Identification of Wheat Germplasm Resistance to Late Sowing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
2.2. Field Design
2.3. Phenotypic Evaluation
2.4. Descriptive Statistics
2.5. Genetic Diversity Analysis
2.6. Cluster Analysis
2.7. Stability Analysis and Comprehensive Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Performance of Plant Height Traits and Spike Related Traits in Wheat
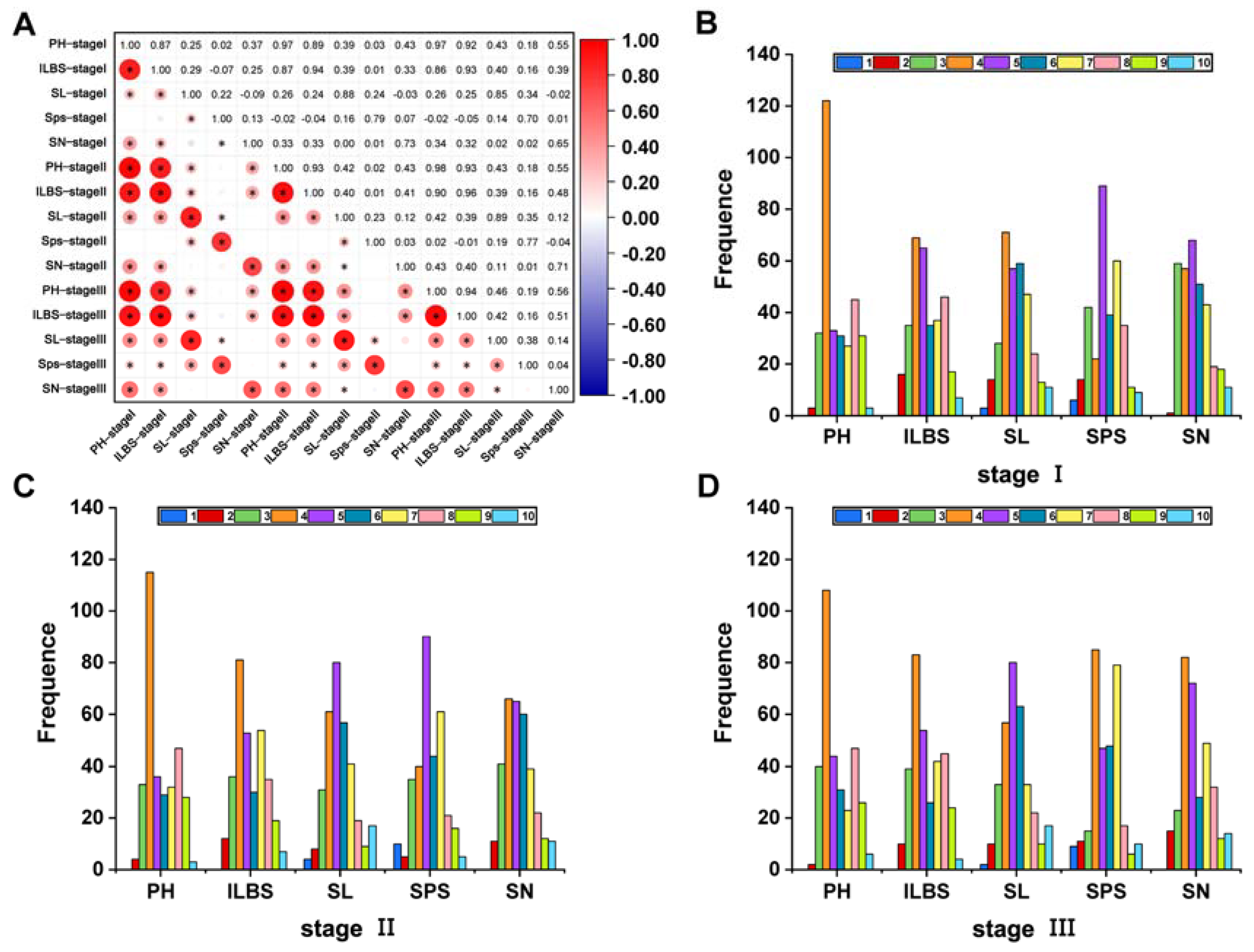
3.2. Correlation Analysis of Plant Height Traits and Spike-Related Traits in Wheat at Different Sowing Dates
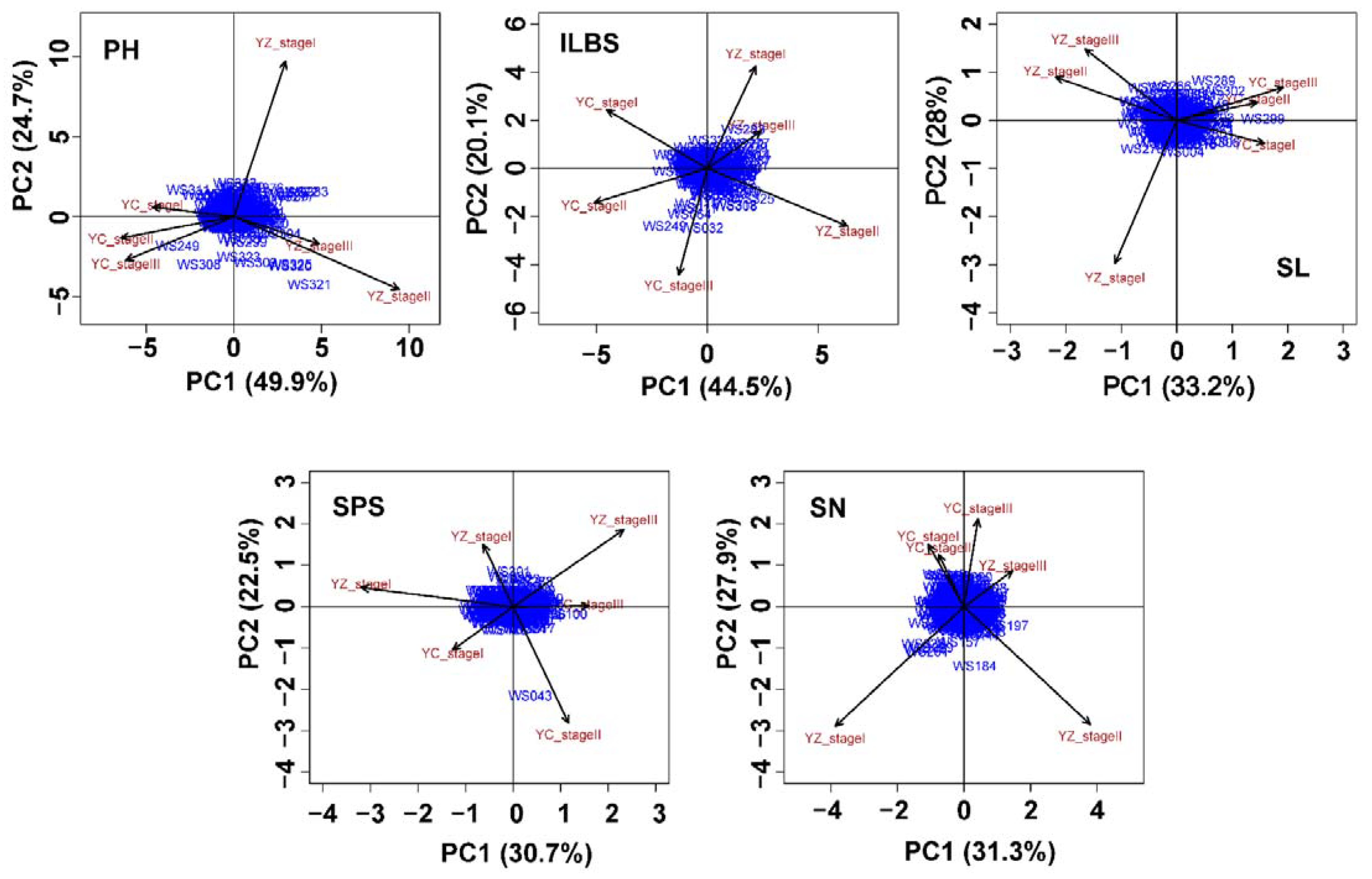
3.3. Genetic Diversity Analysis between Plant Height Traits and Spike-Related Traits in Wheat at Different Sowing Dates
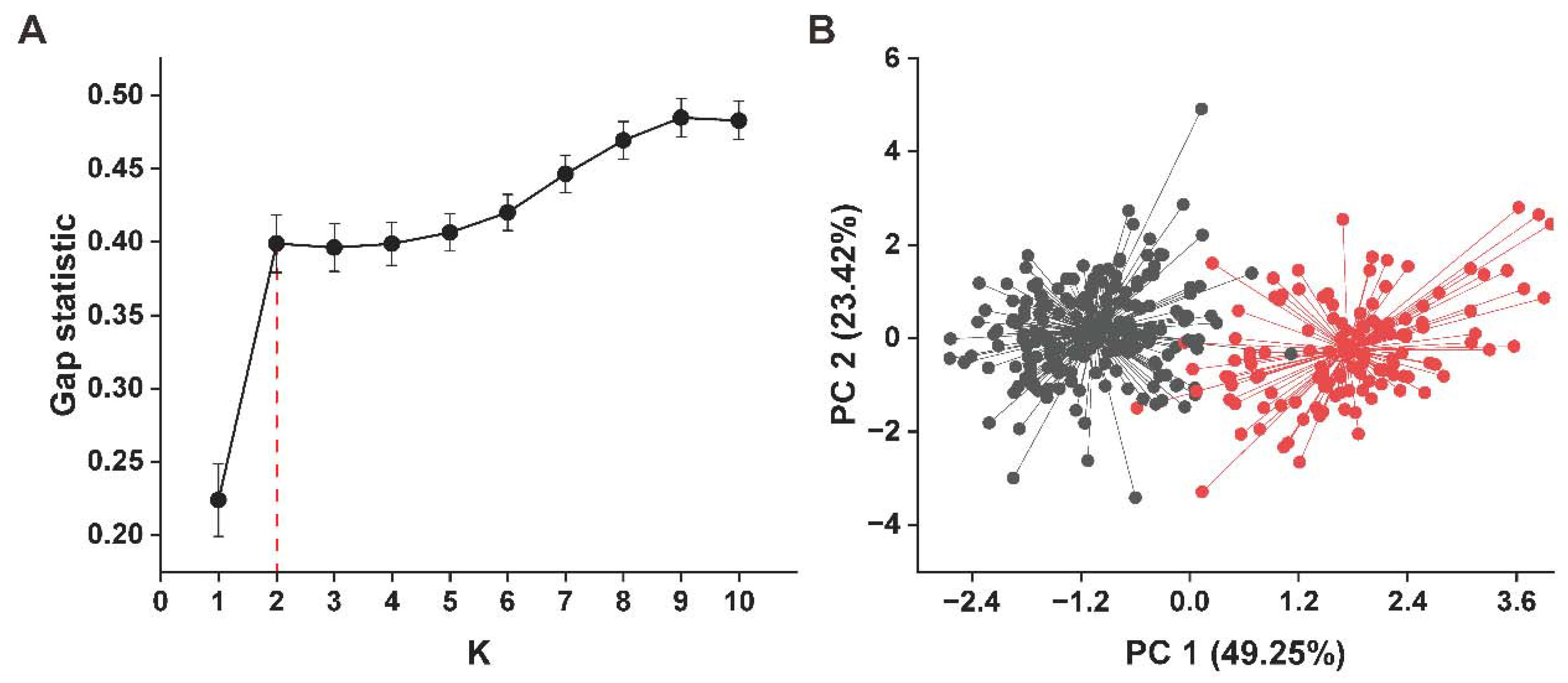
3.4. Phenotypic Clustering of Plant Height Traits and Spike-Related Traits in a Wheat Population
3.5. Stability Analysis and Comprehensive Evaluation of Plant Height Traits and Spike-Related Traits in Wheat
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Sowing Date on Wheat Plant Height Traits and Spike-Related Traits
4.2. Stability and Comprehensive Evaluation of Wheat Plant Height Traits and Spike-Related Traits at Different Sowing Dates
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azameti, M.K.; Ranjan, A.; Singh, P.K.; Gaikwad, K.; Singh, A.K.; Dalal, M.; Arora, A.; Rai, V.; Padaria, J.C. Transcriptome profiling reveals the genes and pathways involved in thermo-tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotype Raj 3765. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Guan, P.; Xin, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, A.; Liu, M.; Hongxia, L.; Zhang, M.; Lu, L. Genome-wide association study identifies QTL for thousand grain weight in winter wheat under normal-and late-sown stressed environments. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 134, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Food Outlook Biannual Report on Global Food Markets; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018; pp. 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Liu, B.; Yao, Y.; Guo, Z.; Jia, H.; Kong, L.; Zhang, A.; Ma, W.; Ni, Z.; Xu, S. Wheat genomic study for genetic improvement of traits in China. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 1718–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Cheng, P.; Ma, H. Transfer of the Resistance to Multiple Diseases from a Triticum-Secale-Thinopyrum Trigeneric Hybrid to Ningmai 13 and Yangmai 23 Wheat Using Specific Molecular Markers and GISH. Genes 2022, 13, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, D.; Amand, P.S.; Bernado, A.; Li, W.; He, F.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Yuan, X. High-Resolution Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Genomic Regions and Candidate Genes for Important Agronomic Traits in Wheat. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1311–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andarzian, B.; Hoogenboom, G.; Bannayan, M.; Shirali, M.; Andarzian, B. Determining optimum sowing date of wheat using CSM-CERES-Wheat model. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2015, 14, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, A.; Basra, S.M.A.; Ahmad, R.; Wahid, A. Performance of late sown wheat in response to foliar application of Moringa oleifera Lam. leaf extract. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 72, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslani, F.; Mehrvar, M.R. Responses of wheat genotypes as affected by different sowing dates. Asian J. Agric. Sci 2012, 4, 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ahamed, K.U.; Nahar, K.; Fujita, M. Sowing date mediated heat stress affects the leaf growth and dry matter partitioning in some spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. IIOAB J. 2010, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Fazily, T. Effect of Sowing dates and seed rates on growth and yield of different wheat varieties: A review. Int. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 8, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, V.; Khajoie-Nejad, G.; Mohammadi-Nejad, G.; Yousefi, K. The effect of different sowing dates on yield and yield components of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Int. J. Agron. Plant Prod. 2010, 1, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.; Dai, X.; He, M. Delayed sowing improves nitrogen utilization efficiency in winter wheat without impacting yield. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 221, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Jia, S.F.; Lv, A.F.; Yang, K.J.; Svensson, J.; Gao, Y.C. Impacts of climate change on growth period and planting boundaries of winter wheat in China under RCP4. 5 scenario. Earth Syst. Dyn. Discuss. 2015, 6, 2181–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Asseng, S.; Zhao, G.; Wu, D.R.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhuang, W.; Jin, N.; Yu, Q. Impacts of recent climate warming, cultivar changes, and crop management on winter wheat phenology across the Loess Plateau of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 200, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.P.; Moiwo, J.P.; Tao, F.L.; Yang, Y.H.; Shen, Y.J.; Xu, Q.H.; Liu, J.F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F.S. Spatiotemporal variability of winter wheat phenology in response to weather and climate variability in China. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2015, 20, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Zheng, D.S.; Cao, Y.S.; Cao, Y.S.; Song, C.H.; Chen, M.Y. Genetic Diversity of Landrace and Bred Varieties of Wheat in China. J. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2000, 33, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tibshirani, R.; Walther, G.; Hastie, T. Estimating the number of data clusters via the Gap statistic. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 2001, 63, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.Z.; Begum, F.; Khan, M.A.A.; Amiruzzaman, M.; Hossain, A. Evaluation of yield stability of seven barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) genotypes in multiple environments using GGE biplot and AMMI model. Open Agric. 2019, 4, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lv, C.; Gou, B.; Shen, H.; Xu, X.; Xu, R. Screening of stable resistant accessions and identification of resistance loci to Barley yellow mosaic virus disease. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Hwang, C.L.; Chen, S.J.; Hwang, C.L. Multiple attribute decision making—An overview. In Fuzzy Multiple Attribute Decision Making; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 16–41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.H.; Sheng, K.; Yang, L.J. Effects of Sowing Date and Seeding Rate on Growth Period, Plant Height and Yield Characters of Xinmai 23. J. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2015, 47, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pei, Z.Y.; Wang, H.B.; Wen, H.Q.; Cheng, T.L.; Li, X.; Zhu, M.; Che, L.; Hao, Y.P. Effect of Sowing Date and Planting Density on Wheat Plant Height of Jintai 182. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2016, 44, 957–961. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.A.; Dang, J.Y.; Zhang, D.Y. Effect of Sowing Dates on Agronomic Character, Yield and Quality of the Main Stalks and Tillers in Wheat. J. Agric. 2013, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.X.; Wu, S.H.; Duan, G. Effects of sowing date on tillering and panicle formation of wheat varieties with different habits. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2007, 37–38. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Xie, Q.G.; Liu, B.; Zhang, H.; Tian, J.C. Correlation Analysis of Wheat Basal Elongated Internode Characteristics at Different Sowing Dates. J. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2012, 44, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, C.; Xiang, Z.H. Analysis of Variety Stability Based on AMMI Model. J. Acta Agron. Sin. 1998, 24, 304–309. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.R. An Improvement on the Method of Variety Stability Analysis Based on the AMMI Model. J. Hered. 2000, 22, 31–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Geng, Z.; Yang, Q.C. Analysis of high yield ability, stability and adaptability of new soybean variety Zhoudou 25. J. China Seed Ind. 2019, 5, 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Mebratu, A.; Wegary, D.; Mohammed, W.; Teklewold, A.; Tarekegne, A. Genotype × environment interaction of quality protein maize hybrids under contrasting management conditions in eastern and Southern Africa. Crop Sci. 2019, 59, 1576–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, K.; Munjal, R.; Kesh, H.; Resh, S.; Kumari, A. AMMI and GGE Biplot Analysis for Yield Stability of Wheat Genotypes under Drought and High Temperature Stress. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2020, 9, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Location | Trait | Stage I | Stage II | Stage III | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Range | CV | Mean | Range | CV | Mean | Range | CV | ||
| YZ | PH (cm) | 108 | 53–189 | 28.71% | 101 | 49–165 | 30.68% | 99 | 46–172 | 31.01% |
| ILBS (cm) | 36 | 18–59 | 28.48% | 36 | 17–62 | 31.18% | 35 | 16–61 | 29.32% | |
| SL (cm) | 10 | 7–17 | 15.09% | 10 | 7–16 | 14.88% | 10 | 6–17 | 15.32% | |
| SPS | 20 | 15–25 | 8.63% | 20 | 16–25 | 7.68% | 19 | 15–25 | 7.88% | |
| SN | 9 | 4–24 | 28.51% | 9 | 5–19 | 28.04% | 8 | 4–16 | 24.19% | |
| YC | PH (cm) | 107 | 56–165 | 24.34% | 101 | 53–160 | 24.46% | 91 | 50–159 | 26.75% |
| ILBS (cm) | 35 | 17–58 | 24.35% | 33 | 16–58 | 25.68% | 34 | 13–66 | 29.38% | |
| SL (cm) | 11 | 7–17 | 14.81% | 10 | 6–16 | 15.17% | 10 | 6–16 | 16.99% | |
| SPS | 19 | 14–24 | 8.90% | 20 | 15–35 | 8.94% | 19 | 15–25 | 7.84% | |
| SN | 7 | 4–15 | 30.79% | 7 | 4–13 | 25.73% | 6 | 4–15 | 30.38% | |
| SOV | Df | PH | ILBS | SL | SPS | SN | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | F | MS | F | MS | F | MS | F | MS | F | ||
| Varieties | 326 | 4402.54 | 84.18 ** | 508.43 | 42.15 ** | 11.78 | 26.18 ** | 10.88 | 11.89 ** | 18.01 | 8.87 ** |
| Environments | 1 | 5229.55 | 99.99 ** | 996.03 | 82.56 ** | 11.23 | 24.96 ** | 0.87 | 0.95 | 2039.4 | 1004.82 ** |
| Sowing dates | 2 | 25,149.87 | 480.86 ** | 106.36 | 8.82 ** | 69.4 | 154.19 ** | 168.94 | 184.63 ** | 231.76 | 114.19 ** |
| Varieties × Environments | 326 | 168.8 | 3.23 ** | 30.2 | 2.5 ** | 1 | 2.22 ** | 1.11 | 1.22 * | 2.74 | 1.35 ** |
| Varieties × Sowing dates | 652 | 44.42 | 0.85 | 10.41 | 0.86 | 0.55 | 1.22 ** | 1.05 | 1.14 * | 2.32 | 1.15 * |
| Error | 654 | 52.3 | 12.06 | 0.45 | 0.92 | 2.03 | |||||
| Trait | Stage I | Stage II | Stage III |
|---|---|---|---|
| PH | 1.8384 | 1.8703 | 1.8875 |
| ILBS | 2.0339 | 2.0082 | 1.9891 |
| SL | 2.0463 | 2.0084 | 2.0089 |
| SPS | 2.0245 | 1.9928 | 1.9419 |
| SN | 1.9534 | 2.0003 | 1.9867 |
| Subgroup | PH (mm) | ILBS (mm) | SL (mm) | SPS | SN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 82 a | 29 a | 10 a | 19 | 7 a |
| 2 | 132 b | 45 b | 11 b | 19 | 9 b |
| IPCA | Df | PH | ILBS | SL | SPS | SN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPCA1 | 330 | 32.93 | 36.96 | 14.54 | 2.50 | 2.02 |
| IPCA2 | 328 | 16.43 | 16.76 | 12.33 | 1.84 | 1.81 |
| IPCA3 | 326 | 9.75 | 12.80 | 10.66 | 1.64 | 1.24 |
| IPCA4 | 324 | 4.91 | 11.84 | 4.65 | 1.26 | |
| IPCA5 | 322 | 2.38 | 5.29 | 2.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basheir, S.M.O.; Hong, Y.; Lv, C.; Xu, H.; Zhu, J.; Guo, B.; Wang, F.; Xu, R. Identification of Wheat Germplasm Resistance to Late Sowing. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041010
Basheir SMO, Hong Y, Lv C, Xu H, Zhu J, Guo B, Wang F, Xu R. Identification of Wheat Germplasm Resistance to Late Sowing. Agronomy. 2023; 13(4):1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041010
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasheir, Samia Mahgoub Omer, Yi Hong, Chao Lv, Hongwei Xu, Juan Zhu, Baojian Guo, Feifei Wang, and Rugen Xu. 2023. "Identification of Wheat Germplasm Resistance to Late Sowing" Agronomy 13, no. 4: 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041010
APA StyleBasheir, S. M. O., Hong, Y., Lv, C., Xu, H., Zhu, J., Guo, B., Wang, F., & Xu, R. (2023). Identification of Wheat Germplasm Resistance to Late Sowing. Agronomy, 13(4), 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041010









