Abstract
The wide use of the insecticide profenofos in crop production has led to serious ecological water problems in agricultural fields. With the increasing global production of nuts, a large amount of nutshell waste has a serious impact on the environment. Turning nutshell waste into biochar to remove high levels of profenofos in water is a cost-effective treatment method. In this study, biochars made from nutshell waste are investigated for the adsorption of aromatic organophosphorus insecticide profenofos. The adsorption amount of nutshell biochar was 13-fold higher than crop stalk biochar in removing profenofos from water. The results indicated that the adsorption of profenofos by nutshell biochar was specific. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) analysis showed that nutshell biochars had a larger specific surface area and more microporous structures. Meanwhile, nutshell biochars could exhibit a stable adsorption capacity at different initial concentrations of profenofos (10–40 mg/L), temperature (298–318 K), and pH (3–7). Desorption and reuse experiments showed that profenofos was firmly bound to nutshell biochars in water and could be extracted from the biochars with acetonitrile. Within 10 times of recycling, nutshell biochar had a stable and strong adsorption capacity for profenofos. The adsorption process of profenofos by nutshell biochar was pore diffusion and surface adsorption, which is consistent with the pseudo second-order kinetic model and the Freundlich isotherm model. Elemental and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analyses showed that the adsorption mechanism of profenofos on nutshell biochar was mainly through π-π and hydrophobic interactions. Nutshell biochar also showed strong adsorption capacity for other aromatic organophosphorus pesticides, and the adsorption rates of methyl parathion, isocarbophos and 2-chloro-4-bromophenol were 85%, 73% and 73%, respectively. Nutshell biochar can serve as an excellent material for removing aromatic organophosphorus insecticide pollution from water.
1. Introduction
Nuts have a large share of global agricultural production because of their high nutritional value. Indonesia is the largest coconut-tree-growing region in the world, and coconut production was estimated at 2.9 million tonnes in 2018 [1]. World production of shelled almonds and walnuts reached 3.2 and 2 million tonnes in 2020, respectively [2,3]. With the increasing production of nuts, a large amount of nutshell waste is generated; for example, coconut shells account for about 35% of the whole fruit [4]. Nutshells are usually treated as worthless household waste, and their large accumulation may lead to ecological problems. An interest is to convert the large amount of nutshell waste into wealth.
Biochar is obtained by the pyrolysis of biomass materials, which has the characteristics of a large specific surface area, a stable structure and the rapid adsorption of pollutants [5]. Due to its excellent physicochemical properties, biochar is widely used to remove heavy metals [6,7], dyes [8] and pesticides [9] from wastewater. Additionally, biochar can be combined with bioremediation to reduce the stressful effects of pollutants on microorganisms [10,11], which means that biochar has great potential for environmental remediation. The content of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin in biomass materials is an important factor affecting the physicochemical properties of biochar [12]. Crop stalk waste is often used for biochar research, such as rice stalk, corn stalk, rice hull and bamboo [13,14]. However, nutshell has higher cellulose or lignin content, which is ideal for preparing biochar [15]. Coconut shells contain about 33% cellulose and 37% lignin [4], almond shells contain about 29% lignin, and walnut shells contain about 36% cellulose and 30% lignin [16]. Walnut shell biochar is an excellent adsorbent for removing estrogenic pollution from water [17]. Pecan shell biochar can effectively remove reactive red 144 from wastewater [18]. Therefore, making biochar from nutshells is an ideal way to turn waste into wealth.
Organophosphorus insecticides (OPs) are a major class of one of the insecticides used to control insect and mite pests in crop fields [19]. Excessive use of OPs has posed potential risks to human and ecological health [19,20,21]. In China, profenofos has a big commercial use, accounting for 10% of OPs [22]. It has become an alternative to highly toxic insecticides in current agricultural production because of its moderate toxicity. However, profenofos is a potential endocrine disruptor [23]. The wide use of profenofos leads to high levels in water and soil which are above permissible limits [23,24]. Profenofos was detectable in surface water, sediment and fish at a mean concentration of 1.40 μg/L, 7.61 μg/g and 13.72 μg/g, respectively [25]. Meanwhile, profenofos could significantly reduce the survival rate of zebrafish and increase the occurrence of organ malformations at different developmental stages [26]. Therefore, how to rapidly and efficiently remove the pollution caused by profenofos in water environments is an important issue to address.
Some researchers have studied methods of profenofos removal, such as chemical, microbial and adsorption methods [22,27,28]. Compared with chemical and microbiological methods, adsorption has the advantages of a good removal effect, such as fast speed, low cost and recyclability [29]. There are relatively few studies on the management of environmental pollution caused by the excessive application of OPs in agricultural production. Baharum et al. investigated the adsorption of diazinon on coconut shell biochar in water [30]. Uchimiya et al. studied the removal of malathion, parathion and diazinon from soil by cotton seed husk biochar [31]. Zheng et al. researched the influences of deashing and aging on the biochar adsorption of chlorpyrifos [32]. However, few studies have investigated the removal of profenofos in water by adsorption, so the study of adsorption of profenofos by biochar is urgently needed.
This study aims to investigate the feasibility of making biochar from nutshell waste to remove aromatic organophosphorus insecticides from water. Comparing nutshell biochars and crop stalk biochars, we investigate the reasons for the differences in the adsorption of profenofos by different biochars. The study investigates the adsorption characteristics of profenofos by nutshell biochars and elucidates the adsorption mechanism of aromatic organophosphorus insecticides by nutshell biochars. The results of the study demonstrate the specificity of different biochars for the removal of pollutants. It provides a theoretical basis for the selection of biochar for the removal of aromatic organophosphorus insecticides. Additionally, the burning of nutshells into biochar is demonstrated to be a good way to reuse waste resources.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biochars and Reagents
Biochars made from coconut shells, almond shells, walnut shells, rice stalks, rice hulls, corn stalks, wood and bamboo at 700 ℃ were purchased from Straw Charcoal Environmental Technology Co., Ltd. (Henan, China). The biochars were sieved with a 200-mesh sieve for further use. Profenofos, methyl parathion, isocarbophos, 2-chloro-4-bromo-phenol and malathion standards were purchased from Dr. Ehrenstorfer (Augsburg, Germany). NaOH and HCl were purchased from Xilong Chemical Co. (Guangzhou, China).
2.2. Adsorption Characteristics of Biochar on Profenofos
Adsorption kinetics: 5 mL of profenofos solution (20 mg/L) with 1 g/L of biochar was placed in a 25 mL glass tube. The tubes were placed in a shaker at 150 rpm at room temperature. The samples were periodically sampled at 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, 20 and 30 min. Residual profenofos was detected on an AcquityTM Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatograph instrument (UPLC, Waters Corp., Milford, MA, USA) as previously reported [33].
Effect of initial concentration: Five milligrams of biochar (a final concentration of 1 g/L) were added to a 5 mL solution with 10, 15, 20, 30 and 40 mg/L of profenofos. The tubes were placed in a shaker at 150 rpm for 20 min at room temperature. Profenofos residues were detected on a UPLC.
Effect of temperature: 5 mL of profenofos solution (20 mg/L) with 1 g/L of biochar was placed in a 25 mL glass tube. The tubes were placed in a shaker at 150 rpm for 20 min at 298, 308 and 318 K. Profenofos residues were detected on a UPLC.
Effect of pH: 5 mL of profenofos solution (20 mg/L) with 1 g/L of biochar was placed in a 25 mL glass tube. The pH of profenofos solutions was separately adjusted to 3, 5, 7 and 9. The tubes were placed in a shaker at 150 rpm for 20 min at room temperature. Profenofos residues were detected on a UPLC.
Desorption of profenofos on nutshell biochars: profenofos on nutshell biochars were desorbed with CaCl2 aqueous solution and acetonitrile, respectively. When the biochars reached adsorption equilibrium, the supernatant was removed by centrifugation, and then 5 mL of acetonitrile or 0.01 mol/L CaCl2 aqueous solution was added to the tube. Then, tubes were placed in a shaker at 150 rpm for 2 h. The concentration of profenofos in the extracts was detected on a UPLC.
Reuse of nutshell biochars: 5 mL of profenofos solution (20 mg/L) with 1 g/L of biochar was placed in a 25 mL glass tube. The tubes were placed in a shaker at 150 rpm for 20 min at room temperature. After the adsorption equilibrium, profenofos was desorbed from the biochar. The biochar was dried at 70 °C, and the saturated adsorption amount of the biochar to profenofos after the regeneration was measured. The above operations were repeated to determine the number of cycles of nutshell biochars.
The adsorption amount (Q) of profenofos was calculated according to Equation (1):
where Q is the adsorption amount of profenofos (mg/g); C0 is the initial concentration of profenofos in the solution (mg/L); Ce is the concentration of profenofos in the solution after adsorption (mg/L); V is the volume of solution (L); m is the amount of biochar added (g).
2.3. Adsorption Kinetics Analysis
The pseudo first- and second-order kinetic models (Equations (2) and (3)) were used to simulate the changes in the adsorption process with time. The equations are as follows:
where Qe is the equilibrium adsorption amount of profenofos (mg/g); Qt is the amount of profenofos adsorbed at t (mg/g); t is the adsorption time (min); K1 (1/min) and K2 (g/mg·min) are the rate constants of the pseudo first-order and pseudo second-order kinetic models.
2.4. Adsorption Isotherm Analysis
The models Langmuir (4) and Freundlich (5) are usually used in the fitting of adsorption isotherms.
where Ce is the equilibrium concentration of adsorption in solution (mg/L); Qe is the adsorption amount at adsorption equilibrium (mg/g); Qm is the maximum adsorption amount (mg/g); KL is the Langmuir adsorption constant (L/mg). KL is used to calculate the separation factor (RL=1/(1 + KLC0)); RL is used to evaluate the affinity of adsorption; KF is the adsorption capacity (L/mg); n is the adsorption strength.
2.5. Adsorption Thermodynamics Analysis
The values of Gibbs free energy (ΔG0), enthalpy (ΔH0) and entropy (ΔS0) were used to evaluate the effects of temperature on the adsorption reaction. The thermodynamic parameters were calculated according to Equations (6)–(8):
where T (K) is the absolute temperature; R (8.314 J/mol K) is the gas constant; the lnK0 and 1/T fit can be plotted as a linear curve; the values of ΔH0 and ΔS0 are obtained from the plot slope and intercept.
2.6. Characterization of Biochars
Elemental analysis: The contents of C, H, N and S in biochars were determined with an elemental analyzer (Elementar Vario EL cube, Hanau, Germany). The content of the O element was calculated by subtracting C, H, N, S and ash content from 100%.
Ash content: The biochars were warmed in a muffle furnace (Milestone PYRO) at 850 °C for 2 h. The ash content was obtained from the biochar mass change.
Specific surface area, pore size distribution: The adsorption and desorption isotherms, specific surface area, pore size distribution, and pore volume of biochars were analyzed with a specific surface area analyzer (Micromeritics ASAP 2460), as previously reported [34].
Morphological characteristics: The morphology of biochars was observed under a field emission scanning electron microscope (SEM, Tescan MIRA3 FEG, Brno, Czech Republic), as previously reported [35].
Analysis of functional groups: Changes in functional groups before and after the adsorption of biochars were analyzed with FTIR (Nicolette is50, Thermo Fourier, Waltham, MA, USA) [36].
2.7. Adsorption of OP Structural Analogs
The adsorption of profenofos and its structural analogs (methyl parathion, isocarbophos) and metabolites (2-chloro-4-bromophenol) on coconut shell biochar was also determined; Five mL of standard solution (20 mg/L) of each substance was placed in a 25 mL glass tube, followed by the addition of coconut shell biochar (1 g/L). The tubes were placed in a shaker at 150 rpm for 20 min at room temperature. The adsorption rate was obtained by calculating the change in the concentration of the adsorbed substance in the solution before and after adsorption.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nutshell Biochar Showed Superior Adsorption Performance for Profenofos
The adsorption capacity of biochars made from eight bio-based materials on profenofos is shown in Table 1. Coconut shell biochar, almond shell biochar and walnut shell biochar had good adsorption capacity for profenofos, with 88%, 84% and 75% removal, respectively. Meanwhile, the removal rates of profenofos in rice stalk biochar, rice hull biochar, bamboo biochar, corn stalk biochar and wood biochar were 15%, 13%, 5.0%, 3.7% and 4.6%, respectively. The results showed that the adsorption capacity of nutshell biochars for profenofos was much stronger than crop stalk biochars.

Table 1.
Adsorption capacity of biochars for profenofos.
The properties of specific surface area, pore size and pore volume were important factors affecting the adsorption capacity of biochar [37]. Coconut shell biochar, almond shell biochar and walnut shell biochar had larger specific surface areas, with 817.254, 710.632 and 640.837 m2/g, respectively. The specific surface area of rice stalks, corn stalks, rice hulls, bamboo and wood biochar were significantly smaller than nutshell biochars, with 72.178, 3.024, 113.774, 144.575 and 1.723 m2/g, respectively (Table 2). Figure 1a shows the pore size distribution of each biochar. The pore size of coconut shell biochar was mostly microporous, with a small number of mesopores. The pore size of almond shell and walnut shell biochars was mainly mesoporous, with a small number of micropores. The pore size of rice stalks and rice hulls biochars was mainly a small number of mesopores. Corn stalks, bamboo and wood biochars had no obvious microporous and mesoporous structures. Total pore volume is an important factor affecting the adsorption capacity of biochar. The total pore volumes of coconut shell, almond shell and walnut shell biochars were much larger than other biochars, with 0.454, 0.434 and 0.397 cm3/g, respectively. Micropore volume accounts for more than 64% of the total pore volume. The total pore volumes of rice stalks, rice hulls, corn stalks, bamboo and wood biochars were 0.052, 0.071, 0.003, 0.073 and 0.002 cm3/g, respectively. Figure 1b shows the pore diameter–pore volume relationship. The cumulative pore volume of nutshell biochars increased sharply at pore sizes less than 2 nm. The cumulative pore volume of coconut shell biochar remained basically constant after the pore size was larger than 2 nm. The cumulative pore volume of almond shell biochar and walnut shell biochar still increased slowly between pore sizes of 2–50 nm, which was mainly caused by the mesoporous structure.

Table 2.
Properties of biochars.
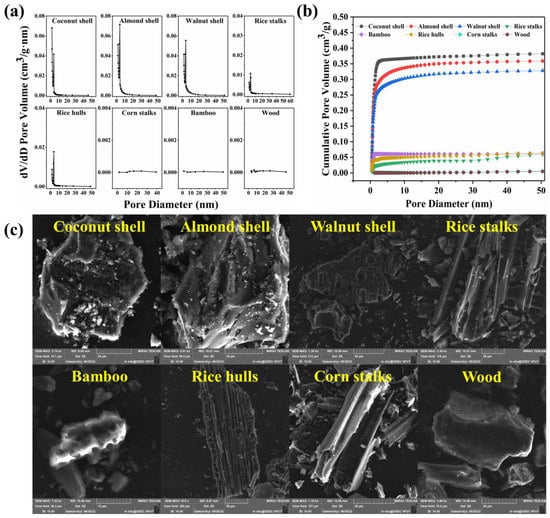
Figure 1.
(a) Pore diameter distribution; (b) pore diameter–pore volume relationship; (c) SEM of biochars.
Figure 1c shows the microscopic morphology of biochars. Coconut shell biochar, almond shell biochar and walnut shell biochar were irregular particles with rough surface structures and a large number of pores. Rice stalk biochar, rice hull biochar and corn stalk biochar presented a tubular pore structure externally, with a smooth surface and a regular lamellar arrangement structure of internal voids. Bamboo biochar appears as a rod structure with a smooth surface and uniformly sized and regularly arranged voids. Wood biochar appears granular, with a smooth surface and no obvious pore structure. The results showed that the morphological characteristics of the biochars made from different raw materials were quite different. Nutshell biochars have a rough and porous surface, which is conducive to the adsorption of profenofos [38].
The results of the elemental analysis are shown in Table 2. The coconut shell biochar, almond shell biochar and walnut shell biochar had higher carbon contents, with 85.1%, 78.9% and 83.5%, respectively. Correspondingly, the ash contents of the three biochars were 1.7%, 5.7% and 3.0%, which are significantly lower than the other biochars. The H/C ratio was used to characterize the aromaticity of biochar, with smaller values indicating greater aromaticity [39]. The high aromaticity of biochar would provide more π-π binding sites for the interaction with profenofos. Meanwhile, the smaller O/C indicates the stronger hydrophobicity of the biochar. The hydrophobic groups of the biochar could interact hydrophobically with profenofos, so the strong hydrophobicity of biochar was beneficial to the adsorption of profenofos [40]. Compared with crop stalk biochars, the higher aromaticity and hydrophobicity of nutshell biochars is one of the reasons for the stronger adsorption capacity of profenofos.
Through BET, SEM and elemental analysis, it was found that there were great differences in the physicochemical properties of biochars made from different bio-based materials. Compared with traditional crop stalk biochars, nutshell biochars have a larger specific surface area, higher aromatization and stronger hydrophobicity. This is the main reason why nutshell biochars have a stronger ability to adsorb profenofos compared to other biochars.
3.2. Nutshell Biochars Showed Extremely Fast Adsorption Rate for Profenofos
As shown in Figure 2a, the adsorption of profenofos on nutshell biochars showed a fast and then slow trend. Due to the abundant binding sites on biochar before the onset of adsorption, the amount of profenofos adsorbed on biochar increased dramatically in the first 30 s. After 10 min, the adsorption of profenofos on biochar gradually reached an equilibrium state. In the first 30 s, the adsorption of profenofos on coconut shell biochar was close to the adsorption equilibrium state, and the removal rate was more than 80%. Compared with the reported adsorption materials for profenofos (Fe/Ni bimetallic nanoparticles and M-M-ZIF-8), the used time of the adsorption equilibrium state for coconut shell biochar was shortened by 32 and 30 times. The coconut shell biochar showed a faster adsorption speed compared with other materials that have been reported to adsorb OPs (Table S1).
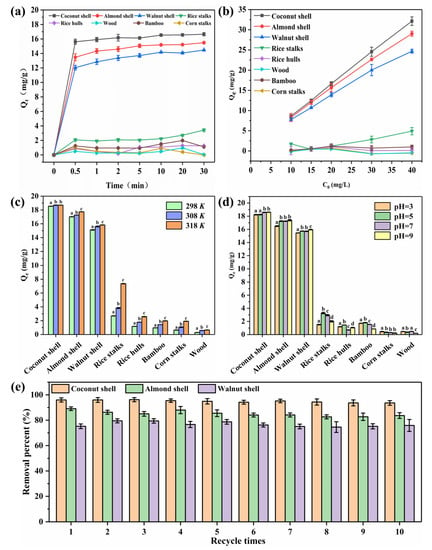
Figure 2.
(a) Adsorption kinetics of profenofos on biochars; effects of initial adsorbate concentration (b), temperature (c), pH (d) on the adsorption of profenofos; (e) recycling of nutshell biochars. All values are means ± standard deviation of triplicate measurements. Mean values with the same letter (a, b, c, d) are not significantly different from temperature (298 K, 308 K, 318 K) and pH (3, 5, 7, 9) by LSD at the 5% level.
The adsorption curves of coconut shell biochar, almond shell biochar, walnut shell biochar, rice stalk biochar, and bamboo biochar were well-fitted with the pseudo second-order kinetic model (Table 3). The Qe values fitted by the pseudo second-order kinetic model were closer to the actual adsorption. Pseudo second-order kinetics suggest the adsorption process of profenofos in biochar through multiple steps, including liquid film diffusion, intra-particle diffusion and surface adsorption [41]. However, rice hull biochar, corn stalk biochar and woody biochar did not fit the two adsorption models because of their poor adsorption capacity.

Table 3.
Parameters of adsorption kinetics and adsorption isotherm models.
The N2 adsorption and desorption curves can indicate the structural properties of biochar [42] (Figure S1). According to the classification of IUPAC, coconut shell biochar, almond shell biochar and walnut shell biochar conform to the type I curve (Langmuir type), indicating that the adsorption reaction was dominated by micropores and the adsorption rates were controlled by the pore volume. Rice stalk biochar, bamboo biochar and rice hull biochar conformed to the type II curve (S type), indicating that the macropores on the biochar dominated the adsorption process. The inflection point at low P/P0 showed the completion of single molecular layer adsorption and the gradual formation of the second layer adsorption as the relative pressure increased. Corn stalk biochar and wood biochar conformed to the type III curve, which was common in the case of weak adsorption.
Kinetic modeling and N2 adsorption and desorption analysis revealed that the rapid adsorption capacity of nutshell biochars was mainly attributed to the rich microporous structure.
3.3. Nutshell Biochars Showed a Stabile Adsorption Capacity in Different Environments
3.3.1. Effect of Initial Concentration of Profenofos
Figure 2b shows the concentration-dependent adsorption relationship of profenofos in nutshell biochars at the adsorption equilibrium. A higher initial concentration of profenofos could lead to a bigger concentration difference between the biochar and the solution, which could help a greater amount of profenofos to be adsorbed [43]. When the initial concentration of profenofos changed from 10 to 40 mg/L, the adsorption amount of other biochars did not change significantly at equilibrium because of the poor adsorption capacity of profenofos.
The results of isothermal adsorption experiments were fitted by the Freundlich and Langmuir models (Table 3). The R2 of the Langmuir model for coconut shell, almond shell, walnut shell, rice stalk, bamboo, rice hull, corn stalk and wood biochars were 0.806, 0.976, 0.937, 0.077, 0.776, 0.733, 0.190 and 0.503, respectively. The R2 of the Freundlich model for coconut shell, almond shell, walnut shell, rice stalk, bamboo and rice hull biochars were 0.990, 1.000, 0.990, 0.316, 0.727 and 0.004, respectively. The adsorption process of profenofos in nutshell biochars could be fitted well by the Freundlich model than the Langmuir model (R2 larger), which means that the adsorption of profenofos by nutshell biochars occurs in a multilayer on a non-uniform surface [44]. The constant Kf reflects the adsorption capacity. Nutshell biochars fitted larger Kf values than the other biochars. This indicated that nutshell biochars had a stronger adsorption capacity for profenofos. Meanwhile, the Freundlich model parameter n > 1 indicates that nutshell biochars have a good affinity for profenofos and can easily react with profenofos by adsorption [18].
3.3.2. Effect of Temperature
As shown in Figure 2c, with an increase in temperature, the adsorption of profenofos on biochars shows an increasing trend, which indicates that high temperature can improve the adsorption of profenofos in biochars [45].
The thermodynamics of biochars for the adsorption of profenofos are shown in Figure S2 and Table S2. The Gibbs free energy of nutshell biochars was less than zero (ΔG0< 0) at a reaction temperature between 298–318 K, suggesting that the adsorption is a spontaneous behavior. When the temperature was increased from 298 K to 318 K, the ΔG0 showed a decreasing trend, suggesting that the higher temperature promoted the adsorption of profenofos in nutshell biochars [46]. The other biochars had higher Gibbs free energy, suggesting that the adsorption process did not easily occur, which resulted in a poor adsorption capacity for profenofos. Meanwhile, ΔH0 > 0 showed that the adsorption of profenofos on biochar was an endothermic reaction [45]. The ΔH0 of coconut shell, almond shell, walnut shell, rice stalk, bamboo, rice hull, corn stalk and wood biochars were 4.89, 12.5, 8.07, 51.71, 30.38, 34.02, 45.87 and 32.11 kJ mol−1, respectively. The ΔH0 showed that the higher temperature was beneficial to the adsorption of profenofos on biochars. ΔS0 > 0 reflects the increases of randomness between the solid–liquid interface, which is favorable to the movement of profenofos onto the biochar [47]. The ΔS0 of coconut shell, almond shell, walnut shell, rice stalk, bamboo, rice hull, corn stalk and wood biochars were 37.7, 56.3, 36.6, 157.38, 77.24, 91.12, 125.38 and 73.58 J mol−1K−1, respectively. The ΔH0 and ΔS0 of nutshell biochars were smaller than the other biochars, indicating that the strong adsorption capacity of nutshell biochars could not change significantly in a wide temperature range.
3.3.3. Effect of pH
Figure 2d shows the effects of pH on the adsorption of profenofos. The results showed no significant change in the adsorption capacity of nutshell biochars within pH values of 3–9. The pKa of the adsorbed material can have a large effect on the adsorption capacity of biochar. Some adsorbates undergo electrical changes with pH because of their pKa. Adsorbents such as biochars undergo an electrostatic reaction of mutual attraction or mutual repulsion [48]. However, the pKa of profenofos has not been reported. Therefore, the zeta potential of nutshell biochars was measured before and after adsorption at pH 3–9 (Figure S3). The results showed that the amount of charge on the surface of nutshell biochars did not change significantly before and after adsorption. The self-made Fe/Ni bimetallic nanoparticles by Mansouriieh et al. were stable for the adsorption of profenofos at pH 5–7.3, and the adsorption capacity decreased significantly when the pH was 2 and 8.36 [28]. Compared with synthetic materials, nutshell biochars can have stable adsorption capacity for profenofos in a wider pH range, which shows the excellent performance of nutshell biochars.
3.3.4. Desorption and Reuse
CaCl2 aqueous solution and acetonitrile were used to desorb profenofos adsorbed by nutshell biochars, respectively. The results showed that profenofos could not be desorbed by the aqueous solution (not detectable). It was proved that profenofos had a good binding ability with nutshell biochars in water. This can avoid the secondary pollution caused by leakage after the adsorption of profenofos by nutshell biochars.
Acetonitrile was found to have a good desorption capacity for profenofos in nutshell biochars. The results showed that acetonitrile could desorb 58%, 70% and 93% of profenofos in coconut shell biochar, almond shell biochar and walnut shell biochar, respectively (Figure S4). Desorption of profenofos by acetonitrile could be a good way to recycle nutshell biochars.
The number of cycles is one of the important indicators to measure the performance of nutshell biochars. The results are shown in Figure 2e. According to the figure, with repeated adsorption–desorption, the removal percent of profenofos by nutshell biochars showed a slightly decreasing trend, but the change was not significant. The self-made magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotube organic framework ZIF-8 (M-M-ZIF-8) by Liu et al. exhibited good stability and performance for the adsorption of profenofos within five cycles [49]. Compared with M-M-ZIF-8, nutshell biochars have more reusability and a slower decrease in adsorption effect.
3.4. Adsorption of Profenofos in Biochars by π-π and Hydrophobic Interactions
3.4.1. FTIR Analysis of Biochars
Figure 3 shows the FTIR analysis of biochars. The absorption peak at 3439 cm−1 was the −OH stretching vibration of alcohol; 1094 cm−1 was the C−O bond stretching vibration of alcohols, esters and ethers [50]. The peak at 2971–2871 cm−1 was the C−H bond stretching vibration of methyl [51]. The peaks at 1637 and 778–692 cm−1 were C=C bond stretching vibrations and C−H bond deformation vibrations in the aromatic ring [52]. Coconut shell biochar has a stretching vibration of C≡C bond at 2346 cm−1, while other biochars do not have this characteristic peak [53].
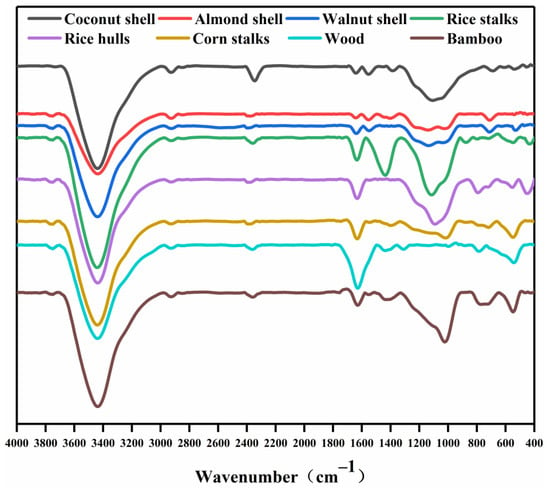
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of biochars.
The FTIR spectra indicating functional groups on the biochars were different before and after the adsorption of profenofos (Figure S5). After the adsorption of profenofos, the peak intensity of the C=C bond increased due to the aromatic structure in the biochar, which forms a π-π stacking structure with the benzene ring in profenofos [39]. The characteristic peak of the C=Br bond at wavenumber 534 cm−1 presented the adsorption of profenofos onto biochar. The intensity of the C-O bond peak was significantly weakened after the adsorption of profenofos, indicating that oxygen-containing functional groups interacted with profenofos during the adsorption process. The intensity of the C≡C bond peak of coconut shell biochar weakened after adsorption, indicating that the C≡C bond also played a role in the reaction.
3.4.2. Adsorption of Similarly Structured OPs onto Coconut Shell Biochar
A previous study showed that π-π interaction and hydrophobic interaction were the main mechanisms of adsorption. Therefore, the adsorption of methyl parathion, isocarbophos, 2-chloro-4-bromophenol (metabolin of profenofos) and malathion (without a benzene ring) by coconut shell biochar was investigated (Figure 4b). The initial concentrations of the five organic insecticides were 20 mg/L. The adsorption rates of coconut shell biochar for profenofos, methyl parathion, isocarbophos, 2-chloro-4-bromophenol and malathion were 88%, 85%, 73%, 73% and 24%, respectively. The results showed that the adsorption of OPs with a benzene ring by coconut shell biochar was significantly stronger than the OPs with a chain structure (no benzene ring). Therefore, it was demonstrated that π-π interaction dominated the adsorption of profenofos by coconut shell biochar.
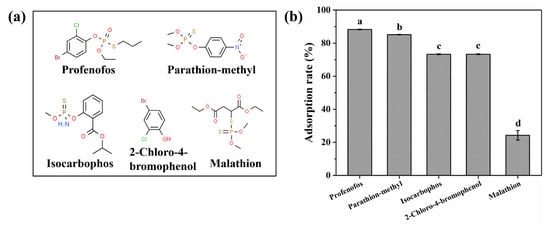
Figure 4.
(a) Structural formulae of five organic substances; (b) removal rate of adsorption of coconut shell biochar for five organic substances. Mean values with the same letter (a, b, c, d) are not significantly different from five organic substances (profenofos, methyl parathion, isocarbophos, 2-chloro-4-bromophenol and malathion) by LSD at the 5% level.
The octanol–water distribution coefficient (Kow) indicates the hydrophobicity of the adsorbed materials [39]. A larger Kow indicated a stronger hydrophobicity of the OPs. The log Kow values of profenofos, methyl parathion, isocarbophos and 2-chloro-4-bromophenol were 4.60, 2.78, 1.66 and 3.00, respectively. Pesticides with higher hydrophobicity have stronger hydrophobic interactions with biochar [54]. The 2-chloro-4-bromophenol was more hydrophobic than isocarbophos but its adsorption capacity was poorer than isocarbophos. The reason may be that isocarbophos has longer branched chains on the benzene ring, and chain entanglement occurs between pesticide molecules during adsorption, which enhances the binding effect of the pesticide molecules to biochar [55] (Figure 4a).
3.5. Adsorption Mechanism of Nutshell Biochars
The mechanism of adsorption of aromatic compounds by biochar mainly includes pore diffusion, electrostatic interaction, hydrophobic interaction, patting interaction, etc. [56]. The specific adsorption mechanism depends on the physicochemical characteristics of the biochar and the adsorbed material.
As discussed in Section 3.3.3, electrostatic interaction was excluded from this study. This is related to the self-property of profenofos, which always remains electrically neutral with a change in pH and, therefore, cannot interact electrostatically with biochar.
The BET and SEM tests revealed that compared with crop stalk biochars, nutshell biochars inherently had a larger specific surface area and a greater number of micropores. This is the main reason that the ability of nutshell biochars to adsorb profenofos was much higher than crop stalk biochars. The adsorption process of nutshell biochars was fitted by the model, and the results showed that the adsorption process of profenofos by nutshell biochars was consistent with the pseudo second-order kinetic model and the Freundlich isotherm model. It was demonstrated that profenofos was combined with nutshell biochars through pore diffusion and surface adsorption.
Elemental analysis revealed that nutshell biochars had higher aromaticity and hydrophobicity compared with crop stalk biochars and were positively correlated with adsorption capacity. The FTIR analysis and adsorption experiments on different aromatic insecticides proved that the binding mode of nutshell biochars to aromatic insecticides was mainly a π-π interaction, and nutshell biochars showed a strong adsorption ability towards compounds with a benzene ring structure. Comparing the Kow values of each aromatic insecticide showed that there was a hydrophobic interaction between the nutshell biochar and the compounds. The higher hydrophobicity of the compound, the higher the adsorption capacity of the biochar.
Therefore, the adsorption mechanisms of aromatic insecticides by nutshell biochars were mainly pore diffusion, π-π interaction and hydrophobic interaction (Figure 5).
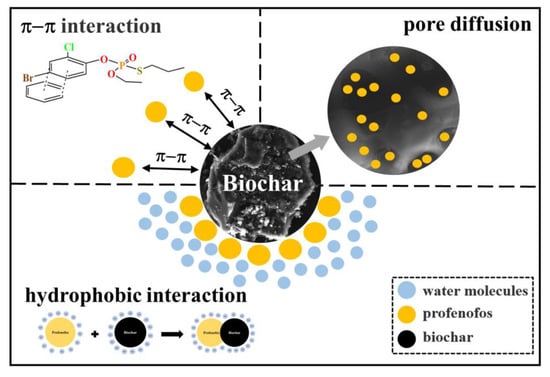
Figure 5.
Proposed adsorption mechanism of nutshell biochars.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we compared the adsorption of profenofos by different biochars. The results showed that nutshell biochars had strong adsorption specificity for profenofos and the other aromatic organophosphorus insecticides. The nutshell biochars showed excellent application prospects in removing organophosphorus insecticides from agricultural water environments. Nutshell biochars exhibited faster and stronger adsorption of profenofos than traditional crop stalk biochars and reported adsorbent materials. Nutshell biochars had a larger specific surface area, a higher number of micropores, higher hydrophobicity and a higher degree of aromaticity. Nutshell biochars showed stable adsorption capacity in different initial concentrations of profenofos (10–40 mg/L), temperatures (298–318 K) and pH (3–9). The adsorption process of profenofos by nutshell biochar was pore diffusion and surface adsorption, which is consistent with the pseudo second-order kinetic model and the Freundlich isotherm model. Thermodynamic analysis showed that the adsorption of profenofos by nutshell biochars was a spontaneous endothermic reaction. High temperatures can enhance the adsorption capacity of nutshell biochars for profenofos. π-π and hydrophobic interactions were the main binding form of nutshell biochars with profenofos. Hence, the high aromaticity and hydrophobicity of nutshell biochars make it equally excellent in adsorbing aromatic organophosphorus insecticides. Reuse experiments showed that nutshell biochars had a stable and strong adsorption capacity within 10 times of recycling. The stable and efficient adsorption capacity and excellent recycling times prove that nutshell biochars have a good application prospect in removing aromatic organophosphorus insecticide pollution from water.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy13020543/s1, Figure S1: N2 adsorption and desorption isothermal curve; Figure S2: Thermodynamic fitting diagram; Figure S3: Zeta potential of nutshell biochars before and after adsorption; Figure S4: Desorption of profenofos on nutshell biochars by acetonitrile; Figure S5: FTIR of biochars before and after adsorption of profenofos; Table S1: Reported materials for adsorption of organophosphorus pesticides [57,58,59,60]; Table S2: Thermodynamic fitting parameters.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.S.; methodology, X.M.; software, T.S.; validation, T.S.; formal analysis, G.Z.; investigation, G.Z.; resources, G.Z. and Z.C.; data curation, G.Z. and Z.C.; writing—original draft preparation, G.Z.; writing—review and editing, Q.X.L. and L.F.; visualization, G.Z.; supervision, R.H. and Q.X.L.; project administration, R.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31972314), the Key Scientific Research Projects of Universities in Anhui Province (KJ2021A0133), the High-level Talent Introduction Project of Anhui Agricultural University (rc522101), and the USDA (HAW05044R).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Kangping Cui and Fangyue Wang of Hefei University of Technology for their help in the characterization of eight kinds of biochars.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Alouw, J.; Wulandari, S. Present Status and Outlook of Coconut Development in Indonesia; IOP Publishing: Bogor, Indonesia, 2020; p. 012035. [Google Scholar]
- Massantini, R.; Frangipane, M.T. Progress in Almond Quality and Sensory Assessment: An Overview. Agriculture 2022, 12, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orooji, Y.; Han, N.; Nezafat, Z.; Shafiei, N.; Shen, Z.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Luque, R.; Bokhari, A.; Klemeš, J.J. Valorisation of nuts biowaste: Prospects in sustainable bio (nano) catalysts and environmental applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 347, 131220. [Google Scholar]
- Yuliusman Sipangkar, S.P.; Fatkhurrahman, M.; Farouq, F.A.; Putri, S.A. Utilization of Coconut Husk Waste in the Preparation of Activated Carbon by Using Chemical Activators of KOH and NaOH; AIP Publishing LLC: Bali, Indonesia, 2020; p. 060026. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Preparation, modification and environmental application of biochar: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 1002–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tang, L.; Hu, Y.; Geng, Y.; Meng, L.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Huo, Z. Investigating the pathways of enhanced Pb immobilization by chlorine-loaded biochar. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 344, 131097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Dilinuer, Y.; Pasang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, Z. Combination of biochar and phosphorus solubilizing bacteria to improve the stable form of toxic metal minerals and microbial abundance in Lead/Cadmium-contaminated soil. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, S.; Jegan, J.; Bhagavathi Pushpa, T.; Gokulan, R.; Bulgariu, L. Biochar for removal of dyes in contaminated water: An overview. Biochar 2022, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.K.; Goswami, M.; Mishra, R.K.; Chaturvedi, P.; Awashthi, M.K.; Singh, R.S.; Giri, B.S.; Pandey, A. Biochar for remediation of agrochemicals and synthetic organic dyes from environmental samples: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tang, L.; Wang, Z.; Su, M.; Tian, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z. Evaluating the protection of bacteria from extreme Cd (II) stress by P-enriched biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Tang, L.; Su, M.; Tian, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Hu, S. Enhanced Pb immobilization via the combination of biochar and phosphate solubilizing bacteria. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.; Sokołowska, Z.; Boguta, P. Biochar physicochemical properties: Pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2020, 19, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, X.; Li, Y.; Han, L. Effect of pyrolysis temperature and correlation analysis on the yield and physicochemical properties of crop residue biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 296, 122318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-Y.; Lin, P.-Y.; Hsieh, S.-L.; Kirankumar, R.; Patel, A.K.; Singhania, R.-R.; Dong, C.-D.; Chen, C.-W.; Hsieh, S. Engineered mesoporous biochar derived from rice husk for efficient removal of malachite green from wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, B. Influence of organic composition of biomass waste on biochar yield, calorific value, and specific surface area. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2018, 10, 013109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, C.S.; Cardoso, S.; Lourenço, A.; Ferreira, J.; Miranda, I.; Lourenço MJ, V.; Pereira, H. Characterization of walnut, almond, and pine nut shells regarding chemical composition and extract composition. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2020, 10, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Han, Y.; Wang, G.; Deng, P.; Feng, L. Walnut shell biochar based sorptive remediation of estrogens polluted simulated wastewater: Characterization, adsorption mechanism and degradation by persistent free radicals. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazycki, M.A.; Godinho, M.; Perondi, D.; Foletto, E.L.; Collazzo, G.C.; Dotto, G.L. New biochar from pecan nutshells as an alternative adsorbent for removing reactive red 141 from aqueous solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Tan, P.; Wang, R.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z. Advances in organophosphorus pesticides pollution: Current status and challenges in ecotoxicological, sustainable agriculture, and degradation strategies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127494. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, P.; Lu, S.; Liu, X.; Zhai, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Wan, Z. Occurrence and risk evaluation of organophosphorus pesticides in typical water bodies of Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhu, L. Organophosphorus pesticides in greenhouse and open-field soils across China: Distribution characteristic, polluted pathway and health risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Shi, Q.; Xu, L.; Shi, T.; Wu, X.; Li, Q.X.; Hua, R. Enantioselective Uptake Determines Degradation Selectivity of Chiral Profenofos in Cupriavidus nantongensis X1T. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 6493–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Yang, F. Integrated gender-related effects of profenofos and paclobutrazol on neurotransmitters in mouse. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushwaha, M.; Verma, S.; Chatterjee, S. Profenofos, an Acetylcholinesterase-Inhibiting Organophosphorus Pesticide: A Short Review of Its Usage, Toxicity, and Biodegradation. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 1478–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboob, S.; Niazi, F.; Alghanim, K.; Sultana, S.; Al-Misned, F.; Ahmed, Z. Health risks associated with pesticide residues in water, sediments and the muscle tissues of Catla catla at Head Balloki on the River Ravi. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, Z.; Khan, M.; Mostakim, G.M.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Rahman, M.; Shahjahan, M.; Islam, M.S. Studying the effects of profenofos, an endocrine disruptor, on organogenesis of zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 20659–20667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, T.; Hammad, A.A.; Elmarsafy, A.M.; Halawa, E.; Soliman, M. Degradation of some organophosphorus pesticides in aqueous solution by gamma irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouriieh, N.; Sohrabi, M.; Khosravi, M. Adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics of organophosphorus profenofos pesticide onto Fe/Ni bimetallic nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zhang, N.; Xing, C.; Cui, Q.; Sun, Q. The adsorption, regeneration and engineering applications of biochar for removal organic pollutants: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 223, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharum, N.A.; Nasir, H.M.; Ishak, M.Y.; Isa, N.M.; Hassan, M.A.; Aris, A.Z. Highly efficient removal of diazinon pesticide from aqueous solutions by using coconut shell-modified biochar. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 6106–6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchimiya, M.; Wartelle, L.H.; Boddu, V.M. Sorption of triazine and organophosphorus pesticides on soil and biochar. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2989–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, G.; Luo, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Characteristics and mechanisms of chlorpyrifos and chlorpyrifos-methyl adsorption onto biochars: Influence of deashing and low molecular weight organic acid (LMWOA) aging and co-existence. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Fang, L.; Qin, H.; Wu, X.; Li, Q.X.; Hua, R. Minute-speed biodegradation of Organophosphorus insecticides by Cupriavidus nantongensis X1T. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13558–13567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Park, J.; Lim, K.H.; Park, S.; Heo, J.; Her, N.; Oh, J.; Yun, S.; Yoon, Y. Adsorption of selected endocrine disrupting compounds and pharmaceuticals on activated biochars. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somsesta, N.; Sricharoenchaikul, V.; Aht-Ong, D. Adsorption removal of methylene blue onto activated carbon/cellulose biocomposite films: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 240, 122221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, S.; Mao, W.; Bai, Y.; Chiang, K.; Shah, K.; Paz-Ferreiro, J. Novel Bi2WO6 loaded N-biochar composites with enhanced photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B and Cr (VI). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, P.T.; Jitae, K.; Al Tahtamouni, T.; Tri, N.L.M.; Kim, H.-H.; Cho, K.H.; Lee, C. Novel activation of peroxymonosulfate by biochar derived from rice husk toward oxidation of organic contaminants in wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Song, S.; Chen, Z.; Hu, B.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Biochar-based materials and their applications in removal of organic contaminants from wastewater: State-of-the-art review. Biochar 2019, 1, 45–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Mcnamara, P.J.; Mayer, B.K. Adsorption of organic micropollutants onto biochar: A review of relevant kinetics, mechanisms and equilibrium. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, X.; Yu, B.; Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Dong, F.; Zheng, Y. Characterization of peanut-shell biochar and the mechanisms underlying its sorption for atrazine and nicosulfuron in aqueous solution. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, M.; Kumar, R.; Neogi, S. Activated biochar derived from Opuntia ficus-indica for the efficient adsorption of malachite green dye, Cu2+ and Ni2+ from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, M.J.B.; Silva, T.H.A.; Ribeiro, T.R.S.; Da Silva, A.O.S.; Pedrosa, A.M.G. Thermal and catalytic pyrolysis of polyvinyl chloride using micro/mesoporous ZSM-35/MCM-41 catalysts. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 140, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, S.; Taheri, E.; Amin, M.M.; Fatehizadeh, A.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Adsorption of 4-chlorophenol by magnetized activated carbon from pomegranate husk using dual stage chemical activation. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 128623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Ren, D.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Gong, X. Adsorption behavior of 2, 4-DCP by rice straw biochar modified with CTAB. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 3797–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J. Biochars prepared from rabbit manure for the adsorption of rhodamine B and Congo red: Characterisation, kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic studies. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Q.; Bi, E.; Li, B. Roles of polar groups and aromatic structures of biochar in 1-methyl-3-octylimidazolium chloride ionic liquid adsorption: pH effect and thermodynamics study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 22265–22274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Tomul, F.; Ha, N.T.H.; Nguyen, D.T.; Lima, E.C.; Le, G.T.; Chang, C.-T.; Masindi, V.; Woo, S.H. Innovative spherical biochar for pharmaceutical removal from water: Insight into adsorption mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewage, N.B.; Liyanage, A.S.; Pittman, C.U., Jr.; Mohan, D.; Mlsna, T. Fast nitrate and fluoride adsorption and magnetic separation from water on α-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 dispersed on Douglas fir biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 165–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Li, L.; Huang, X.; Zheng, S.; Xu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, H.; Xu, D. Adsorption and removal of organophosphorus pesticides from environmental water and soil samples by using magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes@ organic framework ZIF-8. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 10772–10783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Marrakchi, F.; Yuan, C.; Cheng, X.; Jiang, D.; Zafar, F.F.; Fu, Y.; Wang, S. Adsorption modeling, thermodynamics, and DFT simulation of tetracycline onto mesoporous and high-surface-area NaOH-activated macroalgae carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.S.; Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Abu-Dieyeh, M.; Mckay, G. Novel bioadsorbents based on date pits for organophosphorus pesticide remediation from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, M.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Tarelho, L.A.; Hellemans, R.; Cuypers, J.; Capela, I.; Costa, M.E.V.; Dewil, R.; Appels, L. Acclimatized activated sludge for enhanced phenolic wastewater treatment using pinewood biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 131708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipinas, J.Q.; Rivera, K.K.P.; Ong, D.C.; Pingul-Ong, S.M.B.; Abarca, R.R.M.; De Luna, M.D.G. Removal of sodium diclofenac from aqueous solutions by rice hull biochar. Biochar 2021, 3, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguyal, F.; Sarmah, A.K. Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole by magnetic biochar: Effects of pH, ionic strength, natural organic matter and 17α-ethinylestradiol. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zheng, J.W.; Yang, Q.; Dang, Z.; Zhang, L.J. Effect of carbon chain structure on the phthalic acid esters (PAEs) adsorption mechanism by mesoporous cellulose biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Xi, F.; Tan, W.; Meng, X.; Hu, B.; Wang, X. Review of organic and inorganic pollutants removal by biochar and biochar-based composites. Biochar 2021, 3, 255–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, I.; Kumarathilaka, P.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; Abduljabbar, A.; Ahmad, M.; Usman, A.R.; Vithanage, M. Mechanistic modeling of glyphosate interaction with rice husk derived engineered biochar. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2016, 225, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, A.; Malik, J.; Kakkar, R. Mesoporous rGO@ ZnO composite: Facile synthesis and excellent water treatment performance by pesticide adsorption and catalytic oxidative dye degradation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 160, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadeen, H.M.; Elkhatib, E.A.; Badawy, M.E.; Abdelgaleil, S.A. Green low cost nanomaterial produced from Moringa oleifera seed waste for enhanced removal of chlorpyrifos from wastewater: Mechanism and sorption studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.A.; Shah, A.V.; Jadav, P.Y. Extractive efficacy of microwave synthesized zeolitic material for acephate: Equilibrium and kinetics. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2013, 78, 1055–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).