Abstract
Potato is the dominant tuber and root crop grown in Tigray. However, the productivity is very low due to moisture stress, traditional production techniques, and low-yielding varieties. Hence, this study aimed to optimize potato yield by selecting suitable genotypes under both supplemental and non-supplemental irrigation conditions. The study involved five potato genotypes and two irrigation levels used as treatments arranged in a split plot using a randomized complete block design with three replications. Results revealed a significant difference in days to flowering and maturity, marketable and total tuber yield, and water productivity due to the main and interaction effect of genotype and irrigation. CIP-3960478.90 recorded significantly higher marketable yield (27.13 t ha−1), total tuber yield (28.71 t ha−1), and water productivity (7.59 kg m−3) under supplemental irrigation. Genotype CIP-394611.112 had achieved high marketable yield (24.45 t/ha), total yield (25.60 t/ha) and total water productivity (8.51 kg m−3) under non-irrigated treatment. Additionally, the potato water requirements in September and October exceeded the rainfall amounts, suggesting that supplemental irrigation is necessary during this period for optimal yields. Likewise, genotypes CIP-394611.112 and CIP-3960478.90, are recommended for semi-arid areas to enhance tuber yield with or without irrigation.
1. Introduction
Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) is among the most productive food crops in terms of yield of edible energy and high-quality protein per unit area per unit time [1]. Potato is a staple food consumed worldwide and is categorized as a dietary vegetable containing many minerals and vitamins [1,2]. Potato is a potential food security crop due to its ability to produce high productivity, adapt to diversified cropping systems, and produce quality products per unit input with a shorter crop cycle [3]. In addition, it provides income and employment [4]. Exploring these merits seems to be the right way to secure food in developing countries like Ethiopia.
Potato is one of the most vulnerable crops in changing climates, with events such as long-lasting droughts, extreme heat, and unanticipated frosts [5,6]. Potato yields depend on water and soil management practices, seed quality, chemical and bio-fertilization, soil moisture content, elevation, slope, and supplement irrigation [7]. Potato requires 400 to 800 mm of rain/water, which invariably depends on meteorological variables and other factors [8,9]. Water shortage beyond 60 to 65% causes drought that reduces the growth rate [8]. Water stress conditions can likewise affect optimal potato yield [8,10]. Potato is generally considered to be sensitive to drought. A short root length in the soil profile [11] results in the limited ability of potato roots to absorb water and has been suggested as the basis of potato drought sensitivity. Water stress at any growth stage has a considerable negative impact on potato tuber yield and quality [12,13]. The impact of water restriction on potato production will also likely increase over the next decades due to climate change and the extension of potato cultivation in drought-prone areas [14].
Crop production in semi-arid areas is highly influenced not only by the amount of rainfall but also by its extreme variability, with high intensities and poor spatial and temporal distributions [15,16]. Similarly, Tigray is located in northern Ethiopia, which is characterized by a semi-arid climate, where crop production is highly influenced by rainfall distribution. In Tigray, rainfall is a key source of agricultural water for crop production; however, it is erratic, torrential, highly variable, and poorly distributed throughout the growing season. More than 70% of the annual rainfall in the region is found only in July and August [17]. In addition, the rainfall is either too much at one time or there is no rain at another time [18]. Thus, frequent dry spells and shorter growing periods due to the late-onset and early cessation of rainfall and dry spells in between are the major causes of crop failure in Tigray [18]. This implies that there is a pressing need to supply water to the crops, as rainfall is inadequate to fulfill the crop water requirement.
Potato is one of the staple crops growing in Tigray in both the middle and highland areas under rainfed and irrigation conditions. It contains an important essential amino acid that is often lacking in crops like cereals and other vegetables [19]. However, the average yield of potato in Tigray is (8.1 t/ha), which is far below the national average of 13.5 t ha−1 [20] and other countries like New Zealand (50.2 t ha−1) and North America (41.2 t ha−1). Even the yield potential of potato has been reported to reach about 100 t ha−1 [21], which indicates the prospect of the crop to feed the rising population.
Despite its importance, potato production in Tigray is plagued by numerous problems, such as water stress, lack of drought-tolerant genotypes, uneven distribution of rainfall, and disease and pests. In addition, potato yield is affected by fertilizer type and method. However, no varieties have been released for drought tolerance, particularly in Ethiopia. The existing varieties have not been evaluated for their relative tolerance to drought stress conditions. The requirements of the potato crop for supplemental irrigation in the study areas have not been well investigated. Supplemental irrigation (SI) is the addition of limited amounts of water to rainfed crops to improve and stabilize yields during a shortage of rainfall by providing sufficient moisture for normal plant growth [22]. Supplemental irrigation can improve crop yield and water productivity, especially during critical crop growth stages. Moreover, supplemental irrigation can play an important role in efforts to adapt to climate change in rainfed agro-ecosystems [23]. The hypothesis is that potato genotypes possess the plasticity to grow in water-limited areas with a small amount of supplemental irrigation to complement the natural short rainy seasons. Therefore, the general objective of this study was to evaluate potato genotypes under supplemental and non-supplemental irrigation conditions. This evaluation aims to identify drought-tolerant genotypes and assess the impact of supplemental irrigation on potato yield and water productivity, thereby contributing to improved potato production in the region amidst ongoing challenges such as water stress and climate change
2. Materials and Methods
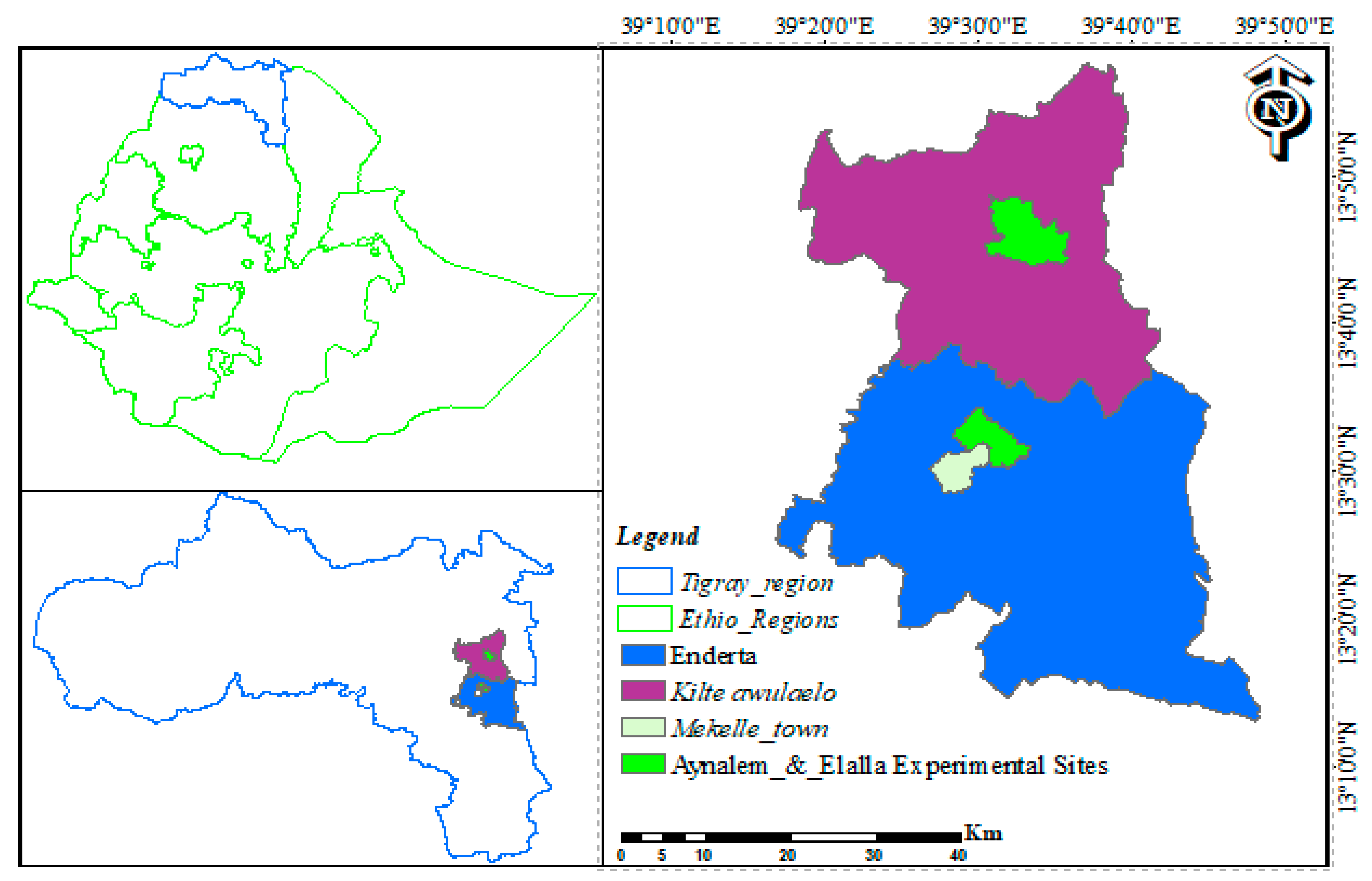
2.1. Description of the Study Area
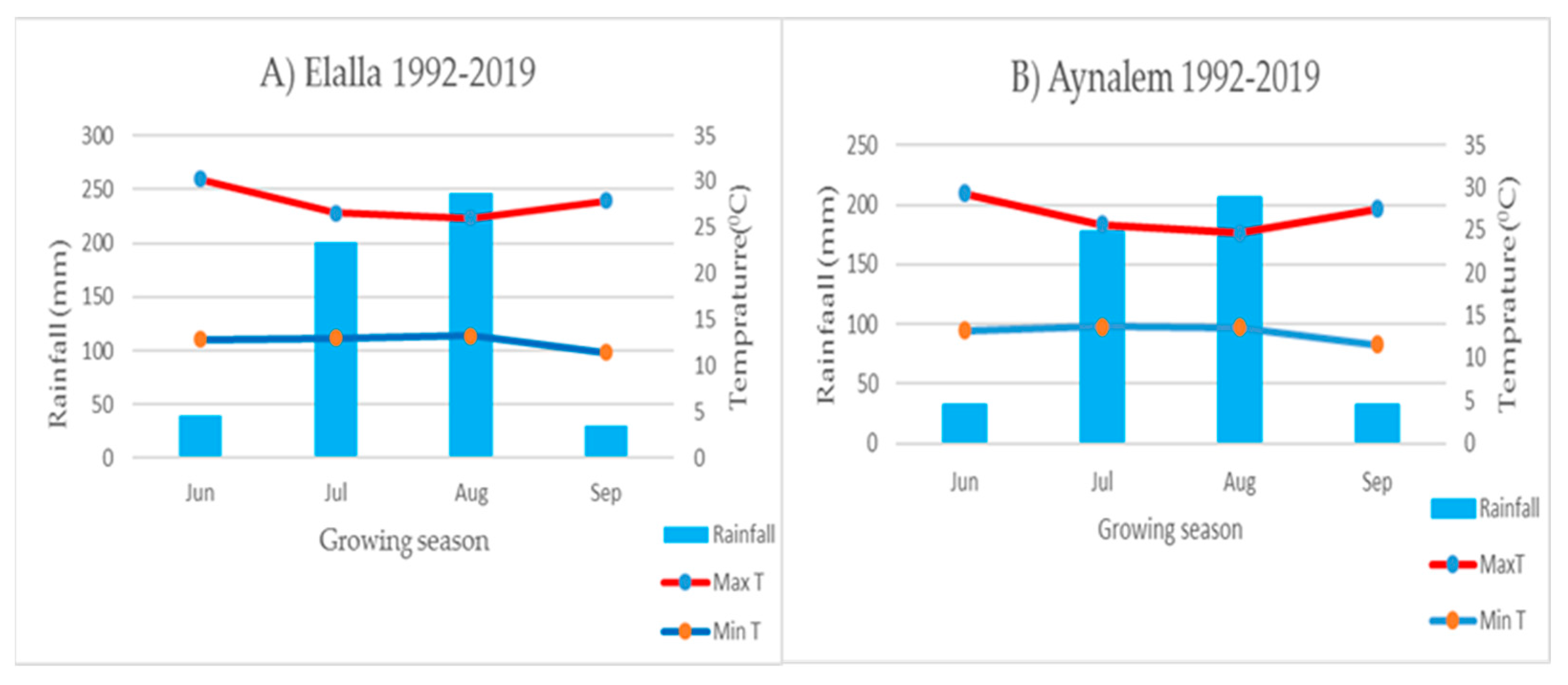
Field studies were conducted at the Mekelle Agricultural Research Center Sites at Elalla and Aynalem. Elalla is located at 39°28′14″–39°33′18″ E Longitude and 13°29′23”–13°34′27″ N Latitude with an elevation of 2004 m above sea level (masl) in Mekelle. Aynalem is found in Kilte Awlaelo Wereda, located North of Mekelle City 45 km, and is located at 39°35′60″ E Lon and 13°46′38″ N lat with an elevation of 2020 masl (Figure 1). The study areas are characterized by unimodal rainfall ranging from June to September with erratic spatial and temporal distributions [24]. The long-term (1992–2019) mean annual rainfall of Mekelle and Kilte Awlaelo is about 541. 5 and 612.7 mm, respectively. More than 70% of the rainfall occurs in July and August in the study area; however, the dry season extends up to ten months, from October to May (Figure 2). The average annual potential evapotranspiration (ETo) is estimated based on FAO Penman-Monteith [25] (Allen et al., 1998). The long-term mean maximum and minimum temperatures of the Mekelle and Elalla sites are 26.7 and 11.8 °C, respectively (Figure 2A), and the mean maximum and minimum temperatures of Kilte Awlaelo and Aynalem sites are 27.7 and 11.2 °C, respectively (Figure 2B).
Figure 1.
The Study areas of Aynalem and Elalla experimental sites (from the present study).
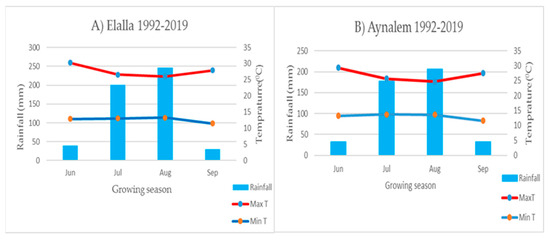
Figure 2.
Long-term (1992–2019) monthly rainfall, maximum and minimum temperature of (A) Mekelle, Elalla site and (B) Kilte Awlaelo, Aynalem site under rainfall conditions. Note: Rainfall amount and temperature are plotted on the left and right sides of the Y-axis, respectively, and the months are plotted on the X-axis.
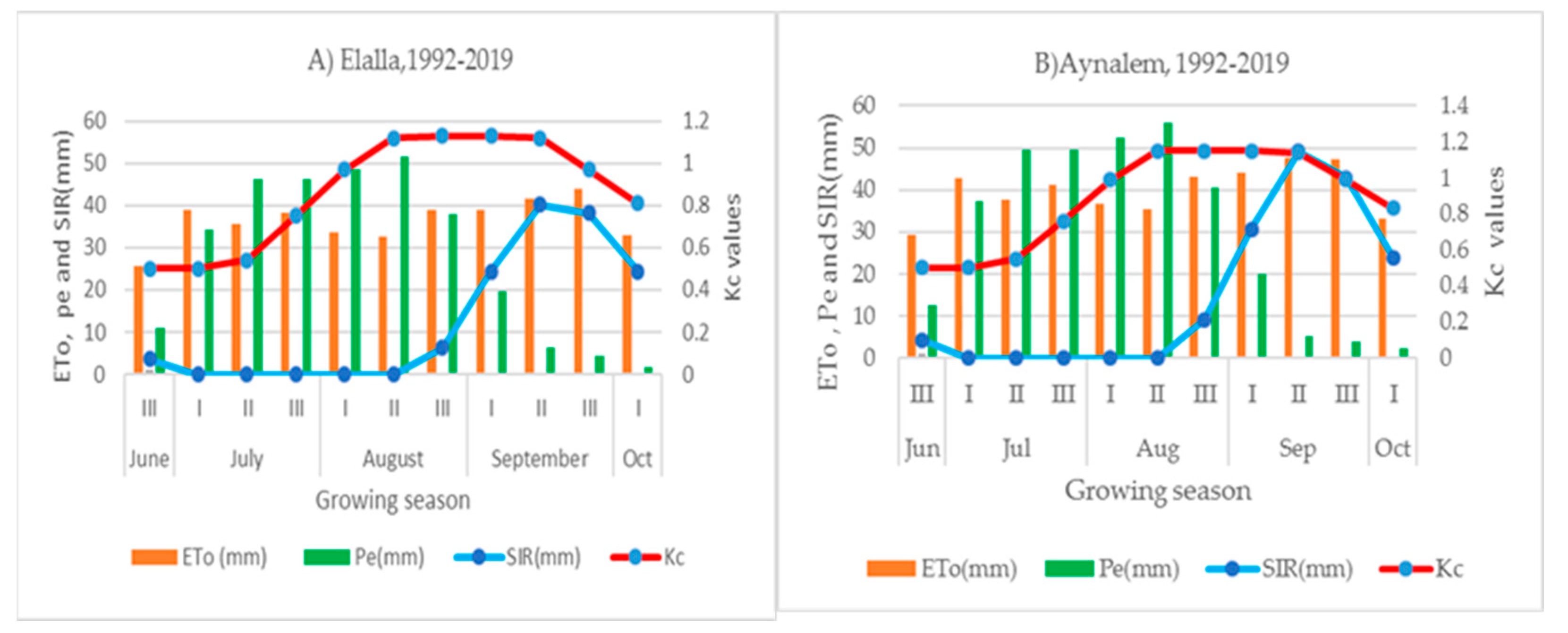
The soil type of the Mekelle, Elalla experimental site is dominated by clay loam with field capacity and permanent wilting points of 32% and 18.5%, respectively and Kilte Awlaelo, Aynalem site dominated by sandy clay soil with field capacity and permanent wilting points of 30.5% and 15.5%, respectively (Table 1). The major crops grown in these areas are wheat, barley, teff, and potato. This study site was selected based on its suitability in terms of climate and soil conditions for potato production. During the growing season, supplemental irrigation was applied as needed for the potato genotypes. The growing season for potatoes typically starts at the end of June, with harvesting conducted by early October (Figure 3)

Table 1.
Soil physio-chemical properties of Elalla and Aynalem experimental sites at depths of 0–30 cm.
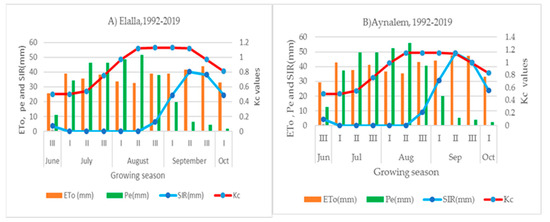
Figure 3.
Decadal seasonal reference evapotranspiration (ETo), crop coefficient (Kc), effective rainfall (Pe), and supplement irrigation needs (SIR) estimated for potato using long-term mean climate inputs, used for planning purposes under rainfall conditions (1992–2019). Note: I, II, and III are 1st, 2nd and 3rd decades (10 days) of a month. Note: The Y-axis is the ETo, Pe, SIR and Kc value of the months on the left and right side of Y, respectively, and the X-axis is the months.
2.2. Treatments and Experimental Design
Five potato genotypes, CIP-3960478.90, CIP-394611.112, CIP-392661, Seohong, and Gudanie (standard check), and two irrigation treatments, non-irrigated (NI) check where natural rainfed occurred (RF) and supplementary irrigation (SI), were tested. The field experiment was arranged in a split plot using a randomized complete block design (RCBD) and replicated three times. The genotypes were kept as a subplot, whereas supplemental irrigation was the main plot. The field experiment was conducted at Mekelle, Elalla site, and Wukro, Aynalem site, for two consecutive years. Genotype and irrigation were kept as fixed effects in the model, whereas location and year were random effects.
The gross plot size used in each site is 4.5 m × 3 m (13.5 m2), with spacing between rows and plants of 75 cm and 30 cm, respectively. A distance of one meter was maintained between plots 1.5 and 2 m between subplot plots and blocks, respectively. The experimental field was well prepared, and the potato crop was grown under optimal planting practices. The recommended fertilizer rate and type were applied to all treatments equally; that is, the full dose of NPSZn at the rate of 250.4 kg/ha (18 N: 35.9 P2O5:7 S and 2.2 Zn) was applied at planting, while 165 kg/ha urea was applied by splitting, half dose of urea was applied at planting in all plots uniformly, whereas half of urea per treatment was applied at the early flowering stage.
2.3. Crop Water Requirement and Irrigation Application
Supplemental irrigation was applied after the onset of rainfall during the growing season. Supplemental irrigation was applied to maintain soil moisture at field capacity from planting to maturity during the rainy season. Crop water needs depend on climate data (temperature, wind humidity, sunshine hours, evaporation, and rain), crop type, crop stage of growth, and soil type. The potato crop water requirement (ETc) of the study area was determined from the reference evapotranspiration (ETo) and the respective crop coefficients (Kc) of each growth stage [25]. The Kc of potato at different growth stages was adopted from [25]. The amount of water required by the crop to fulfill its demand was estimated using the FAO CROPWAT program version.8 [25], as indicated in Equation (1). Furthermore, Irrigation scheduling of the crop was computed using the FAO CROPWAT program [25] at irrigation critical depletion after the soil moisture reached 25% of the field capacity. Irrigation critical depletion (to refine soil to 100% of the field capacity) and irrigation efficiency 70% scheduling criteria were adopted in this study. The amount of water required in the supplement irrigation treatment was measured and applied using a Parshall flume device with a 2-inch throat width. The Parshall flume had a known discharging rate (l/s) for different heads (cm). The irrigation water source was a river pumped from a nearby river to the study sites through a water pump with a specific capacity of 30 m3ha−1 efficiency. The furrow irrigation method was used to irrigate the experimental plots. This method applies water through a series of small furrows between plant rows. The combined mean amount of supplemental irrigation water applied was 85.06 mm at the Mekelle Elalla site and 94.75 mm at the Kilte Awlaelo Aynalem site, respectively. Furthermore, depending on the genotypes, the difference in maturity and water requirement of 59.0 to 127.7 mm was applied as supplement irrigation. The combined mean total amount of water supplied to the crop was 293.2 and 383.4 mm for non-irrigated (effective rainfall only) and irrigated plots (effective rainfall + supplement irrigation), respectively.
where: ETc = Crop water requirement, ETo = Reference Evapotranspiration (climate data), Kc = Crop coefficient
The amount of water supplied by irrigation during the crop growth period under rainfed conditions is termed the supplement irrigation requirement (SIR). SIR is the difference between the crop water requirement and effective rainfall, as indicated in Equation (2).
SIR (mm) = ETcrop (mm) − Effective rainfall (mm)
The effective rainfall was calculated based on the formula developed by [26], as shown in Equations (3) and (4).
TRF is the total rainfall in the month, and * is the multiplication sign [27]. It also calculated the relative water satisfaction (RWS) as the ratio of effective rainfall (Pe) to crop water requirement (ETc), as given in Equation (5).
2.4. Data Collection
2.4.1. Climatic Data
Daily rainfall data and minimum and maximum air temperature relative humidity, wind speed, and sunshine hours during the study period for each study site were collected from the Ethiopian Metrological Service Agency, Mekelle branch, and Mekelle Agricultural Research Center.
2.4.2. Soil Data Sampling and Analysis
Profile pits were excavated at representative locations in each experimental field during the growing season before planting. Disturbed and undisturbed soil samples at 0–30 cm depth were collected manually to determine soil physical properties, including field capacity (%FC), permanent wilting point (%PWP), bulk density, and total available water (mm/m) of the experimental field soil (Table 1). The soil sample was analyzed at the Mekelle University and Mekelle soil center to determine the particle size distribution (texture). Composite soil of the surface layer (0–0.3 m) from representative plots was also collected before planting, following the standard soil sampling procedure. Each composite soil sample was used for selected physico-chemical analysis, such as soil texture, pH, total nitrogen (N), organic carbon (OC), cation exchange capacity (CEC), available potassium (K), and available phosphorous (P). Soil analysis was conducted at the Mekelle Soil Research Center laboratory following standard procedures to determine total nitrogen (Kjeldahl method), available phosphorus [28] organic carbon [29] and soil pH (on 1:2.5 soil: water suspension) (Table 1)
2.4.3. Plant Data
Fresh mature leaf samples of potato from each treatment were collected nine weeks after planting and oven-dried overnight at 70 °C (constant weight). Then, the samples were ground and sieved through a 2 mm sieve for N content analysis in the Mekelle Soil Research laboratory. In addition, to determine the N content, potato tuber samples were taken in a harvest oven, dried in an oven at 80 °C for 72 h, ground, and sieved in order to analyze the N content in the laboratory as described by [30]. The total nitrogen content in the tuber and leaf samples was determined using the Kjeldahl method, as described previously [31].
2.4.4. Growth, Yield and Yield Component Data Collection
Data on days to flowering and philological maturity, number of tubers per plant, tuber diameter, tuber weight, final tuber yield (marketable and unmarketable), biomass yield, and harvest index were collected. Days to flowering and physiological maturity were recorded when 50% of the plant population reached the flowering stage and when the leaves of 75% of the plants in the plot turned yellowish, respectively. Plant height was determined by measuring the height from the base of the main stem to the apex at full maturity. For tuber number and tuber diameter estimation, an average of 12 hills from the center of the subplot treatment was used. Healthy tubers with weight > 25 gm were considered marketable, while rotten, diseased, insect-attacked, deformed tuber and those having <25 gm in weight were categorized as unmarketable, as described by [32]. Dry aboveground biomass at harvest and final tuber yield were obtained from two middle rows of each plot with an area of 3 m × 1.5 m (4.5 m2). The dry weight was recorded after air-drying the fresh samples and further oven-drying at 70 °C for 72 h (constant weight).
The harvest index was determined as the ratio of total tubers to total dry biomass taken at harvest.
Incremental Yield = (Irrigated Crop Yield − Non-Irrigated Crop Yield)/Non-Irrigated Crop Yield
2.4.5. Determination of Potato Tuber Quality
Samples of potato tuber were taken at harvest, sliced, and oven-dried at a temperature of 80 °C for 72 h. Following the procedures of [30], the dried samples were ground and sieved in order to analyze the nitrogen (N) contents at the Mekelle Soil Research laboratory. The total nitrogen content in tuber samples was determined using the Kjeldahl method, as described previously [31]. Then, the protein content of the potato tuber (%) was calculated by multiplying the nitrogen (N) content of the potato tuber by 6.25 [33]. Similarly, the starch content (%) was obtained indirectly after measuring the specific gravity, as described by [34], using Equations (6) and (7).
where, S.G—Specific gravity, gm is gram
Starch content (%) = 17.565 + 199.07 (S.G − 1.0988)
To determine the dry matter content of each genotype, five plants from each subplot treatment were selected randomly, and from each plant, ten potato tubers were randomly selected. The tubers’ fresh weights were recorded first, and then the samples were allowed to dry in an oven at a temperature of 80 °C for 72 h. After a constant weight was attained, the samples were weighed to determine the dry matter (DM). Finally, the dry matter content was calculated as the ratio between the dry and fresh mass, expressed as a percentage.
2.4.6. Determination of Water Use Efficiency (WUE) and Water Productivity
The terms water use efficiency (WUE) and water productivity (WP) are often confused. In the context of crops, water use efficiency (WUEc) is defined as the ratio of crop output per amount of water lost by the process of actual evapotranspiration (ETa) [35]. Water use efficiency (WUE) and irrigation water use efficiency (IWUE) of the potato were calculated following the procedures described in [36]. Similarly, crop water productivity (WPc) is calculated as the marketable yield produced by a crop during the growing season (in kg ha−1) divided by the water consumed by the crop during the same period (in m3 ha−1) [37,38]. Based on the work of these authors, the water use efficiency (WUE), total crop water productivity (TWPC), and irrigation water productivity (IWP) of potatoes were calculated using Equations (8)–(10), as follows:
where; TMI = Total Marketable tuber yield of an irrigated plot, TMNI = total marketable tuber yield in of a non-irrigated plot, and I = amount of irrigation supplied during the growing season of potato.
2.5. Data Analysis
Data on crop yield and yield components were subjected to analysis of variance using the ANOVA Mixed model procedure of SAS statistical software (SAS version 10). This software also checked ANOVA assumptions (normality, homogeneity, independence of group variances and means, and independence of scores). In ANOVA, genotype and irrigation were considered as fixed effects, while year, location, and replication were considered as random effects. Most of the measured data derived from each experiment were non-significant, and homogeneity of variance combined with analysis was implemented. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to determine whether the treatments (variety and water) and the interaction between them had significant differences in response variables. Differences between the treatment means were computed by means of Duncan’s Multiple Range Test (DMRT) at a 5% level of significance because it is a widely used procedure for comparing all pairs of means.
3. Results
3.1. Climate and Potato Water Requirement During the Growing Period
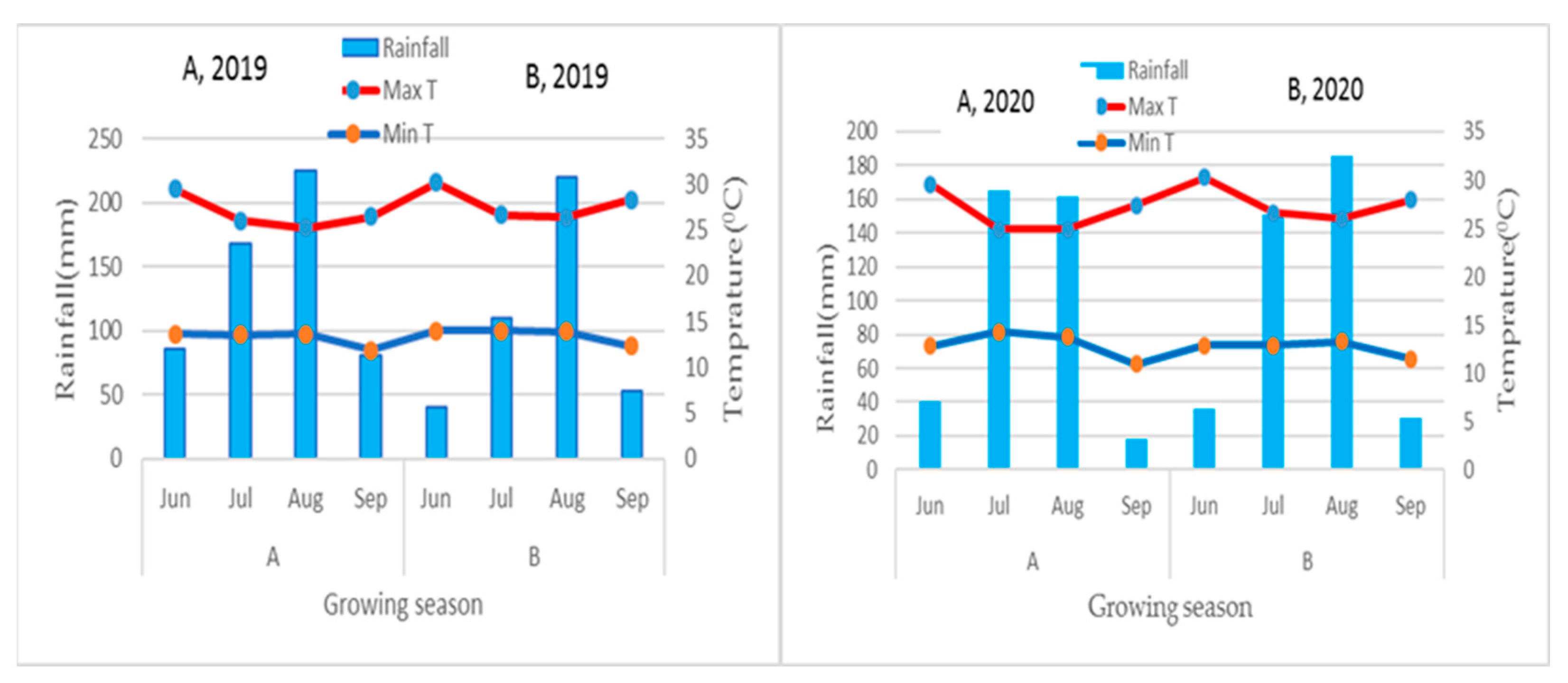
During the study period of 2019 and 2020, the total monthly rainfall and maximum and minimum temperature of the study areas are indicated in Figure 4. The total seasonal rainfall and mean maximum and minimum temperatures of the Mekelle and Elalla sites were 559.4 mm, 26.8 and 13.6 °C respectively (Figure 4A). In the same period, the seasonal total rainfall and mean maximum and minimum temperatures of the Kilte Awlaelo and Aynalem sites were 423 mm, 27.9 °C and 13.6 °C, respectively (Figure 4B). The study areas Elalla and Aynalem sites received combined effective seasonal rainfall of 301.6 and 289.6 mm, respectively, during the growing season of potato. Furthermore, 97.03 mm and 73.09 mm of supplemental irrigation water were applied at the Elalla site in the 2019 and 2020 growing seasons, respectively. In contrast, 89.22 mm and 100.27 mm of supplemental irrigation water were applied at the Aynalem site in the 2019 and 2020 cropping seasons, respectively. In general, 85.06 mm and 94.75 mm combined mean of irrigation water was applied as supplement irrigation at Elalla and Aynalem sites, respectively, to the effective rainfall.
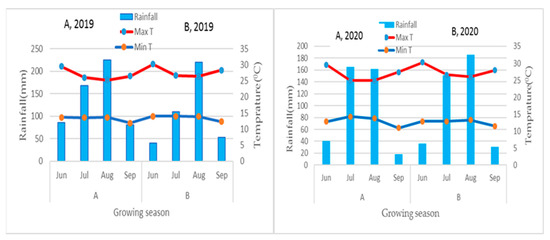
Figure 4.
Monthly rainfall, mean maximum and minimum temperature of the study areas Mekelle, Elalla site (A) and Kilte Awlaelo, Aynalem site (B) in 2019 and 2020 growing season under rainfall conditions. Note: Rainfall amount and temperature are plotted on the Y-axis, and the months in the growing season are plotted on the X-axis.
The long-term agrometeorological analyses indicated that the mean effective rainfall (Pe) of the rainy seasons of Mekelle, Elalla site and Wukro, Aynalem site was 307.6 and 329.3 mm, respectively. Accordingly, relative water satisfaction was 87.1% and 83.6% at the Elalla and Aynalem sites, respectively (Figure 3). While the combined mean seasonal effective rainfall during the two growing seasons in Elalla and Aynalem sites were 321.3 and 289.5 mm, respectively; consequently, the relative water satisfaction was 86.98 and 67.93% for Elalla and Aynalem, respectively (Table 2). The long-term and two-year experimental period combined mean of seasonal crop water requirement (ETc) at the experimental sites in the months of July and August was not lower than the effective rainfall; however, in September and October, the crop water requirement was higher than the effective rainfall (Pe) (Figure 3).

Table 2.
The Interaction effect of genotype and irrigation on growth parameters of potato.
3.2. Growth Parameters and Yield Component of Potato Genotypes,
The results in Table 2 indicate that the interaction effects of genotype and supplement irrigation significantly influenced days to flowering and maturity; furthermore, the main effect of genotype and irrigation level affected potato growth parameters (Table 3).

Table 3.
The main effect of genotype and irrigation on the growth and yield components of potato.
3.2.1. Days to Flowering and Maturity
Days to flowering and philological maturity were significantly affected by the main and interaction effects of genotype and irrigation. Early average days to flowering and days to maturity were determined for the interaction effect of genotypes CIP-394611.112 and CIP-3960478.90, with supplement irrigation and no irrigation, while the late average days to flowering days to maturity were recorded for the interaction effect of genotype CIP-392661.18, with supplement irrigation (Table 2).
3.2.2. Plant Height (cm)
According to this study, plant height was significantly influenced by genotype, but not by irrigation, location, or their interaction. Gudanie and CIP-392661.18 were the tallest of the other genotypes. Whereas, Seohong was the shortest genotype (Table 3).
3.2.3. Yeild Component
The results of the study also show that the average number of tubers per plant, average tuber weight (gm), and average tuber diameter were highly significantly influenced by the main effect of genotype and irrigation (Table 3). Meanwhile, the average tuber length (mm) was significantly influenced only by the main effect of genotype. However, neither yield component was significantly influenced by the interaction effect of the two factors (genotype and irrigation). The largest number of tubers per plant and tuber weight were obtained from CIP-3960478.90, Gudanie, and CIP-394611.112 (Table 3). With respect, the main effect of irrigation was a higher and significant average number of tubers per plant and tuber weight obtained in the irrigated treatment, while the lowest was observed in the non-irrigated treatment. The largest tuber diameter and tuber length, 48.72 and 68.18 mm, respectively, were recorded in the genotype Gudanie (Table 3).
3.3. Effect of Supplement Irrigation on Yield of Potato Genotypes
The main and interaction effects of genotype and irrigation significantly affected the marketable, total tuber, and biomass yield of potato (Table 4). The interaction of genotype with irrigation was not significantly influenced by unmarketable yield or harvest index. There was no significant interaction among location, irrigation, genotype, and year.

Table 4.
Interaction effect of genotype and irrigation on yield of potato under rainfall conditions.
3.3.1. Tuber Yield
The highest significant marketable total tuber and biomass yield was obtained with the interaction of genotypes CIP-394611.112 and CIP-3960478.90, by supplement irrigation. The interaction of these genotypes CIP-394611.112 with no irrigation (rainfall only) was also significantly different from the other interaction of genotypes through supplement irrigation (Table 4). Genotypes CIP-3960478.90 and CIP-394611.112 had the highest marketable yield of 27.13 and 26.65 t ha−1, respectively. Furthermore, the highest total tuber yield, 28.71 and 27.14 t ha−1, was recorded in genotypes CIP-3960478.90 and CIP-394611.112, respectively. However, the lowest marketable yield and total tuber yield were registered in the interaction of genotype Seohong with either no irrigation or supplemental irrigation treatments (Table 4). Mean comparisons of attributes among interactions of genotype by irrigation showed that marketable and total tuber yield of genotypes CIP-3960478.90 and CIP-394611.112 interaction by either supplement irrigation or no irrigation was higher than the tuber yields of other genotype interactions by irrigation treatments (Table 4).
3.3.2. Tuber Yield Increase
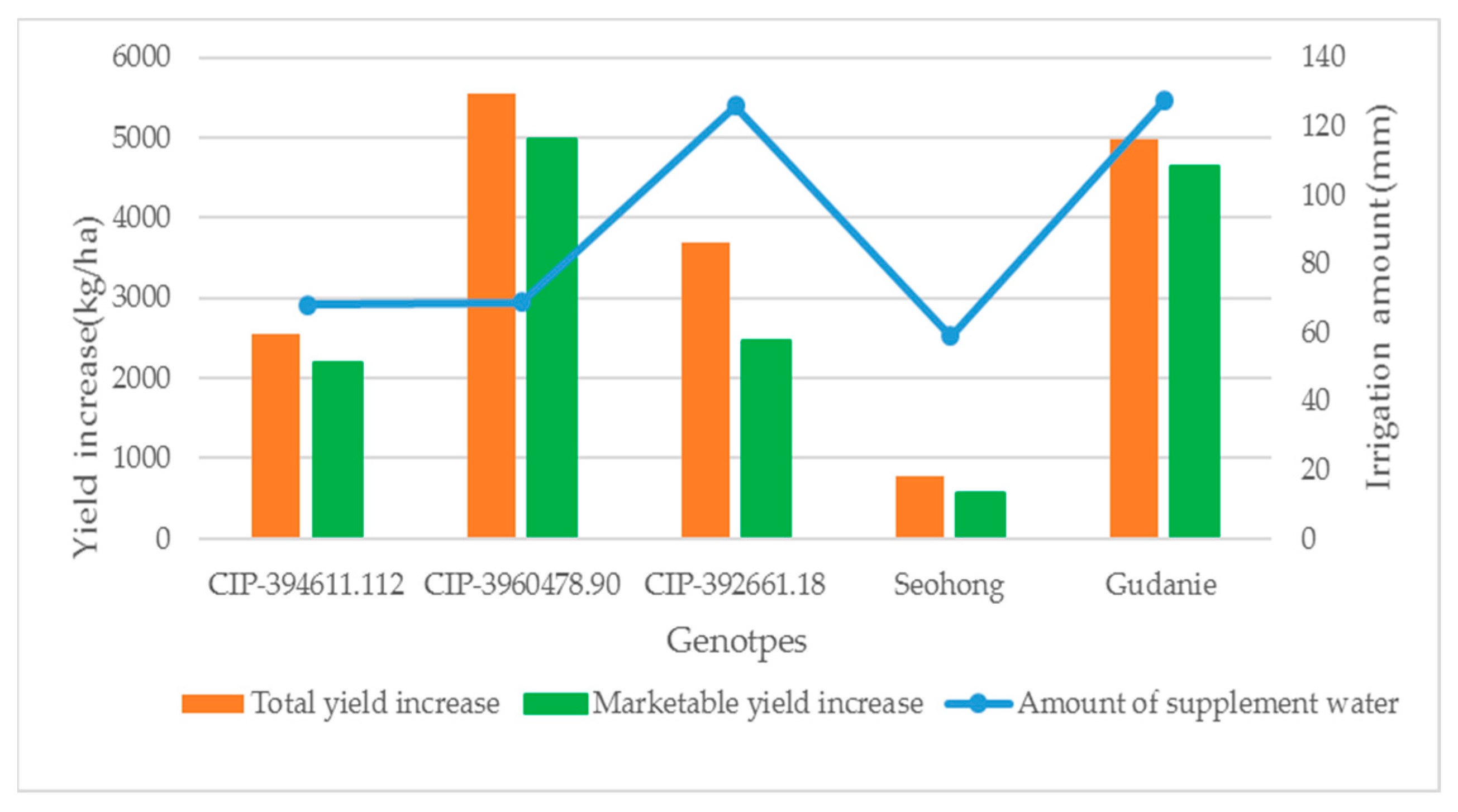
The study found that the highest marketable and total tuber yields were obtained by applying 68.77 mm of supplemental irrigation during the rainy season, compared to no irrigation. The lowest yields were associated with the lowest amount of supplemental irrigation at 59.00 mm. Furthermore, the genotypes Gudanie and CIP-392661.18 received the highest amounts of supplemental irrigation at 127.7 mm and 125.9 mm, respectively (Figure 5), but these genotypes did not achieve the highest marketable and total tuber yields. Instead, genotypes CIP-3960478.90 and CIP-394611.112, which received lower amounts of supplemental irrigation and effective rainfall, achieved the highest marketable and total tuber yields (Table 5). The increment in marketable and total tuber yield due to the application of supplemental irrigation, compared to rainfed conditions, was also significantly different among the genotypes. The highest increment in total tuber yield (5540.0 kg/ha) and total marketable yield (4986.7 kg/ha) was obtained from genotype CIP-3960478.90, while the lowest was from the genotype Seohong (Figure 5).
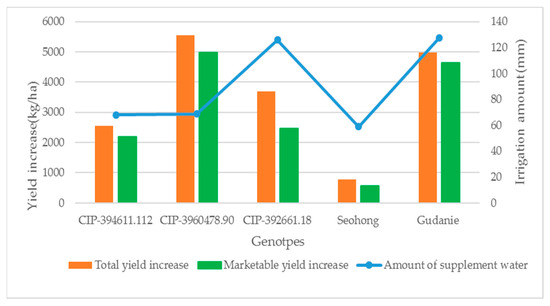
Figure 5.
Tuber yield increases (kg/ha) due to supplement irrigation. Note: The Y-axis is the yield increment value (left) and irrigation amount applied (right) of the genotypes, and the X-axis is the genotypes.

Table 5.
Effect of genotype and irrigation on tuber quality of potato.
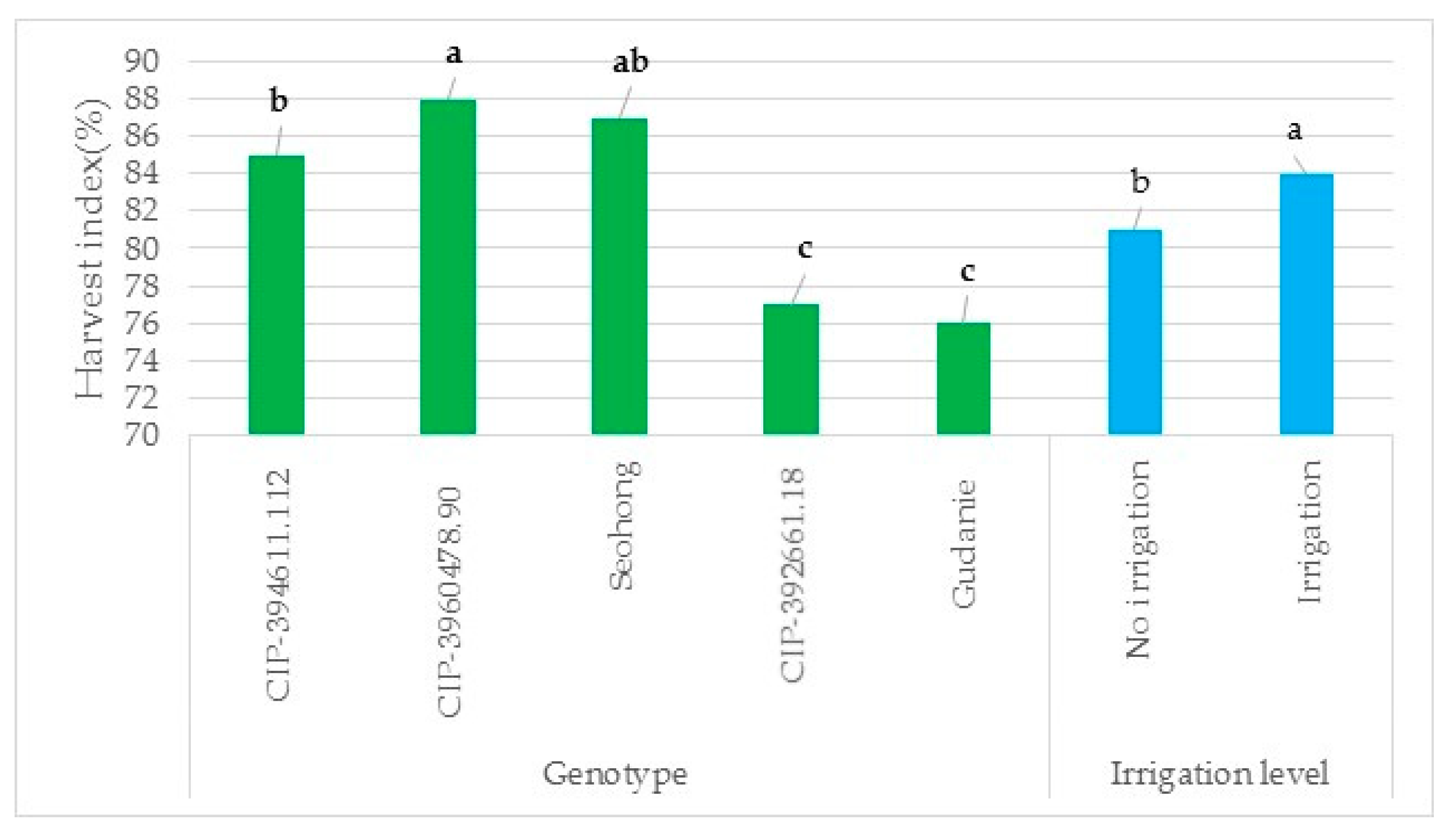
3.3.3. Harvest Index
The results indicated that the harvest index was affected significantly by genotype and irrigation, but not by their interaction (Figure 6). The maximum harvest index of 0.88 and 0.87 was found in the genotypes CIP-3960478.90 and Seohong, respectively, while the lowest was determined in the genotype Gudanie. In the case of irrigation, the highest harvest index was obtained with supplemental irrigation (Figure 6).
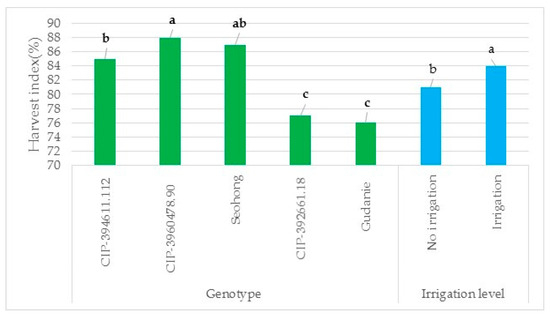
Figure 6.
Effect of genotype on harvest index. Graph with the same color level with different letters showed significant differences in harvest index among genotypes at (p < 0.001) and between irrigation levels at p ≤ 0.05, but the similar letter had no significant difference. Note: The Y-axis is the harvest index value of the genotype and irrigation, and X-axis is the genotypes and irrigation level.
3.4. Effect of Supplement Irrigation on Yield Quality of Potato Genotypes
The analysis of variance indicated that the interaction effect of genotype and irrigation did not significantly affect the tuber quality of potato, such as dry matter (DM), specific gravity (SG), starch content (%), and protein content. The main effect of genotype and irrigation did not affect specific gravity, starch content, and protein content. The dry matter of potato tuber was affected by genotype but not by irrigation. Significantly, the highest dry matter content of potato was found in genotypes CIP-3960478.90, CIP-394611.112, and CIP-392661.18, in descending order (Table 5). The minimum value of dry matter was recorded for the genotype Gudanie. Maximum specific gravity and starch content were found due to the main effect of genotype CIP-3960478.90, whereas minimum specific gravity and starch content were obtained for genotypes CIP-394611.112 and Seohong, respectively (Table 5).
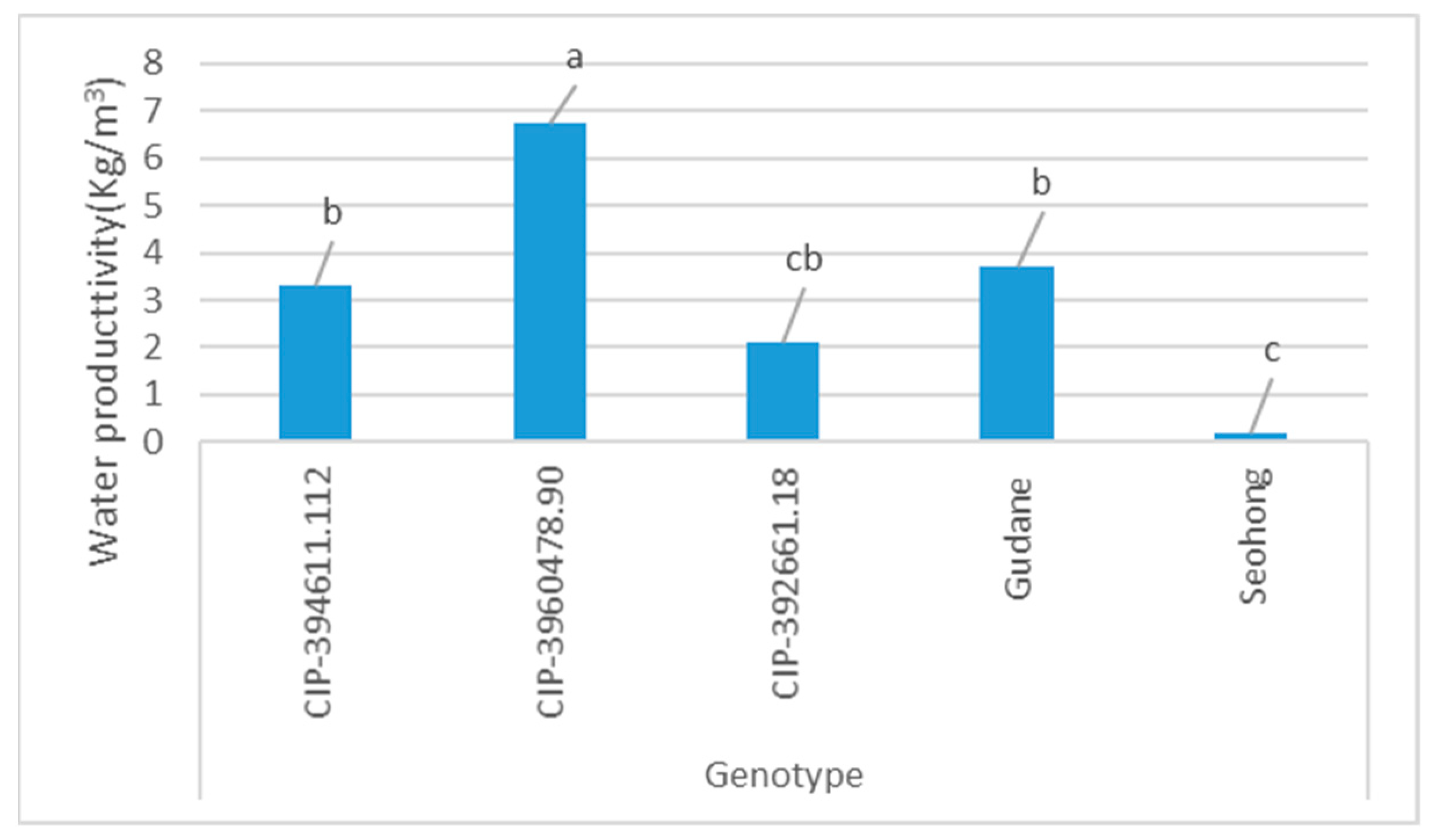
3.5. Effect of Supplement Irrigation on Water Productivity and Irrigation Water Productivity of Potato Genotypes
The results in Table 6 indicate that the total water productivity (TWP) of potato was affected by the main interaction effect of irrigation and genotype. Irrigation water productivity was only affected by the main effect of genotype (Table 6 and Figure 7). The maximum total water productivity of potato (8.51 kg m−3) and irrigation water productivity (6.76 kg m−3) was recorded at the interaction of genotype CIP-394611.12 with no irrigation (Table 6) and due to the main effect of CIP-3960478.90 (Figure 7) respectively.

Table 6.
Interaction effect of genotype and irrigation on water use efficiency and water productivity.
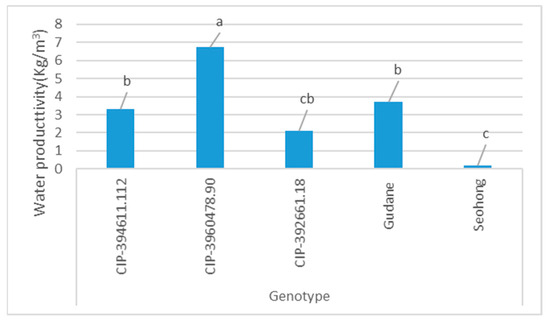
Figure 7.
The main effect of genotype on irrigation water productivity (IWP). The graph with the same color and different letters shows significant differences in irrigation water productivity among genotypes at p ≤ 0.05; however, the same letter indicates no significant difference. Note: The Y-axis is the water productivity value of the genotype and the X-axis is the genotype.
4. Discussion
4.1. Climate and Potato Water Requirement
The long-term mean total seasonal rainfall amount was less than the crop water requirement of potato in both locations, indicating that the potato requires supplement irrigation; in addition, the seasonal amount of rainfall during the experiment period was also less than the potato water requirement. As a result, water was applied as supplement irrigation, relatively similar to the long-term water required to apply as supplement irrigation for potato. The total seasonal rainfall was relatively stable at the Mekelle, Elalla site compared to the Kilte Awlaelo, Aynalem area. This implies that the application of water as a supplement to irrigation in these areas is paramount. However, its high temporal variations could cause an indeterminate drought that deters potato production. Similarly, ref. [39] reported that the total seasonal water requirement for the wheat crop was relatively stable in this area. The number of irrigations depends on the length of the dry period and the potato genotype growing period. Accordingly, 3–5 irrigations were applied based on the water deficit of the seasons. The long-term and short-term seasonal rainfall results imply that the crop water requirement of potato needs supplement irrigation due to crop water deficit in late June (due to late-onset) during emergence and late August and early September (due to early cessation) when germination flowering and tuber initiation takes place, respectively; therefore, for the application of measured SI based on the deficit level, it is important to minimize yield reduction and increase yield. This result indicates that natural rainfall alone is inadequate for potato production; hence, supplement irrigation based on potato crop water requirement is important in late June, late August, September, and even October (depending on the potato growing period and planting date) to produce potato (Figure 3). In line with this, [17] reported that more than 70% of the annual rainfall in Tigray, Ethiopia, is received only in July and August. In addition, the rainfall is either too much at one time or with no rain at another time [18].
4.2. Potato Growth Parameters
The highest average days to philological maturity were recorded for the interaction of each genotype with supplement irrigation (SI); this indicates that as the water amount increases, the days to maturity of the potato genotype increase; the reverse is also true. The difference in days to maturity and flowering may be mainly due to the genetic variation of the genotype, which is similar to the application of supplement irrigation. In agreement with this result, ref. [40] reported that varieties could affect the flowering and maturity, and it provides the basis for the selection of late- or early-maturing varieties depending on the rainfall duration, temperature, and labor availability. Furthermore, ref. [41] reported that variations in the length of the growing period among varieties might be due to differences in genetic makeup. Ref. [27] Also reported that flowering and maturity are heritable traits of the potato crop. Therefore, these genotypes have early days to flowering and days to maturity, which is an important characteristic of the semi-arid areas of Tigray, when rainfall starts late and early onset with a small amount of seasonal rainfall. The present study also confirms that early-maturing potato genotypes can be grown in semi-arid areas under rainfall conditions with satisfactory yield. In addition, the number of days of flowering and maturity is vital for farmers to plan and develop a suitable production system. The tallest plant height was recorded for the genotype Gudanie, whereas the shortest was recorded for the genotype Seohong; this is due to genetic variation among genotypes. In agreement with this result, ref. [42,43] reported that plant height is affected by variety. Refs. [44,45] also reported that varieties showing different results in terms of plant height could be due to their genetic and inherent characteristics. In contrast to this result, [46] found that the environment, cultivar, and their interaction in Eastern Ethiopia affected plant height.
4.3. Tuber Yield Component and Yield
The results of this study indicate that the major yield component of potato, such as the number of tubers per plant and average tuber weight attributed to total potato tuber yield, was affected by genotype and irrigation; therefore, this study identifies potato genotype (s) with high tuber number and tuber weight that could possibly produce the potato in the semi-arid areas of Tigray with supplement irrigation and selected genotypes. The genotypes tested were not affected to the same degree by irrigation. Responsiveness to irrigation in terms of tuber number and tuber weight varied greatly between the different genotypes. In agreement with the results of this study, ref. [47] reported that the number of tubers per plant was statistically significantly affected by water treatment and potato cultivars. [48] reported that plant height marketable tuber number per plant was influenced by genotype and irrigation. In addition, they reported that the plant height genotype by irrigation interaction did not affect plant height. However, the total number of tubers per plant and marketable tuber weight were not significantly influenced by genotype and irrigation interaction, which was contradictory to this result. Ref. [49] also reported the highest number of tubers per plant of the irrigated potato compared to rainfed production. The plant height, tuber number per plant, and tuber weight differences in the irrigated treatment among the genotypes are mainly due to genetic differences. Many researchers like [50,51,52] also reported that the number of tubers per plant was affected by variety; similarly, [40,53] found that different varieties had significantly differed in terms of tuber number per plant and weight of tuber.
Applying water as supplement irrigation (SI) to the potato crop resulted in significant differences in marketable and total tuber yield among genotypes. This result indicates that the genotypes tested were not affected to the same degree by supplement irrigation. Responsiveness to irrigation in terms of marketable and total tuber yield varied greatly among the different genotypes. Therefore, marketable and total tuber yield differences among the genotypes are mainly due to genetic differences. In agreement with this result, Luitel et al. (2015) [48] reported that marketable tuber yield was significantly affected by genotype, irrigation, and genotype by irrigation interaction. Similarly, ref. [39] indicated that the grain yield of wheat was significantly affected by supplement irrigation in semi-arid areas. Refs. [22,54] found that supplemental irrigation, especially during critical crop growth stages, can improve crop yield and water productivity, and yield increases are remarkable, even when rainfall is as high as 500 mm. Moreover, ref. [55] found that supplemental irrigation at different critical crop growth stages, higher yield, and economic returns were achieved with less irrigation water usage. Ref. [56] also reported that Supplemental irrigation had a significant effect on grain yield. Ref. [57] reported that good yields of potato under irrigation in temperate and subtropical climates are 25 to 35 t ha−1 fresh tubers, and in tropical climates, yields are 15 to 25 t ha−1. This result implies that tuber yield of potato is directly associated with genotype and irrigation as an agronomic practice. Therefore, genotypes CIP-394611.112 and CIP-3960478.90 are promising potato genotypes for the semi-arid areas of Tigray to produce high tuber yield under rainfed conditions. The maximum harvest index was found in the genotype CIP-3960478.90, while the lowest was determined in the genotype Gudanie. In the case of irrigation, the highest harvest index was obtained with supplemental irrigation. This result implies that the harvest index was affected by the genetic difference in the genotype and the application of water. In contradiction, this result, ref. [58] reported that diverse water supplies did not change the harvest index (HI) values of potato. Therefore, HI is a novel trait directly associated with the yield of potato and is more influenced by genetic traits; it is an important indicator and is directly proportional to the economic yield of a crop.
The highest increase in marketable and total tuber yield from irrigated to non-irrigated conditions does not guarantee that a genotype will have the highest overall yields. The yield gap between irrigated and non-irrigated conditions is more important, as seen with genotype CIP-394611.112, which had high yields under both irrigated and non-irrigated conditions, but a lower yield increase compared to genotypes like Gudanie, which had a larger yield gap between the two conditions and low marketable and total tuber yield. In summary, the application of 68.77 mm and 68.12 mm of supplemental irrigation during the rainy season resulted in the highest marketable and total tuber yields from genotype CIP-3960478.90 and CIP-394611.112, respectively, but the genotypic response to supplemental irrigation varied, and the yield gap between irrigated and non-irrigated conditions was more important than the absolute yield increase from irrigation.
4.4. Quality of Potato
The results of this study indicate that the quality of potato, such as specific gravity, starch content, and protein content, is not influenced by the genotype or genetic traits of the potato, the application of irrigation, or the amount of water applied. Moreover, slightly higher specific gravity and starch content were recorded in supplement irrigation (SI) treatment than non-irrigated (NI). The highest and lowest protein contents were found in genotypes Gudanie and Seohong, respectively. Furthermore, almost similar protein content was found in the supplemental and no irrigation treatments. However, the differences in specific gravity, starch content, and protein content were not significant due to the genotype and irrigation interaction. This result indicates that genotypes with high specific gravity displayed a higher percentage of dry matter content, while low dry matter was observed in genotypes with low specific gravity. In agreement with this result, ref. [59] reported that in most of the cultivars, there is no significant difference in specific gravity, but there is a significant difference between the lowest and highest specific gravity, which is contradictory to this result. Therefore, a higher specific gravity of tubers from either the irrigated or genotype treatments is an indicator of improved tuber quality for frying and better flavor. In agreement with this result, Haider and Ramanathan [60] reported that the specific gravity of tubers in irrigated treatments was higher than that in non-irrigated treatments. Previous studies have indicated that a lower specific gravity of potato tuber is obtained by deficient irrigation [61]. In contrast, some researchers [62] (Eldredge et al., 1996) observed an increase in specific gravity in the Russet Burbank potato cultivar under deficit irrigation. In general, the difference in dry matter, specific gravity, starch content, and protein content might be related to genetic variations among different genotypes. Similar observations have been reported earlier for different cultivars of potatoes [63]. This study indicates that the main and interaction effects of genotype and supplemental irrigation did not influence the starch and protein contents of potato tuber. The advantages of potatoes include a rich chemical composition and high nutritional value; moreover, they can grow in any climate and conditions [64]. Similar to this study, ref. [65] reported that potato tubers contain approx. 17% of complex carbohydrates (starch), approx. 0.5% sugars, 2% proteins, 2.3% dietary fiber, approx. 0.1% lipids, and a wide range of vitamins and minerals. In contrast to this result, other authors showed differences in the protein composition of potato tuber depending on cultivar or variety [65]. Dry matter was affected by genetic traits but not by the amount of water applied as supplement irrigation to the potato crop. In agreement with this result, it was reported that the dry matter content of potato was affected by the cultivar. Ref. [66] reported that variety determined the dry matter and starch contents of potato tuber. Furthermore, ref. [67] defined dry matter content as an important quality determinant in potato processing, and its higher content (>20%) allows lesser oil uptake, desirable texture, and enhanced yield in the finished products. Therefore, the results of this study indicate that regardless of their significant difference, all the genotypes had good quality in the case of dry matter.
4.5. Water Productivity and Irrigation Water Productivity of Potato Genotypes
The higher total water productivity was recorded in the interaction of genotype with no irrigation, whereas lower water productivity was found in the interaction of genotype with supplement irrigation within the same genotype. In this study, plots received a higher amount of water through rainfall in July and August that was not less than the crop evapotranspiration (ETc); however, in September and October, the potato water requirement was higher than the plot received rainfall; as a result, it is important to supply water as supplement irrigation. In line with this, [17] reported that more than 70% of annual rainfall in Tigray, Ethiopia, is received only in July and August. In addition, the rainfall is either too much at one time or with no rain at another time [18]. Furthermore, the significant difference in water productivity and irrigation water productivity among the genotypes was due to the difference in the genetic makeup of the crop in terms of physiological maturity and water requirement. This result also implies that genotypes that received the lower amount of irrigation water with constant effective rainfall gave higher water productivity and irrigation water productivity. There was also a significant difference in the interaction of supplement irrigation and genotype, and no irrigation with genotype; this may be due to the genetic makeup of the genotype. Therefore, water productivity and irrigation water productivity were influenced by the genotypes of the same crop and the amount of irrigation water applied. Similarly, ref. [68,69] confirmed this result, as the lower the utilization rate of irrigation water received, the higher the water use efficiency. In agreement with the present results, ref. [70] found that water use efficiencies/productivity of potato were significantly influenced by irrigation. Many researchers have reported variability in water use efficiency with variable variety, as well as irrigation regimes. In agreement with this result, ref. [58] indicated that supplemental irrigation, especially during critical crop growth stages, could improve water productivity. This result agrees with the findings of [71], who reported that the highest water use efficiency obtained from the Jaleni variety increased with increased irrigation water amounts up to 80%, and disagrees with the result that the interaction effect of variety and supplement irrigation affects water use efficiency. An increase in irrigation water amounts resulted in a decrease in water use efficiency; this may be due to the accumulation of excess moisture in the root zone and consequently resulted in a decrease in the yield of potato. In line with this result, ref. [60] reported that water utilization efficiency for harvestable tubers was 4–7 kg/m3. Genotypes with high water use efficiency alone may not be rewarding, as it may be associated with low yield. In this study, we found that genotypes with high tuber yield have high water use efficiency in semi-arid areas of Tigray. Therefore, genetic variation has considerable importance in water productivity and irrigation water productivity of potato in the study area. Considering the cost of water, other factors are constant; the genotype that gave a high tuber yield and water productivity with a low amount of water is profitable. In this case, genotypes CIP-394611.112 and CIP-3960478.90 are appropriate in terms of tuber yield, water productivity, irrigation water productivity, and profitability in semi-arid areas of Tigray.
5. Conclusions
It could be concluded that the main and interaction effects of irrigation and genotypes significantly affected days to flowering, days to maturity, marketable yield, total tuber yield, irrigation, and total water productivity. Whereas the harvest index was affected by the main effect of genotype and irrigation. The highest marketable and total tuber yield, with shorter days to flowering and maturity, were obtained from the genotypes CIP-394611.112 and CIP-3960478.90 under supplemental irrigation. In this study, 27.13 and 28.71 t/ha of marketable and total tuber yield, respectively, were obtained from genotype CIP-3960478.90 under the application of 68.77 mm of water as supplemental irrigation to effective rainfall of 289.1 mm followed by genotype CIP-394611.112. The highest marketable (24.45 t/ha) and total tuber yield (25.60 t/ha) was achieved from genotype CIP-394611.112 under no irrigation. Applying supplemental irrigation improved total tuber yield in the range of 781.7 to 5540.0 kg/ha, depending on the genotype. However, potato tuber qualities were not significantly influenced by irrigation or genotype. Furthermore, the unmarketable quality of potato was not significantly influenced by the interaction effect of genotype and irrigation (supplemental irrigation and no irrigation). The highest total water productivity (8.51 kg m−3) and irrigation water productivity (6.76 kg m−3) were achieved from genotypes CIP-394611.112 interaction with no irrigated and duet to the main effect CIP-3960478.90, respectively. The genotype (s), which received a lower amount of irrigation water, showed high water productivity. It is also concluded from this study that the amount of effective rainfall was less than the crop evapotranspiration in September and early October; therefore, to fulfill the water requirement of the crop, the rainfall amount of water alone is inadequate for potato production in the semi-arid areas of Tigray. Hence, it is recommended to apply supplemental irrigation from September to early October to produce a high yield of potato. Higher water productivity of potato was recorded in non-irrigated plots; however, lower water productivity was recorded in irrigated or supplemented plots. Genotypes CIP-394611.112 and CIP-3960478.90 can be recommended in semi-arid areas to produce high tuber yield with high water productivity in a short growing period. We also recommend these genotypes for National Potato Breeding programs for further verification and release.
Author Contributions
N.A.M.: contributed to the literature search, study design, conducting the research experiment, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, draft writing, and revision. Final approval of the version to publish and be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. H.M.B.: contributed to the literature search, study design, supervision, data analysis, data interpretation, editing, revising, final approval of the version to publish, and accountability for all aspects of the work. D.B.Y.: contributed to the literature search, study design, supervision, data analysis, data interpretation, editing, revising, final approval of the version to publish, and accountability for all aspects of the work. G.H.G.: contributed to literature search, study design, supervising the experiment field, data analysis, data interpretation, editing and writing of the report, revising, final approval of the version to publish, and accountability for all aspects of the work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the following institutions and personnel for funding and facilitating the research: Tigray Agricultural Research Institute (TARI), Hawassa University, and the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) LiveGene Program, supported by the CGIAR Research Program on Livestock (CRP livestock project) and sponsored by the CGIAR funding contributors to the Trust Fund (http://www.cgiar.org/about-us/our-funders/), the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and UK aid from the UK Foreign Commonwealth and Development Office (Grant Agreement OPP1127286). This study was conducted as part of Niguse Abebe’s Ph.D. research.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study, titled “Growth, Yield, and Water Productivity of Potato Genotypes under Supplemental and Non-supplemental “Irrigation in Semi-Arid Areas of Northern Ethiopia” was conducted in accordance with ethical standards and approved by the Tigray Agricultural Research Institutional.
Informed Consent Statement
Tigray Agricultural Research Institute, Mekelle Agricultural center certifies the research entitled ‘Growth, Yield, and Water Productivity of Potato Genotypes under Supplemental and Non-supplemental Irrigation in Semi-Arid areas of Northern Ethiopia’ has been thoroughly reviewed in our annual research review. By investigating the scientific and ethical merits of the study and competency of the investigation of the investigators, it has been approved and conducted at our center.
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript is the product of my own original fieldwork date. Data supporting reported results included in the article were found on the Internet and referenced.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Tigray Agricultural Research Institute Mekelle Agricultural Research Center for providing the necessary materials and office equipment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Górska-Warsewicz, H.; Rejman, K.; Kaczorowska, J.; Laskowski, W. Vegetables, potatoes and their products as sources of energy and nutrients to the average diet in Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beals, K.A. Potatoes, nutrition and health. Am. J. Potato Res. 2019, 96, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, A.; Goffart, J.P.; Kromann, P.; Andrade-Piedra, J.; Polar, V.; Hareau, G. The Potato of the Future: Opportunities and Challenges in Sustainable Agri-food Systems. Potato Res. 2021, 64, 681–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaux, A.; Goffart, J.P.; Petsakos, A.; Kromann, P.; Gatto, M.; Okello, J.; Suarez, V. Global Food Security, Contributions from Sustainable Potato Agri-Food Systems. In The Potato Crop; Campos, H., Ortiz, O., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, S.A.; Koehler, A.K.; Nicklin, K.J.; Deva, C.; Sait, S.M.; Challinor, A.J. Global Potato Yields Increase under Climate Change with Adaptation and CO2 Fertilisation. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 519324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz, R.; Ramírez, D.A.; Kroschel, J.; Andrade-Piedra, J.; Barreda, C.; Condori, B.; Mares, V.; Monneveux, P.; Perez, W. Impact of Climate Change on the Potato Crop and Biodiversity in Its Center of Origin. Open Agric. 2018, 3, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, J.; Farooque, A.A.; Wang, X.; Abbas, F.; Acharya, B.; Afzaal, H. Contribution of Climate Extremes to Variation in Potato Tuber Yield in Prince Edward Island. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handayani, T.; Gilani, S.A.; Watanabe, K.N. Climatic Changes and Potatoes: How Can We Cope with the Abiotic Stresses? Breed Sci. 2019, 69, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daccache, A.; Weatherhead, E.K.; Stalham, M.A.; Knox, J.W. Impacts of Climate Change on Irrigated Potato Production in a Humid Climate. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Talla, A.; Swain, D.K.; Panda, R.K. Quantitative Approaches in Adaptation Strategies to Cope with Increased Temperatures Following Climate Change in Potato Crop. Potato Res. 2019, 62, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwama, K.; Yamaguchi, J. Abiotic stresses. In Handbook of Potato Production, Improvement, and Postharvest Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 231–278. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, S.H.; Andersen, M.N.; Plauborg, F.; Poulsen, R.T.; Jensen, C.R.; Sepaskhah, A.R.; Hansen, S. Effects of irrigation strategies and soils on field grown potatoes: Yield and water productivity. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayannejad, M.; Moharreri, A. Effect of every-other furrow irrigation on water use efficiency, starch and protein contents of potato. J. Agric. Sci. 2009, 1, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Monneveux, P.; Ramírez, D.A.; Pino, M.T. Drought tolerance in potato (S. tuberosum L.): Can we learn from drought tolerance research in cereals? Plant Sci. 2013, 205–206, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johan, R.; Lousise, K.; Suhas, P.W.; Jennie, B.; Nuhu, H.; Theib, O.; Adriana, B.; Jalali, F.; Zhu, Q. Managing water in rain fed agriculture-the need for a paradigm shift. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 543–550. [Google Scholar]
- Oweis, T.; Hachum, A. Water harvesting and supplemental irrigation for improved water productivity of dry farming systems in West Asia and North Africa. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrehiwot, T.; Van der Veen, A.; Maathuis, B. Spatial and temporal assessment of drought in the Northern highlands of Ethiopia. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, A.; Stroosnijder, L. Assessing drought risk and irrigation need in northern Ethiopia. Agr. Forest Meteorol. 2011, 151, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waglay, A.; Karboune, S.; Alli, I. Potato protein isolates: Recovery and characterization of their properties. Food Chem. 2014, 142, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Central Statistical Agency of Ethiopia (CSA). Agricultural Sample Survey 2016/2017: Report on Area and Production of Major Crops; CSA: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2017; Volume I, pp. 12–18.
- Grewal, J.S.; Sharma, R.C.; Saini, S.S. Agritechniques for Intensive Potato Cultivation in India; Publications and Information Division, Indian Council of Agricultural Research, Krishi Anusandhan Bhauan: New Delhi, India, 1992; 126p. [Google Scholar]
- Oweis, T.; Hachum, A. Supplemental irrigation for improved rainfed agriculture in WANA region. In Rainfed Agriculture: Unlocking the Potential; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2009; pp. 182–196. [Google Scholar]
- Nangia, V.; Oweis, T.; Francis, H.K.; Schnetzer, J. Supplemental irrigation: A promising climate-smart practice for dryland agriculture. In Climate-Smart Agriculture Practice Brief; CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS): Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hagos, B.G. Impact of agricultural technology adoption of smallholder farmers on wheat yield: Empirical evidence from Southern Tigray State of Ethiopia. J. Agric. Ext. Rural Dev. 2016, 8, 211–223. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop evapotranspiration: Guidelines for computing crop water requirements. In FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 300, p. D05109. [Google Scholar]
- NRCS; United States Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Plants Database. 1999. Available online: http://plants.usda.gov (accessed on 23 September 2024).
- Assefa, S.; Biazin, B.; Muluneh, A.; Yimer, F.; Haileslassie, A. Rainwater harvesting for supplement irrigation of onions in the southern dry lands of Ethiopia. Agric.Water Manag. 2016, 178, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Mylavarapu, R.; Sikora, F.J.; Moore, K.P. Walkley-Black Method. Soil Test Methods; from the Southeastern United States. 2014; p. 158. Available online: https://aesl.ces.uga.edu/Sera6/PUB/Methodsmanualfinalsera6.Pdf (accessed on 23 September 2024).
- Karam, F.; Rouphael, Y.; Ladoud, R.; Baried, J.; Colla, G. Influence of Genotypes and Potassium application rates on the yield and potassium use efficiency of potato. J. Agron. 2009, 8, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis; Prentice-Hall of India Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 1967; p. 498. [Google Scholar]
- Chapagain, T.R.; Tiwari, D.N.; Adhikaari, R.C.; Khatri, B.B.; Luitel, B. Performance of Potato Clones in Mid Hill of Western Nepal. In Proceedings of the National Potato Research Workshop, Lalitpur, Nepal, 31 March–2 April 2014; pp. 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ranganna, S. Manual of Analysis of Fruit and Vegetable products Central Food; Technological Research Institute Mysore: Columbus, OH, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Hassel, R.L.; Kelly, D.M.; Wittmeyer, E.C.; Wallace, C.; Grassbaugh, E.M.; Elliott, J.Y.; Wenneker, G.L. Ohio Potato Cultivar Trials; Ohio State University Horticulture Series; Ohio State University: Columbus, OH, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Raes, D.; Geerts, S.; Vandersypen, K. More Food, Less Water. In Lectures for the 21st Century; Raymaekers, B., Ed.; Leuven University Press: Leuven, Belgium, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ati, A.S.; Iyada, A.D.; Najim, S.M. Water use efficiency of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) under different irrigation methods and potassium fertilizer rates. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2012, 57, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E. Editorial note on terms for crop evapotranspiration, water use efficiency and water productivity. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 289, 108548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, T.; Erdem, Y.; Orta, H.; Okursoy, H. Water-yield relationships of potato under different irrigation methods and regimens. Sci. Agric. 2006, 63, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremedhin, T.; Haile, G.G.; Gebremicael, T.G.; Libsekal, H.; Reda, K.W. Balancing crop water requirements through supplemental irrigation under rainfed agriculture in a semi-arid environment. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantaw, S.; Ayalew, A.; Tadesse, D.; Agegnehu, E. Evaluation of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) varieties for yield and yield components. J. Hortic. For. 2019, 11, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Girma, T. Effect of Variety and Earthing up Frequency on Growth, Yield and Quality of Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) at Bure, Northwestern Ethiopia. Master’s Thesis, Jimma University, Jimma, Ethiopia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Asmita, O.; Rajkumari, A.D. Varietal evaluation of different potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) varieties. Pharma Innov. J. 2022, 11, 909–918. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, S.; Manandhar, H.K.; Shrestha, S.M.; Karkee, A. Response of local potato cultivars to late blight disease (Phytophthora infestans) under field and laboratory conditions at Pakhribas, Dhankuta, Nepal. Adv. Cytol. Pathol. 2019, 4, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuvaneswari, S.; Sharma, S.K.; Punitha, P.; Shashidhar, K.S.; Naveenkumar, K.L.; Prakash, N. Evaluation of morphological diversity of field pea [Pisum sativum subsp. arvense (L.)] germplasm under sub-tropical climate of Manipur. Legume Res. 2017, 40, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Bernier, J.; Verulkar, S.; Lafitte, H.R.; Atlin, G.N. Breeding for drought tolerance: Direct selection for yield, response to selection and use of drought-tolerant donors in upland and lowland-adapted populations. Field Crops Res. 2008, 107, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilate, B.; Mulualem, T. Performance evaluation of released and farmers’ potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) varieties in eastern Ethiopia. Sky J. Agric. Res. 2016, 5, 034–041. [Google Scholar]
- Lahlou, O.; Ouattar, S.; Ledent, J.F. The effect of drought and cultivar on growth parameters, yield and yield components of potato. Agronomie 2003, 23, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luitel, B.P.; Khatri, B.B.; Choudhary, D.; Paudel, B.P.; Jung-Sook, S.; Hur, O.S.; Baek, H.J.; Cheol, K.H.; Yul, R.K. Growth and Yield characters of potato genotypes grown in drought and irrigated conditions of Nepal. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djaman, K.; Irmak, S.; Koudahe, K.; Allen, S. Irrigation management in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) production: A review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luitel, B.P.; Bhandari, B.B.; Thapa, B. Evaluation of Potato Variety for Plant and Yield Characters in Field at Dailekh. Nepal J. Sci. Technol. 2020, 19, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessema, G.; Mohammed, W.; Abebe, T. Evaluation of Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) Varieties for Yield and Some Agronomic Traits. Open Agric. 2019, 5, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, E.T.; Azad, A.K.; Kabir, H.; Siddiq, A.B. Evolution of Six modern varieties of potatoes for yield, Pant Growth Parameters and Resistance to Insects and Diseases. Agric. Sci. 2017, 8, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Banjade, S.; Shrestha, S.M.; Pokhrel, N.; Pandey, D.; Rana, M. Evaluation of Growth and Yield Attributes of Commonly Grown Potato (Solanum tuberosum) Varieties at Kavre, Nepal. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2019, 9, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oweis, T.; Hachum, A. Improving water productivity in the dry areas of west Asia and North Africa. In Water Productivity in Agriculture: Limits and Opportunities for Improvement; Kijne, W.J., Barker, R., Molden, D., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2003; pp. 179–197. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, R.; Ravisankarmdin, N.N.; Ghoshal, C.S.; Ambast, S.K.; Subhash, C.; Babulal, M.M.; Subramani, T.T.; Ahmed, Z. Effect of supplemental irrigation on yield and water productivity of dry season crops in Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2011, 82, 122–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.; Rockstrom, J. Supplemental irrigation for dry-spell mitigation of rainfed agriculture in the Sahel. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 61, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna-Chopra, R.; Singh, S. Approaches to increase water use efficiency in horticultural and grain crops—An overview. Plant Stress 2011, 5, 52–63. [Google Scholar]
- Mazurczyk, W.; Wierbicka, A.; Trawczynski, C. Harvest index of potato crop grown under different nitrogen and water supply. Acta Sci. Pol. Agric. 2009, 8, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, S.; Aggarwal, P. Evaluation of antioxidant phytochemicals in different genotypes of potato. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2014, 4, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, H.; Ranjan, R.S. Effect of soil moisture deficit on marketable yield and quality of potatoes. Can. Biosyst. Eng. J. 2015, 57, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, J.C.; Starck, J.C.; Kleinofkopf, G.E. Infulence of irrigation and nitrogen management on yield and quality of Potato. Am. Potato J. 1999, 67, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldredge, E.P.; Holumes, Z.A.; Mosley, A.R.; Shock, C.C.; Steiber, T.D. Effect of transitory water stress on potato tuber stem-end reducing sugar and fry color. Am. Potato J. 1996, 73, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, B.B. Managing the Potato Production System; The Haworth Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Silveira, A.C.; Orena, S.; Medel-Maraboli, M.; Escalona, V.H. Determination of some functional and sensory attributes and suitability of colored- and non-colored-flesh potatoes for different cooking methods. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwona, M.; Krystyna Agnieszka, G.; Marek, G.; Anna, S. Total and Protein Nitrogen Content in Potato Tubers under the Influence of Various Care and Nutrition Methods with the Use of Biostimulants. J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 247–255. [Google Scholar]
- Zarzecka, K.; Gąsiorowska, B. The effect of varied care on the consumption value of edible potato. Zesz. Nauk. AP w Siedlcach Rol. 2002, 61, 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Marwaha, R.S.; Pandey, S.K.; Kumar, D.; Singh, S.V.; Kumer, P. Potato processing scenario in India: Industrial constraints, future projections, challenges ahead and remedies: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 47, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, M.A.; El-Tohamy, W.A.; Zaghloul, A.M. Yield and water use efficiency of potato grown under different irrigation and nitrogen levels in an arid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 110, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.Z.; Nishiyama, S.; Kang, Y. Effects of different irrigation regimes on the growth and yield of drip-irrigated potato. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 63, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.A.; Salih, S.A.; Mahmood, Y.A. The Effect of Different Irrigation Interval on Tuber Yield and Quality of Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Kurd. J. Appl. Res. 2018, 3, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Tolessa, E.S.; Belew, D.; Debela, A.; Kedi, B. Effect of Nitrogen Rates and Irrigation Regimes on Water Use Efficiency of Selected Potato Varieties in Jimma Zone, West Ethiopia. Adv. Crop Sci. Technol. 2016, 4, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).