Intercropping Forage Sorghum with Sunnhemp at Different Seeding Rates to Improve Forage Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Environmental Conditions
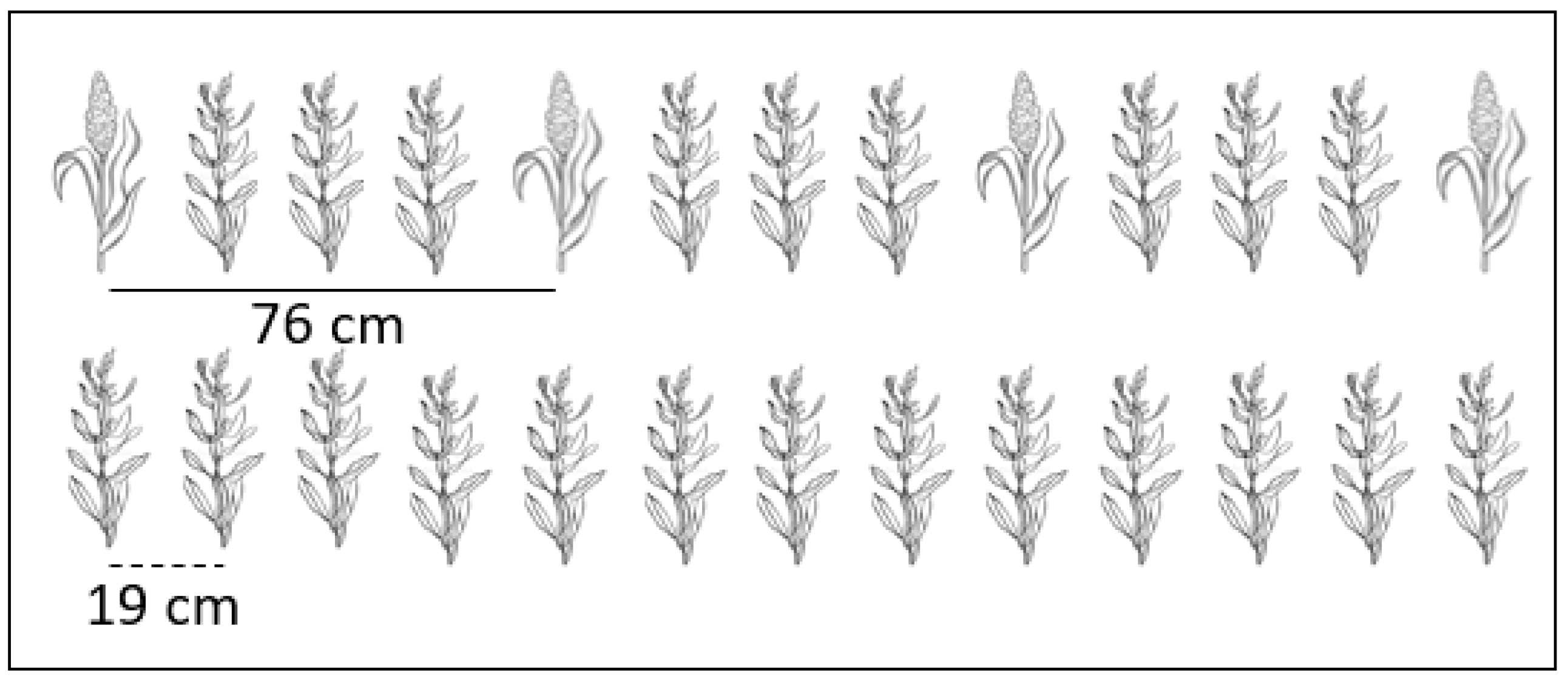
2.2. Agronomics and Experimental Design
2.3. Canopy Development and Irrigation Water Use Efficiency
2.4. Dry Matter and Forage Quality
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Weather
3.2. Canopy Development
3.3. Irrigation Water Use Efficiency
3.4. Dry Matter Production
3.5. Forage Nutritive Value
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Agricultural Statistics Service. 2020. Available online: http://www.nass.gov (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, R.; Mahmood, N.; Tanveer, A. Performance of forage sorghum intercropped with forage legumes under different planting patterns. Pak. J. Bot. 2007, 39, 431–439. [Google Scholar]
- Mrad, A.; Katu, G.G.; Levia, D.F.; Guswa, A.J.; Boyerm, E.W.; Bruen, M.; Carlyle-Moses, D.E.; Coyte, R.; Creed, I.F.; Van De Giesen, N.; et al. Peak grain forecasts for the US High Plains amid withering waters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 26145–26150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Going back to grassland? Assessing the impact of groundwater decline on irrigated agriculture using remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, V.L. Water-Level and Recoverable Water in Storages Changes, High Plains Aquifer, Predevelopment to 2015 and 2013-15; U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2017; p. 5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, S.; Adusumilli, N.C.; Wang, H.; Almas, L.K. Irrigation water demand and elasticities: A case study of the High Plains aquifer. Irrig. Sci. 2022, 40, 941–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Bastiaans, L.; Anten, N.P.R.; Makowski, D.; van der Werf, W. Annual intercropping suppresses weeds: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 322, 107658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreau, M.A. Diseases in intercropping systems. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 499–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stomph, T.; Dordas, C.; Baranger, A.; de Rijk, J.; Dong, B.; Evers, J.; Gu, C.; Li, L.; Simon, J.; Jensen, E.S. Designing intercrops for high yield, yield stability and efficient use of resources: Are there principles? Adv. Agron. 2020, 160, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, W.F.; Hoffland, E.; Li, L.; Janssen, B.H.; van der Werf, W. Intercropping affects the rate of decomposition of soil organic matter and root litter. Plant. Soil. 2015, 391, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, P.; Singh, R.S.; Bharati, V.R. Enhancing crop production by enhancing water use efficiency- a review. Agric. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 5, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Wahab, T.I.; Abdel-Wahab, S.I.; Abdel-Wahab, I. Benefits of intercropping legumes with cereals. Int. J. Conf. Proc. 2019, 10, 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Struik, P.C.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, J.; Stomph, T. Forage quality in cereal/legume intercropping: A meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2023, 304, 109174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Lauriault, L.M.; Marsalis, M.; Angadi, S.; Puppula, N. Performance of forage sorghum-legume mixtures in southern High Plains, USA. Forage Grazinglands 2009, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, J.A. Handbook of Legumes World Economic Importance; Springer Science & Business Media: New York City, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Bearden, J. Sunn Hemp for Forage or Wildlife Food Plots; University of Florida IFAS Extension: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Balkcom, K.S.; Massey, J.M.; Mosjidis, J.A.; Price, A.J.; Enloe, S.F. Planting date and seeding rate effects on sunn hemp biomass and nitrogen production for a winter cover crop. Intl. J. Agron. 2011, 2011, 237510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomberg, H.; Martini, N.; Díaz-Pérez, J.C.; Phatak, S.C.; Balkcom, K.S.; Bhardwaj, H. Potential for using sunn hemp as a souce of biomass and nutrition for the Piedmont and Coastal Plains regions of the southeaster USA. Argonomy J. 2007, 99, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, H.L.; Webber, C.L., III; Sakamoto, G.S. Cultivation of kenaf and sunn hemp in the mid-Atlantic United States. Ind. Crops Prod. 2005, 22, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, C.G.; Scott, A.W., Jr.; Chow, P. Planting date and cultivar effects on growth and stalk yield of sunn hemp. Ind. Crops Prod. 1998, 8, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.B.; Chase, C.; Treadwell, D.; Koenig, R.; Cho, A.; Morales-Payan, J.P.; Murphy, T.; Antonious, G.F. Effect of sunn hemp hemp (Crotalaria juncea L.) cutting date and planting density on weed suppression in Georgia, USA. J. Env. Sci. Health Part B 2015, 50, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosjidis, J.A.; Wehtje, G. Weed control in sunn hemp and its ability to suppress weed growth. Crop Prot. 2011, 30, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darapuneni, M.K.; Angadi, S.V.; Umesh, M.R.; Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Annadurai, K.; Begna, S.H.; Maraslis, M.A.; Cole, N.A.; Gowda, P.H.; Hagevoort, G.R.; et al. Canopy development of annual legumes and forage sorghum intercrops and its relation to dry matter accumulation. Agronomy J. 2018, 110, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.K.; Roth, G.W. Forage sorghum. In PennState Ext. [Brochure]; Pennsylvania State University: University Park, PA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bean, B.W.; Baumhardt, R.L.; McCollum, F.T., III. McCuistion, K.C. Comparison of sorghum classes for grain and forage yield and forage nutritive value. Field Crops Res. 2013, 142, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.W.; Frederiksen, R.A. Sorghum: Origin, History, Technology, and Production; John Wiley & Sons: College Station, TX, USA, 2000; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Blum, A.; Arkin, G.F. Sorghum root growth and water-use as affected by water supply and growth duration. Field Crops Res. 1984, 9, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA-NRCS. SSM—Appendix 1. Official Soil Series Description. 2016. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/tx/home/?cid=nrcs142p2_054248 (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- Lepcha, I.; Naumann, H.D.; Fritschi, F.B.; Kallenbach, R.L. Herbage accumulation, nutritive value, and regrowth potential of sunn hemp at different harvest regimes and maturity. Crop. Sci. 2018, 59, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machicek, J.A.; Blaser, B.C.; Darapuneni, M.; Rhoades, M.B. Harvesting regimes affect brown midrib sorghum-sudangrass and brown midrib pearl millet forage production and quality. Agronomy 2019, 9, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crookston, B.; Blaser, B.C.; Darapuneni, M.; Rhoades, M.B. Pearl millet forage water use efficiency. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzvene, A.R.; Weldemichael, A.T.; Walker, S.; Ceronio, G. Planting time and stand density effect on radiation interception and use efficiency of maize and sunn hemp intercopping in semi-arid South Africa. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 341, 109690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shaughnessy, S.A.; Mosqueda, H.M.; Brauer, D.K. Sunn hemp as an alternative forage in the Texas High Plains Region. Grasslands for Animal, Soil and Human Health. In Proceedings of the International Grassland Congress 2023, Covington, KY, USA, 15–17 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zegada-Lizarazu, W.; Parenti, A.; Monti, A. Intercropping grasses and legumes can contribute to the development of advanced biofuels. Biomass Energy 2021, 149, 106086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.; Naylor, C.; Heflin, K.; Sirmon, P.; Porter, N.; Schnell, R.; Horn, K. 2021 Texas A&M AgriLife Bushland forage sorghum silage trial. In Texas A&M AgriLife Research and Extension [Brochure]; Texas A&M University: College Station, TX, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Eberle, C.; Shortnacy, L. Sunn hemp planting date effect on growth, biomass accumulation, and nutritive value in southeastern Wyoming. Crop. Sci. 2021, 61, 4447–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoer, Z.; Reeves, D.W.; Wood, C.W. Suitability of sunn hemp as an alternative late summer legume cover crop. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA Livestock, Poultry, and Grain Market News. Hay Quality Designation Guidelines [Brochure]. 2020. Available online: https://www.ams.usda.gov/sites/default/files/media/HayQualityGuidelines.pdf.
- La Guardia Nave, R.; Corbin, M.D. Forage warm-season legumes and grasses intercropped with corn as an alternative for corn silage production. Agronomy 2018, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfouz, H.; Ali, A.M.M.; Megawer, E.A.; Mahmoud, A.S. Response of growth parameters, forage quality and yield of dual-purpose sorghum to re-growth and different levels of FYM and N fertilizers in new reclaimed soil. Intl. J. Curr. Micr. Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 762–782. [Google Scholar]
- Atis, I.; Konuskan, O.; Duru, M.; Gozubenli, H.; Yilmaz, S. Effect of harvesting time on yield, composition, and forage quality of some forage sorghum cultivars. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2012, 14, 879–886. [Google Scholar]







| Month | Average Air Temp | Total Rainfall | Forage Sorghum GDDs a | Sunnhemp GDDs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| °C | mm | °C d | °C d | |
| 2020 Growing Season | ||||
| June | 25 | 20 | 254 | 291 |
| July | 28 | 43 | 464 | 553 |
| August | 26 | 21 | 431 | 509 |
| September | 20 | 8 | 144 | 144 |
| Total | 92 | 1293 | 1497 | |
| 2021 Growing Season | ||||
| June | 24 | 83 | 221 | 252 |
| July | 24 | 68 | 424 | 452 |
| August | 25 | 7 | 431 | 479 |
| September | 23 | 78 | 144 | 239 |
| Total | 236 | 1358 | 1422 | |
| FS Rate | CP a | ADF | NDF | TDN | RFV b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ----------------------------------%----------------------------------- | |||||
| 2020 Growing Season | |||||
| no | 8.1 ± 0.82 a | 55.8 ± 1.26 a (38.4) c | 69.4 ± 0.60 a | 40.2 ± 1.24 a (10.5) | 61.8 ± 1.39 a (12.8) |
| lo | 5.1 ± 0.47 b | 44.3 ± 0.22 b (19.0) | 67.5 ± 0.44 a | 53.0 ± 0.23 b (29.9) | 75.1 ± 0.29 b (28.1) |
| md | 5.0 ± 0.52 c | 44.3 ± 2.48 b (18.9) | 66.9 ± 1.42 a | 53.0 ± 2.65 b (29.7) | 75.8 ± 4.13 b (28.8) |
| hi | 4.5 ± 0.27 c | 44.5 ± 1.84 b (21.6) | 67.1 ± 2.25 a | 52.9 ± 2.15 b (28.0) | 75.3 ± 4.34 b (28.4) |
| p value | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.706 | 0.001 | 0.010 |
| 2021 Growing Season | |||||
| no | 8.8 ± 0.89 a (36.0) | 58.3 ± 0.14 a (36.0) | 67.8 ± 0.81 a (27.2) | 37.5 ± 0.26 a (6.0) | 60.3 ± 1.26 a (5.0) |
| lo | 4.0 ± 0.18 b (20.3) | 39.4 ± 1.33 b (16.2) | 60.1 ± 0.51 a (19.0) | 58.5 ± 1.46 b (26.3) | 89.9 ± 2.18 b (25.6) |
| md | 3.7 ± 0.62 b (14.8) | 38.5 ± 0.63 b (13.6) | 59.5 ± 0.26 a (14.6) | 59.4 ± 0.77 b (29.0) | 92.1 ± 1.01 b (30.9) |
| hi | 3.8 ± 0.38 b (14.8) | 40.4 ± 0.46 b (19.2) | 61.5 ± 0.65 a (24.6) | 52.4 ± 8.01 b (21.2) | 86.8 ± 0.95 b (21.0) |
| p value | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.087 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| FS Rate | CP a | ADF | NDF | TDN | RFV b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ----------------------------------%----------------------------------- | |||||
| 2020 Growing Season | |||||
| no | 16.9 ± 1.38 a (36.9) c | 37.9 ± 2.24 a | 43.3 ± 2.18 a (5.5) | 60.2 ± 2.74 a (20.8) | 128.3 ± 10.12 a (31.4) |
| low | 12.8 ± 1.19 b (21.3) | 39.1 ± 0.90 a | 59.1 ± 1.82 b (25.3) | 58.9 ± 1.00 a (22.0) | 92.3 ± 3.51 a (20.9) |
| med | 12.3 ± 0.83 b (18.5) | 39.2 ± 0.12 a | 59.4 ± 0.38 b (26.8) | 58.7 ± 0.12 a (21.4) | 91.3 ± 0.58 a (19.7) |
| high | 11.3 ± 0.50 b (12.6) | 38.6 ± 1.18 a | 60.4 ± 0.95 b (31.0) | 59.5 ± 1.56 a (23.8) | 91.3 ± 2.08 a (17.6) |
| p value | <0.001 | 0.771 | <0.001 | 0.958 | 0.077 |
| 2021 Growing Season | |||||
| no | 17.7 ± 0.83 a (42.5) | 35.2 ± 0.50 a | 42.8 ± 1.04 a (6.5) | 63.2 ± 0.29 a (35.7) | 130.2 ± 6.00 a (42.5) |
| low | 11.3 ± 0.16 b (26.5) | 36.9 ± 0.54 b | 61.2 ± 0.25 b (24.1) | 61.2 ± 0.68 a (31.1) | 91.8 ± 0.90 b (25.6) |
| med | 10.4 ± 0.64 b (19.3) | 38.0 ± 0.80 bc | 62.0 ± 1.46 bc (29.0) | 60.0 ± 0.80 b (19.9) | 89.5 ± 2.70 b (20.7) |
| high | 9.5 ± 0.82 c (9.79) | 38.9 ± 0.52 c | 64.0 ± 1.60 c (38.4) | 58.9 ± 0.65 b (11.3) | 85.2 ± 2.92 c (9.2) |
| p value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| FS Rate | CP a | ADF | NDF | TDN | RFV b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ----------------------------------%----------------------------------- | |||||
| 2020 Growing Season | |||||
| no | 8.9 ± 0.64 a (42.0) c | 56.8 ± 1.27 a (40.2) | 67.9 ± 0.40 a | 49.1 ± 1.22 a (8.9) | 61.9 ± 1.89 a (12.6) |
| low | 5.2 ± 0.45 b (18.5) | 46.3 ± 1.63 b (21.5) | 68.4 ± 1.97 a | 50.8 ± 1.84 b (27.7) | 72.3 ± 3.04 b (27.2) |
| med | 5.3 ± 0.10 b (18.5) | 44.5 ± 1.21 b (16.1) | 67.0 ± 0.45 a | 52.8 ± 1.36 b (32.9) | 75.3 ± 1.04 b (32.4) |
| high | 5.3 ± 0.25 b (19.0) | 45.8 ± 1.11 b (20.2) | 68.3 ± 1.29 a | 51.2 ± 1.29 b (28.6) | 72.7 ± 1.23 b (25.8) |
| p value | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.774 | <0.001 | 0.005 |
| 2021 Growing Season | |||||
| no | 10.1 ± 0.20 a (31.5) | 53.7 ± 2.40 a | 66.2 ± 0.87 a (14.8) | 42.8 ± 2.71 a (4.5) | 66.5 ± 2.18 a (4.5) |
| low | 5.1 ± 0.18 b (13.8) | 40.7 ± 0.61 b | 63.3 ± 0.83 a (22.5) | 57.1 ± 0.79 b (26.2) | 84.2 ± 0.54 b (24.3) |
| med | 5.5 ± 0.48 b (16.4) | 42.2 ± 0.94 b | 63.3 ± 1.58 a (23.7) | 55.4 ± 1.18 b (20.8) | 82.4 ± 3.24 b (20.9) |
| high | 5.1 ± 0.31 b (15.1) | 41.9 ± 0.60 b | 62.6 ± 1.00 a (19.9) | 55.6 ± 0.57 b (21.7) | 83.5 ± 1.98 b (23.4) |
| p value | 0.014 | 0.008 | 0.331 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mosqueda, H.M.; Blaser, B.C.; O’Shaughnessy, S.A.; Rhoades, M.B. Intercropping Forage Sorghum with Sunnhemp at Different Seeding Rates to Improve Forage Production. Agronomy 2023, 13, 3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13123048
Mosqueda HM, Blaser BC, O’Shaughnessy SA, Rhoades MB. Intercropping Forage Sorghum with Sunnhemp at Different Seeding Rates to Improve Forage Production. Agronomy. 2023; 13(12):3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13123048
Chicago/Turabian StyleMosqueda, Haley M., Brock C. Blaser, Susan A. O’Shaughnessy, and Marty B. Rhoades. 2023. "Intercropping Forage Sorghum with Sunnhemp at Different Seeding Rates to Improve Forage Production" Agronomy 13, no. 12: 3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13123048
APA StyleMosqueda, H. M., Blaser, B. C., O’Shaughnessy, S. A., & Rhoades, M. B. (2023). Intercropping Forage Sorghum with Sunnhemp at Different Seeding Rates to Improve Forage Production. Agronomy, 13(12), 3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13123048







