The Effects of Various Long-Term Fertilizer Applications on Soil Carbon Fractions in a Winter Wheat Monoculture Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
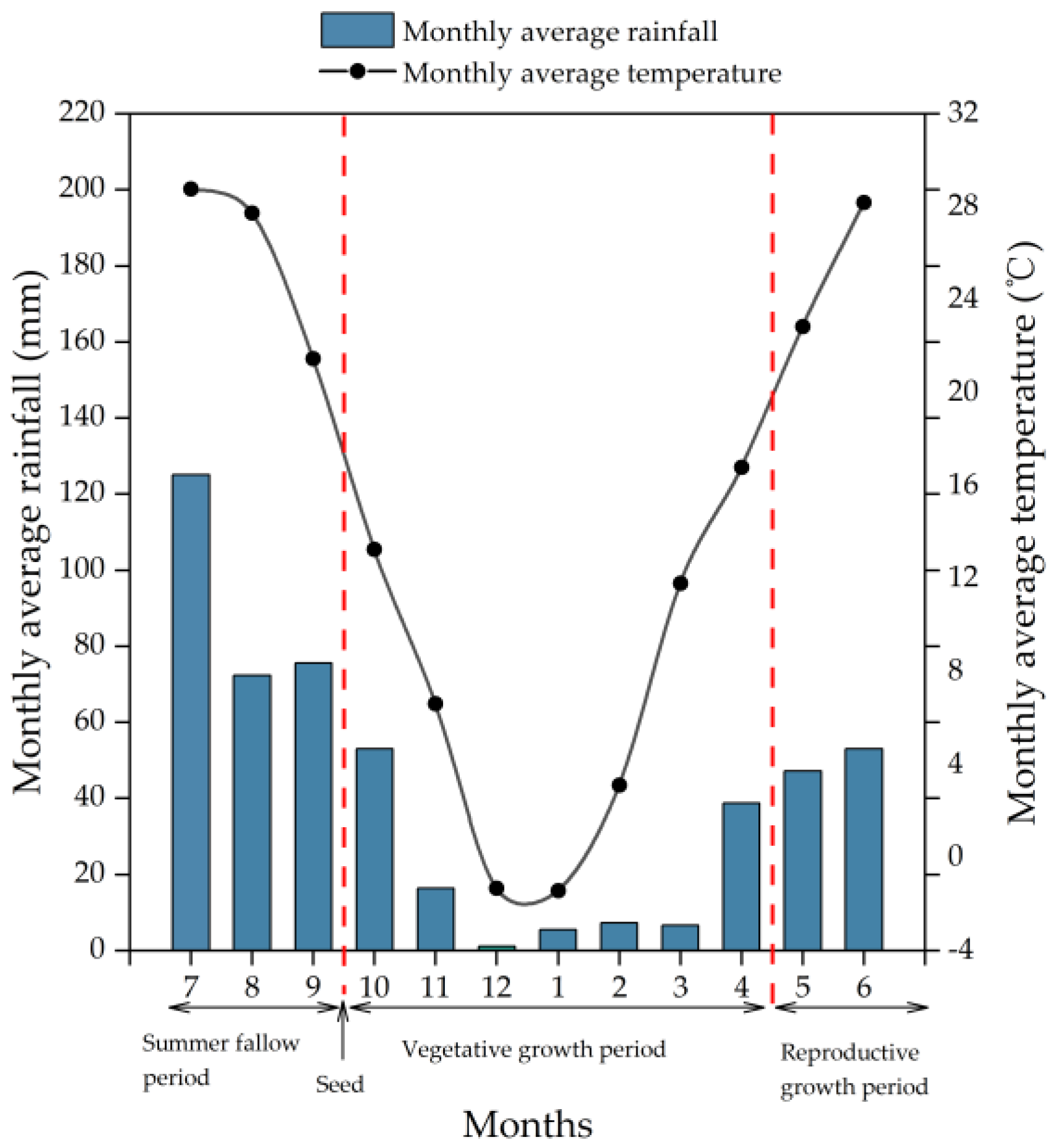
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.4. Calculation of Soil Carbon Pool-Related Indicators and the Farmland Carbon Input
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
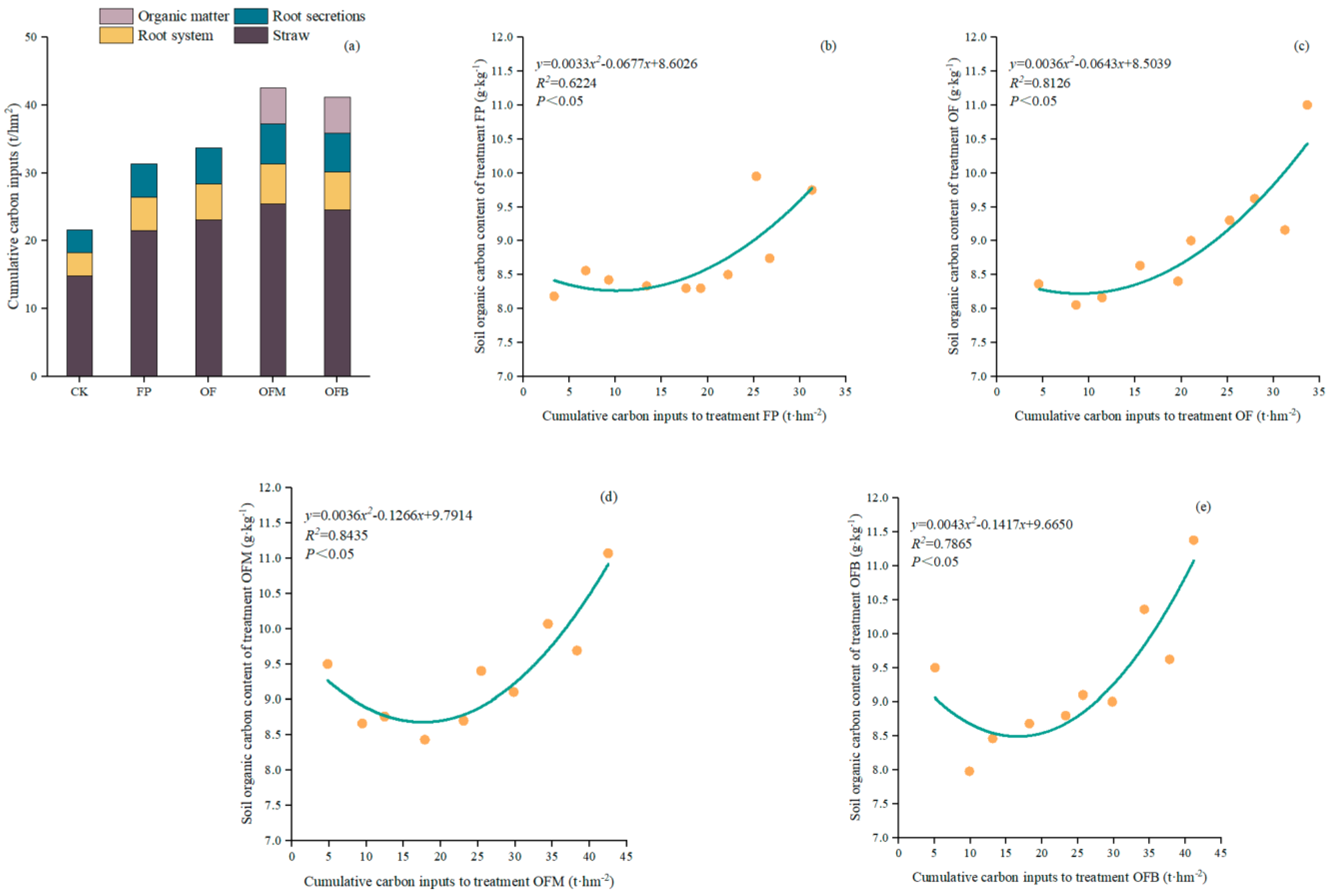
3.1. Effect of Carbon Inputs on SOC after Different Fertilizer Treatments
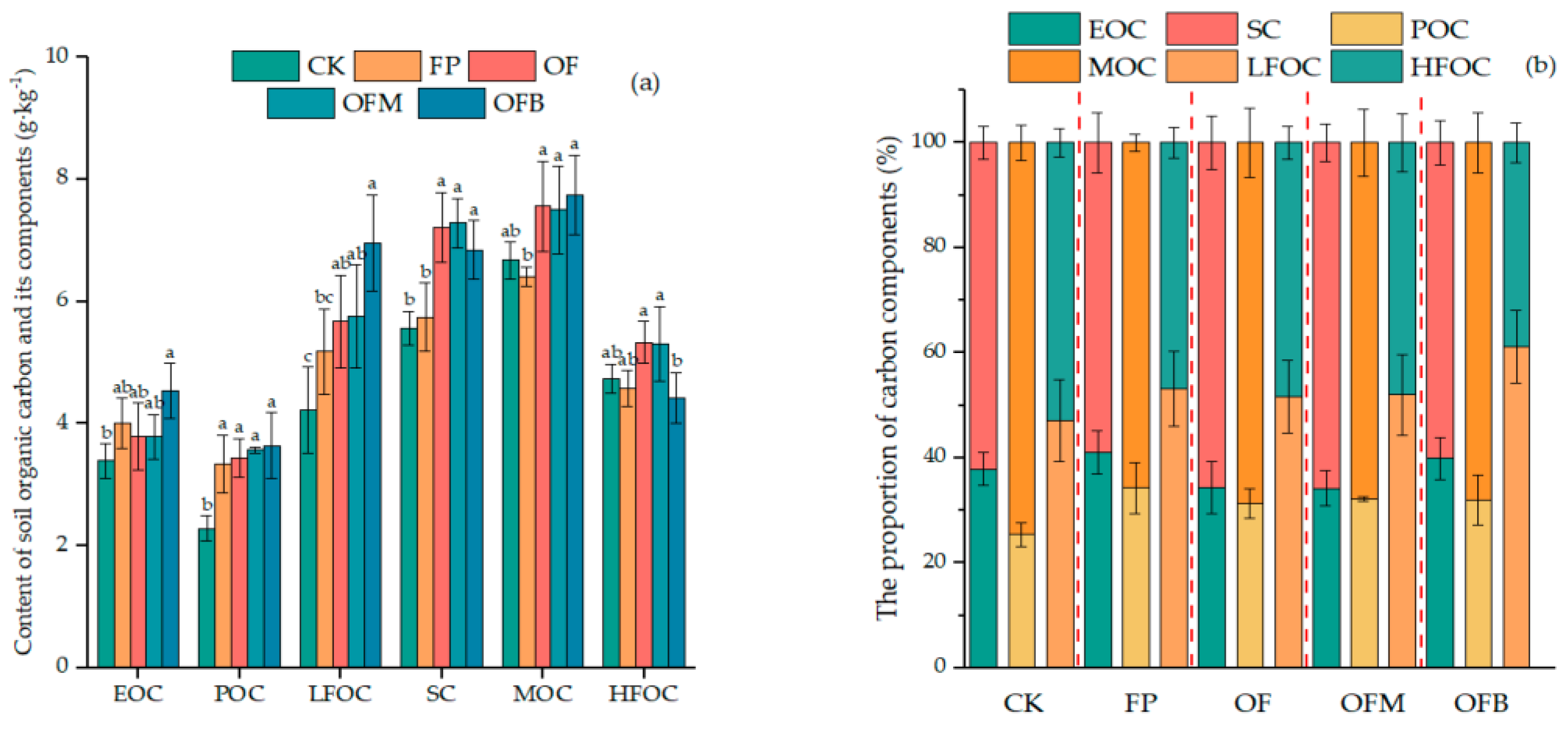
3.2. Effects of Different Fertilization Practices on the SOC Fractions
3.3. Effects of Various Fertilization Practices on Soil Carbon Pools
3.4. Effect of Different Fertilization Practices on Soil Characteristics
3.5. Effect of Fertilizer Application on Soil Carbon Pool Stability
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Fertilizer Application on Soil Carbon Pools
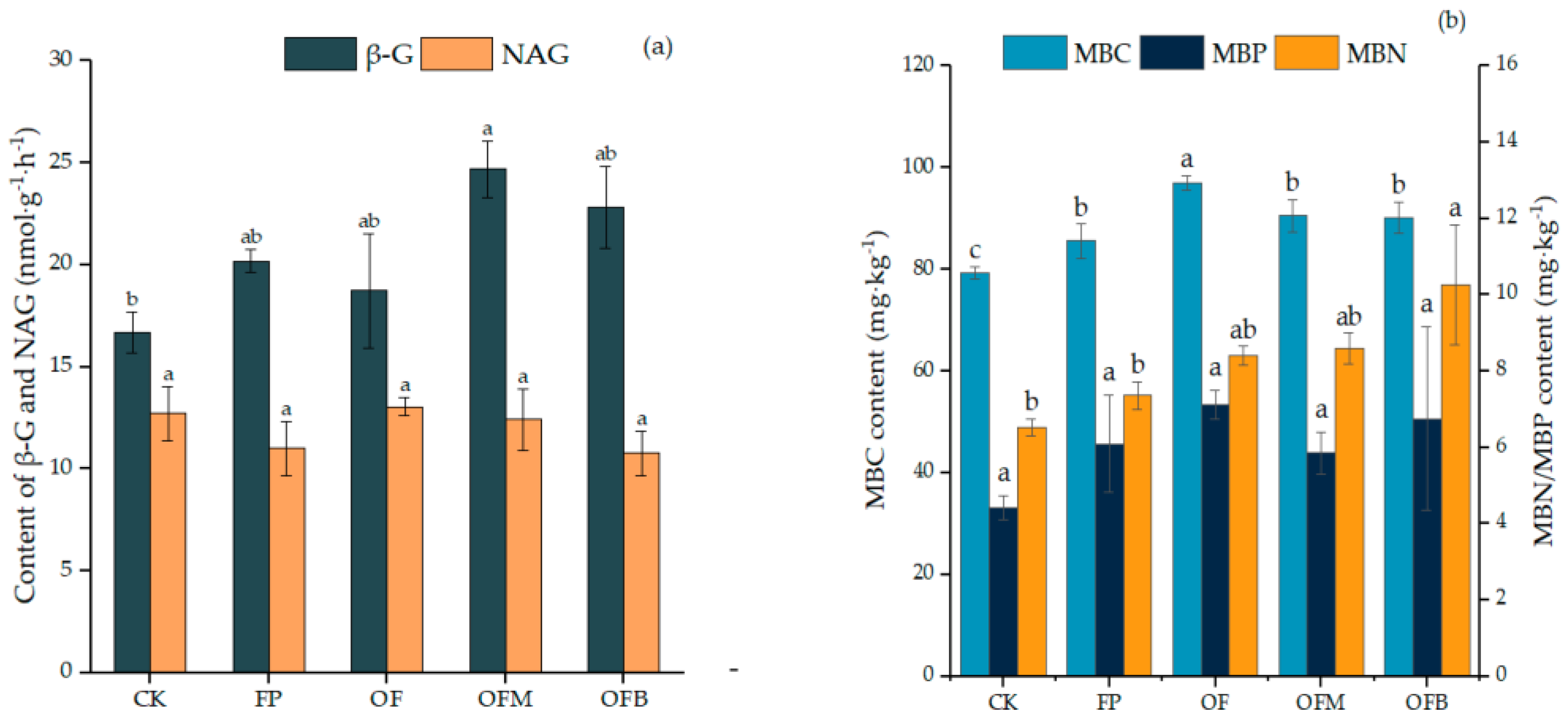
4.2. Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus and Two Enzymes
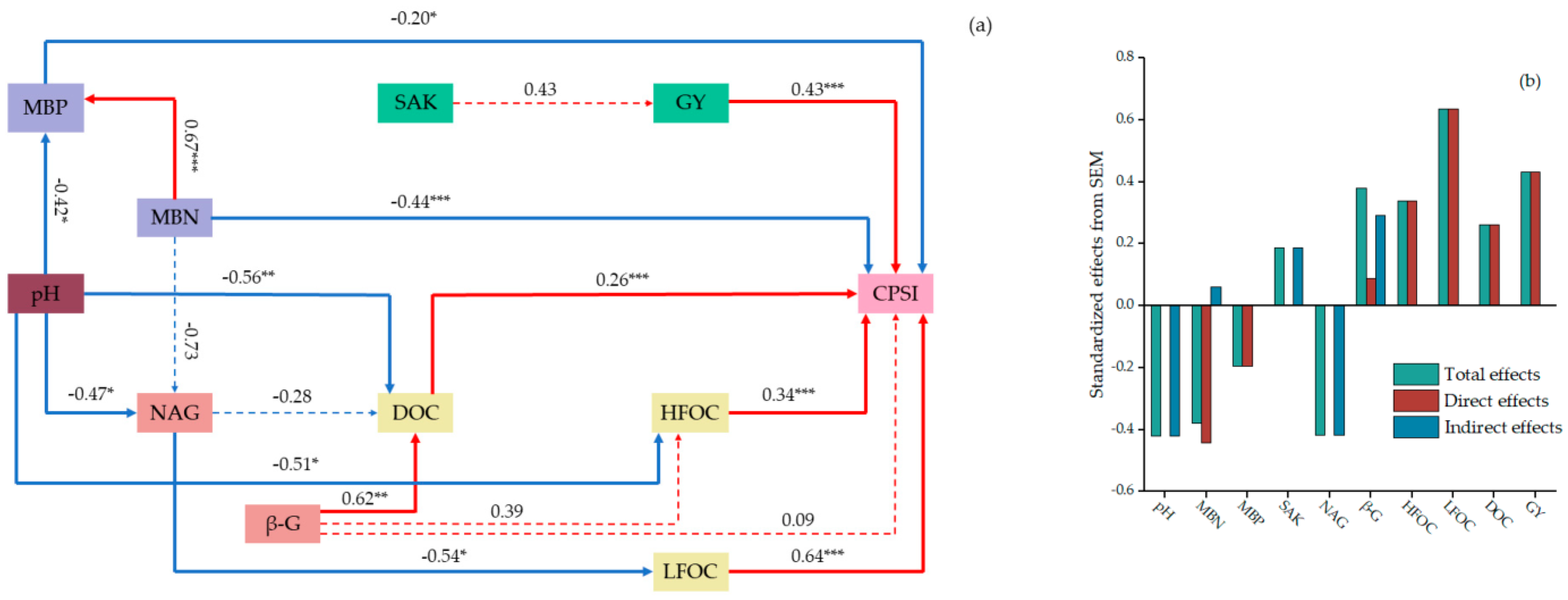
4.3. Effects of Various Environmental Factors on Differently Fertilized Soil Carbon Pools
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Batjes, N.H. Total carbon and nitrogen in the soils of the world. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Cheng, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Y.; Hu, L.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, L.; Chang, L.; et al. Straw Strip Mulching Increased Soil Organic Carbon Components of a Wheat Field in Dry Farming Regions of the Loess Plateau. Water 2022, 14, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.P.; Schaeffer, S.M. Microbial control over carbon cycling in soil. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keenan, T.; Williams, C.J. The terrestrial carbon sink. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2018, 43, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladele, S.O.; Adetunji, A.T. Agro-residue biochar and N fertilizer addition mitigates CO2-C emission and stabilized soil organic carbon pools in a rain-fed agricultural cropland. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbi, D.K.; Kiranvir, B.; Sharma, S. Sensitivity of labile soil organic carbon pools to long-term fertilizer, straw and manure management in rice-wheat system. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiorno, G.; Bünemann, E.K.; Oguejiofor, C.U.; Meier, J.; Gort, G.; Comans, R.; Mäder, P.; Brussaard, L.; de Goede, R. Sensitivity of labile carbon fractions to tillage and organic matter management and their potential as comprehensive soil quality indicators across pedoclimatic conditions in Europe. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, K.; Minami, K. Effect of organic matter application on methane emission from some Japanese paddy fields. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1990, 36, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.M.; Wen, D.Z.; Zhang, L.L.; Li, J. Altitudinal changes in active and recalcitrant soil carbon pools of forests in the Dinghu Mountains. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 18, 6089–6099. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Lou, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, W.; Baniyamuddin, M.; Zhao, K. Soil organic carbon active fractions as early indicators for total carbon change under straw incorporation. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.-S.; Luo, B.-Z.; Wei, S.-J.; Hu, H.-Q.; Li, X.-C.; Wu, Z.-P.; Wang, Z.-S.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Zhong, Y.-X. Effects of moderate forest fires on soil organic carbon density in secondary forests of Pinus massoniana. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2020, 44, 1073. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miltner, A.; Bombach, P.; Schmidt-Brücken, B.; Kästner, M. SOM genesis: Microbial biomass as a significant source. Biogeochemistry 2012, 111, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindler, R.; Miltner, A.; Richnow, H.-H.; Kästner, M. Fate of gram-negative bacterial biomass in soil—Mineralization and contribution to SOM. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 2860–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Balser, T.C. Microbial production of recalcitrant organic matter in global soils: Implications for productivity and climate policy. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile-Doelsch, I.; Balesdent, J.; Pellerin, S. Reviews and syntheses: The mechanisms underlying carbon storage in soil. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 5223–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nie, C.; Liu, Y.; Du, W.; He, P. Soil microbial community composition closely associates with specific enzyme activities and soil carbon chemistry in a long-term nitrogen fertilized grassland. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.X. Dryland Agriculture in China 2007; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, K.L. Soil Erosion in China; Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2004; p. 845. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gwon, H.S.; Khan, M.I.; Yoon, Y.E.; Lee, Y.B.; Kim, P.J.; Hwang, H.Y. Unexpected higher decomposition of soil organic matter during cold fallow season in temperate rice paddy. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 192, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duiker, S.; Lal, R. Crop residue and tillage effects on carbon sequestration in a Luvisol in central Ohio. Soil Tillage Res. 1999, 52, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hou, R.; Gong, Y.; Li, H.; Fan, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Effects of 11 years of conservation tillage on soil organic matter fractions in wheat monoculture in Loess Plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 106, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.; Hu, S.; Zhang, X.; Ouyang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Huang, B.; Zhao, S.; Wu, J.; Xie, D.; et al. Economics-and policy-driven organic carbon input enhancement dominates soil organic carbon accumulation in Chinese croplands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4045–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benbi, D.K.; Dar, R.A.; Toor, A.S. Improving soil organic carbon and microbial functionality through different rice straw management approaches in rice–wheat cropping sequence. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021, 13, 15659–15669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.; Hai, N.; Huang, B.; Deng, W. Effects of long-term fertilization and residue management on soil organic carbon changes in paddy soils of China: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 204, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Stewart, B.A.; Zhang, F. Long-term experiments for sustainable nutrient management in China. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 31, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninh, H.; Grandy, A.; Wickings, K.; Snapp, S.; Kirk, W.; Hao, J. Organic amendment effects on potato productivity and quality are related to soil microbial activity. Plant Soil 2015, 386, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Yan, Y.; Cao, J.; Christie, P.; Zhang, F.; Fan, M. Effects of combined application of organic amendments and fertilizers on crop yield and soil organic matter: An integrated analysis of long-term experiments. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 225, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Yan, X.; Chen, D. How Does Recycling of Livestock Manure in Agroecosystems Affect Crop Productivity, Reactive Nitrogen Losses, and Soil Carbon Balance? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7450–7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Xiao, X.; Tang, W.; Li, C.; Wang, K.; Li, W.; Cheng, K.; Pan, X. Long-term effects of NPK fertilizers and organic manures on soil organic carbon and carbon management index under a double-cropping rice system in Southern China. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2018, 49, 1976–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Cheng, K.; Shi, L.; Li, C.; Wen, L.; Li, W.; Sun, M.; Sun, G.; Long, Z. Effects of long-term organic matter application on soil carbon accumulation and nitrogen use efficiency in a double-cropping rice field. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Su, J.; Liu, W.; Lang, X.; Huang, X.; Jia, C.; Tong, Q.; Tang, H. Changes in soil organic carbon and nitrogen stocks in Pinus kesiya var. langbiannesis plantation. For. Res. 2015, 28, 810–817. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaojiao, W. Study on Ecosystem Carbon Balance and Stability of Soil Organic Carbon Pool in Dryland Corn Farmland of the Loess Plateau of Central Gansu Province under Different Fertilization Measures. Ph.D. Thesis, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Qian, X. The Single Season Wheat Straw Returning to Promote the Synergistic Improvement of Carbon Efficiency and Economic Benefit in Wheat-Maize Double Cropping System. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2022, 55, 350–364. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bolinder, M.; Angers, D.; Giroux, M.; Laverdiere, M. Estimating C inputs retained as soil organic matter from corn (Zea mays L.). Plant Soil 1999, 215, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, B.; Clivot, H.; Blaszczyk, N.; Labreuche, J.; Ferchaud, F. Soil carbon storage and mineralization rates are affected by carbon inputs rather than physical disturbance: Evidence from a 47-year tillage experiment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 299, 106972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.; Baumann, K.; Marschner, P. Frequent addition of wheat straw residues to soil enhances carbon mineralization rate. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perveen, N.; Barot, S.; Maire, V.; Cotrufo, M.F.; Shahzad, T.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Stewart, C.E.; Ding, W.; Siddiq, M.R.; Dimassi, B.; et al. Universality of priming effect: An analysis using thirty five soils with contrasted properties sampled from five continents. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 134, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-J.A.; Sun, J.; Mau, R.L.; Finley, B.K.; Compson, Z.G.; Van Gestel, N.; Brown, J.R.; Schwartz, E.; Dijkstra, P.; Hungate, B.A. Labile carbon input determines the direction and magnitude of the priming effect. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 109, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Nazaries, L.; Singh, B.K.; Singh, B.P. Microbial mechanisms of carbon priming effects revealed during the interaction of crop residue and nutrient inputs in contrasting soils. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 2775–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, T.; Anwar, F.; Hussain, S.; Mahmood, F.; Arif, M.S.; Sahar, A.; Nawaz, M.F.; Perveen, N.; Sanaullah, M.; Rehman, K.; et al. Carbon dynamics in surface and deep soil in response to increasing litter addition rates in an agro-ecosystem. Geoderma 2019, 333, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, S.; Bardoux, G.; Abbadie, L.; Mariotti, A. Carbon input to soil may decrease soil carbon content. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Z.; Xiao-li, W.; Jin, H.; Sheng-mei, Y.; Qin-wen, Z.; Ming-rui, L. Effects of Replacing Chemical Nitrogen Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer on Active OrganicCarbon Fractions, Enzyme Activities, and Crop Yield in Yellow Soil. Environ. Sci. 2023, 1–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalambukattu, J.G.; Singh, R.; Patra, A.K.; Arunkumar, K. Soil carbon pools and carbon management index under different land use systems in the Central Himalayan region. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B—Soil Plant Sci. 2013, 63, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, G.J.; Lefroy, R.D.; Lisle, L. Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zheng, Z.X.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Feng, T.Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhai, B.N. Effects of Long-term Combined Application of Organic and lnorganic Fertilizers on Soil CarbonPool and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Orchards. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 5823–5831. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Wilson, B.; Ghoshal, S.; Senapati, N.; Mandal, B. Organic amendments influence soil quality and carbon sequestration in the Indo-Gangetic plains of India. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 156, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Dong, W.; Li, X.; Gu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Deng, S.; Wei, S.; Li, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, T. Research progress on the response of soil enzyme activity to changes in soil environment. South China Agric. 2023, 17, 42–46+52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Liang, W.J.; Wen, D. Effects of No-Tillage on Soil Biological Properties in Farmlands: A Review. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 35, 347–351. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.J.; Xia, X.; Chen, G.M.; Mao, D.; Che, S.G.; Li, Y.X. Study Progress on Functions and Affecting Factors of Soil Enzymes. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2011, 27, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qi, R.; Li, J.; Lin, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B. Temperature effects on soil organic carbon, soil labile organic carbon fractions, and soil enzyme activities under long-term fertilization regimes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 102, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Tian, J.H.; Wei, K.; Chen, Z.H.; Chen, L.J. Effects of carbon and nitrogen additions on soil organic C, N, P contents and their catalyzed enzyme activities in a grassland. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 2470–2476. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Q.; Zheng, M.; Su, Y.; Xiao, K.; Wang, K.; Li, D. Responses of soil microbial resource limitation to multiple fertilization strategies. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Lv, M.; Tian, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Jiang, Y.; Ge, S. Soil fertility, microbial biomass, and microbial functional diversity responses to four years fertilization in an apple orchard in North China. Hortic. Plant J. 2020, 6, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Shahid, M.; Tripathi, R.; Mohanty, S.; Kumar, A.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Lal, B.; Gautam, P.; Raja, R.; Panda, B.B.; et al. Variation of functional diversity of soil microbial community in sub-humid tropical rice-rice cropping system under long-term organic and inorganic fertilization. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 73, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, B.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, R.; Zhu, L.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, F. Effects of Different Fertilization Systems on Soil Microbe and Its Relation to Soil Fertility. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2005, 38, 1591–1599. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kamble, P.N.; Bååth, E. Induced N-limitation of bacterial growth in soil: Effect of carbon loading and N status in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 74, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, S.; Männistö, M.K.; Eskelinen, A. Nutrient availability and pH jointly constrain microbial extracellular enzyme activities in nutrient-poor tundra soils. Plant Soil 2014, 383, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hong, M.; Wen, X.; Pei, Z.; Zhao, H.; Chen, C.; Wen, X. Effect of Different Organic Amendments on Soil Organic Carbon Pool and Chemical Properties in Soda Alkaline Soil. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 311–318. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Y.; Wang, Y.; Brookes, P.; Dang, T.H.; Wang, W.Z. Effect of Soil pH on Soil Microbial Carbon Phosphorus Ratio. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2013, 46, 2709–2716. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Hao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dang, Y. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in the farmland of the Loess Plateau, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 1783–1791. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Xie, J.; Ciren, Q.; Guo, L.; Hong, J.; Jing, Y.; Meng, H. Effects of fertilization regimes on carbon and nitrogen contents of aggregates and maize yield in reclaimed soils. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
| Treatment | Cumulative Fertilizer Application (kg·hm−2) | Cumulative Organic Fertilizer Application (kg·hm−2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | ||
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| FP | 1500.0 | 261.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| OF | 899.3 | 284.6 | 236.1 | 0.0 |
| OFM | 567.8 | 158.6 | 32.0 | 19,991 |
| OFB | 567.8 | 158.6 | 32.0 | 19,991 |
| MBN (mg·kg−1) | SAK (mg·kg−1) | MBP (mg·kg−1) | Dissolved Organic Carbon (g·kg−1) | LFOC (g·kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | 0.0002 | 0.0009 | 0.0002 | 0.0006 | 0.0002 |
| Mean | 8.129 | 169.6 | 6.352 | 0.182 | 5.892 |
| HFOC (g·kg−1) | β-G (nmol·g−1·h−1) | NAG (nmol·g−1·h−1) | Soil pH | GY (exp (kg·hm−2)) | |
| p | 0.0003 | 0.0013 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 |
| Mean | 4.909 | 20.729 | 10.813 | 7.748 | 8.104 |
| A | AI | CPI | CPMI | CPSI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.609 ab | 1.000 ab | 1.000 b | 100.000 a | 2.938 a |
| FP | 0.704 a | 1.158 a | 1.092 b | 126.454 a | 1.939 b |
| OF | 0.529 ab | 0.873 b | 1.231 a | 107.466 a | 2.219 b |
| OFM | 0.499 b | 0.829 b | 1.342 a | 111.252 a | 2.102 b |
| OFB | 0.609 ab | 0.992 ab | 1.121 a | 111.203 a | 2.172 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Hu, X.; Chang, Z.; Song, H.; Li, T.; Li, L. The Effects of Various Long-Term Fertilizer Applications on Soil Carbon Fractions in a Winter Wheat Monoculture Area. Agronomy 2024, 14, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010082
Yang L, Hu X, Chang Z, Song H, Li T, Li L. The Effects of Various Long-Term Fertilizer Applications on Soil Carbon Fractions in a Winter Wheat Monoculture Area. Agronomy. 2024; 14(1):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010082
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Lifan, Xuan Hu, Zixuan Chang, Hongmei Song, Tingliang Li, and Li Li. 2024. "The Effects of Various Long-Term Fertilizer Applications on Soil Carbon Fractions in a Winter Wheat Monoculture Area" Agronomy 14, no. 1: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010082
APA StyleYang, L., Hu, X., Chang, Z., Song, H., Li, T., & Li, L. (2024). The Effects of Various Long-Term Fertilizer Applications on Soil Carbon Fractions in a Winter Wheat Monoculture Area. Agronomy, 14(1), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010082





