Contrasting Effects of Nitrogen and Organic Fertilizers on Iron Dynamics in Soil after 38–Year Fertilization Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental–Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Selected Treatments
2.4. Soil– and Plant–Sample Collection
2.5. Soil–Aggregate Separation
2.6. Chemical Analysis
2.7. Sequential Extraction of Fe
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Properties
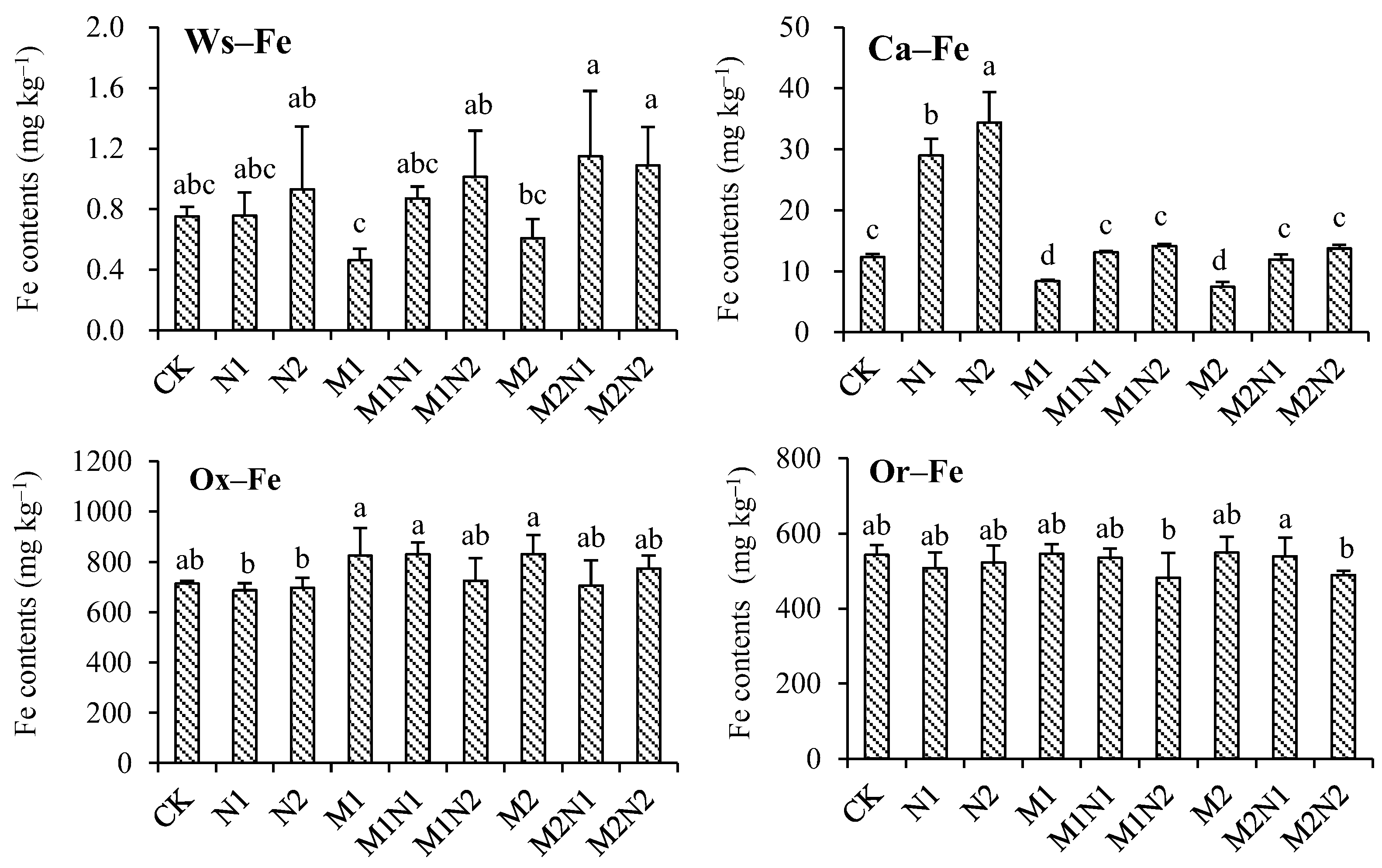
3.2. Iron speciation in Bulk Soil
3.3. Iron contents in Soil Aggregates
3.4. Iron Speciation in Soil Aggregates
3.5. Organic–Carbon Contents in Soil Aggregates
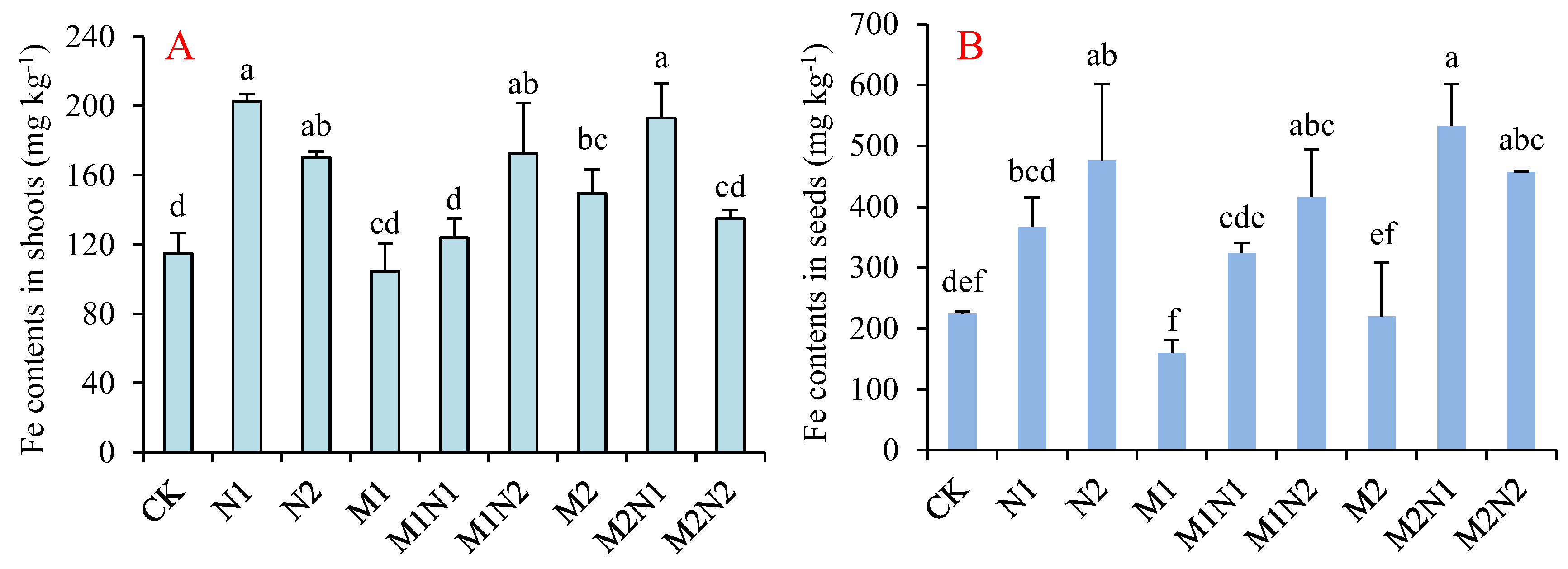
3.6. Iron Contents in Shoots and Seeds of Soybean
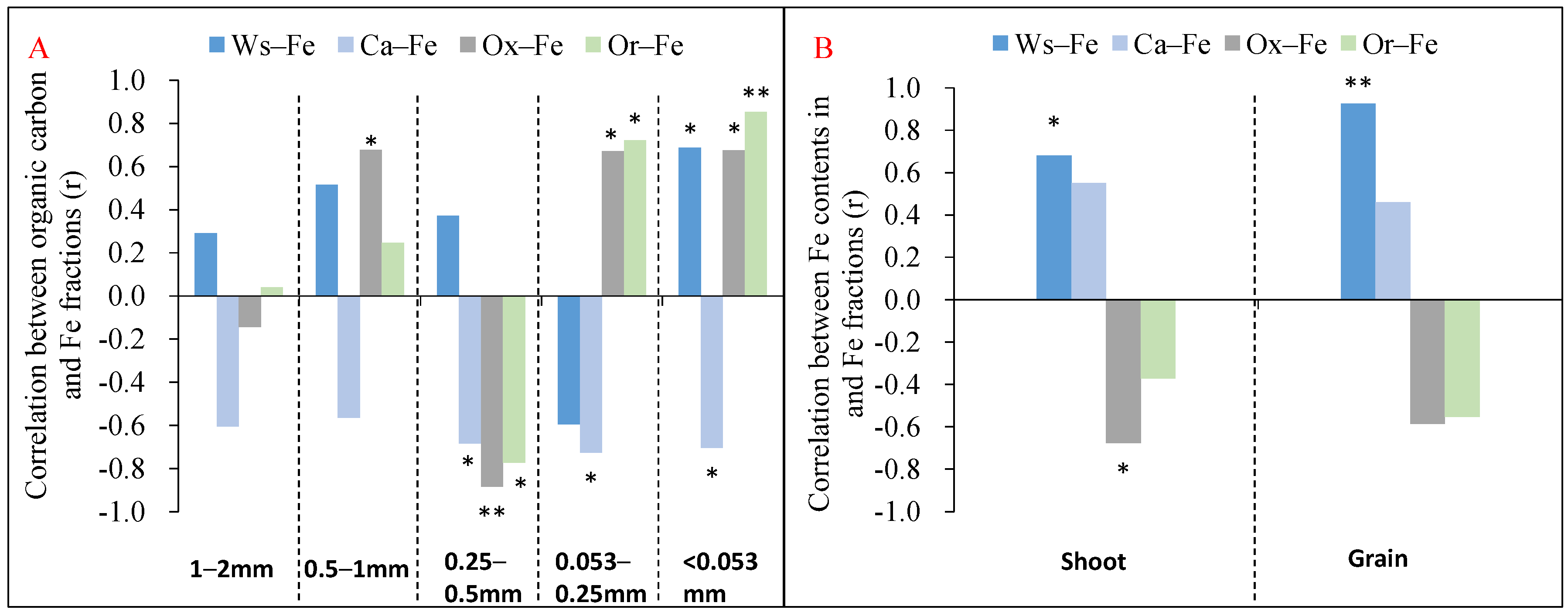
3.7. Correlations between Indices
4. Discussion
4.1. Long–Term Application of Nitrogen Fertilizer Improved Fe Availability in Soil
4.2. Long–Term Application of Organic Fertilizer Enhances Iron Immobilization
4.3. Nitrogen Fertilizer Alleviated the Organic–Fertilizer–Induced Iron Immobilization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melton, E.D.; Swanner, E.D.; Behrens, S.; Schmidt, C.; Kappler, A. The interplay of microbially mediated and abiotic reactions in the biogeochemical Fe cycle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Hu, R.; Zhao, J.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Liu, S. Iron oxidation affects nitrous oxide emissions via donating electrons to denitrification in paddy soils. Geoderma 2016, 271, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borch, T.; Masue, Y.; Kukkadapu, R.K.; Fendorf, S. Phosphate imposed limitations on biological reduction and alteration of ferrihydrite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, K.; Xue, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.B.; Liu, Z. Inhibition effects of long–term calcium–magnesia phosphate fertilizer application on Cd uptake in rice: Regulation of the iron–nitrogen coupling cycle driven by the soil microbial community. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.X.; Xie, S.R.; Song, Z.L.; Xia, S.P.; Åstrom, M.E. Biogeochemical cycling of iron (hydr–)oxides and its impact on organic carbon turnover in coastal wetlands: A global synthesis and perspective. Earth. Sci. Rev. 2021, 218, 103658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shaheen, S.M.; Jiang, Y.H.; Li, R.H.; Slaný, M.; Abdelrahman, H.; Kwon, E.; Bolan, N.; Rinklebe, J.; Zhang, Z.Q. Fe/Mn– and P–modified drinking water treatment residuals reduced Cu and Pb phytoavailability and uptake in a mining soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.H.; Xiao, J.; Hu, S.J.; Polizzotto, M.L.; Zhao, F.J.; McGrath, S.P.; Li, H.; Ran, W.; Shen, Q.R. Mineral availability as a key regulator of soil carbon storage. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4960–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Xiao, J.; Liu, F.; Goodman, B.A.; Li, W.; Jia, Z.; Ran, W.; Zhang, R.; Shen, Q.; Yu, G. Contrasting effects of inorganic and organic fertilisation regimes on shifts in Fe redox bacterial communities in red soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 117, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Qin, Y.; Chen, S. Nitrogen loss through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to Iron reduction from ecosystem habitats in the Taihu estuary region. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Luo, W.; Qin, Y.; Li, Z. Effects of the addition of nitrogen and phosphorus on anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled with iron reduction (Feammox) in the farmland soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, H.; Clark, I.; Blazewicz, S.; Iavarone, A.; Coates, J. Fe(II) oxidation is an innate capability of nitrate–reducing bacteria that involves abiotic and biotic reactions. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 3260–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratering, S.; Schnell, S. Nitrate–dependent iron (II) oxidation in paddy soil. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 3, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Chen, D.; Luo, X.; Li, X.; Li, F. Microbially mediated nitrate–reducing Fe (II) oxidation: Quantification of chemodenitrification and biological reactions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 256, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chai, C.W.; Thomas Arrigo, L.K.; Zhao, S.C.; Kretzschmar, R.; Zhao, F.J. Nitrite accumulation is required for microbial anaerobic iron oxidation, but not for arsenite oxidation, in two heterotrophic denitrifiers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4036–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.H.; Weber, K.A.; Silver, W.L. Nitrogen loss from soil through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron reduction. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetta, B.; de Souza, D.O.; Aquilanti, G.; Celi, L.; Said–Pullicino, D. Redox–driven changes in organic C stabilization and Fe mineral transformations in temperate hydromorphic soils. Geoderma 2022, 406, 115532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.T.; Rathod, J.; Liang, B.Q.; Wang, C.C.; Yoshiyuki, I.; Nobumichi, T.; Chen, C.L.; Lee, Y.C. Black carbon enriches short–range–order ferrihydrite in Amazonian Dark Earth: Interplay mechanism and environmental implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Bolan, N.S.; Lai, J.; Wang, Y.; Jin, X.; Kirkham, M.B.; Wu, X.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Interactions between organic matter and Fe (hydr) oxides and their influences on immobilization and remobilization of metal (loid)s: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 52, 4016–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, K.; Mucci, A.; Ouellet, A.; Gelinas, Y. Preservation of organic matter in sediments promoted by iron. Nature 2012, 483, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hall, S.J.; Coward, E. Thompson A Iron–mediated organic matter decomposition in humid soils can counteract protection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Yu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zou, Y. Iron–bound organic carbon is conserved in the rhizosphere soil of freshwater wetlands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 149, 107949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, S.; Ahmed, W.; Alatalo, J.M.; Mahmood, M.; Imtiaz, M.; Ditta, A.; Ali, E.F.; Abdelrahman, H.; Slaný, M.; Antoniadis, V.; et al. Herbal plants– and rice straw–derived biochars reduced metal mobilization in fishpond sediments and improved their potential as fertilizers. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 154043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.Y.; Chen, T.Y.; Chan, Y.T.; Cheng, C.Y.; Tzou, Y.M.; Liu, Y.T.; Teah, H.Y. Stabilization of natural organic matter by short–range–order iron hydroxides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 12612–12620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Y.T.; Wang, C.C.; Chiang, C.C.; Tsai, H.; Song, Y.F.; Huang, S.T.; Liang, B. In situ evidence of mineral physical protection and carbon stabilization revealed by nanoscale 3–D tomography. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 3133–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belay, A.; Claassens, A.S.; Wehner, F. Effect of direct nitrogen and potassium and residual phosphorus fertilizers on soil chemical properties, microbial components and maize yield under long–term crop rotation. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2002, 35, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, C.; Anane, P.S.; Liu, S.; Paz–Ferreiro, J. Nitrogen fertilizer is a key factor affecting the soil chemical and microbial communities in a Mollisol. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.J.; Su, J.Q.; Xu, H.J.; Jia, Z.J.; Zhu, Y.G. Long–term nitrogen fertilization of paddy soil shifts iron–reducing microbial community revealed by RNA–13C–acetate probing coupled with pyrosequencing. ISME J. 2015, 9, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtier–Murias, D.; Simpson, A.J.; Marzadori, C.; Baldoni, G.; Ciavatta, C.; Fernández, J.M.; López–de–Sá, E.G.; Plaza, C. Unraveling the long–term stabilization mechanisms of organic materials in soils by physical fractionation and NMR spectroscopy. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 171, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.T.; Zhang, W.J.; Xu, M.G.; Tong, X.G.; Sun, F.X.; Wang, J.Z.; Huang, S.M.; Zhu, P.; He, X.H. Long–term combined chemical and manure fertilizations increase soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in aggregate fractions at three typical cropland soils in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Conant, R.T.; Paul, E.A.; Paustian, K. Stabilization mechanisms of soil organic matter: Implications for C–saturation of soils. Plant Soil 2002, 241, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, Z.; Huang, J. Distribution characteristics of heavy metal (loid)s in aggregates of different size fractions along contaminated paddy soil profile. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 23939–23952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.K.; Ke, Z.X. Copper and zinc enrichment in different size fractions of organic matter from polluted soils. Pedosphere 2004, 14, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, Z. Distribution and bioavailability of heavy metals in soil aggregates from the fenhe river basin, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 104, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.; Han, X.; Wang, Y.; Han, M.; Shi, H.; Liu, N.; Bai, H. Influence of long–term fertilization on soil microbial biomass, dehydrogenase activity, and bacterial and fungal community structure in a brown soil of northeast China. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, M.I.; Li, N.; Han, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, S.; Irshad, M.; Mahmood, Q. Temporal changes in trace elements in brown soil and soybean after long–term fertilization. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wen, Q.X.; Zhang, S.Y.; Li, N.; Yang, J.F.; Han, X.R. Long–term rotation fertilisation has differential effects on soil phosphorus. Plant Soil Environ. 2020, 66, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wu, X.; Liao, P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, N.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L. Morphological transformation of heavy metals and their distribution in soil aggregates during biotransformation of livestock manure. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 32, 101963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, D.D.; Wang, H.M.; Chen, F.S.; Fu, X.L.; Fang, X.M.; Sun, X.M.; Yu, G.R. Impacts of nitrogen and phosphorus additions on the abundance and community structure of ammonia oxidizers and denitrifying bacteria in Chinese firplantations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xiao, W.; Zheng, C.; Zhu, B. Nitrogen addition has contrasting effects on particulate and mineral–associated soil organic carbon in a subtropical forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 142, 107708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, B.; Lahav, O. The effect of pH on the kinetics of spontaneous Fe (II) oxidation by O2 in aqueous solution–basic principles and a simple heuristic description. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 2080–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q.S.; Cao, W.Z.; Wang, M.; Wu, G.J.; Wang, F.F.; Jiang, C.; Tao, Y.R.; Gao, Y. Nitrogen loss through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled with iron reduction in a mangrove wetland. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hou, L.; Liu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yin, G.; Lin, X.; Cheng, L.; Li, Y.; Hu, X. Evidence of nitrogen loss from anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled with ferric iron reduction in an intertidal wetland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11560–11568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.J.; An, X.L.; Li, S.; Zhang, G.L.; Zhu, Y.G. Nitrogen loss through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron reduction from paddy soils in a chronosequence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10641–10647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansel, C.; Fendorf, S.; Sutton, S.; Newville, M. Characterization of Fe plaque and associated metals on the roots of mine–waste impacted aquatic plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3863–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; He, X.; Hao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, L.; Ran, W.; Shen, Q.; Yu, G. New strategies for submicron characterization the carbon binding of reactive minerals in long–term contrasting fertilized soils: Implications for soil carbon storage. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 3607–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eusterhues, K.; Wagner, F.E.; Hausler, W.; Hanzlik, M.; Knicker, H.; Totsche, K.U.; Kögel–Knabner, I.; Schwertmann, U. Characterization of ferrihydrite–soil organic matter coprecipitates by X–ray diffraction and Mossbauer spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7891–7897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torn, M.S.; Trumbore, S.E.; Chadwick, O.A.; Vitousek, P.M.; Hendricks, D.M. Mineral control of soil organic carbon storage and turnover. Nature 1997, 389, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.L.; Li, H.; Xiao, J.; Wang, C.; Shen, Q.R.; Ran, W.; He, X.H.; Zhou, Q.S.; Yu, G.H. Insights into complexation of dissolved organic matter and Al(III) and nanominerals formation in soils under contrasting fertilizations using two–dimensional correlation spectroscopy and high resolution–transmission electron microscopy techniques. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, G.; Mueller, K.E.; Nierop, K.G.; Simpson, M.J. Plant–or microbial–derived? A review on the molecular composition of stabilized soil organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 156, 108189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile–Doelsch, I.; Balesdent, J.; Pellerin, S. Reviews and syntheses: The mechanisms underlying carbon storage in soil. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 5223–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavallee, J.M.; Soong, J.L.; Cotrufo, M.F. Conceptualizing soil organic matter into particulate and mineral–associated forms to address global change in the 21st century. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusack, D.F.; Chadwick, O.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Vitousek, P.M. Mineralogical controls on soil black carbon preservation. Global Biogeochem. Cyc. 2012, 26, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eusterhues, K.; Rumpel, C.; Kögel–Knabner, I. Organo–mineral associations in sandy acid forest soils: Importance of specific surface area, iron oxides and micropores. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2005, 56, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, C.; Torn, M.S.; Southard, R.J. Mineral assemblage and aggregates control carbon dynamics in a California conifer forest. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1711–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorover, J.; Amistadi, M.K. Reaction of forest floor organic matter at goethite, birnessite and smectite surfaces. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Schmitt, J.; Chen, Z.; Liang, L.; McCarthy, J.F. Adsorption and desorption of different organic matter fractions on iron oxide. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, C.L.S.; Püttmann, W. Interactions between mineral phases in the preservation of soil organic matter. Geoderma 2006, 134, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Organic Fertilizer (t ha−1 year−1) | Nitrogen Fertilizer (kg N ha−1 year−1) | Phosphorous Fertilizer (kg P2O5 ha−1 year−1) | Potassium Fertilizer (kg K2O ha−1 year−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (M1) | High (M2) | Low (N1) | High (N2) | |||
| Maize | 13.5 | 27.0 | 120 | 180 | 60 | 60 |
| Soybean | – | – | 30 | 60 | 90 | 90 |
| pH | Eh | SOC (g kg−1) | SON (g kg−1) | NO3−–N (mg kg−1) | NH4+–N (mg kg−1) | DTPA–Fe (mg kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5.67 ± 0.12 d | 273.2 ± 2.3 bc | 0.85 ± 0.03 d | 0.90 ± 0.01 c | 2.51 ± 0.75 g | 5.45 ± 1.57 de | 63.66 ± 1.22 f |
| N1 | 5.16 ± 0.21 e | 299.4 ± 11.5 ab | 0.94 ± 0.03 d | 0.92 ± 0.06 c | 54.50 ± 0.10 a | 12.16 ± 3.42 ab | 91.73 ± 2.43 d |
| N2 | 4.84 ± 0.19 f | 284.3 ± 3.1 ab | 0.90 ± 0.01 d | 0.98 ± 0.04 c | 31.60 ± 4.47 d | 14.36 ± 0.91 a | 94.88 ± 1.04 d |
| M1 | 6.82 ± 0.17 ab | 239.0 ± 37.1 c | 1.16 ± 0.07 abc | 1.19 ± 0.04 b | 10.89 ± 2.71 f | 5.15 ± 0.41 e | 73.59 ± 1.26 e |
| M1N1 | 6.15 ± 0.15 c | 243.1 ± 11.4 c | 1.08 ± 0.02 bc | 1.13 ± 0.06 b | 21.46 ± 2.16 e | 8.54 ± 3.24 dc | 126.13 ± 4.24 b |
| M1N2 | 6.01 ± 0.13 dc | 264.9 ± 32.3 bc | 1.05 ± 0.10 c | 1.13 ± 0.03 b | 38.25 ± 2.19 c | 9.12 ± 2.61 bc | 132.74 ± 2.11 a |
| M2 | 6.83 ± 0.24 a | 323.5 ± 8.5 a | 1.16 ± 0.01 ab | 1.23 ± 0.04 ab | 12.66 ± 0.96 f | 4.04 ± 0.15 e | 68.86 ± 2.71 ef |
| M2N1 | 6.58 ± 0.20 b | 259.1 ± 46.8 bc | 1.13 ± 0.03 bc | 1.18 ± 0.16 b | 45.18 ± 3.97 b | 6.86 ± 0.21 dce | 113.28 ± 1.49 c |
| M2N2 | 6.01 ± 0.25 c | 268.4 ± 9.2 bc | 1.25 ± 0.15 a | 1.33 ± 0.12 a | 46.06 ± 0.06 b | 7.18 ± 0.57 dce | 130.90 ± 4.74 ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Yang, L.; Guo, J.; Yang, J.; Li, N.; Dai, J.; Feng, H.; Liu, N.; Han, X. Contrasting Effects of Nitrogen and Organic Fertilizers on Iron Dynamics in Soil after 38–Year Fertilization Practice. Agronomy 2023, 13, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13020371
Liu H, Yang L, Guo J, Yang J, Li N, Dai J, Feng H, Liu N, Han X. Contrasting Effects of Nitrogen and Organic Fertilizers on Iron Dynamics in Soil after 38–Year Fertilization Practice. Agronomy. 2023; 13(2):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13020371
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Houjun, Lei Yang, Jin Guo, Jinfeng Yang, Na Li, Jian Dai, Huan Feng, Ning Liu, and Xiaori Han. 2023. "Contrasting Effects of Nitrogen and Organic Fertilizers on Iron Dynamics in Soil after 38–Year Fertilization Practice" Agronomy 13, no. 2: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13020371
APA StyleLiu, H., Yang, L., Guo, J., Yang, J., Li, N., Dai, J., Feng, H., Liu, N., & Han, X. (2023). Contrasting Effects of Nitrogen and Organic Fertilizers on Iron Dynamics in Soil after 38–Year Fertilization Practice. Agronomy, 13(2), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13020371







