Swine Wastewater Treatment System Using Constructed Wetlands Connected in Series
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
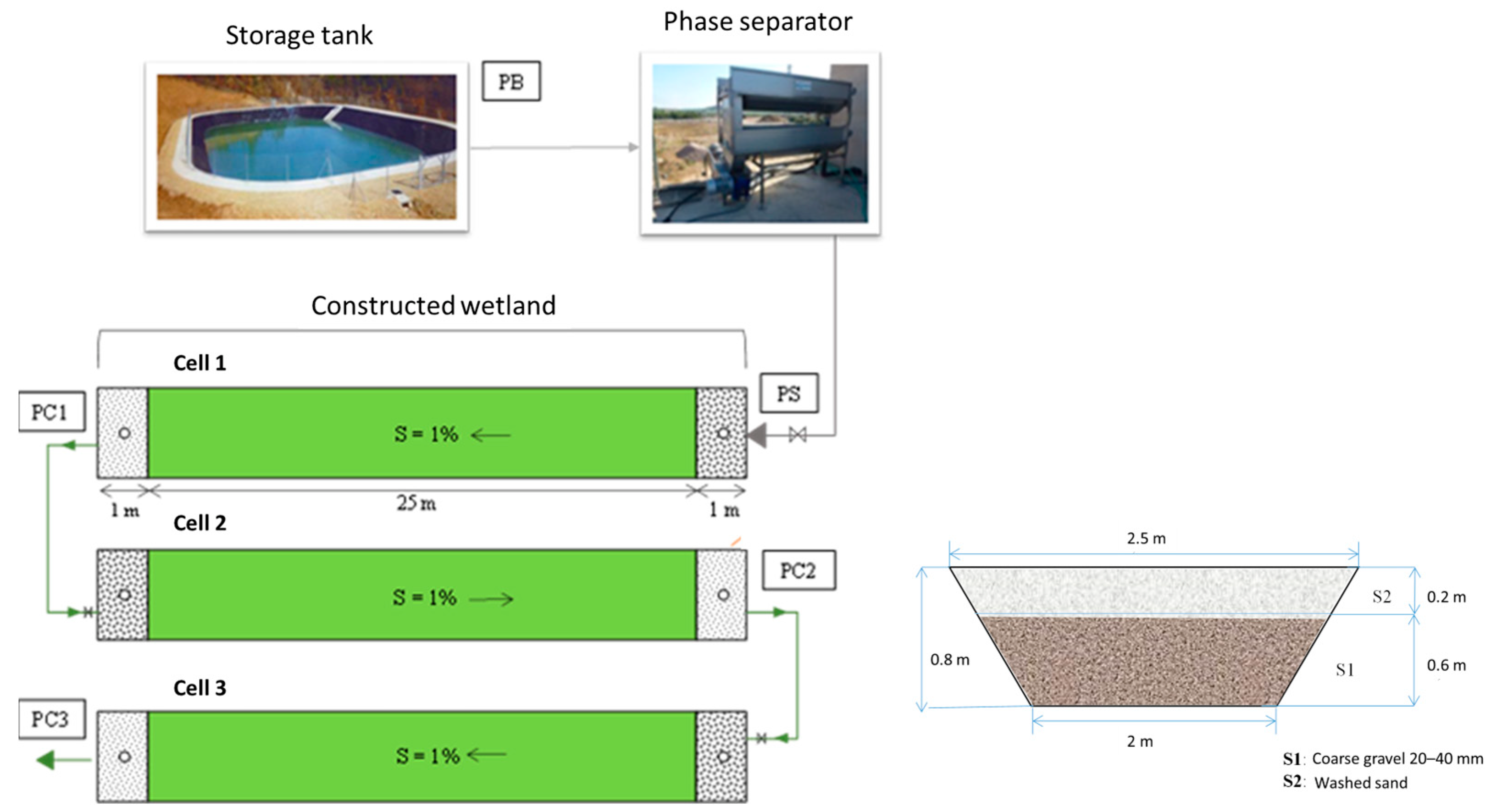
2.2. Treatment System and Sampling
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Pig Slurry during the Treatment
3.2. Efficiency of the Treatment System
3.3. Relationship between Physical–Chemical Properties of Swine Wastewater in the Treatment System
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eurostat. 2019. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/data/database (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Makara, A. Comparative analyses of pig farming management systems using the Life Cycle Assessment method. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Han, G.B. Pig slurry treatment by a hybrid multi-stage unit system consisting of an ATAD and an EGSB followed by a SBR reactor. Biosyst. Eng. 2012, 111, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrero, M.A. Efficiency of an integrated purification system for pig slurry treatment under mediterranean climate. Agronomy 2020, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secco, C. Circular economy in the pig farming chain: Proposing a model for measurement. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, E. Pharmaceuticals removal in an on-farm pig slurry treatment plant based on solid-liquid separation and nitrification-denitrification systems. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Tang, W.; Pei, Y. Constructed wetland substrates: A review on development, function mechanisms, and application in contaminants removal. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-Lajarín, A. Combination of Low-Cost Technologies for Pig Slurry Purification under Semiarid Mediterranean Conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, L.W. Long term heavy metal removal by a constructed wetland treating rainfall runoff from a motorway. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanakis, A.I. The role of constructed wetlands as green infrastructure for sustainable urban water management. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshoodeh, R.; Alavi, N.; Paydary, P. Composting plant leachate treatment by a pilot-scale, three-stage, horizontal flow constructed wetland in central Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 23803–23814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S. Impacts of different media on constructed wetlands for rural household sewage treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, M.E.; El-Reash, Y.G.A.; Ahmed, M.I.; Rizk, F.W. Effect of media variation on the removal efficiency of pollutants from domestic wastewater in constructed wetland systems. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 143, 105668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.-L.; Yang, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. The configuration, purification effect and mechanism of intensified constructed wetland for wastewater treatment from the aspect of nitrogen removal: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 293, 122086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Hernández-Crespo, C.; Santoni, M.; Van Hulle, S.; Rousseau, D.P.L. Horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands as tertiary treatment: Can they be an efficient barrier for microplastics pollution? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, K.S.; Deepa, M.; Anju, R.; Piyush, M. Treatment efficiency of vertical flow constructed wetland systems operated under different recirculation rates. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 474–480. [Google Scholar]
- SIAM. Available online: http://siam.imida.es/ (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Barco, A.; Borin, M. Treatment performance and macrophytes growth in a restored hybrid constructed wetland for municipal wastewater treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 107, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchaufour, P. Precis de Pedologie; Masson: Paris, France, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Shingare, R.P. Constructed wetland for wastewater reuse: Role and efficiency in removing enteric pathogens. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 444–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schierano, M.C.; Panigatti, M.C.; Maine, M.A.; Griffa, C.A.; Boglione, R. Horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland for tertiary treatment of dairy wastewater: Removal efficiencies and plant uptake. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 272, 111094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjorth, M. Solid-liquid separation of animal slurry in theory and practice. Sustain. Agric. 2009, 2, 953–986. [Google Scholar]
- Andreo-Martínez, P. Domestic wastewaters reuse reclaimed by an improved horizontal subsurface-flow constructed wetland. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 233, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bied, O. Purification performance of filtration process for pig slurry using marine sands, silty loam soils, fly ash and zeolite. Agronomy 2021, 118, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, A.; Saleh, T.A. Removal of toxic metals from wastewater in constructed wetlands as a green technology; catalyst role of substrates and chelators. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Mora-Orozco, C.; González-Acuña, I.J.; Saucedo-Terán, R.A.; Flores-López, H.E.; Rubio-Arias, H.O.; Ochoa-Rivero, J.M. Removing organic matter and nutrients from pig farm wastewater with a constructed wetland system. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idris, S.M.; Jones, P.L.; Salzman, S.A.; Croatto, G.; Allinson, G. Evaluation of the giant reed (Arundo donax) in horizontal subsurface flow wetlands for the treatment of recirculating aquaculture system effluent. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Queiroz, R.d.C.S.; Maranduba, H.L.; Hafner, M.B.; Rodrigues, L.B.; de Almeida Neto, J.A. Life cycle thinking applied to phytoremediation of dairy wastewater using aquatic macrophytes for treatment and biomass production. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 122006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóźwiakowski, K.; Bugajski, P.; Mucha, Z.; Wójcik, W.; Jucherski, A.; Nastawny, M.; Siwiec, T.; Mazur, A.; Obroślak, R.; Gajewska, M. Reliability and efficiency of pollution removal during long-term operation of a one-stage constructed wetland system with horizontal flow. Separ. Purif. Technol. 2017, 187, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koretsky, C.M. Influence of Spartina and Juncus on Saltmarsh Sediments. I. Pore Water Geochemistry. Chem. Geol. 2008, 255, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Heavy metals in sediments from constructed wetlands treating municipal wastewater. Biogeochemistry 2010, 101, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzakis, S. Constructed wetlands treating highway runoff in the central Mediterranean region. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, C.H. The potential contribution of separation technologies to the management of livestock manure. Livest. Sci. 2007, 112, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Q. Application of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment in tropical and subtropical regions (2000–2013). J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 30, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, L. Nutrient and organics removal from swine slurry with simultaneous electricity generation in an alum sludge-based constructed wetland incorporating microbial fuel cell technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 266, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.A. Effects of the Hydraulic Retention Time on Pig Slurry Purification by Constructed Wetlands and Stabilization Ponds. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Cui, X.; Li, H. Effects of fillers combined with biosorbents on nutrient and heavy metal removal from biogas slurry in constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, O. Improved pig slurry mechanical separation using chitosan and biochar. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 127, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borin, M.; Politeo, M.; De Stefani, G. Performance of a hybrid constructed wetland treating piggery wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 51, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Valero, A.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Faz, A.; Terrero, M.A.; Muñoz, M.A.; Gómez-López, M.D. Treatment of Wastewater from the Tannery Industry in a Constructed Wetland Planted with Phragmites australis. Agronomy 2020, 10, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PB | PS | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | 12.9 ± 1.6 | 13.5 ± 2.5 | 14.3 ± 2.7 | 14.7 ± 1.5 | 17.6 ± 2.9 |
| pH | 7.8 ± 0.1 | 8.2 ± 0.2 | 8.1 ± 0.4 | 8.1 ± 0.3 | 7.9 ± 0.2 |
| EC (dS m−1) | 13.5 ± 0.4 a | 10.1 ± 1.7 b | 10.8 ± 1.3 b | 10.6 ± 1.6 b | 7.6 ± 1.3 c |
| SS (g L−1) | 158 ± 25.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| TSS (g L−1) | 13.2 ± 2.4 | 10.1 ± 1.3 | 8.7 ± 2.0 | 9.0 ± 0.5 | 10.6 ± 2.9 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 213 ± 39 a | 52 ± 8 b | 86 ± 29 b | 69 ± 16 b | 76 ± 13 b |
| COD (g L−1) | 4.3 ± 1.8 a | 0.8 ± 0.6 b | 0.9 ± 0.5 b | 1.0 ± 0.4 b | 0.8 ± 0.3 b |
| KN (g L−1) | 1.5 ± 0.1 a | 0.7 ± 0.1 b | 0.9 ± 0.3 b | 0.8 ± 0.2 b | 0.2 ± 0.1 c |
| N-NH4+ (g L−1) | 0.9 ± 0.1 a | 0.4 ± 0.1 b | 0.5 ± 0.2 ab | 0.5 ± 0.2 ab | 0.1 ± 0.0 c |
| ON (g L−1) | 0.4 ± 0.2 a | 0.2 ± 0.0 b | 0.2 ± 0.0 b | 0.2 ± 0.1 b | 0.1 ± 0.1 b |
| TN (g L−1) | 1.6 ± 0.1 a | 0.9 ± 0.2 b | 1.1 ± 0.4 ab | 1.0 ± 0.2 b | 0.5 ± 0.0 c |
| Cl− (mg L−1) | 762 ± 55 | 915 ± 213 | 733 ± 102 | 769 ± 16 | 1011 ± 81 |
| N-NO2− (mg L−1) | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 69.7 ± 44.4 | 62.7 ± 6.9 | 6.9 ± 1.9 | 1.6 ± 0.8 |
| N-NO3− (mg L−1) | 7.5 ± 1.2 b | 9.6 ± 3.8 b | 5.4 ± 1.8 b | 5.1 ± 1.4 b | 100.3 ± 28.2 a |
| PO43− (mg L−1) | 147 ± 39 a | 50 ± 13 b | 41 ± 15 b | 37 ± 16 b | 35 ± 4 b |
| SO42− (mg L−1) | 152 ± 51 b | 1515 ± 591 a | 838 ± 161 a | 544 ± 53 a | 1514 ± 496 a |
| Na+ (mg L−1) | 425 ± 2 | 604 ± 172 | 462 ± 65 | 484 ± 17 | 1107 ± 366 |
| K+ (mg L−1) | 787 ± 25 a | 376 ± 18 b | 513 ± 35 ab | 402 ± 70 b | 312 ± 22 b |
| Ca+2 (mg L−1) | 322 ± 131 | 298 ± 169 | 171 ± 70 | 207 ± 67 | 416 ± 137 |
| Mg+2 (mg L−1) | 97 ± 9 | 219 ± 95 | 150 ± 25 | 148 ± 6 | 252 ± 114 |
| Cu (mg L−1) | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Zn (mg L−1) | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.0 |
| Fe (mg L−1) | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 1.0 ± 1.3 | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 0.4 ± 0.3 |
| Mn (mg L−1) | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.1 |
| Phase Separator | Constructed Wetland | Total Efficiency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EC | 25 | 25 | 44 |
| SS | 100 | 100 | |
| TSS | 23 | −5 | 20 |
| Turbidity | 75 | −47 | 64 |
| COD | 81 | 0 | 81 |
| KN | 53 | 71 | 87 |
| NH4+ | 58 | 80 | 92 |
| ON | 50 | 51 | 75 |
| TN | 44 | 33 | 63 |
| Cl− | −20 | −10 | −33 |
| PO43− | 65 | 30 | 76 |
| Na+ | −42 | −83 | −160 |
| K+ | 52 | 17 | 60 |
| Ca2+ | 7 | −40 | −29 |
| Mg2+ | −124 | −15 | −158 |
| Fe | −25 | 60 | 50 |
| pH | −0.72 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| EC | −0.33 | −0.14 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| SS | −0.08 | −0.37 | 0.96 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| STS | 0.18 | −0.41 | 0.77 | 0.89 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Turbidity | 0.12 | −0.56 | 0.85 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| COD | −0.1 | −0.38 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.87 | 0.95 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| KN | −0.35 | −0.2 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.68 | 0.81 | 0.94 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| NH4 | −0.44 | −0.12 | 0.97 | 0.89 | 0.62 | 0.76 | 0.91 | 0.99 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| ON | −0.08 | −0.42 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.8 | 0.91 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| TN | −0.14 | −0.31 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.77 | 0.86 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| Cl− | 0.9 | −0.45 | −0.53 | −0.29 | 0.1 | −0.06 | −0.32 | −0.59 | −0.67 | −0.36 | −0.41 | 1 | |||||||||||
| NO2− | −0.58 | 0.9 | −0.28 | −0.52 | −0.65 | −0.73 | −0.51 | −0.28 | −0.2 | −0.48 | −0.36 | −0.44 | 1 | ||||||||||
| NO3− | 0.96 | −0.55 | −0.49 | −0.24 | 0.1 | −0.02 | −0.27 | −0.54 | −0.62 | −0.28 | −0.34 | 0.98 | −0.48 | 1 | |||||||||
| PO43− | 0.48 | −0.54 | 0.59 | 0.76 | 0.94 | 0.85 | 0.74 | 0.49 | 0.42 | 0.68 | 0.65 | 0.36 | −0.7 | 0.38 | 1 | ||||||||
| SO42− | 0.43 | 0.19 | −0.88 | −0.79 | 0.44 | −0.65 | −0.81 | −0.95 | −0.96 | −0.87 | −0.88 | 0.73 | 0.16 | 0.64 | −0.25 | 1 | |||||||
| Na+ | 0.86 | −0.36 | −0.6 | −0.38 | 0.01 | −0.16 | −0.41 | −0.67 | −0.74 | −0.45 | −0.5 | 0.99 | −0.35 | 0.96 | 0.28 | 0.8 | 1 | ||||||
| K+ | −0.31 | −0.19 | 0.98 | 0.92 | 0.66 | 0.79 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.98 | −0.58 | −0.24 | −0.52 | 0.5 | −0.95 | −0.66 | 1 | |||||
| Ca2+ | 0.76 | −0.43 | −0.21 | 0.03 | 0.45 | 0.26 | −0.01 | −0.32 | −0.4 | −0.09 | −0.16 | 0.9 | −0.59 | 0.85 | 0.63 | 0.55 | 0.88 | −0.33 | 1 | ||||
| Mg2+ | 0.54 | 0.09 | −0.79 | −0.66 | −0.26 | −0.5 | −0.69 | −0.88 | −0.9 | −0.76 | −0.77 | 0.82 | 0.04 | 0.74 | −0.06 | 0.98 | 0.88 | −0.87 | 0.69 | 1 | |||
| Cu | −0.46 | 0.62 | −0.02 | −0.26 | −0.51 | −0.5 | −0.24 | 0.01 | 0.06 | −0.14 | −0.02 | −0.53 | 0.87 | −0.5 | −0.52 | −0.16 | −0.49 | 0.08 | −0.73 | −0.26 | 1 | ||
| Zn | −0.65 | 0.71 | 0.19 | −0.07 | −0.34 | −0.34 | −0.05 | 0.2 | 0.26 | 0.01 | 0.14 | −0.69 | 0.85 | −0.68 | −0.44 | −0.32 | −0.65 | 0.26 | −0.77 | −0.4 | 0.95 | 1 | |
| Fe | −0.9 | 0.72 | 0.16 | −0.12 | −0.45 | −0.36 | −0.09 | 0.21 | 0.3 | −0.04 | 0.04 | −0.89 | 0.78 | −0.9 | −0.66 | −0.38 | −0.84 | 0.22 | −0.93 | −0.52 | 0.77 | 0.86 | 1 |
| Mn | 0.72 | −0.13 | −0.63 | −0.44 | −0.01 | −0.25 | −0.48 | −0.73 | −0.78 | −0.55 | −0.57 | 0.94 | −0.19 | 0.88 | 0.22 | 0.88 | 0.97 | −0.72 | 0.86 | 0.95 | −0.41 | −0.55 | −0.74 |
| T | pH | EC | SS | STS | Turb | COD | KN | NH4+ | ON | TN | Cl− | NO2− | NO3− | PO43− | SO42− | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cu | Zn | Fe |
| Component | C1 | C2 | C3 | Extraction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 0.025 | 0.792 | 0.356 | 0.805 |
| pH | 0.009 | 0.3 | 0.653 | 0.773 |
| Electrical conductivity | 0.865 | 0.094 | 0.404 | 0.922 |
| Settleable solids | 0.867 | −0.141 | −0.081 | 0.788 |
| Total suspended solids | 0.743 | 0.478 | −0.366 | 0.932 |
| Turbidity | 0.812 | −0.016 | −0.214 | 0.736 |
| Chemical Oxygen Demand | 0.952 | −0.046 | −0.13 | 0.932 |
| Kjeldahl nitrogen | 0.928 | −0.158 | 0.317 | 0.987 |
| Ammonium | 0.843 | −0.188 | 0.477 | 0.974 |
| Organic nitrogen | 0.909 | −0.035 | −0.227 | 0.881 |
| Total nitrogen | 0.908 | −0.028 | 0.32 | 0.931 |
| Nitrites | −0.306 | 0.002 | 0.041 | 0.87 |
| Nitrates | −0.343 | 0.412 | −0.205 | 0.622 |
| Phosphates | 0.652 | 0.577 | −0.33 | 0.868 |
| Sulphates | 0.654 | 0.565 | −0.392 | 0.974 |
| Sodium | −0.194 | 0.937 | −0.248 | 0.979 |
| Potassium | 0.872 | −0.008 | 0.454 | 0.967 |
| Calcium | 0.008 | 0.534 | −0.819 | 0.958 |
| Magnesium | −0.432 | 0.817 | −0.262 | 0.97 |
| Copper | 0.02 | 0.061 | 0.696 | 0.776 |
| Zinc | 0.013 | −0.178 | 0.863 | 0.789 |
| Iron | 0.123 | −0.213 | 0.899 | 0.876 |
| Manganese | −0.264 | 0.775 | −0.506 | 0.93 |
| % Variance | 39.4 | 26.9 | 15 | |
| % Cumulative variance | 39.4 | 66.3 | 81.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Valero, A.; Acosta, J.A.; Faz, Á.; Gómez-López, M.D.; Carmona, D.M.; Terrero, M.A.; El Bied, O.; Martínez-Martínez, S. Swine Wastewater Treatment System Using Constructed Wetlands Connected in Series. Agronomy 2024, 14, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010143
García-Valero A, Acosta JA, Faz Á, Gómez-López MD, Carmona DM, Terrero MA, El Bied O, Martínez-Martínez S. Swine Wastewater Treatment System Using Constructed Wetlands Connected in Series. Agronomy. 2024; 14(1):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010143
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Valero, Amalia, José Alberto Acosta, Ángel Faz, María Dolores Gómez-López, Dora María Carmona, Martire Angélica Terrero, Oumaima El Bied, and Silvia Martínez-Martínez. 2024. "Swine Wastewater Treatment System Using Constructed Wetlands Connected in Series" Agronomy 14, no. 1: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010143
APA StyleGarcía-Valero, A., Acosta, J. A., Faz, Á., Gómez-López, M. D., Carmona, D. M., Terrero, M. A., El Bied, O., & Martínez-Martínez, S. (2024). Swine Wastewater Treatment System Using Constructed Wetlands Connected in Series. Agronomy, 14(1), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010143








