Genotypic Variability in Wheat Response to Sodicity: Evaluating Growth and Ion Accumulation in the Root and Shoot
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Genotypes and Seed Collection
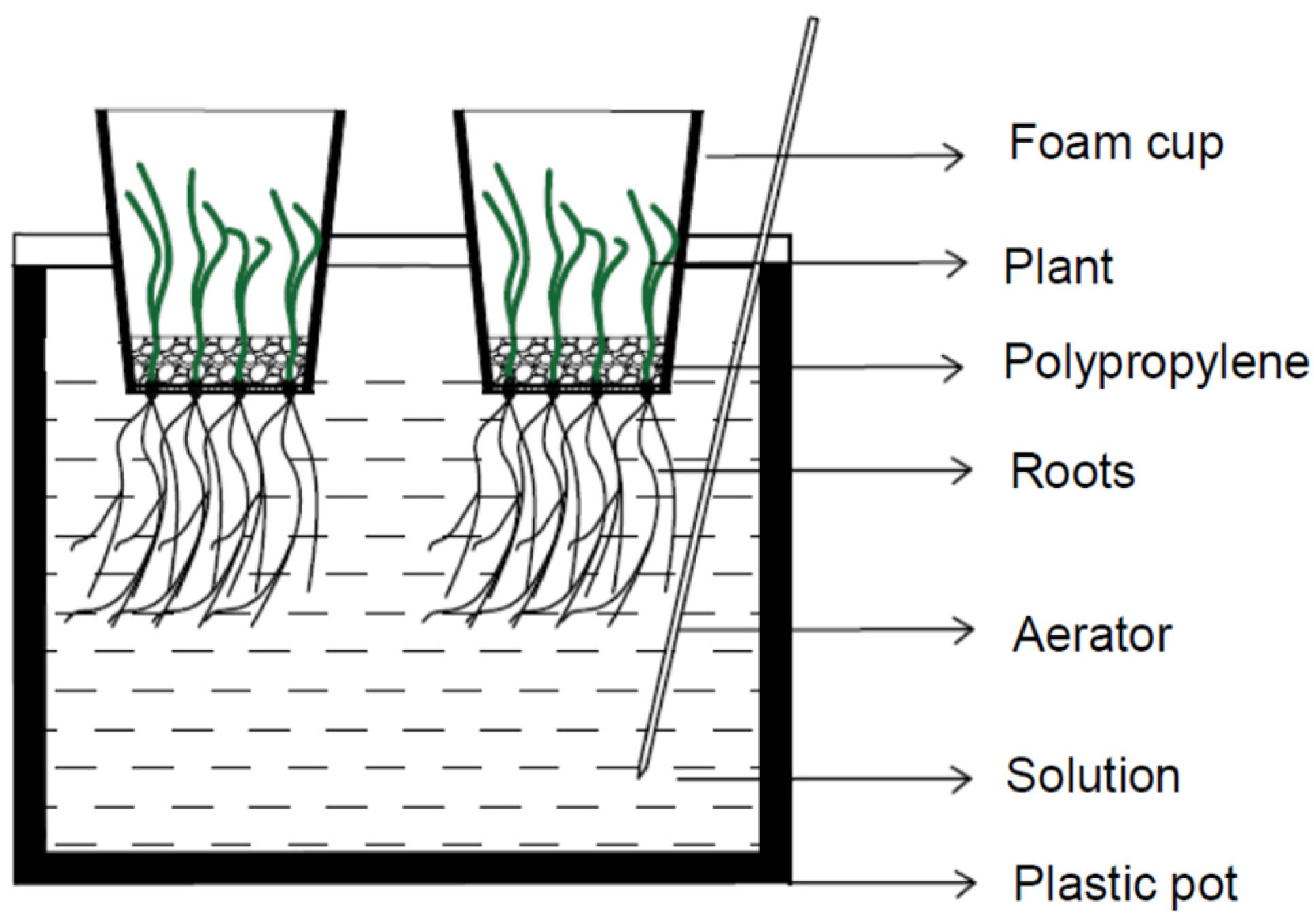
2.2. Solution Preparation and Plant Growth
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
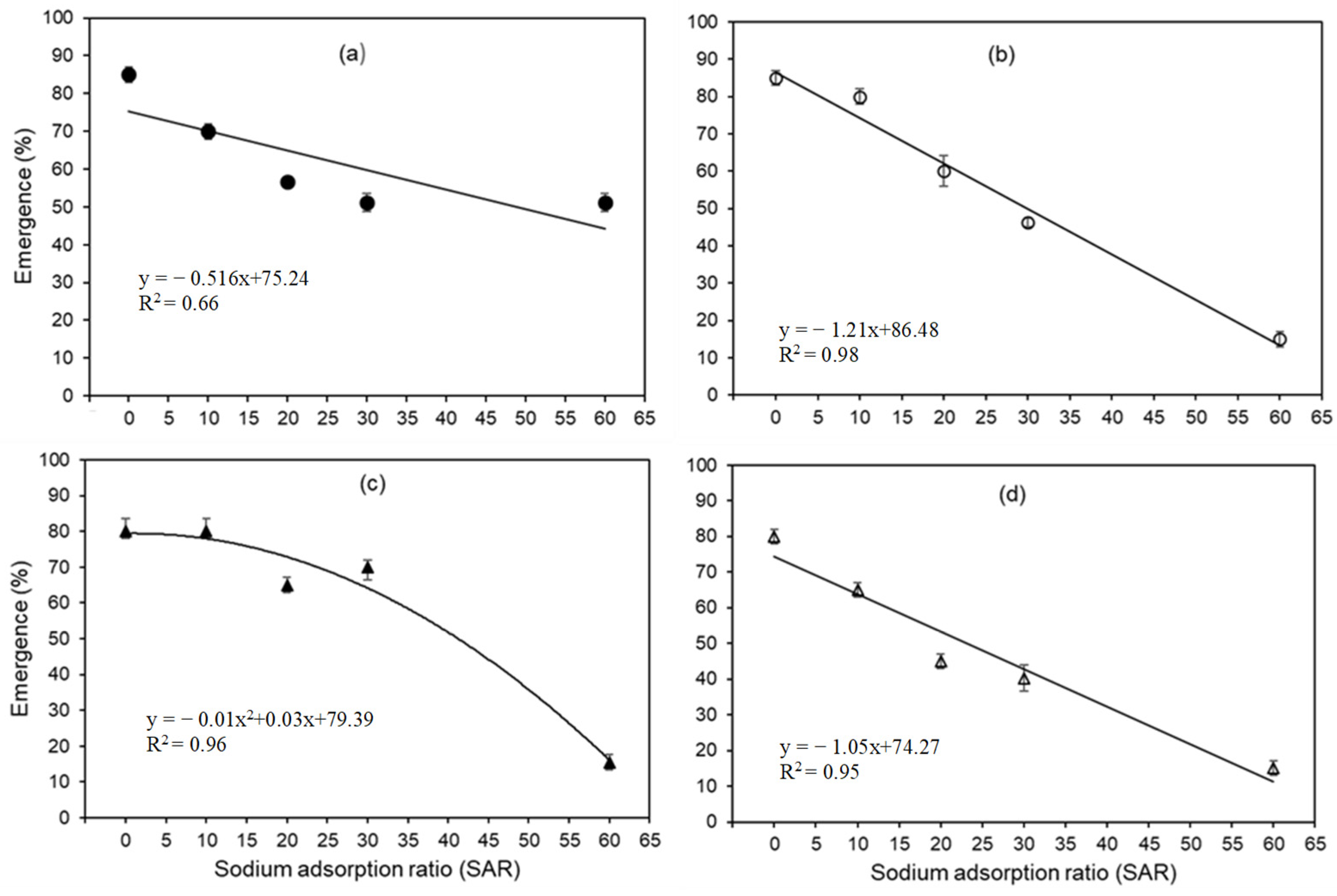
3.1. Impact of SAR on Seedling Emergence
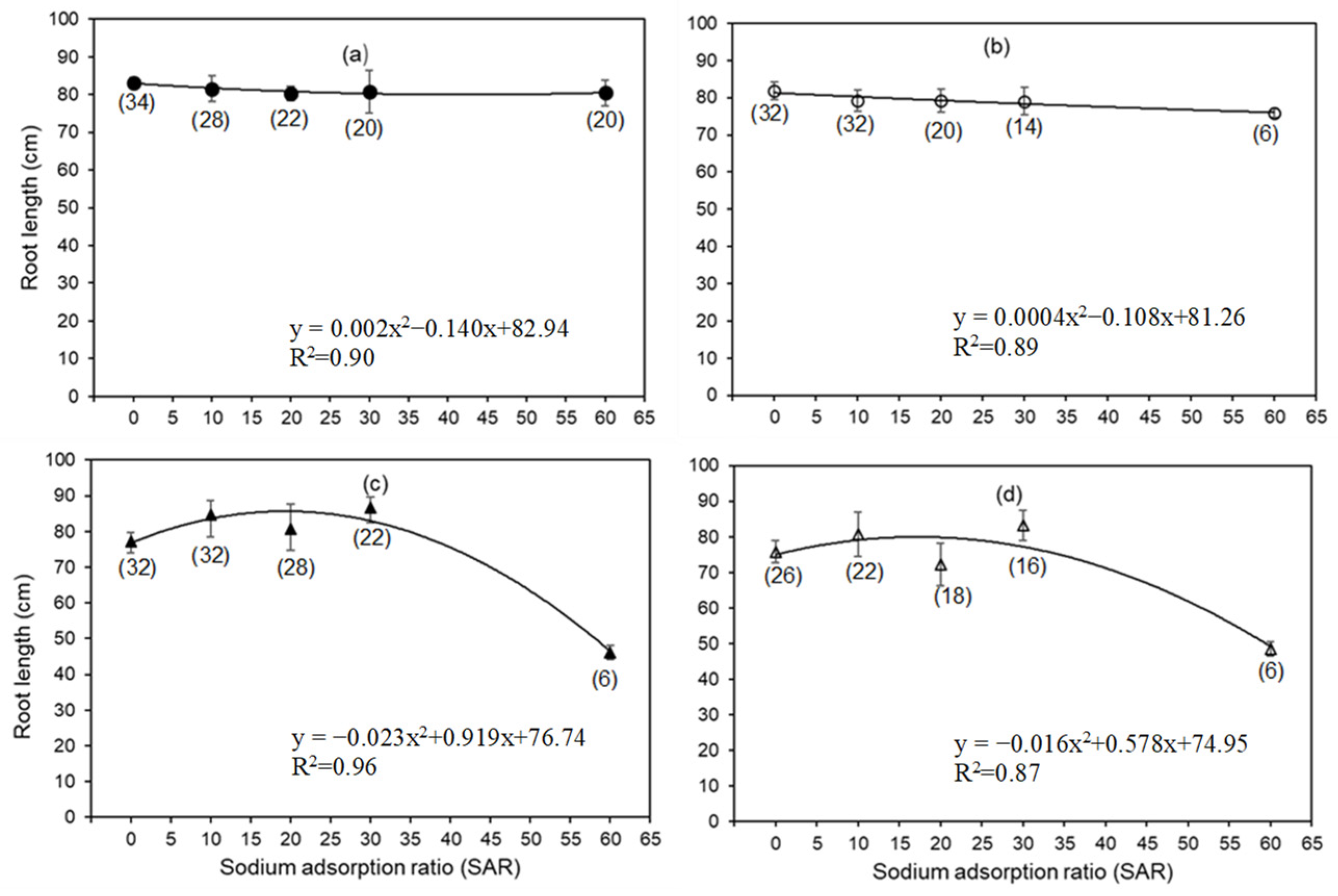
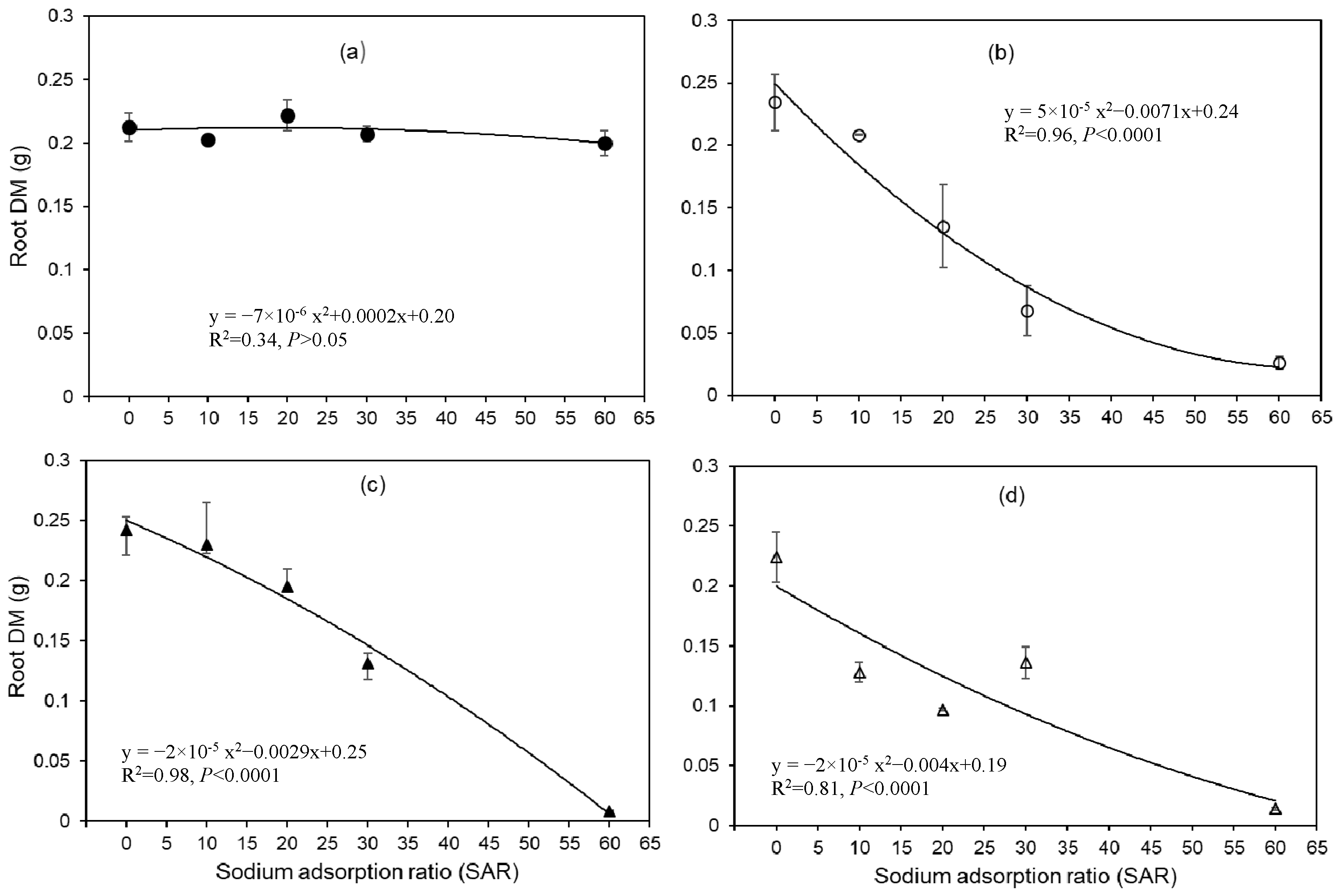
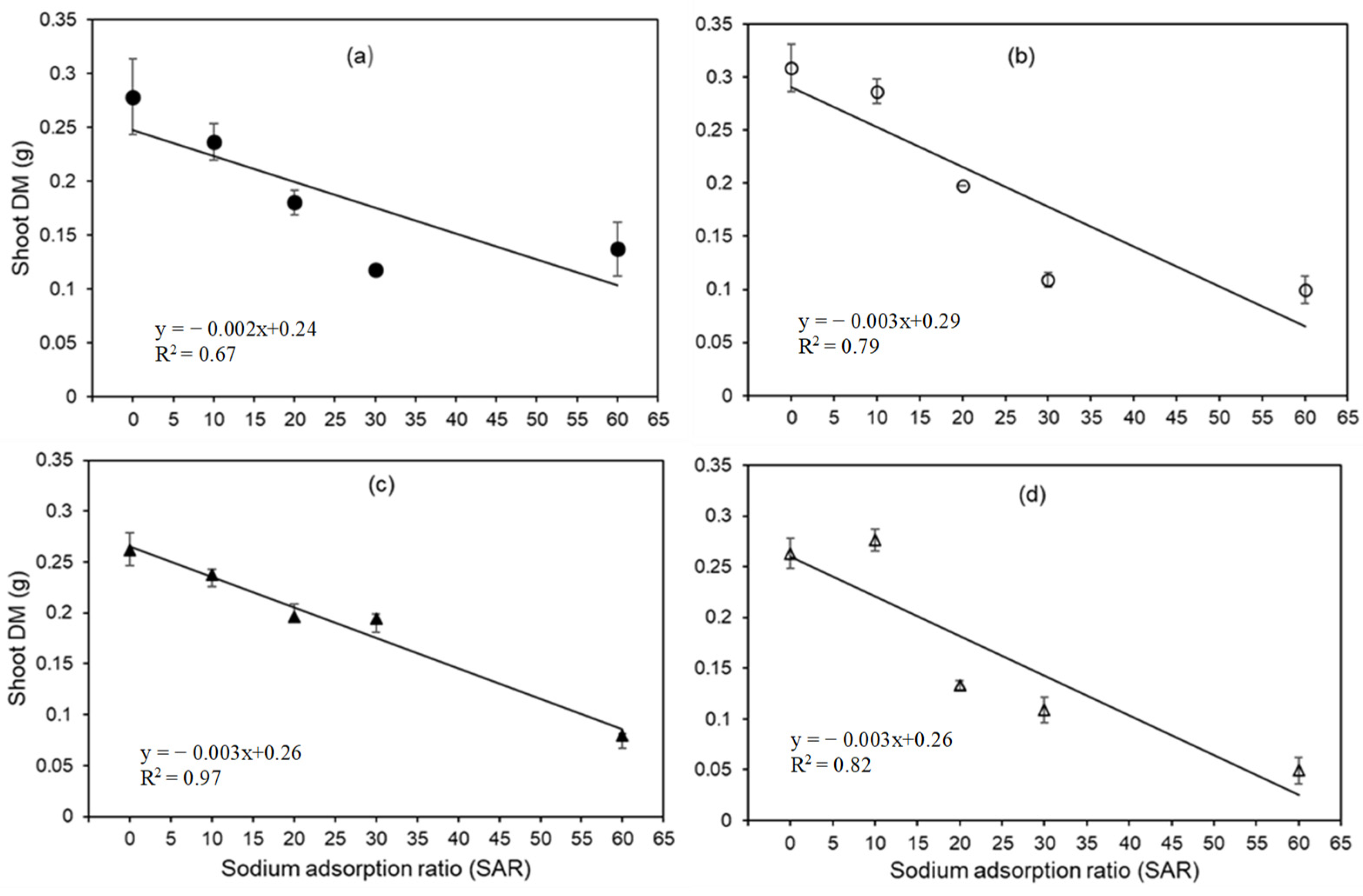
3.2. Impact of SAR on Root Length, Root, and Shoot Mass
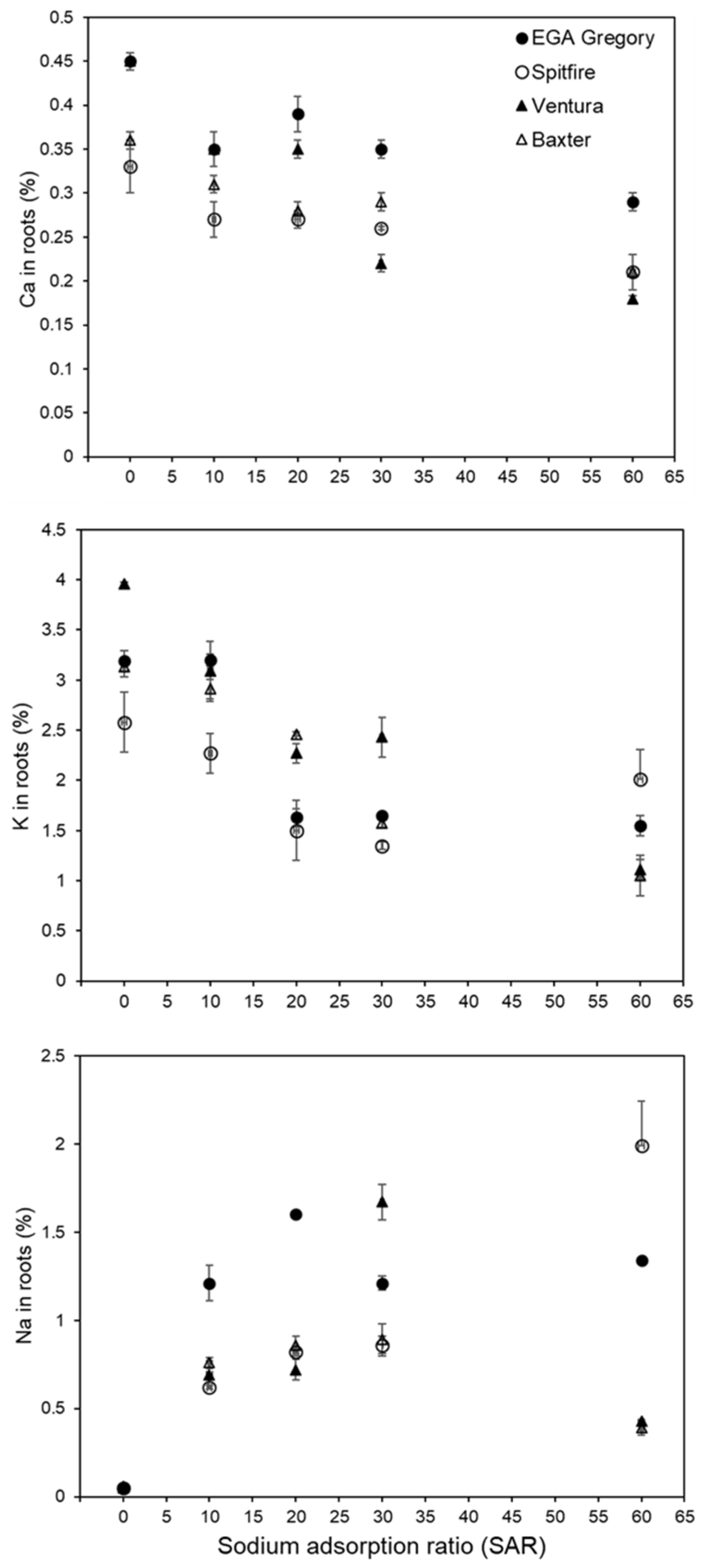
3.3. Elemental Concentrations in Root Tissues
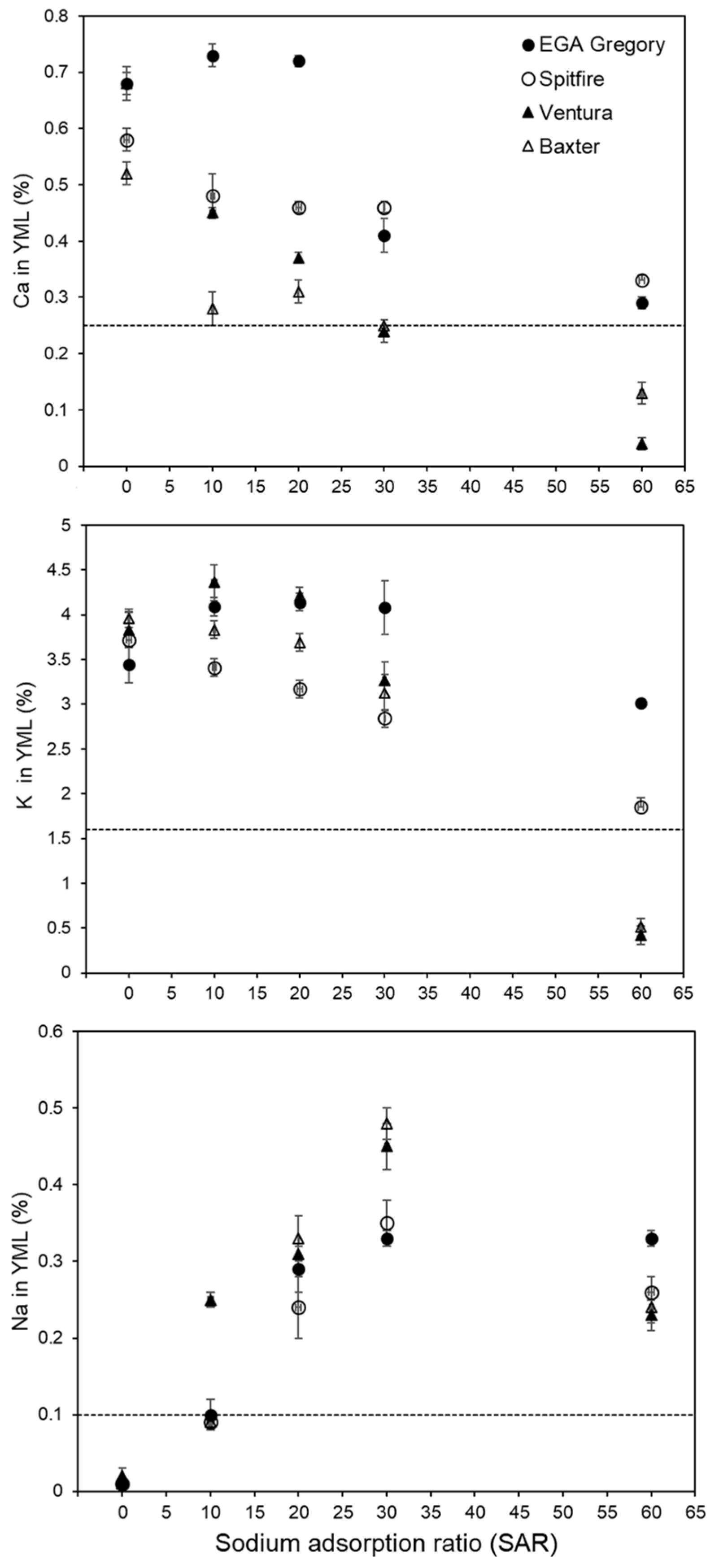
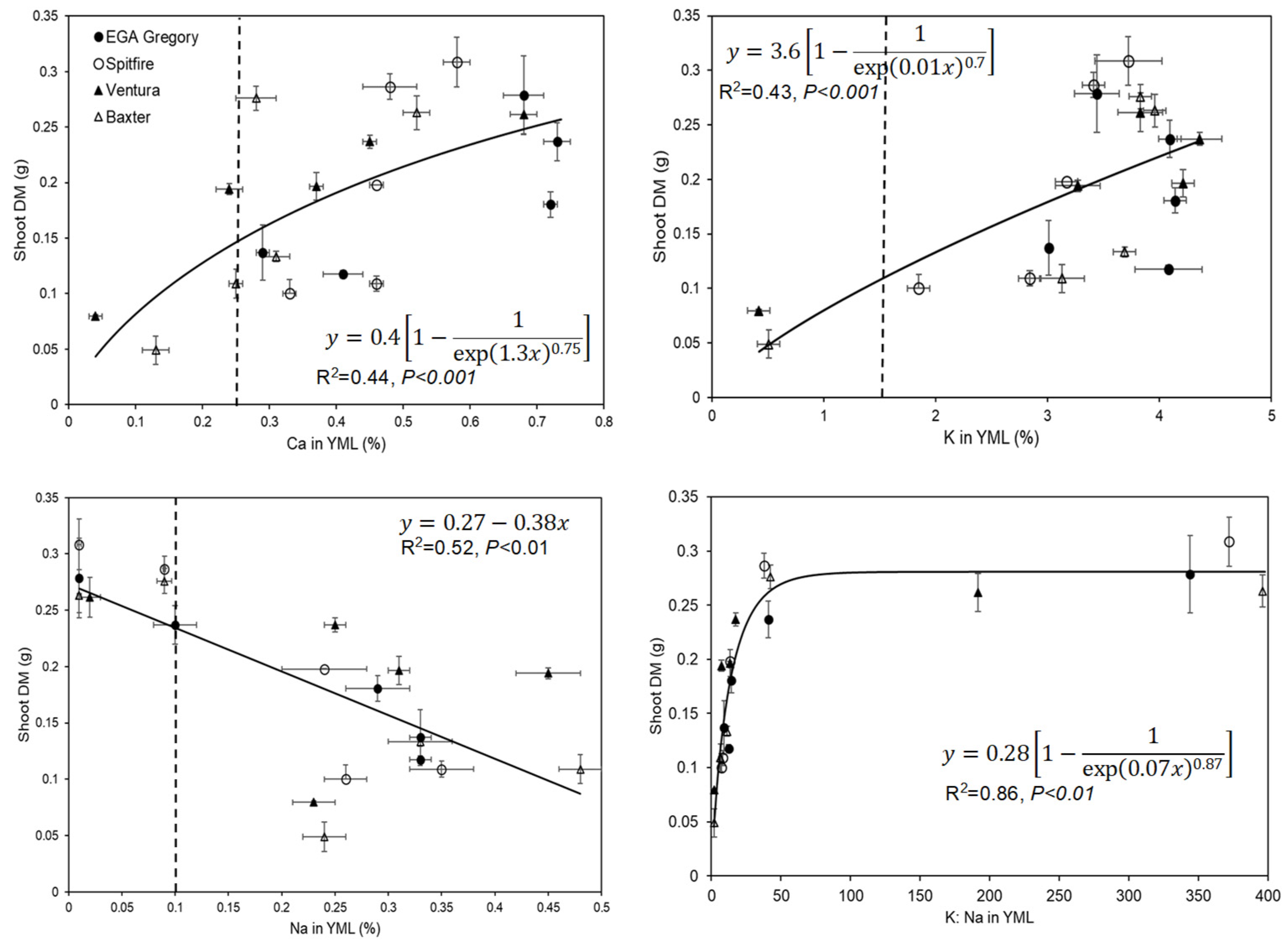
3.4. Elemental Concentrations in the YML Tissues
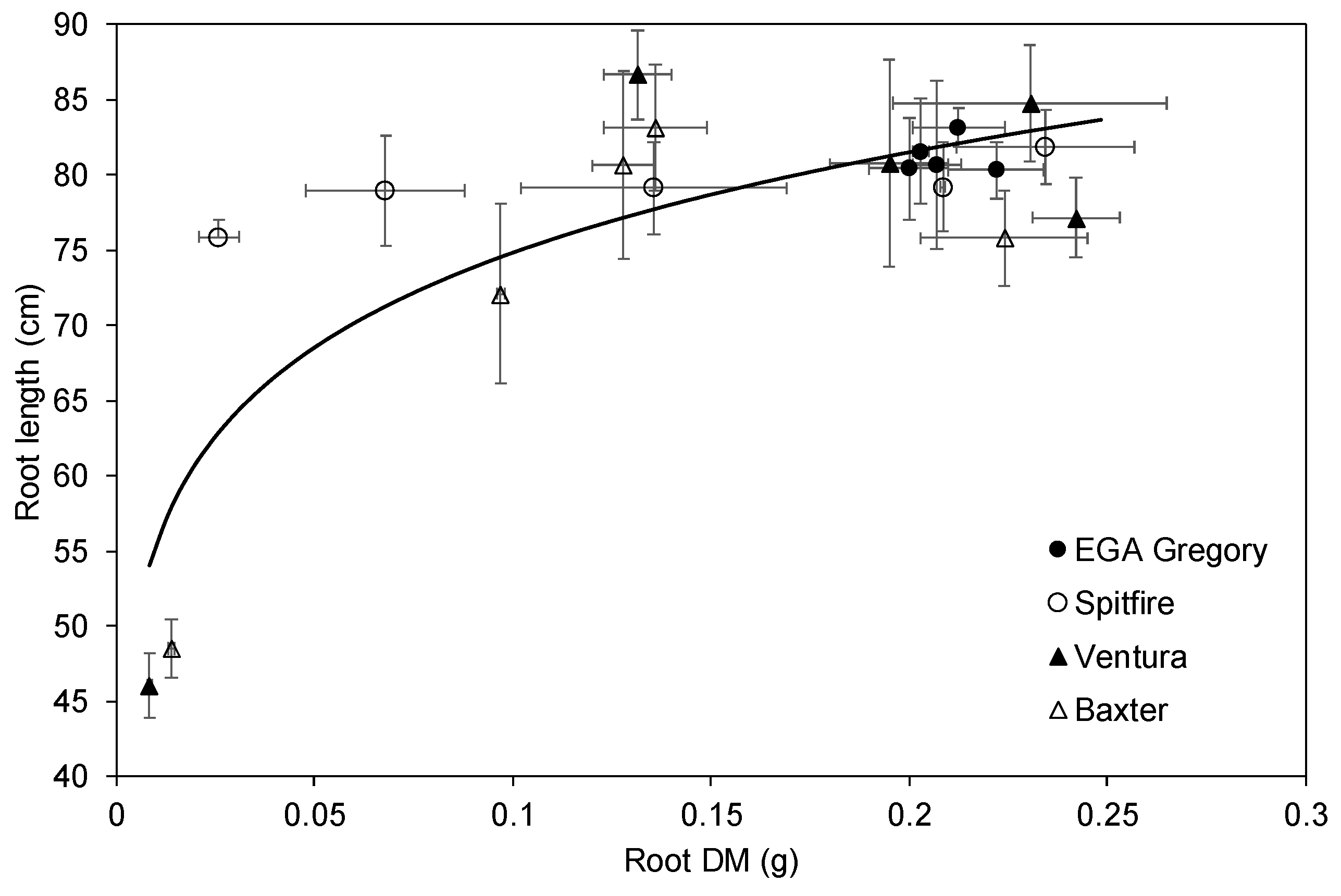
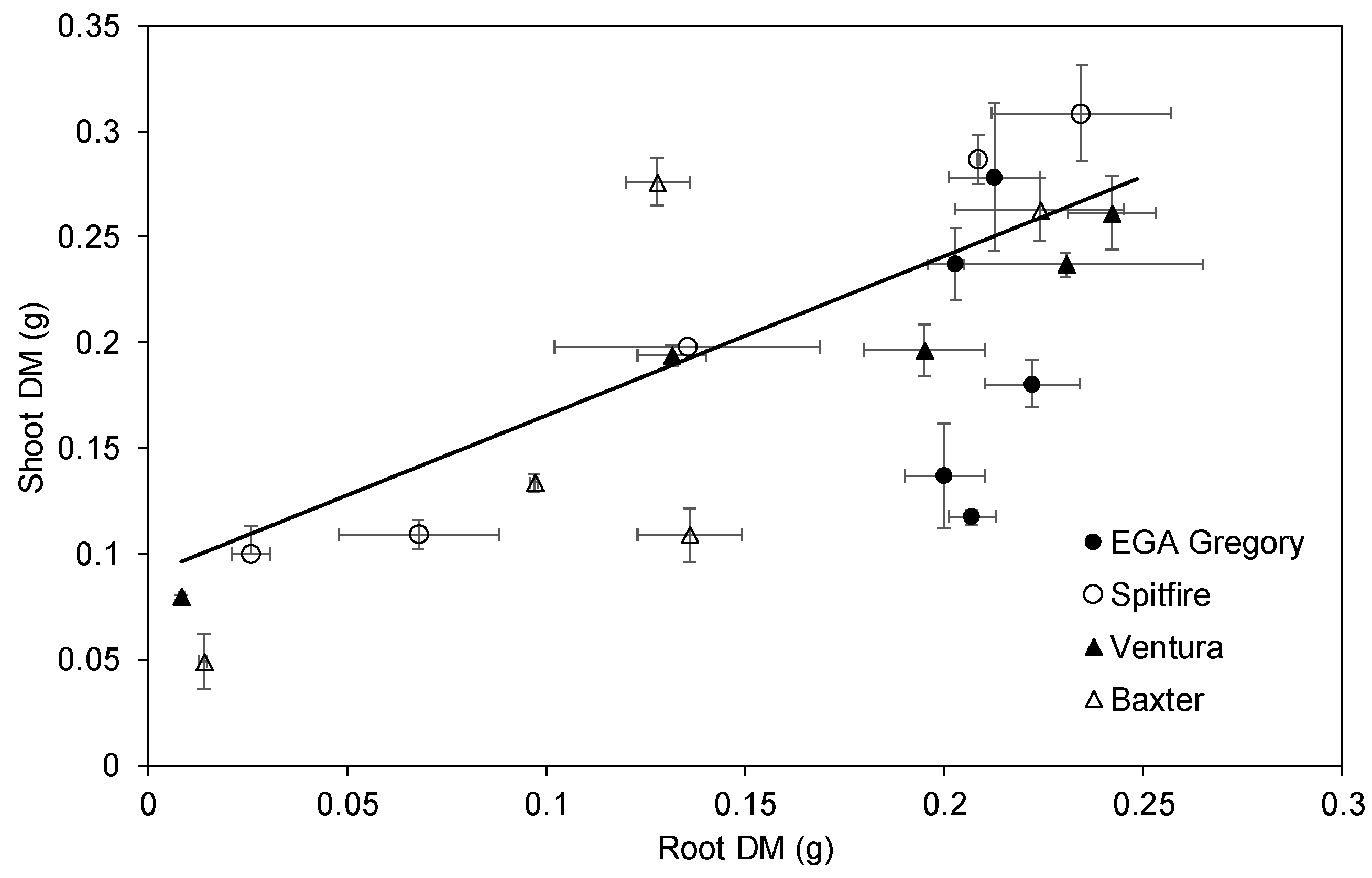
3.5. Relationship between Root and Shoot DM and Root Length
4. Discussion
4.1. Ca Deficiency in the Roots Contributed to Reduced Growth at High SAR
4.2. Nutritional Imbalances in the Shoot
4.3. Comparison between Traits
| Genotype | Relative Seedling Emergence in Soil a | Rapid Germination a | Seedling Emergence Force b | Root Angle c | Ca Concentration in YML (SAR 30 and Above) d | K Concentration in YML (SAR 60) d | Ca Concentration in Root (SAR 60) d | K Concentration in Root (SAR 60) d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGA Gregory | Sensitive | L (50%) | L (0.08N) | L (110°) | H (>) | H (>) | H (>) | H (>) |
| Baxter | Sensitive | M (75%) | L (0.09N) | L (110°) | L (<) | L (<) | L (<) | M (>) |
| Ventura | Tolerant | H (85%) | H (0.25N) | H (88°) | L (<) | L (<) | L (<) | M (>) |
| Spitfire | Tolerant | H (82%) | H (0.22N) | H (90°) | H (>) | H (>) | H (>) | H (>) |
4.4. Is Growth in Sodic Soils Related to Tolerance to Ion Imbalances?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| SAR | Ca | Cu | Fe | K | Mg | Mn | Na | P | S | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mmol/L | ||||||||||
| 0 | 8.96 | 0.0005 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 0.11 | 0.001 | 0.5 | 0.01 | 5.25 | 0.001 |
| 10 | 3.27 | 0.0003 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 0.07 | 0.001 | 16.2 | 0.01 | 6.41 | 0.001 |
| 20 | 1.62 | 0.0003 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 0.07 | 0.001 | 19.6 | 0.01 | 6.84 | 0.001 |
| 30 | 1.35 | 0.0003 | 0.01 | 0.54 | 0.07 | 0.001 | 20.5 | 0.01 | 7.09 | 0.001 |
| 60 | 1.10 | 0.0003 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 0.07 | 0.001 | 21.2 | 0.01 | 7.06 | 0.001 |
| SAR | Ca | Cu | Fe | K | Mg | Mn | Na | P | S | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mmol/L | ||||||||||
| 0 | 12.0 | 0.0002 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.0001 | 0.44 | 0.004 | 7.78 | 119 |
| 10 | 3.77 | 0.0002 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.0000 | 17.2 | 0.004 | 7.69 | 118 |
| 20 | 3.09 | 0.0003 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.0001 | 18.8 | 0.004 | 7.88 | 120 |
| 30 | 1.43 | 0.0003 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.10 | 0.0001 | 23.1 | 0.004 | 8.56 | 131 |
| 60 | 1.24 | 0.0003 | 0.01 | 0.35 | 0.10 | 0.0005 | 23.2 | 0.004 | 8.53 | 130 |

References
- Abbas, G.; Abrar, M.M.; Naeem, M.A.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Ali, H.M.; Li, Y.; Ahmed, K.; Sun, N.; Xu, M. Biochar increases salt tolerance and grain yield of quinoa on saline-sodic soil: Multivariate comparison of physiological and oxidative stress attributes. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 1446–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengasamy, P. Transient salinity and subsoil constraints to dryland farming in Australian sodic soils: An overview. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2002, 42, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, P.D.; Charman, P.E.V. Glossary of Terms Used in Soil Conservation; Soil Conservation Service of NSW: Sydney, Australia, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Läuchli, A.; Epstein, E. Plant responses to saline and sodic conditions. Agric. Salin. Assess. Manag. 1990, 71, 113–137. [Google Scholar]
- Rengasamy, P.; Olsson, K.A. Sodicity and soil structure. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1991, 29, 935–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, H.; Larsen, P.; Koci, J.; Edwards, W.; Nelson, P.N. Long-term effects of gypsum on the chemistry of sodic soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 233, 105780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimmappa, K.; Singh, Y.P.; Raju, R. Reclamation of sodic soils in India: An economic impact assessment. In Bioremediation of Salt Affected Soils: An Indian Perspective; Arora, S., Singh, A., Singh, Y., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Agassi, M.; Morin, J.; Shainberg, I. Effect of raindrop impact energy and water salinity on infiltration rates of sodic soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.; Mishra, B.; Gupta, S. Effects of soil salinity and sodicity on grain quality of tolerant, semi-tolerant and sensitive rice genotypes. Rice Sci. 2013, 20, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, V. Nutrient management in salt affected soils for sustainable crop production. Ann. Plant Soil Res. 2022, 24, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, D.; Robinson, J.B. Plant Analysis: An Interpretation Manual; CSIRO Publishing: Collingwood, VIC, Australia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Qadir, M.; Schubert, S.; Ghafoor, A.; Murtaza, G. Amelioration strategies for sodic soils: A review. Land Degrad. Dev. 2001, 12, 357–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakeel, A. Potassium–sodium interactions in soil and plant under saline-sodic conditions. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2013, 176, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengel, Z. Plant responses to soil-borne ion toxicities. In Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Plants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 665–722. [Google Scholar]
- Rochester, I. Phosphorus and potassium nutrition of cotton: Interaction with sodium. Crop Pasture Sci. 2010, 61, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, K.; Guppy, C.; Lockwood, P.; Rochester, I. The effect of sodicity on cotton: Plant response to solutions containing high sodium concentrations. Plant Soil 2010, 330, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelli, C.A.; Flavio, H.G.B.; Raul, S.L. The K/Na and Ca/Na ratios and repeseed yield, under soil salinity or sodicity. Plant Soil 1995, 175, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Mehla, A.; Chhabra, R.; Kumar, S. Sodicity induced yield losses and changes in mineral concentration of sugarcane genotypes. In Proceedings of the International Society of Sugar Cane Technologists XXIII Congress, New Delhi, India, 22–26 February 1999; pp. 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Qadar, A. Potassium and sodium contents of shoot and laminae of rice cultivars and their sodicity tolerance. J. Plant Nutr. 1995, 18, 2281–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahi, T.S.; Singh, K.; Singh, B. Screening of sodicity tolerance in aloe vera: An industrial crop for utilization of sodic lands. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 44, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Kaur, R. Effect of saline water on growth, yield, quality and soil properties in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 18, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhipa, B.; Lal, P. Na/K ratios as the basis of salt tolerance in wheat. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.; Rajper, I. An assesment of relative effects of adverse physical and chemical properties of sodic soil on the growth and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Soil 2000, 223, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lata, C.; Kumar, A.; Mann, A.; Soni, S.; Meena, B.; Rani, S. Mineral nutrient analysis of three halophytic grasses under sodic and saline stress conditions. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 92, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, D.; Naidu, R. Fertility constraints to plant production. In Sodic Soils: Distribution, Properties, Management and Environmental Consequences; Sumner, M.E., Naidu, R., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Jayawardane, N.; Chan, K. The management of soil physical properties limiting crop production in Australian sodic soils—A review. Soil Res. 1994, 32, 13–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, R. Current and emerging environmental challenges in Australian agriculture—The role of plant breeding. Crop Pasture Sci. 2002, 53, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Dalal, R.C.; Routley, R.; Schwenke, G.D.; Daniel, I. Subsoil constraints to grain production in the cropping soils of the north easter region of Australia: An overview. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2006, 46, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Paull, J.; Rathjen, A. Shoot mineral composition and yield of wheat genotypes grown on a sodic and a non-sodic soil. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2000, 40, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorham, J.; Bridges, J.; Dubcovsky, J.; Dvorak, J.; Hollington, P.; Luo, M.C.; Khan, J. Genetic analysis and physiology of a trait for enhanced K+/Na+ discrimination in wheat. New Phytol. 1997, 137, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, D.P.; Kubota, C.; Miller, S.A. Effects of low pH of hydroponic nutrient solution on plant growth, nutrient uptake, and root rot disease incidence of basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). HortScience 2020, 55, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, C.E.d.O.; Ferreira Filho, A.W.P.; Salomon, M.V. Temperature and pH of the nutrient solution on wheat primary root growth. Sci. Agric. 2004, 61, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzooman, M.; Dang, Y.P.; Christopher, J.; Mumford, M.H.; Menzies, N.W.; Kopittke, P.M. Greater emergence force and hypocotyl cross sectional area may improve wheat seedling emergence in sodic conditions. Plant Sci. 2018, 277, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, M.E.; Miller, W.P. Cation-exchange capacity and exchange coefficients. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, H.; Thompson, R. Recovery of inter-block information when block sizes are unequal. Biometrika 1971, 58, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.; Ciullis, B.; Gilmour, A.; Gogel, B. ASReml-R Reference Manual; The State of Queensland, Department of Primary Industries and Fisheries: Brisbane, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Bryan, J. R Packages; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kopittke, P.M.; Blamey, F.P.C.; Kinraide, T.B.; Wang, P.; Reichman, S.M.; Menzies, N.W. Separating multiple, short-term, deleterious effects of saline solutions on the growth of cowpea seedlings. New Phytol. 2011, 189, 1110–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj-Amor, Z.; Araya, T.; Kim, D.-G.; Bouri, S.; Lee, J.; Ghiloufi, W.; Yang, Y.; Kang, H.; Jhariya, M.K.; Banerjee, A. Soil salinity and its associated effects on soil microorganisms, greenhouse gas emissions, crop yield, biodiversity and desertification: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, S.R.; Grieve, C.M. Salinity–mineral nutrient relations in horticultural crops. Sci. Hortic. 1998, 78, 127–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Redmann, R. Responses of growth, morphology, and anatomy to salinity and calcium supply in cultivated and wild barley. Can. J. Bot. 1995, 73, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peverill, K.; Sparrow, L.; Reuter, D. Soil Analysis: An Interpretation Manual; CSIRO Publishing: Collingwood, VIC, Australia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kurth, E.; Cramer, G.R.; Läuchli, A.; Epstein, E. Effects of NaCl and CaCl2 on cell enlargement and cell production in cotton roots. Plant Physiol. 1986, 82, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R. Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2002, 25, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqib, M.; Abbas, G.; Akhtar, J. Root-mediated acidification and resistance to low calcium improve wheat (Triticum aestivum) performance in saline-sodic conditions. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 156, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodolini, E.M.; Fernández, A.; Morales-Sillero, A.; Mendiano, A.; Martín-Vertedor, D. Influence of pre-harvest calcium applications on table olive characteristics during Spanish-style elaboration process. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 308, 111577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asch, F.; Dingkuhn, M.; Dörffling, K.; Miezan, K. Leaf K/Na ratio predicts salinity induced yield loss in irrigated rice. Euphytica 2000, 113, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzooman, M.; Christopher, J.; Mumford, M.; Dang, Y.P.; Menzies, N.W.; Kopittke, P.M. Selection for rapid germination and emergence may improve wheat seedling establishment in the presence of soil surface crusts. Plant Soil 2018, 426, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzooman, M.; Christopher, J.; Dang, Y.P.; Taylor, J.; Menzies, N.W.; Kopittke, P.M. Chemical and physical influence of sodic soils on the coleoptile length and root growth angle of wheat genotypes. Ann. Bot. 2019, 124, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, Y.P.; Christopher, J.; Dalal, R.C. Genetic diversity in barley and wheat for tolerance to soil constraints. Agronomy 2016, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| SAR | I mM | NaCl mM | Na2SO4 mM | CaCl2·2H2O mM | CaSO4·2H2O mM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 31 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 4.00 | 7.00 |
| 10 | 31 | 5.80 | 5.80 | 1.50 | 1.50 |
| 20 | 31 | 7.00 | 7.00 | 0.55 | 0.55 |
| 30 | 31 | 7.70 | 7.70 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| 60 | 31 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Genotypes | SAR | K:Na |
|---|---|---|
| EGA Gregory | 0 | 344 |
| 10 | 40.9 | |
| 20 | 14.3 | |
| 30 | 12.4 | |
| 60 | 9.12 | |
| Spitfire | 0 | 372 |
| 10 | 37.9 | |
| 20 | 13.2 | |
| 30 | 8.11 | |
| 60 | 7.12 | |
| Ventura | 0 | 192 |
| 10 | 17.4 | |
| 20 | 13.6 | |
| 30 | 7.27 | |
| 60 | 1.83 | |
| Baxter | 0 | 396 |
| 10 | 42.6 | |
| 20 | 11.2 | |
| 30 | 6.52 | |
| 60 | 2.13 | |
| p between treatments | <0.0001 | |
| p between genotypes | 0.17 | |
| Interaction between genotypes and treatments | 0.15 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anzooman, M.; Christopher, J.; Dang, Y.P.; Menzies, N.W.; Kopittke, P.M. Genotypic Variability in Wheat Response to Sodicity: Evaluating Growth and Ion Accumulation in the Root and Shoot. Agronomy 2023, 13, 3035. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13123035
Anzooman M, Christopher J, Dang YP, Menzies NW, Kopittke PM. Genotypic Variability in Wheat Response to Sodicity: Evaluating Growth and Ion Accumulation in the Root and Shoot. Agronomy. 2023; 13(12):3035. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13123035
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnzooman, Monia, Jack Christopher, Yash P. Dang, Neal W. Menzies, and Peter M. Kopittke. 2023. "Genotypic Variability in Wheat Response to Sodicity: Evaluating Growth and Ion Accumulation in the Root and Shoot" Agronomy 13, no. 12: 3035. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13123035
APA StyleAnzooman, M., Christopher, J., Dang, Y. P., Menzies, N. W., & Kopittke, P. M. (2023). Genotypic Variability in Wheat Response to Sodicity: Evaluating Growth and Ion Accumulation in the Root and Shoot. Agronomy, 13(12), 3035. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13123035







