Research Status and Trends in Universal Robotic Picking End-Effectors for Various Fruits
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
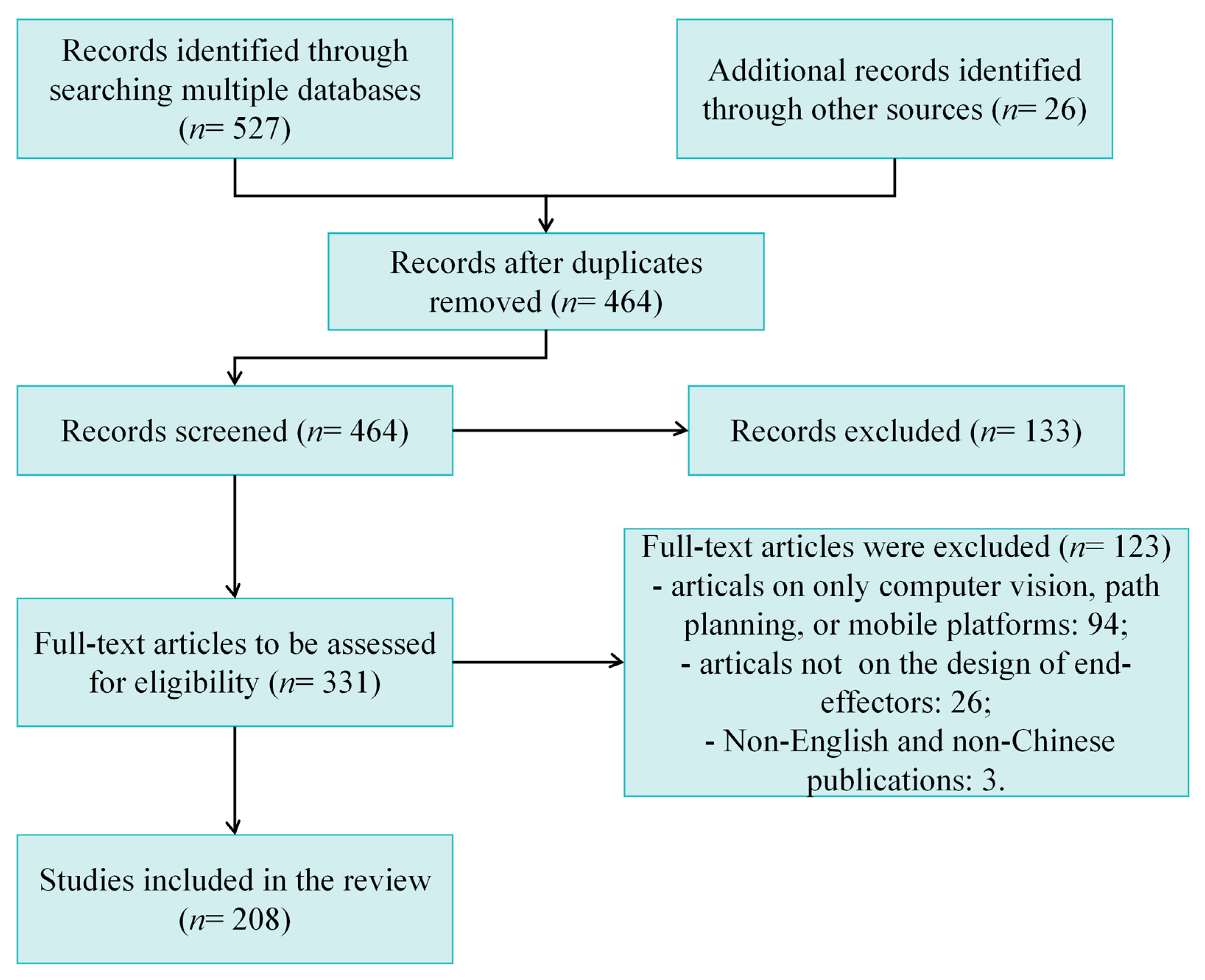
1.2. Literature Search Strategy
1.3. Paper Organization
2. Challenges of Specialized Picking End-Effectors
2.1. A Wide Variety of Fruits
2.2. Complex and Diverse Unstructured Canopy Environments of Fruits
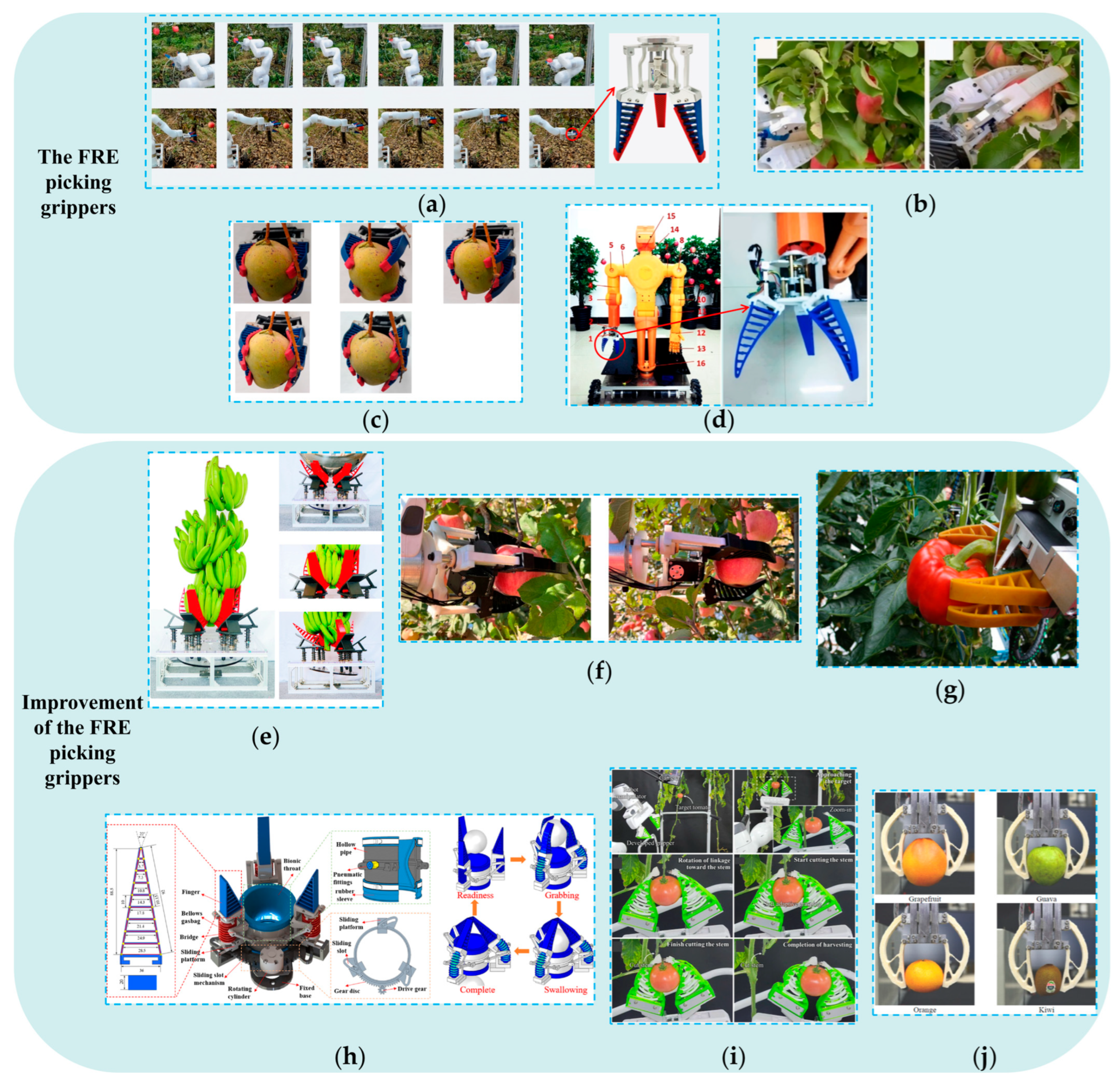
3. Design of End-Effectors Based on Picking Patterns
3.1. Design of End-Effectors Based on Single-Action Picking Patterns
3.1.1. Design of End-Effectors Based on Grasp-And-Pull Picking Patterns
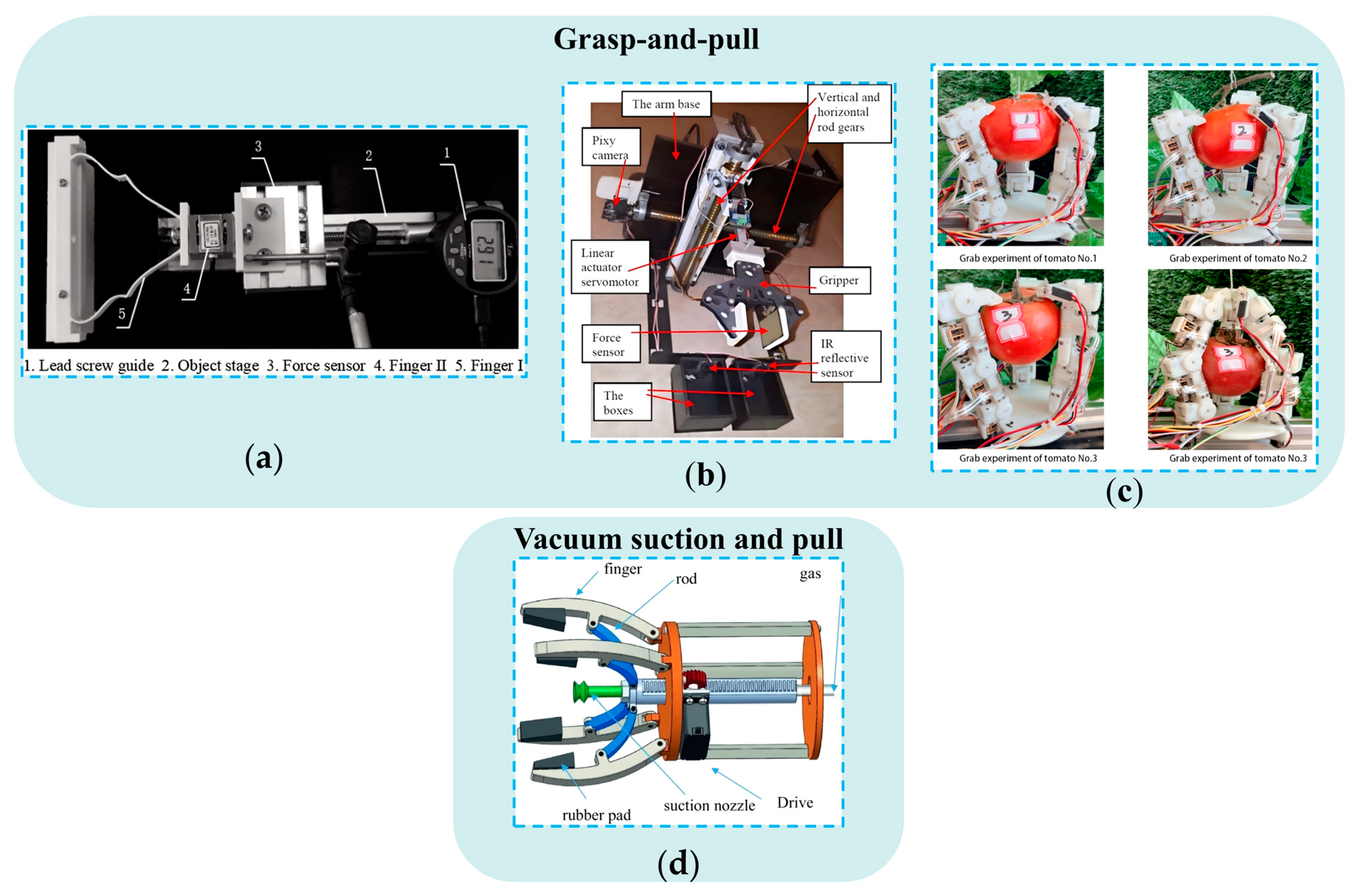
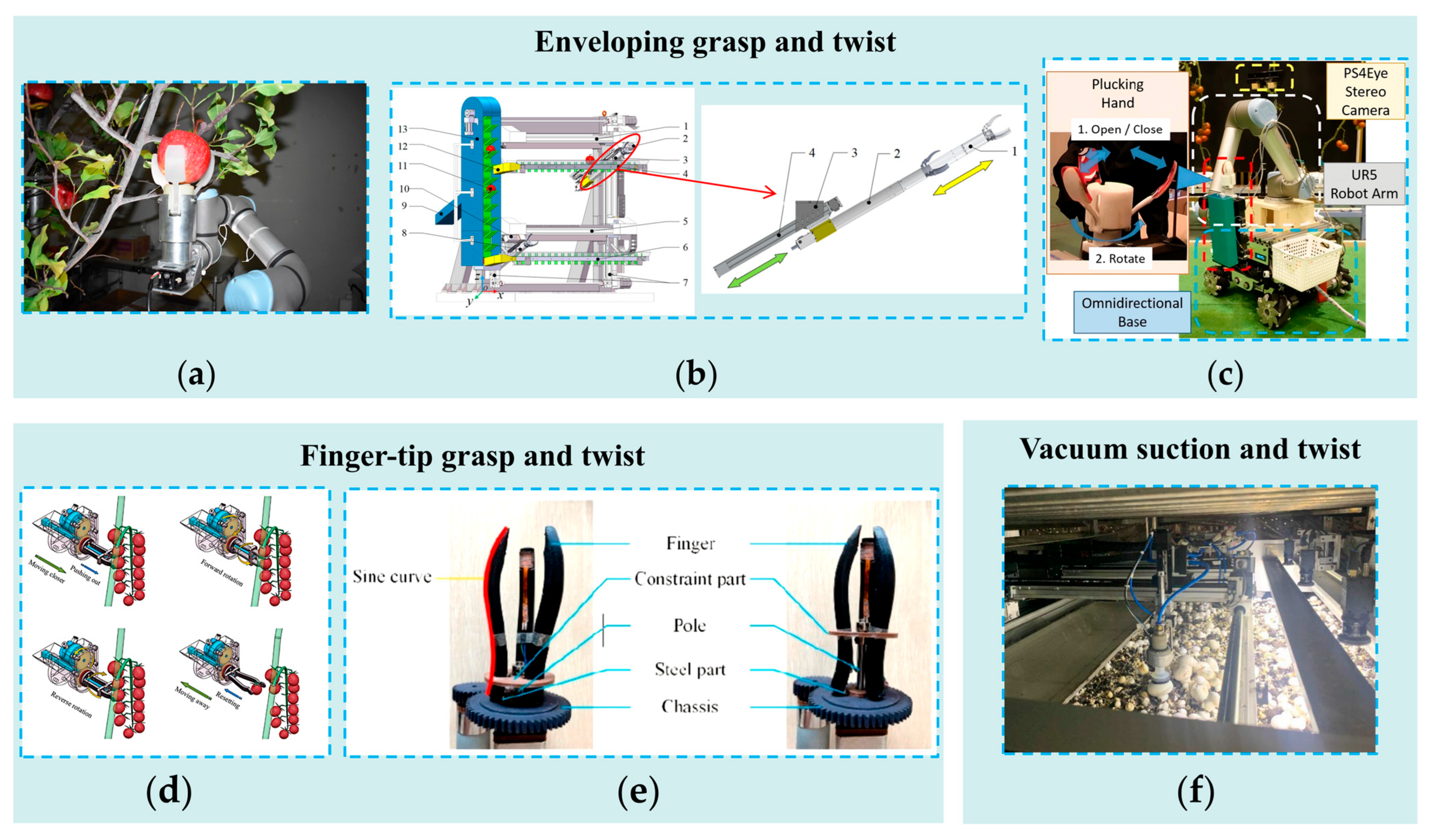
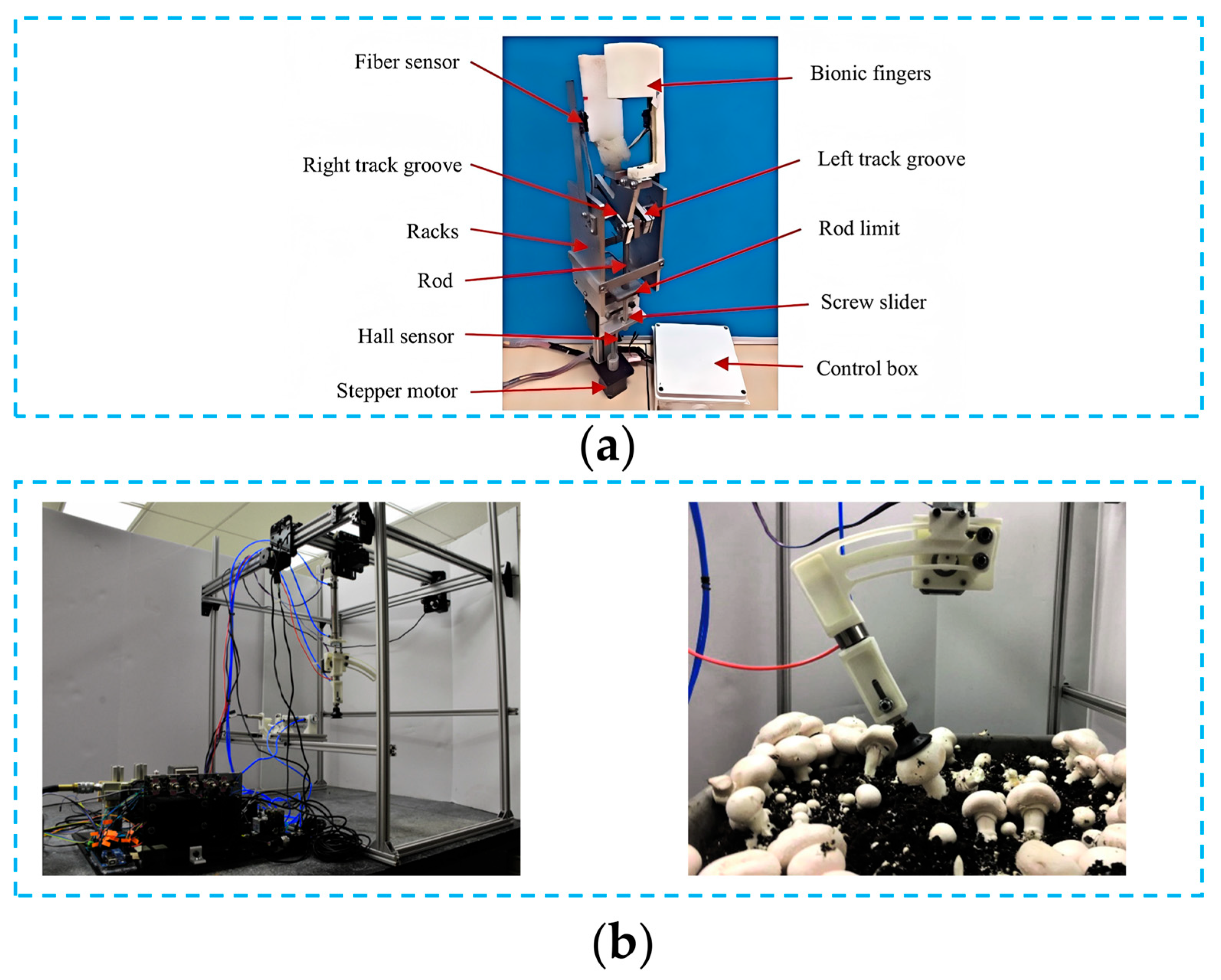
3.1.2. Design of End-Effectors Based on Grasp-And-Twist Picking Patterns
3.1.3. Design of End-Effectors Based on Grasp-And-Bend Picking Patterns
3.1.4. Design of End-Effectors Based on Grasp-And-Cut Picking Patterns
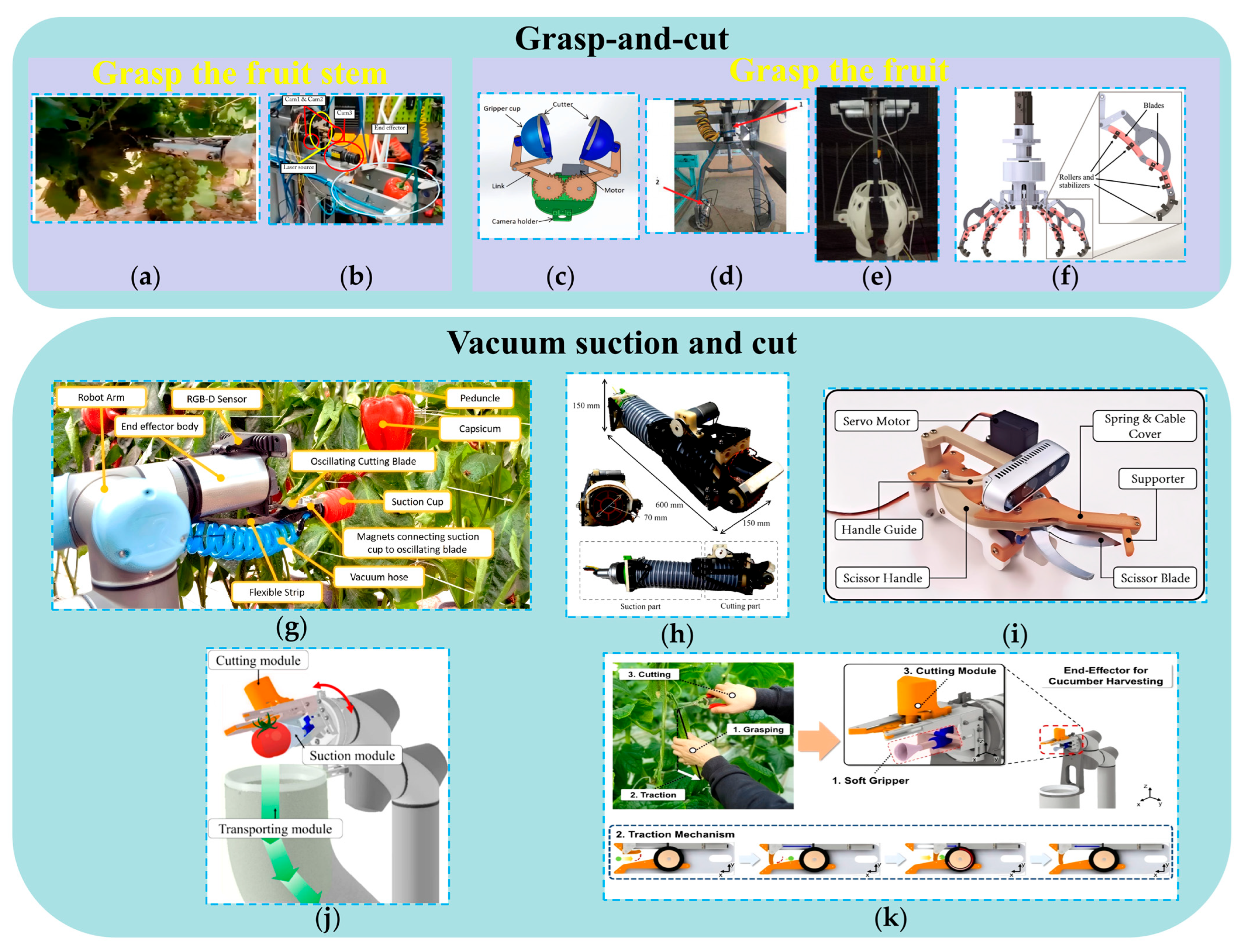
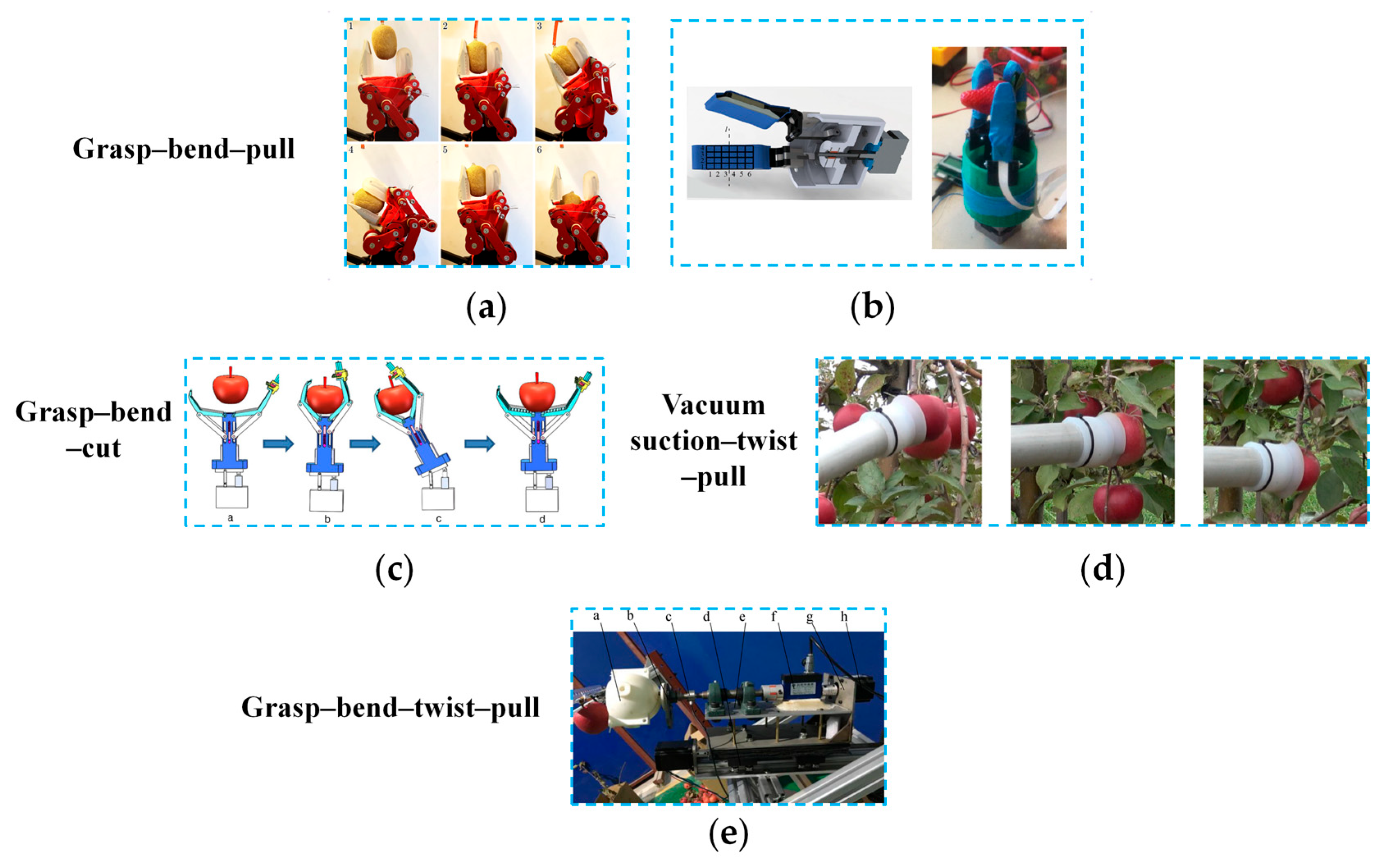
3.2. Design of End-Effectors Based on Combined-Action Picking Patterns
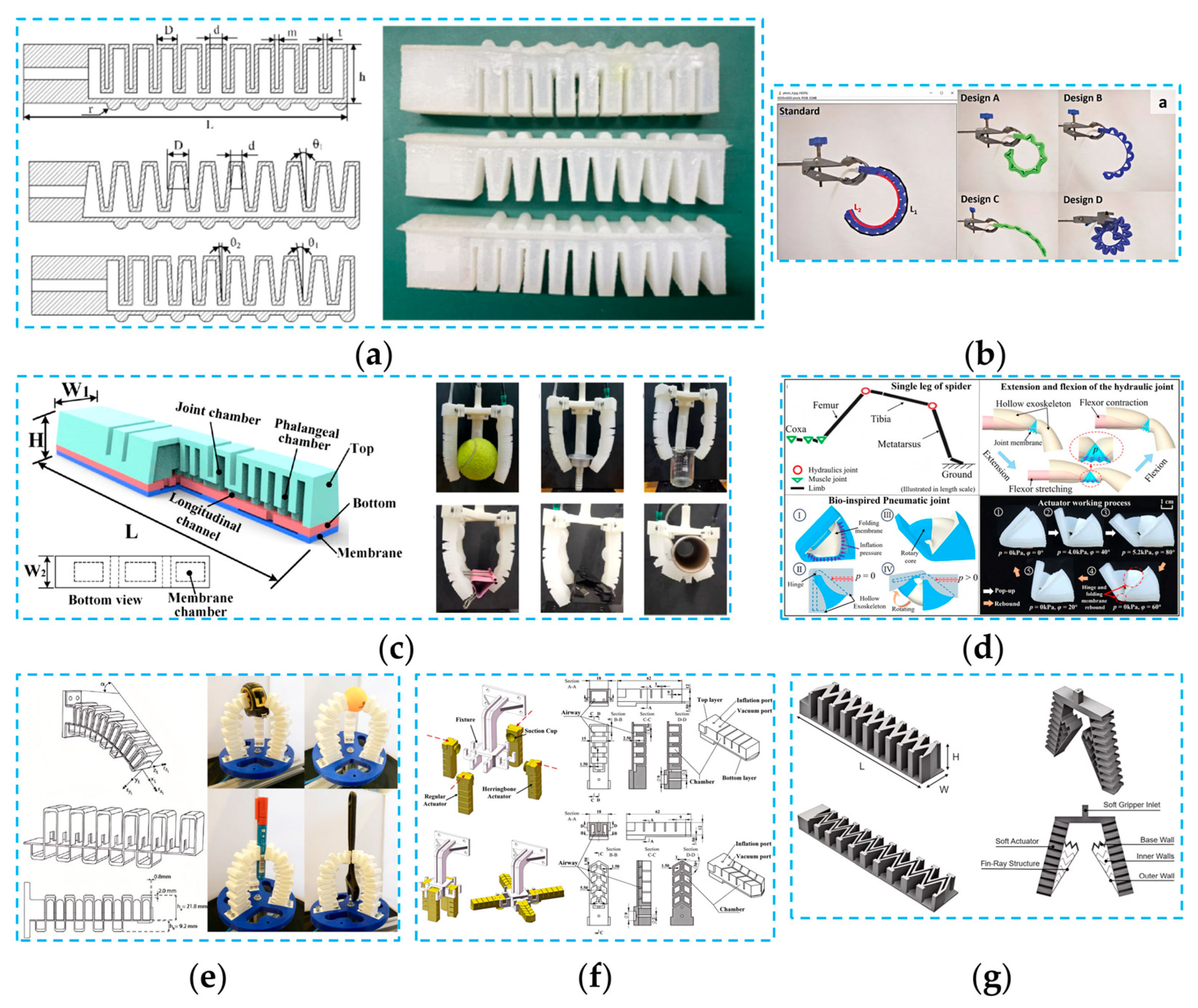
4. Soft Picking End-Effectors
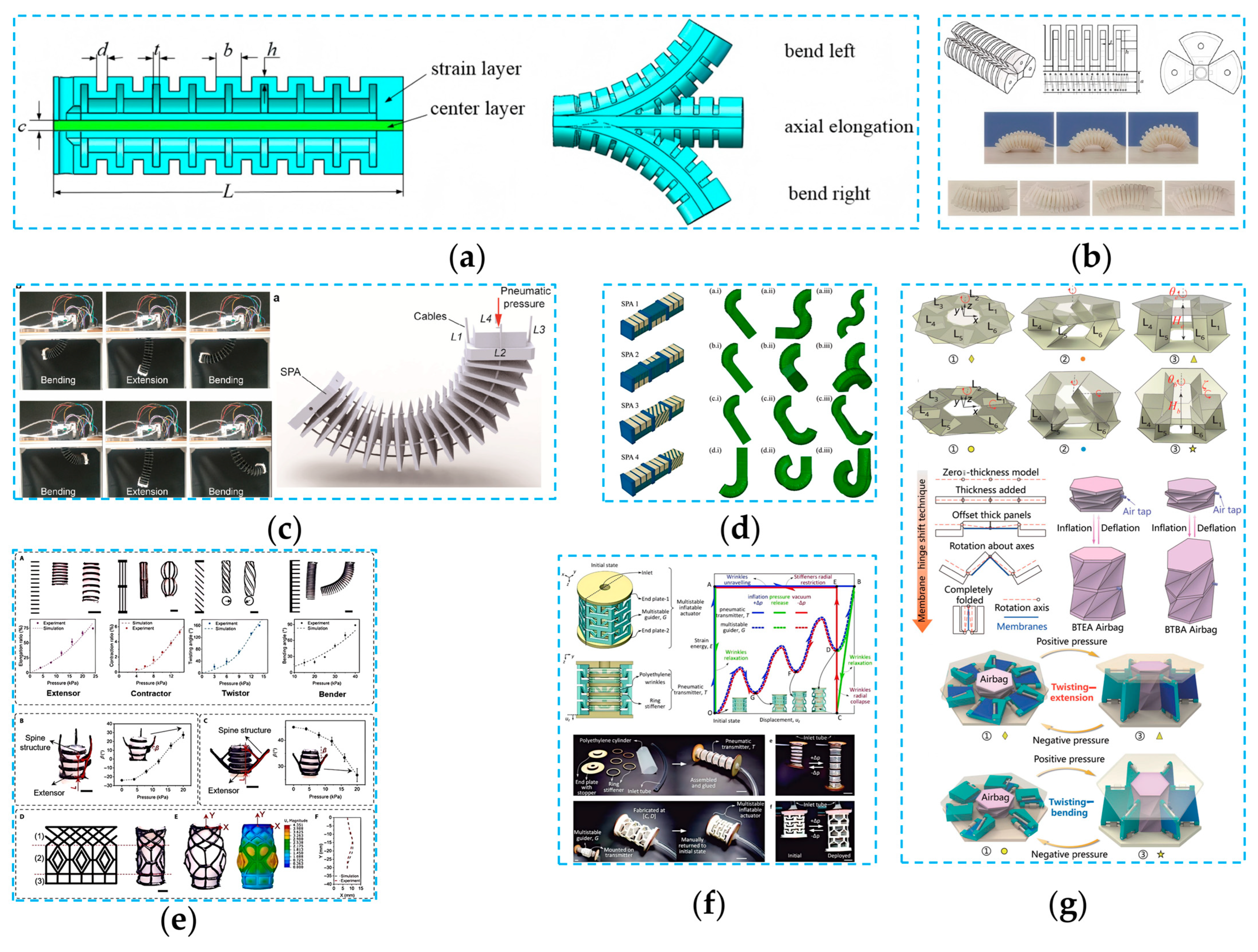
4.1. Picking End-Effectors Based on Pneumatic Driving Mechanisms
4.1.1. Picking End-Effectors Based on Soft Air Chambers
4.1.2. Picking End-Effectors Based on SPAs
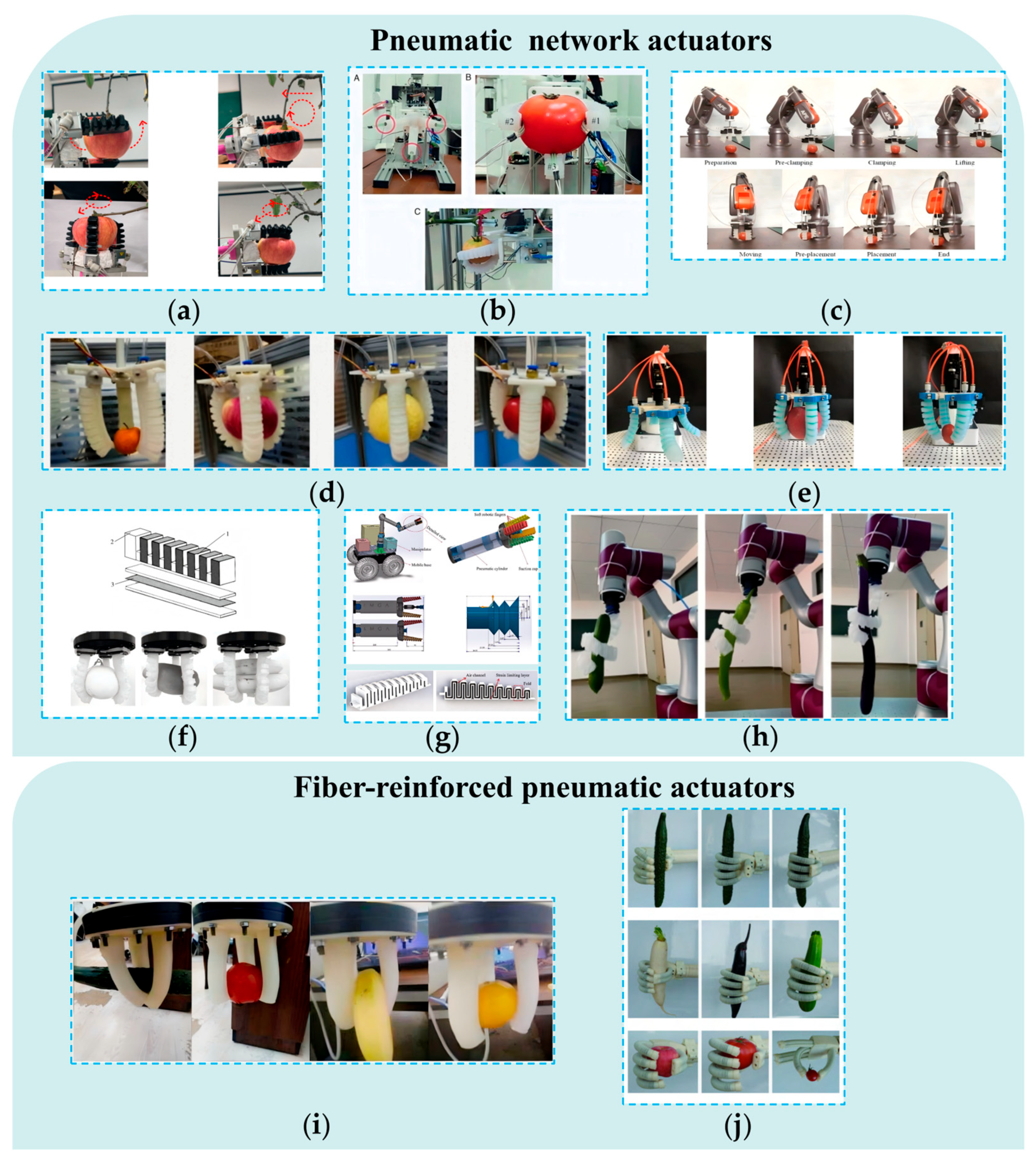
4.1.3. SPAs in Non-Agricultural Fields
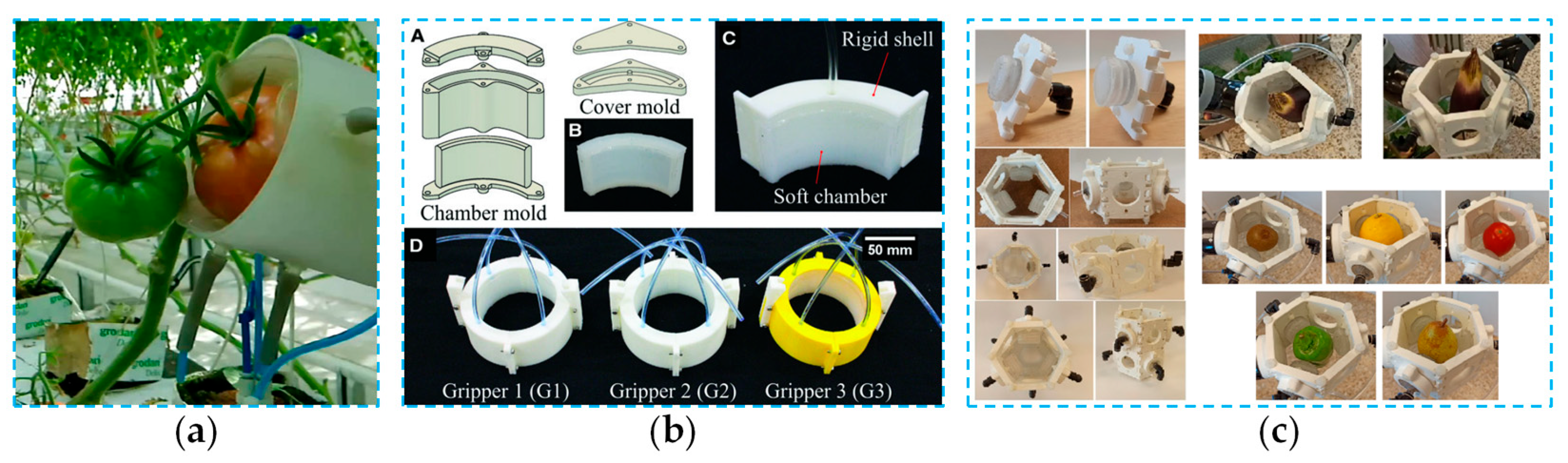
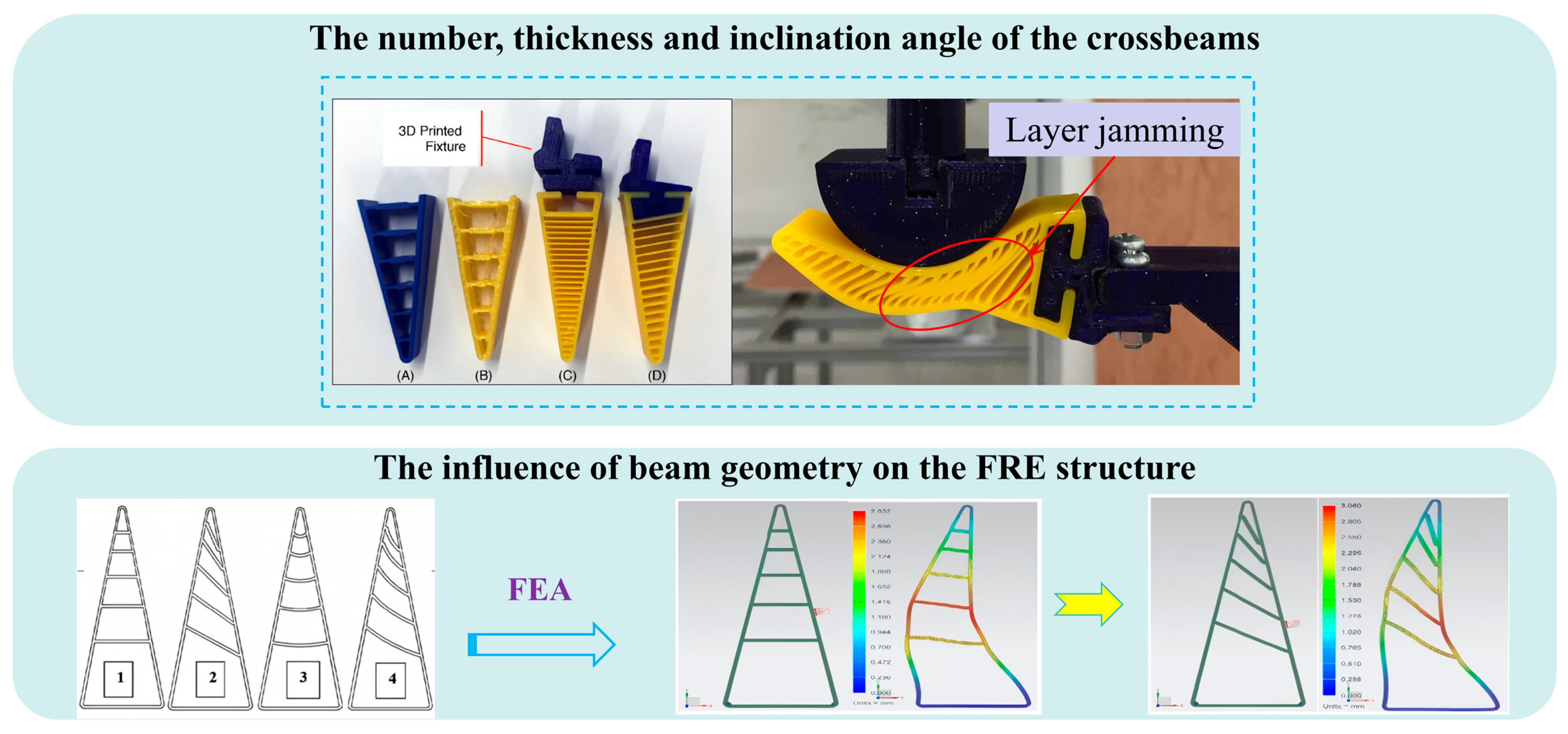
4.2. Picking End-Effectors Based on FRE Structures
4.2.1. Design of Picking End-Effectors Based on FRE Structures
4.2.2. Optimization of Geometric Parameters in FRE Structures
5. Advanced Technology for Picking End-Effectors
5.1. Advanced Tactile Sensing Integration for Enhanced Perception and Feedback
5.2. Advanced Material Technology for Field-Ready End-Effectors
5.3. Learning-Enabled Control of Picking End-Effectors
6. Challenges and Future Trends
6.1. Challenges
6.2. Future Trends
- (1)
- In the future, research should focus on master–slave design strategies for anthropomorphic picking hands. A central challenge lies in effectively integrating the “dexterous” master motion unit of the thumb and index finger with the “compliant” slave unit formed by the three ulnar fingers and the palm. A key breakthrough will be the dimensionality reduction mapping of human hand behaviors to the picking actions of anthropomorphic hands. This requires establishing clear relationships between human hand kinematic features and the core functional indicators of master–slave picking behavior. Furthermore, analyzing the degree of involvement of different DOFs and their interdependencies is expected to enable optimized combinations of motion, thereby providing theoretical guidance for simplified design. In addition, kinematic models of the master and slave units will likely play an important role in evaluating the motion performance of anthropomorphic picking hands. When combined with correlation models that characterize the interaction forces between human hand segments and fruit under different picking patterns, these models can serve as criteria for optimizing the structural design and control strategies of master–slave units, ultimately improving picking stability.
- (2)
- With advances in flexible materials and actuation technologies, the challenge of achieving compliant deformation of the palm is expected to be addressed. To enable palm deformation to support diverse picking behaviors, it is essential to investigate the coordination between the palm and fingers, for which the construction of a combined kinematic model is critical. Moreover, identifying how the interaction forces between fingers and fruit vary with palm motion will help optimize palm–finger coordination and refine palm control strategies. Such insights are vital for achieving distributed curved-surface contact and adaptive envelopment of fruits.
- (3)
- Although the introduction of flexible materials and structures has greatly improved compliance and adaptability, problems remain, including insufficient stiffness, limited load capacity, and slow actuation response. Rigid–flexible coupling offers new opportunities to address these limitations but also imposes higher demands on system design. Achieving a proper balance between the deformability of flexible structures and the load-bearing capacity of rigid elements remains a central challenge. One promising direction is to integrate anisotropic rigid materials or structures within flexible components, enabling deformation to vary significantly across different directions. Another direction is to optimize the layout of rigid–flexible coupled modules so that rigid elements are placed in non-critical deformation regions, while localized stress concentrations are introduced in flexible areas. This approach can accelerate structural deformation and reduce actuation delay.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TRL | Technology readiness level |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization |
| IEEE | Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers |
| ASABE | American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers |
| DOF | Degree of freedom |
| FRE | Fin ray effect |
| SPAs | Soft pneumatic actuators |
| FEA | Finite element analysis |
| ME3P | Multi-material embedded 3D printing |
| MRE | Magnetorheological elastomer |
| LCEs | Liquid crystal elastomers |
| DRL | Deep reinforcement learning |
References
- Ramin Shamshiri, R.; Weltzien, C.; Hameed, I.A.; Yule, I.J.; Grift, T.E.; Balasundram, S.K.; Pitonakova, L.; Ahmad, D.; Chowdhary, G. Research and Development in Agricultural Robotics: A Perspective of Digital Farming. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; He, X.; Ge, X.; Wu, X.; Shen, J.; Song, Y. Detection of Key Organs in Tomato Based on Deep Migration Learning in a Complex Background. Agriculture 2018, 8, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, S.; Tang, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, S.; Guo, X. Intelligent Recognition and Automated Production of Chili Peppers: A Review Addressing Varietal Diversity and Technological Requirements. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xu, L. Design, Development, Integration, and Field Evaluation of a Ridge-Planting Strawberry Harvesting Robot. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, H.E.; Xiaobo, Z.; Jiyong, S.; Mahunu, G.K.; Zhai, X.; Mariod, A.A. Quality and Postharvest-Shelf Life of Cold-Stored Strawberry Fruit as Affected by Gum Arabic (Acacia senegal) Edible Coating. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, e12527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Area Harvested of the Furits and Vegetables in the World. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- FAO. Production Quantity of the Furits and Vegetables in the World. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/zh/#data/QV (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Jin, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Yuan, S.; Li, P.; Wang, J. Development Status and Trend of Agricultural Robot Technology. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Guo, Z.; Li, T.; Feng, Q.; Zhao, C. Dynamic Task Planning for Multi-Arm Harvesting Robots Under Multiple Constraints Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Ji, W.; Feng, Q. Robots and Autonomous Machines for Sustainable Agriculture Production. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, Q.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, S.; Tan, Z.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, H. The Impact of Mechanical Compression on the Postharvest Quality of ‘Shine Muscat’ Grapes during Short-Term Storage. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jia, W.; Ruan, C.; Zhao, D.; Gu, Y.; Chen, W. The Recognition of Apple Fruits in Plastic Bags Based on Block Classification. Precis. Agric. 2018, 19, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhu, W.; Sun, L.; Bai, J.; Zhou, R.; Zhu, Z.; Cai, J. Online Assessment of Soluble Solids Content in Strawberries Using a Developed Vis/NIR Spectroscopy System with a Hanging Grasper. Food Chem. 2025, 478, 143671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yan, H.; Yin, Y.; Wu, C. Strawberry Fruit Deformity Detection and Symmetry Quantification Using Deep Learning and Geometric Feature Analysis. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Guo, Z.; Fernandes Barbin, D.; Dai, Z.; Watson, N.; Povey, M.; Zou, X. Hyperspectral Imaging and Deep Learning for Quality and Safety Inspection of Fruits and Vegetables: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 10019–10035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Liu, J.; Jin, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhao, S.; Peng, Y. Vibration–Collision Coupling Modeling in Grape Clusters for Non-Damage Harvesting Operations. Agriculture 2025, 15, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, Y. Flexible Hand Claw Picking Method for Citrus-Picking Robot Based on Target Fruit Recognition. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Liu, T.; Jiang, P.; Qi, A.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Deng, X. Design and Testing of Bionic-Feature-Based 3D-Printed Flexible End-Effectors for Picking Horn Peppers. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, G.; Yao, P.; Cai, S.; Ying, S.; Yang, Q. Flexible Pneumatic End-Effector for Agricultural Robot: Design & Experiment. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Zhuhai, China, 6–9 December 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 2175–2180. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Zheng, Y.; Bo, W.; Liu, J.; Pi, J.; Chen, W.; Deng, J. Research on the Bionic Flexible End-Effector Based on Tomato Harvesting. J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 2564952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Xia, Z.; Gu, J.; Wang, W.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, W. High-Precision Apple Recognition and Localization Method Based on RGB-D and Improved SOLOv2 Instance Segmentation. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1403872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Fan, P.; Lei, X.; Liu, Z.; Yang, F. A Real-Time Apple Targets Detection Method for Picking Robot Based on Improved YOLOv5. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Wang, C.; Ji, T.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, T. D3-YOLOv10: Improved YOLOv10-Based Lightweight Tomato Detection Algorithm Under Facility Scenario. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liang, J.; Zhao, S.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Jin, Y. Design of a Virtual Multi-Interaction Operation System for Hand–Eye Coordination of Grape Harvesting Robots. Agronomy 2023, 13, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Xiao, H.; Dai, Z.; Wang, C.; Sun, C.; Watson, N.; Povey, M.; Zou, X. Identification of Apple Variety Using Machine Vision and Deep Learning with Multi-Head Attention Mechanism and GLCM. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2025, 19, 6540–6558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, R.A.; Ayepa, E.; Fometu, S.S.; Shittu, S.; Davids, J.S.; Wang, J. Mulberry Fruit Post-Harvest Management: Techniques, Composition and Influence on Quality Traits—A Review. Food Control 2022, 140, 109126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Zhong, M.; Zhu, W.; Rashid, A.; Han, R.; Virk, M.S.; Duan, K.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, X. Advances in Computer Vision and Spectroscopy Techniques for Non-Destructive Quality Assessment of Citrus Fruits: A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2025, 14, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwaw, E.; Tchabo, W.; Ma, Y.; Apaliya, M.T.; Sackey, A.S.; Mintah, B.K.; Farooq, M.; Ma, S. Effect of Storage on Quality Attributes of Lactic-Acid-Fermented Mulberry Juice Subjected to Combined Pulsed Light and Ultrasonic Pasteurization Treatment. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Cai, L.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, S.; Xie, B. Realtime Picking Point Decision Algorithm of Trellis Grape for High-Speed Robotic Cut-and-Catch Harvesting. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Fahad, S.; Naushad, M.; Faisal, S. Grape Production Critical Review in the World. SSRN J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houel, C.; Martin-Magniette, M.-L.; Nicolas, S.D.; Lacombe, T.; Le Cunff, L.; Franck, D.; Torregrosa, L.; Conéjéro, G.; Lalet, S.; This, P.; et al. Genetic Variability of Berry Size in the Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2013, 19, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, T.; Balta, F.; Şensoy, S. Fruit Quality Parameters and Molecular Analysis of Apple Germplasm Resourcesfrom Van Lake Basin, Turkey. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2015, 39, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfattah, A.; Freilich, S.; Bartuv, R.; Zhimo, V.Y.; Kumar, A.; Biasi, A.; Salim, S.; Feygenberg, O.; Burchard, E.; Dardick, C.; et al. Global Analysis of the Apple Fruit Microbiome: Are All Apples the Same? Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 6038–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Ma, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Tang, Z.; Jin, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, W. Apple Mechanical Damage Mechanism and Harvesting Test Platform Design. Int. J. Food Eng. 2024, 20, 507–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strik, B.; Dixon, E.; Detweiler, A.J.; Sanchez, N. Growing Kiwifruit in Your Home Garden; Oregon State University Extension Service: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guroo, I.; Wani, S.A.; Wani, S.M.; Ahmad, M.; Mir, S.A.; Masoodi, F.A. A Review of Production and Processing of Kiwifruit. J. Food Process. Technol. 2017, 8, 1000699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, Z.; Hao, W.; Li, K.; Ding, X.; Cui, Y. Kiwifruit Harvesting Damage Analysis and Verification. Processes 2023, 11, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, C.; Zheng, H.; Zhu, H. Recognizing Strawberry Appearance Quality Using Different Combinations of Deep Feature and Classifiers. J. Food Process Eng. 2022, 45, e13982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Cockerton, H.M.; Johnson, A.W.; Karlström, A.; Stavridou, E.; Deakin, G.; Harrison, R.J. Defining Strawberry Shape Uniformity Using 3D Imaging and Genetic Mapping. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contigiani, E.V.; Jaramillo-Sánchez, G.; Castro, M.A.; Gómez, P.L.; Alzamora, S.M. Postharvest Quality of Strawberry Fruit (Fragaria x Ananassa Duch Cv. Albion) as Affected by Ozone Washing: Fungal Spoilage, Mechanical Properties, and Structure. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastav, M.; Radadiya, N.; Ramachandra, S.; Jayaswal, P.K.; Singh, N.; Singh, S.; Mahato, A.K.; Tandon, G.; Gupta, A.; Devi, R.; et al. High Resolution Mapping of QTLs for Fruit Color and Firmness in Amrapali/Sensation Mango Hybrids. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1135285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, S.; Hosaka, F.; Matsumura, M.; Onoue-Makishi, Y.; Nashima, K.; Urasaki, N.; Ogata, T.; Shoda, M.; Yamamoto, T. Genetic Diversity and Relatedness of Mango Cultivars Assessed by SSR Markers. Breed. Sci. 2019, 69, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirisomboon, P.; Pornchaloempong, P. Instrumental Textural Properties of Mango (Cv Nam Doc Mai) at Commercial Harvesting Time. Int. J. Food Prop. 2011, 14, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pan, Y.; Liu, C.; Ding, Y.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Z.; Meng, H. Cucumber Fruit Size and Shape Variations Explored from the Aspects of Morphology, Histology, and Endogenous Hormones. Plants 2020, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samba, N.; Nunomura, O.; Nakano, A.; Tsukagoshi, S. Effective Training Methods for Cucumber Production in Newly Developed Nutrient Film Technique Hydroponic System. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eboibi, O.; Uguru, H.; Oghnerukevwe, P.O. Moisture-Dependent Mechanical and Textural Properties of Intact Cucumber Fruit. Int. J. Eng. Tech. Res. 2018, 8, 264863. [Google Scholar]
- Quamruzzaman, A.; Islam, F.; Akter, L.; Khatun, A.; Mallick, S.R.; Gaber, A.; Laing, A.; Brestic, M.; Hossain, A. Evaluation of the Quality of Yard-Long Bean (Vigna unguiculata subsp. sesquipedalis L.) Cultivars to Meet the Nutritional Security of Increasing Population. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manneh, N.; Adetimirin, V.O.; Dieng, I.; Ntukidem, S.O.; Fatokun, C.A.; Boukar, O. Response of Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp) Accessions to Moisture Stress. Int. J. Plant Biol. 2024, 15, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adanu, E.; Iya, S.; Yakubu, I.; Kabri, H. Determination of the Physico-Mechanical Properties of Three Cultivars of Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) Grain. Arid. Zone J. Eng. Technol. Environ. 2022, 18, 377–386. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, W.; Gao, X.; Xu, B.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, D. Apple Target Recognition Method in Complex Environment Based on Improved YOLOv4. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, T.N.; Zhou, J.; Lakhiar, I.A.; Marinello, F.; Gemechu, T.T.; Rottok, L.T.; Jiang, Z. Enhancing Autonomous Orchard Navigation: A Real-Time Convolutional Neural Network-Based Obstacle Classification System for Distinguishing ‘Real’ and ‘Fake’ Obstacles in Agricultural Robotics. Agriculture 2025, 15, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, G. Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation for Grasping Prioritization of Stacked Fruit Clusters Based on Relative Hierarchy Factor Set. Agronomy 2022, 12, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Zhai, K.; Xu, B.; Wu, J. Green Apple Detection Method Based on Multidimensional Feature Extraction Network Model and Transformer Module. J. Food Prot. 2025, 88, 100397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, F.; Moreno, J.C.; Sánchez, J.A.; Berenguel, M. Grasping in Agriculture: State-of-the-Art and Main Characteristics. In Grasping in Robotics; Carbone, G., Ed.; Mechanisms and Machine Science; Springer: London, UK, 2013; Volume 10, pp. 385–409. ISBN 978-1-4471-4663-6. [Google Scholar]
- Arikapudi, R.; Vougioukas, S.G. Robotic Tree-Fruit Harvesting with Telescoping Arms: A Study of Linear Fruit Reachability Under Geometric Constraints. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 17114–17126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bac, C.W.; Van Henten, E.J.; Hemming, J.; Edan, Y. Harvesting Robots for High-value Crops: State-of-the-art Review and Challenges Ahead. J. Field Robot. 2014, 31, 888–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaenker, T.; Smitt, C.; McCool, C.; Bennewitz, M. Viewpoint Planning for Fruit Size and Position Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 3271–3277. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Ge, Y.; From, P.J. An Obstacle Separation Method for Robotic Picking of Fruits in Clusters. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 175, 105397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, H.; Sui, Y.; Ma, Z.; Guo, R.; Hu, W.; Zhang, T.; Yan, P.; et al. Accurate Apple Fruit Stalk Cutting Technology Based on Improved YOLOv8 with Dual Cameras. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2025, 41, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, D.; Rahn, C.D.; Kier, W.M.; Walker, I.D. Soft Robotics: Biological Inspiration, State of the Art, and Future Research. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2008, 5, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, M.; Farnioli, E.; Piazza, C.; Catalano, M.; Grioli, G.; Garabini, M.; Gabiccini, M.; Bicchi, A. Grasping with Soft Hands. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Madrid, Spain, 18–20 November 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 581–587. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, W.; Zhang, T.; Xu, B.; He, G. Apple Recognition and Picking Sequence Planning for Harvesting Robot in a Complex Environment. J. Agric. Eng. 2023, 55, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Peng, Y.; Shan, H. Development of a Dual-Arm Rapid Grape-Harvesting Robot for Horizontal Trellis Cultivation. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 881904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.-A.; Xie, H.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.-G.; Xu, Y.-H.; Zhu, X.-H.; Caikasimu, A.; Zhou, X.-W.; Mai, S.-L.; Pan, M.-Q.; et al. Transcriptome and Metabolome Reveal the Effects of Three Canopy Types on the Flavonoids and Phenolic Acids in ‘Merlot’ (Vitis vinifera L.) Berry Pericarp. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, H.; Xu, B.; Jin, Y.; Gao, J. Design and Testing of a Four-Arm Multi-Joint Apple Harvesting Robot Based on Singularity Analysis. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Shen, Z.; Yin, B.; Liang, B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J. Effects of Dwarfing Interstock Length on the Growth and Fruit of Apple Tree. Horticulturae 2022, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; He, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, L.; Wang, Y.; Ding, X.; Cui, Y. A Method of Grasping Detection for Kiwifruit Harvesting Robot Based on Deep Learning. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, B.M.; Minas, I.S. Canopy Architecture Impact on Peach Tree Physiology, Vigor Diffusion, Productivity and Fruit Quality. Sci. Hortic. 2025, 342, 114025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, B.M.; Minas, I.S. Optimizing Peach Tree Canopy Architecture for Efficient Light Use, Increased Productivity and Improved Fruit Quality. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavani, K. Cultivation Technology of Tomato in Greenhouse. In Protected Cultivation and Smart Agriculture; New Delhi Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2020; ISBN 978-81-948993-2-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Jiang, Q.; Guan, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, X. Calculation Method of Phenotypic Traits for Tomato Canopy in Greenhouse Based on the Extraction of Branch Skeleton. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, S.M.; Schumann, A.W.; Boyd, N.S. Goosegrass Detection in Strawberry and Tomato Using a Convolutional Neural Network. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Deng, J.; Xiang, Y.; Qiao, B.; Zhu, X.; Li, C. Estimating Strawberry Weight for Grading by Picking Robot with Point Cloud Completion and Multimodal Fusion Network. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Abd-Elrahman, A.; Whitaker, V.M.; Wang, X.; Dalid, C.; Shen, K. Strawberry Canopy Structural Parameters Estimation and Growth Analysis from UAV Multispectral Imagery Using a Geospatial Tool. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 226, 109440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dian, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, L.; Zhang, J.; Hu, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Characteristics of Photosynthesis and Vertical Canopy Architecture of Citrus Trees under Two Labor-Saving Cultivation Modes Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-Based LiDAR Data in Citrus Orchards. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, T.; Yasutake, D.; Kiyosue, Y. Characterization of Canopy Structure for High-Yield Performance of Greenhouse-Grown Satsuma Mandarins Using Direct Measurements and Indirect Estimations. J. Agric. Meteorol. 2022, 78, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibell, P.T.; Normand, F.; Wright, C.L.; Mahmud, K.; Bally, I.S.E. The Effects of Planting Density, Training System and Cultivar on Vegetative Growth and Fruit Production in Young Mango (Mangifera indica L.) Trees. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, K.P.; Ibell, P.T.; Wright, C.L.; Monks, D.; Bally, I. High-Density Espalier Trained Mangoes Make Better Use of Light. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lou, Q.; Xia, L.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, Q.; et al. Chromosome-Scale Genome Assembly of Cucumis hystrix—A Wild Species Interspecifically Cross-Compatible with Cultivated Cucumber. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Chen, H.; Ji, F.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Hou, M.; Huang, X.; Wang, D.; Lu, T.; et al. New Insights on Canopy Heterogeneous Analysis and Light Micro-Climate Simulation in Chinese Solar Greenhouse. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 233, 110179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Qian, Z.; Xu, B.; Tang, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, D. Grasping Damage Analysis of Apple by End-effector in Harvesting Robot. J. Food Process Eng. 2017, 40, e12589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Ji, W.; Zhang, H.; Ruan, C.; Xu, B.; Wu, K. Grasping Force Optimization and DDPG Impedance Control for Apple Picking Robot End-Effector. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Zheng, J. Optimization Design of Compliant Constant-Force Mechanism for Apple Picking Actuator. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 170, 105232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taqi, F.; Al-Langawi, F.; Abdulraheem, H.; El-Abd, M. A Cherry-Tomato Harvesting Robot. In Proceedings of the 2017 18th International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), Hong Kong, China, 10–12 July 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 463–468. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Du, W.; Zeng, L.; Su, L.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, F.; Liu, L.; Chi, Q. Design and Testing of an End-Effector for Tomato Picking. Agronomy 2023, 13, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Wang, W.; Gu, J.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B. Research on Apple Object Detection and Localization Method Based on Improved YOLOX and RGB-D Images. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, Q.; Ronzhin, A. A Model of Four-Finger Gripper with a Built-in Vacuum Suction Nozzle for Harvesting Tomatoes. In Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 149–160. ISBN 978-981-13-9266-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Z.; Ali, S.; Yang, N.; Fu, S.; Zhang, Y. Multi-Class Detection of Cherry Tomatoes Using Improved YOLOv4-Tiny. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2023, 16, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Sun, J.; Cong, S.; Dai, C.; Cai, Z.; Yao, K.; Zhou, X.; Wu, X.; Liu, J. Detection of Early Damage in Kiwifruit Based on Near-Infrared Technology. J. Food Process Eng. 2025, 48, e70130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Kurita, H.; Fukao, T.; Arihara, H.; Iwai, A. An Automated Fruit Harvesting Robot by Using Deep Learning. ROBOMECH J. 2019, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Feng, Q.; Li, T.; Xie, F.; Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Guo, X.; Zhao, C. Dual-Manipulator Optimal Design for Apple Robotic Harvesting. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaguchi, H.; Nagahama, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Inaba, M. Development of an Autonomous Tomato Harvesting Robot with Rotational Plucking Gripper. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 9–14 October 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 652–657. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Guo, H.; Gao, J. Picking Patterns Evaluation for Cherry Tomato Robotic Harvesting End-Effector Design. Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 239, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Bao, R.; Chen, X.; Fu, S.; Tian, M.; Zhang, Y. Research on Flexible End-Effectors with Humanoid Grasp Function for Small Spherical Fruit Picking. Agriculture 2023, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Xu, G.; Lu, W.; Ding, Q.; Chen, X. An Electric Gripper for Picking Brown Mushrooms with Flexible Force and In Situ Measurement. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Xu, G.; Xie, Y.; Lu, W.; Ding, Q.; Chen, X. Cable-Driven Underactuated Flexible Gripper for Brown Mushroom Picking. Agriculture 2025, 15, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ji, J.; Cai, H.; Chen, H. Modeling and Force Analysis of a Harvesting Robot for Button Mushrooms. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 78519–78526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Cui, G.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Fu, L.; Gejima, Y. Design and Simulation of an Integrated End-Effector for Picking Kiwifruit by Robot. Inf. Process. Agric. 2020, 7, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Jiang, X.; He, L.; Choi, D.; Pecchia, J.; Li, Y. Development of a Robotic Harvesting Mechanism for Button Mushrooms. Trans. ASABE 2021, 64, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Tang, S.; Li, Z. Virtual Model of Grip-and-Cut Picking for Simulation of Vibration and Falling of Grape Clusters. Trans. ASABE 2019, 62, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Yu, Y. Research on the Visual Location Method for Strawberry Picking Points under Complex Conditions Based on Composite Models. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 8566–8579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrochidou, E.; Tziridis, K.; Nikolaou, A.; Kalampokas, T.; Papakostas, G.A.; Pachidis, T.P.; Mamalis, S.; Koundouras, S.; Kaburlasos, V.G. An Autonomous Grape-Harvester Robot: Integrated System Architecture. Electronics 2021, 10, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faheem, M.; Liu, J.; Chang, G.; Ahmad, I.; Peng, Y. Hanging Force Analysis for Realizing Low Vibration of Grape Clusters during Speedy Robotic Post-Harvest Handling. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Kam, D.; Min, B.; Hwa, J.; Oh, S. A Vision Servo System for Automated Harvest of Sweet Pepper in Korean Greenhouse Environment. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshmukhametov, A.; Koganezawa, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Buribayev, Z.; Mukhtar, Z.; Amirgaliyev, Y. Development of Continuum Robot Arm and Gripper for Harvesting Cherry Tomatoes. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, N.P.T.; Hoang, S.; Van Tai, D.; Quoc, B.L.C. Developing Robotic System for Harvesting Pineapples. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Advanced Mechatronic Systems (ICAMechS), Hanoi, Vietnam, 10–13 December 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, A.F.; Li, J.; Guo, L.Q.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, Y.P. Structural Design and Analysis of an Automatic Pineapple Picking and Collecting Straddle Machine. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1777, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanianfard, A.; Noguchi, N. Pumpkin Harvesting Robotic End-Effector. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 174, 105503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, C.; English, A.; McCool, C.; Tow, A.W.; Perez, T. Autonomous Sweet Pepper Harvesting for Protected Cropping Systems. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujinaga, T.; Yasukawa, S.; Ishii, K. Development and Evaluation of a Tomato Fruit Suction Cutting Device. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Fukushima, Japan, 11–14 January 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 628–633. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, J.; Kim, J.; Seol, J.; Kim, J.; Son, H.I. Towards an Efficient Tomato Harvesting Robot: 3D Perception, Manipulation, and End-Effector. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 17631–17640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Yin, X.; Liu, X.; Du, R. Preprocessing Method of Night Vision Image Application in Apple Harvesting Robot. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Seol, J.; Pak, J.; Jo, Y.; Jun, J.; Son, H.I. A Novel End-Effector for a Fruit and Vegetable Harvesting Robot: Mechanism and Field Experiment. Precis. Agric. 2023, 24, 948–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.; Park, Y.; Son, H.I. A Suction Cup-Based Soft Robotic Gripper for Cucumber Harvesting: Design and Validation. Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 238, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.A.M.; Jones, M.H.; Nejati, M.; Seabright, M.J.; Bell, J.; Penhall, N.D.; Barnett, J.J.; Duke, M.D.; Scarfe, A.J.; Ahn, H.S.; et al. Robotic Kiwifruit Harvesting Using Machine Vision, Convolutional Neural Networks, and Robotic Arms. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 181, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimeas, F.; Sako, D.V.; Moulianitis, V.C.; Aspragathos, N.A. Design and Fuzzy Control of a Robotic Gripper for Efficient Strawberry Harvesting. Robotica 2015, 33, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, X.; Yang, Z. Design, Simulation, and Experiment for the End Effector of a Spherical Fruit Picking Robot. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2023, 20, 17298806231213442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lammers, K.; Chu, P.; Li, Z.; Lu, R. System Design and Control of an Apple Harvesting Robot. Mechatronics 2021, 79, 102644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.; Hu, G.; Chen, C.; Sugirbay, A.; Chen, J. Experimental and Simulation Analysis of Optimum Picking Patterns for Robotic Apple Harvesting. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 261, 108937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrochidou, E.; Tsakalidou, V.N.; Kalathas, I.; Gkrimpizis, T.; Pachidis, T.; Kaburlasos, V.G. An Overview of End Effectors in Agricultural Robotic Harvesting Systems. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, H.N.B.; Kawshan, C.; Himaruwan, S.; Kulasekera, A.L.; Dassanayake, P. Soft Pneumatic Grippers for Reducing Fruit Damage During Strawberry Harvesting. In Proceedings of the 2022 Moratuwa Engineering Research Conference (MERCon), Moratuwa, Sri Lanka, 27–29 July 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bottin, M.; Cipriani, G.; Doria, A.; Minto, R.; Rosati, G.; Tommasino, D. Comparison between Hydraulic and Bi-Stable Systems for the Mitigation of the End-Effector Collisions. Int. J. Mech. Control 2023, 24, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Manti, M.; Cacucciolo, V.; Cianchetti, M. Stiffening in Soft Robotics: A Review of the State of the Art. IEEE Robot. Automat. Mag. 2016, 23, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Lv, J.; Dong, C.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Wu, W.; Abdeen, M.A. Classification, Advanced Technologies, and Typical Applications of End-Effector for Fruit and Vegetable Picking Robots. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Zhao, L.; Luo, X.; Guo, J.; Liu, X. Perceptual Soft End-Effectors for Future Unmanned Agriculture. Sensors 2023, 23, 7905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, K.; Qian, M. An Octopus-Inspired Bionic Flexible Gripper for Apple Grasping. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, W.; Xu, B.; Yu, X. Optimizing Contact Force on an Apple Picking Robot End-Effector. Agriculture 2024, 14, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Lu, Y.; Wu, C.; Yan, B. Reconfigurable Bionic Soft Pneumatic Gripper for Fruit Handling Based on Shape and Size Adaptation. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2023, 56, 044003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Li, Z. Design and Test of Tomatoes Harvesting Robot. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Lijiang, China, 8–10 August 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 949–952. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Kanegae, R.; Hirai, S. Circular Shell Gripper for Handling Food Products. Soft Robot. 2021, 8, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, E.; Fernández, R.; Armada, M.; Gonzalez-de-Santos, P. Diaphragm-Type Pneumatic-Driven Soft Grippers for Precision Harvesting. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, F.; Liu, S.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, D. Modeling and Analysis of Soft Pneumatic Network Bending Actuators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 2195–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; He, G.; Xu, B.; Zhang, H.; Yu, X. A New Picking Pattern of a Flexible Three-Fingered End-Effector for Apple Harvesting Robot. Agriculture 2024, 14, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Wu, T.; Lin, T.; Yang, L.; Chowdhary, G.; Ting, K.C.; Ying, Y. Mobile Robotics Platform for Strawberry Sensing and Harvesting within Precision Indoor Farming Systems. J. Field Robot. 2024, 41, 2047–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohimer, C.J.; Wang, H.; Bhusal, S.; Miller, J.; Mo, C.; Karkee, M. Design and Field Evaluation of a Robotic Apple Harvesting System with a 3D-Printed Soft-Robotic End-Effector. Trans. ASABE 2019, 62, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Feng, K.; Hua, C.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H.; Su, H. Model Analysis and Experimental Investigation of Soft Pneumatic Manipulator for Fruit Grasping. Sensors 2022, 22, 4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kultongkham, A.; Kumnon, S.; Thintawornkul, T.; Chanthsopeephan, T. The Design of a Force Feedback Soft Gripper for Tomato Harvesting. J. Agric. Eng. 2021, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, F.; Zhou, W.; Zuo, R. Design of Flexible Spherical Fruit and Vegetable Picking End-Effector Based on Vision Recognition. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2246, 012060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Xia, L.; Liu, J.; Qian, M.; Pi, J. Design of a Flexible End-Effector Based on Characteristics of Tomatoes. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2022, 15, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.A.; Soliman, M.; Mousa, M.A.; Elsamanty, M.; Radwan, A.G. Design and Implementation of Variable Inclined Air Pillow Soft Pneumatic Actuator Suitable for Bioimpedance Applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 314, 112272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Tan, Y.; Hu, S.; Tang, Z. Design and Experiment of Citrus Harvesting Software End-Effector. J. Hebei Agric. Univ. 2024, 47, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Wu, X. Design and Experiment of a Soft Gripper with Enhanced Rigidity for Fruit and Vegetable Picking. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2021, 42, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kang, H.; Zhou, H.; Au, W.; Wang, M.Y.; Chen, C. Development and Evaluation of a Robust Soft Robotic Gripper for Apple Harvesting. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 204, 107552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Ye, Y.; Cheng, P.; Hu, R.; Wu, C. Design and Parameter Optimization of Soft Pneumatic Gripper for Slender Fruits and Vegetables Picking. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Fras, J.; Althoefer, K. Soft Fiber-Reinforced Pneumatic Actuator Design and Fabrication: Towards Robust, Soft Robotic Systems. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 103–114. ISBN 978-3-030-23806-3. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.; Sukkarieh, S. Design and Evaluation of a Modular Robotic Plum Harvesting System Utilising Soft Components. J. Field Robot. 2021, 38, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F. Research on the Software Robot for Fruits and Vegetables Picking in Greenhouse. Master’s Thesis, Hubei University of Technology, Wuhan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Geng, D.; Liu, X.; Sun, G. Kinematics Analysis and Experiment on Pneumatic Flexible Fruit and Vege-table Picking Manipulator. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2019, 50, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Fu, T. Design and Experimental Study of Cavity Structure of Pneumatic Soft Actuator. Actuators 2023, 12, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keong, B.A.W.; Hua, R.Y.C. A Novel Fold-Based Design Approach toward Printable Soft Robotics Using Flexible 3D Printing Materials. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Ignatius, U.C.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y. Design and Experimental Evaluation of a Bionic Two-Joint Soft-Actuator. In Proceedings of the 2023 5th International Symposium on Robotics & Intelligent Manufacturing Technology (ISRIMT), Changzhou, China, 22–24 September 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Shen, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, M. Spider-Inspired Pneumatic Folding Membrane Soft Actuator. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharff, R.B.N.; Wu, J.; Geraedts, J.M.P.; Wang, C.C.L. Reducing Out-of-Plane Deformation of Soft Robotic Actuators for Stable Grasping. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–18 April 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, S.; Dai, J.; Oseyemi, A.E.; Liu, L.; Du, N.; Lv, F. A Modular Soft Gripper with Combined Pneu-Net Actuators. Actuators 2023, 12, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawk, C.; Gao, Y.; Mutlu, R.; Alici, G. Fully 3D Printed Monolithic Soft Gripper with High Conformal Grasping Capability. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Hong Kong, China, 8–12 July 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1139–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Chu, K.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Su, H. Research and Application of a Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Soft Actuator. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 338, 113492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N. Development and Performance Analysis of Pneumatic Soft-Bodied Bionic Actuator. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2021, 2021, 6623059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Zhou, X.; Yeow, C.-H. A Soft Pneumatic Actuator with Multiple Motion Patterns Based on Length-Tuning Strain-Limiting Layers. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Singapore, 3–7 April 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Kang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, M. Design of Multi-Material Soft Pneumatic Modules. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 30, 095006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; He, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, N.; Cui, W. Multimaterial Embedded 3D Printing of Composite Reinforced Soft Actuators. Research 2023, 6, 0122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Wu, L.; El Elmi, A.; Pasini, D. Zero-Power Shape Retention in Soft Pneumatic Actuators with Extensional and Bending Multistability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2304151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Shi, W.; Deng, Z.; Ding, Q. Design and Fabrication of Bistable Actuators with High Load Capacity Based on Origami. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.; Chen, C.; Hu, G.; Sugirbay, A.; Sun, H.; Chen, J. Design and Evaluation of a Robotic Apple Harvester Using Optimized Picking Patterns. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 107092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, C. Geometry-Aware Fruit Grasping Estimation for Robotic Harvesting in Orchards. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 193, 106716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulart, R.; Jarvis, D.; Walsh, K.B. Evaluation of End Effectors for Robotic Harvesting of Mango Fruit. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Fan, Z.; Wang, X.; Wan, H.; Wang, P.; Zeng, X.; Jia, F. A Lab-Customized Autonomous Humanoid Apple Harvesting Robot. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 96, 107459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Jin, M.; Duan, J.; Yang, Z.; Xu, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, H. Design and Analysis of a Flexible Adaptive Supporting Device for Banana Harvest. Agronomy 2022, 12, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Li, T.; Yan, T.; Xie, F.; Feng, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Zhao, C. A Soft Gripper Design for Apple Harvesting with Force Feedback and Fruit Slip Detection. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bac, C.W.; Hemming, J.; Van Tuijl, B.A.J.; Barth, R.; Wais, E.; Van Henten, E.J. Performance Evaluation of a Harvesting Robot for Sweet Pepper. J. Field Robot. 2017, 34, 1123–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemming, J.; Van Tuijl, B.A.J.; Gauchel, W.; Wais, E. Field Test of Different End-Effectors for Robotic Harvesting of Sweet-Pepper. Acta Hortic. 2016, 1130, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Yi, B.; Zhang, B.; Wang, K. A Flexible Swallowing Gripper for Harvesting Apples and Its Grasping Force Sensing Model. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 204, 107489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B.; Choi, T.; Kim, U. Linkage Integrated Fin Ray Gripper Capable of Safe Adaptive Grasping for Tomato Harvesting. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 232, 110118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-H.; Chiu, C.-H.; Chen, T.-L.; Pai, T.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Hsu, M.-C. A Soft Robotic Gripper Module with 3D Printed Compliant Fingers for Grasping Fruits. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Auckland, New Zealand, 9–12 July 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 736–741. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Song, R.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, L.; Liu, F.; Jiang, P.; Sindersberger, D.; Monkman, G.J.; Guo, J. Bio-Inspired Shape-Adaptive Soft Robotic Grippers Augmented with Electroadhesion Functionality. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgeneidy, K.; Lightbody, P.; Pearson, S.; Neumann, G. Characterising 3D-Printed Soft Fin Ray Robotic Fingers with Layer Jamming Capability for Delicate Grasping. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–18 April 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Basson, C.I.; Bright, G. Geometric Conformity Study of a Fin Ray Gripper Utilizing Active Haptic Control. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 15th International Conference on Control and Automation (ICCA), Edinburgh, UK, 16–19 July 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 713–718. [Google Scholar]
- Elgeneidy, K.; Fansa, A.; Hussain, I.; Goher, K. Structural Optimization of Adaptive Soft Fin Ray Fingers with Variable Stiffening Capability. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), New Haven, CT, USA, 15 May–15 July 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 779–784. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.H.; Park, J.G.; Kim, D.I.; Yoon, H.S. A Universal Soft Gripper with the Optimized Fin Ray Finger. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2021, 8, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, R.; Lang, L.; De Aguiar, M.L.; Dutra, T.A.; Gaspar, P.D. Enhancing the Performance of Fin Ray Effect Soft Robotic Finger via Computational Design and Simulation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Autonomous Robot Systems and Competitions (ICARSC), Paredes de Coura, Portugal, 2–3 May 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivas, G.L.; Javed, A.; Faller, L.M. Versatile 3D-Printed Fin-Ray Effect Soft Robotic Fingers: Lightweight Optimization and Performance Analysis. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2024, 46, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Fang, Y.; Li, L. Research on Effects of Different Internal Structures on the Grasping Performance of Fin Ray Soft Grippers. Robotica 2023, 41, 1762–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, T.; Yin, J.; Guo, H.; Yang, C. Development and Evaluation of a Pneumatic Finger-like End-Effector for Cherry Tomato Harvesting Robot in Greenhouse. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 197, 106879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J. Soft Bionic Gripper with Tactile Sensing and Slip Detection for Damage-Free Grasping of Fragile Fruits and Vegetables. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 220, 108904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, F.; Castellini, F.; Muradore, R. A Soft, Sensorized Gripper for Delicate Harvesting of Small Fruits. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 213, 108202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Zheng, Y.; Qian, Y.; Hu, X.; Sun, Z.; Ma, Z.; Bao, G.; Wu, H.; Luo, X.; Hughes, J.; et al. An Optical/Electronic Artificial Skin Extends the Robotic Sense to Molecular Sensing. npj Flex. Electron. 2025, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Ameur, M.A.; El-Sayed, A.M.; Yan, X.T.; Mehnen, J.; Maier, A.M. A Novel Opto-Tactile Sensing Approach to Enhance the Handling of Soft Fruit. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 235, 110397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, C.; Su, J.; Tan, J.M.R.; He, K.; Chen, X.; Magdassi, S. Sensing in Soft Robotics. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 15277–15307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Cheng, W.; Wan, G.; Yang, Z.; Tee, B.C.K. Toward an AI Era: Advances in Electronic Skins. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 9899–9948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maraveas, C.; Kyrtopoulos, I.V.; Arvanitis, K.G.; Bartzanas, T. The Aging of Polymers under Electromagnetic Radiation. Polymers 2024, 16, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.-Y.; Dou, Z.-F.; Li, H.-S.; Li, N.; Liu, X.-R.; Zhang, W.-F. Degradation Behavior and Aging Mechanisms of Silicone Rubber under Ultraviolet–Thermal–Humidity Coupling in Simulated Tropical Marine Atmospheric Environment. Polymer 2025, 328, 128398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Mesery, H.S.; Sarpong, F.; Atress, A.S.H. Statistical Interpretation of Shelf-Life Indicators of Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) in Correlation to Storage Packaging Materials and Temperature. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godana, E.A.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, K.; Dhanasekaran, S.; Mehari, T.G.; Zhang, H. Biotechnological and Biocontrol Approaches for Mitigating Postharvest Diseases Caused by Fungal Pathogens and Their Mycotoxins in Fruits: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 17584–17596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atakuru, T.; Züngör, G.; Samur, E. Layer Jamming of Magnetorheological Elastomers for Variable Stiffness in Soft Robots. Exp. Mech. 2024, 64, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tian, H.; Zhu, X.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Shao, J. Gecko Toe Pad-Inspired Robotic Gripper with Rapidly and Precisely Tunable Adhesion. Research 2025, 8, 0687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.-C.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, Y.-Y.; Zhao, Y. Liquid Crystal Elastomers for Actuation: A Perspective on Structure-Property-Function Relation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2024, 153, 101829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, Z.; Zadan, M.; Wang, J.; Kumar, S.; Majidi, C. Frequency-Selective Actuation of Liquid Crystalline Elastomer Actuators with Radio-Frequency. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 7292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, W.; Chong, J.; You, I.; Kang, J. Self-Healing Electronic Skin with High Fracture Strength and Toughness. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashef Tabrizian, S.; Terryn, S.; Vanderborght, B. Toward Autonomous Self-Healing in Soft Robotics: A Review and Perspective for Future Research. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2025, 7, 2400790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, D.; Guo, T.; Yu, S.; Liu, W.; Li, L.; Sun, Z.; Peng, H.; Hu, D. Classification of Apple Color and Deformity Using Machine Vision Combined with CNN. Agriculture 2024, 14, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherbiny, O.; Gao, J.; Guo, Y.; Tunio, M.H.; Mosha, A.H. Fusion of the Deep Networks for Rapid Detection of Branch-Infected Aeroponically Cultivated Mulberries Using Multimodal Traits. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2025, 18, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, C.; Ma, Y.; Liu, C.; Ru, M.; Sun, J.; Zhao, C. Peduncle Collision-Free Grasping Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning for Tomato Harvesting Robot. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 216, 108488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.; Polydoros, A. Zero-Shot Sim-to-Real Reinforcement Learning for Fruit Harvesting. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.08458. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Au, W.; Kang, H.; Chen, C. Intelligent Robots for Fruit Harvesting: Recent Developments and Future Challenges. Precis. Agric. 2022, 23, 1856–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, N.; Yang, H.-J.; Jha, D.K.; Sarkar, S. Find the Fruit: Designing a Zero-Shot Sim2Real Deep RL Planner for Occlusion Aware Plant Manipulation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.16547. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, T.; Han, X.; Wang, P.; Lyu, Y.; Chang, E.; Jeong, H.; Xiang, L. Performance Evaluation of Robotic Harvester with Integrated Real-Time Perception and Path Planning for Dwarf Hedge-Planted Apple Orchard. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, S.; Chen, H.; Li, G.; Dong, H.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, R. A Review of Visual Perception Technology for Intelligent Fruit Harvesting Robots. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1646871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Faheem, M. Experimental and Theoretical Analysis of Fruit Plucking Patterns for Robotic Tomato Harvesting. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 173, 105330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Fruit Name | Number of Main Varieties | Shape | Weight/(g) | Mechanical Damage Force/(N) | Photographs | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grape | Over 10,000 | Nearly spherical | 1–10 | 2–7 |  | [30,31,32] |
| Apple | Over 7500 | Spherical, ellipsoidal, hyperbolic paraboloid | 90–315 | 15–40 |  | [33,34,35] |
| Kiwifruit | Approximately 76 | Ellipsoidal | 50–115 | 180 |  | [36,37,38] |
| Strawberry | Over 460 | Spherical, conical | 15–30 | 2–4 |  | [39,40,41] |
| Mango | Over 1000 | Ellipsoidal, rectangular | 121–720 | 20 |  | [42,43,44] |
| Cucumber | Over 3342 | Oval, cylindrical | 109–616 | 199–375 |  | [45,46,47] |
| Cowpea | Approximately 768 | Cylindrical | 1–204 | 35–100 |  | [48,49,50] |
| Fruit Crop Types | Main Cultivation Methods | Typical Plant Shapes | Photographs | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grape | Pergola and vertical trellis cultivation | V-shaped, T-shaped, U-shaped |  | [64,65] |
| Apple | Dense planting cultivation | Open layered shape, high spindle shape, open-center shape |  | [66,67] |
| Kiwifruit | Pergola and vertical trellis cultivation | Pergola support structure, T-bar support structure |  | [36,68] |
| Peach | Dense planting cultivation | Open vase, Quad-V, Hex-V, SSA, Y-shaped |  | [69,70] |
| Tomato | Vertical vine training | Erect type, dwarf vine type |  | [71,72] |
| Strawberry | Elevated cultivation, ridge cultivation | Creeping shape, upright open shape, upright spherical shape |  | [73,74,75] |
| Citrus | Trellis-training method with multiple leaders | Round-headed shape, open-center shape, modified central trunk shape | 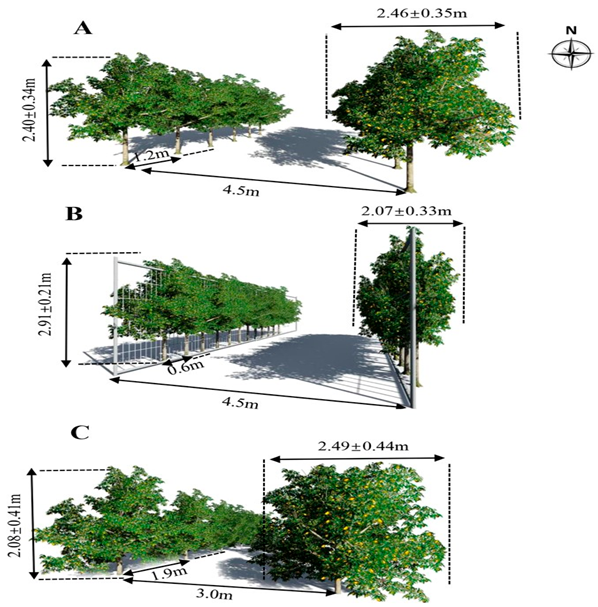 | [76,77] |
| Mango | High-density espalier | Natural round-headed shape, central trunk shape, natural open-center shape |  | [78,79] |
| Cucumber | Vertical vine training | Erect type | 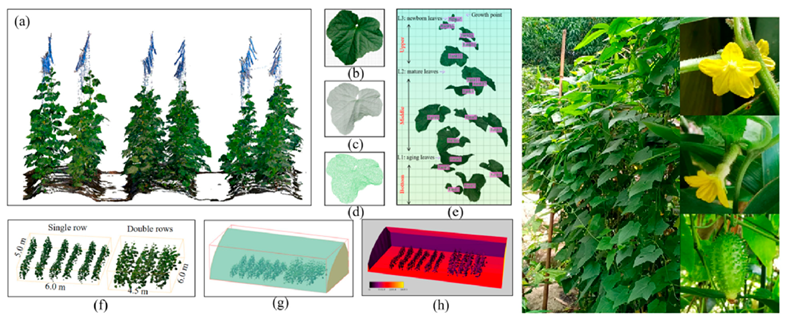 | [80,81] |
| End-Effector type | Picking Success Rate/(%) | Fruit Damage Rate/(%) | Average Time per Pick/(Seconds/Fruit) | Maximum Payload/(g) | Application Object | Year | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grasp-and-pull | 100 | / | 30 | / | Cherry tomato | 2017 | [85] |
| 95.3 | 0 | / | 400 | Apple | 2020 | [84] | |
| 100 | 0 | / | 230 | Tomato | 2023 | [86] | |
| Grasp-and-twist | 60 | 0 | 23 | / | Tomato | 2016 | [93] |
| 92.31 | / | 16 | 300 | Apple | 2019 | [91] | |
| 95 | / | / | 250 | Apple | 2022 | [92] | |
| 79.7 | 1.9 | 6.4 | 15.7 | Cherry tomato | 2022 | [183] | |
| 95.82 | 2.9 | 4.86 | / | Cherry tomato | 2022 | [95] | |
| 88.2 | 2.9 | 3.5 | / | Button mushroom | 2022 | [98] | |
| Grasp-and-bend | 94.2 | 4.9 | 4–5 | 128.7 | Kiwifruit | 2019 | [99] |
| 94.2 | / | / | 42.1 | Button mushroom | 2020 | [100] | |
| Grasp-and-cut | 46 | 11.5–25 | 35–40 | / | Sweet pepper | 2016 | [110] |
| 53.3 | / | 51.1 | / | Sweet pepper | 2019 | [105] | |
| 85 | 15.4 | 23 | 120 | Tomato | 2020 | [111] | |
| 41.67–100 | 0–58.33 | 5.874 | / | Tomato | 2020 | [112] | |
| 95.56 | / | 12 | 1500 | Pineapple | 2020 | [107] | |
| / | / | 2.2 | 1520 | Pineapple | 2021 | [108] | |
| / | / | 56 | / | Cherry tomato | 2022 | [106] | |
| 80.6 | 8 | 15.5 | 289.1 | Tomato | 2022 | [114] | |
| End-effectors based on combined-action picking patterns | 65–100 | / | / | / | Strawberry | 2014 | [117] |
| 51 | 24.6 | 5.5 | / | Kiwifruit | 2018 | [116] | |
| 100 | / | / | / | Apple | 2019 | [120] | |
| 64.06–82.47 | 0 | 8.8 | / | Apple | 2021 | [119] | |
| 80–100 | 0 | 9.6–12.5 | / | Spherical fruits | 2023 | [118] | |
| End-effectors based on pneumatic driving mechanisms | 79.4–83.9 | / | 24 | / | Tomato | 2014 | [130] |
| / | 0 | / | 1000 | Spherical and cylindrical fruits | 2019 | [149] | |
| 100 | / | 2.55–5.15 | 549 | Food products | 2020 | [131] | |
| / | 0 | / | 266 | Tomato | 2020 | [138] | |
| / | 0 | 3.6 | 340 | Slender fruits | 2021 | [145] | |
| / | 0 | / | 583 | Spherical fruits | 2022 | [137] | |
| 70.77 | 4.55 | 14.69 | 6710 | Apple | 2022 | [144] | |
| / | 3–11 | 1.9–3.9 | / | Apple | 2023 | [134] | |
| End-effectors based on FRE structures | 70–85 | 0 | / | / | Spherical fruits | 2021 | [165] |
| 80.17–82.93 | 0 | 12.53–17.17 | / | Apple | 2022 | [164] | |
| 80 | 0 | / | 309.8 | Spherical fruits | 2022 | [169] | |
| / | 0 | / | / | Spherical fruits | 2022 | [172] | |
| 67–84 | 0 | 6 | 840 | Mango | 2023 | [166] | |
| / | 0 | / | / | Tomato | 2024 | [173] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, W.; Liu, J.; Deng, J.; Jiang, Y.; Jin, Y. Research Status and Trends in Universal Robotic Picking End-Effectors for Various Fruits. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102283
Gao W, Liu J, Deng J, Jiang Y, Jin Y. Research Status and Trends in Universal Robotic Picking End-Effectors for Various Fruits. Agronomy. 2025; 15(10):2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102283
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Wenjie, Jizhan Liu, Jie Deng, Yong Jiang, and Yucheng Jin. 2025. "Research Status and Trends in Universal Robotic Picking End-Effectors for Various Fruits" Agronomy 15, no. 10: 2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102283
APA StyleGao, W., Liu, J., Deng, J., Jiang, Y., & Jin, Y. (2025). Research Status and Trends in Universal Robotic Picking End-Effectors for Various Fruits. Agronomy, 15(10), 2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102283






