Influence of Long-Term Soil Management Practices on Carbon Emissions from Corn (Zea mays L.) Production in Northeast Croatia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
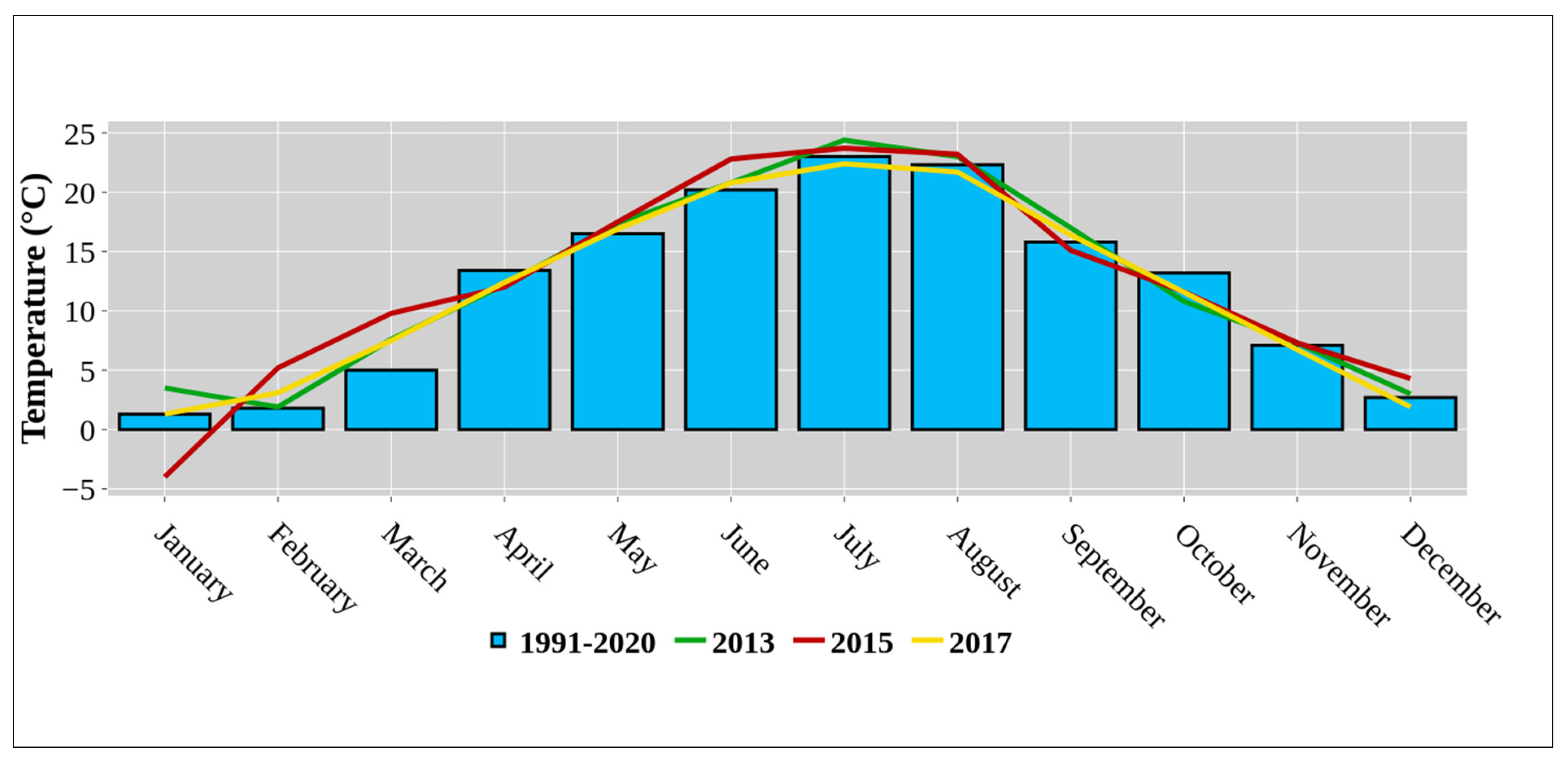
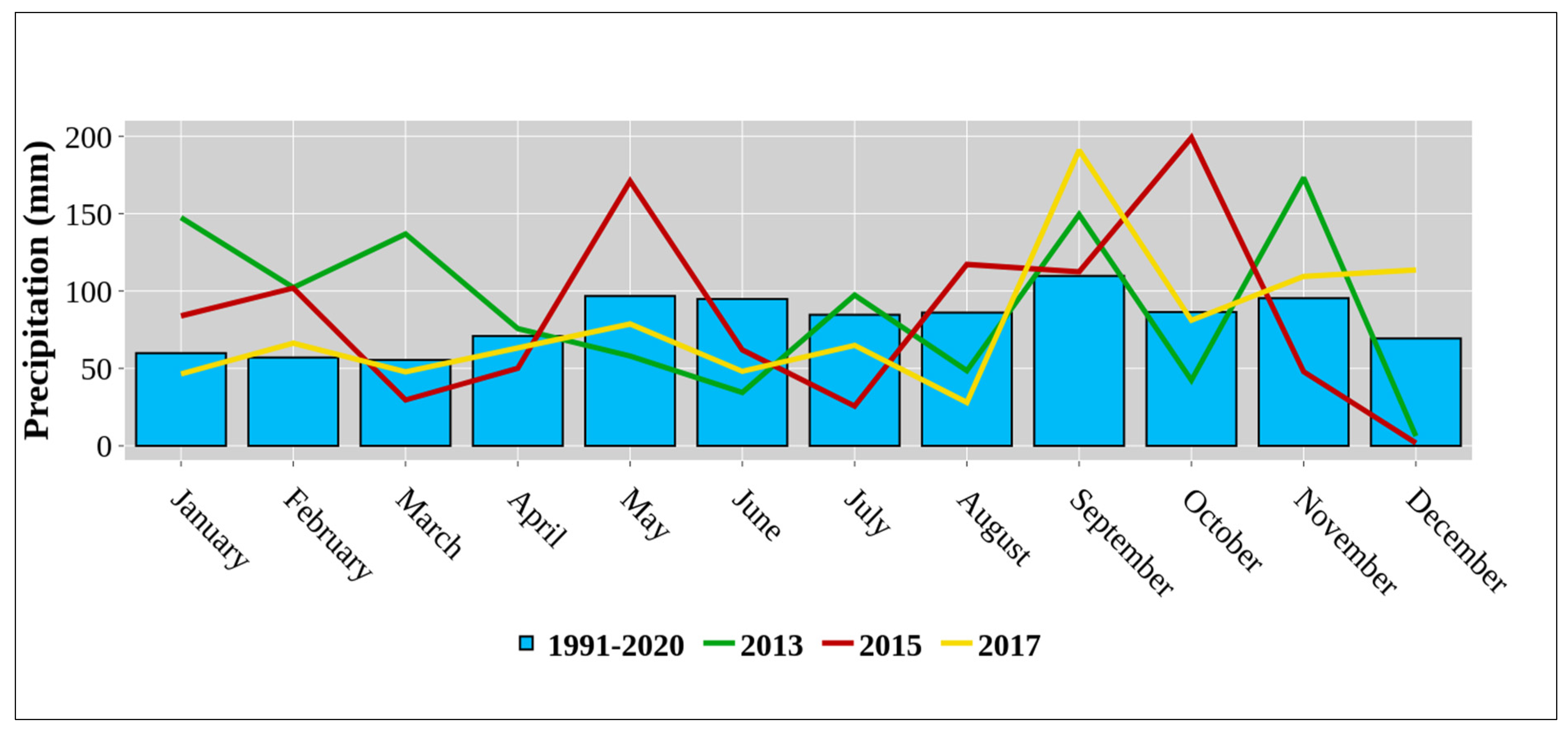
2.1. Study Site and Climate
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Laboratory Work
2.4. Soil CO2 Concentration Measurement
2.5. Measurements of Agro-Ecological Factors
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
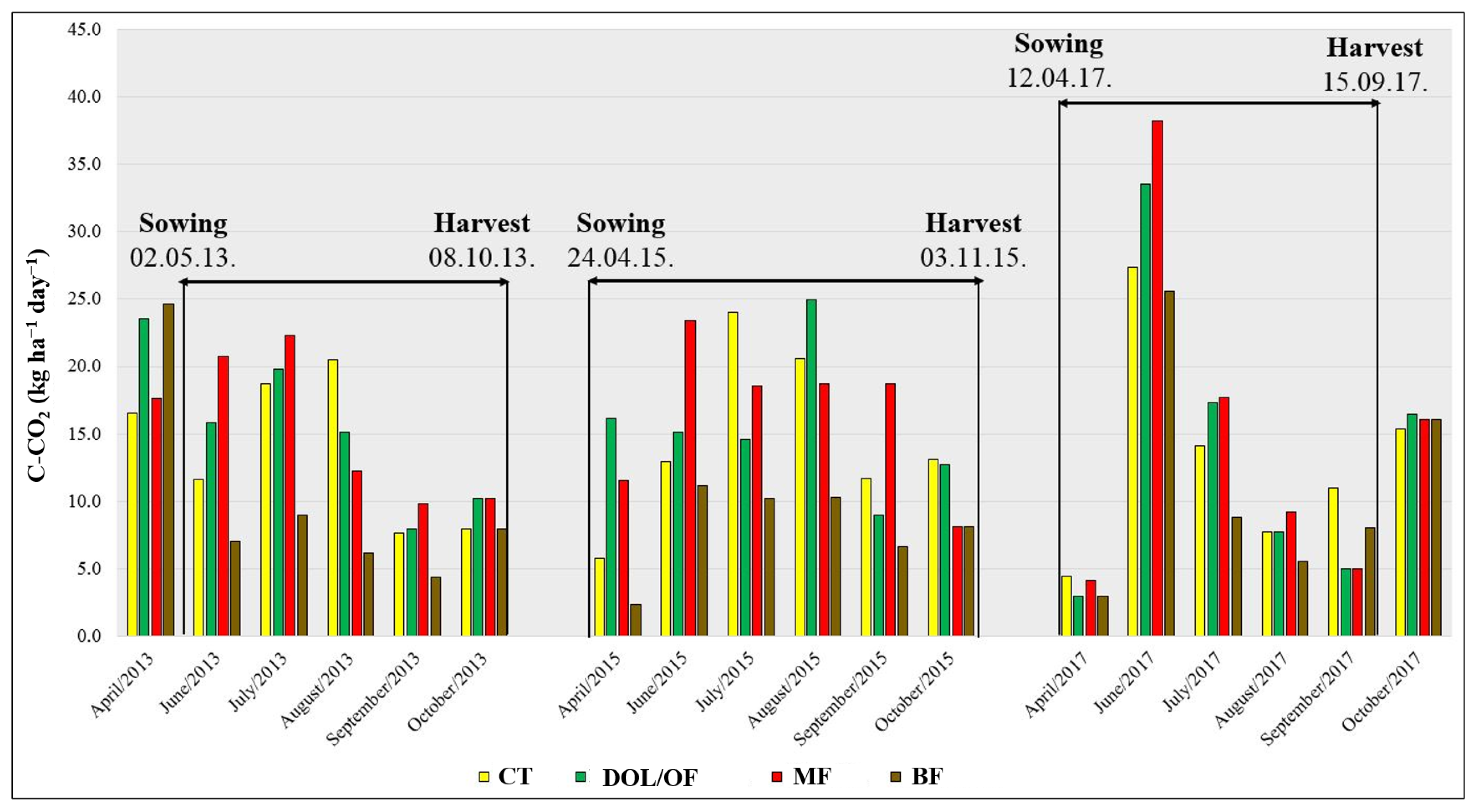
3.1. Soil C-CO2 Emissions under Different Soil Management
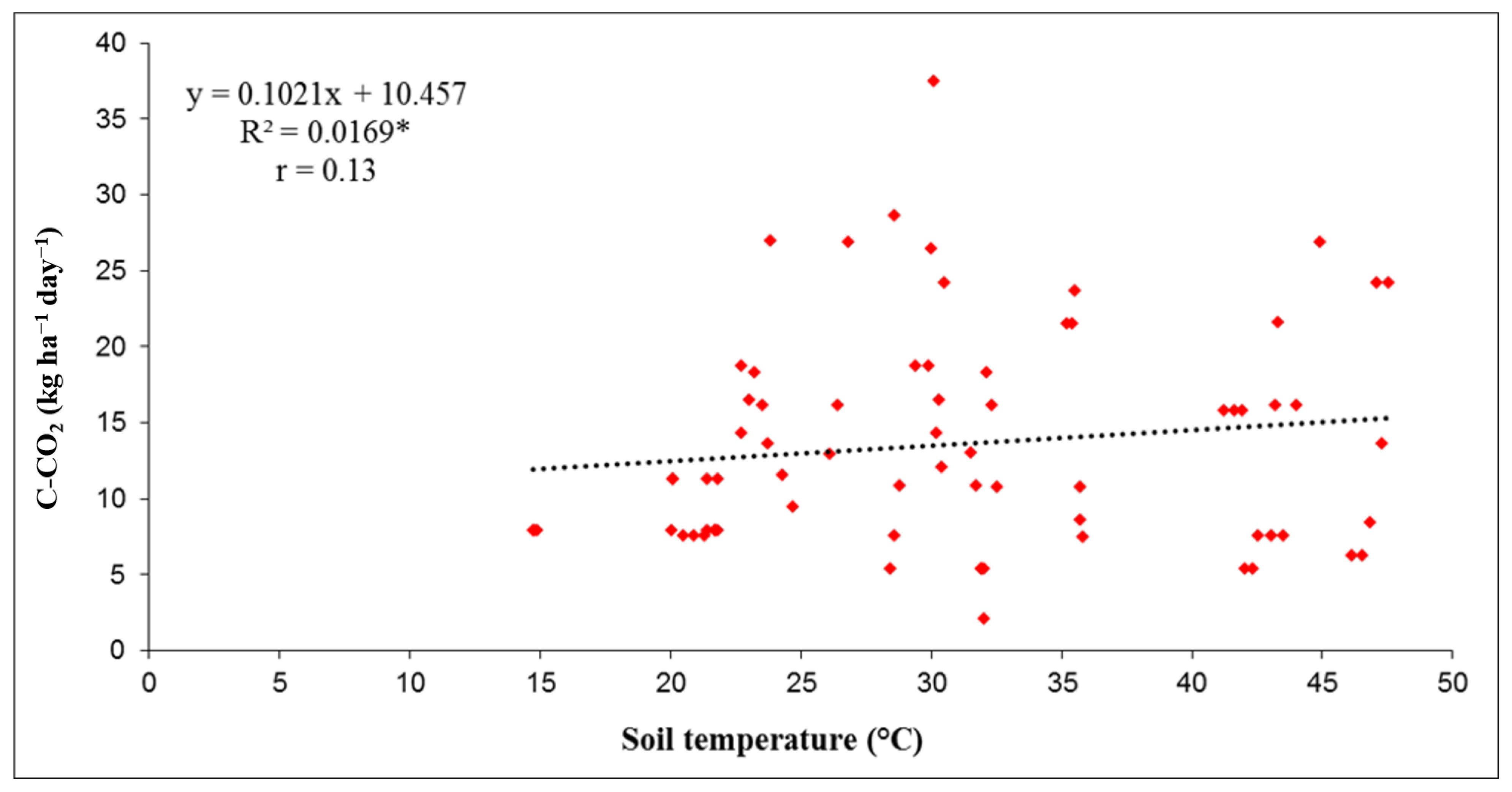
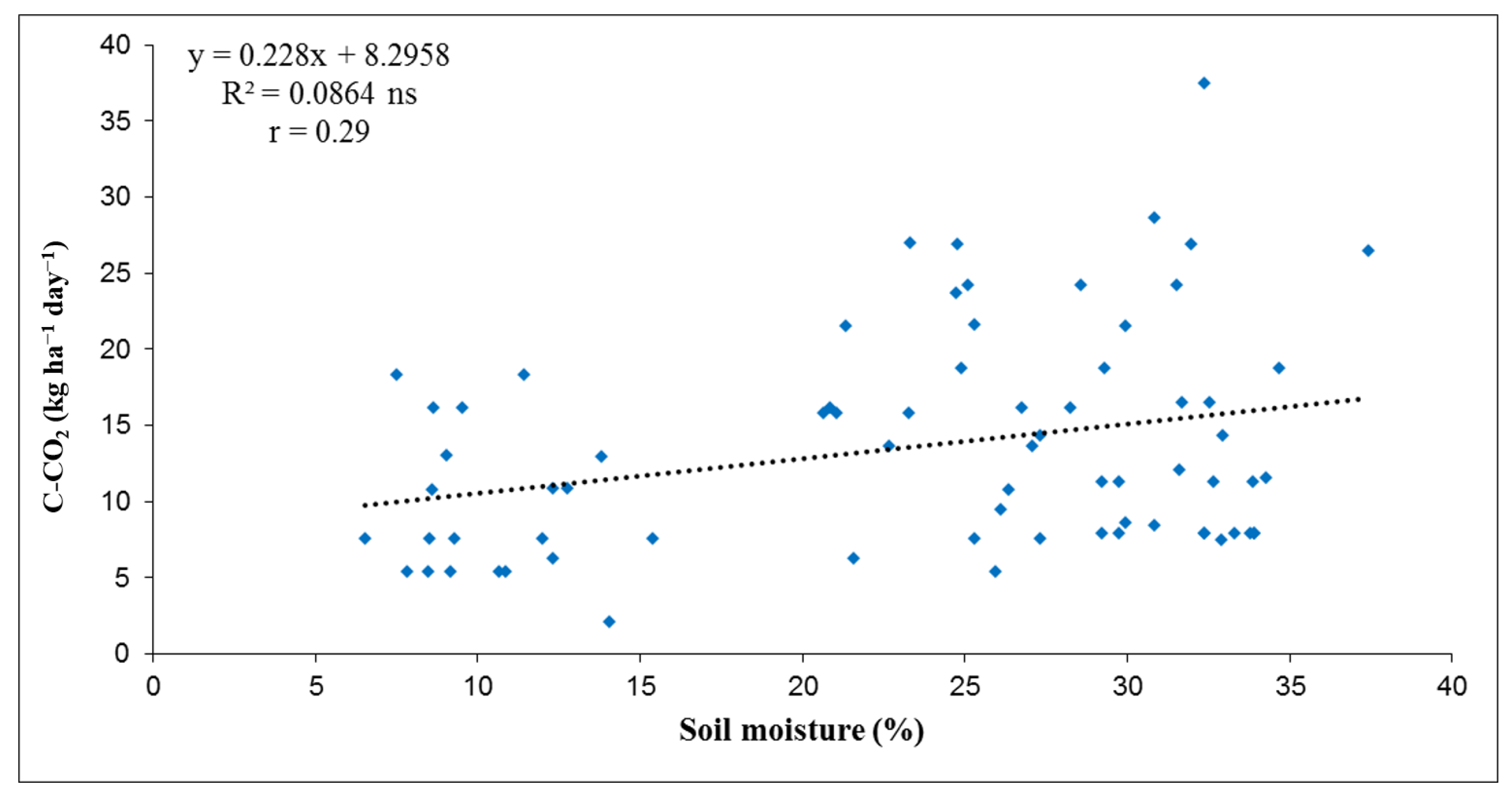
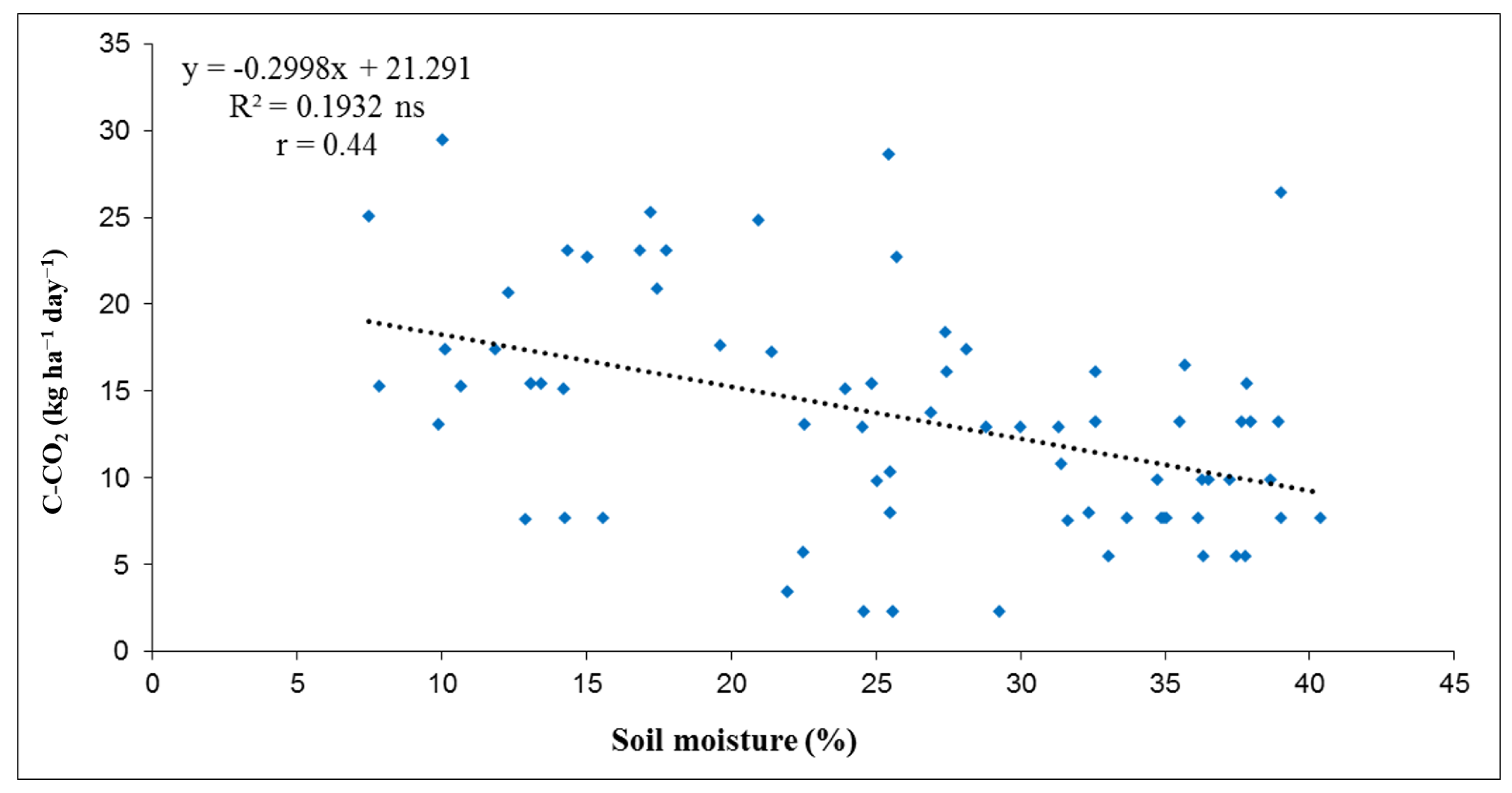
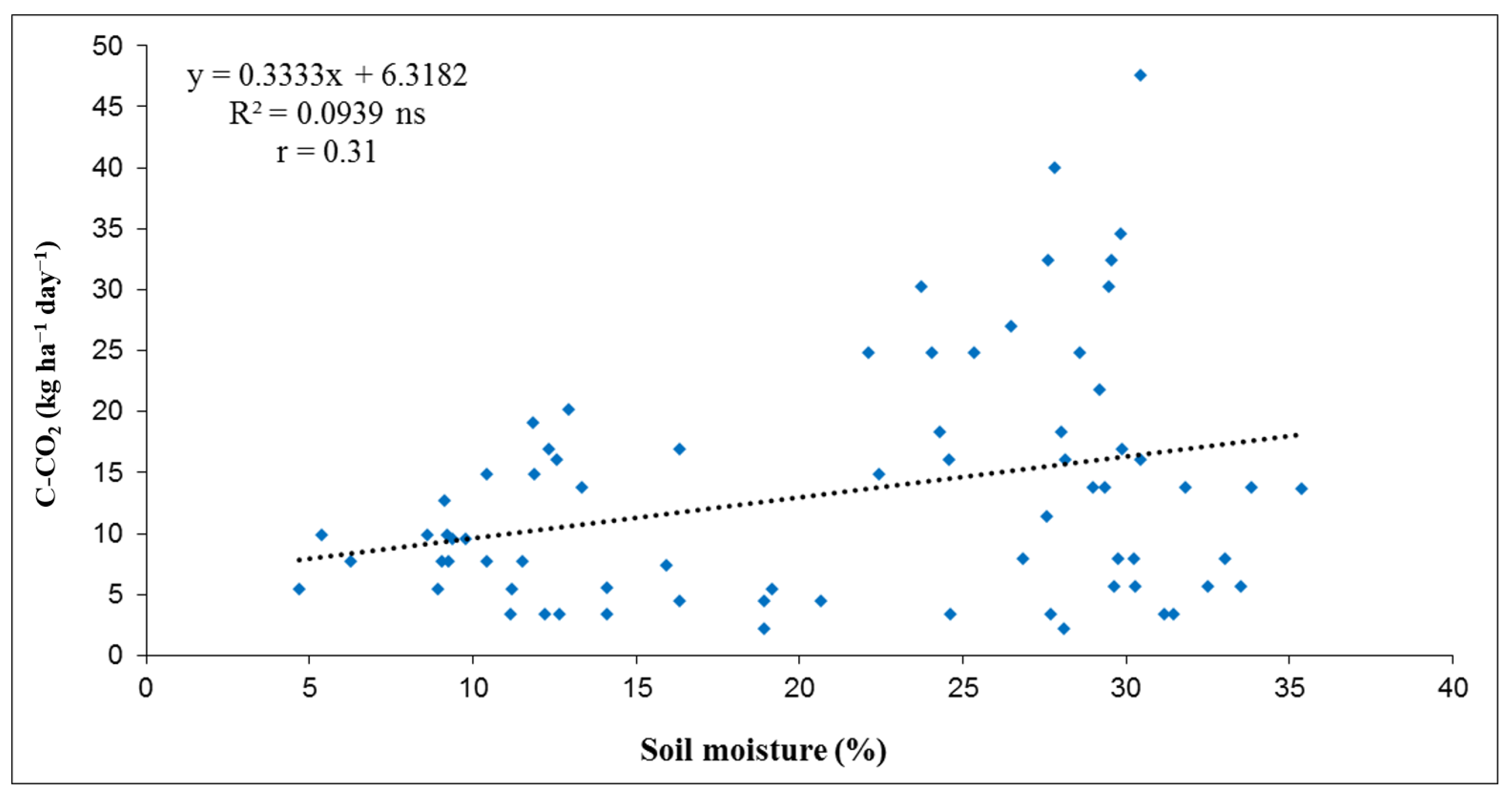
3.2. Relation of Soil C-CO2 Emissions with Soil Temperature and Soil Moisture
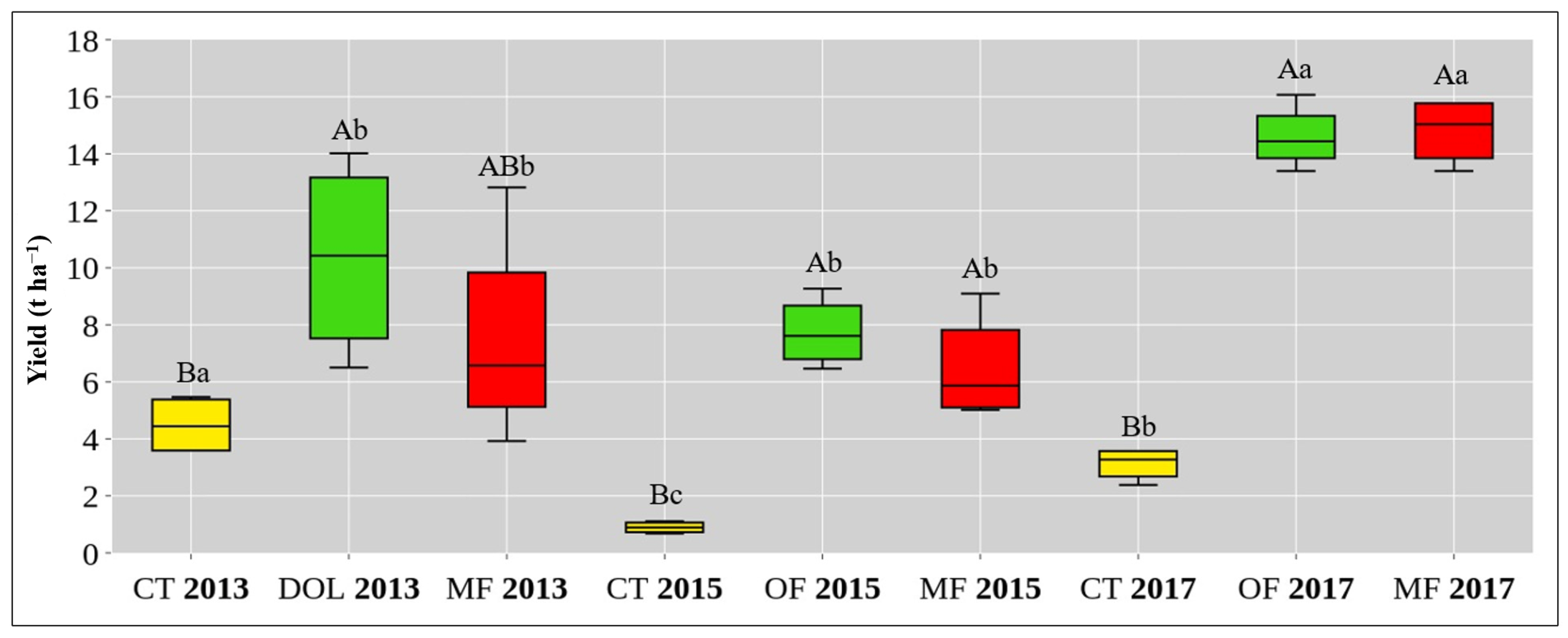
3.3. Crop Yield
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Umesha, S.; Manukumar, H.M.; Chandrasekhar, B. Sustainable agriculture and food security. In Biotechnology for Sustainable Agriculture; Woodhead Publishing: Shaxton, UK, 2018; pp. 67–92. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Vuorinen, H.S.; Nikolaidis, C.; Juuti, P.S.; Katko, T.S.; Juuti, R.P.; Zhang, J.; Samonis, G. Water quality and life expectancy: Parallel courses in time. Water 2021, 13, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterthwaite, D. The implications of population growth and urbanization for climate change. Environ. Urban. 2009, 21, 545–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, K.; Rao, S.; Krey, V.; Cho, C.; Chirkov, V.; Fischer, G.; Kindermann, G.; Nakicenovic, N.; Rafaj, P. RCP 8.5—A scenario of comparatively high greenhouse gas emissions. Clim. Change 2011, 109, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, C.; Spirandelli, D.; Franklin, E.C.; Lynham, J.; Kantar, M.B.; Miles, W.; Smith, C.Z.; Freel, K.; Moy, J.; Louis, L.V.; et al. Broad threat to humanity from cumulative climate hazards intensified by greenhouse gas emissions. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Feng, Y. Air pollution, greenhouse gases and climate change: Global and regional perspectives. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, O. Global climate change. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2014, 2, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockmann, U.; Adams, M.A.; Crawford, J.W.; Field, D.J.; Henakaarchchi, N.; Jenkins, M.; Minasny, B.; Mcbratney, A.B.; Courcelles, V.D.R.D.; Singh, K.; et al. The knowns, known unknowns and unknowns of sequestration of soil organic carbon. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 164, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharlemann, J.; Tanner, E.; Hiederer, R.; Kapos, V. Global soil carbon: Understanding and managing the largest terrestrial carbon pool. Carbon Manag. 2014, 14, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations. 2015 Publications; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Plaza, C.; Zaccone, C.; Sawicka, K.; Méndez, A.M.; Tarquis, A.; Gascó, G.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Schuur, E.A.G.; Maestre, F.T. Soil resources and element stocks in drylands to face global issues. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Andrews, J.A. Soil respiration and the global carbon cycle. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson-Kanyama, A. Climate change and dietary choices—How can emissions of greenhouse gases from food consumption be reduced? Food Policy 1998, 23, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, H.; Lal, R. Principles of Soil Conservation and Management, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; p. 617. [Google Scholar]
- Canadell, J.G.; Schulze, E.D. Global potential of biospheric carbon management for climate mitigation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilandzija, D.; Zgorelec, Z.; Kisic, I. Influence of Tillage Practices and Crop Type on Soil CO2 Emissions. Sustainability 2016, 8, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Agricultural activities and the global carbon cycle. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2004, 70, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäder, P.; Fliessbach, A.; Dubois, D. Soil Fertility and Biodiversity in Organic Farming Science. Science 2002, 296, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fließach, A.; Oberholzer, H.R.; Gunst, L.; Mäder, P. Soil organic matter and biological soil quality indicators after 21 years of organic and conventional farming. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 118, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilandzija, D. Emisija Ugljikovog Dioksida pri Različitim Načinima Obrade Tla. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Agriculture University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe, D.B.; Meir, P.; Aragaõ, L.E.O.C.; da Costa, A.C.L.; Braga, A.; Goncalves, P.H.L.; de Athaydes, J.; de Almeida, S.S.; Williams, M. Factors controlling spatio-temporal variation in carbon dioxide efflux from surface litter, roots, and soil organic matter at four rain forest sites in the eastern Amazon. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2007, 112, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyano, F.; Kutsch, W.L.; Schulze, E.D. Response of mycorrhizal, rhizosphere and soil basal respiration to temperature and photosynthesis in a barley field. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Ascher, J.; Ceccherini, M.T.; Landi, L.; Pietramellara, G.; Renella, G. Microbial diversity and soil functions. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2003, 68, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y. Sources of CO2 efflux from soil and review of partitioning methods. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 425–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgorelec, Z.; Blazinkov, M.; Mesic, M.; Bilandzija, D.; Percin, A.; Sestak, I.; Cacic, M. Gospodarenje Tlom i Klimatske Promjene. Report. 2017. Available online: https://www.agr.unizg.hr/en/project/528/Gospodarenje+tlom+i+klimatske+promjene (accessed on 25 June 2023).
- Kirschbaum, M.U. Will changes in soil organic carbon act as a positive or negative feedback on global warming? Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 21–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumbore, S. Age of soil organic matter and soil respiration: Radiocarbon constraints on belowground C dynamics. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, R.A.; House, J.I.; Pongratz, J.; Van Der Werf, G.R.; Defries, R.S.; Hansen, M.C.; Le Quéré, C.; Ramankutty, N. Carbon emissions from land use and land-cover change. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 5125–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.F.; Dou, Z.X.; He, P.; Ju, X.T.; Powlson, D.; Chadwick, D.; Norse, D.; Lu, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; et al. New technologies reduce greenhouse gas emissions from nitrogenous fertilizer in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8375–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Song, Y.; Zhao, S.; Tang, M.; Guo, Y.; Su, M.; Li, H. Dynamic Linkage between Aging, Mechanizations and Carbon Emissions from Agricultural Production. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, M.L.; Thomason, W.E.; Fike, J.H.; Evanylo, G.K.; Stewart, R.D.; Gross, C.D.; Seleiman, M.F.; Babur, E.; Sadeghpour, A.; Harrison, M.T. Corn and wheat residue management effects on greenhouse gas emissions in the mid-Atlantic USA. Land 2022, 11, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searchinger, T.; Heimlich, R.; Houghton, R.A.; Dong, F.; Elobeid, A.; Fabiosa, J.; Tokgoz, S.; Hayes, D.J.; Yu, T.H. Use of US croplands for biofuels increases greenhouse gases through emissions from land-use change. Science 2008, 319, 1238–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Xu, M.G.; Sun, N.; Wang, X.J.; Wu, L.; Wang, B.R.; Li, D.C. How do environmental factors and different fertilizer strategies affect soil CO2 emission and carbon sequestration in the upland soils of southern China? Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013, 72, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikièma, P.; Rothstein, D.E.; Min, D.H.; Kapp, C.J. Nitrogen fertilization of switchgrass increases biomass yield and improves net greenhouse gas balance in northern Michigan, USA. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 4356–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, L.F.; Amado, T.J.C.; Bayer, C.; Chavez, L.F.; Zanatta, J.A.; Fiorin, J.E. Postharvest nitrous oxide emissions from a subtropical oxisol as influenced by summer crop residues and their management. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2010, 34, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilandzija, D.; Zgorelec, Z.; Kisic, I. The influence of agroclimatic factors on soil CO2 emissions. Coll. Antropol. 2014, 38, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Jabro, J.D.; Sainju, U.; Stevens, W.B.; Evans, R.G. Carbon Dioxide Flux as Affected by Tillage and Irrigation in Soil Converted from Perennial Forages to Annual Crops. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, T. Carbon Dioxide Flux in a Subtropical Agricultural Soil of China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 149, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015: International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; pp. 150–200. [Google Scholar]
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HRN ISO11464; Soil Quality—Pre-Treatment of Samples for Physico-Chemical Analysis. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- HRN ISO 10390; Soil Quality—Determination of pH. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- HRN ISO 14235; Soil Quality—Determination of Organic Carbon by Sulfochromic Oxidation. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- Egner, H.; Riehm, H.; Domingo, W.R. Studies on the Chemical Soil Analysis as a Basis for the Assessment of the Nutrient Status of Soils. K. Lantbruksakad. Ann. 1960, 26, 45–61. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Mesic, M.; Percin, A.; Bogunovic, I.; Zgorelec, Z.; Gandjaeva, L. Environmental and Production Aspects of Maize Cultivation in Relation with the Different Time-applied Nitrogen. Columella 2017, 4, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- HRN ISO 11277:2004; Soil Quality—Determination of Particle Size Distribution in Mineral Soil Material—Method by Sieving and Sedimentation. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- Widen, W.; Lindroth, A. A Calibration System for Soil Carbon Dioxide-efflux Measurement Chambers: Description and Application. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 67, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, T.; Fórizs, I.; Kuti, L.; Wardell, J.L. Data on the elements of carbon cycle in a solonetz and solonchak soil. Cereal Res. Commun. 2005, 33, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdi, L.; Mancini, M.; Napoli, M.; Vivoli, R.; Pardini, A.; Orlandini, S.; Marta, A.D. Soil carbon emissions from maize under different fertilization methods in an extremely dry summer in Italy. Ital. J. Agrometeorol. 2019, 2, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mignon, S.; Maxim, A.; Opruia, C. Soil Respiration in Mineral and Organic Fertilized Soils During Springtime in a Potato Field. ProEnviron. Promediu 2011, 4, 316–319. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, H.M.; Al-Kaisi, M.M. Crop rotation and nitrogen fertilization effect on soil CO2 emissions in central Iowa. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 39, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Shao, H.B.; Wang, B.C.; Zhang, L.W.; Qin, X.C. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on the production of carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide in salt-affected soils under different vegetation communities. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 204, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Fu, X.; Liu, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, R.; Liu, D.L.; Wu, J. Measurement and modeling of nitrous and nitric oxide emissions from a tea field in subtropical central China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2017, 1107, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Di, H. Heterotrophic nitrification and denitrification are the main sources of nitrous oxide in two paddy soils. Plant Soil 2018, 445, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, X.; Shen, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xiao, R.; Wei, W.; Wu, J. Effect of controlled-release fertilizer on N2O emissions and tea yield from a tea field in subtropical central China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 25580–25590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oo, A.Z.; Sudo, S.; Akiyama, H.; Win, K.T.; Shibata, A.; Yamamoto, A.; Sano, T.; Hirono, Y. Effect of dolomite and biochar addition on N2O and CO2 emissions from acidic tea field soil. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, J.P.; Bezdicek, D.F.; Flury, M.; Albrecht, S.; Smith, J.L. Microbial activity affected by lime in a long-term no-till soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 88, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valzano, F.; Murphy, B.; Greene, R. The long-term effects of lime (CaCO3), gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O), and tillage on the physical and chemical properties of a sodic red-brown earth. Soil Res. 2001, 39, 1307–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.; Wu, L.; Peng, Q.; Van Zwieten, L.; Chhajro, M.A.; Wu, Y.; Lin, S.; Ahmed, M.M.; Khalid, M.S.; Abid, M.; et al. Influence of ameliorating soil acidity with dolomite on the priming of soil C content and CO2 emission. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 9241–9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galic, M.; Bilandzija, D.; Percin, A.; Sestak, I.; Mesic, M.; Blazinkov, M.; Zgorelec, Z. Effects of Agricultural Practices on Carbon Emission and Soil Health. J. Sustain. Dev. Energy Water Environ. Syst. 2019, 7, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galic, M.; Bilandzija, D.; Reis, I.; Zgorelec, Z. Soil fluxes of carbon dioxide in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) agroecosystem. In Proceedings of the 57th Croatian and 17th International Symposium of Agriculture, Vodice, Croatia, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 691–696. [Google Scholar]
- Bogunovic, I.; Pereira, P.; Galic, M.; Bilandzija, D.; Kisic, I. Tillage system and farmyard manure impact on soil physical properties, CO2 emissions, and crop yield in an organic farm located in a Mediterranean environment (Croatia). Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosulski, T.; Stepien, W.; Was, A.; Szymanska, M. N2O and CO2 Emissions from Bare Soil: Effect of Fertilizer Management. Agriculture 2020, 10, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Pumpanen, J.; Kang, S. Spatio-temporal variability and controls of soil respiration in a furrow-irrigated vineyard. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhao, N.; Lu, Y.; Han, X.; Yang, Z. Effects of Supplementary Irrigation on Soil Respiration of Millet Farmland in a Semi-Arid Region in China. Atmosphere 2020, 13, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, A.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Jia, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; McLaughlin, N. Chapter 14—Climate change impacts on soil fertility in Chinese Mollisols. In Sustainable Crop Productivity and Quality Under Climate Change, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 275–293. [Google Scholar]
- Yuste, J.C.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Gershenson, A.; Goldstein, A.; Misson, L.; Wong, S. Microbial soil respiration and its dependency on carbon inputs, soil temperature and moisture. Glob. Change Biol. 2007, 13, 2018–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicentini, M.E.; Pinotti, C.R.; Yoshio Hirai, W.; de Moraes, M.L.T.; Montanari, R.; Filho, M.C.M.T.; Milori, D.M.B.P.; Junior, N.L.S.; Panosso, A.R. CO2 emission and its relation to soil temperature, moisture, and O2 absorption in the reforested areas of Cerrado biome, Central Brazil. Plant Soil 2019, 444, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warembourg, F.R.; Roumet, C.; Lafont, F. Differences in rhizosphere carbon partitioning among plant species of different families. Plant Soil 2003, 256, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Roldan, A.; Hernandez, T. Ability of different plant species to promote microbiological processes in semiarid soil. Geoderma 2005, 124, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.G.; Law, B.E. Interpreting, measuring, and modeling soil respiration. Biogeochemistry 2005, 73, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.I.N.; Chang-Yi, L.U.; Yong, Y.E.; Gong-Fu, Y.E. Soil respiration in a subtropical mangrove wetland in the Jiulong River Estuary, China. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 678–685. [Google Scholar]
- Chanda, A.; Akhand, A.; Manna, S.; Dutta, S.; Das, I.; Hazra, S.; Rao, K.H.; Dadhwal, V.K. Measuring daytime CO2 fluxes from the inter-tidal mangrove soils of Indian Sundarbans. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomotsune, M.; Yoshitake, S.; Iimura, Y.; Kida, M.; Fujitake, N.; Koizumi, H.; Ohtsuka, T. Effects of soil temperature and tidal condition on variation in carbon dioxide flux from soil sediment in a subtropical mangrove forest. J. Trop. Ecol. 2018, 34, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W.; Schlesinger, W.H. The global carbon dioxide flux in soil respiration and its relationship to vegetation and climate. Tellus 1992, 44, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Ramirez, G.; Brouder, S.M.; Smith, D.R.; Van Scoyoc, G.E. Greenhouse gas fluxes in an Eastern corn belt soil: Weather, nitrogen source, and rotation. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buragienė, S.; Šarauskis, E.; Romaneckas, K.; Adamavicienė, A.; Kriauciunienė, Z.; Avižienytė, D.; Marozas, V.; Naujokienė, V. Relationship between CO2 emissions and soil properties of differently tilled soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ussiri, D.A.N.; Lal, R. Long-term tillage effects on soil carbon storage and carbon dioxide emissions in continuous corn cropping system from an alfisol in Ohio. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 104, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, T.E.; Detto, M.; Silver, W.L. Sensitivity of Soil Respiration to Variability in Soil Moisture and Temperature in a Humid Tropical Forest. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Yu, H.; Cai, Z.; Han, F.; Xu, Z. Responses of soil respiration to N fertilization in a loamy soil under maize cultivation. Geoderma 2010, 155, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, R. Soil microorganisms as controllers of atmospheric trace gases (H2, CO, CH4, OCS, N2O, and NO). Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 60, 609–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, H.; Mu, X.; Zhao, G.; Gao, P.; Sun, W. Effects of Different Fertilization Regimes on Crop Yield and Soil Water Use Efficiency of Millet and Soybean. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucheru-Muna, M.; Mugendi, D.; Kungu, J.; Mugwe, J.; Bationo, A. Effects of organic and mineral fertilizer inputs on maize yield and soil chemical properties in a maize cropping system in Meru South District, Kenya. Agrofor. Syst. 2007, 69, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Boom, F.; Magid, J.; Jensen, L.S. Long-term P and K fertilisation strategies and balances affect soil availability indices, crop yield depression risk and N use. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 86, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Johnson, S.; Schmidt, A. Calculating the Value of Manure for Crop Production. In NebGuide; The Board of Regents of the University of Nebraska: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Macholdt, J.; Piepho, H.P.; Honermeier, B. Mineral NPK and manure fertilisation affecting the yield stability of winter wheat: Results from a long-term field experiment. Eur. J. Agron. 2019, 102, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galic, M.; Zgorelec, Z.; Bilandzija, D. Soil carbon dioxide emissions in winter wheat vegetation influenced by agro-ecological factors and fertilization. In Proceedings of the 12th International Scientific/Proffesional Conference Agriculture in Nature and Environment Protection, Osijek, Croatia, 7–9 September 2019; pp. 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.X.; Yang, L.Q.; Yu, J.B.; Wang, G.M.; Mao, P.L.; Gao, Y.J. Environmental Controls on Net Ecosystem CO2 Exchange Over a Reed (Phragmites Australis) Wetland in the Yellow River Delta, China. Estuaries Coasts 2012, 36, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, J.; Amthor, J.S.; McCarty, D.R.; Messina, C.D.; Wilson, M.A.; Millar, H.; Hanson, A.D. Why cutting respiratory CO2 loss from crops is possible, practicable, and prudential. Mod. Agric. 2023, 1, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, A.C.; Siwar, C.; Isma’il Shaharudin, M.; Anizan, I. Carbon Sequestration in Soils: The Opportunities and Challenges. In Carbon Capture, Utilization and Sequestration; Intech Open: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018. [Google Scholar]



| Soil Layer (cm) | 0–30 |
|---|---|
| Soil color (in dry condition) | 2.5Y 7/4 |
| Organic matter (g kg−1) | 10.1 |
| pH in H2O (1:2.5) | 5.74 |
| pH in KCl (1:2.5) | 4.84 |
| P2O5 (g kg−1) | 1.77 |
| K2O (g kg−1) | 1.05 |
| Clay (g kg−1) | 205 |
| Fine silt (g kg−1) | 308 |
| Coarse silt (g kg−1) | 485 |
| Coarse sand (g kg−1) | 1.5 |
| Texture classification | Loam |
| Vegetation Year | Sowing Date | Harvest Date | Fertilization | Crop Protection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 2 May 2013. | 8 October 2013. | Basic f.—7 November 2012. Supplement I—28 May 2013. Supplement II—19 June 2013. | 10 May 2013. |
| 2015 | 24 April 2015. | 3 November 2015. | Manure f.—21–22 November 2014. P&K—2 November 2014. Basic f.—3 March 2014. Supplement—6 June 2015. | 31 May 2015. |
| 2017 | 12 April 2017. | 15 September 2017. | Basic f., supplements I and II—5 June 2017. | 8 May 2017. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galic, M.; Bilandzija, D.; Zgorelec, Z. Influence of Long-Term Soil Management Practices on Carbon Emissions from Corn (Zea mays L.) Production in Northeast Croatia. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13082051
Galic M, Bilandzija D, Zgorelec Z. Influence of Long-Term Soil Management Practices on Carbon Emissions from Corn (Zea mays L.) Production in Northeast Croatia. Agronomy. 2023; 13(8):2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13082051
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalic, Marija, Darija Bilandzija, and Zeljka Zgorelec. 2023. "Influence of Long-Term Soil Management Practices on Carbon Emissions from Corn (Zea mays L.) Production in Northeast Croatia" Agronomy 13, no. 8: 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13082051
APA StyleGalic, M., Bilandzija, D., & Zgorelec, Z. (2023). Influence of Long-Term Soil Management Practices on Carbon Emissions from Corn (Zea mays L.) Production in Northeast Croatia. Agronomy, 13(8), 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13082051









