Abstract
The use of biochar as a soil amendment has substantial potential to enhance soil quality and carbon sequestration. However, the responses to the addition of biochar based on soil microbial residues are not well understood, particularly at the aggregate level. Herein, a two-year field experiment investigated the characteristics of distribution of microbial residues in calcareous fluvo-aquic soil aggregates (SA) in Henan Province, China. Four treatments were established as follows: no fertilizer (CK), chemical fertilizer (NPK), biochar (BC), and biochar combined with chemical fertilizer (NPK + BC). The results showed that the effects of particle size substantially impacted the microbial residues with 2–0.25 mm SA having the largest contents of amino sugars and microbial residual carbon (MRC), followed by >2 mm SA. Compared with the CK, the NPK treatment markedly enhanced the levels of glucosamine (GluN), galactosamine (GalN), muramic acid (MurA), total amino sugar (TAS), and MRC in the 2–0.25 mm SA by 26.69%, 24.0%, 23.62%, 25.11%, and 24.82%, respectively. The NPK + BC treatment significantly increased the contents of GluN, GalN, TAS, and MRC in the bulk soil and 0.25–0.053 mm SA compared with the NPK treatment. Bacterial biomass and the activity of N-acetyl-glucosaminidase in the bulk soil and SA markedly and positively affected the content of carbon in the amino sugars and microbial residues. Overall, the 2–0.25 mm SA were microenvironments with the largest accumulation of soil microbial residues, and the combined application of NPK + BC was more effective at increasing the accumulation of microbial residues in the SA, which provides an ideal fertilization strategy to improve the soil microenvironment and enhance soil quality.
1. Introduction
Soil aggregates (SA) are the fundamental units of soil composition that are formed through the cementation of soil mineral particles and organic complexes, and the levels and distribution impact soil quality [1,2]. Soil microbial residues, which are formed by cellular residues that accumulate in the soil over time after the death of living microorganisms, are the major origin of carbon for the stable carbon pool, and the rate of contribution of the stable soil organic matter (SOM) is approximately 50% [3,4]. The SA structure is closely related to the aggregation and decomposition processes of microbial residues in the soil [5,6]. A study has shown that microbial residues have a positive effect on the formation and stabilization of SA [7], and they may have a longer lasting effect on SA than living microorganisms [8,9]. Moreover, the accumulation of soil microbial residues depends primarily on the degree of physical protection of the shape of SA [8,10].
As unique components of the microbial cell wall, amino sugars can be chronically maintained in the environment even after the death of microorganisms as described by Joergensen [11] and can be used as important markers for microbial residues [12] and to measure the accumulation of MRC in the soil [5]. There are currently up to 26 amino sugars recognized in soil microorganisms. However, most studies have only quantified glucosamine (GluN), galactosamine (GalN), muramic acid (MurA), and mannosamine as described by Joergensen [11]. A study has shown that GluN (primarily of fungal origin) was more likely to be enriched in the large particle sizes of SA, while MurA (exclusively of bacterial origin) was more likely to be enriched in the small particle sizes of SA [10]. However, Angst et al. [3] synthesized the results of 14 studies on amino sugars from agricultural soil and found that both macroSA (macroaggregates) and microSA (microaggregates) had a higher content of carbon from fungal residues compared with silt-clay, but it was difficult to assess whether the bacterial or fungal residues dominated between macroSA and microSA. The distribution of SA-based amino sugars in different particle sizes appeared to depend on the ecosystem properties.
Numerous studies have confirmed that the application of organic materials facilitates the production and accumulation of soil microbial residues [1,13,14]. Luan et al. [13] suggested that organic materials combined with chemical fertilizers not only increased the living microbial biomass and microbial residues content within the SA, but microbial residues also promoted the accumulation of organic carbon in SA compared with chemical fertilizer treatment. Ding et al. [7] proposed that high applications of manure (15 and 22.5 Mg ha−1 yr−1) remarkably promoted the accumulation of total amino sugars (TAS) in 0.25–0.053 mm and 0.25 mm SA and augmented the contribution of microbial residues to organic carbon in the 0.25–0.053 mm and 2–0.25 mm SA. However, they had no impact on the content of amino sugars in silt-clay. In addition, the response of amino sugars of fungal or bacterial origin to manure application differed in the SA with varying particle sizes, and the increase in GluN in the > 0.25 mm SA was greater than that in the <0.25 mm SA, while the increase in MurA in the > 0.25 mm SA was similar to that in the 0.25–0.053 mm SA [7]. Most of these studies concentrated on the influences of application of organic material or organic fertilizer on microbial residues in the bulk soil or SA, but there are few studies on how biochar (BC) affects soil microbial residues after being applied to the soil, particularly at the aggregate level.
Owing to its unique properties, BC can augment the content of soil organic carbon (SOC) and enhance the ability of soil to hold water and retain nutrients, as well as improving microbial activity after application to the soil [15,16,17]. BC and soil particles can form SA and organic–inorganic complexes, which facilitate the formation and stabilization of SA [18,19]. The SOC content in SA with different particle sizes is intimately related to the soil quantity of BC [20]. Therefore, BC is considered to be a new tactic to enhance soil quality and improve the soil microhabitat environment, which is widely used in agroecosystems [21]. The calcareous fluvo-aquic soil on the North China Plain is deficient in nutrients and has a relatively low content of SOM. The long-term excessive use of fertilizer has led to soil crusting and nutrient imbalances, which reduces the ability to produce crops [22]. There is an urgent need to explore reasonable and efficient fertilization measures to improve the quality and health of soil in this region.
This study hypothesized that the combined applications of BC and NPK could more significantly increase the accumulation of microbial residues in SA than the single application of BC or NPK and that microbial residues in the soil were influenced by particle size effects. Therefore, the objectives of this study were to (1) investigate the distribution characteristics of amino sugars and MRC in fluvo-aquic SA for the BC and NPK application and (2) identify the dominant factors that drive changes in amino sugar and MRC in soil aggregates after different fertilization treatments. Our results could provide a scientific fertilization strategy to improve the soil microenvironment and enhance soil quality.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil and Biochar
A long-term field experiment was located at the Modern Agricultural Research Base in Henan, China (35°0′ N and 113°43′ E). The mean yearly precipitation is 542.15 mm; the duration of sunshine is approximately 1870 h; the average temperature is 15.60 °C, and the frost-free duration lasts for 209 d. The soil type is a calcareous fluvo-aquic soil, and according to the world reference base for soil resources (WRB) classification standards, the fluvo-aquic soils belong to cambisols [23,24]. The basic soil physicochemical characteristics were as follows: bulk density 1.18 g cm−3, pH 8.14, SOC 3.56 g kg−1, total N 0.44 g kg−1, and available phosphorus and potassium 4.14 and 91.16 mg kg−1, respectively. The planting method was a rotation of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum) and summer maize (Zea mays). After the end of the experiment, the physicochemical characteristics of bulk soil in differ-ent treatments were shown in Table S1. Henan Sanli New Energy Co., Ltd. (Xinxiang, Henan, China) was used to produce peanut shell biochar as described by Zhang et al. [1]. The physicochemical characteristics of the biochar were as follows: pH 9.16, surface area 5.10 m2 g–1, total carbon 71.70%, total nitrogen (TN) 1.51%, total phosphorus 0.18%, total potassium 0.54%, hydrogen 2.61%, and oxygen 12.49%.
2.2. Experimental Design
The field trial started in the 2017 wheat season with a randomized complete block design that involved four treatments and three replicates. The plot sizes were a rectangle of 4 square meters. The treatments selected for this study were as follows: CK, NPK, BC, and NPK + BC. Before starting the experiment, the biochar was passed through 0.154 mm sieves. The biochar was spread evenly on the soil surface and then mixed with the topsoil (0–20 cm) using a rotary tiller. Biochar was applied at 22.5 t ha−1 only once before the wheat was sown in 2017. The fertilizers that were provided for the wheat were nitrogen (N) 165 kg ha−1, P2O5 82.5 kg ha−1, and K2O 82.5 kg ha−1. The N ratio of basic fertilization to the wheat season topdressing was 1:1 in the N fertilizer. The base fertilizers were N and phosphorus (P), which were applied in a single application. The N fertilizer applied to the maize was provided at 225 kg ha−1 in such a manner that the ratio of the part applied as basal fertilizer to the part applied as topdressing in the bell-mouthed period was 7:3. The application of P and K fertilizers was consistent with those used in the wheat season. Urea (N 46%), calcium superphosphate (P2O5 12%), and K chloride (K2O 60%) were utilized as N, P, and potassium (K) fertilizers in the field experiment, respectively.
2.3. Soil Sample Harvesting and Aggregate Classification
Soil samples were taken from each plot after the maize harvest in September 2019. The soil aggregate samples were collected from the bulk soil by randomly determining two points in each plot. A flat soil profile was dug with a shovel to construct an outwardly protruding soil column (length × width × height: 18 cm × 8 cm × 12 cm, the same size as that of a rigid plastic box) on the profile. The soil column was then carefully slid into a rigid plastic box. The two-point soil samples taken from the respective plots were mixed, and large pieces of soil were then separated along the fissures of the soil blocks themselves and passed through a 10 mm sieve.
The SA of varying particle sizes were sorted by wet sieving of the fresh soil as follows: a certain amount of sieved fresh soil (equivalent to 100 g of dry soil) was weighed and evenly coated on the top layer of the sieve nest. It was prewetted in water for 5 min. After that, the sieve nest was moved up and down at a constant speed within a range of 3 cm, and the movement was repeated 50 times during a period of 2 min. After sieving, aggregate samples with different particle sizes were obtained: >2 mm SA (MacroSA), 2–0.25 mm SA (small MacroSA), 0.25–0.053 mm SA (MicroSA), and <0.053 mm silt-clay obtained by static settling and centrifugation of the solution [25,26]. The SA of the respective levels of particle sizes were collected in weighed aluminum boxes and followed by drying at 60 °C. They were then weighed and documented to calculate the distribution and mean weight diameter (MWD) of the SA, as well as the contents of TN and total organic carbon (TOC) of the SA. Sufficient soil agglomerates were repeatedly sieved and collected for testing. Some of the fresh samples were retained at 4 °C to determine the amounts of soil microbial carbon (MBC) and nitrogen (MBN) and the extracellular enzymatic activity, while others were freeze-dried before storage at –20 °C to determine the soil phospholipid fatty acids and amino sugars, among others.
2.4. Soil C- and N-Related Properties and Amino Sugar Extraction
The TOC within soil was determined by the potassium dichromate oxidation method as described by Juliana [27]. The content of TN in the soil was measured by the potassium dichromate oxidation method as previously described [28]. The amino sugars were extracted as described by Indorf et al. [29]. A volume of 10 mL of 6 mol L−1 HCl was introduced into 200 mg of dry soil. The samples were hydrolyzed at 105 °C for 8 h, and the soil slurry was filtered and centrifuged for 5 min at 12,000 rpm. The supernatant was freeze-dried, and the residue was washed with 3 mL of methanol to wash out the soil amino sugars. The amino sugars were converted into aldehyde nitrile derivatives using derivatization reagents and then extracted from the aqueous solution with dichloromethane. The three types of amino sugars standards utilized were GluN, GalN, and MurA at 10 mg mL−1. The chromatographic column was selected from an analytical column (3 × 150 mm) and a Dionex CarboPac PA20 guard column (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) (3 × 30 mm). The temperature of the column was set to 30 °C. After the preheating of the equipment was completed, ortho-phthaldialdehyde was added to the sample vial, and after 120 s of reaction, 15 μL of indole derivative was injected to derivatize the sample. The vial was then placed into the autosampler for measurement with a volume of 5 µL per injection. Three mobile phases were used, including H2O, 15 mmol L−1 NaOH, and 15 mmol L−1 NaOH and 100 mmol L−1 NaOAc. The mobile phase was delivered at a flow rate of 0.3 mL min−1 to separate the aminose, which was finally determined using an electrochemical detector. The concentrations of GalN, GluN, and MurA in the bulk soil, as well as in each particle size aggregate sample, were calculated and expressed in mg kg−1.
2.5. Data and Statistical Analysis
The experimental data were organized and plotted in Excel 2019 (Microsoft, Redmond, Washington, USA), and regression analyses were conducted using SPSS 24.0 (IBM, Inc., Armonk, New York, USA). A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was utilized to compare the significant differences between treatments and SA particle sizes, and a two-way ANOVA was used to investigate the fertilization outcomes and SA particle size effects on alterations within the microbial community composition (MCC). Stepwise regression analysis methods were utilized to analyze associations between the microbial residue, C and N, MBC and MBN, extracellular enzymatic activity, and MCC.
The mass percentages of individual particle size water-stable aggregates were calculated as follows:
where represents the i-size SA mass percentage (%), represents the weight of i-size SA (g), and refers to the sum of SA weights (g).
The mean weight diameter (MWD) of SA and the content of SA with particle size > 0.25 mm (R0.25) were determined as shown below:
where represents the mean diameter of SA in any particle size range sieved out, refers to the percentage (%) of the SA corresponding to in the total SA, and represents the SA weight with a particle size larger than 0.25 mm (g). represents the sum of SA weights (g).
The following equations were used to calculate the contents of amino sugar carbon (TAS-C) and amino sugar nitrogen (TAS-N):
where constant 6 is the atomic weight of C in GluN, and the 12, 14, and 179 constants are the atomic weights of C and N and the molecular weight of GluN (C6H13NO5), respectively. Similarly, the C and N amounts of GalN (C6H13NO5) and MurA (C9H17NO7) were calculated. The contents of TAS-C and TAS-N were the sum of individual amino sugar C (GluN-C, GalN-C, MurA-C) and N (GluN-N, GalN-N, MurA-N) contents, respectively [30].
Glucosamine carbon (GluN-C) = GluN content × (12 × 6)/179
Glucosamine nitrogen (GluN-N) = GluN content × 14/179
The following equations were utilized to calculate the content of carbon (C) in the microbial sources (fungi and bacteria):
where 179.2 and 251 represent the GluN and MurA molecular weights, respectively; 9 is the fungal GluN to carbon conversion factor; and MRC is the sum of the fungal and bacterial residual C [31,32,33].
Fungal residue carbon (FRC) = (GluN/179.2 − 2 × MurA/251) × 179.2 × 9/1000
Bacterial residue carbon (BRC) = MurA × 45/1000
3. Results
3.1. Amino Sugar Content in Bulk Soil and SA
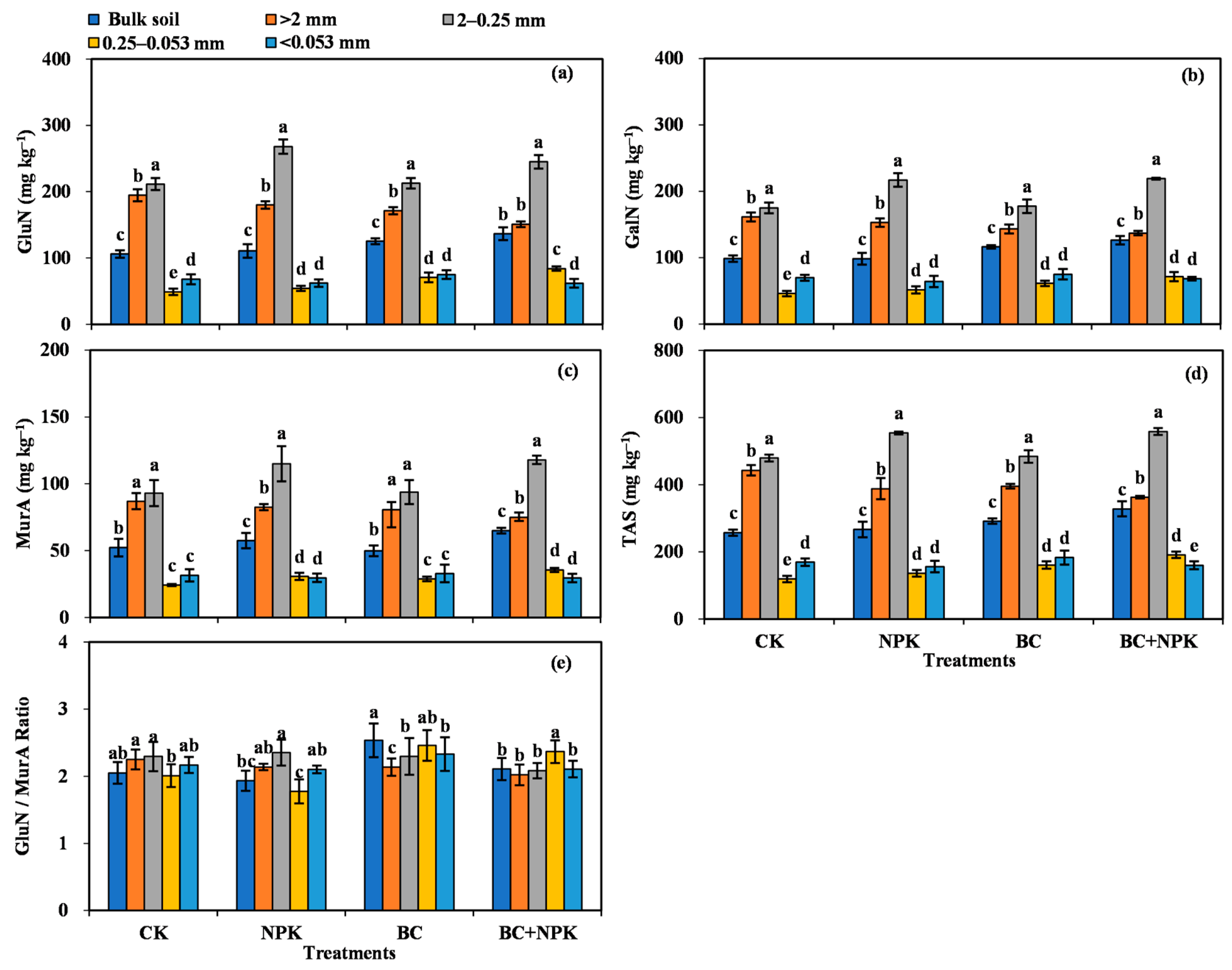
The results of a two-way ANOVA revealed that fertilization had no significant effect on the contents of GluN, GalN, MurA, and TAS, whereas the aggregate particle size and the interaction between fertilization and particle size substantially influenced the contents of individual amino sugars and TAS (p < 0.05, Table 1). Fertilization and particle sizes, as well as their interaction, had no significant effect on the GluN/MurA ratio.

Table 1.
Two-way ANOVA for soil amino sugars and microbial residue carbon among four aggregate size fractions under four treatments (n = 48).
The contents of amino sugars varied significantly among the SA (p < 0.05) and showed the same pattern of distribution, i.e., their contents were highest in the 2–0.25 mm SA, followed by the >2 mm and 0.25–0.053 mm SA, and <0.053 mm silt-clay (Figure 1). The fertilizer treatments significantly influenced the contents of amino sugar in the bulk soil and SA. Compared with the CK, the NPK treatment clearly improved the levels of individual amino sugars by 23.62–26.69% in the 2–0.25 mm SA and substantially enhanced the content of MurA in the 0.25–0.053 mm SA by 26.20% (p < 0.05). However, there was no apparent influence on the content of amino sugars in the bulk soil and other particle sizes of SA (Figure 1a–d). Compared with the CK, the BC treatment significantly increased the contents of GluN, GalN, and TAS in the 0.25–0.053 mm SA (18.24–44.54%) and markedly increased the content of GluN and the GluN/MurA ratio in the bulk soil (p < 0.05) (Figure 1a,b,d,e). In addition, compared with the CK, the NPK + BC treatment markedly enhanced the levels of individual amino sugars and TAS in the bulk soil and the 0.25–0.053 mm SA by 24.33–28.97% and 46.37–71.93%, respectively. The NPK + BC treatment markedly enhanced the levels of GluN, GalN, and TAS in the bulk soil by 22.97–28.32% and the levels of individual amino sugars (GluN, GalN, MurA, and TAS) in the 0.25–0.053 mm SA by 15.98–55.27% compared with NPK. Compared with the BC, the NPK + BC markedly enhanced the levels of MurA in the bulk soil by 30.41% and the contents of GluN, MurA, and TAS in the 0.25–0.053 mm SA by 18.95–23.80% (Figure 1a–d).
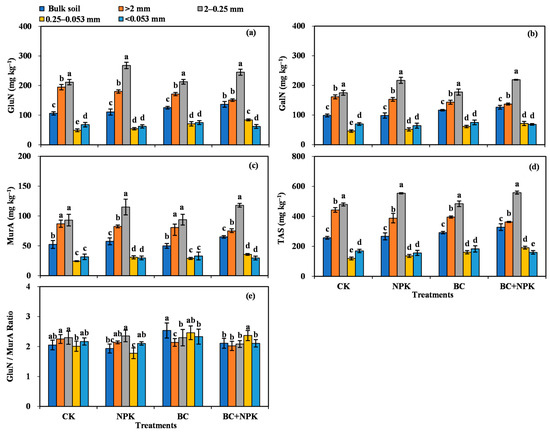
Figure 1.
Contents of amino sugars in bulk soil and aggregates among different treatments (a–e). Diverse lowercase letters denote significant differences (p < 0.05) among different particle sizes of bulk soil and every fraction. Abbreviations: GluN, glucosamine; GalN, galactosamine; MurA, muramic acid; TAS, total amino sugars.
3.2. Content of MRC in Bulk Soil and SA
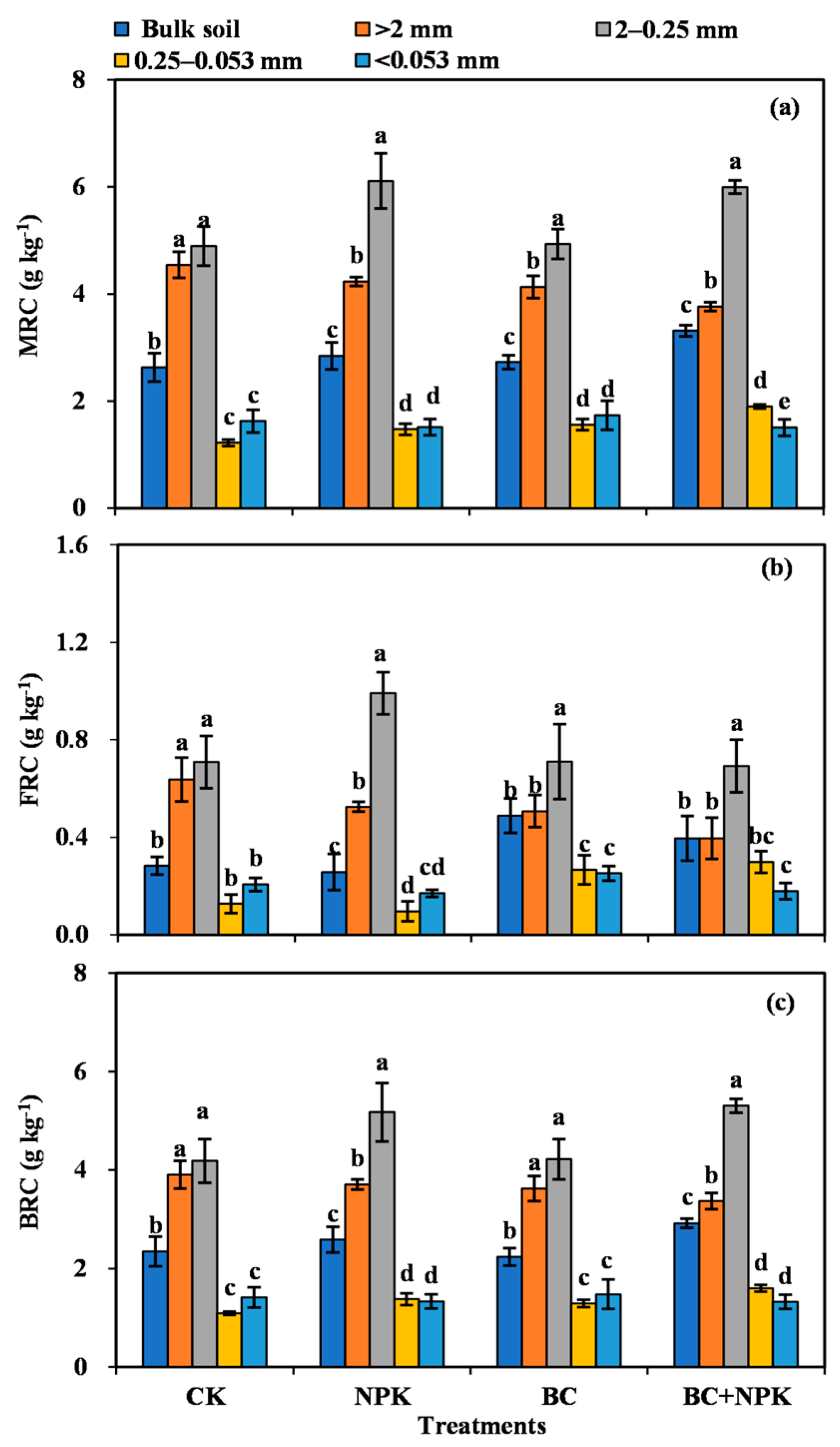
The results of two-way ANOVA showed that the contents of FRC, BRC, and MRC were affected by the aggregate particle size (p < 0.05), but they were not markedly influenced by the fertilization effect. Moreover, the interaction of fertilization and particle size significantly affected the BRC and MRC (p < 0.05, Table 1).
The contents of FRC, BRC, and MRC varied notably among the SA (p < 0.05) and showed the same regularity of distribution, i.e., they were the highest in the 2–0.25 mm SA, followed by the >2 mm and 0.25–0.053 mm SA, and then by the <0.053 mm silt-clay (Figure 2). The fertilization treatments also substantially influenced the content of MRC in the bulk soil and individual particle size aggregates. Compared with the CK, the NPK treatment significantly increased the content of MRC in the 2–0.25 mm SA by 24.82% (Figure 2a). The BC treatment significantly increased the levels of FRC in the bulk soil by 72.67% and markedly enhanced the contents of FRC (+109.0%) and MRC content (+27.71%) in the 0.25–0.053 mm SA (Figure 2a,b). Compared with the CK, the NPK + BC treatment significantly increased the contents of MRC and BRC in the bulk soil and 2–0.25 mm SA by 22.51–26.72% and significantly increased the contents of FRC, BRC, and MRC in the 0.25–0.053 mm SA by 134.56%, 46.37%, and 55.58%, respectively. Compared with the NPK treatment, that of NPK + BC markedly enhanced the levels of MRC in the bulk soil by 16.58% and substantially augmented the contents of FRC and MRC in the 0.25–0.053 mm SA by 222.25% and 28.97%, respectively. Compared with the BC treatment, the NPK + BC treatment significantly increased the contents of BRC and MRC in the bulk soil and the 2–0.25 mm SA by 21.57–30.41% and the content of MRC in the 0.25–0.053 mm SA by 21.82% (Figure 2a–c).
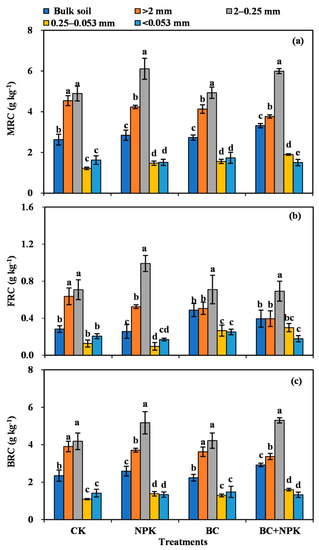
Figure 2.
Contents of microbial residue carbon, fungal residue carbon, and bacterial residue carbon in bulk soil and aggregates among different treatments (a–c). Error bars are the SD of mean from three duplicates. Diverse lowercase letters denote significant differences (p < 0.05) among different particle sizes. Abbreviations: MRC, microbial residue carbon; FRC, fungal residue carbon; BRC, bacterial residue carbon.
3.3. TAS-C and TAS-N Contents and Contribution to TOC and TN
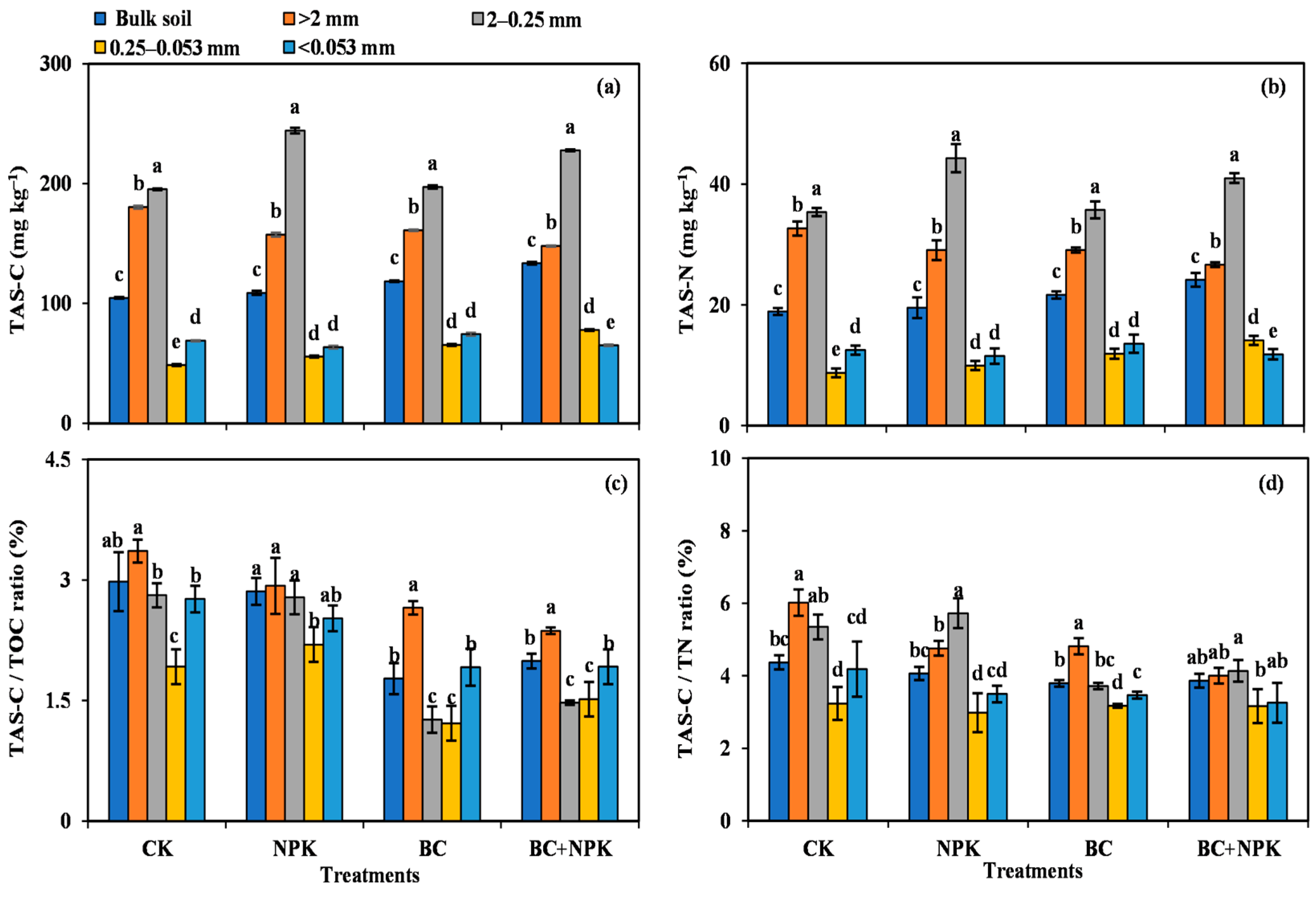
Figure 3a,b depict the contents of TAS-C and TAS-N in the bulk soil and SA compared with the CK and NPK treatments. The NPK + BC treatment significantly increased the contents of TAS-C and TAS-N within the bulk soil, and the BC-amended treatments significantly increased the contents of TAS-C and TAS-N in the 0.25–0.053 mm SA. Compared with the CK and BC treatments, that of NPK remarkably increased the contents of TAS-C and TAS-N in the 2–0.25 mm SA. However, in the > 2 mm SA, the treatments amended with BC significantly reduced the contents of TAS-C and TAS-N compared with the CK.
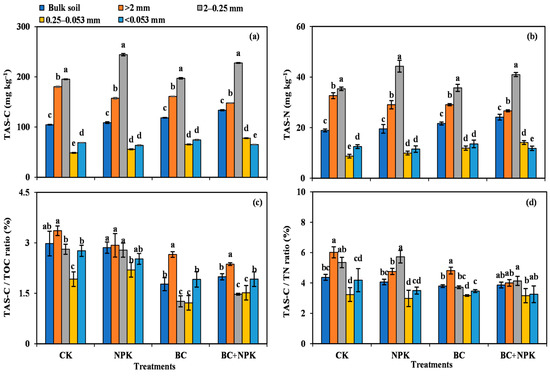
Figure 3.
Amino sugar carbon and nitrogen contents in the bulk soil and aggregates among different treatments (a,b) and contribution of amino sugars to soil total organic carbon and total nitrogen (c,d). Error bars are the SD of mean from three duplicates. Diverse lowercase letters denote significant differences (p < 0.05) among different particle sizes. Abbreviations: TAS-C and TAS-N, contents of amino sugar carbon and nitrogen.
The ratio of TAS-C to TOC (TAS-C/TOC) and the that of TAS-N to total nitrogen (TAS-N/TN) characterized the share of amino sugars to the soil TOC and TN. As shown in Figure 3c, the treatments with biochar (BC and NPK + BC) significantly reduced the TAS-C/TOC ratio in the bulk soil and individual particle size aggregates compared with the treatments without biochar (CK and NPK). The TAS-C/TOC ratio in the 0.25–0.053 mm SA markedly increased in the NPK compared with the CK treatment and in the NPK + BC treatment compared with that of the BC (p < 0.05). The treatments with biochar (BC and NPK + BC) significantly reduced the TAS-N/TN ratio in the 2–0.25 mm SA compared with the treatments that lacked biochar (CK and NPK), while the TAS-N/TN ratios in the bulk soil and the 0.25–0.053 mm and <0.053 mm SA were not markedly different among the various treatments (Figure 3d).
3.4. Ratios of FRC, BRC, and MRC to TOC
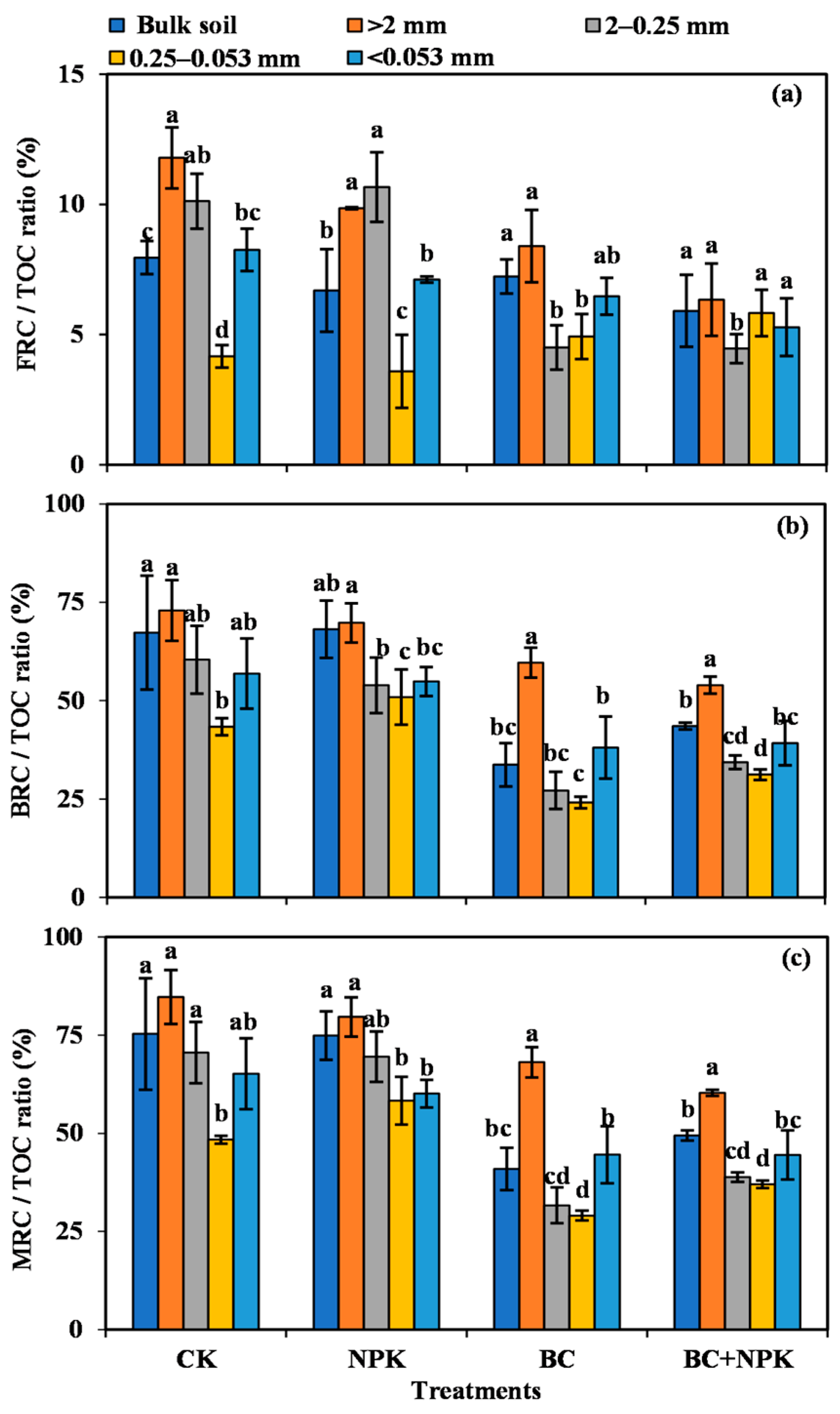
The ratios of FRC, BRC, and MRC to TOC in the bulk soil and each particle size aggregate are shown in Figure 4a–c, respectively. The MRC/TOC values in SA with different particle sizes were 48.37–89.24% under the treatments without biochar (CK and NPK), while they were 29.04–68.07% under the treatments with biochar (BC and NPK + BC). The treatments with biochar (BC and NPK + BC) significantly reduced the ratios of MRC/TOC and BRC/TOC in the bulk soil, and each particle size aggregate compared with the CK and markedly reduced the ratios of MRC/TOC and BRC/TOC in the bulk soil, and >0.053 mm SA compared with the NPK treatment (p < 0.05). Moreover, treatment with BC drastically reduced the FRC/TOC ratio in the 2–0.25 mm SA compared with the CK and NPK treatments, and the NPK + BC treatment appreciably reduced the FRC/TOC ratio in SA of various particle sizes compared with the CK and significantly decreased the FRC/TOC ratio in the 2–0.25 mm SA compared with the NPK treatment (p < 0.05). In contrast, the FRC/TOC ratios were not markedly different in the bulk soil and the 0.25–0.053 mm SA (p > 0.05).
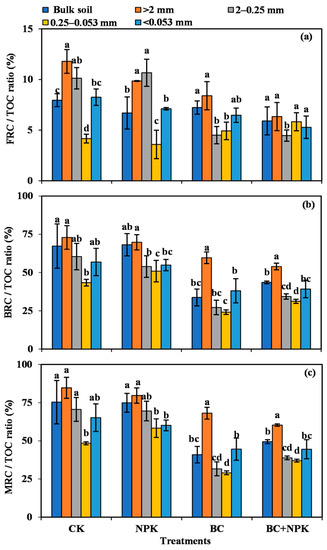
Figure 4.
Contribution of microbial residue carbon to total organic carbon in bulk soil and aggregates among different treatments (a–c). Error bars are the SD of mean from three duplicates. Diverse lowercase letters denote significant differences (p < 0.05) among different particle sizes.
3.5. Association between Microbial Residues and Soil Properties
This experiment explored the correlation of microbial residues in the bulk soil with SA stability and the contents of C and N and MBC and MBN. A Pearson correlation analysis indicated that the MWD of SA clearly and actively correlated with the content of each amino sugar, FRC, and MRC. The TOC and TN were significantly and directly associated with the GluN, GalN, TAS, and FRC, while the C/N ratio was only markedly and directly associated with the FRC. The MBC was markedly and directly associated with the GluN, GalN, TAS, and MRC, while the MBN was markedly and directly associated with the GluN, MurA, TAS, BRC, and MRC (Table 2).

Table 2.
Pearson correlations between the microbial residues and aggregate stability.
Stepwise regression analyses were utilized to assess the correlation of microbial residue indices in the bulk soil and each particle size aggregated with C, N, enzyme activities, and the MCC (Table 3). The results showed that the GluN, GalN, MurA, TAS, BRC, and MRC were all positively influenced by bacterial biomass and acetyl-glucosidase activity and were negatively influenced by β-xylosidase activity. In addition, GluN and GalN were also positively affected by the total content of N and were negatively affected by the TOC; the FRC was positively influenced by the actinomycete biomass and N-acetyl-glucosaminidase activity and negatively influenced by the fungal biomass and urease activity (Table 3).

Table 3.
Stepwise regression analysis between soil microbial residues and soil physicochemical properties within aggregates.
4. Discussion
4.1. Distribution of Microbial Residues within the SA
Amino sugars are essential microbial residue indicators that are extensively examined for their cycling of microbial residues [4,11]. The SA are an assemblage of a myriad of organic and mineral particles, and the soil aggregate structure is closely related to the aggregation and decomposition processes of microbial residues in the soil [3,5,6]. In this study, we demonstrated a marked direct association between soil aggregate stability (MWD) and the content of amino sugars, which corroborates the conclusions of Ding et al. [7], indicating that microbial residues have a positive effect on the formation and stability of SA and may have a longer lasting effect on SA than living microorganisms [8,9]. Moreover, the stability of accumulation of soil microbial residues primarily depends on the degree of physical protection of the aggregate structure [8].
Soil microbial residues can be encapsulated by small pores within the SA, thereby blocking their contact with soil enzymes or living microorganisms for protection [3,6]. Small particle sizes of SA are more closely correlated with the soil amino sugars, thus providing physical protection and increasing the likelihood of accumulating microbial residues and stably preserving them compared with the spatial structure of particle size SA [3,5,34]. Our results revealed that the contents of amino sugar and MRC were maximal in the 2–0.25 mm SA, then the >2 mm SA, <0.25 mm SA, and silt-clay. This is consistent with the findings of Ding et al. [7], who found that the amino sugar contents in the >0.25 mm SA were higher than those in the <0.25 mm SA. Ni et al. [5] reported that the contents of amino sugars were directly associated with the contents of soil organic C and microbial biomass C, which is similar to our results. This indicated that the 2–0.25 mm SA in the fluvo-aquic soil maintained high nutrient levels, microbial activity, and accumulation of microbial residues, as well as a good balance between the transformation of nutrients and accumulation of organic matter [6]. However, the amino sugars were more stable in the microSA than in the macroSA; thus, the amino sugars in the microSA were not sensitive to changes in the soil nutrient status [7]. These disparate results suggest a synergistic but distinct participation of fungal and bacterial residues in the formation of SA [10].
4.2. Effects of the Application of Biochar and Fertilizer on the Response of Microbial Residues in SA
Microbial growth and biomass formation were influenced by fertilization and could contribute to the microbial residues [31,35]. This study showed that the content of each amino sugar in the silt-clay did not change significantly under different treatments, probably because the accumulation of amino sugar residues first reached saturation in the small particle size SA, and more residues continued to accumulate in the large particle size SA, which suggests that the accumulation of microbial residues within SA has a grading phenomenon [7]. The application of BC to the 0.25–0.053 mm SA significantly increased the contents of GluN, GalN, and FRC, while the application of chemical fertilizer (NPK) improved the contents of MurA and BRC. This could be because the application of BC increased the fungal biomass and, thus, the accumulation of fungal residues, whereas the application of chemical fertilizers favored bacterial growth and, thus, increased the accumulation of bacterial residues [11,35]. Warnock et al. [36] also confirmed that the application of BC could provide suitable sites for the survival and growth of fungi and bacteria through its specific pore structure and improved the availability of soil nutrients through its own C reservoir and specific mineral nutrients, thereby increasing the soil fungal biomass. As N-based compounds, amino sugars can decompose in the absence of soil N, partially meeting the needs of microorganisms for N [6]. The research revealed that the treatments with fertilizers increased the content of amino sugars in the 2–0.25 mm SA, possibly because the fertilizers provided an adequate available source of N, thereby reducing the microbial decomposition of amino sugars [37,38]. However, in the >2 mm SA, the application of BC or NPK reduced the content of amino sugars, possibly because the physical protection effect of the >2 mm SA on amino sugars was weak, and the microbial activity under fertilization conditions was stronger. Thus, the rate of decomposition of amino sugars was higher than the rate of accumulation of amino sugars after microbial death.
4.3. Contribution of Microbial Residues to the SOC within SA
Microbial residues are the source of the soil C pool and accumulation of SOC that is influenced by the balance between the formation and decomposition of microbial residues [39]. Chen et al. [40] reported that paddy soils contained more bacterial residues, while upland soils had more fungal residues. Herein, we demonstrated that the amount of bacterial residues in SOC was significantly higher than that of the fungal residues in the fluvo-aquic soil. The variations in bacterial and fungal residues are intimately associated with living microbial biomass [30,41]. Our previous findings revealed that the bacterial biomass was significantly higher than the fungal biomass [1], indicating that an increase in the levels of soil C was owed to the continuous accumulation of the living microbial biomass pool through necrotic material [35]. The higher accumulation of necrotic material was primarily owed to rapid microbial development and turnover rates (particularly of bacteria) and larger live biomass [35,42,43]. Our findings also showed that the proportion of MRC in the SOC was the lowest in the 0.25–0.053 mm SA compared with the >0.25 mm and <0.053 mm SA fractions, which corroborates the conclusions of Luan et al. [13]. This could possibly be owed to a limitation of the share of microbial residues with the accumulation of SOC in the microhabitat of microSA. Davinic et al. [44] also indicated that the carbon in the 0.25–0.053 mm SA primarily originated from nonmicrobial-based carbon, but the carbon in other SA was primarily derived from microorganisms.
As soil-dominant microorganisms, the contributions of bacteria and fungi to microbial residues in the soil are modulated by various factors, such as soil type, soil environment, and human interference [35,45]. Multiple studies reported that the organic materials influence the contribution of microbial residues to the SOC [13,14]. Based on our analysis, the contributions of TAS-C, BRC, and MRC to SOC in the bulk soil and SA were significantly reduced in all the treatments amended with BC compared with the CK and NPK, suggesting that an increase in the imbalance of C/N could explain the reduced sequestration of MRC because the soils amended with BC had a higher C/N ratio [1]. Huang et al. [28] confirmed that the proportion of microbial residues in the SOC negatively correlated with the stoichiometric imbalance of the C/N ratio. However, Luan et al. [13] reported that organic amendments increase the microbial biomass and residues in a fluvo-aquic soil, as well as augment the microbial residues shared with SOC aggregation in the SA compared with the chemical fertilization treatment. Ding et al. [7] found that the application of manure substantially enhanced the contribution of microbial residues to the SOC in the 2–0.25 mm and 0.25–0.053 mm SA of a clay soil. It has also been shown that bacteria and fungi are the primary participants in the production of soil C pools [46,47], and these inconsistencies are potentially related to the types of organic materials and soil and the duration of experimental testing.
The accumulation of soil amino sugars was ultimately dependent on the intricate balance between their production and decomposition [14], which was jointly controlled by soil type, soil structure, nutrient conditions, and microbial activity [6]. Our regression analysis revealed that the soil bacterial communities significantly and positively affected the accumulation of the microbial residues, which could be explained by the dominance of bacterial biomass in the soil MCC and, therefore, its marked influence on the aggregation of microbial residues. Moreover, the regression analysis also revealed that the activity of N-acetyl-glucosaminidase (NAG) was significantly and positively affected by the microbial residues, possibly because NAG can degrade chitin and other glucosamine polymers linked to β-1,4 glycosidic bonds [48]. Chitin, an important component of the fungal cell wall, is a polysaccharide formed by the dehydration and condensation of acetyl-aminoglucose with β-1,4 glycosidic bonds, while peptidoglycan, a unique member of the bacterial cell wall, is a polymer formed by the combination of MurA and acetyl-aminoglucose with β-1,4 glycosidic bonds. Therefore, increased NAG activity could promote the breakdown of microbial cell wall members, such as chitin and peptidoglycans, in soil, thereby promoting the accumulation of monosaccharides, such as GluN and MurA.
5. Conclusions
The content and distribution of microbial residues in the fluvo-aquic SA were studied two years after biochar had been applied, and the responses of microbial residues in the fluvo-aquic soil to fertilizer application and particle size components were elucidated. This study showed that the 2–0.25 mm SA were microenvironments with the largest accumulation of soil microbial residues, and the BC + NPK treatment was more effective at increasing the accumulation of microbial residues in the SA. A stepwise regression analysis indicated that the bacterial biomass and the activity of NAG in the soil significantly and positively affected the contents of amino sugar and MRC. However, no systematic study was performed on whether the distribution of profiles of microbial residues in the SA depend on factors, such as biochar properties, duration of the experiment, and soil fertility, and multisite field experiments are urgently needed for further verification.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy13020392/s1.
Author Contributions
Y.C. and S.Z. designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. D.S., H.W. and L.W. collected and analyzed data. X.W. designed research and revised the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial supports were provided by the National Key Research and Development Project (No. 2018YFD0200500) and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (No. CAAS-ZDRW202201).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented during this study are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, S.; Cui, J.; Wu, H.; Zheng, Q.; Song, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S. Organic carbon, total nitrogen, and microbial community distributions within aggregates of calcareous soil treated with biochar. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 314, 107408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.J.; Zeng, X.B.; E, S.Z.; Bai, L.Y.; Su, S.M.; Huang, T. Effects of freeze-thaw on aggregate stability and the organic carbon and nitrogen enrichment ratios in aggregate fractions. Soil Use Manag. 2014, 30, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, G.; Mueller Kevin, E.; Nierop Klaas, G.J.; Simpson Myrna, J. Plant-or microbial-derived? A review on the molecular composition of stabilized soil organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 156, 108189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Chen, G.; Du, E.; Tian, D.; Xing, A.; Shen, H.; Ji, C.; Zheng, C.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, J.; et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on microbial residues and their contribution to soil organic carbon in China’s forests from tropical to boreal zone. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 268, 115941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Liao, S.; Tan, S.; Wang, D.; Peng, Y.; Yue, K.; Wu, F.; Yang, Y. A quantitative assessment of amino sugars in soil profiles. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 143, 107762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wilson, C.B.; He, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, F.; Schaeffer, S.M. Physical, biochemical, and microbial controls on amino sugar accumulation in soils under long-term cover cropping and no-tillage farming. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Liang, C.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Han, X. Higher rates of manure application lead to greater accumulation of both fungal and bacterial residues in macroaggregates of a clay soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 84, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Frey, S.D.; Thiet, R.K.; Batten, K.M. Bacterial and Fungal Contributions to Carbon Sequestration in Agroecosystems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelung, W.; Miltner, A.; Zhang, X.; Zech, W. Fate of microbial residues during litter decomposition as affected by minerals. Soil Sci. 2001, 166, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, R.; Djukic, I.; Keiblinger, K.; Zehetner, F.; Bierbaumer, M.; Zechmeister-Bolternstern, S.; Joergernsen, R.G. Spatial distribution of microbial biomass and residues across soil aggregate fractions at different elevations in the Central Austrian Alps. Geoderma 2019, 339, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joergensen, R.G. Amino sugars as specific indices for fungal and bacterial residues in soil. Biol. Fert. Soils 2018, 54, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Liu, X.; He, H.; Chen, W.; Zhuge, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wang, H. Accumulation Characteristics of Amino Sugars in Salinized Soils of Different Types in the Yellow River Delta. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2018, 55, 390–398. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luan, H.; Yuan, S.; Gao, W.; Tang, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, H.; Huang, S. Aggregate-related changes in living microbial biomass and microbial necromass associated with different fertilization patterns of greenhouse vegetable soils. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2021, 103, 103291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, F.; Hu, G.; Shao, S.; He, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, L. Dynamic contribution of microbial residues to soil organic matter accumulation influenced by maize straw mulching. Geoderma 2019, 333, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Eltohamy, K.M.; Liu, C.; Li, F.; Fang, Y.; Kawasaki, A.; Liang, X. Biochar reduces colloidal phosphorus in soil aggregates: The role of microbial communities. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.; Xi, X.; Zheng, Q.; Liang, G.; Zhou, W.; Wang, X. Soil nutrient and microbial activity responses to two years after maize straw biochar application in a calcareous soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Chen, C.; Mooney, S.J.; Peng, X.; Du, Z. Biochar enhances soil hydraulic function but not soil aggregation in a sandy loam. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 70, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Song, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yan, X.; Gunina, A.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Xiong, Z. Effects of six-year biochar amendment on soil aggregation, crop growth, and nitrogen and phosphorus use efficiencies in a rice-wheat rotation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obia, A.; Mulder, J.; Martinsen, V.; Cornelissen, G.; Børresen, T. In situ effects of biochar on aggregation, water retention and porosity in light-textured tropical soils. Soil Till. Res. 2016, 155, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, K.; Li, Z.; Qian, X.; Zang, H.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Water-stable aggregates and carbon accumulation in barren sandy soil depend on organic amendment method: A three-year field study. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhan, L.; Xu, X.; Bi, R.; Xiong, Z. Biochar addition stabilized soil carbon sequestration by reducing temperature sensitivity of mineralization and altering the microbial community in a greenhouse vegetable field. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 313, 114972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Ma, W.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W.; Mi, G.; Miao, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Pursuing sustainable productivity with millions of smallholder farmers. Nature 2018, 555, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Reference Base of Soil Resources. International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World Soil Recourses Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.L.; Xu, A.G.; Zhang, R.L.; Ji, H.J. Review of Soil Classification and Revision of China Soil Classification System. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2014, 47, 3214–3230. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Hao, X.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q. Complexity of bacterial and fungal network increases with soil aggregate size in an agricultural Inceptisol. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 154, 103640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, M.C.; Swarup, A.; Wanjari, R.H.; Mishra, B.; Shahi, D.K. Long-term fertilization, manure and liming effects on soil organic matter and crop yields. Soil Till. Res. 2006, 94, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliana, H.S.; Cícero, C.D.F.; Robélio, L.M.; Madari, B.E.M.; Luiz, E.C.B.; Jader, G.B.; Diego, M.D.S. Methods of soil organic carbon determination in Brazilian savannah soils. Sci. Agric. 2014, 71, 302–308. [Google Scholar]
- Skjemstad, J.O.; Reeve, R. The determination of nitrogen in soils by rapid high-temperature Kjeldahl digestion and autoanalysis. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2008, 7, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indorf, C.; Dyckmans, J.; Khan, K.S.; Joergensen, R.G. Optimisation of amino sugar quantification by HPLC in soil and plant hydrolysates. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liang, C.; Duan, X.; Chen, H.; Li, D. Variation of microbial residue contribution to soil organic carbon sequestration following land use change in a subtropical karst region. Geoderma 2019, 353, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Yuan, S.; Gao, W.; Tang, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, H.; Huang, S. 10-Year fertilization alters soil C dynamics as indicated by amino sugar differentiation and oxidizable organic C pools in a greenhouse vegetable field of Tianjin, China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 169, 104226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, S.; Heinze, S.; Ngosong, C.; Sradnick, A.; Oltmanns, M.; Raupp, J.; Geisseler, D.; Joergensen, R.G. Effect of biodynamic soil amendments on microbial communities in comparison with inorganic fertilization. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 114, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Koal, P.; Liu, D.; Gerl, G.; Schroll, R.; Gattinger, A.; Joergensen, R.G.; Munch, J.C. Soil microbial community and microbial residues respond positively to minimum tillage under organic farming in Southern Germany. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 108, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lützow, M.V.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Ekschmitt, K.; Matzner, E.; Guggenberger, G.; Marschner, B.; Flessa, H. Stabilization of organic matter in temperate soils: Mechanisms and their relevance under different soil conditions—A review. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 57, 426–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; An, S.; Liang, C.; Liu, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y. Microbial necromass as the source of soil organic carbon in global ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 162, 108422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnock, D.D.; Lehmann, J.; Kuyper, T.W.; Rillig, M.C. Mycorrhizal responses to biochar in soil -concepts and mechanisms. Plant Soil 2007, 300, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, W.; Shao, S.; He, H.; Zhang, X. Comparing microbial transformation of maize residue-N and fertilizer-N in soil using amino sugar-specific 15N analysis. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 71, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Han, X. Effects of long-term fertilization on contents and distribution of microbial residues within aggregate structures of a clay soil. Biol. Fert. Soils 2014, 50, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, J.; Yang, F.; Dong, W.; Dai, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, X. Specific Responses of Soil Microbial Residue Carbon to Long-Term Mineral Fertilizer Applications to Reddish Paddy Soils. Pedosphere 2018, 28, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zheng, S.; Ma, C.; Rui, Y.; He, H.; Huang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Ge, T.; et al. Contrasting pathways of carbon sequestration in paddy and upland soils. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 2478–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, D.; Shen, J.; Yuan, Q.; Fan, F.; Wei, W.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. Biochar alters soil microbial communities and potential functions 3–4 years after amendment in a double rice cropping system. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 311, 107291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicharanloo, B.; Shirvan, M.B.; Keitel, C.; Dijkstra, F.A. Rhizodeposition mediates the effect of nitrogen and phosphorous availability on microbial carbon use efficiency and turnover rate. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 142, 107705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Klaus, K.; Wanek, W.; Richter, A. Microbial carbon use efficiency and biomass turnover times depending on soil depth—Implications for carbon cycling. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 96, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davinic, M.; Fultz, L.M.; Acosta-Martinez, V.; Calderón, F.J.; Cox, S.B.; Dowd, S.E.; Allen, V.G.; Zak, J.C.; Moore-Kucera, J. Pyrosequencing and mid-infrared spectroscopy reveal distinct aggregate stratification of soil bacterial communities and organic matter composition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 46, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Chen, X.; Zheng, X.; Deng, S.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, S.; He, X.; Wu, J.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Su, Y. Preferential uptake of hydrophilic and hydrophobic compounds by bacteria and fungi in upland and paddy soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Amelung, W.; Lehmann, J.; Kästner, M. Quantitative assessment of microbial necromass contribution to soil organic matter. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 3578–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Mondéjar, R.; Brabcová, V.; Štursová, M.; Davidová, A.; Jansa, J.; Cajthaml, T.; Baldrian, P. Decomposer food web in a deciduous forest shows high share of generalist microorganisms and importance of microbial biomass recycling. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1768–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, S.; Bertilsson, S. Bacterial chitin degradation-mechanisms and ecophysiological strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).