3 Composite with Enhanced Efficiency for Phosphate Removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, V.; Boukhvalov, D.W.; Philip, L. Role of Inner-Sphere Complexation in Phosphate Removal by Metal–Organic Frameworks: Experimental and Theoretical Investigation. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2023, 9, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Z.; Cai, Z.; Chen, F.; Hu, J. Defect-Engineered Cerium-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks via Dynamic Ligand Competition: Increasing Coordinatively Unsaturated Sites for Enhanced Phosphate Adsorption. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2025, 701, 138784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Hong, L.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhan, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, S. Growth Inhibition of Microcystic aeruginosa by Metal-Organic Frameworks: Effect of Variety, Metal ion and Organic Ligand. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 35314–35326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baati, T.; Njim, L.; Neffati, F.; Kerkeni, A.; Bouttemi, M.; Gref, R.; Najjar, M.F.; Zakhama, A.; Couvreur, P.; Serre, C.; et al. In Depth Analysis of The In Vivo Toxicity of Nanoparticles of Porousiron(iii) Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, W.; Min, K.; Ling, W.; Ma, W.; Zhang, W.; Hou, X.; Wei, L.; Liu, Q.; et al. Dose-Dependent Effect on Plant Growth of Exposure to Metal–Organic Framework MIL-101(Cr). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 8009–8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).