Response of Evapotranspiration, Photosynthetic Characteristics and Yield of Soybeans to Groundwater Depth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
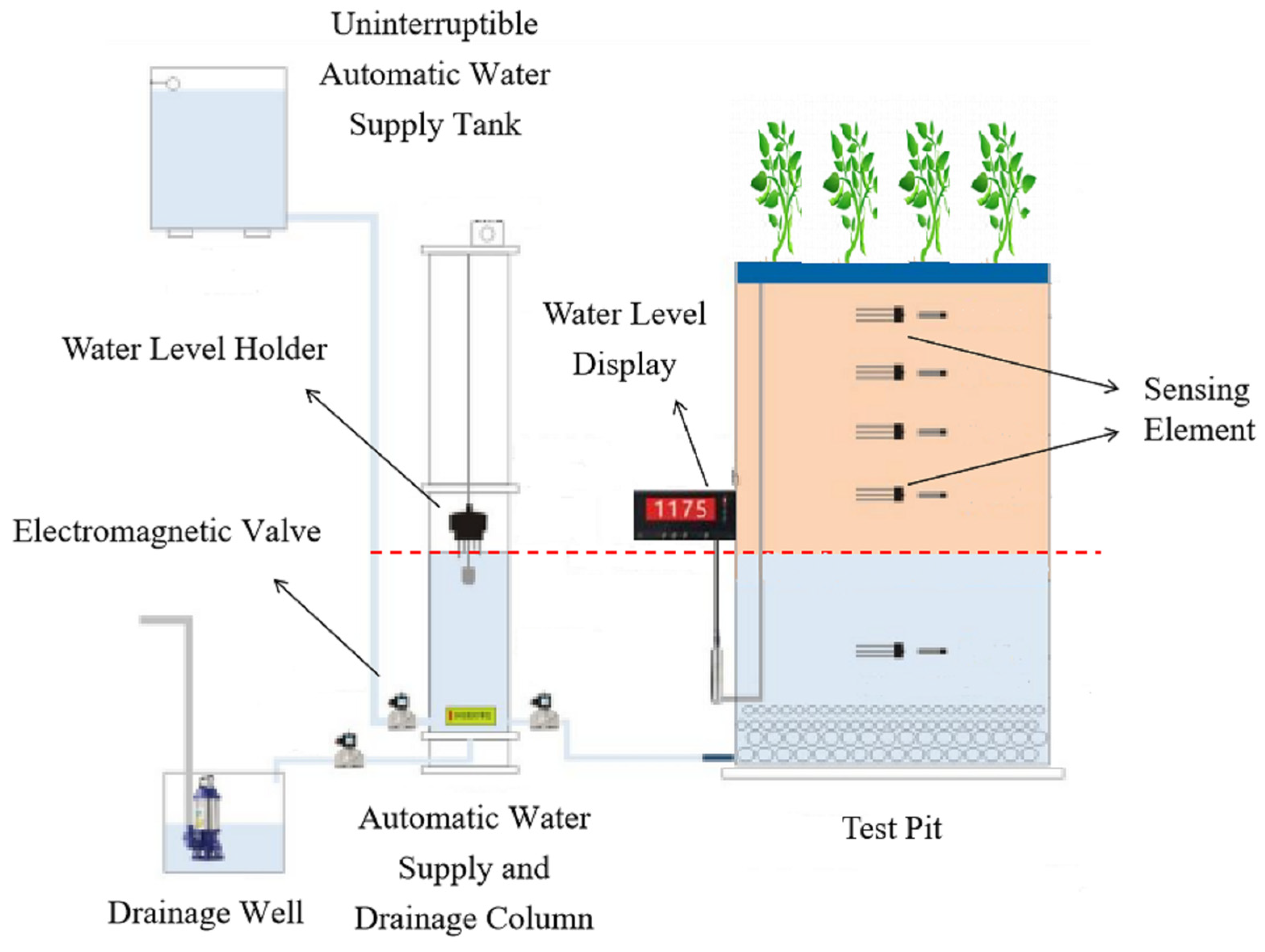
2.2. Research Program
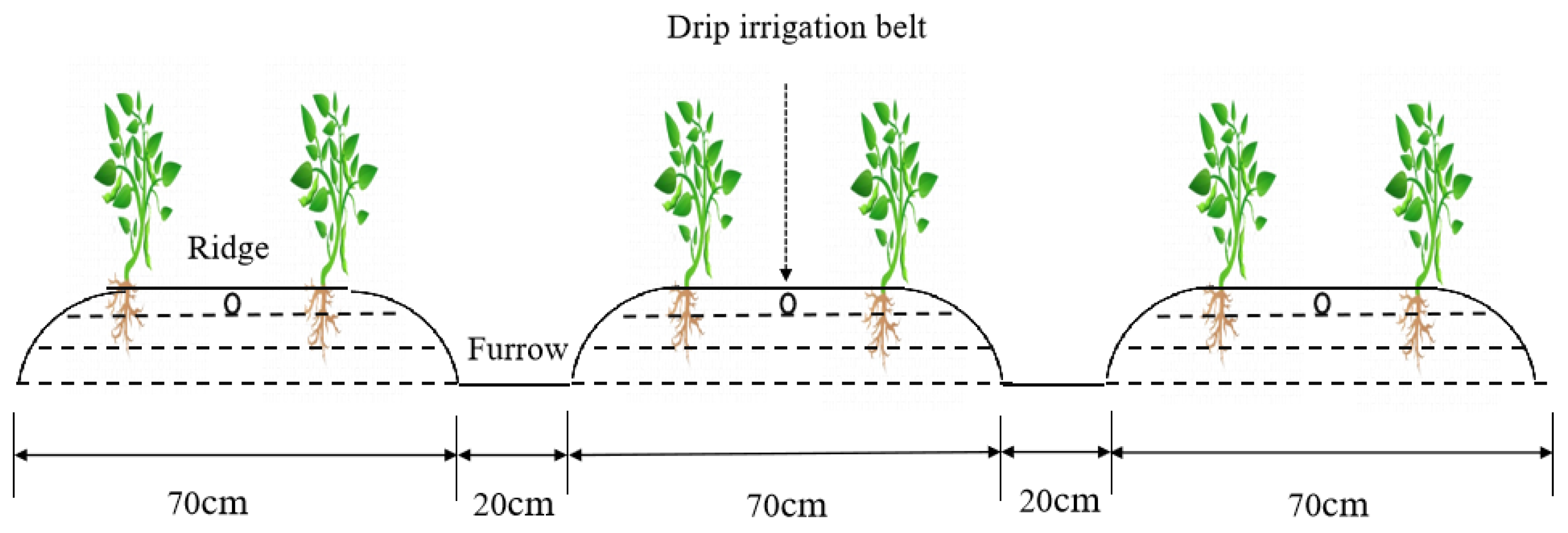
2.2.1. Experimental Design
2.2.2. Crop Management and Irrigation
2.3. Measurements
2.3.1. Groundwater Recharge and Irrigation
2.3.2. Evapotranspiration (ET) and Groundwater Contribution
2.3.3. Leaf Area Index (LAI)
2.3.4. Chlorophyll Relative Content (SPAD)
2.3.5. Intercepted Photosynthetic Active Radiation (IPAR)
2.3.6. Photosynthetic Gas Exchange Parameters
2.3.7. Dry Matter Accumulation (DMA) and Yield
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Groundwater Recharge and Irrigation
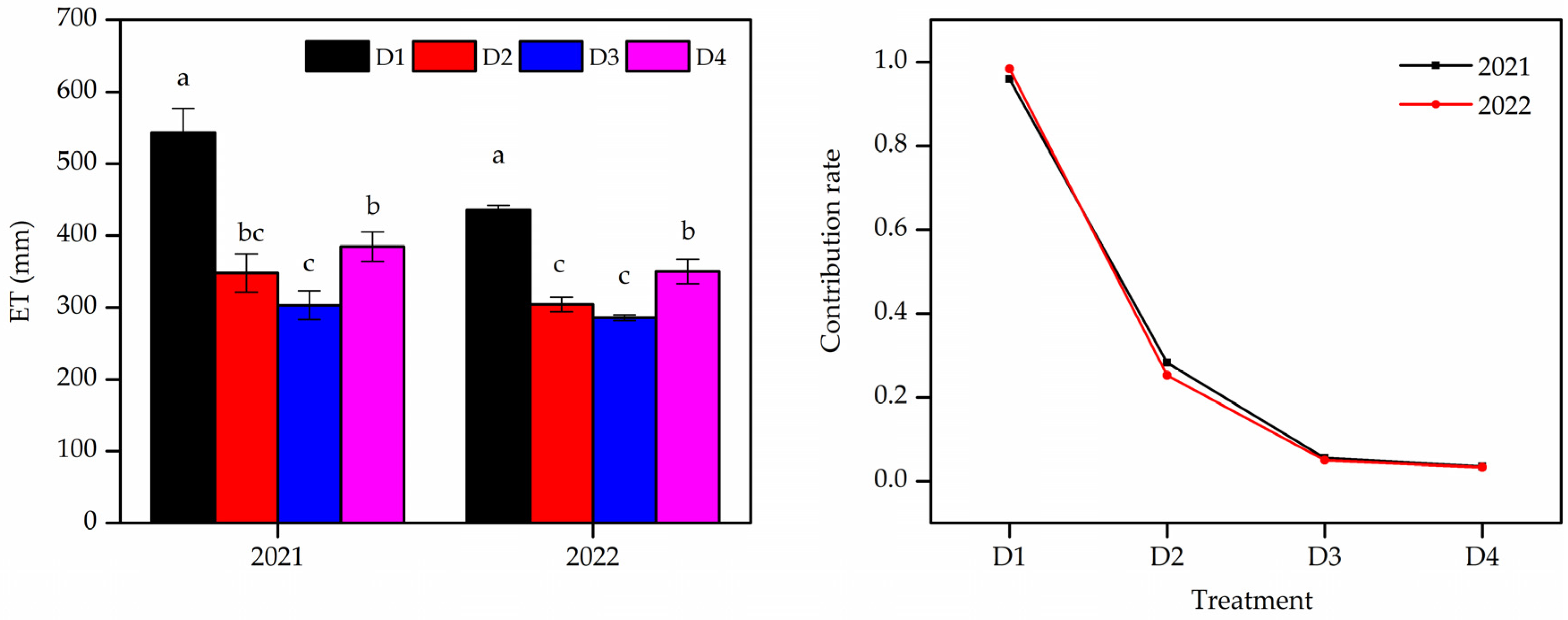
3.2. Evapotranspiration (ET) and Groundwater Contribution
3.3. Leaf Area Index (LAI)
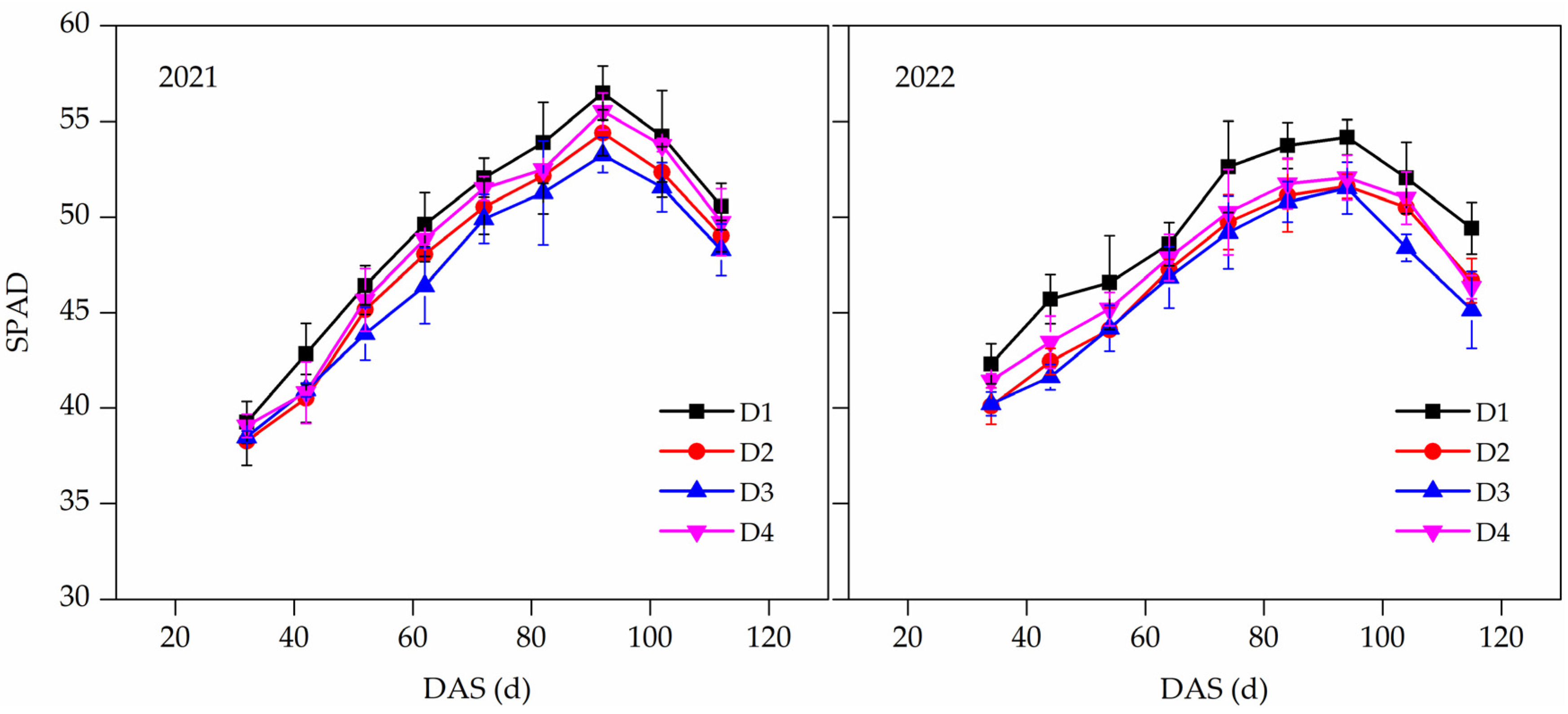
3.4. Chlorophyll Content Index (SPAD)
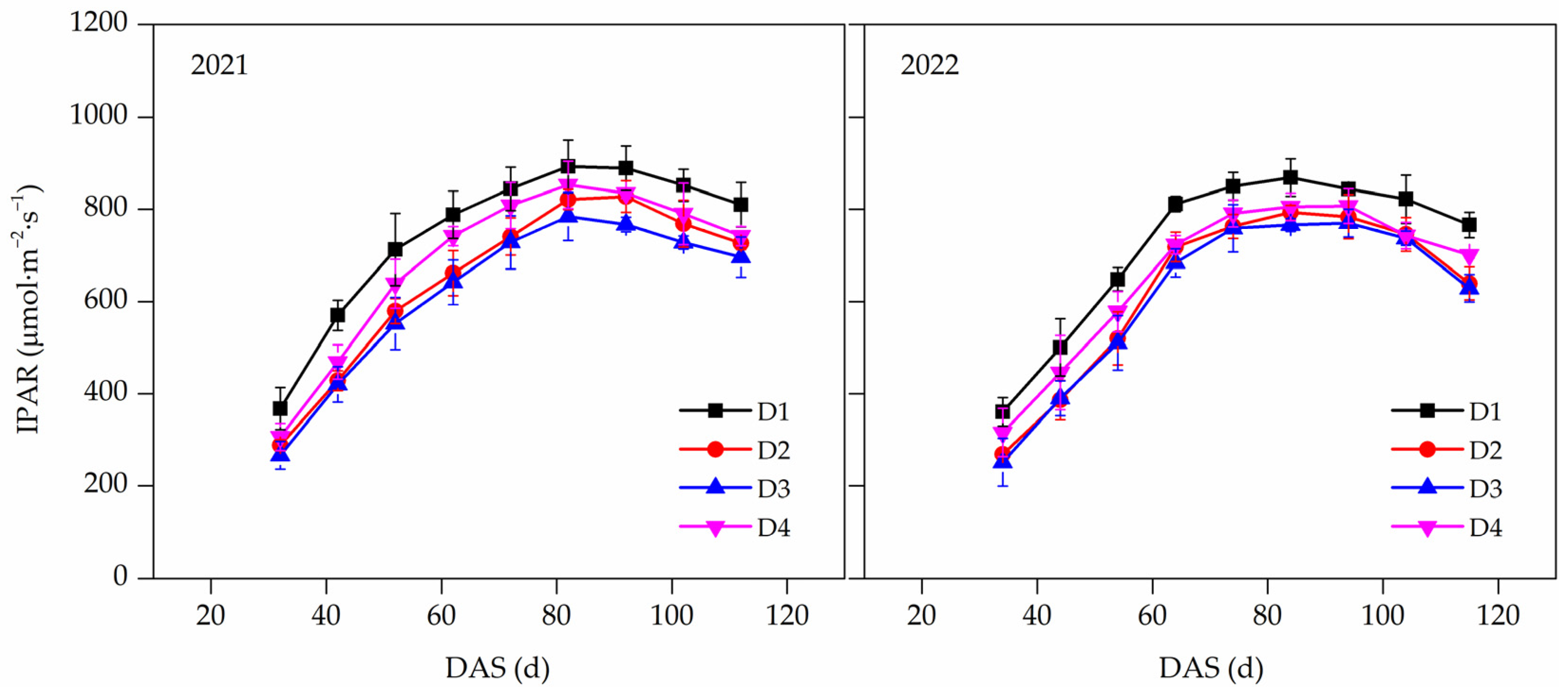
3.5. Intercepted Photosynthetic Active Radiation (IPAR)
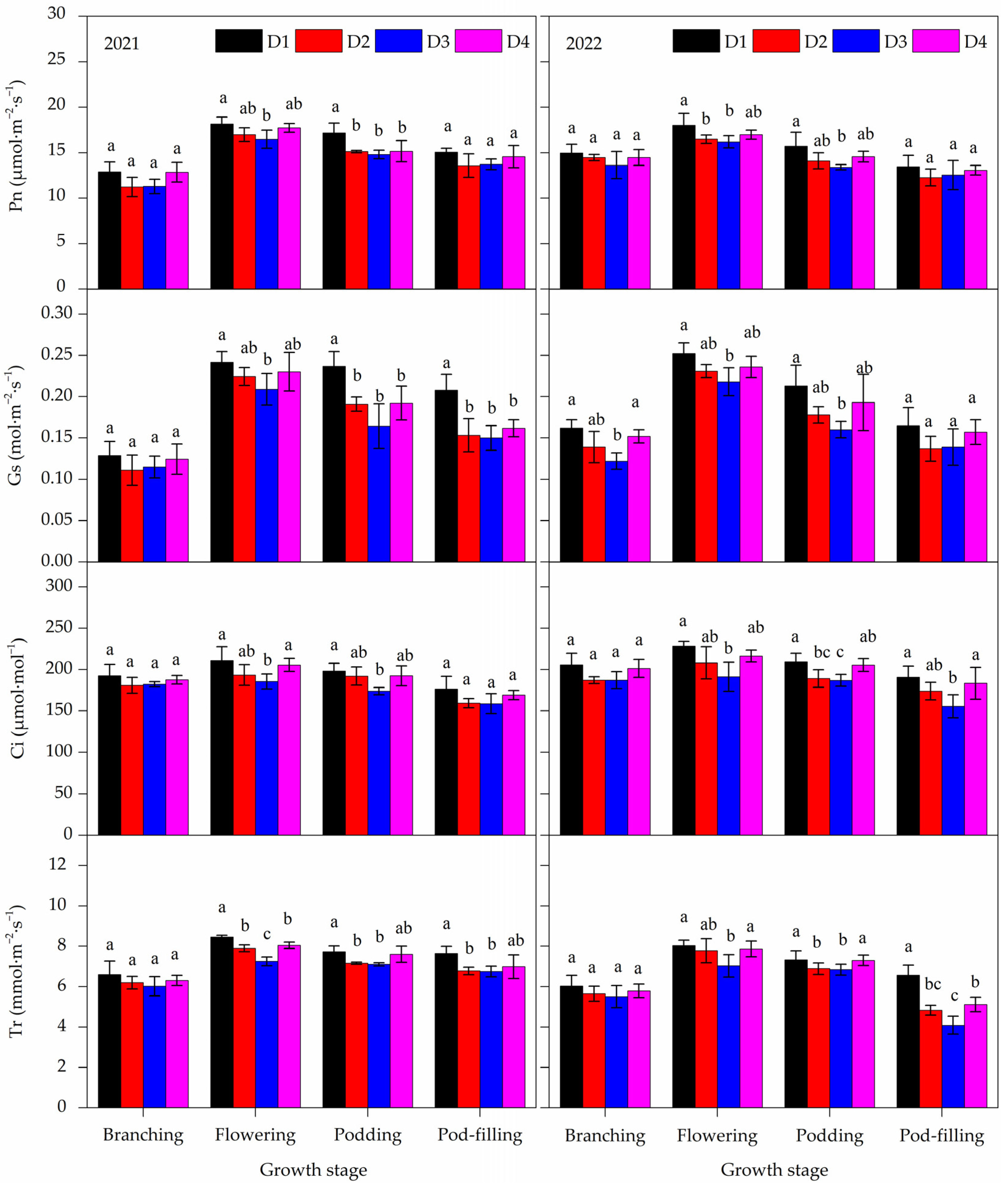
3.6. Photosynthetic Gas Exchange Parameters
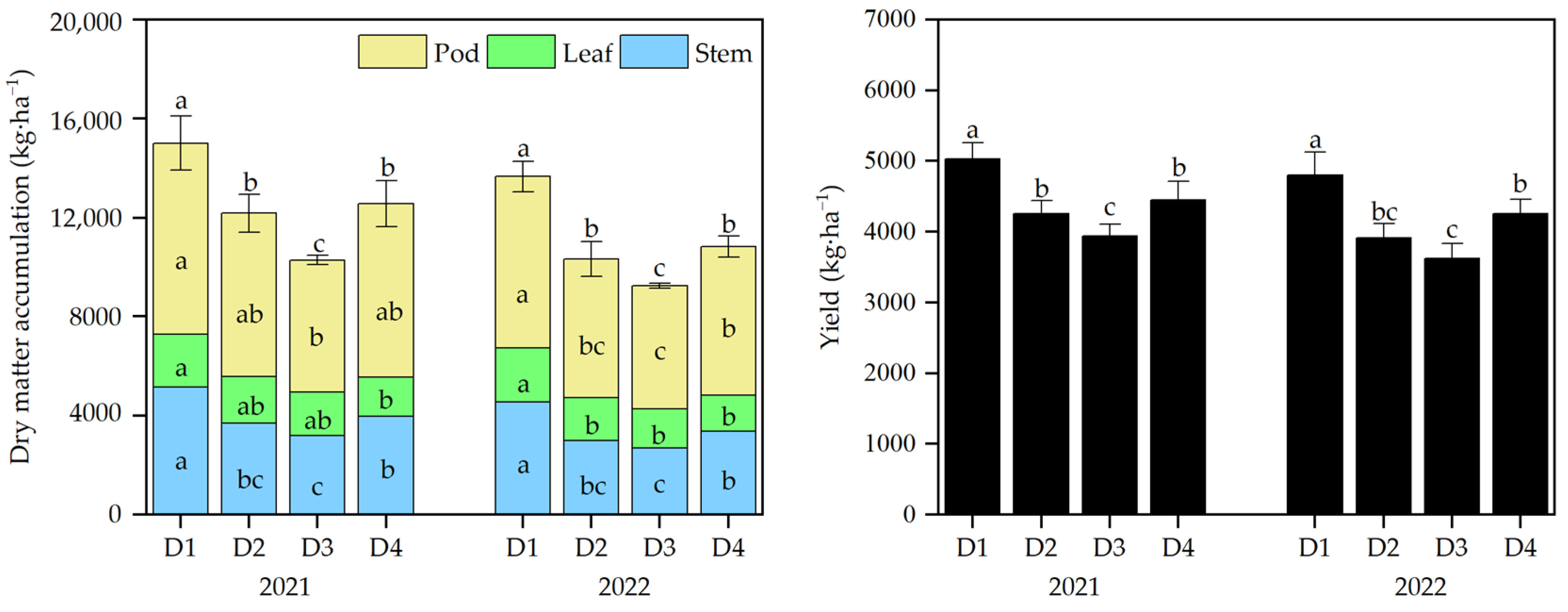
3.7. Dry Matter Accumulation (DMA) and Yield
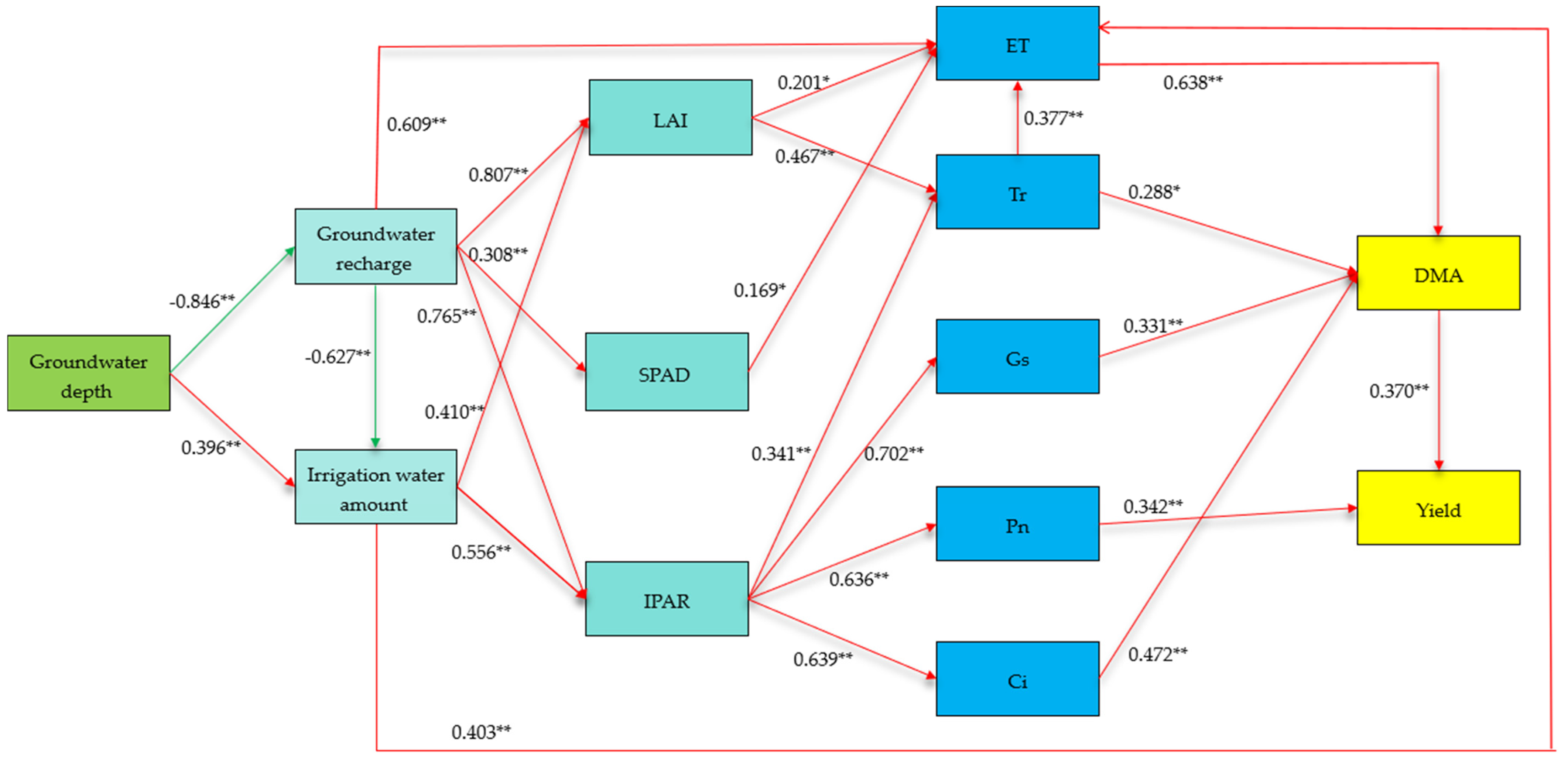
3.8. Structural Equation Modeling Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feldman, A.F.; Gianotti, D.J.S.; Konings, A.G.; Gentine, P.; Entekhabi, D. Patterns of plant rehydration and growth following pulses of soil moisture availability. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 831–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, R.; Irmak, S. Effects of subsurface drip-irrigated soybean seeding rates on grain yield, evapotranspiration and water productivity under limited and full irrigation and rainfed conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 267, 107614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.J.; Li, P.; Qi, X.B.; Guo, W.; Rahman, S.U.; Lu, H.F.; Ma, C.C.; Du, Z.J.; Cui, J.X.; Liang, Z.J. Effects of shallow groundwater depth and nitrogen application level on soil water and nitrate content, growth and yield of winter wheat. Agriculture 2022, 12, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, U.K.; Tischbein, B.; Martius, C. A GIS-based approach for up-scaling capillary rise from field to system level under soil–crop–groundwater mix. Irrig. Sci. 2014, 32, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, I.; Fleige, H.; Horn, R. Longtime effects of deep groundwater extraction management on water table levels in surface aquifers. J. Soil Sediment 2017, 17, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huang, G.H.; Sun, C.; Pereira, L.S.; Ramos, T.B.; Huang, Q.Z.; Hao, Y.Y. Assessing the effects of water table depth on water use, soil salinity and wheat yield: Searching for a target depth for irrigated areas in the upper Yellow River Basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 125, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.Q.; Qi, X.B.; Ma, Y.G.; Qiao, D.M.; Li, P.; Huang, Z.D.; Fan, X.Y. Effects of reclaimed water irrigation on winter wheat growth under different groundwater tables. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. 2007, 6, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- She, Y.J.; Li, P.; Bai, F.F.; Du, Z.J.; Liang, Z.J.; Qi, X.B. The combined effects of groundwater depth and nitrogen fertilization on yield of summer maize and nitrate distribution in soil. J. Irrig. Drain. 2021, 40, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.Y. Soybean Water Consumption and Growth in Response to Varying Groundwater Depths; Shenyang Agricultural University: Shenyang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ghobadi, M.E.; Ghobadi, M.; Zebarjadi, A. Effect of waterlogging at different growth stages on some morphological traits of wheat varieties. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2017, 61, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langan, P.; Bernád, V.; Walsh, J.; Henchy, J.; Khodaeiaminjan, M.; Mangina, E.; Negrão, S. Phenotyping for waterlogging tolerance in crops: Current trends and future prospects. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 5149–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abliz, A.; Tiyip, T.; Ghulam, A.; Halik, Ü.; Ding, J.L.; Sawut, M.; Zhang, F.; Nurmemet, I.; Abliz, A. Effects of shallow groundwater table and salinity on soil salt dynamics in the Keriya Oasis, Northwestern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlown, M.A.; Ashraf, M.; Ziaul, H. Effect of shallow groundwater table on crop water requirements and crop yields. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 76, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.B.; Simionesei, L.; Jauch, E.; Almeida, C.; Neves, R. Modelling soil water and maize growth dynamics influenced by shallow groundwater conditions in the Sorraia Valley region, Portugal. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 185, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.S.; Eshmuratov, D.; Bezborodov, G. Determining optimal groundwater table depth for maximizing cotton production in the Sardarya province of Uzbekistan. Irrig. Drain. 2011, 60, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tian, Z.X. Genomics progress will facilitate molecular breeding in soybean. Sci. China Life Sci. 2015, 58, 813–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.C.; Torre, M.; Marina, M.L.; Laborda, F.; Rodriquez, A.R. Composition and characterization of soyabean and related products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 1997, 37, 361–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Q.; Jiang, A.H.; Ma, R.H.; Gao, W.R.; Tan, P.T.; Li, X.; Du, C.Z.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhang, L.; et al. QTL mapping for seed quality traits under multiple environments in soybean (Glycine max L.). Agronomy 2023, 13, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Y.Y.; You, N.S.; Dong, J.W.; Liao, X.Y.; Song, K.S.; Fu, P. Recent soybean subsidy policy did not revitalize but stabilize the soybean planting areas in Northeast China. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 147, 126841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Soybean Revitalization Program. Available online: https://www.moa.gov.cn (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- The Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. The Chinese No. 1 Central Documents. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- Dong, Z. Physiology of Soybean Yield; China Agricultural Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Cassel, D.K.; Nielsen, D.R. Field capacity and available water capacity. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1 Physical and Mineralogical Methods; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; Volume 5, pp. 901–926. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.L.; Wu, W.Y.; Xiao, J.; Huang, Q.N.; Hu, Y.Q. Effects of different drip irrigation modes on water use efficiency of pear trees in northern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.L.; Chen, L.D.; Fu, B.J.; Huang, J.L.; Gong, J. The wheat yields and water-use efficiency in the loess plateau: Straw mulch and irrigation effects. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 72, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, J.; Drury, C.F. Effect of conservation and conventional tillage on soil water storage, water use efficiency and productivity of corn and soybean in Northeast China. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2013, 63, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, A.B.; Nascimento, J.G.; Moura, L.B.; Lopes, T.R.; Duarte, S.N.; Coelho, D.; Marques, P.A.A. Non-destructive and destructive methods to determine the leaf area of zucchini. J. Agric. Stud. 2020, 8, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, Z.D.; Wei, S.Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Q.F.; Zong, R.; Li, Q.Q. Response of water radiation utilization of summer maize to planting density and genotypes in the north China plain. Agronomy 2022, 13, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.Y.; Jin, M.G.; Liang, X.; Lin, D. Changes of vertical groundwater recharge with increase in thickness of vadose zone simulated by one-dimensional variably saturated flow model. J. Earth Sci. 2014, 25, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiyono, T.D.; Weiss, A.; Specht, J.E.; Cassman, K.G.; Dobermann, A. Leaf area index simulation in soybean grown under near-optimal conditions. Field Crop. Res. 2008, 108, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.H.; Chen, S.Z.; Li, X.X.; Cunha, M.; Jayavelu, S.; Cammarano, D.; Fu, T.S. Machine learning-based approaches for predicting SPAD values of maize using multi-spectral images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-ghawry, A.; Yazar, A.; Unlu, M.; Colak, Y.B. Comparison of physiological response to growth stage-based supplemental and conventional irrigation management of wheat. J. Agri. Sci. 2021, 159, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, M.; Murchie, E.H.; Lindfors, A.V.; Urban, O.; Aphalo, P.J.; Robson, T.M. Diffuse solar radiation and canopy photosynthesis in a changing environment. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 311, 108684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakoda, K.; Yamori, W.; Groszmann, M.; Evans, J.E. Stomatal, mesophyll conductance, and biochemical limitations to photosynthesis during induction. Plant Physiol. 2021, 185, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.B.; Lang, Y.; Zhao, Q.K.; Liu, P.; Su, L. Photosynthetic characteristics of Tamarix chinensis under different groundwater depths in freshwater habitats. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal-Sala, D.; Grote, R.; Birami, B.; Knüver, T.; Rehschuh, R.; Schwarz, S.; Ruehr, N.K. Leaf shedding and non-stomatal limitations of photosynthesis mitigate hydraulic conductance losses in scots pine saplings during severe drought stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 715127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Growth Stage | Lower Limits of Soil Moisture (%) | Upper Limits of Soil Moisture (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Seedling stage | 65 | 75 |
| Branching stage | 70 | 80 |
| Flowering stage | 75 | 85 |
| Podding stage | 75 | 85 |
| Pod-filling stage | 65 | 75 |
| Year | Treatment | Branching Stage | Flowering Stage | Podding Stage | Pod-Filling Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | D1 | 3.40 ± 0.37 a | 5.05 ± 0.34 a | 5.66 ± 0.39 a | 4.98 ± 0.23 a |
| D2 | 2.46 ± 0.25 b | 4.00 ± 0.41 bc | 5.15 ± 0.33 ab | 4.63 ± 0.36 ab | |
| D3 | 2.39 ± 0.29 b | 3.91 ± 0.31 c | 4.87 ± 0.29 b | 4.32 ± 0.26 b | |
| D4 | 2.89 ± 0.30 ab | 4.44 ± 0.19 b | 5.30 ± 0.21 ab | 4.67 ± 0.32 ab | |
| 2022 | D1 | 2.93 ± 0.43 a | 4.81 ± 0.31 a | 5.07 ± 0.42 a | 4.44 ± 0.10 a |
| D2 | 2.20 ± 0.27 b | 3.80 ± 0.34 b | 4.25 ± 0.28 b | 3.78 ± 0.19 b | |
| D3 | 2.17 ± 0.25 b | 3.71 ± 0.44 b | 4.06 ± 0.33 b | 3.60 ± 0.24 b | |
| D4 | 2.38 ± 0.36 ab | 4.25 ± 0.31 ab | 4.42 ± 0.28 ab | 3.83 ± 0.28 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Shen, R.; Sun, S. Response of Evapotranspiration, Photosynthetic Characteristics and Yield of Soybeans to Groundwater Depth. Agronomy 2024, 14, 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010183
Zhu Z, Chen Z, Wang Z, Shen R, Sun S. Response of Evapotranspiration, Photosynthetic Characteristics and Yield of Soybeans to Groundwater Depth. Agronomy. 2024; 14(1):183. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010183
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Zhenchuang, Zhijun Chen, Zhe Wang, Ruxuan Shen, and Shijun Sun. 2024. "Response of Evapotranspiration, Photosynthetic Characteristics and Yield of Soybeans to Groundwater Depth" Agronomy 14, no. 1: 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010183
APA StyleZhu, Z., Chen, Z., Wang, Z., Shen, R., & Sun, S. (2024). Response of Evapotranspiration, Photosynthetic Characteristics and Yield of Soybeans to Groundwater Depth. Agronomy, 14(1), 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010183






