The Interaction Effects of Drought–Flood Abrupt Alternation on Rice Yield and Dry Matter Partitioning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setting
2.2. Water Control Method
2.3. Determination of Dry Matter Quality and Yield
2.4. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
- (1)
- Relative rate of yield and yield components
- (2)
- Partitioning index of roots, stems, leaves, and panicles
3. Results
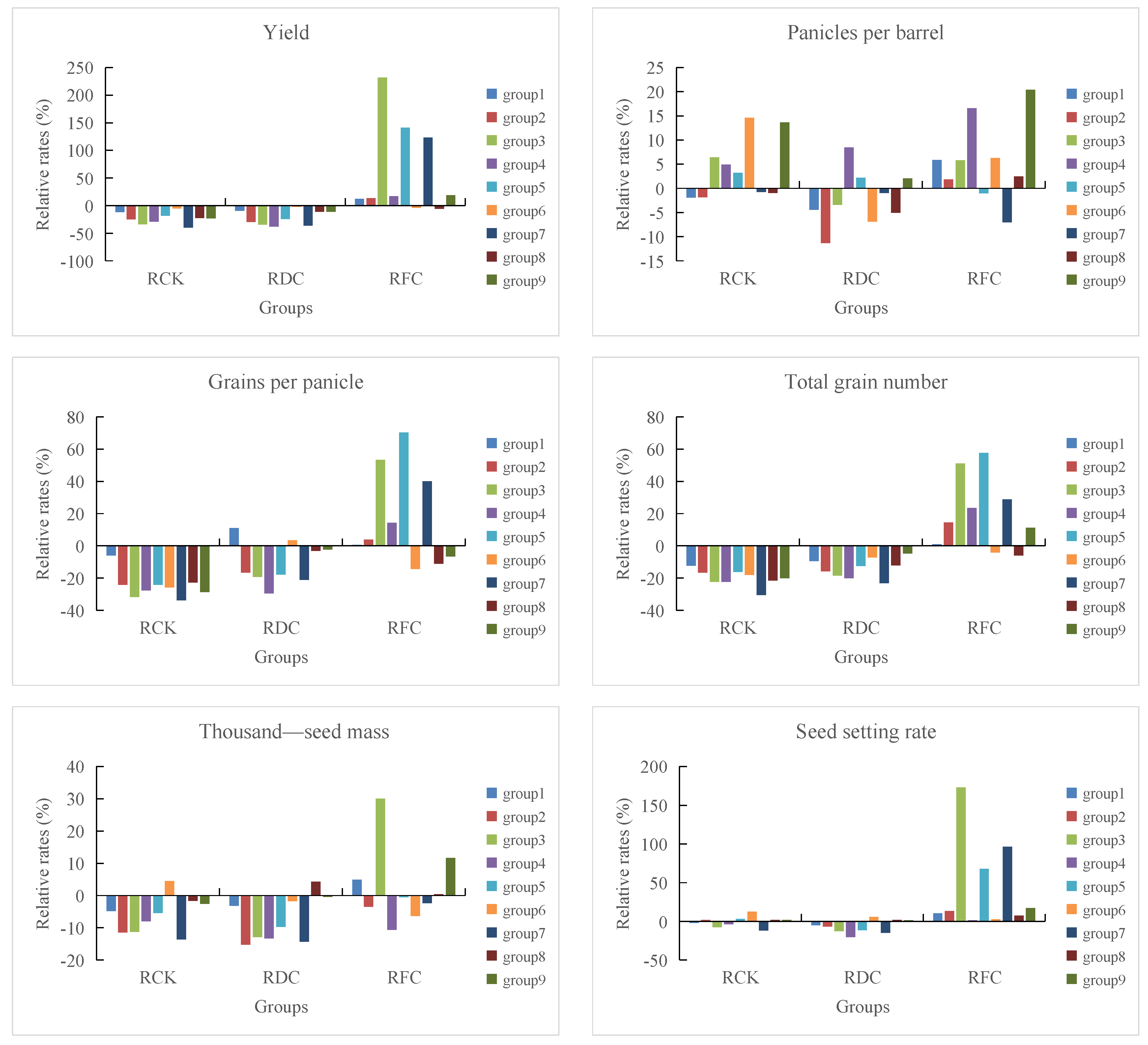
3.1. Effects of DFAA Stress on Rice Yield
3.2. Variance and Range Analyses of the Four Factors of Dfaa Stress
3.3. Effect of DFAA Stress on the Rice Partitioning Index
4. Discussion
4.1. Interaction Effect of DFAA on Rice Yield
4.2. Effects of DFAA Interaction on the Dry Matter Partitioning of Rice
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DFAA | Drought–flood abrupt alternation |
| DC | Drought control |
| FC | Flood control |
| CK | Normal irrigation |
| RCK | Rate relative to the CK group |
| RDC | Rate relative to DC groups |
| RFC | Rate relative to FC groups |
References
- Bi, W.X.; Weng, B.S.; Wang, X.; Yan, D.H.; Wang, M.K.; Dong, N.P. Research progress of sudden turn of drought and flood based on knowledge map. Water Resour. Prot. 2021, 37, 40–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.K.; Bi, W.X.; Weng, B.S.; Yu, Z.L.; Xu, T. Review on impact from drought-flood abrupt alternation on crop growth and yield. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2019, 50, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.H.; Wu, D.; Huang, R.; Wang, L.N.; Yang, G.Y. Drought evolution characteristics and precipitation intensity changes during alternating dry-wet changes in the Huang-Huai-Hai River basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2859–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Ye, X.C. Spatiotemporal characteristics of dry-wet abrupt transition based on precipitation in Poyang Lake Basin, China. Water 2015, 7, 1943–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Bureau of the People’s Republic of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Hu, T.S.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, H.W.; Yang, J.W. Effect of Drought-Flood Abrupt Alternation on Rice Yield and Yield Components. Crop Sci. 2019, 58, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hu, T.S.; Yuan, H.W.; Yang, J.W. Analysis on yield reduced law of rice in Huaibei plain under drought-flood abrupt alternation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, I.; Nazir, N. Effect of waterlogging and drought stress in plants. Int. J. Water Resour. Environ. Sci. 2013, 2, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Q.Q.; Shen, T.H.; Zhong, L.; Chen, X.R.; Zhu, C.L.; Peng, X.S.; He, H.H. Effect of a sudden change from drought to waterlogging at the tilleringor young spiking stage on yield and grain of hybrid rice. J. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 36, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Zhong, L.; Chen, X.R.; Zhu, C.L.; Peng, X.S.; He, X.P.; Fu, J.R.; Bian, J.M.; Hu, L.F.; Ou Yang, L.J.; et al. Effects of drought-floods abrupt alternation on physiological and yield characteristics in super hybrid early rice during panicle differentiation stage. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2017, 31, 768–776. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Q.Q.; Zhong, L.; Shen, T.H.; Chen, X.R.; Zhu, C.L.; Peng, X.S.; Fu, J.R.; He, H.H. Effects of drought-floods abrupt alternation during panicle differentiation stage on matter accumulation and yield formation in double-season super hybrid rice. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2017, 38, 597–608. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.P.; Yang, S.; Wang, Z.C.; Yang, J.H.; Li, X.P. Effects of Alternative stress of drought and waterlogging on rice yield and quality. J. Irrig. Drain. 2015, 34, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Hu, T.S.; Yasir, M.; Gao, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhu, R.; Wang, X.; Yuan, H.; Yang, J. Root growth dynamics and yield responses of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under drought–flood abrupt alternating conditions. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 157, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xue, Y.G.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yang, J.C.; Zhang, J.H. An alternate wetting and moderate soil drying regime improves root and shoot growth in rice. Crop Sci. 2009, 49, 2246–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, J.H.; Yang, J.C.; Zhu, Q.S. Effect of Water Stress on Metabolism of Stored Carbohydrate of Stem and Yield in Rice Grown under Unfavorable-delayed Senescence. Acta Agron. Sin. 2004, 30, 196–204. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Cai, Y.X.; Zhang, Z.J.; Lang, Y.Z.; Yang, J.C.; Zhu, Q.S. Effects of Low Soil Water Potential on the Grain-filling Characters and the Main Quality Properties of Superior and Inferior Grains in Rice during Filling Period. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2005, 21, 170–183. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.C.; Xu, G.W.; Wang, Z.Q.; Chen, X.H.; Zhu, Q.S. Remobilization of Carbon Assimilates in the Stems during Grain Filling and Its Phy-siological Mechanism in Dry-cultivated Rice. Acta Agron. Sin. 2004, 30, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.Z.; Xu, G.W.; Ma, J.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, R.P. Effects of water stress on growth, development and yield of rice. China Seed Ind. 2009, 1, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, G.X.; Shen, Q.R.; Cui, G.Q.; Li, L.Y. Advances in studies on upland planting and upland adaptability of rice. Crop Res. 2001, 15, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Engelaar, W.M.H.G.; Matsumaru, T.; Yoneyama, T. Combined effects of soil waterlogging and compaction on rice (Oryza sativa L.) growth, soil aeration, soil N transformations and 15N discrimination. Biol. Fertil. Soil 2000, 32, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.Z.; Tang, G.M. Effects of Submergence Stress on Rice Yield Factors in Jointing-booting Stage. J. Irrig. Drain. 2015, 34, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.Z.; Tang, G.M. Experimental Study of Response Rice Jointing-booting Stage to Inundation Condition. China Rural. Water Hydropower 2016, 58, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.M.; Li, F.H.; Lian, P.; Jiang, L.X.; Meng, Y. Effects of submergence stress on rice growth in jointing stage. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2018, 29, 240–244. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Q.Q.; Zhong, L.; Chen, X.R.; Zhu, C.L.; Peng, X.S.; He, X.P.; Fu, J.R.; Bian, J.M.; Hu, L.F.; Ouyang, L.J.; et al. Effects of Drought-floods Abrupt Alternation During Panicle Initiation Stage on δ13C and δ15N Stable Isotope Ratios of Leaves in Double-season Super Hybrid Rice. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2017, 31, 559–565. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.C.; Guo, X.P.; Yang, J.H.; Chen, S.; Huang, S.S.; Wang, F.; Qiu, R.J.; Liu, C.W.; Cao, X.C.; Zhu, J.B.; et al. Effect of alternate flooding and drought stress on biomass production, distribution and lodging characteristic of rice. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 114–123. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.P.; Li, X.P.; Lu, H.F.; Wang, Z.C.; Yang, S. Study on Dry Matter Accumulation and Nitrogen Uptake under Alternating Drought and Flooding Stress in Rice Tillering Stage. J. Irrig. Drain. 2015, 34, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.F. Study on Response Law and Water Production Function of Rice under the Condition of Rapid Drought and Flood; Wuhan University: Wuhan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Wu, F.; Hu, T.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Liang, C.; Liu, J. Interactive Effects of Drought-Flood Abrupt Alternation on Morpho-Agronomic and Nutrient Use Traits in Rice. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.C.; Cheng, X.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Z. Effect of drought pretreatment before anthesis and post-anthesis waterlogging on water relation, photosynthesis, and growth of tomatoes. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2016, 62, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Hu, J.C.; Li, Y.X.; Xie, X.J.; Li, Y.X. Effects of flooding stress on leave’s photosynthetic capability of paddy rice. Meteorol. Environ. Sci. 2019, 42, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, B.; Zhou, X.G.; Lu, H.F.; Li, H.Z. The effects of alternate hot wave and waterlogging on physiological traits of rice at booting stage. J. Irrig. Drain. 2019, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lawson, T.; Blatt, M.R. Stomatal size, speed, and responsiveness impact on photosynthesis and water use efficiency. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 1556–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, D. Stomatal Conductance Is Essential for higher yield potential of C3 crops. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2015, 34, 429–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Ju, H.; Wang, H.F.; Jiang, S.; Hao, X.Y.; Han, X.; Gao, J. Effects of elevated CO2 concentration on accumulation and translocation of carbon and nitrogen of winter wheat under different water conditions. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2015, 23, 954–963. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Straeten, D.; Zhou, Z.; Prinsen, E.; Van Onckelen, H.A.; Van Montagu, M.C. A comparative molecular-physiological study of submergence response in lowland and deepwater rice. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kende, H.; Van Der Knaap, E.; Cho, H.T. Deepwater rice: A model plant to study stem elongation. Plant Physiol. 1998, 118, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, J.H.; Lu, K.D.; Huo, Z.G.; Xie, N.; Huang, W.H. Effects of waterlogging stress on rice morphology and yield component at the jointing stage. Chin. J. Ecol. 2014, 33, 1818–1825. [Google Scholar]
- Vergara, B.S.; Jackson, B.; De Datta, S.K. Deepwater rice and its response to deepwater stress Proceedings of the Symposium on Climate and Rice. LosBanos Philipp. Int. Rice Res. Inst. 1976, 1, 301–319. [Google Scholar]
- Sauter, M. Rice in deep water: “how to take heed against a sea of troubles”. Naturwissenschaften 2000, 87, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Hu, J.C.; Lin, Z.J. Effects of submergence stress on partition of dry matter and yield of rice plant. J. Henan Agric. Univ. 2019, 53, 689–693. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, R.; Zhai, L.N.; Hu, T.S. Post-effects of waterlogging on the rice growth at the jointing-booting stage. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
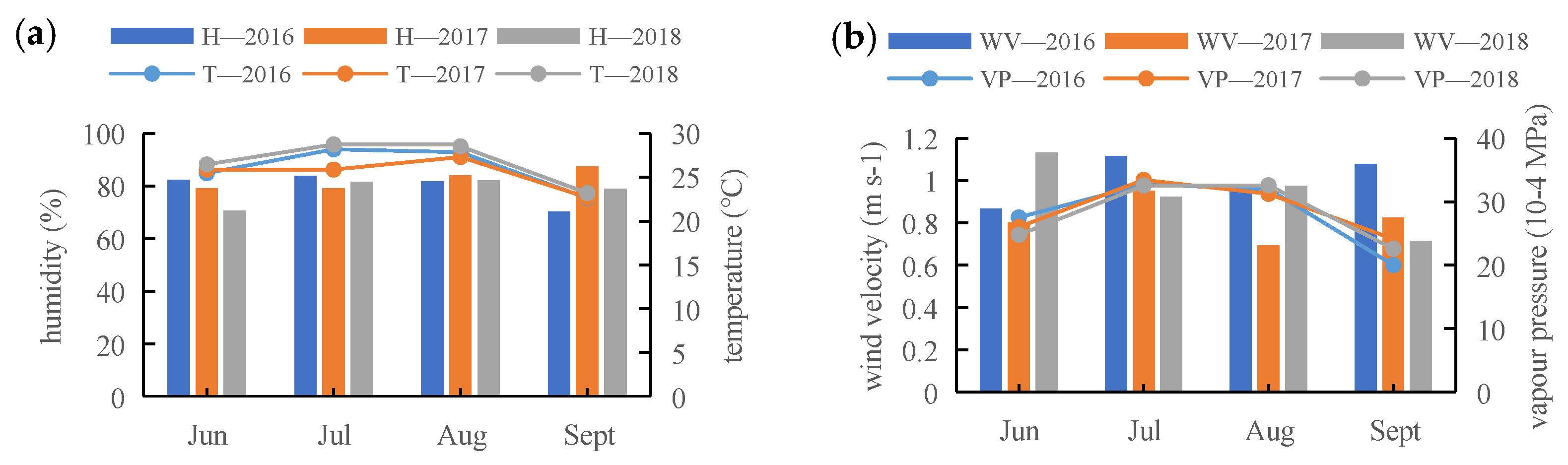



| Treatment | Drought Degree (%) | Drought Time (d) | Flood Degree (%) | Flood Time (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DFAA1 | 70 | 5 | 50 | 5 |
| DFAA2 | 70 | 10 | 75 | 7 |
| DFAA3 | 70 | 15 | 100 | 9 |
| DFAA4 | 60 | 5 | 75 | 9 |
| DFAA5 | 60 | 10 | 100 | 5 |
| DFAA6 | 60 | 15 | 50 | 7 |
| DFAA7 | 50 | 5 | 100 | 7 |
| DFAA8 | 50 | 10 | 50 | 9 |
| DFAA9 | 50 | 15 | 75 | 5 |
| DC1 | 70 | 5 | normal irrigation | |
| DC2 | 70 | 10 | ||
| DC3 | 70 | 15 | ||
| DC4 | 60 | 5 | ||
| DC5 | 60 | 10 | ||
| DC6 | 60 | 15 | ||
| DC7 | 50 | 5 | ||
| DC8 | 50 | 10 | ||
| DC9 | 50 | 15 | ||
| FC1 | normal irrigation | 50 | 5 | |
| FC2 | 75 | 7 | ||
| FC3 | 100 | 9 | ||
| FC4 | 75 | 9 | ||
| FC5 | 100 | 5 | ||
| FC6 | 50 | 7 | ||
| FC7 | 100 | 7 | ||
| FC8 | 50 | 9 | ||
| FC9 | 75 | 5 | ||
| CK | normal irrigation | |||
| Treatment | Tillering Stage | Jointing Stage | Heading Stage | Milking Stage | Harvest Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DFAA | 20 June | 17 July | 14 August | 26 August | 23 September |
| DC | 20 June | 17 July | 9 August | 25 August | 22 September |
| FC | 20 June | 20 July | 8 August | 23 August | 20 September |
| CK | 20 June | 20 July | 8 August | 21 August | 20 September |
| Drought/Flood Degree and Time | Yield | Panicles per Bucket | Grains per Panicle | Total Grain Number | Thousand-Seed Mass | Seed Setting Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | Drought degree | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.012 * | 0.000 ** |
| Drought time | 0.001 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.985 NS | 0.099 NS | 0.000 ** | |
| Flood degree | 0.000 ** | 0.066 NS | 0.033 * | 0.005 ** | 0.082 NS | 0.000 ** | |
| Flood time | 0.000 ** | 0.019 * | 0.011 * | 0.004 ** | 0.960 NS | 0.260 NS | |
| 2017 | Drought degree | 0.003 ** | 0.693 NS | 0.155 NS | 0.114 NS | 0.066 NS | 0.159 NS |
| Drought time | 0.013 * | 0.031 * | 0.540 NS | 0.299 NS | 0.655 NS | 0.290 NS | |
| Flood degree | 0.000 ** | 0.461 NS | 0.001 ** | 0.003 ** | 0.002 ** | 0.000 ** | |
| Flood time | 0.000 ** | 0.004 ** | 0.021 * | 0.192 NS | 0.106 NS | 0.083 NS | |
| 2018 | Drought degree | 0.000 ** | 0.820 NS | 0.013 * | 0.000 ** | 0.082 NS | 0.000 ** |
| Drought time | 0.000 ** | 0.073 NS | 0.001 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.112 NS | 0.003 ** | |
| Flood degree | 0.000 ** | 0.165 NS | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.126 NS | 0.000 ** | |
| Flood time | 0.000 ** | 0.654 NS | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.332 NS | 0.006 ** | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Hu, T.; Li, P.; Qi, X. The Interaction Effects of Drought–Flood Abrupt Alternation on Rice Yield and Dry Matter Partitioning. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13122994
Gao Y, Hu T, Li P, Qi X. The Interaction Effects of Drought–Flood Abrupt Alternation on Rice Yield and Dry Matter Partitioning. Agronomy. 2023; 13(12):2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13122994
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yun, Tiesong Hu, Ping Li, and Xuebin Qi. 2023. "The Interaction Effects of Drought–Flood Abrupt Alternation on Rice Yield and Dry Matter Partitioning" Agronomy 13, no. 12: 2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13122994
APA StyleGao, Y., Hu, T., Li, P., & Qi, X. (2023). The Interaction Effects of Drought–Flood Abrupt Alternation on Rice Yield and Dry Matter Partitioning. Agronomy, 13(12), 2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13122994








