Abstract
The development of higher nutritional sorghum varieties requires the identification of high protein content germplasm that expands the genetic diversity of breeding programs. Therefore, a near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy method was developed to predict the protein concentration of whole-grain sorghum with R2 = 0.83, root-mean-square error of prediction = 1.44%, and bias = 0.16%. We evaluated 228 tropical accessions from West and Central Africa maintained by the National Plant Germplasm System (NPGS) of the United States for protein content for three years. The analysis found that the protein concentrations among accessions varied from 5.05 to 15.00% with an average of 10.24%. Correlation analysis between years revealed changes in protein content and ranking across years for multiple accessions. However, heritability of protein concentration was moderately high (H2 = 0.81) indicating most of the observed variation could be determined by genetic differences among accessions. Sixteen tropical accessions with the highest protein concentration (>12.84%) may be used in breeding programs for the development of new and improved nutritional varieties. This assessment documented the range of natural variation for protein content in the NPGS sorghum tropical germplasm collection that could be used to enhance breeding programs focused on biofortification.
1. Introduction
Cereal grains are an important source of protein, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals for humans and animals. Cereal grains provide more than 50% of the food energy and 50% of the protein consumed worldwide [1]. Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] is the fifth most important cereal worldwide behind wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), rice (Oryza sativa L.), barley (Hordeum vulgare L.), and maize (Zea mays L.) [2], and it is used for human and animal consumption. Sorghum is a vital cereal grain in the nutrition of people from Africa and India [3] and today is an important gluten-free alternative to wheat [4]. Nevertheless, sorghum nutritional research is limited compared to other cereals; thus, its full nutritional potential has not been achieved.
Multiple research studies have found that sorghum protein concentration varies from 4.4 to 21.1% [5,6,7]. Sorghum proteins are known as kafirins, which belong to the group of proteins called prolamins [8]. This group of simple proteins is found in other cereals, however, kafirin is more hydrophobically than zein (corn), gliadin (wheat), and hordein (barley). Therefore, sorghum has lower protein digestibility, especially when wet cooked, than other cereal grains reducing its nutritional value for humans and animals [9]. There are significant differences in the behavior of kafirins with other proteins that remain to be understood and could be crucial to increase the nutritional value of sorghum. Certainly, the development of new sorghum varieties with improved nutritional properties should include the digestibility of the protein and the cooking process.
The complex inheritance of nutritionally related traits requires recombination among multiple highly nutritional sources to achieve a significant improvement. For instance, the continued recombination of maize with high-kernel protein content has resulted in a 27% increase during the Illinois’ long-term selection-breeding program [10]. Certainly, the genetic improvement of sorghum’s nutritional value will require the assembly of multiple variants with high protein content and digestibility. Sorghum is a highly diverse tropical crop that was domesticated in Northeast Africa 5000–7000 years ago. During its expansion to other African regions, the crop was redomesticated leading to five botanical races (bicolor, caudatum, durra, guinea, and kafir) that have unique inflorescence types and environmental adaptations [11]. For instance, the races bicolor, caudatum, durra, and guinea belong to the tropical regions of Africa, and most of these accessions are photoperiod sensitive (i.e., flowering during short days), while the race kafir was domesticated in the temperate regions of Southern Africa, and most of its accessions are nonphotoperiod sensitive (i.e., day neutral). Today, most of the genetic diversity of sorghum is found among photoperiod-sensitive accessions that cannot be directly evaluated or used in breeding programs located in temperate regions.
Ex situ sorghum germplasm is the primary source of genetic diversity for breeding programs. Thus, adequate preservation and screening are essential for crop improvement. The National Plant Germplasm Systems (NPGS) of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) preserves the largest worldwide sorghum collection with >41,860 accessions from 114 countries. However, screening for agronomically important traits from germplasm collections has been constrained by the photoperiod sensitivity of most accessions (>80% of the collection). Today, a limited number of NPGS tropical accessions have been evaluated for nutritional-quality parameters. However, an assessment of the nutritional value of temperate-adapted germplasm present in the Sorghum Association Panel (SAP) [12] demonstrated the existence of genetic diversity for protein, fat, and starch [5,13]. Similarly, genetic diversity for nutritional traits has been found in tropical-sorghum germplasm from Ethiopia [14], South Africa [15], Sudanese wild sorghum [16], and a global core collection [17]. Certainly, the NPGS tropical-sorghum germplasm collection must include useful sources of genetic variation for nutritional traits that have not been discovered. The development of a high-throughput screening system for nutritional traits is the first step to mine the NPGS sorghum collection.
Near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy is a nondestructive, rapid, and low-cost method used to measure multiple grain nutritional traits. NIR instruments measure transmitted or diffusely reflected radiation (350 to 2500 nm) through a fixed pathlength for bulk grain samples or flour, which is later correlated to multiple nutritional traits. The technique has been used to estimate protein content in sorghum [6,17], triticale [18], and wheat [19] with high correlation coefficients (r2 ≥ 0.80). Today, NIR is an official method to estimate protein content in flour in the AACC Approved Methods of Analysis of the Cereals and Grain Associations (AACC 39-10.01). Nevertheless, the existence of various instruments and approaches to NIR scanning of grain or flour requires that each breeding or research program calibrates and validates its own sample set.
The identification of novel sources of high protein content in NPGS tropical-sorghum germplasm is the first step to increasing the genetic diversity of breeding programs for nutritional traits. In the current study, we established a reliable NIR system to measure the protein concentration for whole-grain sorghum samples. A subset of 228 NPGS tropical accessions from West and Central Africa was evaluated for three years to identify high protein content accessions. This work initiates a larger-scale screening of the NPGS accessions for nutritional traits that will benefit sorghum breeders worldwide.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Germplasm
A set of 228 tropical-sorghum accessions from West and Central Africa from the NPGS sorghum core collection [Supplementary Table S1; [20]], seven breeding lines with high grain weathering and mold resistance [SC15, Red Amber, Rox Orange, Kansas Orange, SC309, Keller and 6550 Sumac; [21]], and the lines SC112 and RTx430 were evaluated for protein content (Figure 1). This panel of 237 accessions was planted at the research farms of the USDA-ARS Tropical Agriculture Research Station in Isabela (18°28′18.6″ N 67°02′37.1″ W), Puerto Rico, during the short day-length season (i.e., from September to April) of 2018, 2020 and 2022. Sorghum-race classification of accessions was obtained from the NPGS database GRIN Global (https://www.grin-global.org (accessed on 20 June 2018)) and seeds were visually inspected to classify the different pericarp colors.
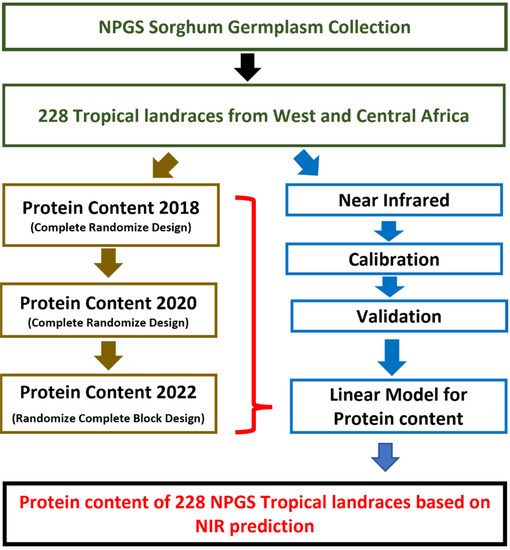
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the experimental design to determine the protein content of 228 tropical sorghum landraces from West and Central Africa from the National Plant Germplasm System of the United States.
2.2. Experimental Design
The initial limited number of seeds obtained from the NPGS sorghum germplasm collection were planted in a completely randomized design in 2018 and 2020. Seed increase from previous experiments were planted in 2022 using a completely randomized block design consisting of two blocks. All experimental plots were 1.8 m in long with 0.9 m between rows. Three to five representative panicles per plot were hand harvested at 35–40 days after anthesis, dried to normalize moisture content, threshed, and the whole seeds were used for protein quantification and NIR scanning.
2.3. Near-Infrared Scanning
Sorghum grain samples from 2018, 2020, and 2022 were scanned with a benchtop ASD LabSpec 4 (Analytical Spectral Device-ASD Inc., Boulder CO, USA) spectrometer connected to an ASD Turntable, which provided a 53.22 mm sampling spot size. Approximately 30–50 g of grain were placed in a glass Petri dish (90 mm diameter × 15 mm deep) and leveled to have a uniform distance from the grain surface to the collecting optic of the instrument. Each sample/plate was randomly rotated on the ASD Turntable before the scan, and this process was repeated six times per sample. The NIR spectra in a wavelength range of 350–2500 nm in 5-nm intervals were recorded for each scanned sample.
2.3.1. Near-Infrared Calibration
Protein Content
An NIR protein calibration was completed based on the spectra and protein concentrations of 106 sorghum-grain samples. One set of 51 grain samples, encompassing a wide range of protein-content variation [6] was provided by the USDA-ARS Center for Grain and Animal Health Research, Manhattan, Kansas. Protein concentrations for this set were determined via nitrogen combustion using a LECO FP-528 nitrogen determinator following the AACC International method 46-30.01 with a nitrogen to protein conversion factor of 6.25. Additionally, 55 grain samples were randomly selected from the 2018 experiment. The nitrogen content of these samples was determined with a modified micro-Kjeldahl [22] procedure following the AACC International Method 46-12.01. For this purpose, 10–20 g of grain were dried to constant weight at 70 °C and ground using a Wiley mill with a 1 mm sieve. Three replicates of 0.2 g of sorghum flour per sample were digested for 2 h at 380 °C in a Kjeldahl tube, using one catalyzing tablet (1.5 g K2SO4 + 0.15 g CuSO4), 5 mL concentrated H2SO4, and 3 mL 30% H2O2. The digested samples were distillated in KjeltecTM 2100 distillers and titrated with HCl 0.2N to determine total nitrogen. The 6.25 conversion factor was used to convert the nitrogen-to-protein concentration.
Calibration
The NIR spectral data from 950–1650 nm [6] of the 106 sorghum-grain samples were subject to multiplicative scatter correction and mean centering before spectral data analysis with Grams IQ/AI version 9.2 (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) software. A partial least-square regression model with 19 factors (ProCal-19) was constructed using a subset of 28 samples that covered the full range of protein concentrations (Table 1; 10.36% ± 2.51).

Table 1.
Sorghum-grain protein concentration variability in the calibration and validation samples used to establish a prediction model for near-infrared (NIR) and the range of NIR predictions in a set of tropical accessions from West and Central Africa in the USDA-ARS National Plant Germplasm System evaluated for three years in Puerto Rico. All values expressed as percentages.
Validation
The validation sample set for ProCal-19 included 78 grain samples (30 from the USDA-ARS Center for Grain and Animal Health Research and 48 from the 2018 experiment) not used to build the calibration regression (Table 1; 10.32% ± 2.44).
2.4. Protein Concentrations and Statistical Analysis
Protein concentrations of the 228 tropical-sorghum accessions from West and Central Africa and reference lines were predicted by the ProCal-19 regression. Protein data from the three years were analyzed as a randomized complete block design (RCBD) with four blocks (2018, 2020, and the two reps of 2022). Analysis of variance for RCBC was carried out in SAS (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) using the Proc mixed covtest method = REML procedure, where block (i.e., year) was considered a fixed effect and accessions as random effects. The mean protein concentration of accessions and the reference lines were compared by using the least-significance difference test (LSD) at the 5% level of significance. In addition, means protein content based on origin country and seed color were compared using the least-significance difference test (LSD) at the 5% level of significance. Spearman correlation of mean protein concentration among years was determined with SAS procedure Proc corr. Heritability across years for protein concentration was estimated by the formula:
where and refer to the accessions and error variances, respectively, while e is the number of blocks [23].
3. Results
The most accurate NIR calibration for protein concentration was obtained with a partial least-square regression model with 19 factors (ProCal-19), which had an R2 of 0.98 and a standard error of cross validation (SECV) of 0.58% in the calibration sample (Figure 2). The protein concentration prediction of the validation set with ProCal-19 had an R2 = 0.83, root-mean-square error of prediction (RMSEP) = 1.44% and bias = 0.16% (Figure 2). These results verify the strength of the ProCal-19 regression model for assessing the protein concentration of a diverse set of sorghum germplasm accessions.
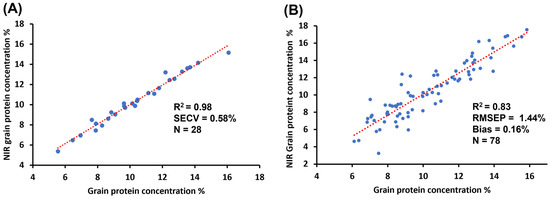
Figure 2.
Actual versus near-infrared (NIR) predicted sorghum-grain protein concentrations. (A) Partial least-squares calibration model including 19 factors. (B) External validation of the prediction of grain protein concentration based on a partial least-square calibration model including 19 factors.
Protein concentration among the 228 accessions ranged from 5.05 to 15.00% with an average of 10.24% (Supplementary Table S1). These values were normally distributed each year, and the ANOVA revealed that protein concentrations varied across years. Spearman correlation between years showed changes in trait magnitude and ranking of accessions (rs = 0.33 to 0.54; Figure 3). The heritability of protein concentration was high (H2 = 0.81) indicating most of the observed variation was determined by genetic differences among accessions.
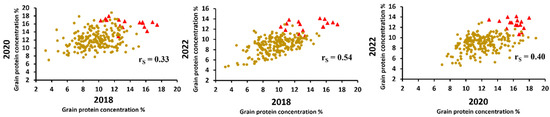
Figure 3.
Variability of sorghum grain protein concentration based on near-infrared prediction for 228 tropical accessions belonging to the USDA-ARS National Plant Germplasm System evaluated for three years in Isabela, Puerto Rico. Spearman correlation coefficient (rs) between years. Red triangle refers to accessions that showed the higher average protein concentration across years.
Mean protein concentration of the 228 tropical accessions was higher ( = 10.24%) than that observed in the reference breeding lines ( = 8.95%). In fact, concentrations of the reference lines RTx430 and 6550 Sumac (<7.54%) were among the lowest values observed. The three-year evaluation found that 16 tropical accessions displayed protein concentrations above >12.84 (Table 2). These 16 accessions (PI 525907, PI 586420, PI 563345, PI 525906, PI 525919, PI 525910, PI 515900, PI 585975, PI 510953, PI 586409, PI 560375, PI 514590, PI 585983, PI 585477, PI 585795, and PI 513901) were not associated with a particular geographic origin. Nevertheless, we found protein content differs among country and seed colors (Table 3 and Table 4). The protein concentration of accessions from countries located in the west regions (Mali, Togo, Benin, Senegal, Ghana, Nigeria, and Burkina Faso; >10.39%) were higher than the observe in accessions from the southeast regions (Burundi, Kenya, Uganda, and Rwanda; <9.05%) of Africa. The accessions from Mali showed the highest protein concentrations. The analysis based on seed color exposed that those with white and lighter colors (white, light brown, and light red) have higher protein concentrations than brown and red seeds.

Table 2.
Tropical sorghum accessions from West and Central Africa in the USDA-ARS National Plant Germplasm System that showed high protein concentrations and nine reference lines.

Table 3.
Protein concentration and seed-color distribution in a subset of 228 tropical sorghum accessions the USDA-ARS National Plant Germplasm System clustered by origin country.

Table 4.
Protein concentration and seed-color distribution in a subset of 228 tropical sorghum accessions the USDA-ARS National Plant Germplasm System clustered by sorghum-race classification.
Sorghum racial classification among the 228 accessions included caudatum (30), durra (1), guinea (85), kafir (26), racial intermediates (76), and ten unclassified (Table 4). We found that the guinea race and its intermediate with bicolor, kaffir, and caudatum had higher protein concentration (>10.53%) than the caudatum, kafir, and kafir intermediates with bicolor, caudatum, and durra (<9.81%). In fact, we found that the guinea race included 12 of the 16 accessions with high protein concentrations (Table 2). This result may suggest that a relationship between the sorghum redomestication process and protein content might exist.
4. Discussion
The identification of sorghum accessions with high protein concentration is important for developing improved nutritional quality. Nevertheless, slow, expensive screening methods for protein quantification and the fact that most of the NPGS sorghum germplasm collection is tropical (i.e., photoperiod sensitive) hamper its evaluation for important nutritional traits. Herein, the first large screen for a subset of NPGS sorghum tropical germplasm by using a rapid NIR prediction system was presented and documented wide genetic variation for grain protein concentration.
Grain protein content is considered a domesticated trait subject to human selection [24]. Therefore, high-protein alleles should occur at low frequency within sorghum landraces and wild natural populations. The range of protein concentrations within these accessions revealed a limited number with high protein concentrations, with most of the accessions performing similarly to breeding lines. Starch, the main component of sorghum grain, is negatively correlated to protein content [13]. Certainly, sorghum breeding programs have increased starch-grain content but indirectly reduced its protein content. The introgression of high-protein alleles from tropical germplasm into sorghum-breeding lines will require the parallel selection of both traits. In this regard, the 16 accessions with the highest protein concentration could serve as parental lines in breeding programs focused on developing grain with improved nutritional quality.
The guinea race, originally from West Africa, has been associated with grain mold resistance and diseases caused by multiple fungi [25]. Certainly, seed quality might have a significant effect on protein concentration. However, most accessions used in this screening had high seed quality (determined by visual inspection); thus, protein concentrations should not have been unduly affected. In addition, our sample sizes (>200) and multiyear evaluation provided an appropriate approach for identifying accessions with consistently higher protein concentrations. In this regard, the high heritability that we observed indicates that screening and selection in breeding programs for protein content may require a minimum of three “environments” (locations or years) to select accessions with consistently high protein. Although the accessions we evaluated did not include a full representation of all sorghum races, it is likely that the Guinea race includes a higher frequency of high-protein alleles than those found in the caudatum and kafir races. In fact, grain-composition analysis of the SAP found that the group with most of the kafir accessions showed the lowest protein content [5]. Further screening of NPGS germplasm or selected diversity panels should provide insight into how sorghum domestication processes contributed to variation in grain protein.
The protein concentration of sorghum might be associated with its distribution in Africa. Previous studies of tannin content found the guinea types have a lower frequency of tannin accessions than that observed in caudatum and kaffir [26]. Herein, the protein concentration appeared to have a similar population structure to the observed for tannin concentration. The white pericarp phenotype and the tannin accumulation are determined by major genes in chromosomes 1 and 4, respectively [27,28]. The inheritance of protein concentration in sorghum is not well understood, but a genomic region in chromosome 2 have been associated with protein concentration in the SAP [29] and NPGS Ethiopian germplasm [30]. The absence of linkage disequilibrium between tannin, protein, and white pericarp color suggests that the domestication process might shape the protein concentration in sorghum kernels. Defining the inheritance of protein concentration in sorghum is necessary to understand its association with other nutritional and agronomically important traits.
NIR spectroscopy is a reliable method to determine protein content in grain sorghum [6]. Herein, we showed that a small sample (n = 28) of accessions with a wide range of protein concentration can be used for reliable NIR calibration. Previous studies have validated NIR calibrations by using samples from similar experiments [31]; however, our calibration regression was validated with samples from two different experiments and protein quantification methods. Certainly, this validation method provided accurate RMSEP and bias values of the calibration regression when applied to further evaluations. Although our evaluations have been based on the assumption of relatively stable and uniform moisture levels across samples (~10%), more accurate results may be obtained by improving the NIR calibration by adding more samples with diverse traits. Herein, we demonstrated that the screening of a large number of accessions from the NPGS collection with this NIR method effectively identified those higher proteins which could later be confirmed using traditional laboratory methods.
5. Conclusions
NIR spectroscopy is a cost-effective method to quantify grain protein content in NPGS tropical germplasm collection without grinding the seeds. The evaluation of the NPGS subset of 228 accessions from West and Central Africa found 16 accessions with high protein concentrations across years. These 16 accessions could be used in breeding programs for the development of new varieties with improved nutritional properties. Further screening of the NPGS sorghum germplasm collection should identify additional high protein accessions and provide insight into how the domestication process contributed to grain protein variation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy13051330/s1, Supplementary Table S1. Protein concentration of 228 tropical sorghum accessions from West and Central Africa from the USDA-ARS National Plant Germplasm System.
Author Contributions
H.E.C.: conceptualization; formal analysis; investigation; methodology; writing—original draft, reviewing and editing. K.H.S.P.: formal analysis; methodology; writing—reviewing. S.R.B.: formal analysis; methodology; writing—reviewing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the USDA-ARS Current Research Information System (Project 6090-21000-053-00-D; HC).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Biel, W.; Kazimierska, K.; Bashutska, U. Nutritional value of wheat, triticale, barley and oat grains. Acta Sci. Pol. Zootech. 2020, 19, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Food and Agriculture Organization. 2022. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 20 June 2018).
- Dahlberg, J.A. Classification and characterization of sorghum. In Sorghum; Smith, C.W., Frederick, J.R., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 99–130. [Google Scholar]
- Awika, J.M.; Rooney, L.W. Sorghum phytochemicals and their potential impact on human health. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 1199–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, D.H.; Hoffmann, L.; Rooney, W.L.; Herald, T.J.; Bean, S.; Boyles, R.; Brenton, Z.W.; Kresovich, S. Genetic architecture of kernel composition in global sorghum germplasm. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, K.H.; Bean, S.R.; Chiluwal, A.; Perumal, R.; Jagadish, S.K. Moisture effects on robustness of sorghum grain protein near-infrared spectroscopy calibration. Cereal Chem. 2019, 96, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnavathi, C.; Patil, J. Sorghum utilization as food. Nutr. Food Sci. 2013, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belton, P.; Delgadillo, I.; Halford, N.; Shewry, P. Kafirin structure and functionality. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 44, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duodu, K.G.; Taylor, J.R.N.; Belton, P.S.; Hamaker, B.R. Factors affecting sorghum protein digestibility. J. Cereal Sci. 2003, 38, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, J.; Lambert, R. 100 generations of selection for oil and protein in corn. Plant. Breed. Rev. 2010, 24, 79–110. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.W.; Frederiksen, R.A. Sorghum: Origin, History, Technology and Production; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Casa, A.M.; Pressoir, G.; Brown, P.J.; Mitchell, S.E.; Rooney, W.L.; Tuinstra, M.R.; Franks, C.D.; Kresovich, S. Community resources and strategies for association mapping in sorghum. Crop Sci. 2008, 48, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumaran, S.; Xiang, W.; Bean, S.R.; Pedersen, J.F.; Kresovich, S.; Tuinstra, M.R.; Tesso, T.T.; Hamblin, M.T.; Yu, J. Association mapping for grain quality in a diverse sorghum collection. Plant Genome 2012, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shegro, A.; Shargie, N.G.; van Biljon, A.; Labuschagne, M.T. Diversity in starch, protein and mineral composition of sorghum landrace accessions from Ethiopia. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 15, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofokeng, M.; Shimelis, H.; Tongoona, P.; Laing, M. Protein content and amino acid composition among selected South African sorghum genotypes. J. Food Chem. Nutr. 2018, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhalim, T.S.; Kamal, N.M.; Hassan, A.B. Nutritional potential of wild sorghum: Grain quality of Sudanese wild sorghum genotypes (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench). Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alencar Figueiredo, L.F.; Davrieux, F.; Fliedel, G.; Rami, J.-F.; Chantereau, J.; Deu, M.; Courtois, B.; Mestres, C. Development of NIRS equations for food grain quality traits through exploitation of a core collection of cultivated sorghum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8501–8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igne, B.; Gibson, L.; Rippke, G.; Schwarte, A.; Hurburgh, C., Jr. Triticale moisture and protein content prediction by near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). Cereal Chem. 2007, 84, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowell, F.; Maghirang, E.; Xie, F.; Lookhart, G.; Pierce, R.; Seabourn, B.; Bean, S.; Wilson, J.; Chung, O. Predicting wheat quality characteristics and functionality using near-infrared spectroscopy. Cereal Chem. 2006, 83, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlberg, J.A.; Burke, J.J.; Rosenow, D.T. Development of a sorghum core collection: Refinement and evaluation of a subset from Sudan. Econ. Bot. 2004, 58, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, H.E.; Fermin-Perez, R.A.; Prom, L.K.; Cooper, E.A.; Bean, S.; Rooney, W.L. Genome-wide association mapping of gain mod resistance in the US Sorghum Association Panel. Plant Genome 2019, 12, 180070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, T. The Determination of Nitrogen According to Kjeldahl Using Block Digestion and Steam Distillation. Hoganas Swed. Appl. Note. 2002. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/doc/160712141/AN300 (accessed on 20 June 2018).
- Bernardo, R. Breeding for Quantitative Traits in Plants; Stemma Press: Woodbury, MN, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Goettel, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Jiang, H.; Hou, D.; Song, Q.; Pantalone, V.R.; Song, B.-H.; Yu, D. POWR1 is a domestication gene pleiotropically regulating seed quality and yield in soybean. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, H.E.; Prom, L.K.; Rosa-Valentin, G. Population structure of the NPGS Senegalese sorghum collection and its evaluation to identify new disease resistant genes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.P.; Rhodes, D.H.; Brenton, Z.; Ramu, P.; Thayil, V.M.; Deshpande, S.; Hash, C.T.; Acharya, C.; Mitchell, S.E.; Buckler, E.S.; et al. Dissecting genome-wide association signals for loss-of-function phenotypes in sorghum flavonoid pigmentation traits. G3—Genes Genomes Genet. 2013, 3, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibraheem, F.; Gaffoor, I.; Chopra, S. Flavonoid Phytoalexin-Dependent Resistance to Anthracnose Leaf Blight Requires a Functional yellow seed1 in Sorghum bicolor. Genetics 2010, 184, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Li, X.R.; Xiang, W.W.; Zhu, C.S.; Lin, Z.W.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.R.; Pandravada, S.; Ridder, D.D.; Bai, G.H.; et al. Presence of tannins in sorghum grains is conditioned by different natural alleles of Tannin1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10281–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, D.H.; Hoffmann, L.; Rooney, W.L.; Ramu, P.; Morris, G.P.; Kresovich, S. Genome-wide association study of grain polyphenol concentrations in global sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] germplasm. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10916–10927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas, H.E.; Rosa-Valentin, G.; Hayes, C.M.; Rooney, L.W.; Hoffmann, L. Genomic characterization of a core set of the USDA-NPGS Ethiopian sorghum germplasm collection: Implications for germplasm conservation, evaluation, and utilization in crop improvement. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dykes, L.; Hoffmann, L.; Portillo-Rodriguez, O.; Rooney, W.L.; Rooney, L.W. Prediction of total phenols, condensed tannins, and 3-deoxyanthocyanidins in sorghum grain using near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 60, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).