Improvement of Saline–Alkali Soil and Straw Degradation Efficiency in Cold and Arid Areas Using Klebsiella sp. and Pseudomonas sp.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Location and Strain Origin
2.2. Experiment Design
2.3. Bacterial Characterization
2.4. Soil Factors
2.5. Straw Degradation and Straw Element Release
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
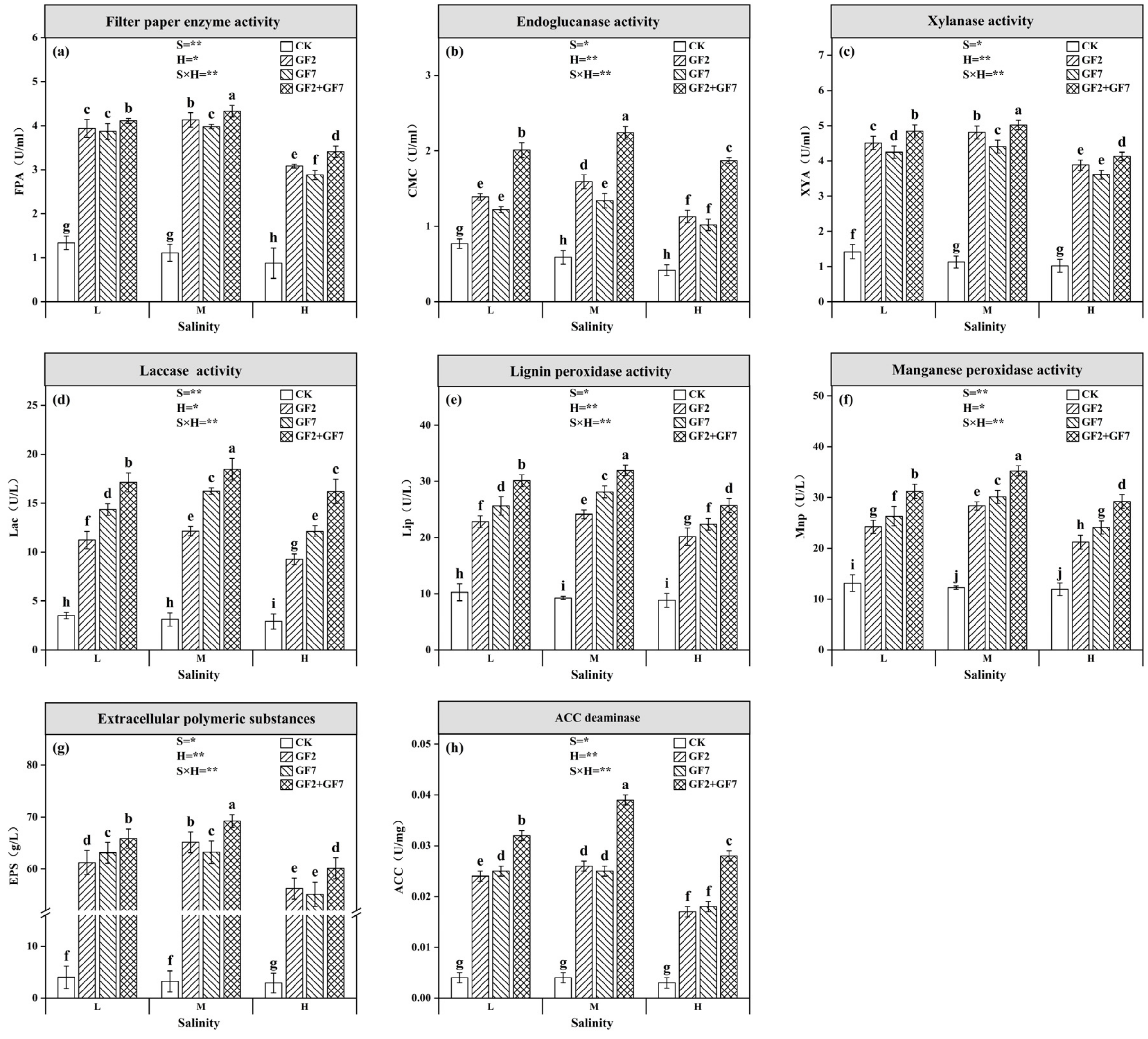
3.1. Characterization of Degrading Bacteria
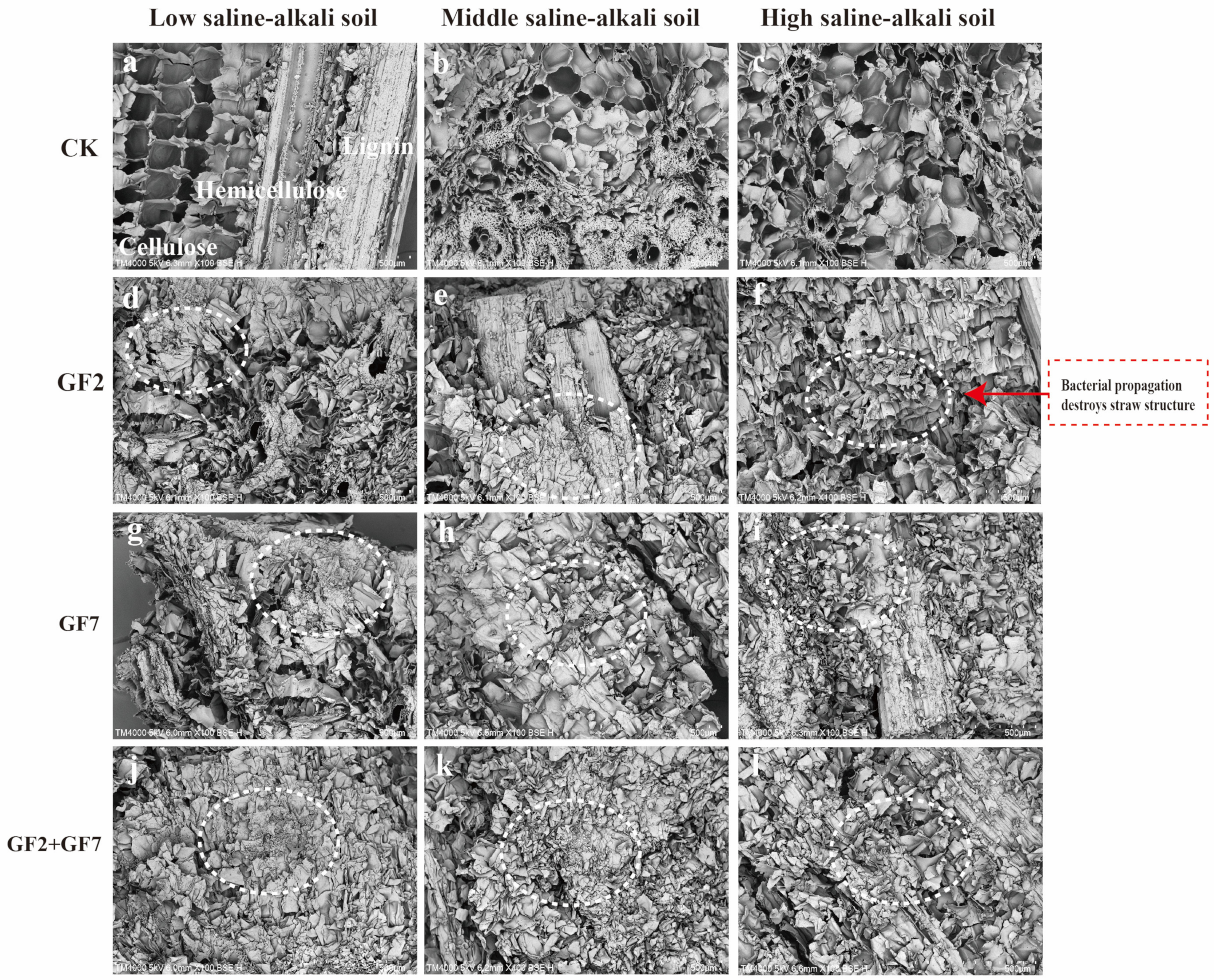
3.2. Degradation of Straw and Its Components
3.3. Release Rate of Straw Elements
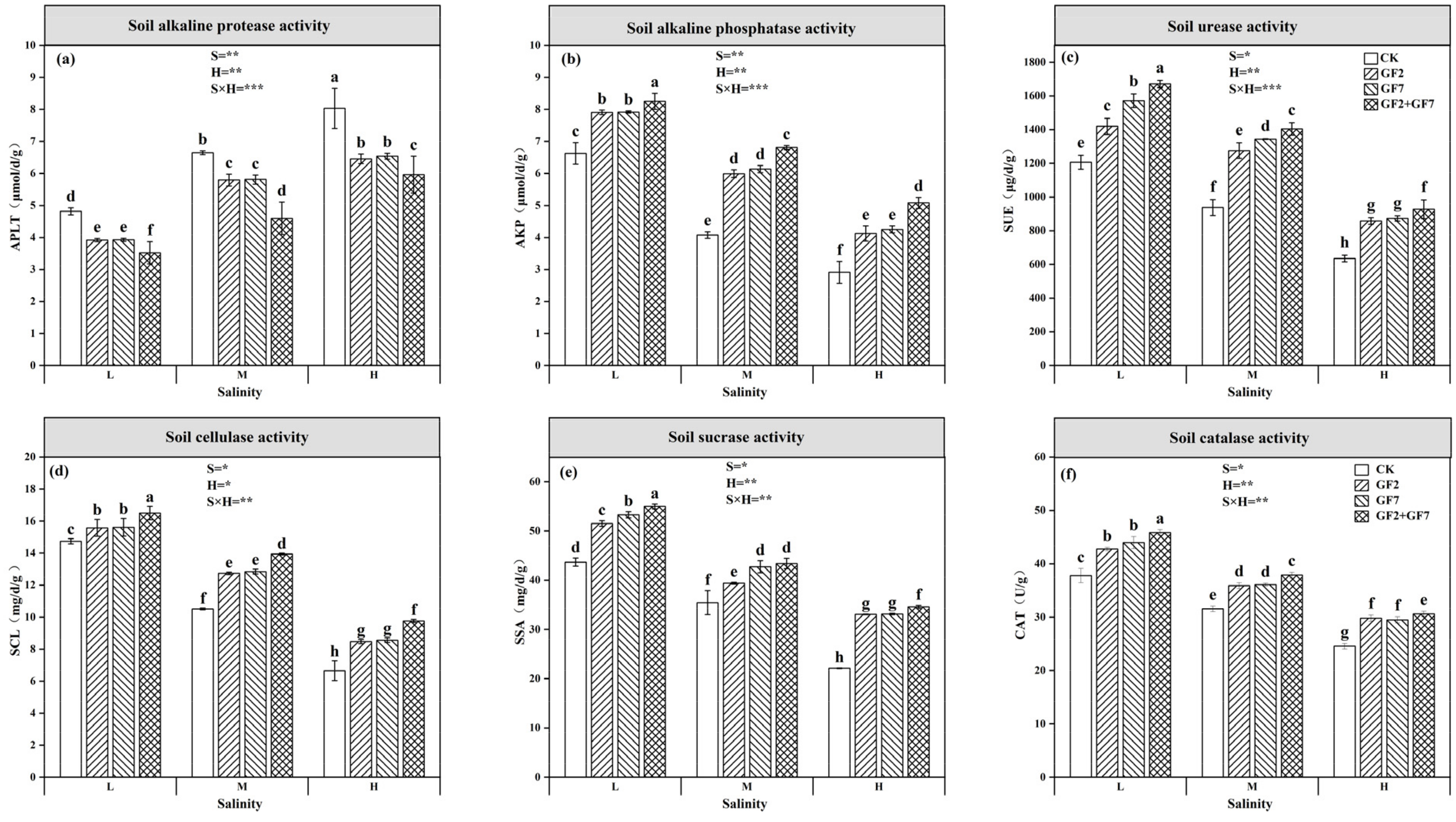
3.4. Soil Enzyme Activity
3.5. Soil Chemical Properties
3.6. Soil Salt and Alkali Ions
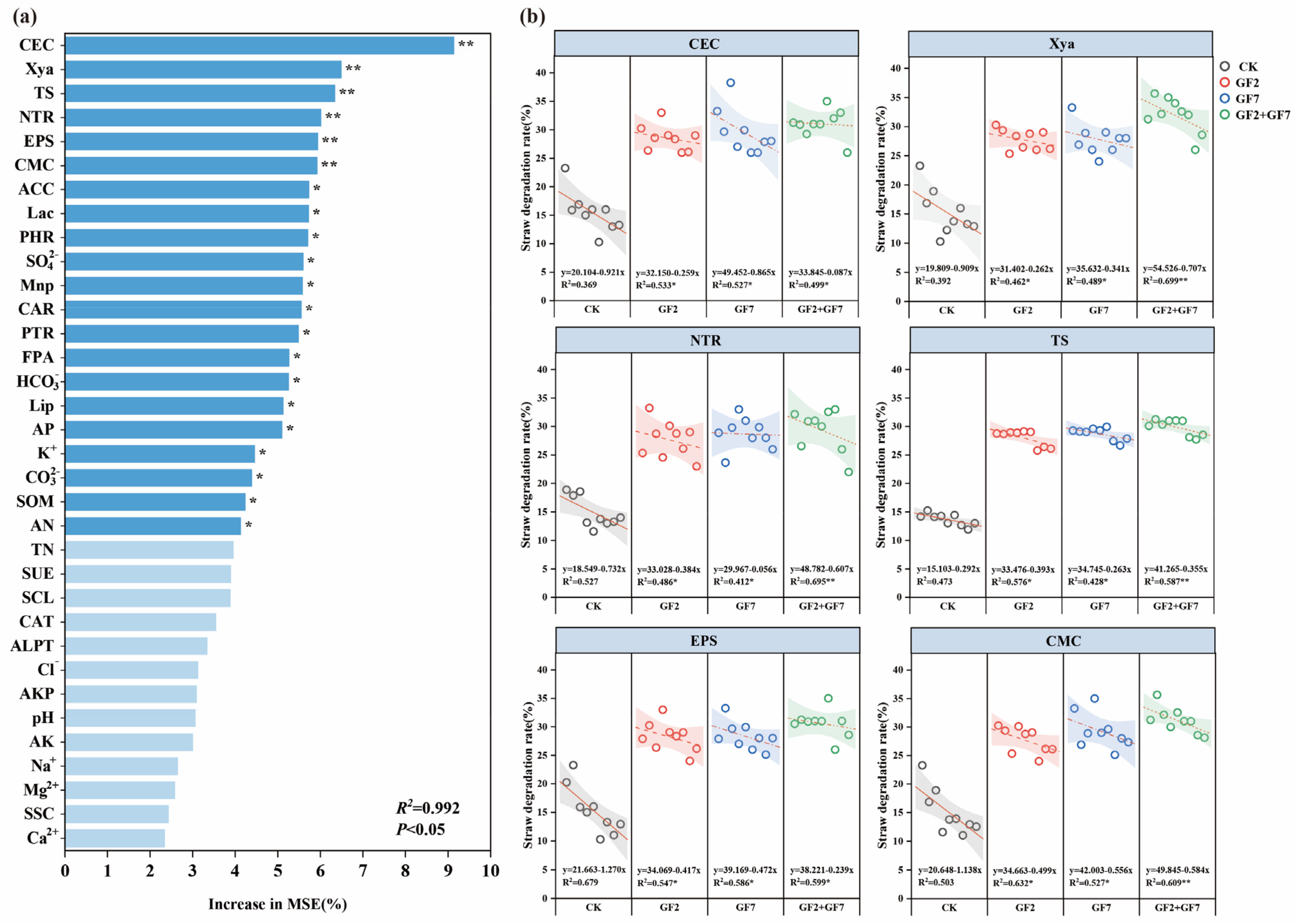
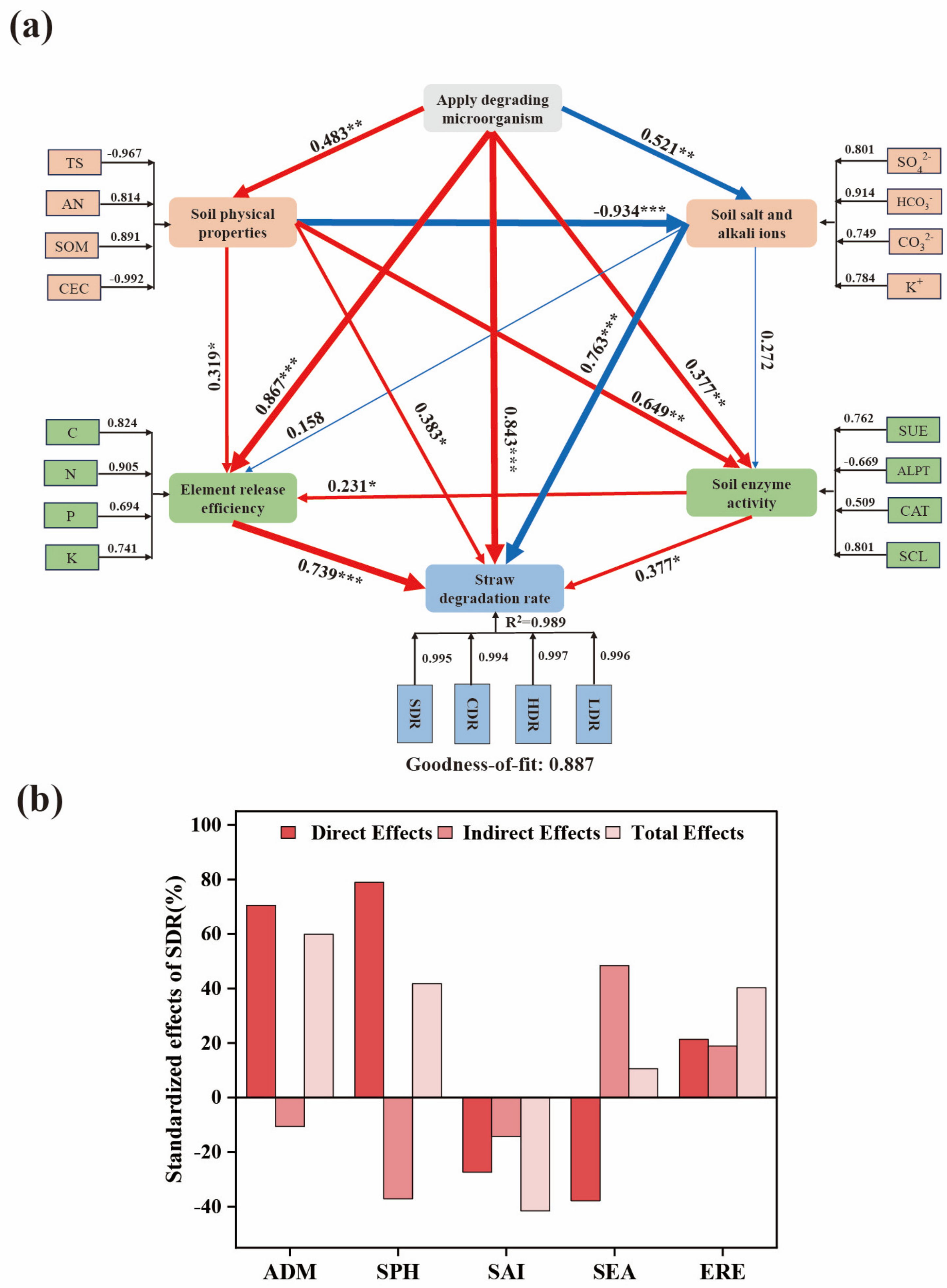
3.7. Correlation Fitting Analysis between Straw Degradation and Soil Factors
3.8. Key Factors Affecting Straw Degradation
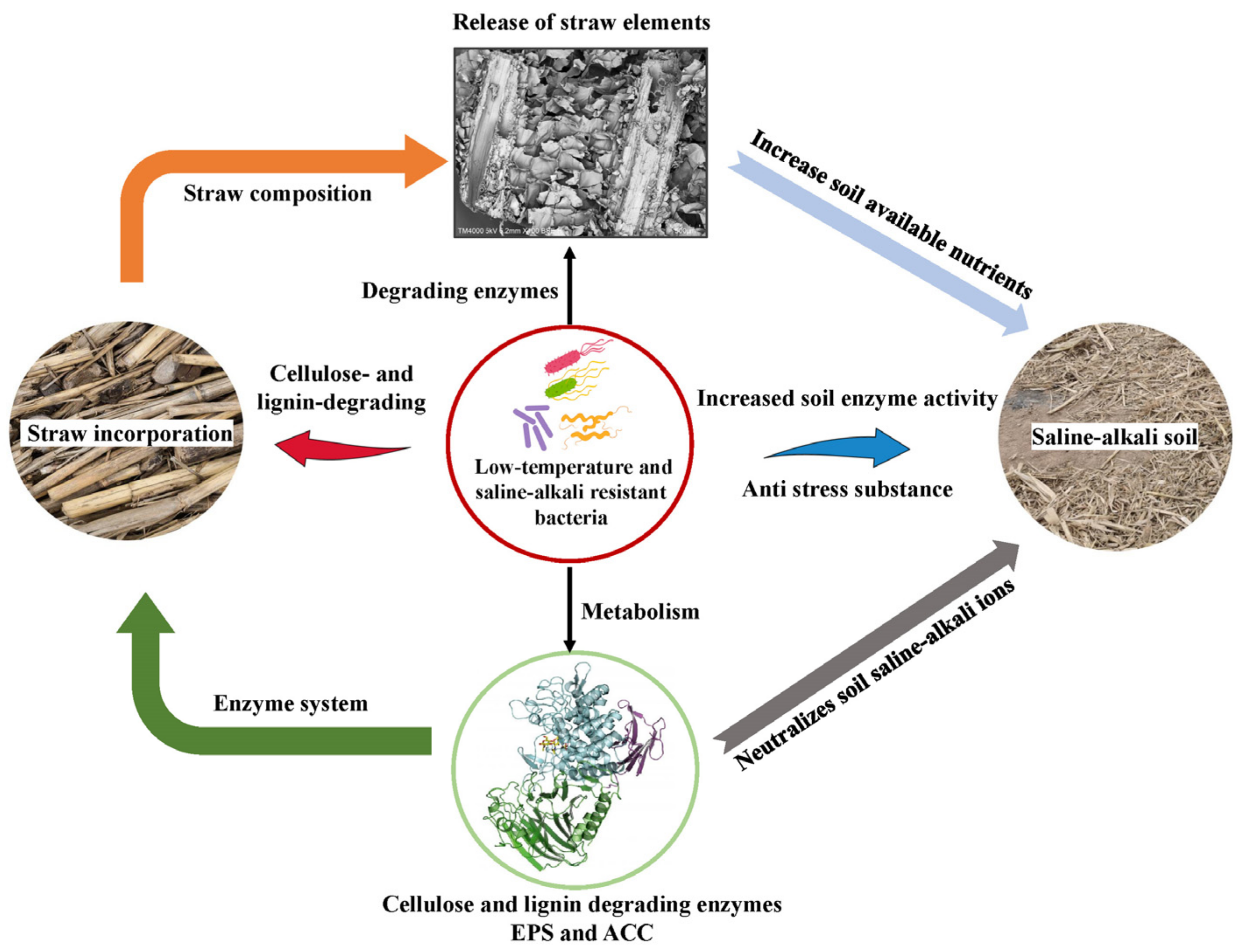
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Pang, H.; Li, Y. Buried straw layer plus plastic mulching reduces soil salinity and increases sunflower yield in saline soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.B.; Liu, M.; Paredes, P.; Shi, H.; Feng, Z.; Lei, H.; Pereira, L.S. Salts dynamics in maize irrigation in the Hetao plateau using static water table lysimeters and HYDRUS-1D with focus on the autumn leaching irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 283, 108306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, Y.F.; Sun, J.Y.; Gao, J.L.; Wang, Z.G.; Yu, X.F. Effects of straw return with potassium fertilizer on the stem lodging resistance, grain quality and yield of spring maize (Zea mays L.). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Feng, Q.; Li, Y.; Deo, R.C.; Liu, W.; Zhu, M.; Zheng, X.; Liu, R. An interplay of soil salinization and groundwater degradation threatening coexistence of oasis-desert ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806 Pt 2, 150599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Shi, Z.; Biswas, A.; Yang, S.; Ding, J.; Wang, F. Updated information on soil salinity in a typical oasis agroecosystem and desert-oasis ecotone: Case study conducted along the Tarim River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 135387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xue, H.; Li, Z.; Li, M. Effects of saline-alkali stress on bacterial and fungal community diversity in Leymus chinensis rhizosphere soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 70000–70013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Yang, T.; Xia, S.; Yin, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Sun, R.; Gao, H.; Chu, H.; Ma, C. Soil depth exerts stronger impact on bacterial community than elevation in subtropical forests of Huangshan Mountain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passoth, V.; Sandgren, M. Biofuel production from straw hydrolysates: Current achievements and perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 5105–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabaan, M.; Asghar, H.N.; Akhtar, M.J.; Saleem, M.F. Assessment of cumulative microbial respiration and their ameliorative role in sustaining maize growth under salt stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. PPB 2023, 196, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, S.; Gaurav, A.K.; Srivastava, S.; Verma, J.P. Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria: Biological Tools for the Mitigation of Salinity Stress in Plants. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, I.C.; Pérez-Alfocea, F. Microbial amelioration of crop salinity stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 3415–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigussie, A.; Dume, B.; Ahmed, M.; Mamuye, M.; Ambaw, G.; Berhiun, G.; Biresaw, A.; Aticho, A. Effect of microbial inoculation on nutrient turnover and lignocellulose degradation during composting: A meta-analysis. Waste Manag. 2021, 125, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, N.; He, H.; Cao, X.; Lv, C.; Zhang, K.; Dai, J. Effects of different types of microbial inoculants on available nitrogen and phosphorus, soil microbial community, and wheat growth in high-P soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 23036–23047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lou, Z.; An, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhao, H.; Fu, M.; Cui, Z. The effects of adding exogenous lignocellulose degrading bacteria during straw incorporation in cold regions on degradation characteristics and soil indigenous bacteria communities. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1141545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Yu, Y.; Hao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ma, J.; Jiang, Y.; Lv, G.; Li, L.; Qian, C. Characterizing corn-straw-degrading actinomycetes and evaluating application efficiency in straw-returning experiments. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1003157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eljonaid, M.Y.; Tomita, H.; Okazaki, F.; Tamaru, Y. Enzymatic Characterization of Unused Biomass Degradation Using the Clostridium cellulovorans Cellulosome. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Cheng, H.; Han, Z.; Wei, Z.; Song, C. Identification of driving factors of lignocellulose degrading enzyme genes in different microbial communities during rice straw composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 381, 129109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zeng, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, W.; Huang, S.; Qiao, X.; Wang, Z.; Di, H.; Qu, J. Degradation of betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase transgenic maize BZ-136 straw and its effects on soil nutrients and fungal community. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1180310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borjigin, Q.; Zhang, B.; Yu, X.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Qu, J.; Ma, D.; Hu, S.; Han, S. Metagenomics study to compare the taxonomic composition and metabolism of a lignocellulolytic microbial consortium cultured in different carbon conditions. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Borjigin, Q.; Gao, J.L.; Yu, X.F.; Hu, S.P.; Zhang, B.Z.; Han, S.C. Community succession and functional prediction of microbial consortium with straw degradation during subculture at low temperature. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xia, H.; Jiang, C.; Riaz, M.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Fan, X.; Xia, X. 14 year applications of chemical fertilizers and crop straw effects on soil labile organic carbon fractions, enzyme activities and microbial community in rice-wheat rotation of middle China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Wu, M.; Che, S.; Yuan, S.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Tian, P.; Wu, L.; Yang, M.; Wu, Z. Effects of Continuous Straw Returning on Soil Functional Microorganisms and Microbial Communities. J. Microbiol. 2023, 61, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y.; Ma, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, C. Hydro-geochemical control of high arsenic and fluoride groundwater in arid and semi-arid areas: A case study of Tumochuan Plain, China. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Han, S.; Gao, J.; Yu, X.; Hu, S. Low-temperature corn straw-degrading bacterial agent and moisture effects on indigenous microbes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 5241–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archibald, F.S. A new assay for lignin-type peroxidases employing the dye azure B. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 3110–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Sha, X. Potential impact of active substances in non-thermal discharge plasma process on microbial community structures and enzymatic activities in uncontaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollister, E.B.; Schadt, C.W.; Palumbo, A.V.; James Ansley, R.; Boutton, T.W. Structural and functional diversity of soil bacterial and fungal communities following woody plant encroachment in the southern Great Plains. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1816–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Liao, G.; Banerjee, S.; Gu, S.; Liang, J.; Guo, X.; Zhao, H.; Liang, Y.; Li, T. Long-term organic fertilization promotes the resilience of soil multifunctionality driven by bacterial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 177, 108922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, B.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Han, F. Dynamic changes of soil microbial community in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantations in the Mu Us Sandy Land. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, J.R.; Dexter, G.N.; Salvachúa, D.; O’Brien, M.; Klingeman, D.M.; Gorday, K.; Michener, J.K.; Peterson, D.J.; Beckham, G.T.; Guss, A.M. Engineered Pseudomonas putida simultaneously catabolizes five major components of corn stover lignocellulose: Glucose, xylose, arabinose, p-coumaric acid, and acetic acid. Metab. Eng. 2020, 62, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, K. Biological function of Klebsiella variicola and its effect on the rhizosphere soil of maize seedlings. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, P.; Li, S.; Lu, S.G.; Zhu, J.G.; Huang, H. Improved 1,3-propanediol production with hemicellulosic hydrolysates (corn straw) as cosubstrate: Impact of degradation products on Klebsiella pneumoniae growth and 1,3-propanediol fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 1815–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, D.J.; Dini-Andreote, F.; van Elsas, J.D. Metataxonomic profiling and prediction of functional behaviour of wheat straw degrading microbial consortia. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2014, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruthamuthu, M.; Jiménez, D.J.; Stevens, P.; van Elsas, J.D. A multi-substrate approach for functional metagenomics-based screening for (hemi)cellulases in two wheat straw-degrading microbial consortia unveils novel thermoalkaliphilic enzymes. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Tang, J.; Sun, H.; Yao, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Ye, S. Straw waste promotes microbial functional diversity and lignocellulose degradation during the aerobic process of pig manure in an ectopic fermentation system via metagenomic analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838 Pt 1, 155637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.J.; Bahrin, N.; Hardiman, E.M.; Bugg, T.D.H. Production of Substituted Styrene Bioproducts from Lignin and Lignocellulose Using Engineered Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, e1900571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Shu, L.; Song, J.; Yang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wu, L.; Yang, M. Microbial consortium composed of Cellulomonas ZJW-6 and Acinetobacter DA-25 improves straw lignocellulose degradation. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, T.T.; Bo, B.; Malec, P.; Fu, P. The effect of a consortium of Penicillium sp. and Bacillus spp. in suppressing banana fungal diseases caused by Fusarium sp. and Alternaria sp. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 1890–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, K.; Zhu, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Meng, Q.; Niu, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, Q. Lignocellulosic depolymerization induced by ionic liquids regulating composting habitats based on metagenomics analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 76298–76309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashora, K.; Gattupalli, M.; Javed, Z.; Tripathi, G.D.; Sharma, R.; Mishra, M.; Bhargava, A.; Srivastava, S. Leveraging multiomics approaches for producing lignocellulose degrading enzymes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2022, 79, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, J.; Monreal, C.M.; Orellana, L.; Calabi-Floody, M.; González, M.E.; Meier, S.; Borie, F.; Cornejo, P. Influence of saprophytic fungi and inorganic additives on enzyme activities and chemical properties of the biodegradation process of wheat straw for the production of organo-mineral amendments. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 109922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Gao, Y.; Mei, Y.; Liu, J.; Kalkhajeh, Y.K.; Hu, H.; Huang, J. Effects of continuous straw returning on bacterial community structure and enzyme activities in rape-rice soil aggregates. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, R.; Miralles, I.; Soria, R.; Rodríguez-Berbel, N.; Villafuerte, A.B.; Zema, D.A.; Lucas-Borja, M.E. Short-term effects of post-fire soil mulching with wheat straw and wood chips on the enzymatic activities in a Mediterranean pine forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857 Pt 2, 159489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Riaz, M.; Babar, S.; Eldesouki, Z.; Liu, B.; Xia, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, X.; Jiang, C. Alterations in the composition and metabolite profiles of the saline-alkali soil microbial community through biochar application. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 120033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Jiang, M.; Liu, H.; Dai, X.; Wang, P. Application of the biogas residue of anaerobic co-digestion of gentamicin mycelial residues and wheat straw as soil amendment: Focus on nutrients supply, soil enzyme activities and antibiotic resistance genes. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 335, 117512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Dai, Y.; Cheng, X.; He, X.; Bei, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, K.; Tian, X.; et al. Straw mulch improves soil carbon and nitrogen cycle by mediating microbial community structure and function in the maize field. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1217966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayyed, R.Z.; Shaikh, S.S.; Wani, S.J.; Rehman, M.T.; Al Ajmi, M.F.; Haque, S.; El Enshasy, H.A. Production of biodegradable polymer from agro-wastes in alcaligenes sp. and pseudomonas sp. Molecules 2021, 26, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, D.; Li, B.; Yan, B.; Mao, L.; Sun, G.; Sun, L.; Li, X. The response of soil bacterial communities to cropping systems in saline–alkaline soil in the songnen plain. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Yu, X.; Ma, D.; Hu, S.; Shen, T. Effect of Deep Straw return under saline conditions on soil nutrient and maize growth in saline–alkali Land. Agronomy 2023, 13, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pei, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Song, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.H. The unique GH5 cellulase member in the extreme halotolerant fungus Aspergillus glaucus CCHA is an endoglucanase with multiple tolerance to salt, alkali and heat: Prospects for straw degradation applications. Extrem. Life Under Extrem. Cond. 2018, 22, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazl, U.; Wang, J.; Yin, J.; Jiang, X.; Meng, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H. Effects of FeSO4 and organic sdditives on soil properties and microbiota during model soybean planting in saline-alkali soil. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Saline–Alkali Soil | pH | TS (g/kg) | CEC (cmol/kg) | Maize Straw | Cellulose Content (%) | Hemicellulose Content (%) | Lignin Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low level | 8.20 | 3.23 | 9.81 | Xianyu 696 | 38.44 | 28.17 | 22.45 |
| Middle level | 8.95 | 5.22 | 15.26 | Xianyu 696 | 38.44 | 28.17 | 22.45 |
| High level | 9.21 | 7.89 | 21.74 | Xianyu 696 | 38.44 | 28.17 | 22.45 |
| Element Release | Handle | Equation Yt (%) | Regression Coefficient | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | CK | Yt = −0.9854x + 6.2553 | −0.9854 | 0.9556 |
| GF2 | Yt = −1.4556x + 14.9273 | −1.4556 | 0.6439 | |
| GF7 | Yt = −1.7971x + 14.5274 | −1.7971 | 0.6551 | |
| GF2+GF7 | Yt = −1.4456x + 19.7647 | −1.4456 | 0.7723 | |
| Nitrogen | CK | Yt = −0.4051x + 4.6933 | −0.4051 | 0.9815 |
| GF2 | Yt = −0.4579x + 14.2278 | −0.4579 | 0.4018 | |
| GF7 | Yt = −0.5547x + 14.8259 | −0.5547 | 0.6218 | |
| GF2+GF7 | Yt = −0.1498x + 17.1836 | −0.1498 | 0.5047 | |
| Phosphorus | CK | Yt = −0.1359x + 3.3973 | −0.1359 | 0.9631 |
| GF2 | Yt = −0.9854x + 11.8773 | −0.9854 | 0.4249 | |
| GF7 | Yt = −1.1127x + 12.7891 | −1.1127 | 0.5033 | |
| GF2+GF7 | Yt = −0.9523x + 14.8415 | −0.9523 | 0.5297 | |
| Potassium | CK | Yt = −1.0025x + 10.1871 | −1.0025 | 0.9016 |
| GF2 | Yt = −0.9854x + 18.2291 | −0.9854 | 0.4252 | |
| GF7 | Yt = −0.8854x + 19.0325 | −0.8854 | 0.5278 | |
| GF2+GF7 | Yt = −1.1653x + 23.1714 | −1.1653 | 0.5491 |
| Salinity | Handle | pH | TS (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | AN (mg/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | AK (mg/kg) | SOM (g/kg) | CEC (cmol/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | CK | 8.21 ± 0.05 b | 3.23 ± 0.06 e | 0.91 ± 0.05 b | 44.12 ± 0.15 c | 27.56 ± 0.26 c | 163.01 ± 4.15 c | 13.56 ± 0.26 c | 9.87 ± 0.15 f |
| GF2 | 8.15 ± 0.13 b | 2.37 ± 0.12 f | 1.01 ± 0.06 a | 45.23 ± 0.26 b | 31.36 ± 0.18 b | 181.23 ± 4.26 b | 14.79 ± 0.21 b | 8.55 ± 0.26 g | |
| GF7 | 8.24 ± 0.24 b | 2.26 ± 0.11 f | 1.12 ± 0.06 a | 46.73 ± 0.31 b | 31.59 ± 0.09 b | 182.47 ± 3.26 b | 15.01 ± 0.15 b | 8.06 ± 0.15 g | |
| GF2+GF7 | 8.07 ± 0.16 b | 2.24 ± 0.08 f | 1.31 ± 0.14 a | 50.11 ± 0.36 a | 32.61 ± 0.15 a | 191.26 ± 5.26 a | 16.29 ± 0.06 a | 7.09 ± 0.09 g | |
| M | CK | 8.95 ± 0.17 b | 5.22 ± 0.21 c | 0.63 ± 0.15 d | 31.56 ± 0.25 e | 24.15 ± 0.36 d | 138.26 ± 5.59 e | 7.18 ± 0.19 e | 15.26 ± 0.13 d |
| GF2 | 8.33 ± 0.16 b | 4.31 ± 0.23 d | 0.82 ± 0.08 c | 40.26 ± 0.31 d | 27.07 ± 0.28 c | 147.26 ± 3.98 d | 11.23 ± 0.26 d | 13.12 ± 0.15 e | |
| GF7 | 8.36 ± 0.14 b | 4.23 ± 0.18 d | 0.84 ± 0.07 c | 41.31 ± 0.18 d | 26.87 ± 0.24 c | 146.26 ± 4.15 d | 11.59 ± 0.31 d | 13.36 ± 0.14 e | |
| GF2+GF7 | 8.25 ± 0.14 b | 3.98 ± 0.31 d | 0.93 ± 0.08 b | 43.74 ± 0.37 c | 27.78 ± 0.26 c | 158.14 ± 5.12 c | 12.01 ± 0.15 c | 12.91 ± 0.17 e | |
| H | CK | 9.18 ± 0.25 a | 7.89 ± 0.26 a | 0.31 ± 0.14 e | 21.36 ± 0.28 g | 15.91 ± 0.31 g | 123.45 ± 5.06 f | 5.23 ± 0.26 f | 21.74 ± 0.19 a |
| GF2 | 9.01 ± 0.21 a | 6.39 ± 0.41 b | 0.41 ± 0.15 e | 28.31 ± 0.26 f | 19.23 ± 0.18 f | 133.26 ± 4.78 e | 6.11 ± 0.26 e | 18.58 ± 0.21 b | |
| GF7 | 8.88 ± 0.15 b | 6.21 ± 0.13 b | 0.39 ± 0.06 e | 28.91 ± 0.34 f | 19.97 ± 0.09 f | 132.63 ± 4.96 e | 6.23 ± 0.15 e | 18.29 ± 0.09 b | |
| GF2+GF7 | 8.91 ± 0.14 ab | 6.13 ± 0.15 b | 0.51 ± 0.08 d | 31.87 ± 0.35 e | 20.31 ± 0.18 e | 134.98 ± 5.69 e | 6.98 ± 0.19 e | 17.99 ± 0.11 c | |
| Source of | |||||||||
| S | * | ** | * | * | * | * | * | ** | |
| H | - | - | * | ** | ** | ** | ** | - | |
| S×H | - | - | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | |
| Salinity | Handle | Cl− (g/kg) | SO42− (g/kg) | HCO3− (g/kg) | CO32− (g/kg) | Ca2+ (g/kg) | Mg2+ (g/kg) | Na+ (g/kg) | K+ (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | CK | 1.15 ± 0.05 d | 2.15 ± 0.15 d | 0.41 ± 0.06 d | 0.15 ± 0.02 c | 0.51 ± 0.02 d | 0.36 ± 0.02 c | 1.09 ± 0.15 e | 0.15 ± 0.02 d |
| GF2 | 0.89 ± 0.15 e | 1.99 ± 0.09 e | 0.36 ± 0.05 d | 0.12 ± 0.02 c | 0.42 ± 0.03 d | 0.35 ± 0.03 c | 0.91 ± 0.26 f | 0.13 ± 0.01 d | |
| GF7 | 0.88 ± 0.11 e | 1.89 ± 0.08 e | 0.37 ± 0.05 d | 0.13 ± 0.03 c | 0.35 ± 0.05 e | 0.32 ± 0.01 c | 0.86 ± 0.19 f | 0.12 ± 0.02 d | |
| GF2+GF7 | 0.78 ± 0.12 e | 1.84 ± 0.12 e | 0.32 ± 0.03 d | 0.14 ± 0.04 c | 0.32 ± 0.04 e | 0.33 ± 0.02 c | 0.85 ± 0.12 f | 0.13 ± 0.02 d | |
| M | CK | 2.36 ± 0.06 c | 3.15 ± 0.15 c | 0.81 ± 0.09 c | 0.31 ± 0.02 b | 0.81 ± 0.03 c | 0.71 ± 0.03 b | 1.41 ± 0.26 c | 0.36 ± 0.01 c |
| GF2 | 1.12 ± 0.15 d | 2.59 ± 0.17 d | 0.71 ± 0.08 c | 0.29 ± 0.02 b | 0.79 ± 0.02 c | 0.69 ± 0.03 b | 1.22 ± 0.33 d | 0.33 ± 0.02 c | |
| GF7 | 1.33 ± 0.08 d | 2.41 ± 0.21 d | 0.69 ± 0.04 c | 0.28 ± 0.03 b | 0.78 ± 0.03 c | 0.65 ± 0.05 b | 1.23 ± 0.15 d | 0.32 ± 0.05 c | |
| GF2+GF7 | 1.32 ± 0.09 d | 2.01 ± 0.06 de | 0.65 ± 0.06 c | 0.29 ± 0.01 b | 0.75 ± 0.01 c | 0.62 ± 0.04 b | 1.19 ± 0.26 d | 0.34 ± 0.02 c | |
| H | CK | 4.01 ± 0.08 a | 5.37 ± 0.14 a | 1.45 ± 0.05 a | 0.52 ± 0.02 a | 1.12 ± 0.02 a | 1.02 ± 0.02 a | 2.01 ± 0.36 a | 0.51 ± 0.02 a |
| GF2 | 2.81 ± 0.14 c | 4.15 ± 0.05 b | 0.98 ± 0.03 b | 0.45 ± 0.03 a | 0.93 ± 0.03 b | 0.93 ± 0.02 a | 1.87 ± 0.14 b | 0.45 ± 0.04 b | |
| GF7 | 3.06 ± 0.15 b | 3.98 ± 0.09 b | 0.95 ± 0.08 b | 0.43 ± 0.03 a | 0.95 ± 0.02 b | 0.95 ± 0.03 a | 1.85 ± 0.18 b | 0.43 ± 0.06 b | |
| GF2+GF7 | 2.98 ± 0.09 c | 3.91 ± 0.11 bc | 0.91 ± 0.06 b | 0.43 ± 0.02 a | 0.96 ± 0.02 b | 0.91 ± 0.02 a | 1.77 ± 0.28 b | 0.41 ± 0.01 b | |
| Source of | |||||||||
| S | ** | ** | * | * | * | * | * | * | |
| H | * | * | - | - | - | - | * | - | |
| S×H | * | ** | - | - | * | - | - | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Yu, X.; Gao, J.; Qu, J.; Borjigin, Q.; Meng, T.; Li, D. Improvement of Saline–Alkali Soil and Straw Degradation Efficiency in Cold and Arid Areas Using Klebsiella sp. and Pseudomonas sp. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112499
Zhao X, Yu X, Gao J, Qu J, Borjigin Q, Meng T, Li D. Improvement of Saline–Alkali Soil and Straw Degradation Efficiency in Cold and Arid Areas Using Klebsiella sp. and Pseudomonas sp. Agronomy. 2024; 14(11):2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112499
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xiaoyu, Xiaofang Yu, Julin Gao, Jiawei Qu, Qinggeer Borjigin, Tiantian Meng, and Dongbo Li. 2024. "Improvement of Saline–Alkali Soil and Straw Degradation Efficiency in Cold and Arid Areas Using Klebsiella sp. and Pseudomonas sp." Agronomy 14, no. 11: 2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112499
APA StyleZhao, X., Yu, X., Gao, J., Qu, J., Borjigin, Q., Meng, T., & Li, D. (2024). Improvement of Saline–Alkali Soil and Straw Degradation Efficiency in Cold and Arid Areas Using Klebsiella sp. and Pseudomonas sp. Agronomy, 14(11), 2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112499





