Assessing the Impact of Saline Irrigation Water on Durum Wheat (cv. Faraj) Grown on Sandy and Clay Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
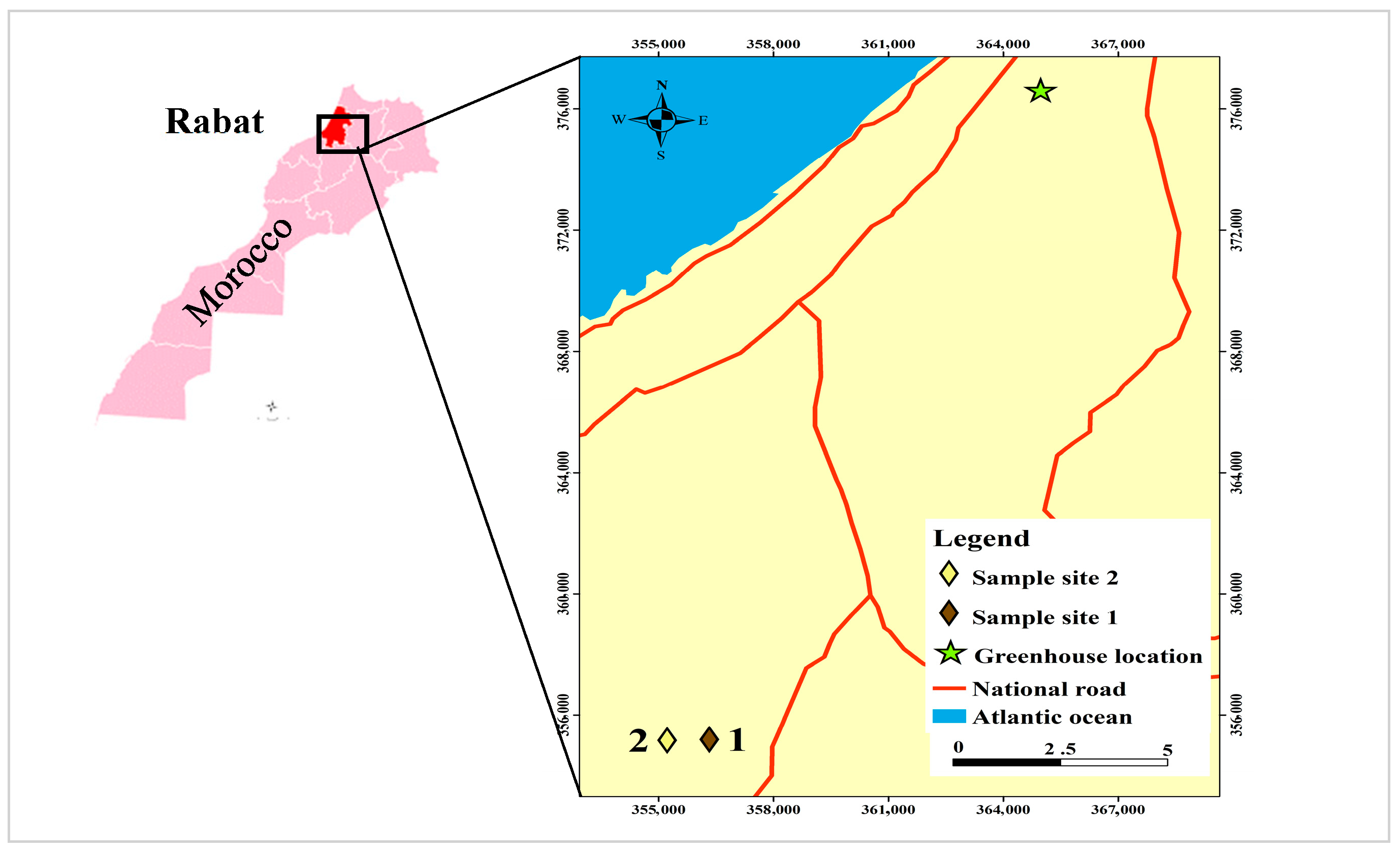
2.1. Test Site and Field Sampling
2.2. Plant Material
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Irrigation Practices in Greenhouse Cultivation
2.5. Fertilization and Phytosanitary Treatment
2.6. Germination Test
2.7. Analytical Methods
2.7.1. Analysis of Physicochemical Soil Parameters
2.7.2. Physiological and Biochemical Assessment
2.7.3. Yield Component Analysis
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Laboratory Results
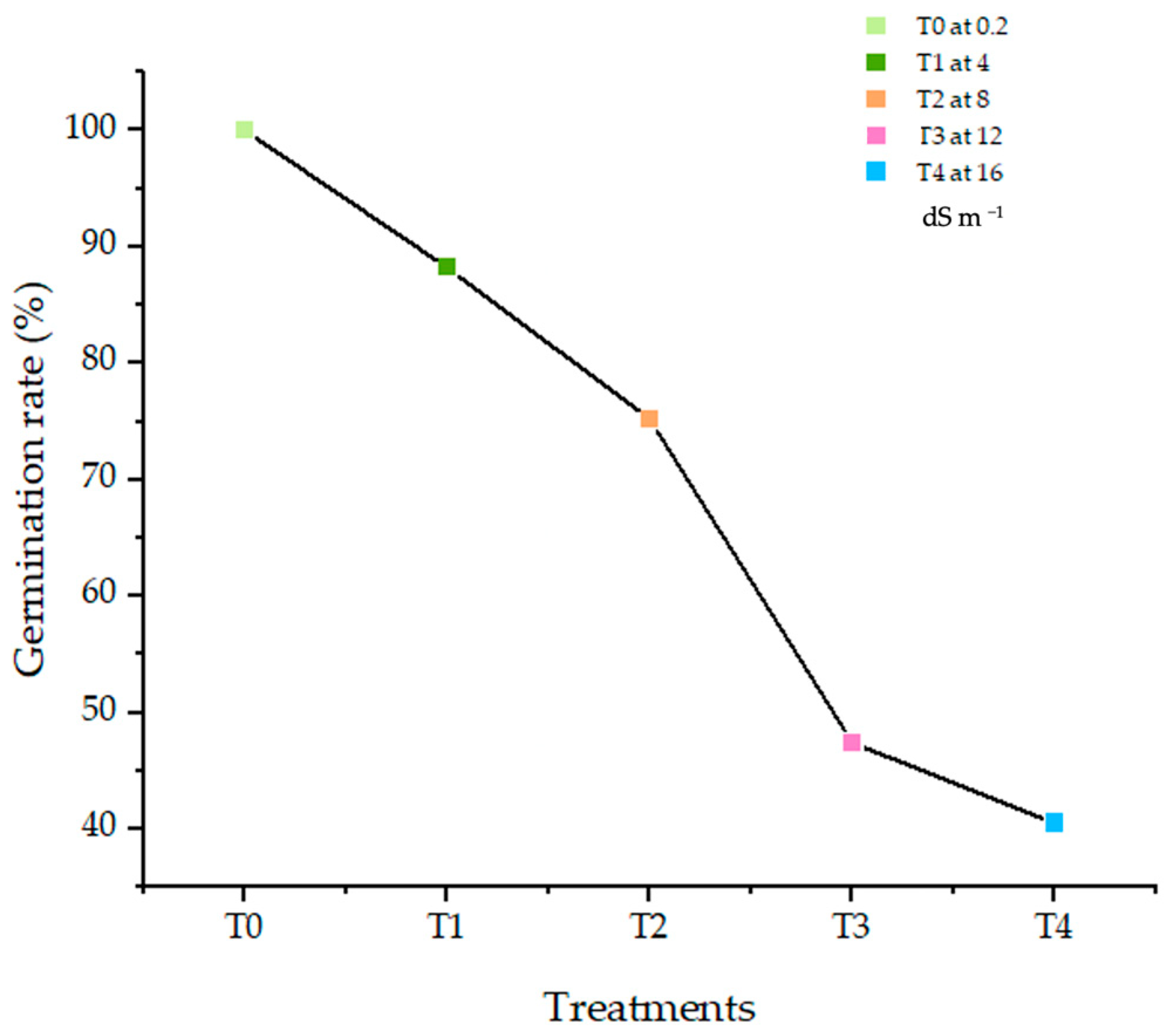
3.2. Effect of Salt Stress on the Germination Dynamics of Durum Wheat
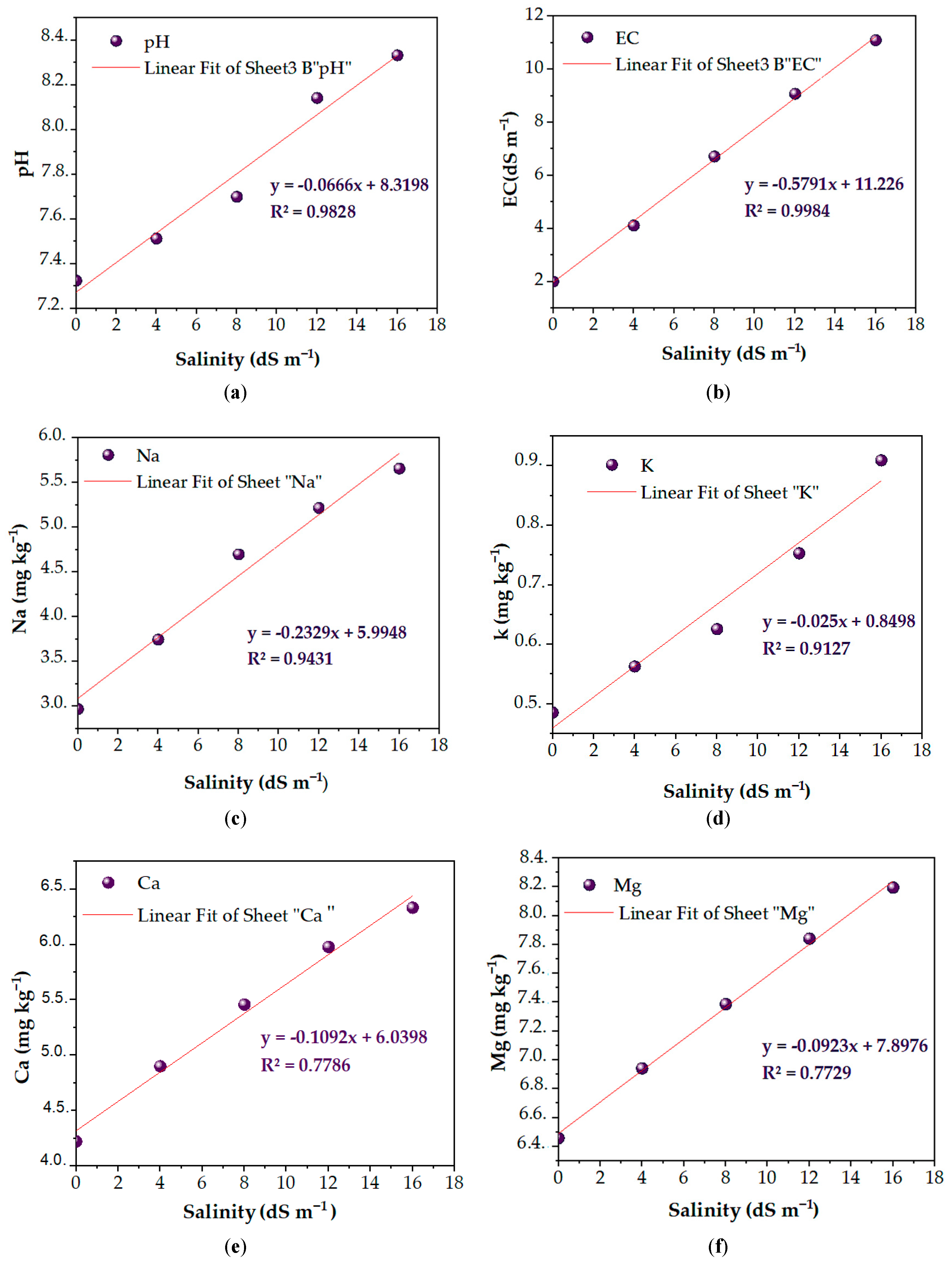
3.3. Effect of Salt Stress on the Chemical Parameters of the Soil
3.4. Relationship Between Salinity and Chemical Parameters
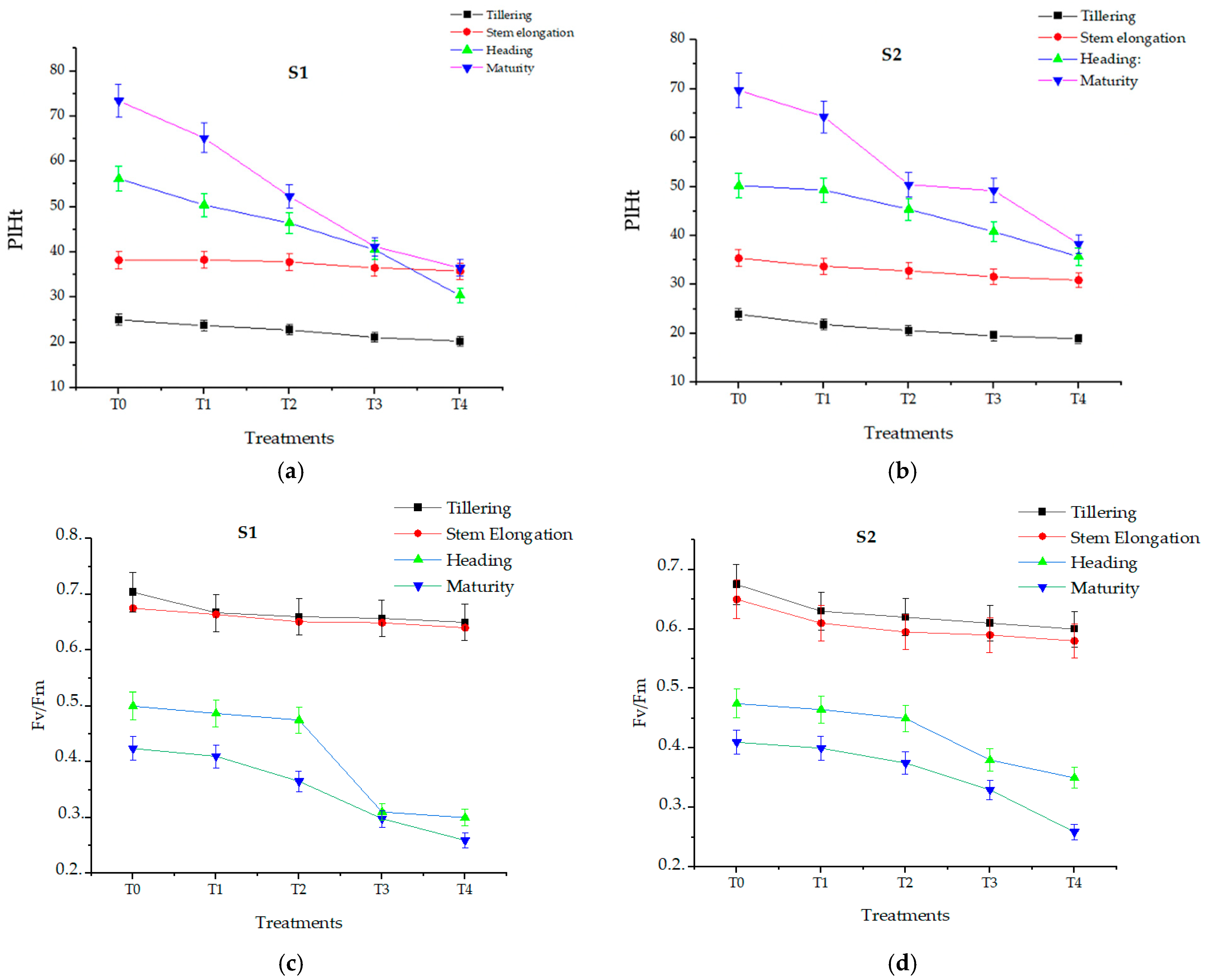
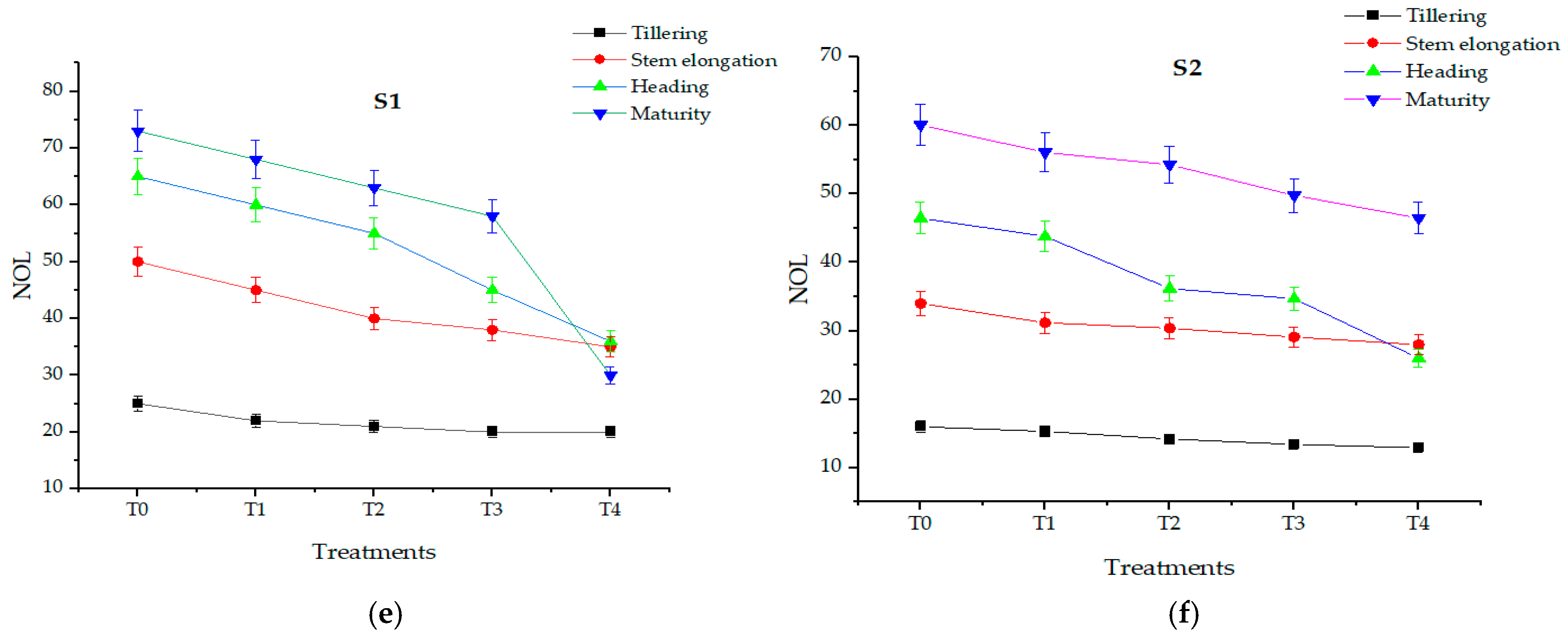
3.5. Effect of Salt Levels on Growth Parameters and Photosynthetic Efficiency
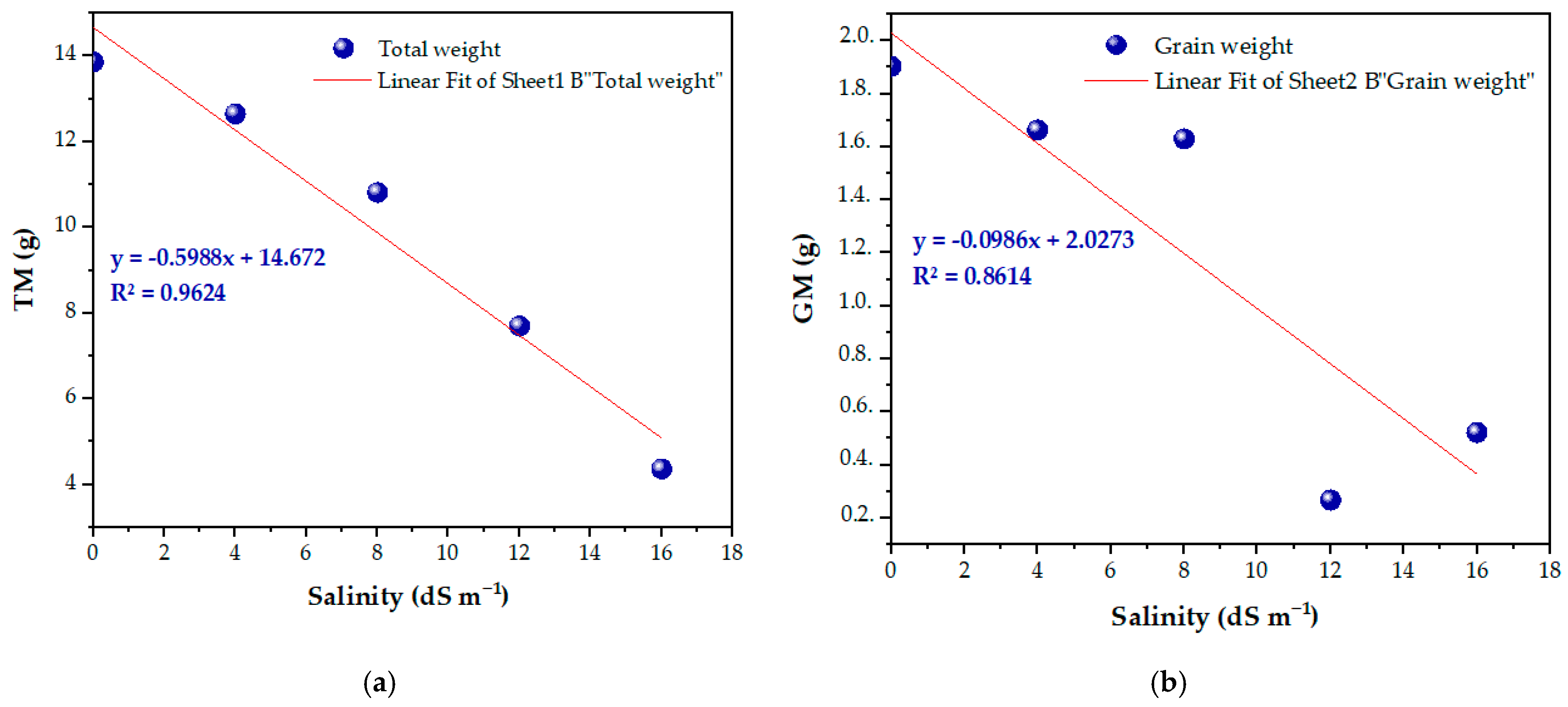
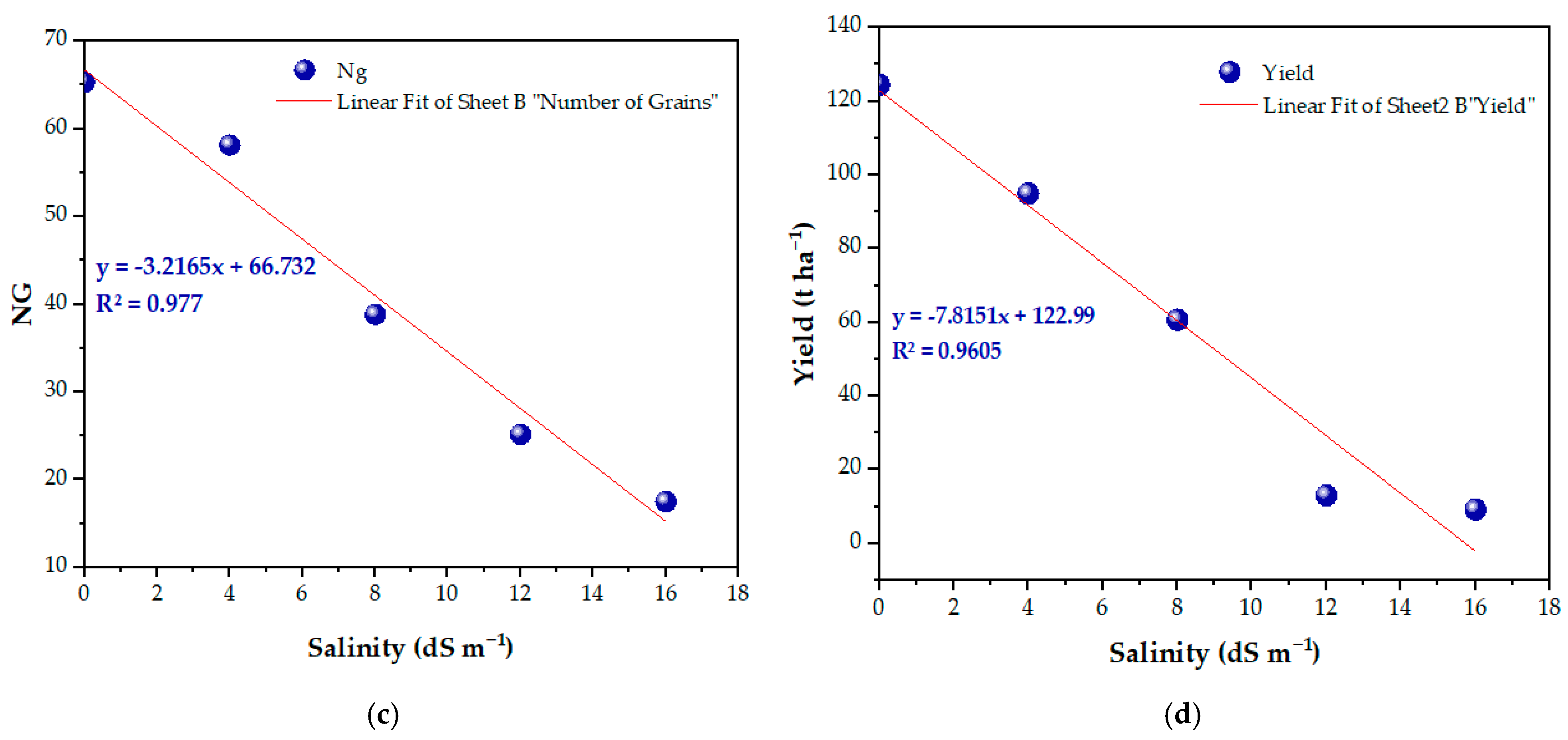
3.6. Yield Parameters and Salt Tolerance Threshold of the Variety
3.7. Relationship Between Salinity and Various Yield Components
4. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pawlak, K.; Kołodziejczak, M. The Role of Agriculture in Ensuring Food Security in Developing Countries: Considerations in the Context of the Problem of Sustainable Food Production. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of Salinity Tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchanda, G.; Garg, N. Salinity and Its Effects on the Functional Biology of Legumes. Acta Physiol. Plant 2008, 30, 595–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zörb, C.; Geilfus, C.-M.; Dietz, K.-J. Salinity and Crop Yield. Plant Biol. J. 2019, 21, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtak, K.; Wolińska, A. The Impact of Extreme Weather Events as a Consequence of Climate Change on the Soil Moisture and on the Quality of the Soil Environment and Agriculture—A Review. CATENA 2023, 231, 107378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanad, H.; Oueld Lhaj, M.; Zouahri, A.; Saafadi, L.; Dakak, H. Groundwater Pollution by Nitrate and Salinization in Morocco: A Comprehensive Review. J. Water Health 2024, 22, 1756–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Lockington, D. Numerical Study of Evaporation-induced Salt Accumulation and Precipitation in Bare Saline Soils: Mechanism and Feedback. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 8084–8106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozema, J.; Flowers, T. Crops for a Salinized World. Science 2008, 322, 1478–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmjid, Z.; Hallam, J.; Dakak, H.; Douaik, A.; Oumaima, I. Soil Salinity: A Challenge for the Resilience of Ecosystems and the Sustainability of Moroccan Agriculture. Afr. Med. Agric. J. 2024, 143, 135–155. [Google Scholar]
- Munns, R.; Gilliham, M. Salinity Tolerance of Crops—What Is the Cost? New Phytol. 2015, 208, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddiq, M.S.; Afzal, I.; Basra, S.M.A.; Iqbal, S.; Ashraf, M. Sodium Exclusion Affects Seed Yield and Physiological Traits of Wheat Genotypes Grown Under Salt Stress. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 1442–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chele, K.H.; Tinte, M.M.; Piater, L.A.; Dubery, I.A.; Tugizimana, F. Soil Salinity, a Serious Environmental Issue and Plant Responses: A Metabolomics Perspective. Metabolites 2021, 11, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheiralipour, K.; Brandão, M.; Holka, M.; Choryński, A. A Review of Environmental Impacts of Wheat Production in Different Agrotechnical Systems. Resources 2024, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Liu, C.; Xie, J.; Han, L.; Zhang, C.; Guo, D.; Niu, J.; Jin, H.; McConkey, B.G. Life Cycle Assessment on Agricultural Production: A Mini Review on Methodology, Application, and Challenges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinci, G.; Ruggieri, R.; Ruggeri, M.; Zaki, M.G. Application of Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) to Cereal Production: An Overview. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1077, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagothu, U.S. (Ed.) Agricultural Development and Sustainable Intensification: Technology and Policy Challenges in the Face of Climate Change, 1st ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-0-203-73330-1. [Google Scholar]
- Horrigan, L.; Lawrence, R.S.; Walker, P. How Sustainable Agriculture Can Address the Environmental and Human Health Harms of Industrial Agriculture. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khondoker, M.; Mandal, S.; Gurav, R.; Hwang, S. Freshwater Shortage, Salinity Increase, and Global Food Production: A Need for Sustainable Irrigation Water Desalination—A Scoping Review. Earth 2023, 4, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanick, B.; Kumar, M.; Naik, B.M.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Singh, S.V. Soil Carbon-Nutrient Cycling, Energetics, and Carbon Footprint in Calcareous Soils with Adoption of Long-Term Conservation Tillage Practices and Cropping Systems Diversification. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uri, N. Cropland Soil Salinization and Associated Hydrology: Trends, Processes and Examples. Water 2018, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiriano, E.; Ruiz, M.; Fité, R.; Carrillo, J.M. Analysis of Genetic Variability in a Sample of the Durum Wheat (Triticum Durum Desf.) Spanish Collection Based on Gliadin Markers. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2006, 53, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pastuszak, J.; Dziurka, M.; Hornyák, M.; Szczerba, A.; Kopeć, P.; Płażek, A. Physiological and Biochemical Parameters of Salinity Resistance of Three Durum Wheat Genotypes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, N.; Ghaffar, A.; Zafar, Z.U.; Javed, M.; Shah, K.H.; Noreen, S.; Manzoor, H.; Iqbal, M.; Hassan, I.F.Z.; Bano, H.; et al. Identification of Novel Source of Salt Tolerance in Local Bread Wheat Germplasm Using Morpho-Physiological and Biochemical Attributes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotula, L.; Zahra, N.; Farooq, M.; Shabala, S.; Siddique, K.H.M. Making Wheat Salt Tolerant: What Is Missing? Crop J. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, H.; Moussadek, R.; Ghanimi, A.; Zouidi, O.; Douaik, A.; Dakak, H.; Amenzou, N.E.; Zouahri, A. Effect of Tillage and Nitrogen Fertilization on Soil Properties and Yield of Five Durum Wheat Germoplasms in a Dry Area of Morocco. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Working Group World Reference Base International Union of Soil Sciences World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2006: A Framework for International Classification, Correlation and Communication; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006.
- Maas, E.V.; Lesch, S.M.; Francois, L.E.; Grieve, C.M. Contribution of Individual Culms to Yield of Salt-Stressed Wheat. Crop Sci. 1996, 36, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, J.C.; Gunn, B.V. Treatments to Promote Seed Germination in Australian Acacias; Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research (ACIAR): Canberra, Australia, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Bouyoucos, G.J. Hydrometer Method Improved for Making Particle Size Analyses of Soils. Agron. J. 1962, 54, 464–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowell, D.L. Soil Science: Methods & Applications; Routledge: London, UK, 2014; ISBN 978-1-315-84485-5. [Google Scholar]
- Page, A.L. (Ed.) Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Agronomy; American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Van Reeuwijk, L.P. Procedures for Soil Analysis; Technical Paper; International Soil Reference and Information Centre: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis: Advanced Course: A Manual of Methods Useful for Instruction and Research in Soil Chemistry, Physical Chemistry of Soils, Soil Fertility, and Soil Genesis; UW-Madison Libraries Parallel Press: London, UK, 1958; ISBN 978-1-893311-47-3. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.R.; Cole, C.V.; Watanabe, F.S.; Dean, L.A. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Aggag, A.M.; Alharbi, A. Spatial Analysis of Soil Properties and Site-Specific Management Zone Delineation for the South Hail Region, Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, C.; Basti, S.; Pradhan, R. Kumar Physicochemical Properties of Soil under Different Land Use Practices Located near Bhawanipatna Town in Odisha, India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 6, 941–953. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils. US Department of Agriculture. Agricultural Handbook No. 60, Washington DC, 7-53. Soil Sci. 1954, 78, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharal, S.; Khanal, B.R.; Panday, D. Assessment of Soil Fertility under Different Land-Use Systems in Dhading District of Nepal. Soil Syst. 2018, 2, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazelton, P.; Murphy, B. Interpreting Soil Test Results: What Do All the Numbers Mean? CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 2007; ISBN 978-0-643-09468-0. [Google Scholar]
- Szabolcs, I.; Várallyay, G. Review of Research on Salt-Affected Soils; Natural Resources Research; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1979; ISBN 978-92-3-101613-4. [Google Scholar]
- Baruah, T.C.; Barthakur, H.P. A Textbook of Soil Analysis; Vikas Publishing House PVT Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hmissi, M.; Chaieb, M.; Krouma, A. Differences in the Physiological Indicators of Seed Germination and Seedling Establishment of Durum Wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) Cultivars Subjected to Salinity Stress. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandil, A.A.; Sharief, A.E.; Abido, W.A.E.; Ibrahim, M.M. Effect of Salinity on Seed Germination and Seedling Characters of Some Forage Sorghum Cultivars. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 4, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.R.; Chaudhry, R.; Singh, A.; Singh, P.K. Salt Tolerance of Sorghum Bicolor Cultivars during Germination and Seedling Growth. Res. J. Recent Sci. 2012, 2277, 2502. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, E.V.; Hoffman, G.J. Crop Salt Tolerance—Current Assessment. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. 1977, 103, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.; Serralheiro, R. Soil Salinity: Effect on Vegetable Crop Growth. Management Practices to Prevent and Mitigate Soil Salinization. Horticulturae 2017, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Naim, A.M.; Mohammed, K.E.; Ibrahim, E.A.; Suleiman, N.N. Impact of Salinity on Seed Germination and Early Seedling Growth of Three Sorghum (Sorghum biolor L. Moench) Cultivars. SCIT 2012, 2, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troyo-Diéguez, E.; Murillo-Amador, B. Effects of Salinity on the Germination and Seedling Characteristics of Cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.]. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2000, 40, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbarki, S.; Skalicky, M.; Vachova, P.; Hajihashemi, S.; Jouini, L.; Zivcak, M.; Tlustos, P.; Brestic, M.; Hejnak, V.; Zoghlami Khelil, A. Comparing Salt Tolerance at Seedling and Germination Stages in Local Populations of Medicago ciliaris L. to Medicago intertexta L. and Medicago scutellata L. Plants 2020, 9, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alom, R.; Hasan, M.A.; Islam, M.R.; Wang, Q.-F. Germination Characters and Early Seedling Growth of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Genotypes under Salt Stress Conditions. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 19, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łuczak, K.; Czerniawska-Kusza, I.; Rosik-Dulewska, C.; Kusza, G. Effect of NaCl Road Salt on the Ionic Composition of Soils and Aesculus hippocastanum L. Foliage and Leaf Damage Intensity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuna, A.L.; Kaya, C.; Higgs, D.; Murillo-Amador, B.; Aydemir, S.; Girgin, A.R. Silicon Improves Salinity Tolerance in Wheat Plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2008, 62, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketehouli, T.; Idrice Carther, K.F.; Noman, M.; Wang, F.-W.; Li, X.-W.; Li, H.-Y. Adaptation of Plants to Salt Stress: Characterization of Na+ and K+ Transporters and Role of CBL Gene Family in Regulating Salt Stress Response. Agronomy 2019, 9, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartzoulakis, K.; Klapaki, G. Response of Two Greenhouse Pepper Hybrids to NaCl Salinity during Different Growth Stages. Sci. Hortic. 2000, 86, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wu, D.; Zhang, G. Advances in Studies on Ion Transporters Involved in Salt Tolerance and Breeding Crop Cultivars with High Salt Tolerance. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2020, 21, 426–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.I.; Dular, A.K.; Solomon, D.M. Biodiversity Conservation in the Thar Desert; with Emphasis on Endemic and Medicinal Plants. Environmentalist 2003, 23, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S.; Mishra, B.; Gupta, S.R. Effects of Soil Salinity and Alkalinity on Grain Quality of Tolerant, Semi-Tolerant and Sensitive Rice Genotypes. Rice Sci. 2013, 20, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, H.; McNeal, B.; O’Connor, G. Soil Chemistry. Soil Sci. 1980, 129, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sritongon, N.; Sarin, P.; Theerakulpisut, P.; Riddech, N. The Effect of Salinity on Soil Chemical Characteristics, Enzyme Activity and Bacterial Community Composition in Rice Rhizospheres in Northeastern Thailand. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, H.; Lan, L.; Huang, R.; Deng, X.; Peng, Y. Effects of Exponential N Application on Soil Exchangeable Base Cations and the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Clonal Chinese Fir Seedlings. Plants 2023, 12, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Motos, J.; Ortuño, M.; Bernal-Vicente, A.; Diaz-Vivancos, P.; Sanchez-Blanco, M.; Hernandez, J. Plant Responses to Salt Stress: Adaptive Mechanisms. Agronomy 2017, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Bu, W.; Xu, Y.; Fei, H.; Zhu, Y.; Ahmad, I.; Nimir, N.E.A.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, G. Effects of Salt Stress on Physiological and Agronomic Traits of Rice Genotypes with Contrasting Salt Tolerance. Plants 2024, 13, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Fricke, W. Salt Stress—Regulation of Root Water Uptake in a Whole-Plant and Diurnal Context. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyro, H.-W. Effect of Salinity on Growth, Photosynthesis, Water Relations and Solute Composition of the Potential Cash Crop Halophyte Plantago coronopus (L.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2006, 56, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALKahtani, M.D.F.; Attia, K.A.; Hafez, Y.M.; Khan, N.; Eid, A.M.; Ali, M.A.M.; Abdelaal, K.A.A. Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters and Antioxidant Defense System Can Display Salt Tolerance of Salt Acclimated Sweet Pepper Plants Treated with Chitosan and Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, G.; Huo, J.; Yang, X.; Mei, W.; Zhang, R.; Khan, A.; Feng, N.; Zheng, D. Photosynthetic Mechanisms Underlying NaCl-Induced Salinity Tolerance in Rice (Oryza sativa). BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roșca, M.; Mihalache, G.; Stoleru, V. Tomato Responses to Salinity Stress: From Morphological Traits to Genetic Changes. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1118383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Zou, D.; Zhao, H. Influence of Natural Saline-Alkali Stress on Chlorophyll Content and Chloroplast Ultrastructure of Two Contrasting Rice (Oryza sativa L. Japonica) Cultivars. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 7, 289–292. [Google Scholar]
- Taïbi, K.; Taïbi, F.; Ait Abderrahim, L.; Ennajah, A.; Belkhodja, M.; Mulet, J.M. Effect of Salt Stress on Growth, Chlorophyll Content, Lipid Peroxidation and Antioxidant Defence Systems in Phaseolus vulgaris L. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2016, 105, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debouba, M.; Gouia, H.; Suzuki, A.; Ghorbel, M.H. NaCl Stress Effects on Enzymes Involved in Nitrogen Assimilation Pathway in Tomato “Lycopersicon esculentum” Seedlings. J. Plant Physiol. 2006, 163, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikobe, T.B.; Mashile, B.; Sinthumule, R.R.; Ruzvidzo, O. Distinct Morpho-Physiological Responses of Maize to Salinity Stress. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 946–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanov, M.A.; Rashkov, G.D.; Borisova, P.B.; Apostolova, E.L. Changes in Photosystem II Complex and Physiological Activities in Pea and Maize Plants in Response to Salt Stress. Plants 2024, 13, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, P.; Jajoo, A.; Mathur, S.; Bharti, S. Chlorophyll a Fluorescence Study Revealing Effects of High Salt Stress on Photosystem II in Wheat Leaves. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, Y.; Singh, P.; Siddiqui, H.; Bajguz, A.; Hayat, S. Salinity Induced Physiological and Biochemical Changes in Plants: An Omic Approach towards Salt Stress Tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 156, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S.; Munns, R. Salinity Stress: Physiological Constraints and Adaptive Mechanisms. In Plant Stress Physiology; Shabala, S., Ed.; CABI: London, UK, 2012; pp. 59–93. ISBN 978-1-84593-996-0. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Choudhary, K.K.; Chaudhary, N.; Gupta, S.; Sahu, M.; Tejaswini, B.; Sarkar, S. Salt Stress Resilience in Plants Mediated through Osmolyte Accumulation and Its Crosstalk Mechanism with Phytohormones. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1006617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Schmidhalter, U. Drought and Salinity: A Comparison of Their Effects on Mineral Nutrition of Plants. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenk. 2005, 168, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goussi, R.; Manaa, A.; Derbali, W.; Cantamessa, S.; Abdelly, C.; Barbato, R. Comparative Analysis of Salt Stress, Duration and Intensity, on the Chloroplast Ultrastructure and Photosynthetic Apparatus in Thellungiella salsuginea. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 183, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzen, B.M.; Smart, C.M.; Maricle, K.L.; MariCle, B.R. Effects of Increasing Salinity on Photosynthesis and Plant Water Potential in Kansas Salt Marsh Species. Trans. Kans. Acad. Sci. 2019, 122, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.A.; Zaman, M.; Heng, L. Soil Salinity: Historical Perspectives and a World Overview of the Problem. In Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques; Zaman, M., Shahid, S.A., Heng, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 43–53. ISBN 978-3-319-96190-3. [Google Scholar]
- Akbarimoghaddam, H.; Galavi, M.; Ghanbari, A.; Panjehkeh, N. Salinity Effects on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Bread Wheat Cultivars. Agronomy 2023, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihmar, M.; Sharma, J.K.; Rani Santal, A.; Singh, N.P. Assessment of salinity stress effect on six contrasting wheat genotypes during grain filling in simulated field growing conditions. Cereal Res. Commun. 2023, 52, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.S. Westcot Water Quality for Agriculture; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1994; ISBN 92-5-102263-1. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, E.V.; Grattan, S.R. Crop Yields as Affected by Salinity. In Agronomy Monographs; Skaggs, R.W., Van Schilfgaarde, J., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2015; pp. 55–108. ISBN 978-0-89118-230-6. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, G.; Saqib, M.; Rafique, Q.; Rahman, M.; Javaid, A.; Anwar-ul-Haq, M.; Nasim, M. Effect of Salinity on Grain Yield and Grain Quality of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Pak. J. Agric. Res 2013, 50, 185–189. [Google Scholar]
- Hannachi, S.; Steppe, K.; Eloudi, M.; Mechi, L.; Bahrini, I.; Van Labeke, M.-C. Salt Stress Induced Changes in Photosynthesis and Metabolic Profiles of One Tolerant (‘Bonica’) and One Sensitive (‘Black Beauty’) Eggplant Cultivars (Solanum melongena L.). Plants 2022, 11, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ramady, H.; Prokisch, J.; Mansour, H.; Bayoumi, Y.A.; Shalaby, T.A.; Veres, S.; Brevik, E.C. Review of Crop Response to Soil Salinity Stress: Possible Approaches from Leaching to Nano-Management. Soil Syst. 2024, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sané, A.K.; Diallo, B.; Kane, A.; Sagna, M.; Sané, D.; Sy, M.O. In Vitro Germination and Early Vegetative Growth of Five Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Am. J. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 796–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieve, C.; Grattan, S. Mineral Nutrient Acquisition and Response by Plants Grown in Saline Environments. In Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress, 2nd ed.; Pessarakli, M., Ed.; Books in Soils, Plants, and the Environment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; Volume 19990540, pp. 203–229. ISBN 978-0-8247-1948-7. [Google Scholar]
- Munns, R.; Termaat, A. Whole-Plant Responses to Salinity. Funct. Plant Biol. 1986, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.L.; Coelho, E.F.; Coelho Filho, M.A.; Santos, A.A.D. Salinity Reduces Nutrients Absorption and Efficiency of Their Utilization in Cassava Plants. Cienc. Rural 2018, 48, e20180351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanad, H.; Mouhir, L.; Zouahri, A.; Moussadek, R.; El Azhari, H.; Hasna, Y.; Ghanimi, A.; Oueld Lhaj, M.; Dakak, H. Assessment of Groundwater Quality Using the Pollution Index of Groundwater (PIG), Nitrate Pollution Index (NPI), Water Quality Index (WQI), Multivariate Statistical Analysis (MSA), and GIS Approaches: A Case Study of the Mnasra Region, Gharb Plain, Morocco. Water 2024, 16, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oueld Lhaj, M.; Moussadek, R.; Mouhir, L.; Mdarhri Alaoui, M.; Sanad, H.; Iben Halima, O.; Zouahri, A. Assessing the Evolution of Stability and Maturity in Co-Composting Sheep Manure with Green Waste Using Physico-Chemical and. Biological Properties and Statistical Analyses: A Case Study of Botanique Garden in Rabat, Morocco. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanad, H.; Moussadek, R.; Dakak, H.; Zouahri, A.; Oueld Lhaj, M.; Mouhir, L. Ecological and Health Risk Assessment of HeavyMetals in Groundwater within an Agricultural Ecosystem Using GIS and Multivariate Statistical Analysis (MSA): A Case Study of the Mnasra Region, Gharb Plain, Morocco. Water 2024, 16, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, M.; Waheed, A.; Wahab, A.; Majeed, M.; Nazim, M.; Liu, Y.-H.; Li, L.; Li, W.-J. Soil Salinity and Drought Tolerance: An Evaluation of Plant Growth, Productivity, Microbial Diversity, and Amelioration Strategies. Plant Stress 2023, 11, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, T.B.; Ribas, A.F.; Hülse de Souza, S.G.; Budzinski, I.G.F.; Domingues, D.S. Physiological Responses to Drought, Salinity, and Heat Stress in Plants: A Review. Stresses 2022, 2, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parul, K.A.; Chourasia, S.; Kumar, R.; Devi, G.; Kumar, A.; Mann, A.; Sheoran, P.; Sanwal, S.K. Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Responses to Salt Stress and Seed Priming Approach to Enhance Salt Tolerance in Bread Wheat. In Salinity and Drought Tolerance in Plants; Kumar, A., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 61–86. [Google Scholar]
- Soni, S.; Jha, A.B.; Dubey, R.S.; Sharma, P. Nanowonders in Agriculture: Unveiling the Potential of Nanoparticles to Boost Crop Resilience to Salinity Stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 925, 171433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Wheat Variety | Faraj |
|---|---|
| The official year of inscription | 2007 |
| Quality: | |
| * Quality characteristics | 15.3% |
| * Yellow index | 29 |
| Drought resistance | Moderately resistant |
| Cycle duration | 154 days |
| Yield (t ha−1): | |
| * Favorable areas | 5.9 |
| * Semi-arid areas | 3.8 |
| Granulometry | S1 | S2 |
|---|---|---|
| Sand (%) | 13.1 | 87.6 |
| Silt (%) | 34.3 | 6.40 |
| Clay (%) | 52.6 | 6.00 |
| Chemical Properties | ||
| pH | 7.80 | 8.40 |
| EC (dS m−1) | 0.20 | 0.51 |
| OM (%) | 1.33 | 1.18 |
| CEC (cmol kg−1) | 0.65 | 0.40 |
| Macronutrients of soils | ||
| N (%) | 0.078 | 0.024 |
| Av.P (mg kg−1) | 120 | 140 |
| Ex.K (mg kg−1) | 229 | 325 |
| Na (mg kg−1) | 1.50 | 2.50 |
| Ca (mg kg−1) | 5.20 | 2.50 |
| Mg (mg kg−1) | 5.00 | 2.50 |
| Cl (mg kg−1) | 0.20 | 0.40 |
| Chemical Variables | pH | EC | K | Na | Ca | Mg | Cl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable Source | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value |
| Sampling (S) | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** |
| Soil (So) | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** |
| Salinity (Sa) | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** |
| S × So | 0.06 ns | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** |
| S × Sa | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | 0.005 ** | 0.002 ** | <0.001 *** |
| So × Sa | 0.006 | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | 0.111 ns | 0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | 0.013 * |
| S × So × Sa | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | 0.008 ** | 0.082 ns | 0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | 0.002 ** |
| Salinity (dS m−1) | Soil Type | pH | EC (dS m−1) | Na (mg kg−1) | K (dS m−1) | Ca (dS m−1) | Mg (dS m−1) | Cl (dS m−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | S1 | 7.20 ± 0.14 | 1.28 ± 0.74 | 2.85 ± 1.04 | 0.45 ± 0.08 | 4.79 ± 0.75 | 6.86 ± 0.59 | 12.45 ± 1.93 |
| S2 | 7.45 ± 0.13 | 2.71 ± 1.52 | 3.09 ± 1.08 | 0.51 ± 0.07 | 3.65 ± 0.80 | 6.05 ± 0.40 | 13.16 ± 1.70 | |
| 4 | S1 | 7.35 ± 0.15 | 3.27 ± 1.28 | 3.64 ± 1.09 | 0.53 ± 0.07 | 5.25 ± 0.76 | 7.34 ± 0.50 | 13.48 ± 1.66 |
| S2 | 7.68 ± 0.08 | 4.25 ± 2.29 | 3.85 ± 1.28 | 0.59 ± 0.10 | 4.55 ± 0.87 | 6.54 ± 0.59 | 13.97 ± 1.74 | |
| 8 | S1 | 7.53 ± 0.16 | 6.05 ± 2.83 | 5.02 ± 1.31 | 0.60 ± 0.08 | 5.80 ± 0.82 | 7.91 ± 0.34 | 15.95 ± 1.11 |
| S2 | 7.86 ± 0.12 | 7.63 ± 3.67 | 4.82 ± 1.30 | 0.64 ± 0.12 | 5.11 ± 0.72 | 6.85 ± 0.75 | 15.72 ± 0.68 | |
| 12 | S1 | 7.93 ± 0.35 | 8.52 ± 4.08 | 5.02 ± 1.31 | 0.67 ± 0.10 | 6.32 ± 0.81 | 8.25 ± 0.39 | 14.86 ± 1.47 |
| S2 | 7.93 ± 0.35 | 9.62 ± 4.28 | 5.40 ± 1.47 | 0.83 ± 0.27 | 5.63 ± 0.76 | 7.43 ± 0.69 | 16.35 ± 0.89 | |
| 16 | S1 | 8.14 ± 0.35 | 10.93 ± 5.16 | 5.50 ± 1.3 | 0.89 ± 0.23 | 6.62 ± 0.75 | 8.85 ± 0.49 | 16.45 ± 1.23 |
| S2 | 8.52 ± 0.30 | 11.25 ± 5.13 | 5.81 ± 1.5 | 0.92 ± 0.31 | 6.04 ± 0.80 | 7.80 ± 0.76 | 16.78 ± 1.14 | |
| Mean | 0.2 | 7.32 a | 2.00 a | 2.97 a | 0.48 a | 4.22 a | 6.45 a | 13.70 a |
| 4 | 7.51 b | 3.76 b | 3.74 b | 0.56 b | 4.90 b | 6.94 b | 13.72 b | |
| 8 | 7.69 c | 6.84 c | 4.92 c | 0.62 c | 5.45 c | 7.38 c | 15.83 c | |
| 12 | 8.14 d | 9.07 d | 5.21 d | 0.75 d | 5.84 d | 7.84 d | 15.60 d | |
| 16 | 8.33 e | 11.09 e | 5.65 e | 0.90 e | 6.33 e | 8.32 e | 16.61 e |
| Salinity (dS m−1) | Soil Type | Grain Yield (t ha−1) | 200-Grain Weight (g) | Straw (t ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | S1 | 1.12 (1.80) | 67.00(1.00) | 1.24 (1.0) |
| S2 | 0.56 (13.70) | 63.6 (1.50) | 1.16 (1.1) | |
| 4 | S1 | 0.70 (15.60) | 38.5 (7.60) | 1.18 (0.4) |
| S2 | 0.40 (13.60) | 58.0 (4.30) | 1.03 (0.8) | |
| 8 | S1 | 0.38 (15.60) | 34.6 (1.50) | 0.97 (0.1) |
| S2 | 0.23 (9.90) | 29.0 (1.70) | 0.86 (0.1) | |
| 12 | S1 | 0.18 (0.20) | 29.3 (1.50) | 0.80 (0.7) |
| S2 | 0.14 (2.30) | 21.0 (2.00) | 0.65 (0.1) | |
| T6 | S1 | 0.16 (0.10) | 11.6 (1.50) | 0.55 (0.3) |
| S2 | 0.12 (0.70) | 7.3 (2.50) | 0.20 (0.6) | |
| Mean | 0.2 | 0.84 a | 65.30 a | 1.20 a |
| 4 | 0.55 b | 48.20 b | 1.10 b | |
| 8 | 0.30 c | 38.80 c | 0.91 c | |
| 12 | 0.16 d | 25.10 c | 0.72 c | |
| 16 | 0.14 d | 14.50 d | 0.37 d |
| Yield Parameters | Grain Yield (t ha−1) | 200 Grain Weight (g) | Straw (t ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable Source | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value |
| Soil (So) | 0.250 ns | 0.259 ns | <0.001 *** |
| Salinity (Sa) | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** |
| So × Sa | 0.451 ns | <0.001 *** | 0.005 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manhou, K.; Moussadek, R.; Yachou, H.; Zouahri, A.; Douaik, A.; Hilal, I.; Ghanimi, A.; Hmouni, D.; Dakak, H. Assessing the Impact of Saline Irrigation Water on Durum Wheat (cv. Faraj) Grown on Sandy and Clay Soils. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122865
Manhou K, Moussadek R, Yachou H, Zouahri A, Douaik A, Hilal I, Ghanimi A, Hmouni D, Dakak H. Assessing the Impact of Saline Irrigation Water on Durum Wheat (cv. Faraj) Grown on Sandy and Clay Soils. Agronomy. 2024; 14(12):2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122865
Chicago/Turabian StyleManhou, Khadija, Rachid Moussadek, Hasna Yachou, Abdelmjid Zouahri, Ahmed Douaik, Ismail Hilal, Ahmed Ghanimi, Driss Hmouni, and Houria Dakak. 2024. "Assessing the Impact of Saline Irrigation Water on Durum Wheat (cv. Faraj) Grown on Sandy and Clay Soils" Agronomy 14, no. 12: 2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122865
APA StyleManhou, K., Moussadek, R., Yachou, H., Zouahri, A., Douaik, A., Hilal, I., Ghanimi, A., Hmouni, D., & Dakak, H. (2024). Assessing the Impact of Saline Irrigation Water on Durum Wheat (cv. Faraj) Grown on Sandy and Clay Soils. Agronomy, 14(12), 2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122865








